Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications
Abstract
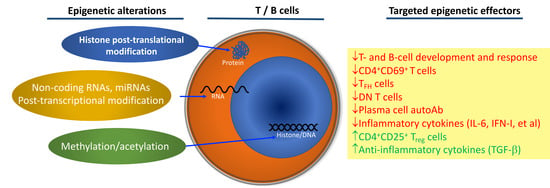
1. Introduction
2. T-Cell Epigenetic Alterations in SLE
3. B-Cell Epigenetic Alterations in Lupus
4. SLE Therapeutics That Target Epigenetic Mechanisms
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Signorini, V.; Elefante, E.; Zucchi, D.; Trentin, F.; Bortoluzzi, A.; Tani, C. One year in review 2020: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2020, 38, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwon, Y.-C.; Chun, S.; Kim, K.; Mak, A. Mak Update on the Genetics of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Genome-Wide Association Studies and Beyond. Cells 2019, 8, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamichou, C.; Bertsias, G. Flares in systemic lupus erythematosus: Diagnosis, risk factors and preventive strategies. Mediterr. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 28, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, M.R.; Clarke, A.E. Systemic lupus erythematosus and risk of infection. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 16, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, H.A.; Duggan, S.T. Belimumab: A Review in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Drugs 2018, 78, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deeks, E.D. Anifrolumab: First Approval. Drugs 2021, 81, 1795–1802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dema, B.; Charles, N. Advances in mechanisms of systemic lupus erythematosus. Discov. Med. 2014, 17, 247–255. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Fueyo, A.; Bradley, S.J.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 43, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giltiay, N.V.; Chappell, C.P.; Clark, E.A. B-cell selection and the development of autoantibodies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2012, 14 (Suppl. 4), S1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Saito, H.; Liang, G.; Friedman, J.M. Epigenetic alterations and microRNA misexpression in cancer and autoimmune diseases: A criti-cal review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2014, 47, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zan, H.; Casali, P. Epigenetics of Peripheral B-Cell Differentiation and the Antibody Response. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paredes, J.L.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Niewold, T.B. T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin. North Am. 2021, 47, 379–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laisné, M.; Gupta, N.; Kirsh, O.; Pradhan, S.; Defossez, P.-A. Mechanisms of DNA Methyltransferase Recruitment in Mammals. Genes 2018, 9, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocki, M.J.; Majewski, D.; Puszczewicz, M.; Jagodziński, P.P. Decreased mRNA expression levels of DNA methyltransferases type 1 and 3A in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strickland, F.M.; Li, Y.; Johnson, K.; Sun, Z.; Richardson, B.C. CD4(+) T cells epigenetically modified by oxidative stress cause lupus-like au-toimmunity in mice. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 62, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Gorelik, G.; Strickland, F.M.; Richardson, B.C. Oxidative Stress, T Cell DNA Methylation, and Lupus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1574–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Li, M.-Y.; Gao, X.-F.; Jia, S.-J.; Gao, K.-Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.-H.; Huang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, H.-J.; et al. Downregulation of BDH2 modulates iron homeostasis and promotes DNA demethylation in CD4 + T cells of systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin. Immunol. 