Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of the Role of Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 in the Development and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Assay of RAB11B Protein in HCC Tissues
2.3. Protein-Protein Interactions of RAB11B
2.4. Human Protein Atlas (HPA)
2.5. Screening of lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Co-Expressed Genes in HCC and Functional Enrichment Analysis
2.6. GSEA Analysis
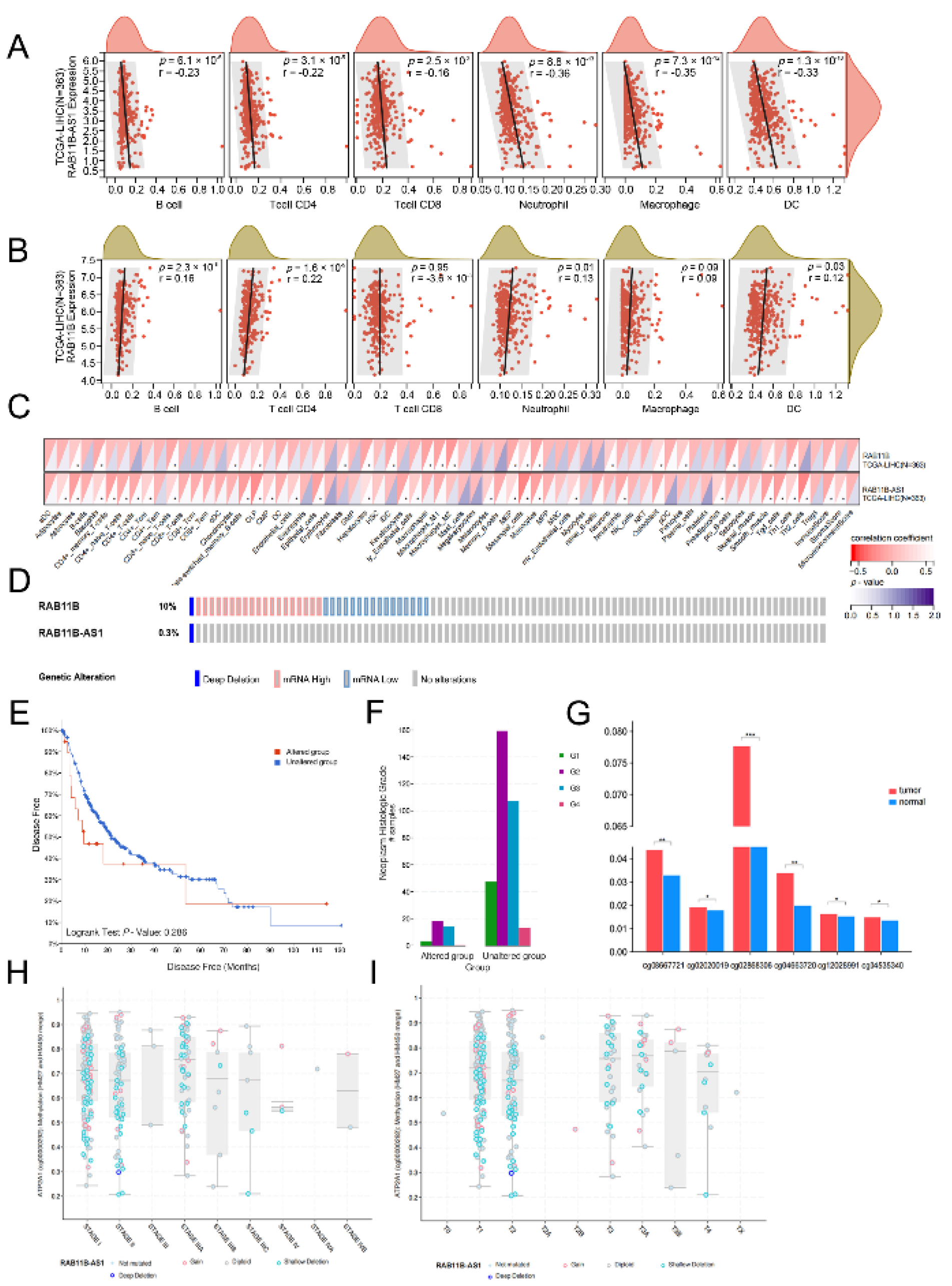
2.7. An Association between lnc-RAB11B-AS1, RAB11B, and Tumor Immune Cell Infiltration
2.8. Alternation of lnc-RAB11B-AS1 and RAB11B in HCC
2.9. Correlation between Methylation and lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Expression
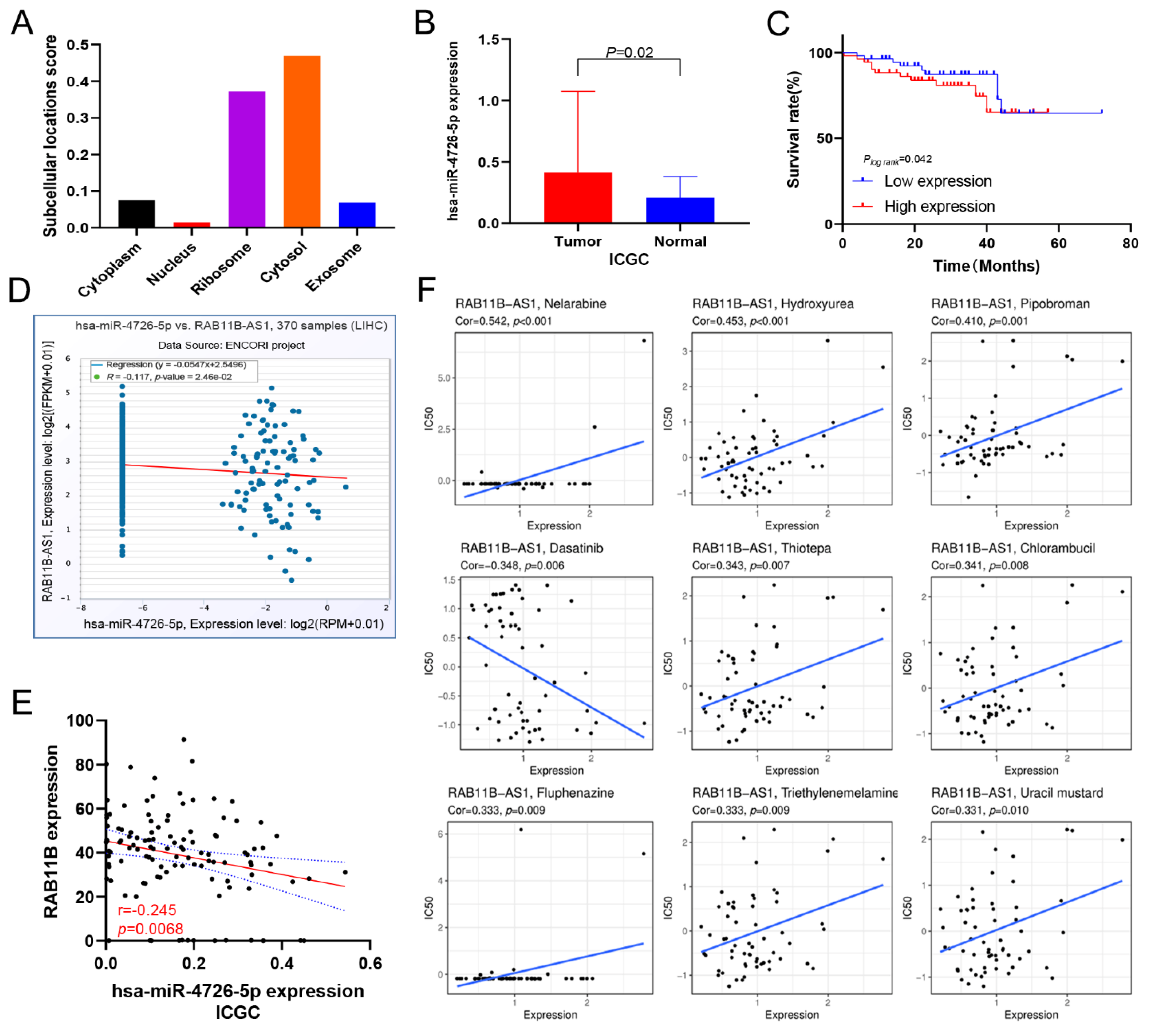
2.10. Drug Susceptibility Analysis
2.11. Prediction of Potential Candidate miRNAs
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Was Markedly Low Expressed and Positively Correlated with RAB11B in HCC
3.2. The Effects of Overexpressed lnc-RAB11B-AS1 and RAB11B on Clinicopathological Characteristics
3.3. The Relationship between lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Expression and Prognosis of HCC Patients
3.4. Cox Regression Model Analysis
3.5. External Validation of RAB11B Protein Expression and Clinicopathologic Features of HCC Patients
3.6. RAB11B-Associated PPI Network
3.7. RAB11B Expression in Different Cells of HCC
3.8. Lnc-RAB11B-AS1-Related Genes and Functional Enrichment Analysis
3.9. Lnc-RAB11B-AS1-Related Signaling Pathways Obtained by GSEA
3.10. Correlation Analysis between lnc-RAB11B-AS1 and RAB11B Expression, and Tumor-Infiltrating Immune Cells in HCC
3.11. Alternation of lnc-RAB11B-AS1 and RAB11B in HCC
3.12. Correlation between mRNA Expression and Methylation of lnc-RAB11B-AS1
3.13. Prediction of lnc-RAB11B-AS1 and RAB11B Targeted miRNAs
3.14. Correlation between lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Expression and Drug Sensitivity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cheng, J.; Wei, D.; Ji, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, L.; Li, G.; Wu, L.; Hou, T.; Xie, L.; Ding, G.; et al. Integrative analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression reveals hepatocellular carcinoma-specific diagnostic biomarkers. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: Globocan estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.Y.; Ren, Z.G.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Gao, Q. 2019 chinese clinical guidelines for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: Updates and insights. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2020, 9, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helmberger, T. Guideline on hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiologe 2022, 62, 197–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.Y.; Sohn, B.H.; Yu, E.; Suh, D.J.; Chung, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Surzycki, S.J.; Lee, Y.I. Aberrant epigenetic modifications in hepatocarcinogenesis induced by hepatitis b virus X protein. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 1476–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xie, H.; Hu, M.; Huang, T.; Hu, Y.; Sang, N.; Zhao, Y. Recent progress in treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 2993–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhary, A.; Satagopam, V.; Schneider, R. Long non-coding RNAs: Mechanisms, experimental, and computational approaches in identification, characterization, and their biomarker potential in cancer. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 649619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Du, X.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Pan, Z.; Li, Q. SMAD4-induced knockdown of the antisense long noncoding Rna BRE-AS contributes to granulosa cell apoptosis. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2021, 25, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Chen, W.C.; Shi, P.C.; Liu, M.R.; Jiang, T.; Song, H.; Wang, J.Q.; Fan, R.Z.; Pei, D.S.; Song, J. Long noncoding RNA MAPKAPK5-as1 promotes colorectal cancer progression by cis-regulating the nearby gene MK5 and acting as a let-7f-1-3p sponge. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2020, 39, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeffer, S.R. Rab gtpases: Master regulators that establish the secretory and endocytic pathways. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 712–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homma, Y.; Hiragi, S.; Fukuda, M. Rab family of small gtpases: An updated view on their regulation and functions. FEBS J. 2021, 288, 36–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhuin, T.; Roy, J.K. Rab11 in disease progression. Int. J. Mol. Cell. Med. 2015, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Wu, D.; Liu, Q.; Chen, J.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, L.; Xie, C.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, Y. Upregulation of long noncoding RNA RAB11B-AS1 promotes tumor metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in lung cancer. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Q.; Fu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Du, Y.; Li, Q.; Qiu, X.; Wang, E. RAB11A promotes proliferation and invasion through regulation of yap in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 27800–27811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, W.; Qin, G.; Shen, R. RAB11-FIP2 promotes the metastasis of gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 138, 1680–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, Y. Rab25 upregulation correlates with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of renal cell carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liang, R.; Huang, B.; Wu, D.; Yang, L.; Lu, H.; Jin, D.; et al. Long non-coding RNA RAB11B-AS1 prevents osteosarcoma development and progression via its natural antisense transcript rab11b. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 26770–26786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gao, G.F.; Parker, J.S.; Reynolds, S.M.; Silva, T.C.; Wang, L.B.; Zhou, W.; Akbani, R.; Bailey, M.; Balu, S.; Berman, B.P.; et al. Before and after: Comparison of legacy and harmonized tcga genomic data commons’ data. Cell Syst. 2019, 9, 24–34.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrett, T.; Wilhite, S.E.; Ledoux, P.; Evangelista, C.; Kim, I.F.; Tomashevsky, M.; Marshall, K.A.; Phillippy, K.H.; Sherman, P.M.; Holko, M.; et al. Ncbi geo: Archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D991–D995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrieri, C.; Cimatti, L.; Biagioli, M.; Beugnet, A.; Zucchelli, S.; Fedele, S.; Pesce, E.; Ferrer, I.; Collavin, L.; Santoro, C.; et al. Long non-coding antisense rna controls uchl1 translation through an embedded SINEB2 repeat. Nature 2012, 491, 454–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.A.; Shah, N.; Wang, K.C.; Kim, J.; Horlings, H.M.; Wong, D.J.; Tsai, M.C.; Hung, T.; Argani, P.; Rinn, J.L.; et al. Long non-coding RNA hotair reprograms