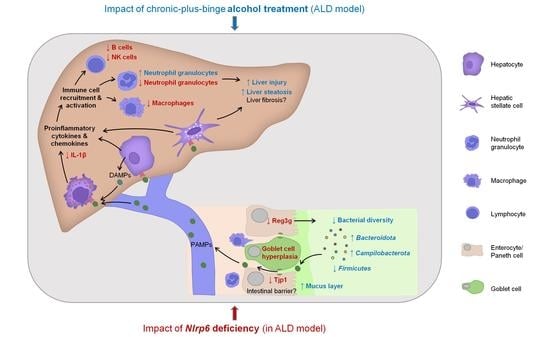
NLRP6 Inflammasome Modulates Disease Progression in a Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Generation and Housing
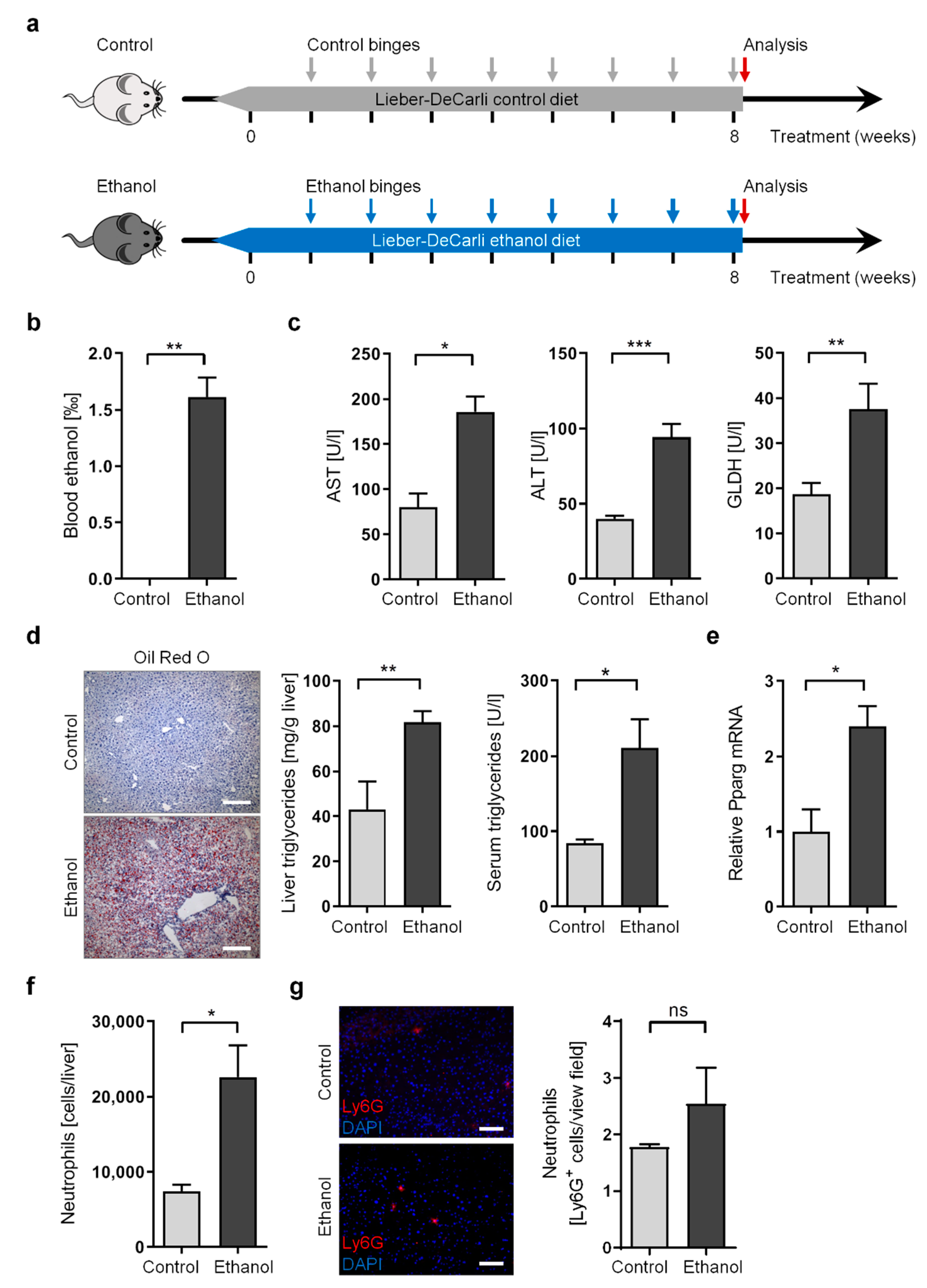
2.2. Mouse Treatment
2.3. Blood Analysis
2.4. Triglyceride Assay
2.5. Histological Staining (Oil Red O, Sirius Red, PAS, Immunofluorescence)
2.6. Reverse Transcription-Quantitative PCR Analysis (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Flow Cytometry
2.8. Isolation of Metagenomic DNA from Cecal Samples
2.9. Illumina Sequencing of 16S rRNA Gene Amplicons
2.10. Sequencing Data Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Long-Term Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of ALD Displays Liver Injury, Steatosis, and Neutrophil Infiltration
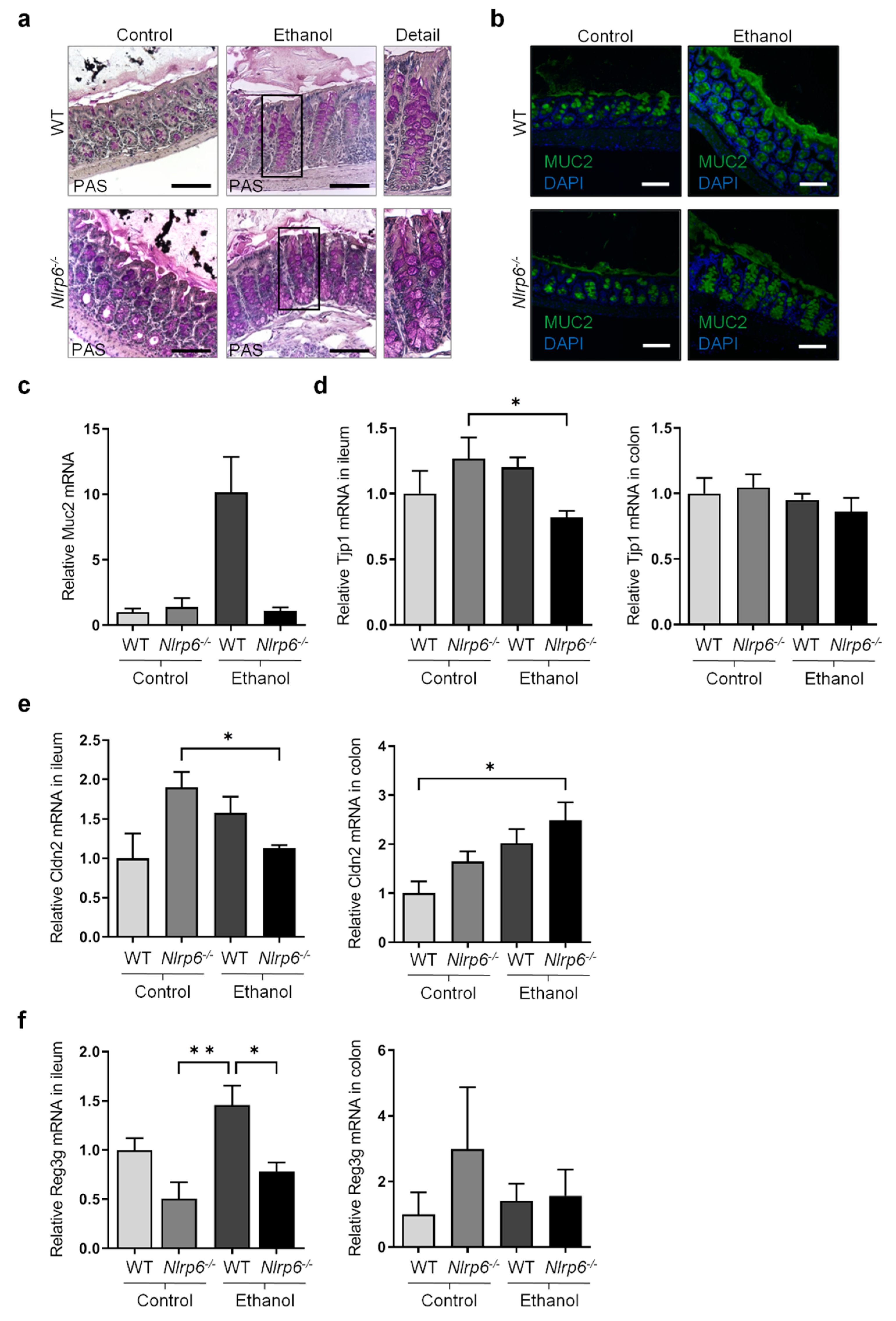
3.2. Chronic Alcohol Consumption and Nlrp6 Deficiency Modulate Intestinal Epithelium
3.3. Chronic Alcohol Treatment and Nlrp6 Deletion Alter the Gut Microbiota
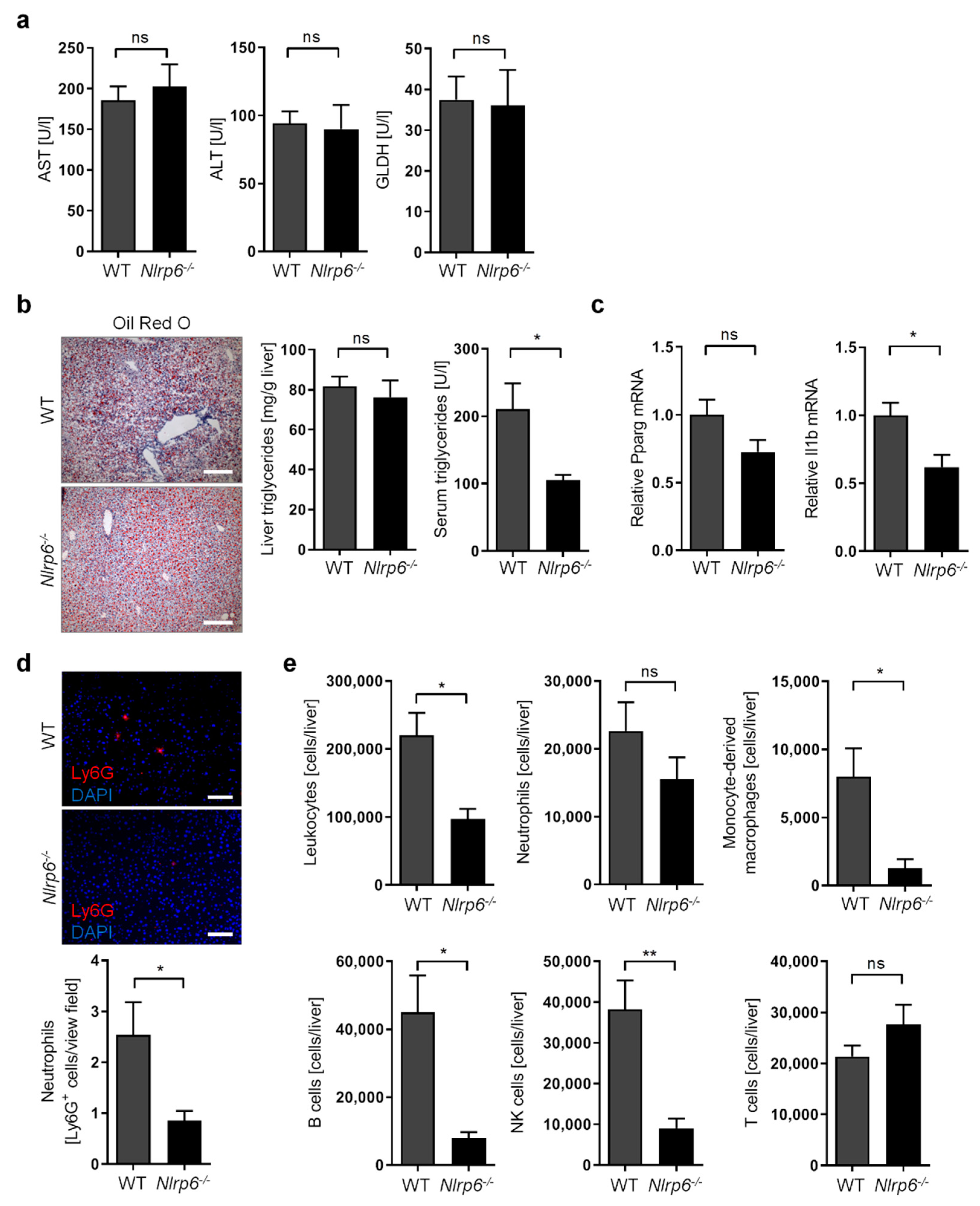
3.4. Abrogation of NLRP6 Inflammasome Signaling Diminishes Liver Immune Cell Infiltration during Chronic Alcohol Consumption
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandayam, S.; Jamal, M.M.; Morgan, T.R. Epidemiology of alcoholic liver disease. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Younossi, Z.; Henry, L. Contribution of alcoholic and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease to the burden of liver-related morbidity and mortality. Gastroenterology 2016, 150, 1778–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, G.; Petrasek, J. Gut-liver axis and sterile signals in the development of alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Alcohol. 2017, 52, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.W.; Fouts, D.E.; Brandl, J.; Starkel, P.; Torralba, M.; Schott, E.; Tsukamoto, H.; Nelson, K.E.; Brenner, D.A.; Schnabl, B. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bull-Otterson, L.; Feng, W.; Kirpich, I.; Wang, Y.; Qin, X.; Liu, Y.; Gobejishvili, L.; Joshi-Barve, S.; Ayvaz, T.; Petrosino, J.; et al. Metagenomic analyses of alcohol induced pathogenic alterations in the intestinal microbiome and the effect of lactobacillus rhamnosus gg treatment. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Tong, J.; Chang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B. Effects of alcohol on intestinal epithelial barrier permeability and expression of tight junction-associated proteins. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 9, 2352–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enomoto, N.; Ikejima, K.; Bradford, B.; Rivera, C.; Kono, H.; Brenner, D.A.; Thurman, R.G. Alcohol causes both tolerance and sensitization of rat kupffer cells via mechanisms dependent on endotoxin. Gastroenterology 1998, 115, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuchi, S.; Tsukamoto, H.; Park, E.; Liu, Z.X.; Brenner, D.A.; Seki, E. Toll-like receptor 4 mediates alcohol-induced steatohepatitis through bone marrow-derived and endogenous liver cells in mice. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2011, 35, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Man, S.M.; Karki, R.; Kanneganti, T.D. Molecular mechanisms and functions of pyroptosis, inflammatory caspases and inflammasomes in infectious diseases. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClain, C.J.; Cohen, D.A.; Dinarello, C.A.; Cannon, J.G.; Shedlofsky, S.I.; Kaplan, A.M. Serum interleukin-1 (il-1) activity in alcoholic hepatitis. Life Sci. 1986, 39, 1479–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; French, B.A.; Tillman, B.; Morgan, T.R.; French, S.W. The inflammasome in alcoholic hepatitis: Its relationship with mallory-denk body formation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2014, 97, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levy, M.; Thaiss, C.A.; Zeevi, D.; Dohnalova, L.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mahdi, J.A.; David, E.; Savidor, A.; Korem, T.; Herzig, Y.; et al. Microbiota-modulated metabolites shape the intestinal microenvironment by regulating nlrp6 inflammasome signaling. Cell 2015, 163, 1428–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ji, X.; Li, L.; Lu, P.; Li, X.; Tian, D.; Liu, M. Nlrp6 exerts a protective role via nf-kb with involvement of ccl20 in a mouse model of alcoholic hepatitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 528, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S.; DeCarli, L.M. The feeding of alcohol in liquid diets: Two decades of applications and 1982 update. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 1982, 6, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieber, C.S.; DeCarli, L.M. Liquid diet technique of ethanol administration: 1989 update. Alcohol Alcohol. 