2018, 187, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renauer, P.; Coit, P.; Jeffries, M.A.; Merrill, J.T.; McCune, W.J.; Maksimowicz-McKinnon, K.; Sawalha, A.H. DNA methylation patterns in naïve CD4+ T cells identify epigenetic susceptibility loci for malar rash and discoid rash in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus Sci. Med. 2015, 2, e000101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vordenbaumen, S.; Rosenbaum, A.; Gebhard, C.; Raithel, J.; Sokolowski, A.; Dusing, C.; Chehab, G.; Richter, J.G.; Brinks, R.; Raithel, J.; et al. Associations of site-specific CD4(+)-T-cell hypomethylation within CD40-ligand promotor and enhancer regions with disease activity of women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2021, 30, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulff-Møller, C.J.; Asmar, F.; Liu, Y.; Svendsen, A.J.; Busato, F.; Grønbæk, K.; Tost, J.; Jacobsen, S. Twin DNA Methylation Profiling Reveals Flare-Dependent Interferon Signature and B Cell Promoter Hypermethylation in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 878–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Qiu, X.; Luo, Y.; Yuan, J.; Li, Y.; Lei, W.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.; Lu, Q. Abnormal histone modification patterns in lupus CD4+ T cells. J. Rheumatol. 2008, 35, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Surace, A.E.A.; Hedrich, C.M. The Role of Epigenetics in Autoimmune/Inflammatory Disease. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsou, P.S.; Coit, P.; Kilian, N.C.; Sawalha, A.H. EZH2 Modulates the DNA Methylome and Controls T Cell Adhesion through Junctional Adhe-sion Molecule A in Lupus Patients. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018, 70, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Hu, L.; Yang, L.; Jia, S.; Du, P.; Min, X.; Wu, J.; Wu, H.; Long, H.; Lu, Q.; et al. UHRF1 downregulation promotes T follicular helper cell differentiation by increasing BCL6 expression in SLE. Clin. Epigenetics 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burmeister, T. EZH2: A pleiotropic protein. Blood 2016, 128, 888–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Xie, F.; Liu, Y.; Tong, Q.; Mochizuki, K.; Lapinski, P.E.; Mani, R.S.; Reddy, P.; Mochizuki, I.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; et al. The histone methyltransferase Ezh2 is a crucial epigenetic regulator of allogeneic T-cell responses mediating graft-versus-host disease. Blood 2013, 122, 4119–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Jiang, X.; Qi, C.; Zhang, C.; Qu, B.; Shen, N. EZH2 Inhibition Interferes With the Activation of Type I Interferon Signaling Pathway and Ameliorates Lupus Nephritis in NZB/NZW F1 Mice. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Y.; Smith, R.D.; Finkelman, F.D.; Shao, W.-H. Ezh2-mediated epigenetic modification is required for allogeneic T cell-induced lupus disease. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2020, 22, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, S.; Liang, G.; Su, Y.; Tan, Y.; Lu, Q. RFX1 regulates CD70 and CD11a expression in lupus T cells by recruiting the histone methyltransferase SUV39H1. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, R227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atianand, M.K.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Long non-coding RNAs and control of gene expression in the immune system. Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taheri, M.; Eghtedarian, R.; Dinger, M.E.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Exploring the Role of Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathophysiology of Systemic Lu-pus Erythematosus. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, N.S.; Yu, H.C.; Huang, K.Y.; Tung, C.H.; Huang, H.B.; Lu, M.C. Decreased T cell expression of H/ACA box small nucleolar RNA 12 promotes lupus pathogenesis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27, 1499–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, S.-M.; Liu, C.; Yin, Z.; Wu, L.; Qu, B.; Shen, N. MicroRNAs in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: A Perspective on the Path from Biological Discoveries to Clinical Practice. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, B.; Shen, N. miRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 9557–9572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, N.; Liang, D.; Tang, Y.; de Vries, N.; Tak, P.P. MicroRNAs--novel regulators of systemic lupus erythematosus pathogenesis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, G.; Wang, H.; Shi, X.; Ye, L.; Yan, K.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Z.; Xue, X. Disease Activity-Associated Alteration of mRNA m5 C Methylation in CD4+ T Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crow, M.K. Type I Interferon in the Pathogenesis of Lupus. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5459–5468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, G.; Shi, X.; Wang, H.; Ye, L.; Tong, X.; Yan, K.; Ding, N.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Xue, X. Epitranscriptomic N4-Acetylcytidine Profiling in CD4(+) T Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Pan, S.; Duan, J.; Liu, F.; Li, G.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z. Integrative Analysis of m6A Regulator-Mediated RNA Methylation Modification Patterns and Immune Characteristics in Lupus Nephritis. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 724837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefanski, A.-L.; Dörner, T. Immune checkpoints and the multiple faces of B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2021, 33, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dörner, T.; Giesecke, C.; Lipsky, P.E. Mechanisms of B cell autoimmunity in SLE. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharer, C.D.; Blalock, E.L.; Mi, T.; Barwick, B.G.; Jenks, S.A.; Deguchi, T.; Cashman, K.S.; Neary, B.E.; Patterson, D.; Hicks, S.L.; et al. Epigenetic programming underpins B cell dysfunction in human SLE. Nat. Immunol. 2019, 20, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breitbach, M.E.; Ramaker, R.C.; Roberts, K.; Kimberly, R.P.; Absher, D. Population-Specific Patterns of Epigenetic Defects in the B Cell Line-age in Patients With Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, S.; Ise, W.; Inoue, T.; Ito, A.; Ono, C.; Shima, Y.; Sakakibara, S.; Nakayama, M.; Fujii, K.; Miura, I.; et al. Tet2 and Tet3 in B cells are required to repress CD86 and prevent autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2020, 21, 950–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gautam, P.; Sharma, A.; Bhatnagar, A. Global histone modification analysis reveals hypoacetylated H3 and H4 histones in B Cells from sys-temic lupus erythematosus patients. Immunol. Lett. 2021, 240, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyfrom, S.; Paneru, B.; Knox, J.J.; Cancro, M.P.; Posso, S.; Buckner, J.H.; Anguera, M.C. The dynamic epigenetic regulation of the inactive X chromo-some in healthy human B cells is dysregulated in lupus patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Chang, C.; Peng, M.; Lu, Q. Translating epigenetics into clinic: Focus on lupus. Clin. Epigenetics 2017, 9, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tsokos, M.G.; Bickerton, S.; Sharabi, A.; Li, Y.; Moulton, V.R.; Kong, P.; Fahmy, T.M.; Tsokos, G.C. Precision DNA demethylation ameliorates disease in lupus-prone mice. JCI Insight 2018, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comte, D.; Karampetsou, M.P.; Tsokos, G.C. T cells as a therapeutic target in SLE. Lupus 2015, 24, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Italiano, A.; Soria, J.C.; Toulmonde, M.; Michot, J.M.; Lucchesi, C.; Varga, A.; Coindre, J.M.; Blakemore, S.J.; Clawson, A.; Suttle, B.; et al. Tazemetostat, an EZH2 inhibitor, in relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma and advanced solid tumours: A first-in-human, open-label, phase 1 study. Lancet Oncol. 2018, 19, 649–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohraff, D.M.; He, Y.; Farkash, E.A.; Schonfeld, M.; Tsou, P.; Sawalha, A.H. Inhibition of EZH2 Ameliorates Lupus-Like Disease in MRL/ lpr Mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.A.; Pone, E.J.; Lam, T.; Tat, C.; Hayama, K.L.; Li, G.; Zan, H.; Casali, P. Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Upregulate B Cell microRNAs That Silence AID and Blimp-1 Expression for Epigenetic Modulation of Antibody and Autoantibody Responses. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 5933–5950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Tang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Liang, G.; Wu, H.; Li, D.; Xie, Y.; Tan, Y.; Dai, Y.; Yung, S.; et al. The effect of mycophenolic acid on epigenetic modifications in lupus CD4+T cells. Clin. Immunol. 2015, 158, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liang, G.; Wu, H.; Liu, Q.; Xie, Y.; Li, D.; Dai, Y.; Yung, S.; et al. Mycophenolic acid upregulates miR-142-3P/5P and miR-146a in lupus CD4+T cells. Lupus 2015, 24, 935–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Luo, X.; Cui, H.; Ni, X.; Yuan, M.; Guo, Y.; Huang, X.; Zhou, H.; de Vries, N.; Tak, P.P.; et al. MicroRNA-146a contributes to abnormal activation of the type I interferon pathway in human lupus by targeting the key signaling proteins. Arthritis Rheum. Off. J. Am. Coll. Rheumatol. 