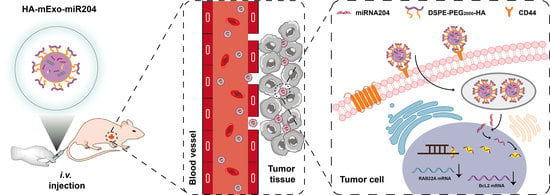
Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Bovine Milk Exosomes for Achieving Tumor-Specific Intracellular Delivery of miRNA-204
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Animals
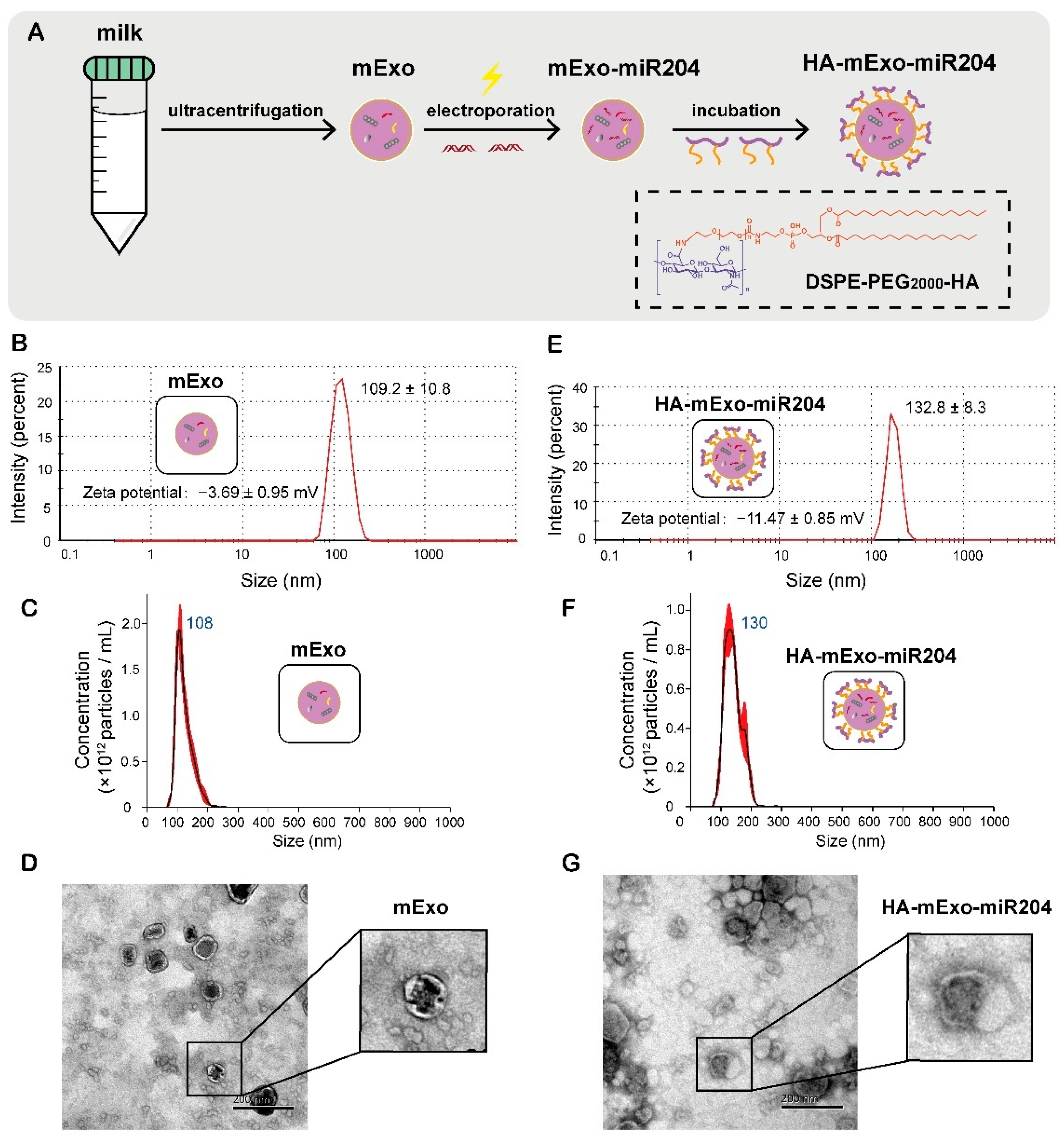
2.3. Exosomes Isolation, miR-204 Loading, and HA Coating
2.4. Size, Zeta Potential, Concentration, and Morphology Characterization of HA-mExo-miR-204
2.5. Western Blot
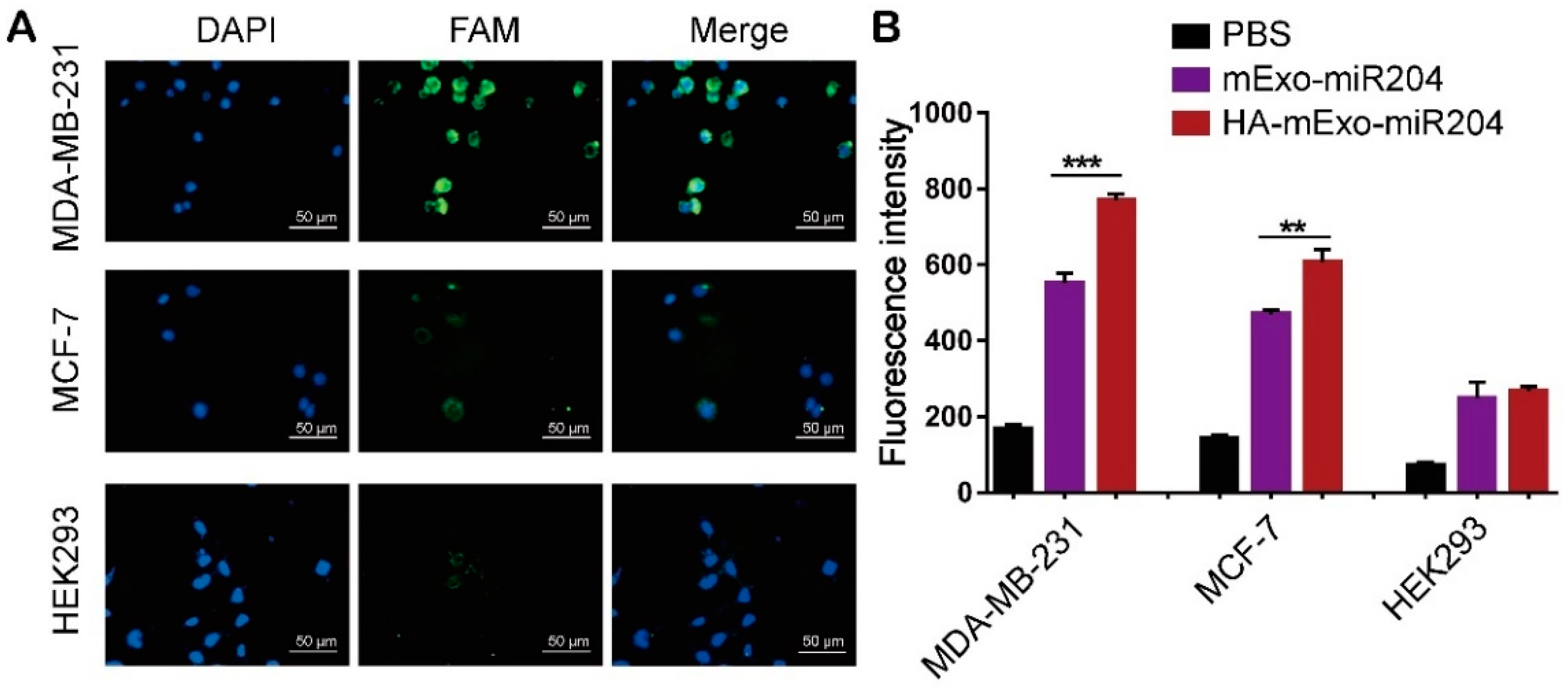
2.6. In Vitro Delivery Specificity and Efficiency of HA-mExo-miR204
2.7. In Vitro Safety of HA-mExos
2.8. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.9. Colony Formation Assay
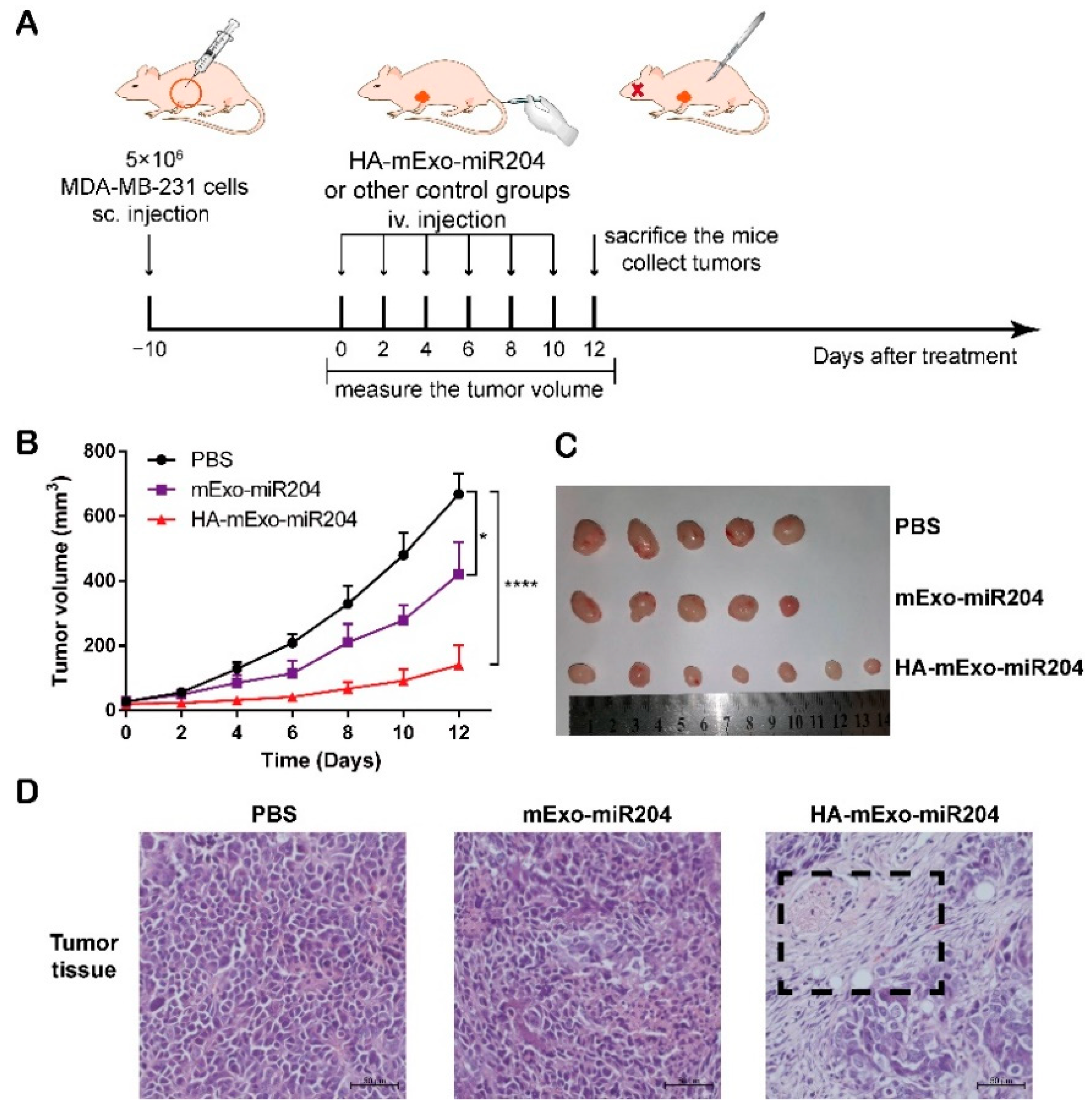
2.10. In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy
2.11. In Vivo Distribution of HA-mExo
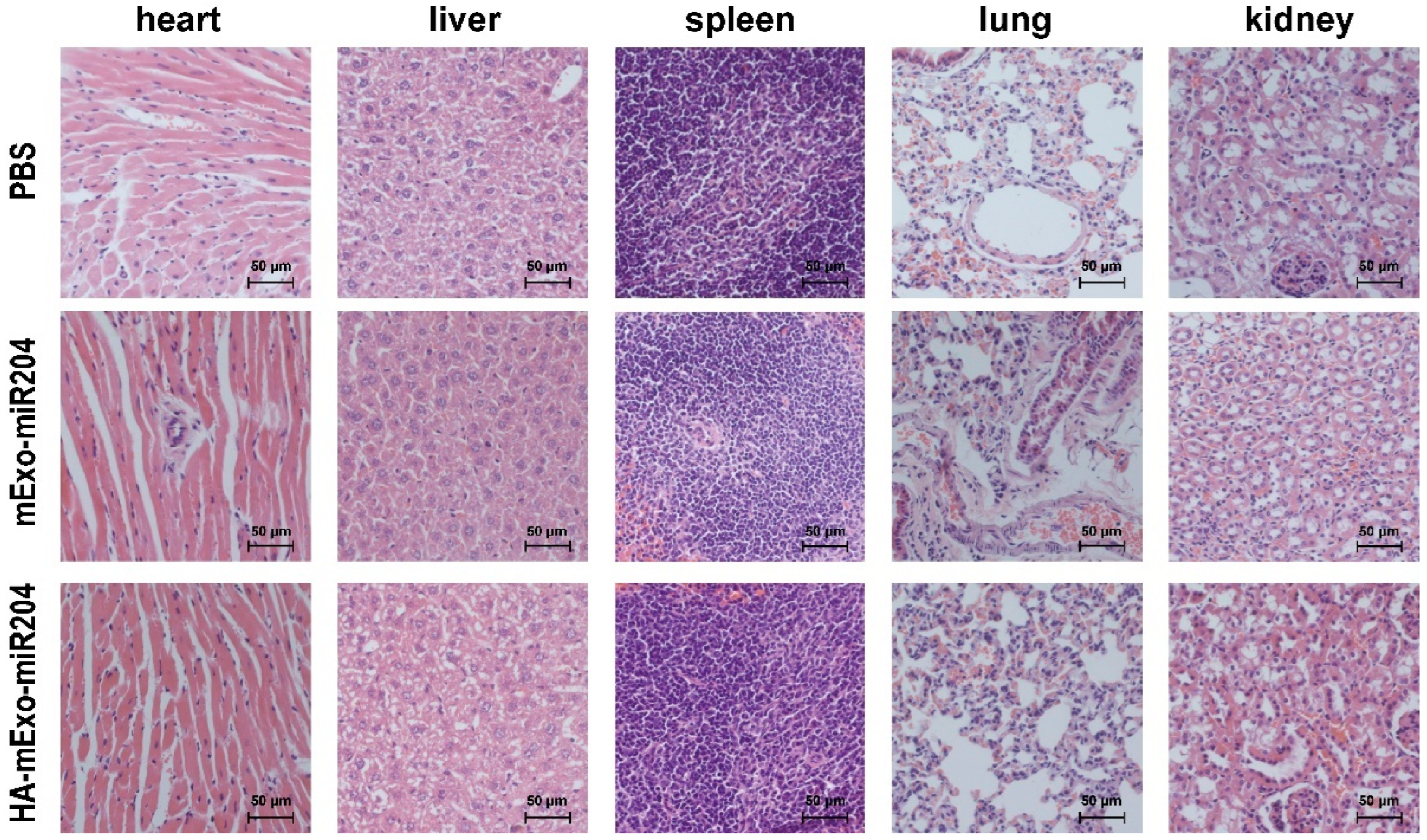
2.12. Histological Analysis of Antitumor Effect and Systemic Toxicity of HA-mExo-miR204
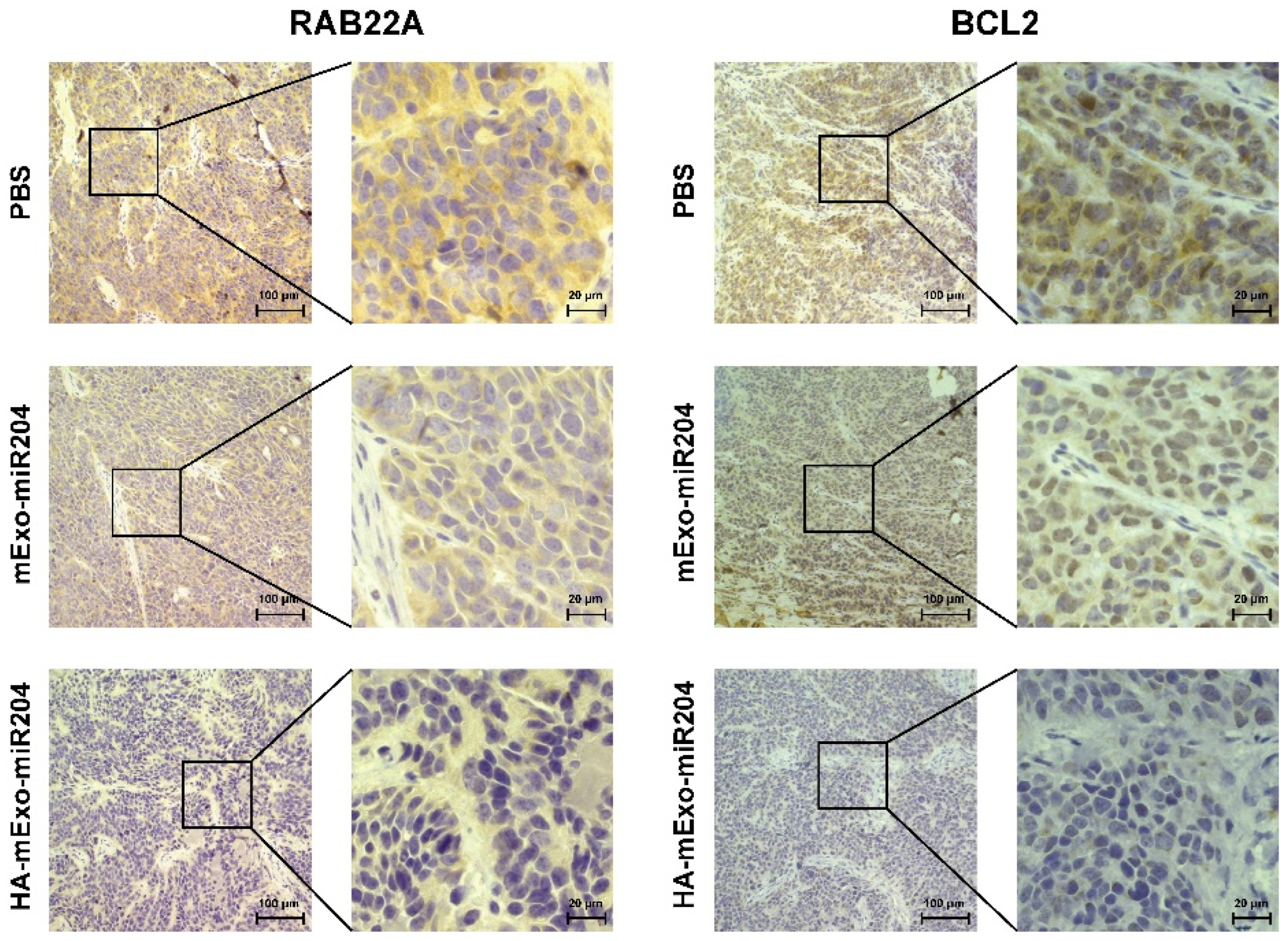
2.13. Immunohistochemistry
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Preparation and Characterization of HA-mExo-miR204
3.2. HA-mExo-miR204 Showed Increased Delivery Specificity and Efficiency
3.3. HA-mExo-miR204 Showed Increased In Vitro Antitumor Activity
3.4. HA-mExo-miR204 Showed Potent In Vivo Antitumor Efficacy
3.5. Safety Evaluation of HA-mExo-miR20
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurung, S.; Perocheau, D.; Touramanidou, L.; Baruteau, J. The exosome journey: From biogenesis to uptake and intracellular signalling. Cell Commun. Signal 2021, 19, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Sun, S.; Huang, C.; Yi, Y.