1989, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bertola, A.; Park, O.; Gao, B. Chronic plus binge ethanol feeding synergistically induces neutrophil infiltration and liver injury in mice: A critical role for e-selectin. Hepatology 2013, 58, 1814–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ki, S.H.; Park, O.; Zheng, M.; Morales-Ibanez, O.; Kolls, J.K.; Bataller, R.; Gao, B. Interleukin-22 treatment ameliorates alcoholic liver injury in a murine model of chronic-binge ethanol feeding: Role of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertola, A.; Mathews, S.; Ki, S.H.; Wang, H.; Gao, B. Mouse model of chronic and binge ethanol feeding (the niaaa model). Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- National Research Council. Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals; National Research Council: Washington, DC, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Godon, J.J.; Zumstein, E.; Dabert, P.; Habouzit, F.; Moletta, R. Molecular microbial diversity of an anaerobic digestor as determined by small-subunit rdna sequence analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 2802–2813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Klaring, K.; Heinzmann, S.S.; Platz, S.; Scholz, B.; Engel, K.H.; Schmitt-Kopplin, P.; Haller, D.; Rohn, S.; Skurk, T.; et al. Gut metabolites and bacterial community networks during a pilot intervention study with flaxseeds in healthy adult men. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 1614–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, D.; Ben Mahfoudh, K.; Wagner, M.; Loy, A. Barcoded primers used in multiplex amplicon pyrosequencing bias amplification. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2011, 77, 7846–7849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klindworth, A.; Pruesse, E.; Schweer, T.; Peplies, J.; Quast, C.; Horn, M.; Glockner, F.O. Evaluation of general 16s ribosomal rna gene pcr primers for classical and next-generation sequencing-based diversity studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Joseph, D.; Kapfhammer, M.; Giritli, S.; Horn, M.; Haller, D.; Clavel, T. Imngs: A comprehensive open resource of processed 16s rrna microbial profiles for ecology and diversity studies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C. Uparse: Highly accurate otu sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 996–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, D.; Clemente, J.C.; Kuczynski, J.; Rideout, J.R.; Stombaugh, J.; Wendel, D.; Wilke, A.; Huse, S.; Hufnagle, J.; Meyer, F.; et al. The biological observation matrix (biom) format or: How i learned to stop worrying and love the ome-ome. Gigascience 2012, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McMurdie, P.J.; Holmes, S. Phyloseq: An r package for reproducible interactive analysis and graphics of microbiome census data. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e61217. [Google Scholar]
