Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Rationale behind Using Ibrutinib in Solid Tumors
2.1. Ibrutinib Targets BTK in Anti-Solid Tumor Therapy
2.2. Ibrutinib’s Mechanism of Action as an Anti-Solid Tumor Drug
3. Ibrutinib in Studies
3.1. Lung Cancer
3.2. Endometrial Cancer
3.3. Ovarian Cancer
3.4. Breast Cancer
3.5. Pancreatic Cancer
3.6. Gastric Cancer
3.7. Colon Cancer
3.8. Prostate Cancer
3.9. Neuroendocrine Tumors
3.10. Glioblastoma
4. Side Effects of the Therapy with Ibrutinib
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roth, G.A.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Age-Sex-Specific Mortality for 282 Causes of Death in 195 Countries and Territories, 1980–2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1736–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omran, A.R. The Epidemiologic Transition: A Theory of the Epidemiology of Population Change. Milbank Mem. Fund Q. 1971, 49, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarzbich, M.-A.; Witzens-Harig, M. Ibrutinib. In Small Molecules in Oncology; Martens, U.M., Ed.; Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 201, pp. 259–267. ISBN 978-3-642-54489-7. [Google Scholar]
- Novero, A.; Ravella, P.M.; Chen, Y.; Dous, G.; Liu, D. Ibrutinib for B Cell Malignancies. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 3, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nisitani, S.; Satterthwaite, A.B.; Akashi, K.; Weissman, I.L.; Witte, O.N.; Wahl, M.I. Posttranscriptional Regulation of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Expression in Antigen Receptor-Stimulated Splenic B Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 2737–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Xu, S. T-Cell Expression of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Promotes Autoreactive T-Cell Activation and Exacerbates Aplastic Anemia. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 1042–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Albini, A.; Sporn, M.B. The Tumour Microenvironment as a Target for Chemoprevention. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2007, 7, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charalambous, A.; Schwarzbich, M.-A.; Witzens-Harig, M. Ibrutinib. In Small Molecules in Hematology; Martens, U.M., Ed.; Recent Results in Cancer Research; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 212, pp. 133–168. ISBN 978-3-319-91438-1. [Google Scholar]
- Honigberg, L.A.; Smith, A.M.; Sirisawad, M.; Verner, E.; Loury, D.; Chang, B.; Li, S.; Pan, Z.; Thamm, D.H.; Miller, R.A.; et al. The Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor PCI-32765 Blocks B-Cell Activation and Is Efficacious in Models of Autoimmune Disease and B-Cell Malignancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13075–13080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartzberg, P.L.; Finkelstein, L.D.; Readinger, J.A. TEC-Family Kinases: Regulators of T-Helper-Cell Differentiation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 284–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mano, H. Tec Family of Protein-Tyrosine Kinases: An Overview of Their Structure and Function. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 1999, 10, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradshaw, J.M. The Src, Syk, and Tec Family Kinases: Distinct Types of Molecular Switches. Cell Signal. 2010, 22, 1175–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.; Xanthopoulos, C.; Kostareli, E. The Role of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in the Immune System and Disease. Immunology 2021, 164, 722–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendriks, R.W.; Yuvaraj, S.; Kil, L.P. Targeting Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in B Cell Malignancies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corneth, O.B.J.; Klein Wolterink, R.G.J.; Hendriks, R.W. BTK Signaling in B Cell Differentiation and Autoimmunity. In B Cell Receptor Signaling; Kurosaki, T., Wienands, J., Eds.; Current Topics in Microbiology and Immunology; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 393, pp. 67–105. ISBN 978-3-319-26131-7. [Google Scholar]
- Burger, J.A. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: Present and Future. Cancer J. 2019, 25, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A Multiprotein Supercomplex Controlling Oncogenic Signalling in Lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.; Toker, A. NFAT Proteins: Emerging Roles in Cancer Progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 810–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Zhao, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Huang, J. NF-ΚB Expression and Outcomes in Solid Tumors: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicine 2015, 94, e1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhiro, T.; Yoshizawa, T.; Daub, H.; Weber, C.; Narita, M.; Kawabata, K. Abstract 2021: ONO-WG-307, a Novel, Potent and Selective Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (Btk), Results in Sustained Inhibition of the ERK, AKT and PKD Signaling Pathways. In Proceedings of the 103rd Annual Meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research, Chicago, IL, USA, 31 March–4 April 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomlinson, M.G.; Woods, D.B.; McMahon, M.; Wahl, M.I.; Witte, O.N.; Kurosaki, T.; Bolen, J.B.; Johnston, J.A. A Conditional Form of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Is Sufficient to Activate Multiple Downstream Signaling Pathways via PLC Gamma 2 in B Cells. BMC Immunol. 