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Wu, M. Exosome-based drug delivery systems in cancer therapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri, A.; Bagherifar, R.; Ansari Dezfouli, E.; Kiaie, S.H.; Jafari, R.; Ramezani, R. Exosomes as bio-inspired nanocarriers for RNA delivery: Preparation and applications. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhong, Y.; Shen, J.; An, W. Biomimetic Exosomes: A New Generation of Drug Delivery System. Front Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 865682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Tang, S.; Chai, Y.; Xu, Z.; Li, M.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; et al. Recent advances in exosome-mediated nucleic acid delivery for cancer therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munagala, R.; Aqil, F.; Jeyabalan, J.; Gupta, R.C. Bovine milk-derived exosomes for drug delivery. Cancer Lett. 2016, 371, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adriano, B.; Cotto, N.M.; Chauhan, N.; Jaggi, M.; Chauhan, S.C.; Yallapu, M.M. Milk exosomes: Nature’s abundant nanoplatform for theranostic applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 2479–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somiya, M.; Yoshioka, Y.; Ochiya, T. Biocompatibility of highly purified bovine milk-derived extracellular vesicles. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1440132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaker, M.A.; Aljoud, F.A.; Alkhilaiwi, F.; Algarni, A.; Ahmed, A.; Khan, M.I.; Saadeldin, I.M.; Alzahrani, F.A. The Therapeutic Potential of Milk Extracellular Vesicles on Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedykh, S.; Kuleshova, A.; Nevinsky, G. Milk Exosomes: Perspective