The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors’ Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Flow Cytometry
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Co-Expression and Numbers of Receptor Molecules in the Main Populations of Mononuclear Cells
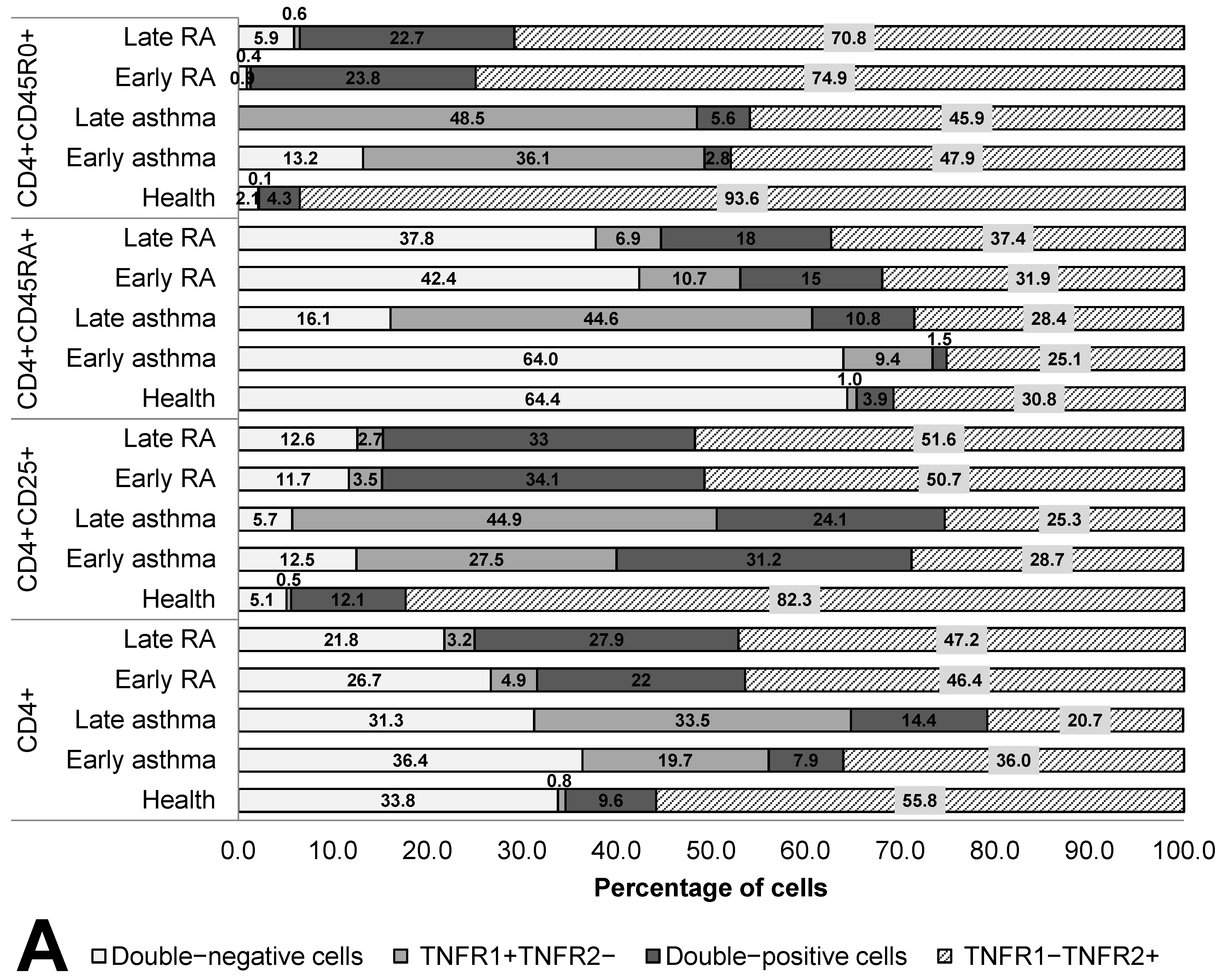
3.2. Co-Expression and Numbers of Receptor Molecules in T Helper Cell Populations
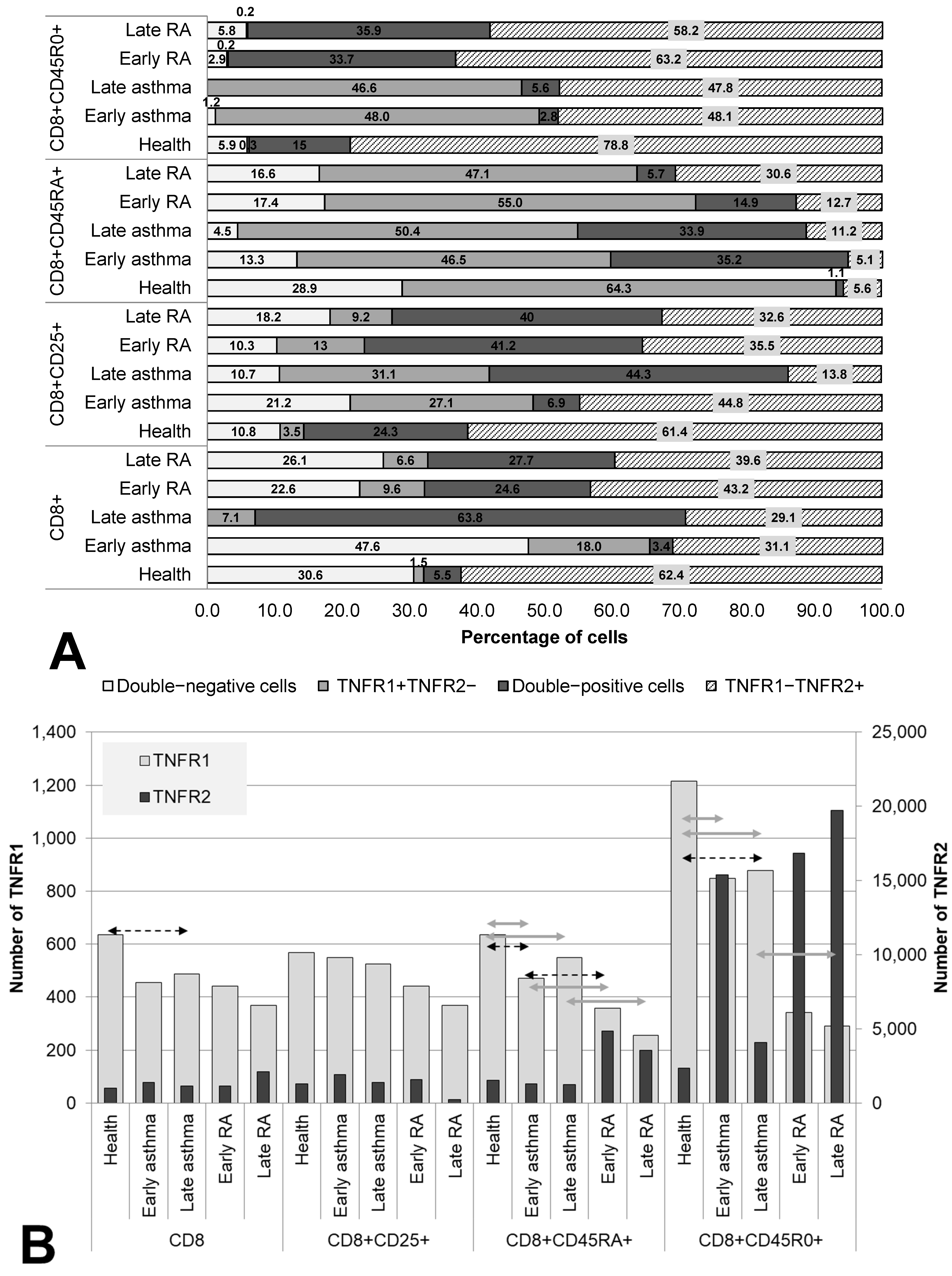
3.3. Co-Expression and Numbers of Receptor Molecules in Cytotoxic Subpopulations of T Cells
3.4. Correlations of Expression and Co-Expression Parameters of TNF Receptors of Types 1 and 2 with the Duration of the Disease
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalliolias, G.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B.; Program, T.D. TNF biology, pathogenic mechanisms and emerging therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Wang, J.; Brand, D.D.; Zheng, S.G. Role of TNF—TNF Receptor 2 Signal in Regulatory T Cells and its Therapeutic implications. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gough, P.; Myles, I.A. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptors: Pleiotropic Signaling Complexes and Their Differential Effects. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 585880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.D.; Vucic, D. The Balance of TNF Mediated Pathways Regulates Inflammatory Cell Death Signaling in Healthy and Diseased Tissues. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucka, K.; Wajant, H. Receptor Oligomerization and Its Relevance for Signaling by Receptors of the Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Superfamily. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 8, 615141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medler, J.; Wajant, H. Tumor necrosis factor receptor-2 (TNFR2): An overview of an emerging drug target. Expert Opin. Targets 2019, 23, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sennikov, S.; Alshevskaya, A.; Zhukova, J.; Lopatnikova, J.; Belomestnova, I.; Karaulov, A. Expression Density of Receptors as a Potent Regulator of Cell Function and Property in Health and Pathology. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2018, 178, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshevskaya, A.; Koneva, O.; Belomestnova, I.; Lopatnikova, J.; Evsegneeva, I.; Zhukova, J.; Kireev, F.; Karaulov, A.; Sennikov, S. Ligand-Regulated Expression of TNF Receptors 1 and 2 Determines Receptor-Mediated Functional Responses. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magliozzi, R.; Howell, O.W.; Durrenberger, P.; Aricò, E.; James, R.; Cruciani, C.; Reeves, C.; Roncaroli, F.; Nicholas, R.; Reynolds, R. Meningeal inflammation changes the balance of TNF signalling in cortical grey matter in multiple sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2019, 16, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wang, Q.; Tian, N.; Lu, M.; Zhang, X.; Dai, S. Knockdown of nrf2 Exacerbates TNF- α -Induced Proliferation and Invasion of Rheumatoid Arthritis Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes through Activating JNK Pathway. J. Immunol. Res. 2020, 2020, 6670464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suto, T.; Tosevska, A.; Dalwigk, K.; Kugler, M.; Dellinger, M. TNFR2 is critical for TNF-induced rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte inflammation. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4535–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.; Capron, J.P.; De Leonardis, F.; Fakhouri, W.; Rose, A.; Kouris, I.; Burke, T. Original article The impact of disease severity and duration on cost, early retirement and ability to work in rheumatoid arthritis in Europe: An economic modelling study. Rheumatol. Adv. Pract. 2020, 4, rkaa041. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Del Mercado, M.; Gomez-Bañuelos, E.; Chavarria-Avila, E.; Cardona-Muñoz, E.; Ramos-Becerra, C.; Alanis-Sanchez, A.; Cardona-Muller, D.; Grover-Paez, F.; Perez-Vazquez, F.D.J.; Navarro-Hernandez, R.E.; et al. Disease duration of rheumatoid arthritis is a predictor of vascular stiffness: A cross-sectional study in patients without known cardiovascular comorbidities. Med. (Baltim.) 2017, 33, e7862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aschenberg, S.; Finzel, S.; Schmidt, S.; Kraus, S.; Engelke, K.; Englbrecht, M.; Rech, J.; Schett, G. Catabolic and anabolic periarticular bone changes in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A computed tomography study on the role of age, disease duration and bone markers. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gothi, D.; Saxena, M.; Sah, R. Disease Duration and Its Impact on Percentage Predicted FEV 1% in Well- Controlled Asthma Patients. Chest 2014, 146, 16A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.R.; Cooper, J.; Koelmeyer, T.I.M.; Paré, P.D.; Weir, T.D. The Effect of Age and Duration of Disease on Airway Structure in Fatal Asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selroos, O.; Ab, S. Effect of disease duration on dose—Response of inhaled budesonide in asthma. Respir. Med. 2008, 102, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Leonard, W.J.; Lin, J.X.; O’Shea, J.J. The γ c Family of Cytokines: Basic Biology to Therapeutic Ramifications. Immunity 2019, 50, 832–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, D.I.; Lee, A.H.; Shin, H.Y.; Song, H.R.; Park, J.H.; Kang, T.B.; Lee, S.R.; Yang, S.H. The role of tumor necrosis factor alpha (Tnf-α) in autoimmune disease and current tnf-α inhibitors in