2001, 2, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maik-Rachline, G.; Hacohen-Lev-Ran, A.; Seger, R. Nuclear ERK: Mechanism of Translocation, Substrates, and Role in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaroglio, I.C.; Mungo, E.; Gazzano, E.; Kopecka, J.; Riganti, C. ERK Is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bubici, C.; Papa, S. JNK Signalling in Cancer: In Need of New, Smarter Therapeutic Targets: JNKs in Cancer. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guinamard, R.; Signoret, N.; Ishiai, M.; Marsh, M.; Kurosaki, T.; Ravetch, J.V. B Cell Antigen Receptor Engagement Inhibits Stromal Cell–Derived Factor (SDF)-1α Chemotaxis and Promotes Protein Kinase C (PKC)-Induced Internalization of CXCR4. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 189, 1461–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsukada, S.; Simon, M.I.; Witte, O.N.; Katz, A. Binding of Beta Gamma Subunits of Heterotrimeric G Proteins to the PH Domain of Bruton Tyrosine Kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 11256–11260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Ma, W.; Wan, Y.; Kozasa, T.; Hattori, S.; Huang, X.-Y. The G Protein Gα12 Stimulates Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and a RasGAP through a Conserved PH/BM Domain. Nature 1998, 395, 808–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal Singh, S.; Dammeijer, F.; Hendriks, R.W. Role of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase in B Cells and Malignancies. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-S.; Chang, B.Y.; Chang, S.; Tong, T.; Ham, S.; Sherry, B.; Burger, J.A.; Rai, K.R.; Chiorazzi, N. BTK Inhibition Results in Impaired CXCR4 Chemokine Receptor Surface Expression, Signaling and Function in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Leukemia 2016, 30, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Jiang, P.; Chen, A.; Luo, X.; Jing, Y.; Yang, L.; Kang, D.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.; Chang, J.; et al. CX3CR1 Positively Regulates BCR Signaling Coupled with Cell Metabolism via Negatively Controlling Actin Remodeling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 4379–4395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kil, L.P.; de Bruijn, M.J.; van Hulst, J.A.; Langerak, A.W.; Yuvaraj, S.; Hendriks, R.W. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Mediated Signaling Enhances Leukemogenesis in a Mouse Model for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Am. J. Blood Res. 2013, 3, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Han, T.-T.; Fan, L.; Li, J.-Y.; Xu, W. Role of Chemokines and Their Receptors in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mortezaee, K. CXCL12/CXCR4 Axis in the Microenvironment of Solid Tumors: A Critical Mediator of Metastasis. Life Sci. 2020, 249, 117534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Adah, D.; Tariq, M.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J. CXCL13/CXCR5 Signaling Axis in Cancer. Life Sci. 2019, 227, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, Y.; Lang, C.; Tang, J.; Geng, J.; Song, H.K.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J. CXCR5 + CD8 + T Cells Could Induce the Death of Tumor Cells in HBV-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 53, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Guo, L.; Sun, H.; Xu, J.; Ba, T. CXCR5+ CD8 T Cells Displayed Higher Activation Potential despite High PD-1 Expression, in Tumor-Involved Lymph Nodes from Patients with Thyroid Cancer. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 62, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, M.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, B.; Zhan, Y.; He, H. CXCR5+ CD8+ T Cells Potently Infiltrate Pancreatic Tumors and Present High Functionality. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 361, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, J.; Zhang, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, E. CXCR5+CD8+T Cells Infiltrate the Colorectal Tumors and Nearby Lymph Nodes, and Are Associated with Enhanced IgG Response in B Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 356, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- E, J.; Yan, F.; Kang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Xing, J.; Yu, E. CD8+CXCR5+ T Cells in Tumor-Draining Lymph Nodes Are Highly Activated and Predict Better Prognosis in Colorectal Cancer. Hum. Immunol. 2018, 79, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wong, J.; Sevinsky, C.J.; Kokabee, L.; Khan, F.; Sun, Y.; Conklin, D.S. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Prevent Therapeutic Escape in Breast Cancer Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2198–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, W.; Liu, R.; Bhardwaj, G.; Yang, J.C.; Changou, C.; Ma, A.