Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts
Abstract
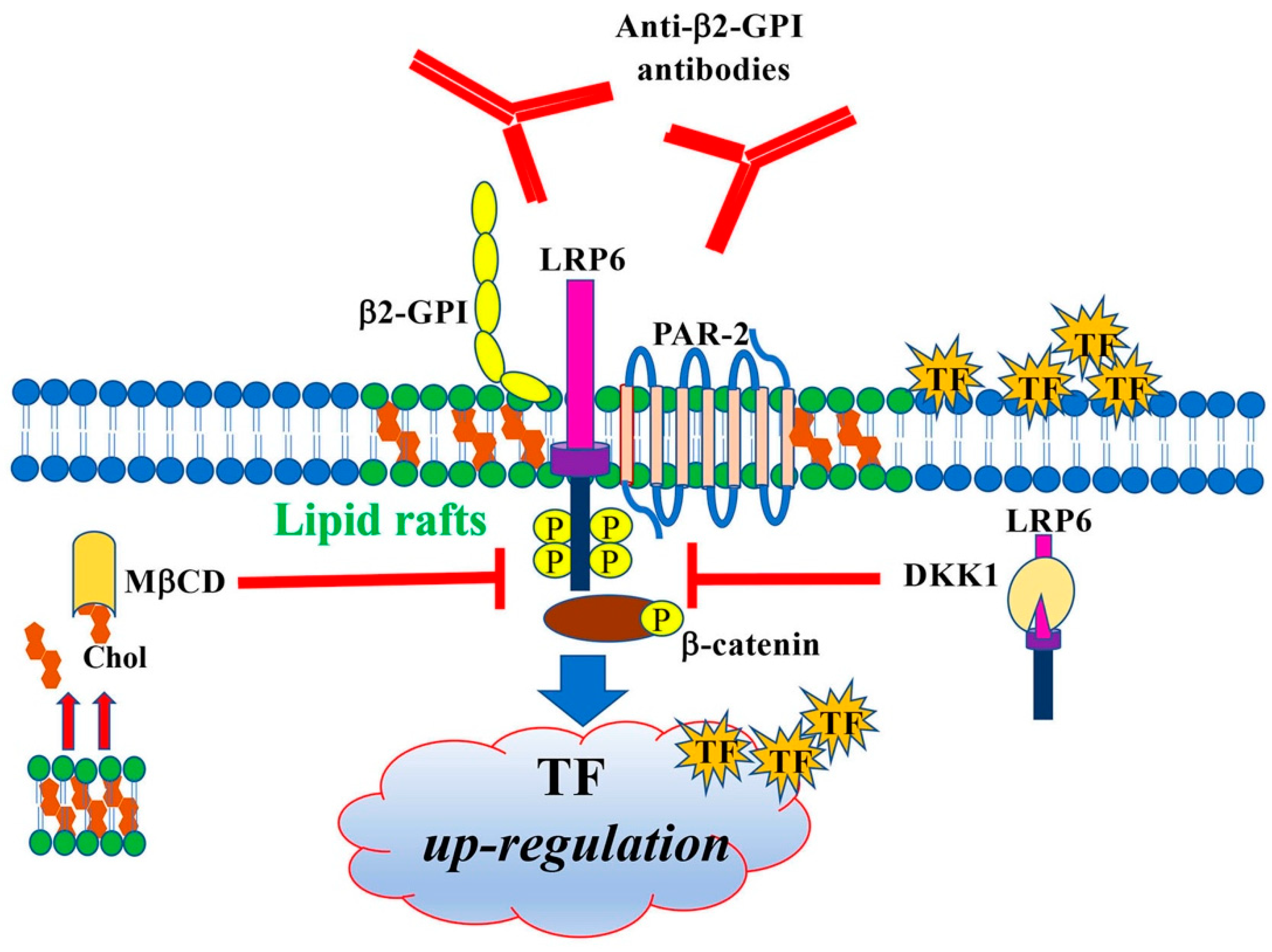
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture and Treatments
2.2. Purification of Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies
2.3. Western Blotting Analysis
2.4. Sucrose-Gradient Fractionation
2.5. Western Blot Analysis of Sucrose-Gradient Fractions
2.6. Immunoprecipitation of LRP6
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
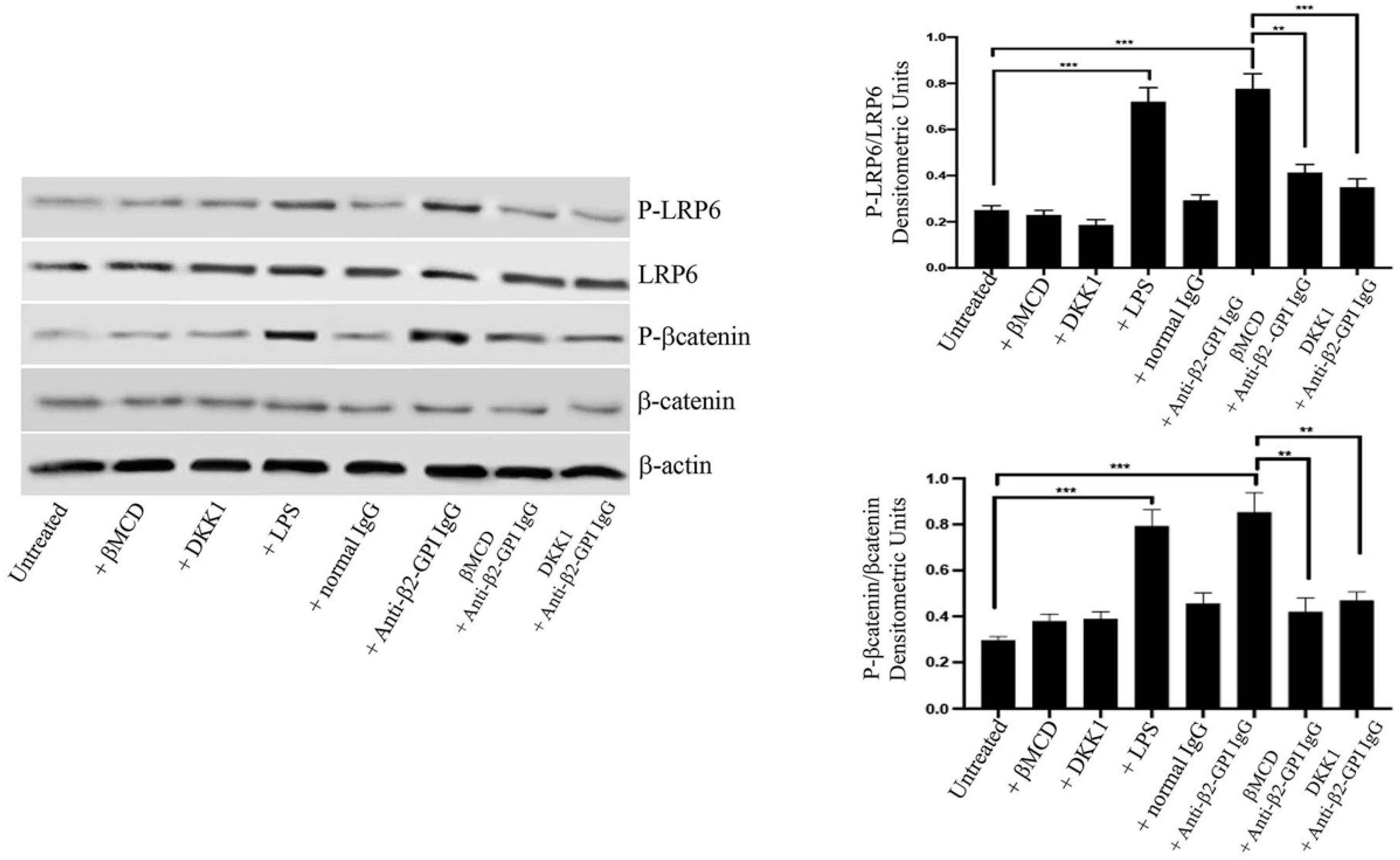
3.1. Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce LRP6 and β-Catenin Phosphorylation
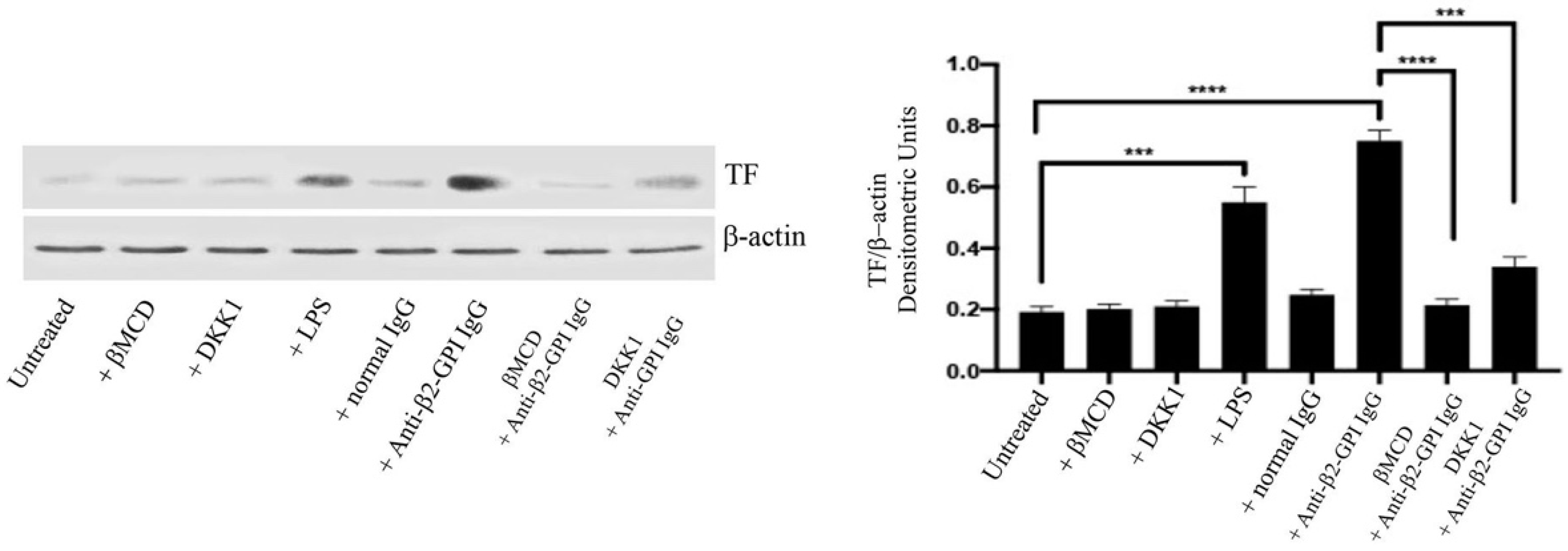
3.2. Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Tissue Factor Expression
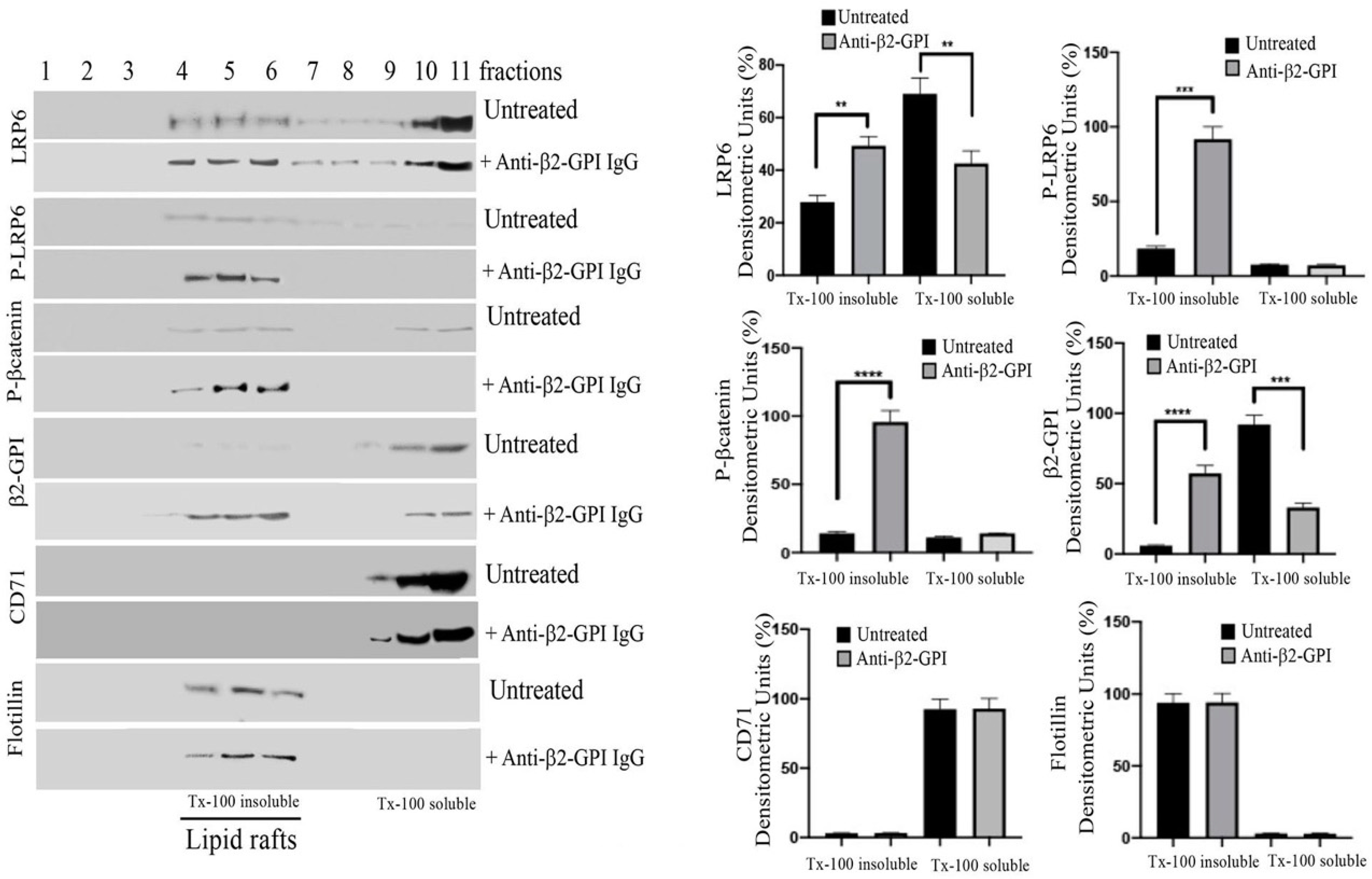
3.3. β2-GPI and LRP6 Preferential Association with Lipid Raft Fractions
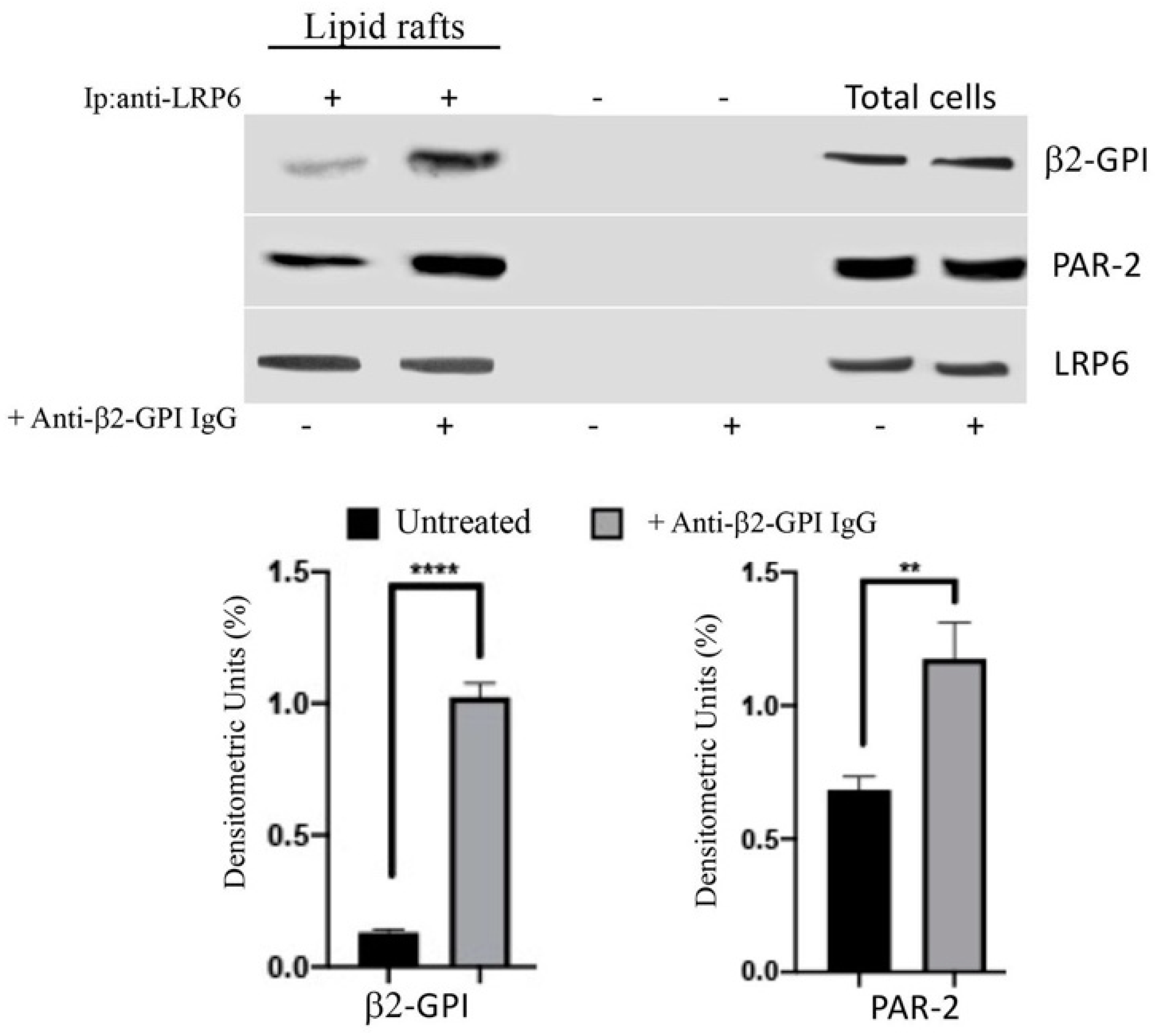
3.4. Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Trigger β2-GPI-LRP6 Interaction within Lipid Rafts of Endothelial Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Miyakis, S.; Lockshin, M.D.; Atsumi, T.; Branch, D.W.; Brey, R.L.; Cervera, R.; Derksen, R.H.; DE Groot, P.G.; Koike, T.; Meroni, P.L.; et al. International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rand, J.H. Molecular pathogenesis of the antiphospholipid syndrome. Circ. Res. 2002, 90, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Radic, M.; Pattanaik, D. Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Anti-Phospholipid Syndrome. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corban, M.T.; Duarte-Garcia, A.; McBane, R.D.; Matteson, E.L.; Lerman, L.O.; Lerman, A. Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Role of Vascular Endothelial Cells and Implications for Risk Stratification and Targeted Therapeutics. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 69, 2317–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velásquez, M.; Rojas, M.; Abrahams, V.M.; Escudero, C.; Cadavid, Á.P. Mechanisms of Endothelial Dysfunction in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Association with Clinical Manifestations. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liao, J.K. Linking endothelial dysfunction with endothelial cell activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2013, 123, 540–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Pedrera, C.; Barbarroja, N.; Patiño-Trives, A.M.; Collantes, E.; Aguirre, M.A.; Perez-Sanchez, C. New Biomarkers for Atherothrombosis in Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Genomics and Epigenetics Approaches. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Kim, S.Y. Antiphospholipid Antibody and Recurrent Ischemic Stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Stroke 2020, 51, 3728–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Grimshaw, M.; Posadas-Pinto, D.R.; Jiménez-Ruiz, A.; Valdés-Ferrer, S.I.; Cadena-Fernández, A.; Torres-Ruiz, J.J.; Barrientos-Guerra, J.D.; Amancha-Gabela, M.; Chiquete, E.; Flores-Silva, F.D.; et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome-mediated acute cerebrovascular diseases and long-term outcomes. Lupus 2022, 31, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zelaya, H.; Rothmeier, A.S.; Ruf, W. Tissue factor at the crossroad of coagulation and cell signaling. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 16, 1941–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folco, E.J.; Mawson, T.L.; Vromman, A.; Bernardes-Souza, B.; Franck, G.; Persson, O.; Nakamura, M.; Newton, G.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Libby, P. Neutrophil Extracellular Traps Induce Endothelial Cell Activation and Tissue Factor Production through Interleukin-1α and Cathepsin G. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2018, 38, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, H.; Wakita, Y.; Shiku, H. Tissue factor expression in endothelial cells in health and disease. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 1995, 6 (Suppl. 1), S26–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, P.G.; Urbanus, R.T. The significance of autoantibodies against β2-glycoprotein I. Blood 2012, 120, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raschi, E.; Testoni, C.; Bosisio, D.; Borghi, M.O.; Koike, T.; Mantovani, A.; Meroni, P.L. Role of the MyD88 transduction signaling pathway in endothelial activation by antiphospholipid antibodies. Blood 2003, 101, 3495–3500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorice, M.; Longo, A.; Capozzi, A.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Alessandri, C.; Conti, F.; Buttari, B.; Riganò, R.; Ortona, E.; et al. Anti-beta2-glycoprotein I antibodies induce monocyte release of tumor necrosis factor alpha and tissue factor by signal transduction pathways involving lipid rafts. Arthritis Rheum. 2007, 56, 2687–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, R.; Pierangeli, S.S. Pathophysiology of the antiphospholipid antibody syndrome. Autoimmun. Highlights 2011, 2, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Knight, J.S.; Kanthi, Y. Mechanisms of immunothrombosis and vasculopathy in antiphospholipid syndrome. Semin. Immunopathol. 2022, 4, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pedrera, C.; Aguirre, M.A.; Buendía, P.; Barbarroja, N.; Ruiz-Limón, P.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Velasco, F.; Khamashta, M.; Cuadrado, M.J. Differential expression of protease-activated receptors in monocytes from patients with primary antiphospholipid syndrome. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 869–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Calleja, N.; Hollerbach, A.; Ritter, S.; Pedrosa, D.G.; Strand, D.; Graf, C.; Reinhardt, C.; Strand, S.; Poncelet, P.; Griffin, J.H.; et al. Tissue factor pathway inhibitor primes monocytes for antiphospholipid antibody-induced thrombosis. Blood 2019, 134, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redecha, P.; Franzke, C.W.; Ruf, W.; Mackman, N.; Girardi, G. Neutrophil activation by the tissue factor/Factor VIIa/PAR2 axis mediates fetal death in a mouse model of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3453–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nag, J.K.; Kancharla, A.; Maoz, M.; Turm, H.; Agranovich, D.; Gupta, C.L.; Uziely, B.; Bar-Shavit, R. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 6 is a novel coreceptor of protease-activated receptor-2 in the dynamics of cancer-associated β-catenin stabilization. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 38650–38667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lara-Castillo, N.; Johnson, M.L. LRP receptor family member associated bone disease. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Semenov, M.; Tamai, K.; Zeng, X. LDL receptor-related proteins 5 and 6 in Wnt/beta-catenin signaling: Arrows point the way. Development 2004, 131, 1663–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ren, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, Y. LRP5 and LRP6 in Wnt Signaling: Similarity and Divergence. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 670960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.C.; Tsai, C.W.; Deak, F.; Rogers, J.; Penuliar, M.; Sung, Y.M.; Maher, J.N.; Fu, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, H.; et al. Deficiency in LRP6-mediated Wnt signaling contributes to synaptic abnormalities and amyloid pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 2014, 84, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Riitano, G.; Manganelli, V.; Capozzi, A.; Mattei, V.; Recalchi, S.; Martellucci, S.; Longo, A.; Misasi, R.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M. LRP6 mediated signal transduction pathway triggered by tissue plasminogen activator acts through lipid rafts in neuroblastoma cells. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 2020, 14, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bafico, A.; Liu, G.; Yaniv, A.; Gazit, A.; Aaronson, S.A. Novel mechanism of Wnt signalling inhibition mediated by Dickkopf-1 interaction with LRP6/Arrow. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 683–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, B.; Wu, W.; Li, Y.; Hoppe, D.; Stannek, P.; Glinka, A.; Niehrs, C. LDL-receptor-related protein 6 is a receptor for Dickkopf proteins. Nature 2001, 411, 321–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenov, M.; Tamai, K.; He, X. SOST is a ligand for LRP5/LRP6 and a Wnt signaling inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26770–26775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ring, L.; Neth, P.; Weber, C.; Steffens, S.; Faussner, A. β-Catenin-dependent pathway activation by both promiscuous “canonical” WNT3a-, and specific “noncanonical” WNT4- and WNT5a-FZD receptor combinations with strong differences in LRP5 and LRP6 dependency. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, F.; Köster, T.; Uhrmacher, A.M. Receptor/Raft Ratio Is a Determinant for LRP6 Phosphorylation and WNT/β-Catenin Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 706731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakane, H.; Yamamoto, H.; Kikuchi, A. LRP6 is internalized by Dkk1 to suppress its phosphorylation in the lipid raft and is recycled for reuse. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Özhan, G.; Sezgin, E.; Wehner, D.; Pfister, A.S.; Kühl, S.J.; Kagermeier-Schenk, B.; Kühl, M.; Schwille, P.; Weidinger, G. Lypd6 enhances Wnt/β-catenin signaling by promoting Lrp6 phosphorylation in raft plasma membrane domains. Dev. Cell 2013, 26, 331–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garofalo, T.; Giammarioli, A.M.; Misasi, R.; Tinari, A.; Manganelli, V.; Gambardella, L.; Pavan, A.; Malorni, W.; Sorice, M. Lipid microdomains contribute to apoptosis-associated modifications of mitochondria in T cells. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 1378–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; London, E. Structure and origin of ordered lipid domains in biological membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 1998, 164, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, D.; London, E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17221–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iessi, E.; Marconi, M.; Manganelli, V.; Sorice, M.; Malorni, W.; Garofalo, T.; Matarrese, P. On the role of sphingolipids in cell survival and death. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2020, 351, 149–195. [Google Scholar]
- Sorice, M.; Mattei, V.; Tasciotti, V.; Manganelli, V.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R. Trafficking of PrPc to mitochondrial raft-like microdomains during cell apoptosis. Prion 2012, 6, 354–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ciarlo, L.; Manganelli, V.; Matarrese, P.; Garofalo, T.; Tinari, A.; Gambardella, L.; Marconi, M.; Grasso, M.; Misasi, R.; Sorice, M.; et al. Raft-like microdomains play a key role in mitochondrial impairment in lymphoid cells from patients with Huntington’s disease. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 2057–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Malorni, W.; Giammarioli, A.M.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M. Dynamics of lipid raft components during lymphocyte apoptosis: The paradigmatic role of GD3. Apoptosis 2007, 12, 941–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorice, M.; Garofalo, T.; Misasi, R.; Manganelli, V.; Vona, R.; Malorni, W. Ganglioside GD3 as a raft component in cell death regulation. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiler, H. Tracing the molecular pathogenesis of antiphospholipid syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3276–3278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Chai, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, H.; Su, W.; Liu, X.; Yu, B.; Lei, W.; Yu, B.; Crane, J.L.; et al. Oxidized phospholipids are ligands for LRP6. Bone Res. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maestrelli, F.; González-Rodríguez, M.L.; Rabasco, A.M.; Mura, P. Preparation and characterisation of liposomes encapsulating ketoprofen-cyclodextrin complexes for transdermal drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 298, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Riitano, G.; Capozzi, A.; Recalchi, S.; Caissutti, D.; Longo, A.; Mattei, V.; Conti, F.; Misasi, R.; Garofalo, T.; Sorice, M.; et al. Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts. Cells 2022, 11, 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081288
Riitano G, Capozzi A, Recalchi S, Caissutti D, Longo A, Mattei V, Conti F, Misasi R, Garofalo T, Sorice M, et al. Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts. Cells. 2022; 11(8):1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081288
Chicago/Turabian StyleRiitano, Gloria, Antonella Capozzi, Serena Recalchi, Daniela Caissutti, Agostina Longo, Vincenzo Mattei, Fabrizio Conti, Roberta Misasi, Tina Garofalo, Maurizio Sorice, and et al. 2022. "Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts" Cells 11, no. 8: 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081288
APA StyleRiitano, G., Capozzi, A., Recalchi, S., Caissutti, D., Longo, A., Mattei, V., Conti, F., Misasi, R., Garofalo, T., Sorice, M., & Manganelli, V. (2022). Anti-β2-GPI Antibodies Induce Endothelial Cell Expression of Tissue Factor by LRP6 Signal Transduction Pathway Involving Lipid Rafts. Cells, 11(8), 1288. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11081288