therapeutics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, R.; Kontermann, R.E.; Pfizenmaier, K. Selective Targeting of TNF Receptors as a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holbrook, J.; Lara-Reyna, S.; Jarosz-Griffiths, H.; McDermott, M. Tumour necrosis factor signalling in health and disease [version 1; referees: 2 approved]. F1000Research 2019, 8, F1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sennikov, S.; Alshevskaya, A.; Zhukova, J.; Belomestnova, I.; Karaulov, A.; Evsegneeva, I. and Lopatnikova, J. Co-expression of membrane-bound TNF-alpha type 1 and 2 receptors differ in the subsets of immunocompetent cells. Immunol Lett. 2019, 207, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niessen, N.M.; Gibson, P.G.; Baines, K.J.; Fricker, M.; Simpson, J.L.; Scott, H.A. Airway monocyte modulation relates to tumour necrosis factor dysregulation in neutrophilic asthma. ERJ OPEN Res. 2021, 7, 00131–02021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornwell, W.D.; Kim, V.; Fan, X.; Vega, M.E.; Ramsey, F.V.; Criner, G.J.; Rogers, T.J. Activation and polarization of circulating monocytes in severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. BMC Pulm. Med. 2018, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Nie, Y.; Xiao, H.; Bian, Z.; Scarzello, A.J.; Song, N.Y.; Trivett, A.L.; Yang, D.; Oppenheim, J.J. TNFR2 expression by CD4 effector T cells is required to induce full-fledged experimental colitis. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2016, 6, 32834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Wei, X.; Zhang, M.; Niu, Y.; Zhou, Q. The Significance of Tumor necrosis Factor Receptor Type ii in CD8 + Regulatory T Cells and CD8 + effector T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavrilă, B.I.; Ciofu, C.; Stoica, V. Biomarkers in Rheumatoid Arthritis, what is new? J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 144–148. [Google Scholar]
- Wajant, H.; Siegmund, D. TNFR1 and TNFR2 in the control of the life and death balance of macrophages. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zhou, T.; Zhou, J.; Qiang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Hua, Z. Attenuated Salmonella VNP20009 mutant (ΔhtrA) is a promising candidate for bacteria-mediated tumour therapy in hosts with TNFR1 deficiency. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 67, 97–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.K.; Fang, K.M.; Huang, H.T.; Chang, W.R.; Chuang, C.C.; Tzeng, S.F. Enhanced microglia activation and glioma tumor progression by inflammagen priming in mice with tumor necrosis factor receptor type 2 deficiency. Life 2021, 11, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Su, X.; Cao, A.; Chen, F.; Chen, P.; Yan, F.; Hu, H. TGF-β1/SMOC2/AKT