chromatin state to promote cancer metastasis. Nature 2010, 464, 1071–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warde-Farley, D.; Donaldson, S.L.; Comes, O.; Zuberi, K.; Badrawi, R.; Chao, P.; Franz, M.; Grouios, C.; Kazi, F.; Lopes, C.T.; et al. The genemania prediction server: Biological network integration for gene prioritization and predicting gene function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, W214–W220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asplund, A.; Edqvist, P.H.; Schwenk, J.M.; Pontén, F. Antibodies for profiling the human proteome-the human protein atlas as a resource for cancer research. Proteomics 2012, 12, 2067–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, B.T.; Hao, M.; Qiu, J.; Jiao, X.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Imamichi, T.; Chang, W. David: A web server for functional enrichment analysis and functional annotation of gene lists (2021 update). Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W216–W221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Li, C.; Kang, B.; Gao, G.; Li, C.; Zhang, Z. Gepia: A web server for cancer and normal gene expression profiling and interactive analyses. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, W98–W102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Fan, J.; Wang, B.; Traugh, N.; Chen, Q.; Liu, J.S.; Li, B.; Liu, X.S. Timer: A web server for comprehensive analysis of tumor-infiltrating immune cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, e108–e110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cbioportal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, l1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, M.J.; Craft, B.; Hastie, M.; Repečka, K.; McDade, F.; Kamath, A.; Banerjee, A.; Luo, Y.; Rogers, D.; Brooks, A.N. Visualizing and interpreting cancer genomics data via the xena platform. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhold, W.C.; Sunshine, M.; Liu, H.; Varma, S.; Kohn, K.W.; Morris, J.; Doroshow, J.; Pommier, Y. Cellminer: A web-based suite of genomic and pharmacologic tools to explore transcript and drug patterns in the NCI-60 cell line set. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 3499–3511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sticht, C.; De La Torre, C.; Parveen, A.; Gretz, N. Mirwalk: An online resource for prediction of microRNA binding sites. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. Starbase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale clip-seq data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertucci, F.; Chaffanet, M.; Birnbaum, D. An ICGC major achievement in breast cancer: A comprehensive catalog of mutations and mutational signatures. Chin. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 6, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Győrffy, B.; Benke, Z.; Lánczky, A.; Balázs, B.; Szállási, Z.; Timár, J.; Schäfer, R. Recurrenceonline: An online analysis tool to determine breast cancer recurrence and hormone receptor status using microarray data. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 132, 1025–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Pan, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Shen, H.B. The lnclocator: A subcellular localization predictor for long non-coding RNAs based on a stacked ensemble classifier. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2185–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, K.V.; Vogt, P.K. Long antisense non-coding rnas and their role in transcription and oncogenesis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 2544–2547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Li, B.P.; Zhang, B.; Ma, P.; Wu, Q.L.; Ming, L.; Xie, L.M. Lncrna sbf2-as1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis by regulating emt and predicts unfavorable prognosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 6333–6341. [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi, K.; Yan, I.K.; Kogure, T.; Haga, H.; Patel, T. Extracellular vesicle-mediated transfer of long non-coding RNA ROR modulates chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular cancer. FEBS Open Bio. 2014, 4, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothzerg, E.; Ho, X.D.; Xu, J.; Wood, D.; Märtson, A.; Kõks, S. Upregulation of 15 antisense long non-coding RNAs in osteosarcoma. Genes 2021, 12, 1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Bao, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, C.; Luo, M.; Zhang, B.; Zhou, M.; Wang, J.E.; Fang, Y.V.; Kumar, A. HIF2-induced long noncoding RNA RAB11B-AS1 promotes hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis and breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Res. 2020, 80, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningbo, Y.; Xiaodong, J.; Yao, K. LncRNA RAB11B-AS1 up-regulating miR-628-3p inhibits proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cell line. Basic Clin. Med. 2021, 41, 1762–1766. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, J.; Ling, J.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, P.; Tang, X.; Zhou, H.; Li, R. Construction of a glycolysis-related long noncoding RNA signature for predicting survival in endometrial cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1431–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.; Williams, C.; Azuero, A.; Burkard, M.E.; Kenzik, K.; Garrett, M.E.; Meersman, S.; Rocque, G. Utilizing data visualization to identify survival and treatment differences between women with de novo and recurrent metastatic breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 2021, 21, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariyama, K.; Nouso, K.; Hiraoka, A.; Wakuta, A.; Oonishi, A.; Kuzuya, T.; Toyoda, H.; Tada, T.; Tsuji, K.; Itobayashi, E. Ez-albi score for predicting hepatocellular carcinoma prognosis. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, X.; Lin, J.; Li, H.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, C.; Qi, X.; Huo, H.; Lou, X. Serum GGT/ALT ratio predicts vascular invasion in HBV-related HCC. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez Abad, M.; Calabuig-Fariñas, S.; Lobo de Mena, M.; Torres, M.S.; García, G.C.; García, G.J.; Iranzo, G.C.V.; Camps, H.C. Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-l1) as immunotherapy biomarker in breast cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Chen, Y.; Ou, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, N. LncRNA MIAT correlates with immune infiltrates and drug reactions in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 89, 107071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.G.; Kim, G.; Jang, S.Y.; Lee, Y.R.; Lee, E.; Lee, H.W.; Han, M.H.; Chun, J.M.; Han, Y.S.; Yoon, J.S. Plasma long noncoding RNA LEXIS is a potential diagnostic marker for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Life 2020, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; You, H.; Tang, R.; Zheng, K. The regulation of proteins associated with the cytoskeleton by hepatitis B virus X protein during hepatocarcinogenesis. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2514–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhu, G.; Hou, Z. The prognostic landscape of tumor-infiltrating immune cell and immunomodulators in lung cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, W.; Liang, L.; Gu, Y.; Qi, Z.; Qiu, H.; Yang, X.; Zeng, W.; Ma, L.; Xie, J. Immune-related lncrna to construct novel signature and predict the immune landscape of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2020, 22, 937–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luzón-Toro, B.; Fernández, R.M.; Martos-Martínez, J.M.; Rubio, M.M.; Antiñolo, G.; Borrego, S. LncRNA LUCAT1 as a novel prognostic biomarker for patients with papillary thyroid cancer. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 14374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, B.; Zhang, M.; Guo, W.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, S.; Xie, W.; Yang, D. LncRNA epigenetic landscape analysis identifies EPIC1 as an oncogenic lncRNA that interacts with MYC and promotes cell-cycle progression in cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 706–720.e709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, X.; Ma, X.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, M. KCNQ1OT1 contributes to sorafenib resistance and programmed death-ligand-1-mediated immune escape via sponging miR-506 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1794–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, L.; Chen, T.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Tong, X.; Yang, W.; Xu, Q.; Huang, D. A novel lncRNA MCM3AP-AS1 promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting miR-194-5p/FOXA1 axis. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
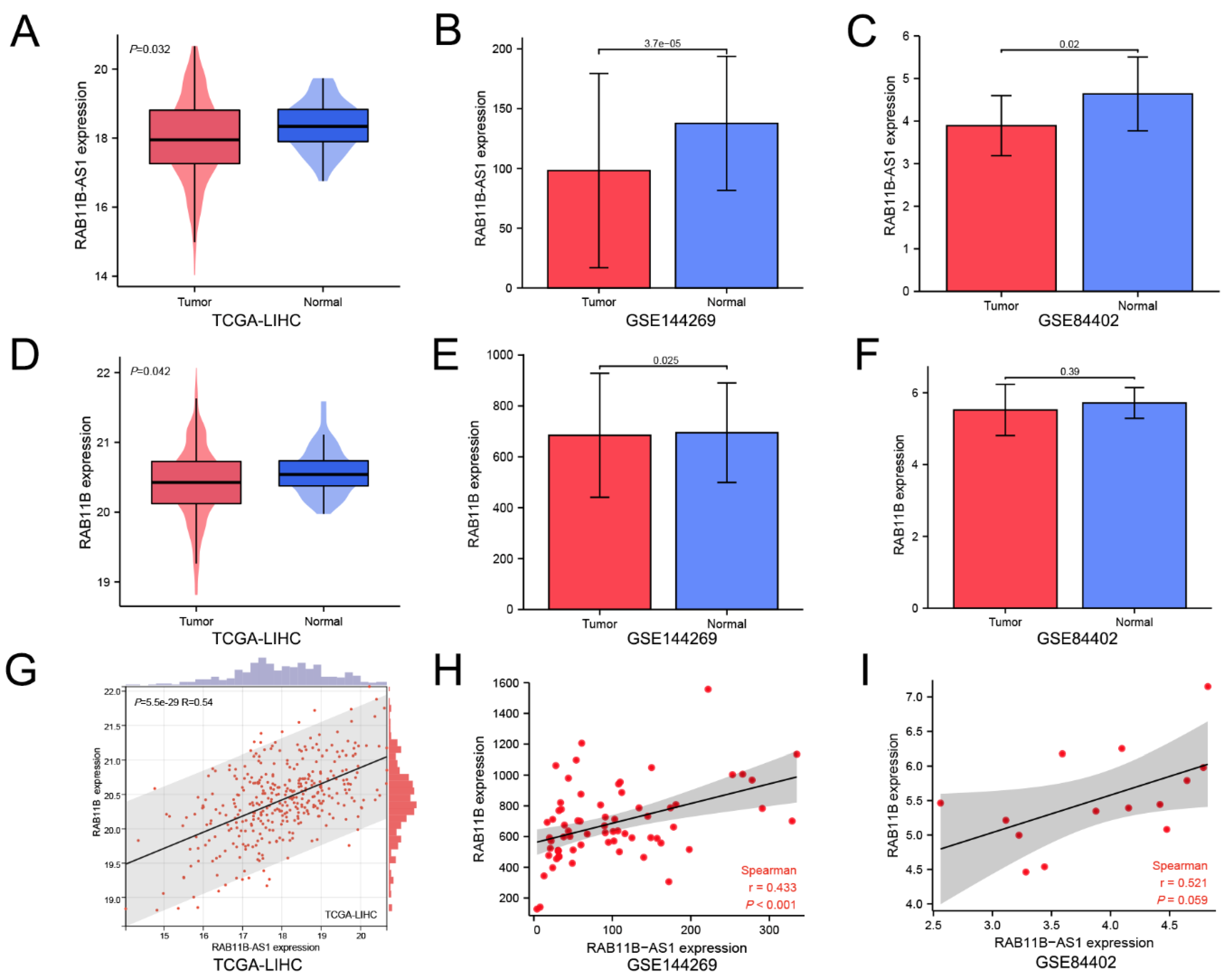
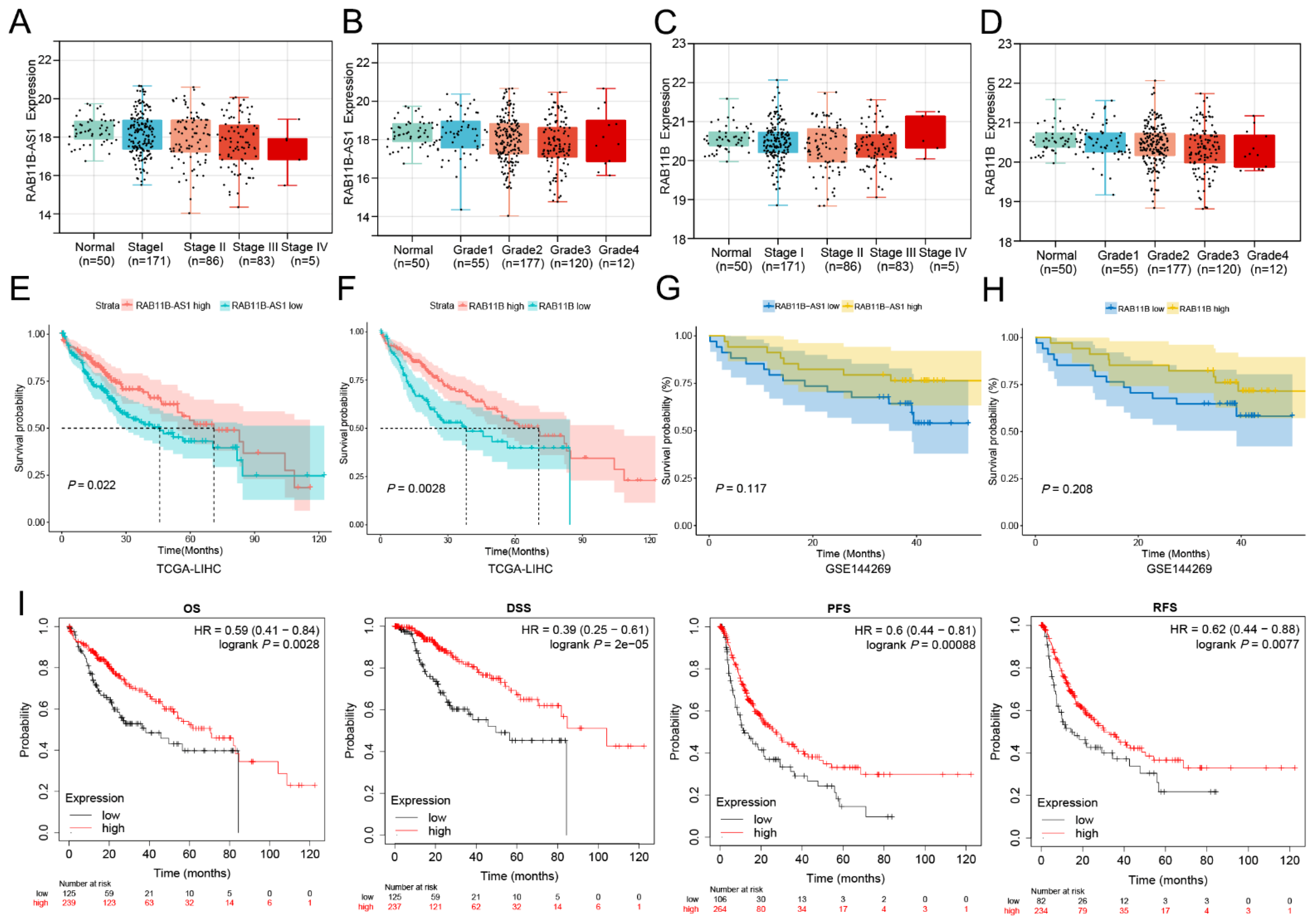
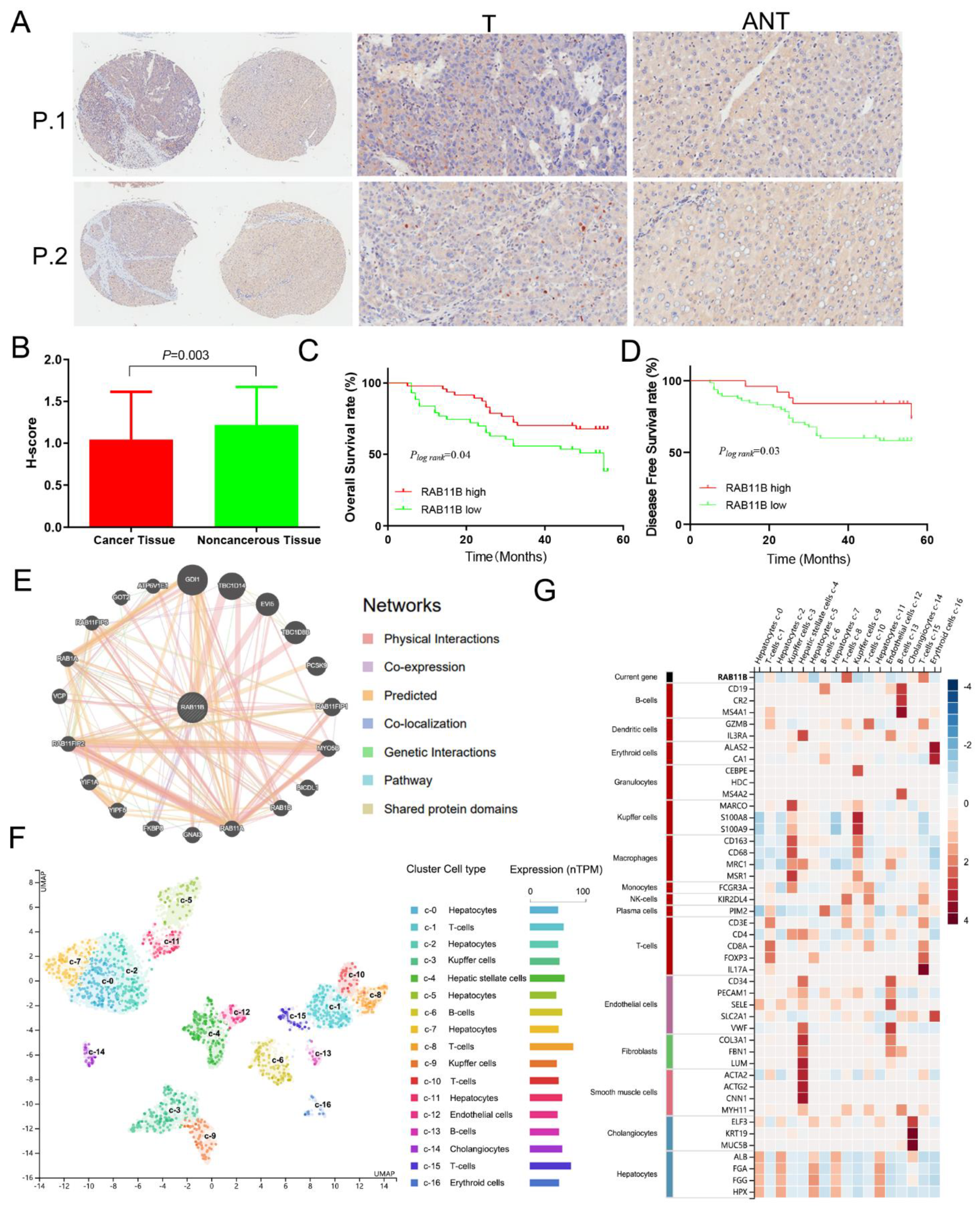
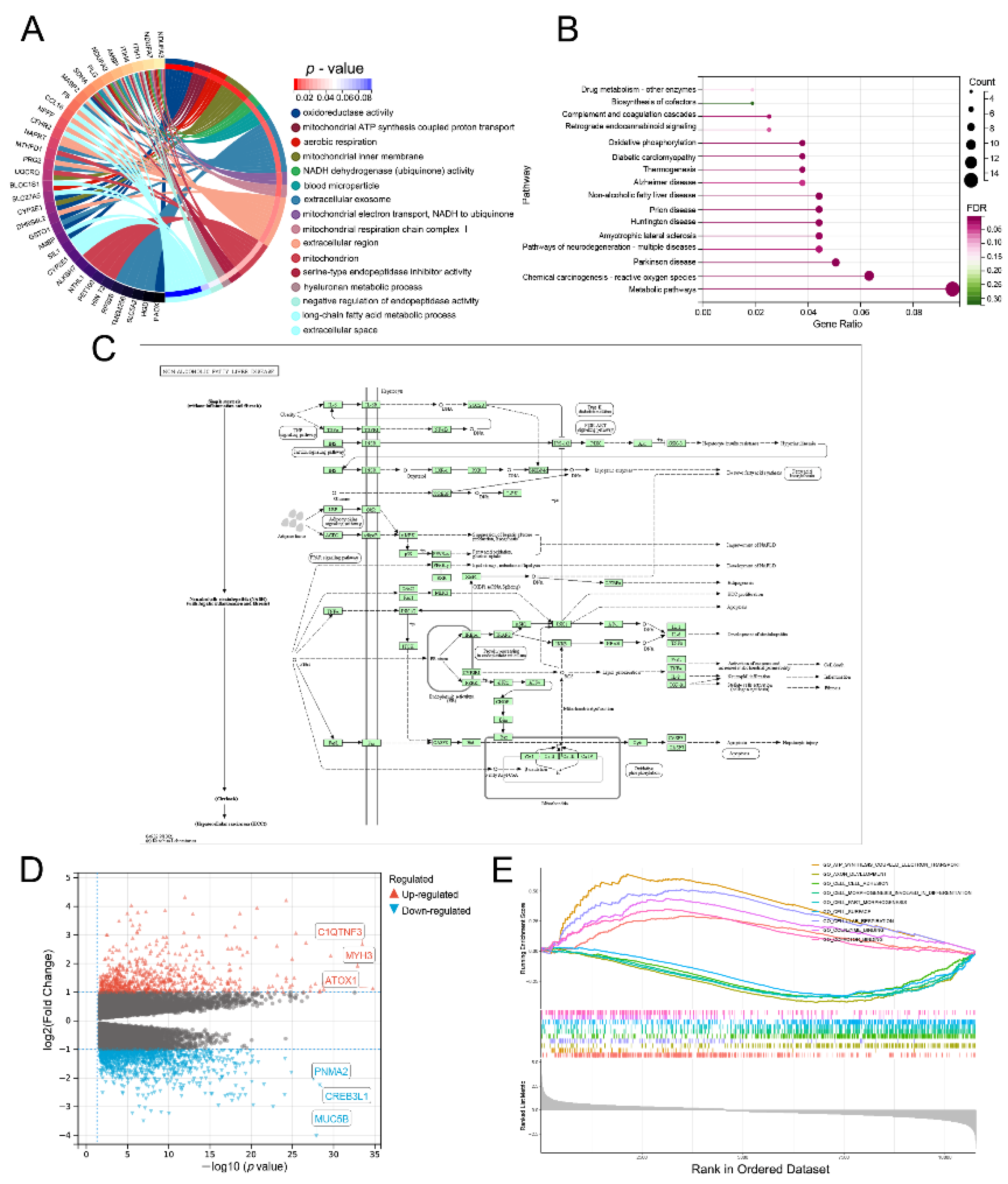
| Characteristics | n | Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 Expression | χ2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 184) | Low (n = 184) | ||||
| Sex | 9.908 | 0.002 | |||
| Male | 248 | 139 (56.1) | 109 (43.9) | ||
| Female | 120 | 46 (38.3) | 74 (61.7) | ||
| Age | 2.297 | 0.130 | |||
| ≤60 | 179 | 82 (45.8) | 97 (54.2) | ||
| >60 | 188 | 101 (53.7) | 87 (46.3) | ||
| Missing | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Race | 0.603 | 0.740 | |||
| Asian | 158 | 75 (47.5) | 83 (52.5) | ||
| White | 182 | 89 (48.9) | 93 (51.1) | ||
| Others | 28 | 14 (50.0) | 14 (50.0) | ||
| Historical risk factors | 4.225 | 0.238 | |||
| History of hepatitis B or hepatitis C | 101 | 53 (52.5) | 48 (47.5) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | 65 | 25 (38.5) | 40 (61.5) | ||
| Smoking | 8 | 4 (50.0) | 4 (50.0) | ||
| Others | 194 | 102 (52.6) | 92 (47.4) | ||
| Clinical stage | 4.054 | 0.044 | |||
| I, II | 257 | 140 (54.5) | 117 (45.5) | ||
| III, IV | 88 | 37 (42.0) | 51 (58.0) | ||
| Missing | 23 | 7 (30.4) | 16 (69.6) | ||
| T | 2.472 | 0.116 | |||
| T1, T2 | 275 | 144 (52.4) | 131 (47.6) | ||
| T3, T4 | 91 | 39 (42.9) | 52 (57.1) | ||
| Missing | 2 | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | ||
| N | 4.605 | 0.032 | |||
| N0 | 250 | 121 (48.2) | 129 (51.8) | ||
| N1 | 5 | 0 (0) | 5 (100.0) | ||
| Missing | 113 | 63 (55.8) | 50 (44.2) | ||
| M | 1.03 | 0.310 | |||
| M0 | 265 | 134 (50.6) | 131 (49.4) | ||
| M1 | 4 | 1 (25.0) | 3 (75.0) | ||
| Missing | 99 | 49 (49.5) | 50 (50.5) | ||
| Histologic grade | 4.416 | 0.036 | |||
| G1, G2 | 232 | 125 (53.9) | 107 (46.1) | ||
| G3, G4 | 132 | 56 (42.4) | 76 (57.6) | ||