-H.; Mazloom, A.; Chintapalli, S.; Xiao, K.; Xiao, W.; et al. Targeting Btk/Etk of Prostate Cancer Cells by a Novel Dual Inhibitor. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5, e1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokabee, L.; Wang, X.; Sevinsky, C.J.; Wang, W.L.W.; Cheu, L.; Chittur, S.V.; Karimipoor, M.; Tenniswood, M.; Conklin, D.S. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Is a Potential Therapeutic Target in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 1604–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campbell, R.; Chong, G.; Hawkes, E. Novel Indications for Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors, beyond Hematological Malignancies. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eifert, C.; Wang, X.; Kokabee, L.; Kourtidis, A.; Jain, R.; Gerdes, M.J.; Conklin, D.S. A Novel Isoform of the B Cell Tyrosine Kinase BTK Protects Breast Cancer Cells from Apoptosis: BTK in Breast Cancer. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2013, 52, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.; Cai, C.; Sowalsky, A.G.; Ye, H.; Ma, F.; Yuan, X.; Simon, N.I.; Gray, N.S.; Balk, S.P. BMX-Mediated Regulation of Multiple Tyrosine Kinases Contributes to Castration Resistance in Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5203–5215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Molina-Cerrillo, J.; Alonso-Gordoa, T.; Gajate, P.; Grande, E. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) as a Promising Target in Solid Tumors. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2017, 58, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavitrano, M.; Ianzano, L.; Bonomo, S.; Cialdella, A.; Cerrito, M.G.; Pisano, F.; Missaglia, C.; Giovannoni, R.; Romano, G.; McLean, C.M.; et al. BTK Inhibitors Synergise with 5-FU to Treat Drug-resistant TP53 -null Colon Cancers. J. Pathol. 2020, 250, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckun, F.M.; Venkatachalam, T. Targeting Solid Tumors with BTK Inhibitors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 650414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Couch, G.S.; Croll, T.I.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure Visualization for Researchers, Educators, and Developers. Protein Sci. 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting Modern Challenges in Visualization and Analysis. Protein Sci. Publ. Protein Soc. 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bender, A.T.; Gardberg, A.; Pereira, A.; Johnson, T.; Wu, Y.; Grenningloh, R.; Head, J.; Morandi, F.; Haselmayer, P.; Liu-Bujalski, L. Ability of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors to Sequester Y551 and Prevent Phosphorylation Determines Potency for Inhibition of Fc Receptor but Not B-Cell Receptor Signaling. Mol. Pharmacol. 2017, 91, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lindvall, J.M.; Blomberg, K.E.M.; Väliaho, J.; Vargas, L.; Heinonen, J.E.; Berglöf, A.; Mohamed, A.J.; Nore, B.F.; Vihinen, M.; Smith, C.I.E. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase: Cell Biology, Sequence Conservation, Mutation Spectrum, SiRNA Modifications, and Expression Profiling. Immunol. Rev. 2005, 203, 200–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uckun, F.M.; Tibbles, H.E.; Vassilev, A.O. Brutons Tyrosine Kinase as a New Therapeutic Target. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2007, 7, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davids, M.S.; Brown, J.R. Ibrutinib: A First in Class Covalent Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2014, 10, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Martin, V.; Cappuzzo, F.; Mazzucchelli, L.; Frattini, M. HER2 in Solid Tumors: More than 10 Years under the Microscope; Where Are We Now? Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1469–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskin, J.J.; Sandler, A.B. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor: A Promising Target in Solid Tumours. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedlaender, A.; Subbiah, V.; Russo, A.; Banna, G.L.; Malapelle, U.; Rolfo, C.; Addeo, A. EGFR and HER2 Exon 20 Insertions in Solid Tumours: From Biology to Treatment. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 51–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, E.G.; Kim, M.S.; Nam, H.K.; Min, C.K.; Lee, S.; Chung, Y.J.; Yoo, N.J.; Lee, S.H. Somatic Mutations of JAK1 and JAK3 in Acute Leukemias and Solid Cancers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 3716–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puzzolo, M.C.; Del Giudice, I.; Peragine, N.; Mariglia, P.; De Propris, M.S.; Cappelli, L.V.; Trentin, L.; Reda, G.; Cuneo, A.; Molica, S.; et al. TH2/TH1 Shift Under Ibrutinib Treatment in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 637186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.T.; Wilcox, H.M.; Lai, Z.; Berg, L.J. Signaling through Itk Promotes T Helper 2 Differentiation via Negative Regulation of T-Bet. Immunity 2004, 21, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Q.; Davidson, D.; Schwartzberg, P.L.; Macchiarini, F.; Lenardo, M.J.; Bluestone, J.A.; Matis, L.A. Identification of Rlk, a Novel Protein Tyrosine Kinase with Predominant Expression in the T Cell Lineage. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 1928–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kashiwakura, J.; Suzuki, N.; Nagafuchi, H.; Takeno, M.; Takeba, Y.; Shimoyama, Y.; Sakane, T. Txk, a Nonreceptor Tyrosine Kinase of the Tec Family, Is Expressed in T Helper Type 1 Cells and Regulates Interferon γ Production in Human T Lymphocytes. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1147–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andreu, P.; Johansson, M.; Affara, N.I.; Pucci, F.; Tan, T.; Junankar, S.; Korets, L.; Lam, J.; Tawfik, D.; DeNardo, D.G.; et al. FcRγ Activation Regulates Inflammation-Associated Squamous Carcinogenesis. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woo, J.R.; Liss, M.A.; Muldong, M.T.; Palazzi, K.; Strasner, A.; Ammirante, M.; Varki, N.; Shabaik, A.; Howell, S.; Kane, C.J.; et al. Tumor Infiltrating B-Cells Are Increased in Prostate Cancer Tissue. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gunderson, A.J.; Kaneda, M.M.; Tsujikawa, T.; Nguyen, A.V.; Affara, N.I.; Ruffell, B.; Gorjestani, S.; Liudahl, S.M.; Truitt, M.; Olson, P.; et al. Bruton Tyrosine Kinase–Dependent Immune Cell Cross-Talk Drives Pancreas Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 270–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wong, S.-C.; Puaux, A.-L.; Chittezhath, M.; Shalova, I.; Kajiji, T.S.; Wang, X.; Abastado, J.-P.; Lam, K.-P.; Biswas, S.K. Macrophage Polarization to a Unique Phenotype Driven by B Cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 2296–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messex, J.K.; Liou, G.-Y. Targeting BTK Signaling in the Microenvironment of Solid Tumors as a Feasible Cancer Therapy Option. Cancers 2021, 13, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Nagaraj, S. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells as Regulators of the Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 162–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrilovich, D.I.; Ostrand-Rosenberg, S.; Bronte, V. Coordinated Regulation of Myeloid Cells by Tumours. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 253–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiff, A.; Trikha, P.; Wesolowski, R.; Kendra, K.; Hsu, V.; Uppati, S.; McMichael, E.; Duggan, M.; Campbell, A.; Keller, K.; et al. Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells Express Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase and Can Be Depleted in Tumor-Bearing Hosts by Ibrutinib Treatment. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2125–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishfaq, M.; Pham, T.; Beaman, C.; Tamayo, P.; Yu, A.L.; Joshi, S. BTK Inhibition Reverses MDSC-Mediated Immunosuppression and Enhances Response to Anti-PDL1 Therapy in Neuroblastoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilfillan, A.M.; Rivera, J. The Tyrosine Kinase Network Regulating Mast Cell Activation. Immunol. Rev. 2009, 228, 149–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiorcari, S.; Maffei, R.; Audrito, V.; Martinelli, S.; ten Hacken, E.; Zucchini, P.; Grisendi, G.; Potenza, L.; Luppi, M.; Burger, J.A.; et al. Ibrutinib Modifies the Function of Monocyte/Macrophage Population in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 65968–65981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massó-Vallés, D.; Jauset, T.; Serrano, E.; Sodir, N.M.; Pedersen, K.; Affara, N.I.; Whitfield, J.R.; Beaulieu, M.-E.; Evan, G.I.; Elias, L.; et al. Ibrutinib Exerts Potent Antifibrotic and Antitumor Activities in Mouse Models of Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 1675–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Von Suskil, M.; Sultana, K.N.; Elbezanti, W.O.; Al-Odat, O.S.; Chitren, R.; Tiwari, A.K.; Challagundla, K.B.; Srivastava, S.K.; Jonnalagadda, S.C.; Budak-Alpdogan, T.; et al. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Targeting in Multiple Myeloma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarboe, J.S.; Dutta, S.; Velu, S.E.; Willey, C.D. Mini-Review: Bmx Kinase Inhibitors for Cancer Therapy. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Lu, H.; Wu, S.; Dai, B.; Ou, Z.; Zhang, L.; Heymach, J.V.; Gold, K.A.; et al. Selective Antitumor Activity of Ibrutinib in EGFR-Mutant Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2014, 106, dju204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Wang, A.; Zhang, W.; Wang, B.; Chen, C.; Wang, W.; Hu, C.; Ye, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. Ibrutinib Selectively and Irreversibly Targets EGFR (L858R, Del19) Mutant but Is Moderately Resistant to EGFR (T790M) Mutant NSCLC Cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31313–31322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, Q. Inhibition of Platelet-Tumour Cell Interaction with Ibrutinib Reduces Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Lung Cancer Cells. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 2018, 17, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, D.; Rasco, D.; Veeder, M.; Luke, J.J.; Chandler, J.; Balmanoukian, A.; George, T.J.; Munster, P.; Berlin, J.D.; Gutierrez, M.; et al. A Phase 1b/2 Study of the Bruton Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Ibrutinib and the PD-L1 Inhibitor Durvalumab in Patients with Pretreated Solid Tumors. Oncology 2019, 97, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, H.; Higa, A.; Hoshi, H.; Hiyama, G.; Takahashi, N.; Ryufuku, M.; Morisawa, G.; Yanagisawa, Y.; Ito, E.; Imai, J.-I.; et al. Evaluation of Anticancer Agents Using Patient-Derived Tumor Organoids Characteristically Similar to Source Tissues. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 635–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zucha, M.A.; Wu, A.T.H.; Lee, W.-H.; Wang, L.-S.; Lin, W.-W.; Yuan, C.-C.; Yeh, C.-T. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (Btk) Inhibitor Ibrutinib Suppresses Stem-like Traits in Ovarian Cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13255–13268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lohse, I.; Azzam, D.J.; Al-Ali, H.; Volmar, C.-H.; Brothers, S.P.; Ince, T.A.; Wahlestedt, C. Ovarian Cancer Treatment Stratification Using Ex Vivo Drug Sensitivity Testing. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 4023–4030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grabinski, N.; Ewald, F. Ibrutinib (ImbruvicaTM) Potently Inhibits ErbB Receptor Phosphorylation and Cell Viability of ErbB2-Positive Breast Cancer Cells. Invest New Drugs 2014, 32, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kinoshita, T.; Sukbuntherng, J.; Chang, B.Y.; Elias, L. Ibrutinib Inhibits ERBB Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and HER2-Amplified Breast Cancer Cell Growth. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prabaharan, C.B.; Yang, A.B.; Chidambaram, D.; Rajamanickam, K.; Napper, S.; Sakharkar, M.K. Ibrutinib as a Potential Therapeutic Option for HER2 Overexpressing Breast Cancer–the Role of STAT3 and P21. Invest New Drugs 2020, 38, 909–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiv-Barfi, I.; Kohrt, H.E.K.; Czerwinski, D.K.; Ng, P.P.; Chang, B.Y.; Levy, R. Therapeutic Antitumor Immunity by Checkpoint Blockade Is Enhanced by Ibrutinib, an Inhibitor of Both BTK and ITK. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E966–E972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varikuti, S.; Singh, B.; Volpedo, G.; Ahirwar, D.K.; Jha, B.K.; Saljoughian, N.; Viana, A.G.; Verma, C.; Hamza, O.; Halsey, G.; et al. Ibrutinib Treatment Inhibits Breast Cancer Progression and Metastasis by Inducing Conversion of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells to Dendritic Cells. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Lin, N. The Effect of Ibrutinib on Radiosensitivity in Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Targeting EGFR/AKT/MTOR Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 128, 110133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempero, M.; Oh, D.-Y.; Tabernero, J.; Reni, M.; Van Cutsem, E.; Hendifar, A.; Waldschmidt, D.-T.; Starling, N.; Bachet, J.-B.; Chang, H.-M.; et al. Ibrutinib in Combination with Nab-Paclitaxel and Gemcitabine for First-Line Treatment of Patients with Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma: Phase III RESOLVE Study. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.D.; Chen, X.Y.; Ji, K.W.; Tao, F. Targeting Btk with Ibrutinib Inhibit Gastric Carcinoma Cells Growth. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 3003–3012. [Google Scholar]
- Grassilli, E.; Pisano, F.; Cialdella, A.; Bonomo, S.; Missaglia, C.; Cerrito, M.G.; Masiero, L.; Ianzano, L.; Giordano, F.; Cicirelli, V.; et al. A Novel Oncogenic BTK Isoform Is Overexpressed in Colon Cancers and Required for RAS-Mediated Transformation. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4368–4378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.W.; Tan, E.; Zhou, J.-M.; Schell, M.J.; Martinez, M.; Yu, J.; Carballido, E.; Mehta, R.; Strosberg, J.; Imanirad, I.; et al. A Phase 1/2 Trial of Ibrutinib in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Mismatch Repair Proficient Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 124, 1803–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Ling, L.; Qi, L.; Chong, Y.; Xue, L. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase (BTK) Inhibitor (Ibrutinib)-Suppressed Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 4113–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Toubah, T.; Schell, M.J.; Cives, M.; Zhou, J.-M.; Soares, H.P.; Strosberg, J.R. A Phase II Study of Ibrutinib in Advanced Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Neuroendocrinology 2020, 110, 377–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Su, Y.-K.; Lin, C.-M.; Chao, T.-Y.; Huang, S.-P.; Huynh, T.-T.; Jan, H.-J.; Whang-Peng, J.; Chiou, J.-F.; Wu, A.T.H.; et al. Preclinical Investigation of Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s Kinase Tyrosine (Btk) Inhibitor, in Suppressing Glioma Tumorigenesis and Stem Cell Phenotypes. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 69961–69975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hong, Y.; Wang, S.; Chen, P.; Gu, A.; Guo, X.; Zhao, P. Ibrutinib, a Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, Exhibits Antitumoral Activity and Induces Autophagy in Glioblastoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hainsworth, J.D.; Cebotaru, C.L.; Kanarev, V.