The Biological Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer Metastasis
Abstract
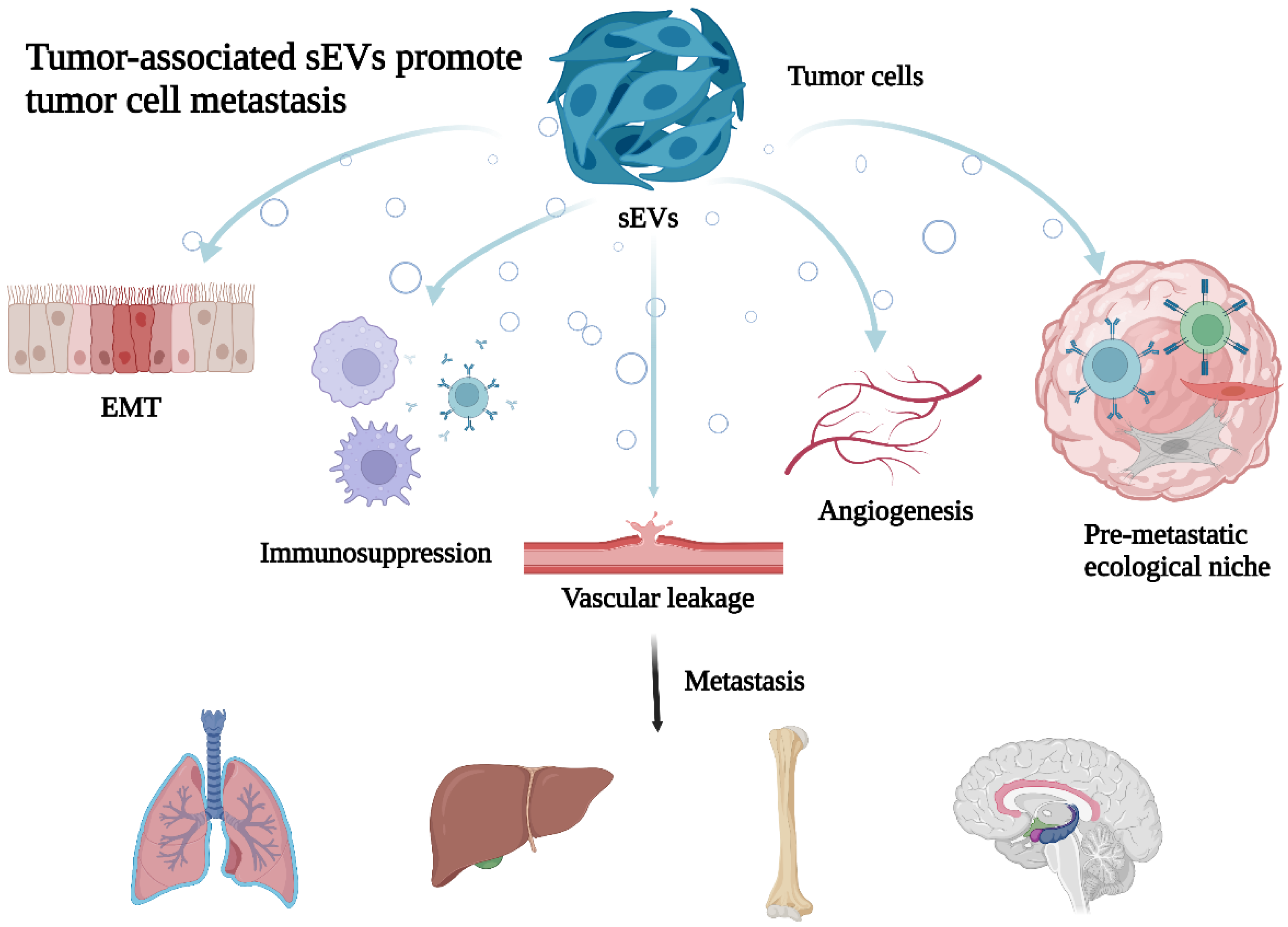
:1. Introduction
2. Small Extracellular Vesicles Affect Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Remodeling the Tumor Microenvironment
3. Small Extracellular Vesicles Mediate Epithelial Mesenchymal Transition Affecting Colorectal Cancer Metastasis
4. Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Macrophages to Undergo M2 Polarization Affecting Colorectal Cancer Metastasis
5. Small Extracellular Vesicles Increase Vascular Leakage and Angiogenesis to Promote Colorectal Cancer Metastasis
6. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzić, J.; Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Karin, M. Inflammation and colon cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 128, 2101–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tauriello, D.V.; Calon, A.; Lonardo, E.; Batlle, E. Determinants of metastatic competency in colorectal cancer. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and opportunities. Front. Med. 2018, 12, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kasprzak, A. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment Cells in Colorectal Cancer (CRC) Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Su, Z.; Barnie, P.A. Crosstalk among colon cancer-derived exosomes, fibroblast-derived exosomes, and macrophage phenotypes in colon cancer metastasis. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 81, 106298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehya, A.H.S.; Asif, M.; Petersen, S.H.; Subramaniam, A.V.; Kono, K.; Majid, A.M.S.A.; Oon, C.E. Angiogenesis: Managing the Culprits behind Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. Medicina 2018, 54, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Fuchs, H.E.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2022, 72, 7–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Xue, M.; Pan, X. ELTD1 promotes invasion and metastasis by activating MMP2 in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 3048–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.L.; Escayg, A. Extracellular vesicles in the treatment of neurological disorders. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 157, 105445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Zhong, J.; Zhong, B.; Huang, J.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, J.; Sun, J.; Dai, L.; Yang, C.; et al. Exosomes as potential sources of biomarkers in colorectal cancer. Cancer Lett. 2020, 476, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenific, C.M.; Zhang, H.; Lyden, D. An exosome pathway without an ESCRT. Cell Res. 2020, 31, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Li, Y.; Sui, Z.; Yuan, H.; Yang, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y. Advances in exosome isolation methods and their applications in proteomic analysis of biological samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 5351–5361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Tong, X.; Deng, K. Research progress of exosomal proteomics in cancer diagnosis based on mass-spectrometic technique. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2021, 42, 2009–2015. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, G.; Zheng, G.; Ge, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, R.; Shu, Q.; Xu, J. Functional proteins of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xia, Y.; Smollar, J.; Mao, W.; Wan, Y. The roles of small extracellular vesicles in lung cancer: Molecular pathology, mechanisms, diagnostics, and therapeutics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2021, 1876, 188539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, M.; Ma, J.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, F.