- Lagkouvardos, I.; Fischer, S.; Kumar, N.; Clavel, T. Rhea: A transparent and modular r pipeline for microbial profiling based on 16s rrna gene amplicons. PeerJ 2017, 5, e2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for rna-seq data with deseq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skat-Rordam, J.; Hojland Ipsen, D.; Lykkesfeldt, J.; Tveden-Nyborg, P. A role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2019, 124, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elinav, E.; Strowig, T.; Kau, A.L.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Thaiss, C.A.; Booth, C.J.; Peaper, D.R.; Bertin, J.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Gordon, J.I.; et al. Nlrp6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell 2011, 145, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Henao-Mejia, J.; Elinav, E.; Jin, C.; Hao, L.; Mehal, W.Z.; Strowig, T.; Thaiss, C.A.; Kau, A.L.; Eisenbarth, S.C.; Jurczak, M.J.; et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of nafld and obesity. Nature 2012, 482, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wlodarska, M.; Thaiss, C.A.; Nowarski, R.; Henao-Mejia, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Brown, E.M.; Frankel, G.; Levy, M.; Katz, M.N.; Philbrick, W.M.; et al. Nlrp6 inflammasome orchestrates the colonic host-microbial interface by regulating goblet cell mucus secretion. Cell 2014, 156, 1045–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birchenough, G.M.; Nystrom, E.E.; Johansson, M.E.; Hansson, G.C. A sentinel goblet cell guards the colonic crypt by triggering nlrp6-dependent muc2 secretion. Science 2016, 352, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Petrasek, J.; Bala, S.; Csak, T.; Lippai, D.; Kodys, K.; Menashy, V.; Barrieau, M.; Min, S.Y.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Szabo, G. Il-1 receptor antagonist ameliorates inflammasome-dependent alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 3476–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scott, C.L.; Zheng, F.; De Baetselier, P.; Martens, L.; Saeys, Y.; De Prijck, S.; Lippens, S.; Abels, C.; Schoonooghe, S.; Raes, G.; et al. Bone marrow-derived monocytes give rise to self-renewing and fully differentiated kupffer cells. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.J.; Cai, Y.; Wang, H.; Altamirano, J.; Chang, B.; Bertola, A.; Odena, G.; Lu, J.; Tanaka, N.; Matsusue, K.; et al. Fat-specific protein 27/cidec promotes development of alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice and humans. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1030–1041 e1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szabo, G.; Bala, S.; Petrasek, J.; Gattu, A. Gut-liver axis and sensing microbes. Dig. Dis. 2010, 28, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-talk between akkermansia muciniphila and intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Llopis, M.; Cassard, A.M.; Wrzosek, L.; Boschat, L.; Bruneau, A.; Ferrere, G.; Puchois, V.; Martin, J.C.; Lepage, P.; Le Roy, T.; et al. Intestinal microbiota contributes to individual susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Gut 2016, 65, 830–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engen, P.A.; Green, S.J.; Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. The gastrointestinal microbiome: Alcohol effects on the composition of intestinal microbiota. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ran, B.; Guo, C.E.; Li, W.; Li, W.; Wang, Q.; Qian, J.; Li, H. Sea buckthorn (hippophae rhamnoides l.) fermentation liquid protects against alcoholic liver disease linked to regulation of liver metabolome and the abundance of gut microbiota. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2846–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Wu, H.; Wu, S.D.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.T.; Liu, H.N.; Dong, L.; Liu, T.T.; Shen, X.Z. Parasutterella, in association with irritable bowel syndrome and intestinal chronic inflammation. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1844–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, H. Role of gut dysbiosis in liver diseases: What have we learned so far? Diseases 2019, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, T.X.; Pu, S.L.; Tan, P.; Du, Y.C.; Qian, B.L.; Chen, H.; Fu, W.G.; Huang, M.Z. Liver metabolomics reveals the effect of lactobacillus reuteri on alcoholic liver disease. Front. Physiol. 2020, 11, 595382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, K.; Yan, G.; Xu, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhou, R.; Bai, L.; Lian, Z.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; et al. Invariant nkt cells promote alcohol-induced steatohepatitis through interleukin-1beta in mice. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1311–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamantopoulos, M.; Ronchi, F.; Van Hauwermeiren, F.