and ERK axis regulates proliferation, migration, and fibroblast to myofibroblast transformation in lung fibroblast, contributing with the asthma progression. Hereditas 2021, 158, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Lang, X.; Xia, S. Elevated expression of microRNA-378 in children with asthma aggravates airway remodeling by promoting the proliferation and apoptosis resistance of airway smooth muscle cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 17, 1529–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Immunol. 2021, 22, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammad, H.; Lambrecht, B.N. The basic immunology of asthma Hamida. Cell 2021, 184, 1469–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonpiyathad, T.; Celebi, Z.; Satitsuksanoa, P. Seminars in Immunology Immunologic mechanisms in asthma. Semin. Immunol. 2019, 46, 101333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, E.; Yoo, S.J.; Choi, S.; Sun, P.; Jung, M.K.; Kwon, S.; Heo, B.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kang, J.G.; Kim, J.; et al. Peripheral Blood from Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Shows Decreased T reg CD25 Expression and Reduced Frequency of effector Treg subpopulation. Cells 2021, 10, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seumois, G.; Ramírez-Suástegui, C.; Schmiedel, B.J.; Liang, S.; Peters, B.; Sette, A.; Vijayanand, P. Single-cell transcriptomic analysis of allergen-specific T cells in allergy and asthma. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaba6087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshevskaya, A.; Lopatnikova, J.; Zhukova, J.; Chumasova, O.; Shkaruba, N.; Sizikov, A.; Evsegneeva, I.; Gladkikh, V.; Karaulov, A.; Sennikov, S.V. Co-expression profile of TNF membrane-bound receptors type 1 and 2 in rheumatoid arthritis on immunocompetent cells subsets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, P.; Hillman, T.; Rajakulasingam, K. Therapeutic targets for persistent airway inflammation in refractory asthma. Biomed Pharm. 2010, 64, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, A.; Henkel, F.D.; Hartung, F.; Bohnacker, S.; Alessandrini, F.; Gubernatorova, E.O.; Drutskaya, M.S.; Angioni, C.; Schreiber, Y.; Haimerl, P.; et al. Macrophages acquire a TNF-dependent inflammatory memory in allergic asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 149, 2078–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mysler, E.; Moots, R.J. Etanercept for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Immunotherapy 2018, 10, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Parameter | Disease Duration <10 Years | Disease Duration ≥10 Years | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Mann–Whitney Test) | |||