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Exosome-mediated secretion of LOXL4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Ren, L.; Li, S.; Li, W.; Zheng, X.; Yang, Y.; Fu, W.; Yi, J.; Wang, J.; Du, G. The biology, function, and applications of exosomes in cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 2783–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibold, T.; Waldenmaier, M.; Seufferlein, T.; Eiseler, T. Small Extracellular Vesicles and Metastasis-Blame the Messenger. Cancers 2021, 13, 4380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miguel Pérez, D.; Rodriguez Martinez, A.; Ortigosa Palomo, A.; Delgado Ureña, M.; Garcia Puche, J.L.; Robles Remacho, A.; Exposito Hernandez, J.; Lorente Acosta, J.A.; Ortega Sánchez, F.G.; Serrano, M.J. Extracellular vesicle-miRNAs as liquid biopsy biomarkers for disease identification and prognosis in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.; Chen, C.; Cui, M.; Zhang, H. miR-140-3p inhibits colorectal cancer progression and its liver metastasis by targeting BCL9 and BCL2. Cancer Med. 2021, 10, 3358–3372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Lu, Z.; Fu, W.; Lu, K.; Gu, X.; Xu, F.; Dai, J.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, J. Exosome-Derived ADAM17 Promotes Liver Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 734351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-Y.; Tao, Y.-W.; Gao, S.; Li, P.; Zheng, J.-M.; Zhang, S.-E.; Liang, J.; Zhang, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts contribute to oral cancer cells proliferation and metastasis via exosome-mediated paracrine miR-34a-5p. eBioMedicine 2018, 36, 209–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Song, Q.; Yu, H.; Cheng, Y.; Han, J.; Li, K.; Zhuang, J.; Lv, Q.; Yang, X.; Yang, H. Bladder cancer-derived exosomal KRT6B promotes invasion and metastasis by inducing EMT and regulating the immune microenvironment. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrissey, S.M.; Zhang, F.; Ding, C.; Montoya-Durango, D.E.; Hu, X.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, F.; Fox, M.; Zhang, H.-G.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes drive immunosuppressive macrophages in a pre-metastatic niche through glycolytic dominant metabolic reprogramming. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 2040–2058.e2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, H.-Y.; Wang, N.; Lam, W.; Guo, W.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, Y.-C. Targeting tumour microenvironment by tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farazi, P.A.; DePinho, R.A. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: From genes to environment. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 674–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forder, A.; Hsing, C.; Trejo Vazquez, J.; Garnis, C. Emerging Role of Extracellular Vesicles and Cellular Communication in Metastasis. Cells 2021, 10, 3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Cai, S.; Li, X.; Li, D. Highly-metastatic colorectal cancer cell released miR-181a-5p-rich extracellular vesicles promote liver metastasis by activating hepatic stellate cells and remodelling the tumour microenvironment. J Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, B.; Pan, S.; Liu, Q.; Shan, Y.; Li, S.; Qi, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jia, L. Exosomal MALAT1 sponges miR-26a/26b to promote the invasion and metastasis of colorectal cancer via FUT4 enhanced fucosylation and PI3K/Akt pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, A.; Gu, C.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Sun, J.; Zeng, B.; Chen, C.; Chang, W.; Ping, Y.; Ji, P.; et al. Exosomal circPACRGL promotes progression of colorectal cancer via the miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p- TGF-β1 axis. Mol. Cancer. 2020, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, P.; He, T.C.; Han, J.H.; Zhang, R.; Lin, J.; Fan, J.; Lu, L.; Zhu, W.W.