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Yilmaz, B.; Martens, L.; Saeys, Y.; Drexler, S.K.; Yazdi, A.S.; Raes, J.; et al. Nlrp6- and asc-dependent inflammasomes do not shape the commensal gut microbiota composition. Immunity 2017, 47, 339–348 e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lemire, P.; Robertson, S.J.; Maughan, H.; Tattoli, I.; Streutker, C.J.; Platnich, J.M.; Muruve, D.A.; Philpott, D.J.; Girardin, S.E. The nlr protein nlrp6 does not impact gut microbiota composition. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3653–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Galvez, E.J.C.; Iljazovic, A.; Gronow, A.; Flavell, R.; Strowig, T. Shaping of intestinal microbiota in nlrp6- and rag2-deficient mice depends on community structure. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 3914–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anand, P.K.; Malireddi, R.K.; Lukens, J.R.; Vogel, P.; Bertin, J.; Lamkanfi, M.; Kanneganti, T.D. Nlrp6 negatively regulates innate immunity and host defence against bacterial pathogens. Nature 2012, 488, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, C.; Liu, Q.; Tang, Q.; Jing, X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific deletion of nlrp6 in mice exacerbates the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2021, 169, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mainz, R.E.; Albers, S.; Haque, M.; Sonntag, R.; Treichel, N.S.; Clavel, T.; Latz, E.; Schneider, K.M.; Trautwein, C.; Otto, T. NLRP6 Inflammasome Modulates Disease Progression in a Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Cells 2022, 11, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11020182
Mainz RE, Albers S, Haque M, Sonntag R, Treichel NS, Clavel T, Latz E, Schneider KM, Trautwein C, Otto T. NLRP6 Inflammasome Modulates Disease Progression in a Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Cells. 2022; 11(2):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11020182
Chicago/Turabian StyleMainz, Rebecca Elena, Stefanie Albers, Madhuri Haque, Roland Sonntag, Nicole Simone Treichel, Thomas Clavel, Eicke Latz, Kai Markus Schneider, Christian Trautwein, and Tobias Otto. 2022. "NLRP6 Inflammasome Modulates Disease Progression in a Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease" Cells 11, no. 2: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11020182
APA StyleMainz, R. E., Albers, S., Haque, M., Sonntag, R., Treichel, N. S., Clavel, T., Latz, E., Schneider, K. M., Trautwein, C., & Otto, T. (2022). NLRP6 Inflammasome Modulates Disease Progression in a Chronic-Plus-Binge Mouse Model of Alcoholic Liver Disease. Cells, 11(2), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11020182