2009, 60, 1065–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Boldin, M.; Yu, Y.; Liu, C.S.; Ea, C.-K.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Taganov, K.D.; Zhao, J.L.; Baltimore, D. miR-146a controls the resolution of T cell responses in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1655–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Liang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liang, G.; Long, H.; Zhao, S.; Wang, Y.; Yin, H.; Zhang, P.; Zhang, Q.; et al. Decreased microRNA-142-3p/5p expression causes CD4+ T cell activation and B cell hyperstimulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 2953–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafin, C.B.; Regna, N.L.; Hammond, S.E.; Reilly, C.M. Cellular and urinary microRNA alterations in NZB/W mice with hydroxychloroquine or prednisone treatment. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 894–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regna, N.L.; Vieson, M.D.; Luo, X.; Chafin, C.B.; Puthiyaveetil, A.G.; Hammond, S.E.; Caudell, D.L.; Jarpe, M.B.; Reilly, C.M. Specific HDAC6 inhibition by ACY-738 reduces SLE pathogenesis in NZB/W mice. Clin. Immunol. 2016, 162, 58–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Liao, X.; Vieson, M.D.; Chen, M.; Scott, R.; Kazmierczak, J.; Luo, X.M.; Reilly, C.M. Selective HDAC6 inhibition decreases early stage of lupus nephritis by down-regulating both innate and adaptive immune responses. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 191, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reilly, C.M.; Thomas, M.; Gogal, R., Jr.; Olgun, S.; Santo, A.; Sodhi, R.; Samy, E.T.; Peng, S.L.; Gilkeson, G.S.; Mishra, N.; et al. The histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A upregulates regulatory T cells and modulates autoimmunity in NZB/W F1 mice. J. Autoimmun. 2008, 31, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reilly, C.M.; Mishra, N.; Miller, J.M.; Joshi, D.; Ruiz, P.; Richon, V.M.; Marks, P.A.; Gilkeson, G.S. Modulation of Renal Disease in MRL/lpr Mice by Suberoylanilide Hydroxamic Acid. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 4171–4178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowdell, K.C.; Pesnicak, L.; Hoffmann, V.; Steadman, K.; Remaley, A.T.; Cohen, J.I.; Straus, S.E.; Rao, V.K. Valproic acid (VPA), a histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor, diminishes lymphoproliferation in the Fas -deficient MRL/lpr(-/-) murine model of autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS). Exp. Hematol. 2009, 37, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
| Drug (Type) | Targets | Effects | Model | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACY-738 | HDAC6 | ↓ T- and B-cell development and response | MRL/lpr mice | [59] |
| NZB/W mice | [60] | |||
| TSA | HDAC | ↓ CD4+CD69+ T cells, ↑ CD4+CD25+ Treg cells; ↓ IL-6, ↑TGF-β. | NZB/W mice | [61] |
| SAHA | HDAC | ↓ cytokines, ↓ DN T cells | MRL/lpr mice | [62] |
| VPA | HDAC | ↓ DN T cells | MRL/lpr mice | [63] |
| AZA nanolipogel | CD4 or CD8 T-cell-specific DNA demethylation | ↑ Treg cells, ↓ DN T cells | MRL/lpr mice | [48] |
| DZNep | Methyltransferase | ↓ DN T cells, ↓ cytokine/chemokine | MRL/lpr mice | [51] |
| GSK503 | Ezh2 methyltransferase | ↓ TFH cells | bm12 cGVHD | [28] |
| GSK126 | Ezh2 methyltransferase | ↓ IFN-I pathway | NZB/W mice | [27] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Adams, D.E.; Shao, W.-H. Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2022, 11, 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030506
Adams DE, Shao W-H. Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications. Cells. 2022; 11(3):506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030506
Chicago/Turabian StyleAdams, David E., and Wen-Hai Shao. 2022. "Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications" Cells 11, no. 3: 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030506
APA StyleAdams, D. E., & Shao, W.-H. (2022). Epigenetic Alterations in Immune Cells of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Therapeutic Implications. Cells, 11(3), 506. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11030506