Agents for Anticancer Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pullan, J.; Dailey, K.; Bhallamudi, S.; Feng, L.; Alhalhooly, L.; Froberg, J.; Osborn, J.; Sarkar, K.; Molden, T.; Sathish, V.; et al. Modified Bovine Milk Exosomes for Doxorubicin Delivery to Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater 2022, 5, 2163–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, N.; Li, Y.; Hou, S.; Zhang, W.; Meng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jia, Q.; Tan, J.; Wang, R.; et al. Engineering a HEK-293T exosome-based delivery platform for efficient tumor-targeting chemotherapy/internal irradiation combination therapy. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 20, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Yao, S.R.; Zhou, Z.F.; Shi, J.; Huang, Z.H.; Wu, Z.M. Hyaluronan decoration of milk exosomes directs tumor -specific delivery of doxorubicin. Carbohydr. Res. 2020, 493, 108032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saneja, A.; Arora, D.; Kumar, R.; Dubey, R.D.; Panda, A.K.; Gupta, P.N. CD44 targeted PLGA nanomedicines for cancer chemotherapy. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 121, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Dai, Y.; Gao, H. Development and application of hyaluronic acid in tumor targeting drug delivery. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2019, 9, 1099–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, M.; Devnarain, N.; Elhassan, E.; Govender, T. Exploring the applications of hyaluronic acid-based nanoparticles for diagnosis and treatment of bacterial infections. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2022, 14, e1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadea, A.; Rios de la Rosa, J.M.; Tirella, A.; Ashford, M.B.; Williams, K.J.; Stratford, I.J.; Tirelli, N.; Mehibel, M. Evaluating the Efficiency of Hyaluronic Acid for Tumor Targeting via CD44. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 2481–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Shu, R.; Liu, J. The development and improvement of ribonucleic acid therapy strategies. Mol. Nucleic Acids 2021, 26, 997–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokirmak, T.; Nikan, M.; Wiechmann, S.; Prakash, T.P.; Tanowitz, M.; Seth, P.P. Overcoming the challenges of tissue delivery for oligonucleotide therapeutics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 588–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, H.; Wu, J. Exosome based miRNA delivery strategy for disease treatment. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1693–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, J.C.; Azevedo-Pouly, A.C.; Schmittgen, T.D. MicroRNA replacement therapy for cancer. Pharm. Res. 2011, 28, 3030–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.S.; Ryu, H.S.; Kim, N.; Kim, J.; Lee, E.; Moon, H.; Kim, K.H.; Jin, M.S.; Kwon, N.H.; Kim, S.; et al. Tumor Suppressor miRNA-204–5p Regulates Growth, Metastasis, and Immune Microenvironment Remodeling in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1520–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Xing, L.; Xu, H.; Wang, K.; She, J.; Shi, F.; Wu, H.; Sun, Y.; Gao, J.; He, S. miR-204–5p Suppress Lymph Node Metastasis via Regulating CXCL12 and CXCR4 in Gastric Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 