| RA patients | Early RA group (n = 26) | Late RA group (n = 15) | |
| Sex: males, n (%) | 6 (23.1%) | 3 (20%) | >0.999 |
| Age, median (IQR) | 49.5 (33; 59) | 48 (40; 61) | >0.999 |
| Disease duration, median (IQR) | 5 (4; 8) | 14 (11; 17) | <0.001 |
| Erosive arthritis, n (%) | 19 (73.1%) | 13 (86.7%) | 0.445 |
| Systemic manifestations of arthritis, n (%) | 8 (30.8%) | 9 (60%) | 0.102 |
| Disease activity [n (%)] | 0/772 | ||
| Low (DAS-28 < 3.2) | 7 (26.9%) | 3 (20%) | |
| Moderate (DAS-28 = 3.2–5.1) | 10 (38.5%) | 5 (33.3%) | |
| High (DAS-28 > 5.1) | 9 (34.6%) | 7 (46.7%) | |
| DAS-28, median (IQR) | 4.47 (3.03; 5.43) | 4.87 (3.81; 5.57) | |
| Patients with asthma | Early asthma group (n = 11) | Late asthma group (n = 11) | |
| Sex: males, n (%) | 4 (36.4%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0.635 |
| Age, median (IQR) | 47 (42; 51) | 46 (27; 57) | 0.699 |
| Disease duration, median (IQR) | 3 (1; 6) | 16 (12; 40) | <0.001 |
| Severity [n (%)] | |||
| Mild (FEV1 > 80%) | 3 (27.3%) | 1 (9.1%) | 0.27 |
| Moderate (FEV1 = 50–79%) | 5 (45.5%) | 4 (36.4%) | |
| Severe (FEV1 = 49–30%) | 2 (18.2%) | 6 (54.5%) | |
| FEV1, %: median (IQR) | 70.05 (62.9; 81.1) | 54.6 (46.5; 63.5) | |
| Control group (healthy individuals) | n = 30 | ||
| Sex: males, n (%) | 9 (30%) | 0.582 * | |
| >0.999 # | |||
| Age, median (IQR) | 45.5 (36; 58) | 0.639 * | |
| 0.876 # | |||
| Parameter of Expression of TNFR1 and/or TNFR2 | RA | Asthma | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients’ Age | Disease Duration | Late RA | Patients’ Age | Disease Duration | Late Asthma | |
| CD14+ monocytes | ||||||
| % of double-positive cells | 0.718 | 0.869 | ||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | −0.483 | −0.526 | ||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | −0.562 | −0.654 | ||||
| n * of TNFR1 | 0.397 | 0.546 | 0.519 | |||
| n of TNFR2 | 0.537 | |||||
| CD3+ T cells | ||||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | 0.329 | |||||
| % of double-negative cells | 0.564 | |||||
| n of TNFR1 | −0.349 | −0.499 | −0.705 | |||
| n of TNFR2 | −0.497 | −0.694 | ||||
| regulatory T cells | ||||||
| % of double-positive cells | −0.342 | |||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | 0.330 | |||||
| % of double-negative cells | −0.541 | −0.529 | ||||
| n of TNFR2 | 0.506 | |||||
| CD4+ T helpers (total pool) | ||||||
| % of double-positive cells | 0.522 | |||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | 0.537 | |||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | −0.619 | −0.661 | ||||
| n of TNFR1 | 0.539 | |||||
| CD4+CD25+ cells | ||||||
| % of double-negative cells | −0.580 | |||||
| % of double-positive cells | ||||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | 0.578 | |||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | −0.727 | |||||
