Application of Liquid Waste from Biogas Production for Microalgae Chlorella sp. Cultivation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- -
- control—BG11: nitrogen concentration—0.12 g/L;
- -
- liquid waste as a source of nitrogen + BG11: nitrogen concentrations from 0.05 g/L to 0.14 g/L;
- -
- liquid waste + BG11 + technical glycerol: nitrogen concentration: 0.08 g/L; glycerol concentration from 2 g/L to 10 g/L.
3. Results
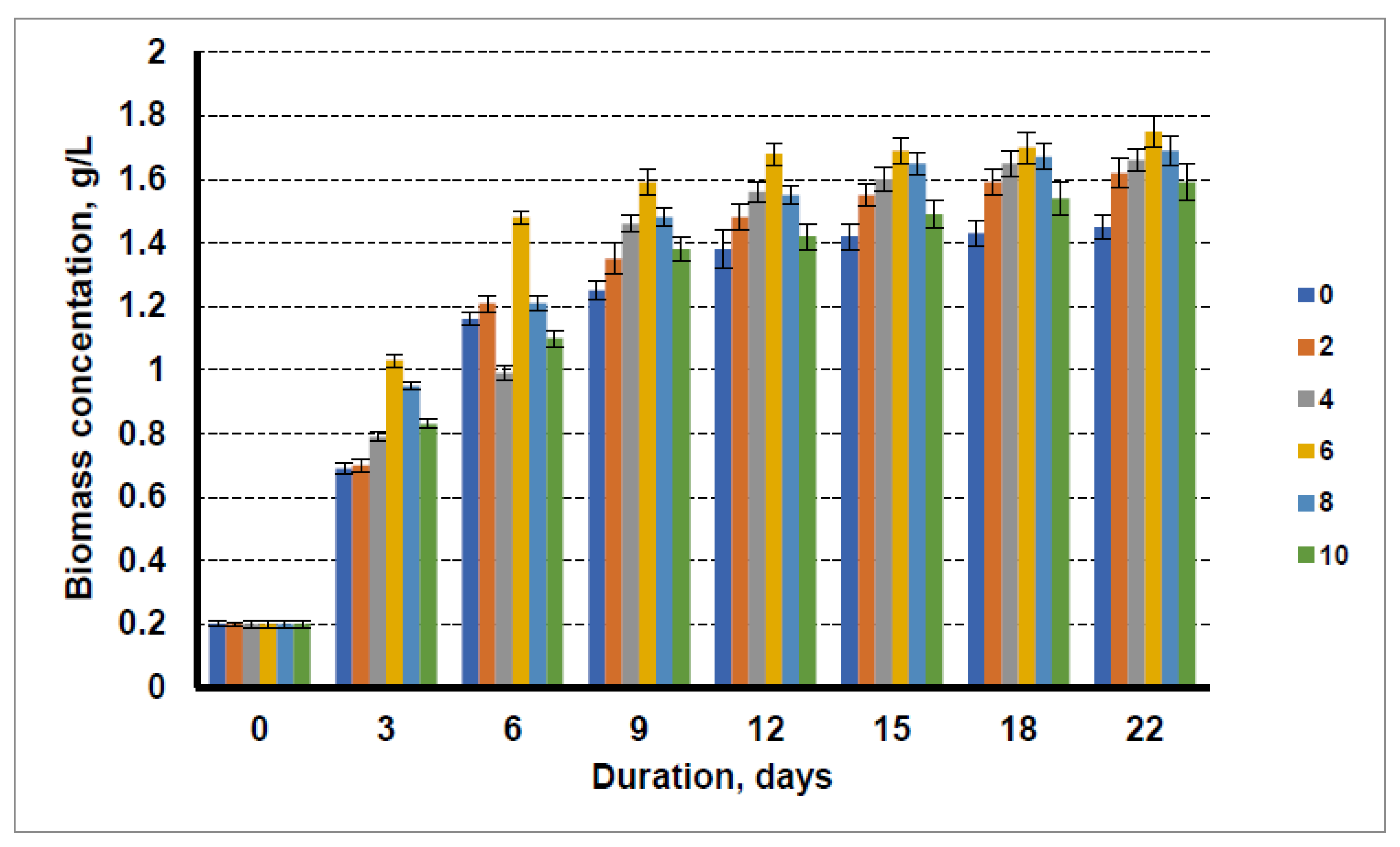
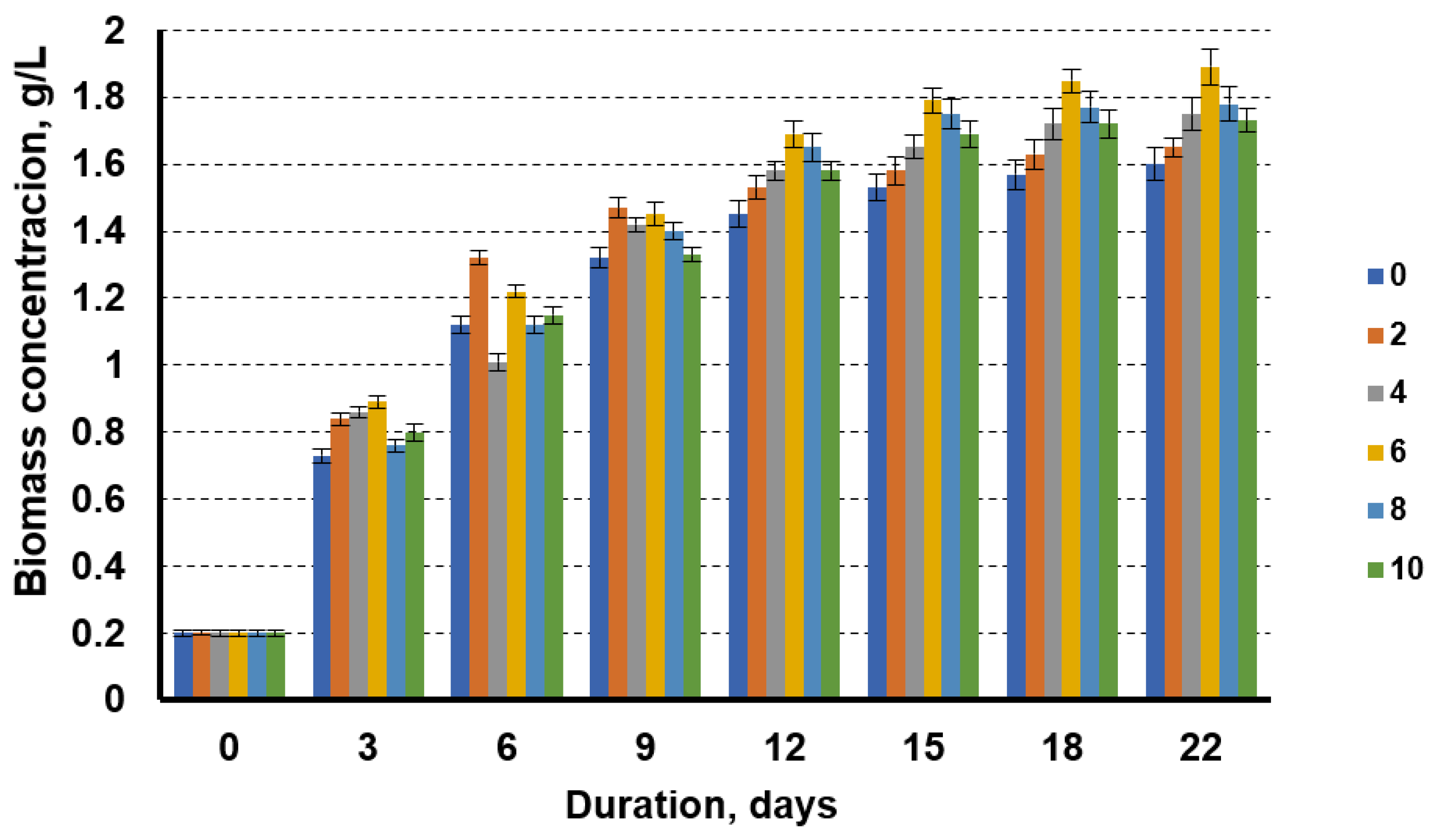
3.1. Application of Liquid Waste from Biofuel Production for Microalgae Cultivation
3.2. Elemental Composition of Microalgae Biomass
4. Discussion
4.1. Application of Liquid Waste from Biofuel Production for Microalgae Cultivation
4.2. Elemental Composition of Microalgae Biomass
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Spolaore, P.; Joannis-Cassan, C.; Duran, E.; Isambert, A. Commercial applications of microalgae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2006, 101, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makareviciene, V.; Sendzikiene, E. Application of microalgae for the production of biodiesel fuel. In Handbook of Algal Science, Technology and Medicine; Konur, O., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Posten, C. Design principles of photo-bioreactors for cultivation of microalgae. Eng. Life Sci. 2009, 9, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aida, T.M.; Maruta, R.; Tanabe, Y.; Oshima, M.; Nonaka, T.; Kujiraoka, H.; Kumagai, Y.M.; Ota, M.; Suzuki, I.; Watanabe, M.M.; et al. Nutrient recycle from defatted microalgae (Aurantiochytrium) with hydrothermal treatment for microalgae cultivation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 228, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, S.A.; Sharma, G.K.; Malla, F.A.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, N. Microalgae based biofertilizers: A biorefinery approach to phycoremediate wastewater and harvest biodiesel and manure. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 211, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, S.S.; Malyan, S.K.; Mathimani, T.; Bishnoi, N.R.; Pugazhendhi, A. Microalgal consortia for municipal wastewater treatment—lipid augmentation and fatty acid profiling for biodiesel production. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 2020, 202, 111638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Kumar, S.S.; Kumar, V.; Malyan, S.K.; Mathimani, T.; Bishnoi, N.R.; Pugazhendhi, A. Upgrading of microalgal consortia with CO2 from fermentation of wheat straw for the phycoremediation of domestic wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 305, 123063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Shao, S.; He, Y.; Luo, Q.; Zheng, M.; Zheng, M.; Chen, B.; Wang, M. Nutrients removal from piggery wastewater coupled to lipid production by a newly isolated self-flocculating microalga Desmodesmus sp. PW1. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 302, 122806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Y.; Gao, F.; Yang, H.L.; Wu, H.W.J.; Li, C.; Lu, M.M.; Yang, Z.Y. Simultaneous removal of nutrient and sulfonamides from marine aquaculture wastewater by concentrated and attached cultivation of Chlorella vulgaris in an algal biofilm membrane photobioreactor (BFMPBR). Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 725, 138524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpozu, O.O.; Ogbonna, I.O.; Ikwebe, J.; Ogbonna, J.C. Phycoremediation of cassava wastewater by Desmodesmus armatus and the concomitant accumulation of lipids for biodiesel production. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2019, 7, 100255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hariz, H.B.; Takriff, M.S.; Yasin, N.H.M.; Ba-Abbad, M.M.; Hakimi, N.I.N.M. Potential of the microalgae based integrated wastewater treatment and CO2 fixation system to treat Palm Oil Mill Effluent (POME) by indigenousmicroalgae; Scenedesmus sp. and Chlorella sp. J. Water Process. Eng. 2019, 32, 100907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.B.; Zhao, X.C.; Yang, L.B. Strategies for enhanced biomass and lipid production by Chlorella pyrenoidosa culture in starch processing wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 236, 117671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silambarasan, S.; Logeswari, P.; Sivaramakrishnan, R.; Incharoensakdi, A.; Cornejo, P.; Kamaraj, B.; Chi, N.T.L. Removal of nutrients from domestic wastewater by microalgae coupled to lipid augmentation for biodiesel production and influence of deoiled algal biomass as biofertilizer for Solanum lycopersicum cultivation. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 129323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Udom, I.; Zaribaf, B.H.; Halfhide, T.; Gillie, B.; Dalrymple, O.; Zhang, Q.; Ergas, S.J. Harvesting microalgae grown on wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 139, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández, D.; Riaño, B.; Coca, M.; García-González, M.C. Treatment of agro-industrial wastewater using microalgae–bacteria consortiumcombined with anaerobic digestion of the produced biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 135, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Garcia, O.; Escalante, F.M.E.; de-Bashan, E.L.; Bashan, Y. Heterotrophic cultures of microalgae: Metabolism and potential products. Water Resour. 