3199–3206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Du, F.; Chen, D.; Ye, T.; Xu, B.; Li, X.; Wang, W.; Qiu, Z.; Liu, H.; et al. miR-204–5p suppresses hepatocellular cancer proliferation by regulating homeoprotein SIX1 expression. FEBS Open Biol. 2018, 8, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Quan, C.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fei, B.; Mao, Y.; et al. LncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-204–5p. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Yin, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Bian, Z.; Song, M.; Hua, D.; Huang, Z. MicroRNA-204–5p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by downregulating USP47 and RAB22A. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Fei, B.; Quan, C.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ni, S.; et al. miR-204–5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6187–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwano, Y.; Nishida, K.; Kajita, K.; Satake, Y.; Akaike, Y.; Fujita, K.; Kano, S.; Masuda, K.; Rokutan, K. Transformer 2beta and miR-204 regulate apoptosis through competitive binding to 3’ UTR of BCL2 mRNA. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 815–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Yin, Y.; Jin, G.; Li, D.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Bian, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Exosome-mediated delivery of miR-204–5p inhibits tumor growth and chemoresistance. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 5989–5998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolny, P.M.; Banerji, S.; Gounou, C.; Brisson, A.R.; Day, A.J.; Jackson, D.G.; Richter, R.P. Analysis of CD44-hyaluronan interactions in an artificial membrane system: Insights into the distinct binding properties of high and low molecular weight hyaluronan. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 30170–30180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, Z.L.; Wu, M.; Ren, J.G.; Xia, H.F.; Sa, G.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Pang, D.W.; Zhao, Y.F.; Chen, G. Magnetic and Folate Functionalization Enables Rapid Isolation and Enhanced Tumor-Targeting of Cell-Derived Microvesicles. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili-Tanha, G.; Moghbeli, M. Long non-coding RNAs as the critical regulators of doxorubicin resistance in tumor cells. Cell Mol. Biol. Lett. 2021, 26, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manca, S.; Upadhyaya, B.; Mutai, E.; Desaulniers, A.T.; Cederberg, R.A.; White, B.R.; Zempleni, J. Milk exosomes are bioavailable and distinct microRNA cargos have unique tissue distribution patterns. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.H.; Liang, J.; Chng, W.H.; Muthuramalingam, R.P.K.; Ng, Z.X.; Lee, C.K.; Neupane, Y.R.; Yau, J.N.N.; Zhang, S.; Lou, C.K.L.; et al. Investigations on Cellular Uptake Mechanisms and Immunogenicity Profile of Novel Bio-Hybrid Nanovesicles. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, J.; Shi, M.; Liu, X.; Jin, C.; Xing, X.; Qiu, L.; Tan, W. Aptamer-Functionalized Exosomes: Elucidating the Cellular Uptake Mechanism and the Potential for Cancer-Targeted Chemotherapy. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2425–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, C.; Liu, X.R.; Chen, Q.B.