| Missing | 4 | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | ||
| AFP (μg/L) | 8.066 | 0.018 | |||
| ≤20 | 147 | 86 (58.5) | 61 (41.5) | ||
| 20 < AFP ≤ 400 | 65 | 28 (43.1) | 37 (56.9) | ||
| >400 | 65 | 26 (40.0) | 39 (60.0) | ||
| Missing | 91 | 44 (48.4) | 47 (51.6) | ||
| T-Bil (μmol/L) | |||||
| Medical reference value | 4 | 4 (100.0) | 0 (0) | 4.500 | 0.034 |
| Abnormal value | 289 | 151 (52.2) | 138 (47.8) | ||
| Missing | 75 | 29 (38.7) | 46 (61.3) | ||
| ALB (g/L) | 3.713 | 0.054 | |||
| Medical reference value | 4 | 4 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Abnormal value | 291 | 150 (51.5) | 141 (48.5) | ||
| Missing | 73 | 30 (41.1) | 43 (58.9) | ||
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 0.165 | 0.685 | |||
| Medical reference value | 182 | 97 (53.3) | 85 (46.7) | ||
| Abnormal value | 114 | 58 (50.9) | 56 (49.1) | ||
| Missing | 72 | 29 (40.3) | 43 (59.7) | ||
| Child pugh grade | 0.018 | 0.895 | |||
| A | 216 | 121 (56.0) | 95 (44.0) | ||
| B,C | 22 | 12 (54.5) | 10 (45.5) | ||
| Missing | 130 | 51 (39.2) | 79 (60.8) | ||
| Treatment or therapy | 1.703 | 0.192 | |||
| Yes | 39 | 16 (41.0) | 23 (59.0) | ||
| No | 307 | 160 (52.1) | 147 (47.9) | ||
| Missing | 22 | 8 (36.4) | 14 (63.6) | ||
| Treatment type | 0.003 | 0.959 | |||
| Pharmaceutical Therapy | 185 | 93 (50.1) | 92 (49.9) | ||
| Radiation Therapy | 183 | 92 (50.3) | 91 (49.7) | ||
| Cancer first-degree relatives | 2.247 | 0.134 | |||
| ≤1 | 65 | 42 (64.6) | 23 (35.4) | ||
| >1 | 53 | 27 (50.9) | 26 (49.1) | ||
| Missing | 250 | 115 (46.0) | 135 (54.0) | ||
| BMI | 335 | 168 (50.1) | 167 (49.9) | 0.884 | 0.377 |
| Missing | 33 | 16 (48.5) | 17 (51.5) | ||
| Characteristics | n | RAB11B Expression | χ2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 184) | Low (n = 184) | ||||
| Sex | 0.012 | 0.911 | |||
| Male | 249 | 124 (49.8) | 125 (50.2) | ||
| Female | 119 | 60 (50.4) | 59 (49.6) | ||
| Age | 0.067 | 0.796 | |||
| ≤60 | 176 | 89 (50.6) | 87 (49.4) | ||
| >60 | 191 | 94 (49.2) | 97 (50.8) | ||
| Missing | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Race | 0.854 | 0.653 | |||
| Asian | 158 | 75 (47.5) | 83 (52.5) | ||
| White | 181 | 93 (51.4) | 88 (48.6) | ||
| Others | 29 | 16 (55.2) | 13 (44.8) | ||
| Historical risk factors | 2.200 | 0.532 | |||
| History of hepatitis B or hepatitis C | 101 | 51 (50.5) | 50 (49.5) | ||
| Alcohol consumption | 65 | 28 (43.1) | 37 (56.9) | ||
| Smoking | 9 | 4 (44.4) | 5 (55.6) | ||
| Others | 193 | 103 (53.4) | 90 (46.6) | ||
| Clinical stage | 3.426 | 0.064 | |||
| I, II | 256 | 134 (52.3) | 122 (47.7) | ||
| III, IV | 89 | 36 (40.4) | 53 (59.6) | ||
| Missing | 23 | 14 (60.9) | 9 (39.1) | ||
| T | 2.472 | 0.116 | |||
| T1, T2 | 275 | 144 (52.4) | 131 (47.6) | ||
| T3, T4 | 91 | 39 (42.9) | 52 (57.1) | ||
| Missing | 2 | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | ||
| N | 0.850 | 0.357 | |||
| N0 | 251 | 121 (48.2) | 130 (51.8) | ||
| N1 | 4 | 1 (25.0) | 3 (75.0) | ||
| Missing | 113 | 62 (54.9) | 51 (45.1) | ||
| M | 0.025 | 0.875 | |||
| M0 | 265 | 122 (46.1) | 143 (53.9) | ||
| M1 | 4 | 2 (50.0) | 2 (50.0) | ||
| Missing | 99 | 60 (60.6) | 39 (39.4) | ||
| Histologic grade | 5.920 | 0.015 | |||
| G1, G2 | 233 | 127 (54.3) | 106 (45.7) | ||
| G3, G4 | 131 | 54 (41.2) | 77 (58.8) | ||
| Missing | 4 | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | ||
| AFP (μg/L) | 0.581 | 0.748 | |||
| ≤20 | 147 | 72 (49.0) | 75 (51.0) | ||
| 20<AFP ≤ 400 | 66 | 32 (48.5) | 34 (51.5) | ||
| >400 | 64 | 34 (53.1) | 30 (46.9) | ||
| Missing | 91 | 46 (50.5) | 45 (49.5) | ||