2011, 45, 11–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupskaite, V.; Makareviciene, V.; Levisauskas, D. Optimization of mixotrophic cultivation of microalgae Chlorella sp. for biofuel production using response surface methodology. Algal Res. 2015, 7, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heredia-Arroyo, T.; Wei, W.; Hu, B. Oil accumulation vie heterotrophic/mixotrophic Chlorella protothecoides. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2010, 162, 1978–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Yang, W.; Shen, G. Mixotrophic cultivation of Botryococcus braunii. Biomass Bioenerg. 2011, 35, 1710–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.B.; Yang, H.; Cao, Y.T.; Song, H.; Hua, S.F.; Xia, C.-G. Effect of glycerol and glucose on the enhancement of biomass, lipid and soluble carbohydrate production by Chlorella vulgaris in mixotrophic culture. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2013, 51, 62–69. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Y.; Zhu, W.; Chen, C.; Nie, Y. Glycine inducted culture-harvesting strategy for Botryococcus brauni. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2016, 121, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xiong, K.; Zhang, Z.; Hao, X.; Liu, T. Effects of cultivation mode on microalgal growth and CO2 fixation. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 1758–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassim, M.A.; Meng, T.K. Carbon dioxide (CO2) biofixation by microalgae and its potential for biorefinery and biofuel production. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 15, 1121–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.F.; Yang, Z.H.; Zeng, R.; Yang, G.; Chang, X.; Yan, J.B.; Hou, Y.L. Microalgae Capture of CO2 from Actual Flue Gas Discharged from a Combustion Chamber. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 6496–6502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, W.Y.; Show, P.L.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C.; Juan, J.C. Biosequestration of atmospheric CO2 and flue gas-containing CO2 by microalgae. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 184, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.Y.; Yeh, K.L.; Aisyah, R.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Cultivation, photobioreactor design and harvesting of microalgae for biodiesel production: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, R.; Cesar, A. Glycerol from biodiesel production: Technological paths for sustainability. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2018, 88, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowitzka, M.A. Commercial production of microalgae: Ponds, tanks, and fermenters. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 70, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jin, H.F.; Lim, B.R.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, K.J. Ammonia removal from anaerobic digestion effluent of livestock waste using green alga Scenedesmus sp. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 8649–8657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skorupskaite, V.; Makareviciene, V.; Siaudinis, G.; Zajancauskaite, V. Green energy from different feedstock processed under anaerobic conditions. Agron. Res. 2015, 13, 420–429. [Google Scholar]
- Biswas, T.; Bhushan, S.; Prajapati, S.K.; Chaudhuri, S.R. An eco-friendly strategy for dairy wastewater remediation with high lipid microalgae-bacterial biomass production. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 286, 112196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.J. Dairy wastewater treatment using microalgae for potential biodiesel application. Environ. Eng. Res. 2016, 21, 393–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Young, E.B.; Beardall, J. Photosynthetic function in Dunaliela tertiolecta (Chlorophyta) during a nitrogen starvation and recovery cycle. J. Phycol. 2003, 39, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minhas, A.K.; Hodson, P.; Barrow, C.J.; Adholeya, A. A review on the assesment of stress conditions for sumultaneous production of microalgae lipids and carotenoids. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Converti, A.; Casazza, A.A.; Ortiz, E.Y.; Perego, P.; Borghi, M.D. Effect of temperature and nitrogen concentration on the growth and lipid content of Nannochloropsis oculata and Chlorella vulgaris for biodiesel production. Chem. Eng. Process. 2009, 48, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, M.J.; van Hille, R.P.; Harrison, S.T.L. Lipid productivity, settling potential and fatty acid profile of 11 microalgal species grown under nitrogen replete and limited conditions. J. Appl. Phycol. 2012, 24, 989–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q. Environmental effects on cell composition. In Handbook of Microalgal Culture; Richmond, A., Ed.; Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2004; pp. 83–93. [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan, J.; Dunahay, T.; Benemann, J.; Roessler, P. A Look Back at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Aquatic Species Program—Biodiesel from Algae; Report: NREL/TP-580-24190; National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL): Golden, CO, USA, 1998.