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal HSPC111 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by reprogramming lipid metabolism in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, F.; Wang, P.; Lin, D.; Dai, J.; Liu, Q.; Guan, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; et al. Exosome-delivered miR-221/222 exacerbates tumor liver metastasis by targeting SPINT1 in colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 3744–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Si, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosomal miR-146a-5p and miR-155-5p promote CXCL12/CXCR7-induced metastasis of colorectal cancer by crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, A.; Nagayama, S.; Sumazaki, M.; Konishi, M.; Fujii, R.; Saichi, N.; Muraoka, S.; Saigusa, D.; Shimada, H.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Colorectal Cancer-Derived CAT1-Positive Extracellular Vesicles Alter Nitric Oxide Metabolism in Endothelial Cells and Promote Angiogenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2021, 19, 834–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Q.; Zhou, L.; Sui, H.; Yang, L.; Wu, X.; Song, Q.; Jia, R.; Li, R.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; et al. Primary tumors release ITGBL1-rich extracellular vesicles to promote distal metastatic tumor growth through fibroblast-niche formation. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Chen, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, S.; Xu, K.; Chen, X.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Shen, Y.; Wang, T.; et al. Colorectal cancer-derived small extracellular vesicles establish an inflammatory premetastatic niche in liver metastasis. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 1368–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.; Yang, F.; Feng, Y. Exosomes Derived from Hypoxic Colorectal Cancer Cells Transfer Wnt4 to Normoxic Cells to Elicit a Prometastatic Phenotype. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, J.; Bao, C. Exosomal circEIF3K from cancer-associated fibroblast promotes colorectal cancer (CRC) progression via miR-214/PD-L1 axis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Zhang, F.; Luo, B.; Qu, Z. CAFs-derived small extracellular vesicles circN4BP2L2 promotes proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer via miR-664b-3p/HMGB3 pathway. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2022, 23, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Q.; Chen, J.; Di, Z.; Yuan, W.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, Z.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Ying, G.; Shu, X.; et al. TM4SF1 promotes EMT and cancer stemness via the Wnt/β-catenin/SOX2 pathway in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzoni, G.; Dejana, E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: Molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 869–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, B.; Ahmad, R.; Giannico, G.A.; Zent, R.; Talmon, G.A.; Harris, R.C.; Clark, P.E.; Lokeshwar, V.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Claudin-2 inhibits renal clear cell carcinoma progression by inhibiting YAP-activation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, R.; Kumar, B.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Muller, D.; Lele, S.M.; Washington, M.K.; Batra, S.K.; Dhawan, P.; Singh, A.B. Loss of claudin-3 expression induces IL6/gp130/Stat3 signaling to promote colon cancer malignancy by hyperactivating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Oncogene 2017, 36, 6592–6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabaries, S.; Annis, M.G.; Lazaris, A.; Petrillo, S.K.; Huxham, J.; Abdellatif, A.; Palmieri, V.; Chabot, J.; Johnson, R.M.; Van Laere, S.; et al. Claudin-2 promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis and is a biomarker of the replacement type growth pattern. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ombrato, L.; Nolan, E.; Kurelac, I.; Mavousian, A.; Bridgeman, V.L.; Heinze, I.; Chakravarty, P.; Horswell, S.; Gonzalez-Gualda, E.; Matacchione, G.; et al. Metastatic-niche labelling reveals parenchymal cells with stem features. Nature 2019, 572, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sai, B.; Wang, F.