| T-Bil (μmol/L) | 0.894 | 0.344 | |||
| Medical reference value | 4 | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | ||
| Abnormal value | 289 | 148 (51.2) | 141 (48.8) | ||
| Missing | 75 | 33 (44.0) | 42 (56.0) | ||
| ALB (g/L) | 0.920 | 0.337 | |||
| Medical reference value | 4 | 3 (75.0) | 1 (25.0) | ||
| Abnormal value | 291 | 148 (50.9) | 143 (49.1) | ||
| Missing | 73 | 33 (45.2) | 40 (54.8) | ||
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 0.109 | 0.741 | |||
| Medical reference value | 182 | 89 (48.9) | 93 (51.1) | ||
| Abnormal value | 114 | 58 (50.9) | 56 (49.1) | ||
| Missing | 72 | 37 (51.4) | 35 (48.6) | ||
| Child pugh grade | 0.092 | 0.762 | |||
| A | 217 | 111 (51.2) | 106 (48.8) | ||
| B,C | 22 | 12 (54.5) | 10 (45.5) | ||
| Missing | 129 | 61 (47.3) | 68 (52.7) | ||
| Treatment or therapy | 0.205 | 0.651 | |||
| Yes | 40 | 21 (52.5) | 19 (47.5) | ||
| No | 306 | 149 (48.7) | 157 (51.3) | ||
| Missing | 22 | 14 (63.6) | 8 (36.4) | ||
| Treatment type | 0.330 | 0.566 | |||
| Pharmaceutical Therapy | 185 | 95 (51.4) | 90 (48.6) | ||
| Radiation Therapy | 183 | 88 (48.1) | 94 (51.9) | ||
| Cancer first-degree relatives | 1.238 | 0.266 | |||
| ≤1 | 66 | 36 (54.5) | 30 (45.5) | ||
| >1 | 52 | 23 (44.2) | 29 (55.8) | ||
| Missing | 250 | 125 (50.0) | 125 (50.0) | ||
| BMI | 335 | 166 (49.6) | 169 (50.4) | 1.112 | 0.267 |
| Missing | 33 | 18 (54.5) | 15 (45.5) | ||
| Variable | Univariable | Multivariable | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95%CI | p | HR | 95%CI | p | ||
| Gender | 1.119 | 0.771–1.624 | 0.556 | 1.192 | 0.610–2.330 | 0.725 | |
| Age | 1.013 | 0.998–1.027 | 0.083 | 1.023 | 0.998–1.051 | 0.076 | |
| BMI | 1.019 | 0.967–1.028 | 0.819 | 1.031 | 0.979–1.086 | 0.377 | |
| Race | 1 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| 2 | 1.301 | 0.879–1.925 | 0.189 | 0.539 | 0.255–1.141 | 0.106 | |
| 3 | 1.526 | 0.647–3.599 | 0.334 | 1.812 | 0.232–14.105 | 0.570 | |
| Clinical stage | 1.312 | 1.011–1.703 | 0.041 | 2.628 | 1.599–4.321 | <0.001 | |
| T | 2.562 | 1.770–3.707 | <0.001 | 20.208 | 0.869–469.5 | 0.061 | |
| N | 1.991 | 1.487–8.144 | 0.038 | 8.846 | 1.013–1.096 | 0.013 | |
| M | 3.907 | 1.225–12.47 | 0.021 | 1.233 | 0.135–11.281 | 0.853 | |
| Histologic grade | 1.060 | 0.726–1.547 | 0.762 | 1.119 | 0.631–1.983 | 0.701 | |
| AFP (μg/L) | 1 | Reference | Reference | ||||
| 2 | 1.352 | 0.621–2.941 | 0.447 | 1.102 | 0.321–2.564 | 0.854 | |
| 3 | 0.924 | 0.385–2.220 | 0.860 | 1.224 | 0.278–2.402 | 0.714 | |
| T-Bil (μmol/L) | 1.356 | 0.185–9.932 | 0.764 | 1.356 | 0.185–9.932 | 0.764 | |
| ALB (g/L) | 1.398 | 0.101–10.240 | 0.742 | 1.284 | 0.175–9.434 | 0.806 | |
| Creatinine (μmol/L) | 1.710 | 1.067–1.374 | 0.031 | 1.744 | 1.297–1.862 | 0.027 | |
| Child pugh grade | 2.205 | 0.296–16.401 | 0.365 | 1.993 | 0.236–16.846 | 0.526 | |
| Treatment type | 1.231 | 0.858–1.766 | 0.260 | 1.734 | 0.979–3.071 | 0.059 | |
| Treatment or therapy | 1.039 | 0.592–1.822 | 0.895 | 1.176 | 0.492–2.807 | 0.716 | |
| Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 | 0.814 | 0.696–0.951 | 0.009 | 0.799 | 0.656–0.972 | 0.025 | |
| RAB11B | 0.651 | 0.467–0.909 | 0.012 | 0.898 | 0.978–1.000 | 0.041 | |
| Characteristics | n | RAB11B Expression | χ2 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High (n = 25) | Low (n = 65) | ||||
| Sex | 0.339 | 0.560 | |||
| Male | 80 | 23 (28.6) | 57 (71.4) | ||
| Female | 10 | 2 (20.0) | 8 (80.0) | ||
| Age | 0.543 | 0.461 | |||
| ≤60 | 71 | 21 (29.6) | 50 (70.4) | ||
| >60 | 19 | 4 (21.1) | 15 (78.9) | ||
| Pathology grade | 15.691 | <0.001 | |||