| Material (Producer) | Concentration in Cultivation Media |
|---|---|
| Primary Materials: | mg/L |
| NaNO3 | 750 |
| K2HPO4 | 40 |
| MgSO4·7H2O | 75 |
| CaCl2·2H2O | 36 |
| Citric acid | 3 |
| C6H8O7·xFe3+·yNH3 | 3 |
| EDTA | 1 |
| Na2CO3 | 20 |
| Microelements: | 1 × 10−3 mg/L |
| H3BO3 | 2.86 |
| MnCl2·4H2O | 1.81 |
| ZnSO4·7H2O | 0.222 |
| NaMoO4·5H2O | 0.39 |
| CuSO4·5H2O | 0.079 |
| Co(NO3)2·6H2O | 0.0494 |
| Nitrogen Concentration, g/L | C, % | H, % | N, % | P, % | S, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.05 | 55.3 ± 0.31 | 10.05 ± 0.09 | 6.98 ± 0.33 | 0.82 ± 0.02 | 0.36 ± 0.04 |
| 0.08 | 56.7 ± 0.11 | 10.31 ± 0.12 | 7.05 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.02 |
| 0.11 | 53.8 ± 0.33 | 9.78 ± 0.05 | 7.48 ± 0.08 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 0.39 ± 0.06 |
| 0.14 | 56.8 ± 0.65 | 10.33 ± 0.06 | 7.67 ± 0.06 | 0.92 ± 0.06 | 0.40 ± 0.01 |
| 0.12 (control BG11) | 57.2 ± 0.42 | 10.40 ± 0.03 | 7.62 ± 0.15 | 0.86 ± 0.01 | 0.37 ± 0.10 |
| Concentration of Glycerol, % | C, % | H, % | N, % | P, % | S, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 56.7 ± 0.11 | 10.31 ± 0.12 | 7.05 ± 0.11 | 0.78 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.02 |
| 2 | 55.8 ± 0.15 | 10.15 ± 0.11 | 7.09 ± 0.12 | 0.77 ± 0.01 | 0.32 ± 0.03 |
| 4 | 56.5 ± 0.55 | 10.13 ± 0.06 | 7.00 ± 0.08 | 0.88 ± 0.04 | 0.34 ± 0.02 |
| 6 | 54.9 ± 0.33 | 9.82 ± 0.04 | 6.98 ± 0.06 | 0.89 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.04 |
| 8 | 54.4 ± 0.17 | 9.66 ± 0.15 | 6.82 ± 0.12 | 0.85 ± 0.08 | 0.36 ± 0.01 |
| 10 | 52.9 ± 0.33 | 9.44 ± 0.08 | 6.89 ± 0.07 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.35 ± 0.05 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sendzikiene, E.; Makareviciene, V. Application of Liquid Waste from Biogas Production for Microalgae Chlorella sp. Cultivation. Cells 2022, 11, 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071206
Sendzikiene E, Makareviciene V. Application of Liquid Waste from Biogas Production for Microalgae Chlorella sp. Cultivation. Cells. 2022; 11(7):1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071206
Chicago/Turabian StyleSendzikiene, Egle, and Violeta Makareviciene. 2022. "Application of Liquid Waste from Biogas Production for Microalgae Chlorella sp. Cultivation" Cells 11, no. 7: 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071206
APA StyleSendzikiene, E., & Makareviciene, V. (2022). Application of Liquid Waste from Biogas Production for Microalgae Chlorella sp. Cultivation. Cells, 11(7), 1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11071206