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Damyanov, D.; Stella, P.; Ganchev, H.; Pover, G.; Morris, C.; Tzekova, V. A Phase II, Open-Label, Randomized Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of AZD6244 (ARRY-142886) Versus Pemetrexed in Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Who Have Failed One or Two Prior Chemotherapeutic Regimens. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2010, 5, 1630–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haura, E.B.; Ricart, A.D.; Larson, T.G.; Stella, P.J.; Bazhenova, L.; Miller, V.A.; Cohen, R.B.; Eisenberg, P.D.; Selaru, P.; Wilner, K.D.; et al. A Phase II Study of PD-0325901, an Oral MEK Inhibitor, in Previously Treated Patients with Advanced Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blumenschein, G.R.; Smit, E.F.; Planchard, D.; Kim, D.-W.; Cadranel, J.; De Pas, T.; Dunphy, F.; Udud, K.; Ahn, M.-J.; Hanna, N.H.; et al. A Randomized Phase II Study of the MEK1/MEK2 Inhibitor Trametinib (GSK1120212) Compared with Docetaxel in KRAS-Mutant Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC). Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 894–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Chavez, A.; Thomas, A.; Rajan, A.; Raffeld, M.; Morrow, B.; Kelly, R.; Carter, C.A.; Guha, U.; Killian, K.; Lau, C.C.; et al. Molecular Profiling and Targeted Therapy for Advanced Thoracic Malignancies: A Biomarker-Derived, Multiarm, Multihistology Phase II Basket Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1000–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oxnard, G.R.; Yang, J.C.-H.; Yu, H.; Kim, S.-W.; Saka, H.; Horn, L.; Goto, K.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Thress, K.S.; et al. TATTON: A Multi-Arm, Phase Ib Trial of Osimertinib Combined with Selumetinib, Savolitinib, or Durvalumab in EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carter, C.A.; Rajan, A.; Keen, C.; Szabo, E.; Khozin, S.; Thomas, A.; Brzezniak, C.; Guha, U.; Doyle, L.A.; Steinberg, S.M.; et al. Selumetinib with and without Erlotinib in KRAS Mutant and KRAS Wild-Type Advanced Nonsmall-Cell Lung Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2016, 27, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; Quan, S. Synergistic Interaction between MEK Inhibitor and Gefitinib in EGFR-TKI-resistant Human Lung Cancer Cells. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 2652–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Allain, E.P.; Rouleau, M.; Lévesque, E.; Guillemette, C. Emerging Roles for UDP-Glucuronosyltransferases in Drug Resistance and Cancer Progression. Br. J. Cancer 2020, 122, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Korprasertthaworn, P.; Chau, N.; Nair, P.C.; Rowland, A.; Miners, J.O. Inhibition of Human UDP-Glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) Enzymes by Kinase Inhibitors: Effects of Dabrafenib, Ibrutinib, Nintedanib, Trametinib and BIBF 1202. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 169, 113616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Hu, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Feng, J.; Lin, N. The Ibr-7 Derivative of Ibrutinib Exhibits Enhanced Cytotoxicity against Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Targeting of mTORC 1/S6 Signaling. Mol. Oncol. 2019, 13, 946–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Metzler, J.M.; Burla, L.; Fink, D.; Imesch, P. Ibrutinib in Gynecological Malignancies and Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, B.; Dong, R.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Y.; Li, Q.; Wang, F.; Lin, N. The Ibr-7 Derivative of Ibrutinib Radiosensitizes Pancreatic Cancer Cells by Downregulating p-EGFR. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalinkeel, R.; Nair, B.B.; Reynolds, J.L.; Sykes, D.E.; Mahajan, S.D.; Chadha, K.C.; Schwartz, S.A. Overexpression of MMP-9 Contributes to Invasiveness of Prostate Cancer Cell Line LNCaP. Immunol. Invest 2011, 40, 447–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Dong, B.; Yan, Y.; Hu, G.; Xu, Y. Association between MMP-2 Expression and Prostate Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Biomed. Rep. 2016, 4, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bitar, C.; Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Valdez, J.; Saba, N.S.; Soto, S.; Bray, A.; Marti, G.; Wiestner, A.; Cowen, E.W. Hair and Nail Changes During Long-Term Therapy With Ibrutinib for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Flinn, I.W.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Grant, B.; Sharman, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; et al. Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Brown, J.R.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.C.; Kay, N.E.; Reddy, N.M.; Coutre, S.; Tam, C.S.; Mulligan, S.P.; Jaeger, U.; et al. Ibrutinib versus Ofatumumab in Previously Treated Chronic Lymphoid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.L.; Rule, S.; Martin, P.; Goy, A.