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Li, G.; Tang, J.; Xiang, J. Hypoxic BMSC-derived exosomal miRNAs promote metastasis of lung cancer cells via STAT3-induced EMT. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Liao, R.; Wu, Z.; Du, C.; You, Y.; Que, K.; Duan, Y.; Yin, K.; Ye, W. Hepatic stellate cell exosome-derived circWDR25 promotes the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via the miRNA-4474-3P-ALOX-15 and EMT axes. Biosci. Trends 2022, 16, 267–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.L.; Wang, W.; Lan, X.L.; Zeng, Z.C.; Liang, Y.S.; Yan, Y.R.; Song, F.Y.; Wang, F.F.; Zhu, X.H.; Liao, W.J.; et al. CAFs secreted exosomes promote metastasis and chemotherapy resistance by enhancing cell stemness and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Liu, F.; Sun, W.; Zhu, W.; Fang, D.; Luo, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, L. Exosome-transmitted miRNA-335-5p promotes colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis by facilitating EMT via targeting RASA1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.W.; Chen, M.; Bamodu, O.A.; Hsieh, M.S.; Huang, T.Y.; Yeh, C.T.; Lee, W.H.; Cherng, Y.G. Exosomal lncRNA PVT1/VEGFA Axis Promotes Colon Cancer Metastasis and Stemness by Downregulation of Tumor Suppressor miR-152-3p. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9959807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannavola, F.; Pezzicoli, G.; Tucci, M. DLC-1 down-regulation via exosomal miR-106b-3p exchange promotes CRC metastasis by the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Clin. Sci. 2020, 134, 955–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bigagli, E.; Luceri, C.; Guasti, D.; Cinci, L. Exosomes secreted from human colon cancer cells influence the adhesion of neighboring metastatic cells: Role of microRNA-210. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 1062–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vu, T.; Datta, P. Regulation of EMT in Colorectal Cancer: A Culprit in Metastasis. Cancers 2017, 9, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, H.; Lan, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Su, P.; Chu, Z.; Lai, W.; Chu, Z. The mechanisms of colorectal cancer cell mesenchymal-epithelial transition induced by hepatocyte exosome-derived miR-203a-3p. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wan, Y.; Su, Z.; Li, J.; Han, M.; Zhou, C. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomal microRNA-3940-5p Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Metastasis by Targeting Integrin α6. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, S.; Yang, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, S.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Exosomal miR-128-3p Promotes Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Colorectal Cancer Cells by Targeting FOXO4 via TGF-β/SMAD and JAK/STAT3 Signaling. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 568738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, S.; Zaidi, M. TAMeless traitors: Macrophages in cancer progression and metastasis. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 1583–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, C.; Yang, C.; Wang, S.; Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Lin, X.; Liu, Q.; Dou, R.; Xiong, B. Crosstalk between cancer cells and tumor associated macrophages is required for mesenchymal circulating tumor cell-mediated colorectal cancer metastasis. Mol. Cancer. 2019, 18, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, S.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.; Wei, C.; Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, B.J. miR-195-5p/NOTCH2-mediated EMT modulates IL-4 secretion in colorectal cancer to affect M2-like TAM polarization. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, A.; Tousif, S.; Wang, Y.; Hough, K.; Khan, S.; Strenkowski, J.; Chacko, B.K.; Darley-Usmar, V.M.; Deshane, J.S. Lung Tumor Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote M2 Macrophage Polarization. Cells 2020, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Mi, Y.; Guan, B.; Zheng, B.; Wei, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Cai, S.; Xu, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomal miR-934 induces macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.X.; Liu, H.; Wang, F.W.; Xiong, L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, T.; He, X.W.; Wu, X.J.; Xie, D.; Wu, X.R.; et al. LncRNA RPPH1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by interacting with TUBB3 and by promoting exosomes-mediated macrophage M2 polarization. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, X.; Si, M.; Yang, J.; Sun, S.; Wu, H.; Cui, S.; Qu, X.; Yu, X. Exosome-encapsulated miRNAs contribute to CXCL12/CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages. Cancer Lett. 2020, 474, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, W. LncRNA HLA-F-AS1 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by inducing PFN1 in colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles and mediating macrophage polarization. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 1269–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Ye, J.; Pei, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, H.; Tian, J.; Si, G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, K.; Liu, G. Extracellular vesicles from colorectal cancer cells promote metastasis via the NOD1 signalling pathway. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takano, Y.; Masuda, T.; Iinuma, H.; Yamaguchi, R.; Sato, K.; Tobo, T.; Hirata, H.; Kuroda, Y.; Nambara, S.; Hayashi, N.; et al. Circulating exosomal microRNA-203 is associated with metastasis possibly via inducing tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 78598–78613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lan, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.; Song, D.; Hou, Z.; Wu, W.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; et al. M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.; Dou, R.; Wei, C.; Liu, K.; Shi, D.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Xiong, B. Tumor-derived exosomal microRNA-106b-5p activates EMT-cancer cell and M2-subtype TAM interaction to facilitate CRC metastasis. Mol. Ther. 2021, 29, 2088–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Jenkins, L.M.; Patel, K.M.; Robles, A.I.; Morris, J.; Forshew, T.; Appella, E.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; Harris, C.C. Mutant p53 cancers reprogram macrophages to tumor supporting macrophages via exosomal miR-1246. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, X. Ovarian cancer cell-secreted exosomal miR-205 promotes metastasis by inducing angiogenesis. Theranostics 2019, 9, 8206–8220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Chen, J.; Shang, F.; Lian, M.; Shen, X.; Fang, J. Tumor-Derived Exosome FGD5-AS1 Promotes Angiogenesis, Vascular Permeability, and Metastasis in Thyroid Cancer by Targeting the miR-6838-5p/VAV2 Axis. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 4702855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.G.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, Y.M.; Yan, R.M.; Wei, W.F.; Chen, X.J.; Yi, H.Y.; Liang, L.J.; Fan, L.S.; Liang, L.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-221-3p promotes angiogenesis by targeting THBS2 in cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Angiogenesis 2019, 22, 397–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, K.; Chen, H.; Fang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhong, C.; Bu, T.; Dai, S.; Pan, X.; Fu, D.; Qian, Y.; et al. Exosomal ANGPTL1 attenuates colorectal cancer liver metastasis by regulating Kupffer cell secretion pattern and impeding MMP9 induced vascular leakiness. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Z.; Li, Y.; Pan, Y.; Lan, X.; Song, F.; Sun, J.; Zhou, K.; Liu, X.; Ren, X.; Wang, F.; et al. Cancer-derived exosomal miR-25-3p promotes pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing vascular permeability and angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 5395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dokhanchi, M.; Pakravan, K.; Zareian, S.; Hussen, B.M.; Farid, M.; Razmara, E.; Mossahebi-Mohammadi, M.; Cho, W.C.; Babashah, S. Colorectal cancer cell-derived extracellular vesicles transfer miR-221-3p to promote endothelial cell angiogenesis via targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 3. Life Sci. 2021, 285, 119937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, Y.J.; Kim, D.K.; Yoon, C.M.; Park, J.; Kim, Y.K.; Roh, T.Y.; Gho, Y.S. Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dou, R.; Liu, K.; Yang, C.; Zheng, J.; Shi, D.; Lin, X.; Wei, C.; Zhang, C.; Fang, Y.; Huang, S.; et al. EMT-cancer cells-derived exosomal miR-27b-3p promotes circulating tumour cells-mediated metastasis by modulating vascular permeability in colorectal cancer. Clin. Transl. Med. 2021, 11, e595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-W.; Cao, C.-H.; Han, K.; Zhao, Y.-X.; Cai, M.-Y.; Xiang, Z.-C.; Zhang, J.-X.; Chen, J.-W.; Zhong, L.-P.; Huang, Y.; et al. APC-activated long noncoding RNA inhibits colorectal carcinoma pathogenesis through reduction of exosome production. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- SE, W. Extracellular Vesicles and Metastasis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2020, 10, a037275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Z.; Cheong, J.; Xiang, L.; Le, M.T.N.; Grimson, A.; Zhang, D.X. Extracellular vesicle-associated organotropic metastasis. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, R.; Chen, L.; Qin, D.; Guo, Q.; Zhu, S.; Li, P.; Min, L.; Zhang, S. Liquid Biopsy of Extracellular Vesicle-Derived miR-193a-5p in Colorectal Cancer and Discovery of Its Tumor-Suppressor Functions. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, R.X.; Chan, K.W.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Wei, L.; Tan, H.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. Exosomal transfer of p-STAT3 promotes acquired 5-FU resistance in colorectal cancer cells. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bi, J.; Huang, J.; Tang, Y.; Du, S.; Li, P. Exosome: A Review of Its Classification, Isolation Techniques, Storage, Diagnostic and Targeted Therapy Applications. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 6917–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jiao, Z.; Mo, J.; Huang, D.; Li, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yang, T.; Zhao, M.; Xie, F.; Hu, D.; et al. Comparison of the Variability of Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Liver Cancer Tissues and Cultured from the Tissue Explants Based on a Simple Enrichment Method. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 18, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowal, J.; Arras, G.; Colombo, M.; Jouve, M.; Morath, J.P.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Dingli, F.; Loew, D.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Proteomic comparison defines novel markers to characterize heterogeneous populations of extracellular vesicle subtypes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E968–E977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hosseini, R.; Sarvnaz, H.; Arabpour, M.; Ramshe, S.M.; Asef-Kabiri, L.; Yousefi, H.; Akbari, M.E.; Eskandari, N. Cancer exosomes and natural killer cells dysfunction: Biological roles, clinical significance and implications for immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergani, E.; Daveri, E.; Vallacchi, V.; Bergamaschi, L.; Lalli, L.; Castelli, C.; Rodolfo, M.; Rivoltini, L.; Huber, V. Extracellular vesicles in anti-tumor immunity. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, T.; Wei, Z.; Gan, L.; Yang, X. Extracellular-Vesicle-Based Drug Delivery Systems for Enhanced Antitumor Therapies through Modulating the Cancer-Immunity Cycle. Adv. Mater. 2022, e2201054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, N.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, J.; Wei, Q.; Han, M. The role of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in tumor progression and relevant advance in targeted therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Cancer Type | sEVs Cargos | Tissues and/or Cells | Mechanism | Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | miR-181a-5p | HT29, SW480, RKO, SW620 and plasma from CRLM | Promote liver metastasis by activating hepatic stellate cells and remodeling the tumor microenvironment | Promote metastasis | [30] |