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.L.; Zhou, L.Y.; Zou, T. Hyaluronic acid and albumin based nanoparticles for drug delivery. J. Control Release 2021, 331, 416–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipoor, R.; Ayan, M.; Hamblin, M.R.; Ranjbar, R.; Rashki, S. Hyaluronic Acid-Based Nanomaterials as a New Approach to the Treatment and Prevention of Bacterial Infections. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 913912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, D.; Gong, L.; Lin, H.; Yao, S.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, J.; Wu, Z.; Huang, Z. Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Bovine Milk Exosomes for Achieving Tumor-Specific Intracellular Delivery of miRNA-204. Cells 2022, 11, 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193065
Li D, Gong L, Lin H, Yao S, Yin Y, Zhou Z, Shi J, Wu Z, Huang Z. Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Bovine Milk Exosomes for Achieving Tumor-Specific Intracellular Delivery of miRNA-204. Cells. 2022; 11(19):3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193065
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Dan, Liang Gong, Han Lin, Surui Yao, Yuan Yin, Zhifang Zhou, Jie Shi, Zhimeng Wu, and Zhaohui Huang. 2022. "Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Bovine Milk Exosomes for Achieving Tumor-Specific Intracellular Delivery of miRNA-204" Cells 11, no. 19: 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193065
APA StyleLi, D., Gong, L., Lin, H., Yao, S., Yin, Y., Zhou, Z., Shi, J., Wu, Z., & Huang, Z. (2022). Hyaluronic Acid-Coated Bovine Milk Exosomes for Achieving Tumor-Specific Intracellular Delivery of miRNA-204. Cells, 11(19), 3065. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11193065