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.S.; Jurczak, W.; Advani, R.H.; Romaguera, J.E.; Williams, M.E.; et al. Targeting BTK with Ibrutinib in Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iberri, D.J.; Kwong, B.Y.; Stevens, L.A.; Coutre, S.E.; Kim, J.; Sabile, J.M.; Advani, R.H. Ibrutinib-Associated Rash: A Single-Centre Experience of Clinicopathological Features and Management. Br. J. Haematol. 2018, 180, 164–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.L.; Lee, H.; Chuang, H.; Wagner-Bartak, N.; Hagemeister, F.; Westin, J.; Fayad, L.; Samaniego, F.; Turturro, F.; Oki, Y.; et al. Ibrutinib in Combination with Rituximab in Relapsed or Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: A Single-Centre, Open-Label, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, F.; Leong, D.P.; Hillis, C.; Fraser, G.; Siegal, D. Current Understanding of Bleeding with Ibrutinib Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, J.C.; Furman, R.R.; Coutre, S.E.; Burger, J.A.; Blum, K.A.; Coleman, M.; Wierda, W.G.; Jones, J.A.; Zhao, W.; Heerema, N.A.; et al. Three-Year Follow-up of Treatment-Naïve and Previously Treated Patients with CLL and SLL Receiving Single-Agent Ibrutinib. Blood 2015, 125, 2497–2506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.L.; Blum, K.A.; Martin, P.; Goy, A.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.S.; Jurczak, W.; Advani, R.H.; Romaguera, J.E.; Williams, M.E.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up of MCL Patients Treated with Single-Agent Ibrutinib: Updated Safety and Efficacy Results. Blood 2015, 126, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oda, A.; Ikeda, Y.; Ochs, H.D.; Druker, B.J.; Ozaki, K.; Handa, M.; Ariga, T.; Sakiyama, Y.; Witte, O.N.; Wahl, M.I. Rapid Tyrosine Phosphorylation and Activation of Bruton’s Tyrosine/Tec Kinases in Platelets Induced by Collagen Binding or CD32 Cross-Linking. Blood 2000, 95, 1663–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsky, A.H.; Farooqui, M.Z.H.; Tian, X.; Martyr, S.; Cullinane, A.M.; Nghiem, K.; Sun, C.; Valdez, J.; Niemann, C.U.; Herman, S.E.M.; et al. Incidence and Risk Factors of Bleeding-Related Adverse Events in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Treated with Ibrutinib. Haematologica 2015, 100, 1571–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mato, A.R.; Nabhan, C.; Barr, P.M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Howlett, C.; Pu, J.J.; Sehgal, A.R.; et al. Outcomes of CLL Patients Treated with Sequential Kinase Inhibitor Therapy: A Real World Experience. Blood 2016, 128, 2199–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Sivina, M.; Thompson, P.A.; Ferrajoli, A.; Estrov, Z.; Kantarjian, H.; O’Brien, S.; Burger, J.A. Long-Term Follow-up of Treatment with Ibrutinib and Rituximab in Patients with High-Risk Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 2154–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jain, P.; Thompson, P.A.; Keating, M.; Estrov, Z.; Ferrajoli, A.; Jain, N.; Kantarjian, H.; Burger, J.A.; O’Brien, S.; Wierda, W.G. Long-Term Outcomes for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Who Discontinue Ibrutinib: Long-Term Outcome After Ibrutinib in CLL. Cancer 2017, 123, 2268–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Kung, H.-J. Signaling Network of the Btk Family Kinases. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loury, D.; Sukbuntherng, J.; Clow, F.; James, D.F.; Kunkel, L.A. Open Label Evaluation of ECG in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) Receiving Ibrutinib Monotherapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, D.P.; Caron, F.; Hillis, C.; Duan, A.; Healey, J.S.; Fraser, G.; Siegal, D. The Risk of Atrial Fibrillation with Ibrutinib Use: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Blood 2016, 128, 138–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mato, A.R.; Hill, B.T.; Lamanna, N.; Barr, P.M.; Ujjani, C.S.; Brander, D.M.; Howlett, C.; Skarbnik, A.P.; Cheson, B.D.; Zent, C.S.; et al. Optimal Sequencing of Ibrutinib, Idelalisib, and Venetoclax in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results from a Multicenter Study of 683 Patients. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Parikh, S.A.; Noseworthy, P.A.; Goede, V.; Chaffee, K.G.; Bahlo, J.; Call, T.G.; Schwager, S.M.; Ding, W.; Eichhorst, B.; et al. Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL). Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 58, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampson, B.L.; Yu, L.; Glynn, R.J.; Barrientos, J.C.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Banerji, V.; Jones, J.A.; Walewska, R.; Savage, K.J.; Michaud, G.F.; et al. Ventricular Arrhythmias and Sudden Death in Patients Taking Ibrutinib. Blood 2017, 129, 2581–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tomcsányi, J.; Nényei, Z.; Mátrai, Z.; Bózsik, B. Ibrutinib, an Approved Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor as a Potential Cause of Recurrent Polymorphic Ventricular Tachycardia. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2016, 2, 847–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Vincelette, N.D.; Acharya, U.; Abraham, I. Risk of Atrial Fibrillation and Bleeding Diathesis Associated With Ibrutinib Treatment: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis of Four Randomized Controlled Trials. Clin. Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2017, 17, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, I.E.; Jerussi, T.; Farooqui, M.; Tian, X.; Wiestner, A.; Gea-Banacloche, J. Atypical Pneumocystis Jirovecii Pneumonia in Previously Untreated Patients with CLL on Single-Agent Ibrutinib. Blood 2016, 128, 1940–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ghez, D.; Calleja, A.; Protin, C.; Baron, M.; Ledoux, M.-P.; Damaj, G.; Dupont, M.; Dreyfus, B.; Ferrant, E.; Herbaux, C.; et al. Early-Onset Invasive Aspergillosis and Other Fungal Infections in Patients Treated with Ibrutinib. Blood 2018, 131, 1955–1959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, S.P.; Chen, K.; Pandit, A.; Davids, M.S.; Issa, N.C.; Marty, F.M. Risk of Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation in Patients Treated with Ibrutinib. Blood 2018, 131, 1987–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyling, M.; Jurczak, W.; Jerkeman, M.; Silva, R.S.; Rusconi, C.; Trneny, M.; Offner, F.; Caballero, D.; Joao, C.; Witzens-Harig, M.; et al. Ibrutinib versus Temsirolimus in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Mantle-Cell Lymphoma: An International, Randomised, Open-Label, Phase 3 Study. Lancet 2016, 387, 770–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
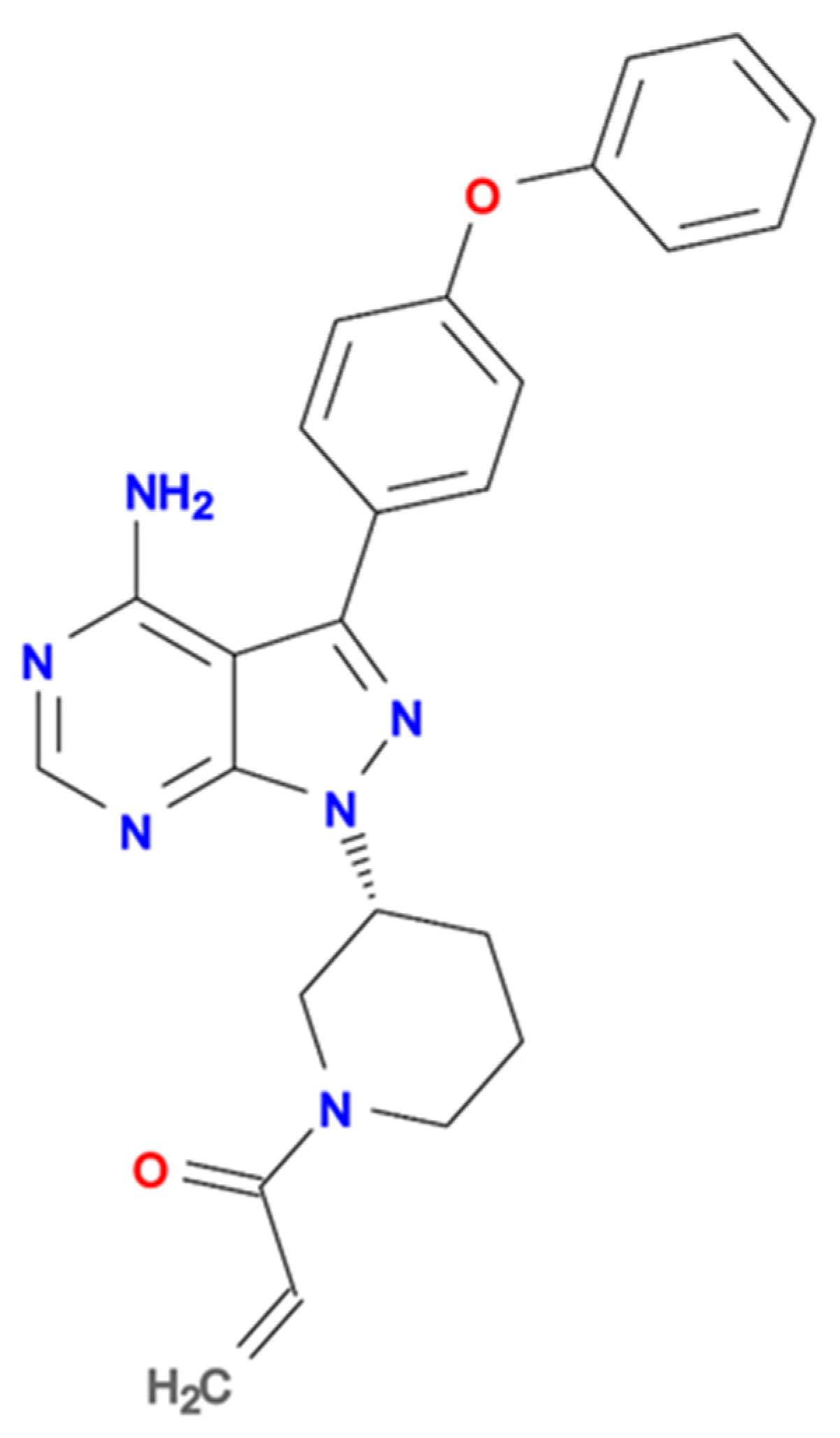
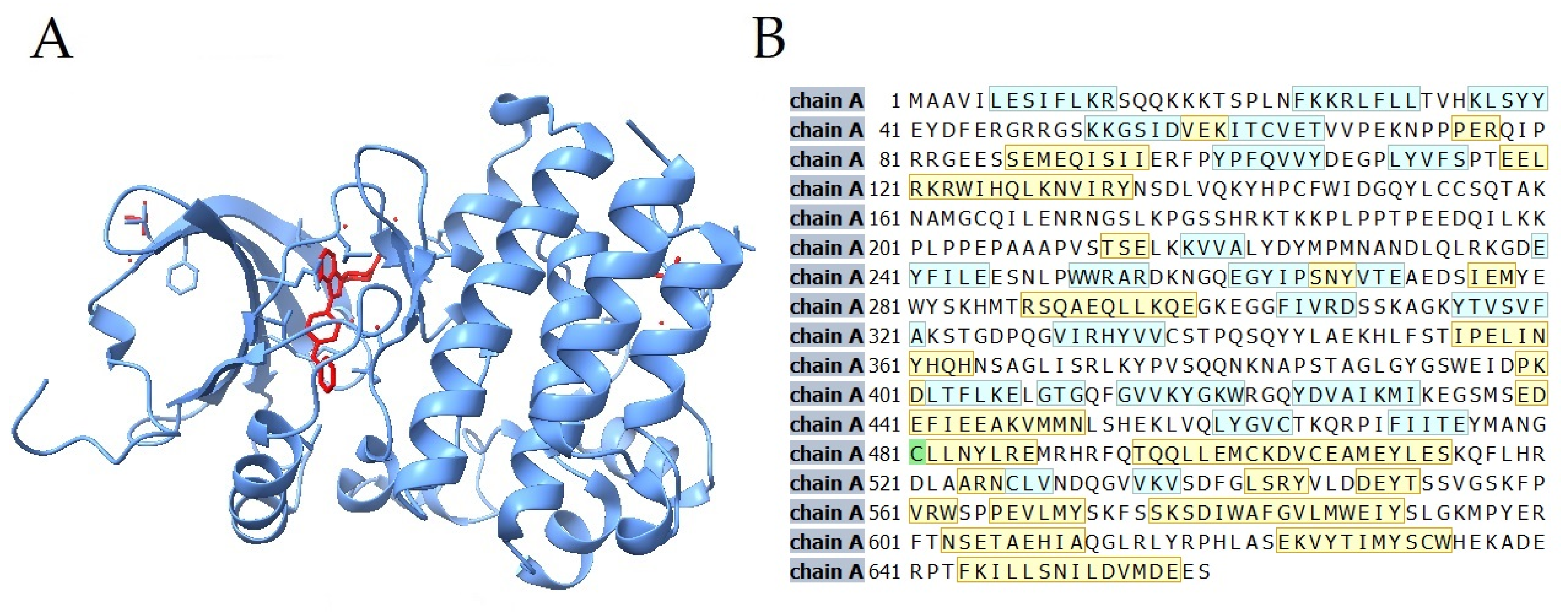
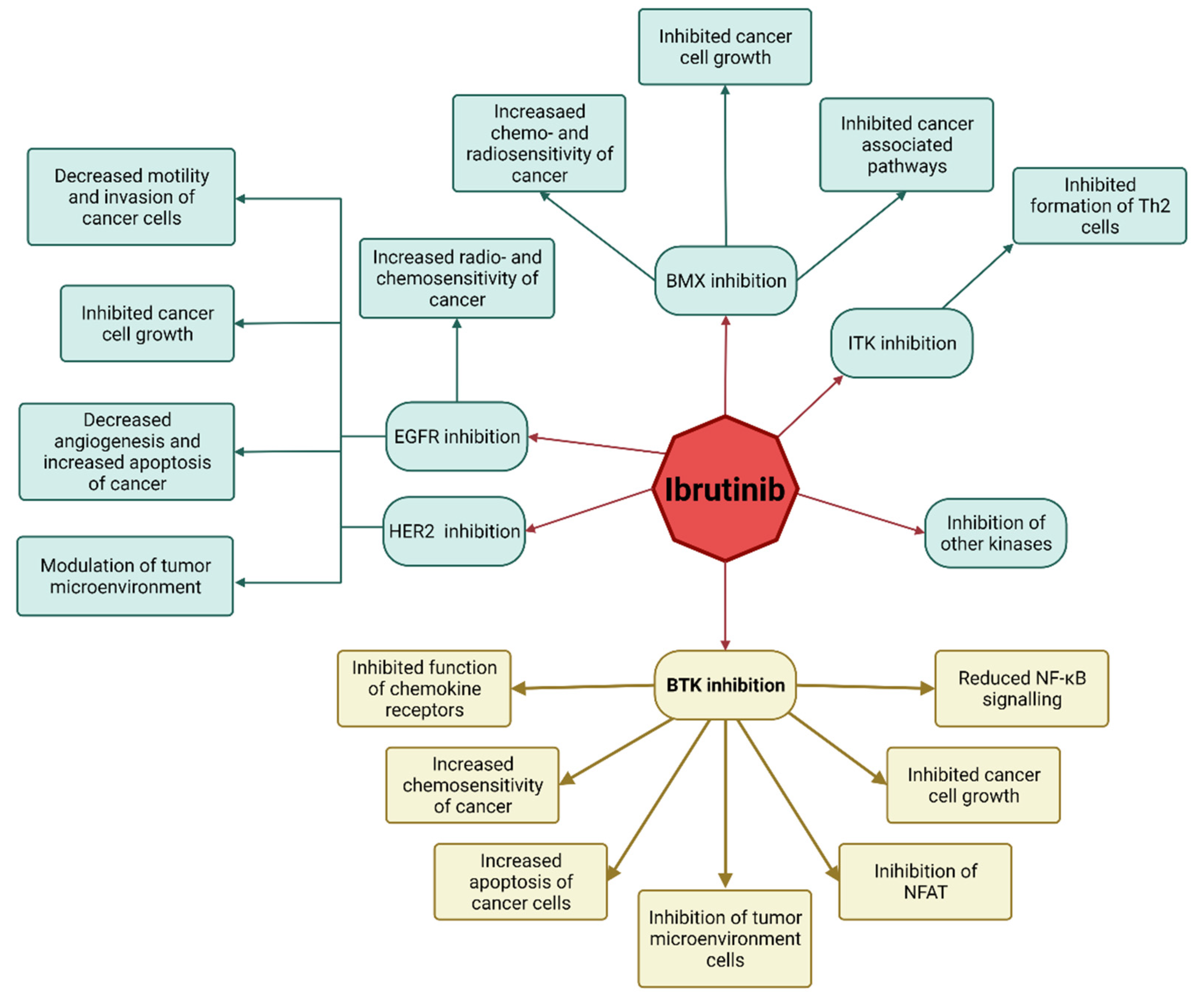
| Kinase | IC50 (nM) |
|---|---|
| BTK | 0.5 |
| BLK | 0.5 |
| BMX | 0.8 |
| CSK | 2.3 |
| BRK | 3.3 |
| HCK | 3.7 |
| EGFR | 5.6 |
| YES | 6.5 |
| HER2 | 9.4 |
| ITK | 10.7 |
| JAK3 | 16.1 |
| FRK | 29.2 |
| LCK | 33.2 |
| RET | 36.5 |
| FLT3 | 73 |
| TEC | 78 |
| RIPK2 | 152 |
| c-SRC | 171 |
| LYN | 200 |
| PDGFRα | 718 |
| mTOR | 4253 |
| Malignancy | Ibrutinib in Preclinical Studies | Ibrutinib in Clinical Trials |
|---|---|---|
| Lung cancer | Increased ST in animal studies [79] Effective towards mutant EGFR cell lines; synergistic effect with MEK-inhibitor in vitro [80] Suppressed tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion [81] | No effect towards NSCLC [82] |
| Endometrial cancer | Suppressed growth of the tumor; higher activity towards endometrioid adenocarcinoma with squamous differentiation than towards clear cell adenocarcinoma [83] | n.a. |
| Ovarian cancer | Platinum sensitizer [84] No activity towards endometrial clear cell adenocarcinoma [85] | n.a. |
| Breast cancer | Activity towards HER2+ cell lines [46,86,87,88] Synergistic effect with PI3K/mTOR inhibitor [86] Synergistic effect with PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor in triple negative cell line [89] Inhibited generation of MDSC [72,90] Reduced mRNA expression of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase [90] Reduced tumor mass and progression [87] | Very poor (OR–3%) activity; mPFS—4.2 months; mOS—1.7 months [82] |
| Pancreatic cancer | Reduced proliferation [76] Radiosensitizer [91] Ibrutinib reduced toxicity caused by gemcitabine [76] | Decrease in mPFS as compared to placebo [92] |
| Gastric cancer | Suppressed growth and survival of cancer cells; chemosensitizer for docetaxel [93] | n.a. |
| Colon cancer | Suppressed growth and survival of cancer cells [94] Synergistic effect with PD-L1 inhibitor [89] Chemosensitizer for 5-fluorouracil [49] | Well tolerated, but with limited anti-cancer activity; mPFS—1.4 months; mOS—6.6 months [95] |
| Prostate cancer | Suppressed tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion [96] | n.a. |
| Neuroendocrine tumors | n.a. | No activity [97] |
| Glioblastoma | Suppressed tumor cell proliferation, migration and invasion [98,99] Synergistic effect with PI3K inhibitor [99] | n.a. |
| Neoplasm | Comedication | Phase | NCT |
|---|---|---|---|
| HER2+ breast cancer | Trastuzumab | I/II | NCT03379428 |
| Prostate cancer | n.a. | II | NCT02643667 |
| Colon cancer | Pembrolizumab | I/II | NCT03332498 |
| Melanoma | n.a. | II | NCT02581930 |
| Ependymoma Medulloblastoma Glioblastoma PNET | Indoximod Cyclophosphamide Etoposide | I | NCT05106296 |
| Solid tumors | Nivolumab | I | NCT03525925 |
| Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma | Nivolumab Cetuximab | II | NCT03646461 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szklener, K.; Michalski, A.; Żak, K.; Piwoński, M.; Mańdziuk, S. Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions. Cells 2022, 11, 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081338
Szklener K, Michalski A, Żak K, Piwoński M, Mańdziuk S. Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions. Cells. 2022; 11(8):1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081338
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzklener, Katarzyna, Adam Michalski, Klaudia Żak, Michał Piwoński, and Sławomir Mańdziuk. 2022. "Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions" Cells 11, no. 8: 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081338
APA StyleSzklener, K., Michalski, A., Żak, K., Piwoński, M., & Mańdziuk, S. (2022). Ibrutinib in the Treatment of Solid Tumors: Current State of Knowledge and Future Directions. Cells, 11(8), 1338. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081338