| Colorectal cancer | MALAT1 | LoVo, HCT-8, SW620, SW480 and CRC tissues | Promote the malignant behavior of CRC cells by sponging miR-26a/26b via regulating FUT4 and activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway | Promote metastasis | [31] |
| Colorectal cancer | circPACRGL | HCT116 and SW480 | Enhance CRC cell proliferation, migration and invasion, as well as differentiation of N1-N2 neutrophils via miR-142-3p/miR-506-3p-TGF-β1 axis | Promote metastasis | [32] |
| Colorectal cancer | HSPC111 | HCT116, SW620, HT29 and SW480 | Facilitate pre-metastatic niche formation and CRLM | Promote metastasis | [33] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-221/222 | Tissues and SW480 | Induce the formation of a hospitable metastatic environment, providing an appropriate colonization environment for incoming metastatic tumor cells | Promote metastasis | [34] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-146a-5p and miR-155-5p | HCT116 and SW620 | Promote CXCL12/CXCR7-induced metastasis of colorectal cancer by crosstalk with cancer-associated fibroblasts | Promote metastasis | [35] |
| Colorectal cancer | CAT1 | HCT116 and tissues | Enhance vascular endothelial cell growth and tubule formation via up-regulation of arginine transport and downstream NO metabolic pathway | Promote metastasis | [36] |
| Colorectal cancer | ITGBL1 | Tissues and NCM460, SW480 and SW620 | Promote metastatic cancer growth by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokine | Promote metastasis | [37] |
| Colorectal cancer | microRNA-21-5p | SW480, SW620 and LoVo | Promote liver metastasis by inducing an inflammatory premetastatic niche | Promote metastasis | [38] |
| Colorectal cancer | Wnt4 | HT29 and HCT116 | Enhance pro-metastatic behaviors | Promote metastasis | [39] |
| Colorectal cancer | circEIF3K | CAF | Promote CRC progression via miR-214/PD-L1 axis | Promote metastasis | [40] |
| Colorectal cancer | circN4BP2L2 | CAF | Promote subcutaneous tumorigenesis and liver metastasis in CRC nude mice | Promote metastasis | [41] |
| Cancer Type | sEVs Cargos | Tissues and/or Cells | Mechanism | Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | miR-92a-3p | CAFs and serum from CRC | Activate Wnt/β-catenin pathway contributing to cell stemness, EMT, metastasis and in CRC | Promote metastasis | [50] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-335-5p | SW620 | Promotes CRC invasion and metastasis by facilitating EMT via targeting RASA1 | Promote metastasis | [51] |
| Colorectal cancer | PVT1 | Serum from metastatic CRC | Increase expression of metastatic markers such as VEGFA and EGFR | Promote metastasis | [52] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-106b-3p | Serum from metastatic CRC | Decrease the expression of DLC-1 and Inhibit the EMT | Inhibit metastasis | [53] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-210 | HCT-8 | Promote the expression of key EMT proteins | Promote metastasis | [54] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-203a-3p | LO2 | Induce MET in PRL-3 overexpressing CRC cells | Promote metastasis | [56] |
| Colorectal cancer | microRNA-3940-5p | MSC | Inhibit colorectal cancer metastasis by Targeting Integrin α6 | Inhibit metastasis | [57] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-128-3p | HCT116 cell culture fluid and serum | Induce the activation of TGF-β/SMAD and JAK/STAT3 signaling in CRC cells and xenografted tumors, which led to EMT | Promote metastasis | [58] |
| Cancer Type | sEVs Cargos | Tissues and/or Cells | Mechanism | Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | miR-934 | FHC, SW480, SW620, HCT-8, HT-29, CaCo2, LoVo and RKO | Induce macrophage M2 polarization to promote liver metastasis of colorectal cancer | Promote metastasis | [63] |