| n of TNFR2 | 0.729 | 0.756 | ||||
| naïve CD4+ cells | ||||||
| % of double-negative cells | −0.855 | −0.862 | ||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | 0.821 | 0.868 | ||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | 0.869 | 0.798 | ||||
| n of TNFR1 | −0.588 | |||||
| memory CD4+ cells | ||||||
| % of double-negative cells | 0.393 | −0.521 | −0.667 | |||
| % of double-positive cells | −0.338 | |||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | 0.565 | |||||
| n of TNFR2 | 0.523 | 0.805 | ||||
| CD8+ cytotoxic T cells (total pool) | ||||||
| % of double-negative cells | −0.588 | −0.849 | ||||
| % of double-positive cells | 0.555 | 0.850 | ||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | −0.363 | |||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | 0.361 | |||||
| CD8+CD25+ | ||||||
| % of double-negative cells | −0.595 | −0.518 | ||||
| % of double-positive cells | 0.820 | 0.590 | ||||
| % of TNFR1+TNFR2− cells | −0.420 | |||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | −0.741 | −0.751 | ||||
| n of TNFR2 | −0.685 | −0.689 | ||||
| naïve CD8+ cells | ||||||
| % of double-positive cells | 0.466 | 0.567 | ||||
| n of TNFR1 | −0.489 | |||||
| memory CD8+ cells | ||||||
| % of TNFR1−TNFR2+ cells | 0.343 | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alshevskaya, A.; Lopatnikova, J.; Zhukova, J.; Chumasova, O.; Shkaruba, N.; Sizikov, A.; Evsegneeva, I.; Demina, D.; Nepomniashchikch, V.; Karaulov, A.; et al. The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors’ Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells 2023, 12, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010005
Alshevskaya A, Lopatnikova J, Zhukova J, Chumasova O, Shkaruba N, Sizikov A, Evsegneeva I, Demina D, Nepomniashchikch V, Karaulov A, et al. The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors’ Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells. 2023; 12(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlshevskaya, Alina, Julia Lopatnikova, Julia Zhukova, Oksana Chumasova, Nadezhda Shkaruba, Alexey Sizikov, Irina Evsegneeva, Daria Demina, Vera Nepomniashchikch, Aleksander Karaulov, and et al. 2023. "The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors’ Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis" Cells 12, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010005
APA StyleAlshevskaya, A., Lopatnikova, J., Zhukova, J., Chumasova, O., Shkaruba, N., Sizikov, A., Evsegneeva, I., Demina, D., Nepomniashchikch, V., Karaulov, A., & Sennikov, S. (2023). The Influence of Severity and Disease Duration on TNF Receptors’ Redistribution in Asthma and Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cells, 12(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12010005