| I | 3 | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | ||
| II | 43 | 19 (44.2) | 24 (55.8) | ||
| III | 44 | 4 (9.1) | 40 (90.9) | ||
| Clinical stage | 2.018 | 0.365 | |||
| 1 | 63 | 20 (31.7) | 43 (68.3) | ||
| 2 | 25 | 5 (20.0) | 20 (80.0) | ||
| 3 | 2 | 0 (0) | 2 (100.0) | ||
| T | 2.225 | 0.329 | |||
| T1 | 63 | 20 (31.7) | 43 (68.3) | ||
| T2 | 24 | 5 (20.8) | 19 (79.2) | ||
| T3 | 3 | 0 (0) | 3 (100.0) | ||
| Recurrence | 1.522 | 0.217 | |||
| Yes | 49 | 11 (22.4) | 38 (77.6) | ||
| No | 41 | 14 (34.1) | 27 (65.9) | ||
| HBsAg | 2.811 | 0.094 | |||
| Positive | 70 | 16 (22.9) | 54 (77.1) | ||
| Negative | 19 | 8 (42.1) | 11(57.9) | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| HBcAb | 0.018 | 0.894 | |||
| Positive | 80 | 21 (26.3) | 59 (73.7) | ||
| Negative | 7 | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | ||
| Unknown | 3 | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | ||
| AntiHCV | 2.815 | 0.093 | |||
| Positive | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| Negative | 86 | 22 (25.6) | 64 (74.4) | ||
| Unknown | 3 | 2 (66.7) | 1 (33.3) | ||
| T-Bil (μmol/L) | 4.107 | 0.043 | |||
| Medical reference value | 63 | 21 (33.3) | 42 (66.7) | ||
| Abnormal value | 25 | 3 (12.0) | 22 (88.0) | ||
| Unknown | 2 | 1 (50.0) | 1 (50.0) | ||
| ALT (U/L) | 0.224 | 0.636 | |||
| Medical reference value | 52 | 15 (28.8) | 37 (71.2) | ||
| Abnormal value | 37 | 9 (24.3) | 28 (75.7) | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| AFP (μg/L) | 0.716 | 0.397 | |||
| ≤20 | 36 | 10 (27.8) | 26 (72.2) | ||
| >20 | 53 | 14 (26.4) | 39 (73.6) | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| GGT(U/L) | 3.903 | 0.048 | |||
| ≤40 | 30 | 12 (40.0) | 18 (60.0) | ||
| >40 | 59 | 12 (20.3) | 47 (79.7) | ||
| Unknown | 1 | 1 (100.0) | 0 (0) | ||
| PD-L1 expression | 9.357 | 0.002 | |||
| Low | 39 | 18 (46.2) | 21 (53.8) | ||
| High | 45 | 7 (15.6) | 38 (84.4) | ||
| Unknown | 6 | 0 (0) | 6 (100.0) | ||
| CTLA4 expression | 0.786 | 0.375 | |||
| Low | 2 | 0 (0) | 2 (100.0) | ||
| High | 81 | 23 (28.4) | 58 (71.6) | ||
| Unknown | 7 | 2 (28.6) | 5 (71.4) | ||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, D.; Hu, X.; Chen, J.; Liang, B.; Zhang, L.; Qin, P.; Wu, D. Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of the Role of Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 in the Development and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells 2022, 11, 3517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213517
Wang D, Hu X, Chen J, Liang B, Zhang L, Qin P, Wu D. Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of the Role of Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 in the Development and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells. 2022; 11(21):3517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213517
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Dedong, Xiangzhi Hu, Jinbin Chen, Boheng Liang, Lin Zhang, Pengzhe Qin, and Di Wu. 2022. "Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of the Role of Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 in the Development and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma" Cells 11, no. 21: 3517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213517
APA StyleWang, D., Hu, X., Chen, J., Liang, B., Zhang, L., Qin, P., & Wu, D. (2022). Bioinformatics Analysis and Validation of the Role of Lnc-RAB11B-AS1 in the Development and Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cells, 11(21), 3517. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11213517