| Colorectal cancer | LncRNA RPPH1 | HCT8, SW620 and HT29 | Promote colorectal cancer metastasis by interacting with TUBB3 and by promoting exosome-mediated macrophage M2 polarization | Promote metastasis | [64] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-25-3p, miR-130b-3p and miR-425-5p | HCT116 | Contribute to CXCL12/CXCR4-induced liver metastasis of colorectal cancer by enhancing M2 polarization of macrophages | Promote metastasis | [65] |
| Colorectal cancer | LncRNA HLA-F-AS1 | DLD-1, HT-29, SW620, SW480,HCT116, and Caco-2 | Promote colorectal cancer metastasis by inducing PFN1 in colorectal cancer-derived extracellular vesicles and mediating macrophage polarization | Promote metastasis | [66] |
| Colorectal cancer | - | HT-29, HCT116 and plasma | Promote metastasis via the NOD1 signaling pathway | Promote metastasis | [67] |
| Colorectal cancer | microRNA-203 | Serum, tissues, CaR-1, RKO, Colo205, Colo320DM, DLD1, HCT116, Lovo, SW480 and SW620 | Promote metastasis possibly via inducing tumor-associated macrophages in colorectal cancer | Promote metastasis | [68] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-21-5p and miR-155-5p | SW48, SW480, and CO-115 | Down-regulate BRG1 expression and promote CRC metastasis | Promote metastasis | [69] |
| Colorectal cancer | microRNA-106b-5p | HCT116 and HT29 | Activate EMT-cancer cell and M2-subtype TAM interaction to facilitate CRC metastasis | Promote metastasis | [70] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-1246 | HT-29 and HCT116 | Promote macrophage M2 polarization to promote colorectal cancer metastasis | Promote metastasis | [71] |
| Cancer Type | sEVs Cargos | Tissues and/or Cells | Mechanism | Function | Refs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Colorectal cancer | ANGPTL1 | SW620 and tissues | Attenuate CRLM by regulating Kupffer cell secretion pattern and impeding MMP9-induced vascular leakiness | Inhibit metastasis | [75] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-25-3p | SW480, LS174T, SW620, LOVO, HCT116 and tissues | Promote pre-metastatic niche formation by inducing vascular permeability and angiogenesis | Promote metastasis | [76] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-221-3p | HCT116 and Caco2 | Promote endothelial cell angiogenesis via targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 | Promote metastasis | [77] |
| Colorectal cancer | - | SW480 and HCT116 | Egr-1 activation by cancer-derived extracellular vesicles promotes endothelial cell migration via the ERK1/2 and JNK signaling pathways | Promote metastasis | [78] |
| Colorectal cancer | miR-27b-3p | LOVO, HCT-116, DLD-1, SW620 and SW480 | Promote circulating tumor cell-mediated metastasis by modulating vascular permeability in colorectal cancer | Promote metastasis | [79] |
| Colorectal cancer | lncRNA-APC1 | HCT-116 | Enhance tumor angiogenesis by activating the MAPK pathway in endothelial cells. | Promote metastasis | [80] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Huang, D.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Yi, X.; Zhong, T. The Biological Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Cells 2022, 11, 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244071
Wang X, Huang D, Wu J, Li Z, Yi X, Zhong T. The Biological Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Cells. 2022; 11(24):4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244071
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaoxing, Defa Huang, Jiyang Wu, Zhengzhe Li, Xiaomei Yi, and Tianyu Zhong. 2022. "The Biological Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer Metastasis" Cells 11, no. 24: 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244071
APA StyleWang, X., Huang, D., Wu, J., Li, Z., Yi, X., & Zhong, T. (2022). The Biological Effect of Small Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Cells, 11(24), 4071. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11244071






