WIN55212-2 Modulates Intracellular Calcium via CB1 Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cells
2.2. Imaging
2.3. Drugs
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
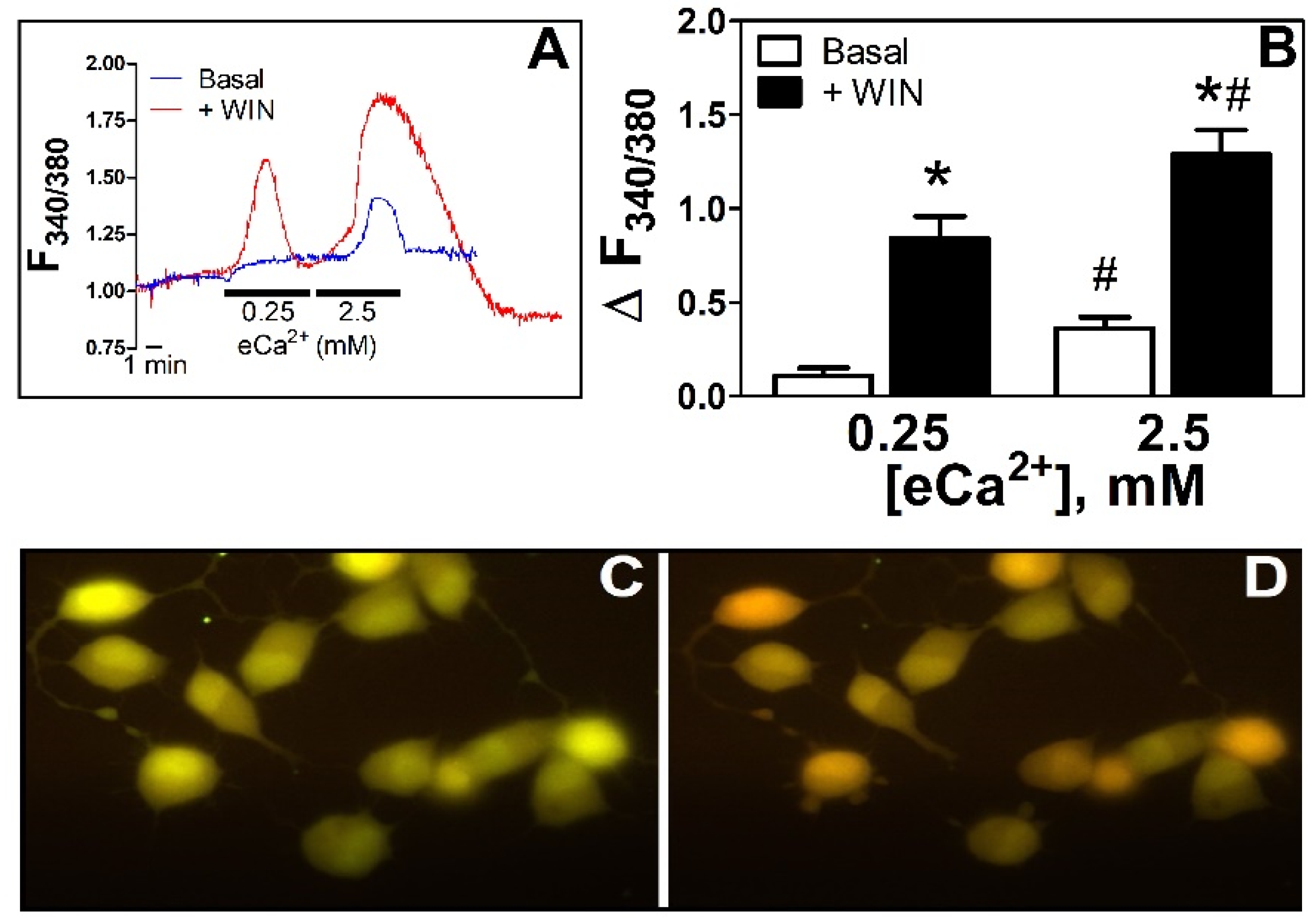
3.1. WIN55212-2 Increased [Ca2+]i in N18TG2 Cells at Both Low eCa2+ and during a High-eCa2+ Stimulus
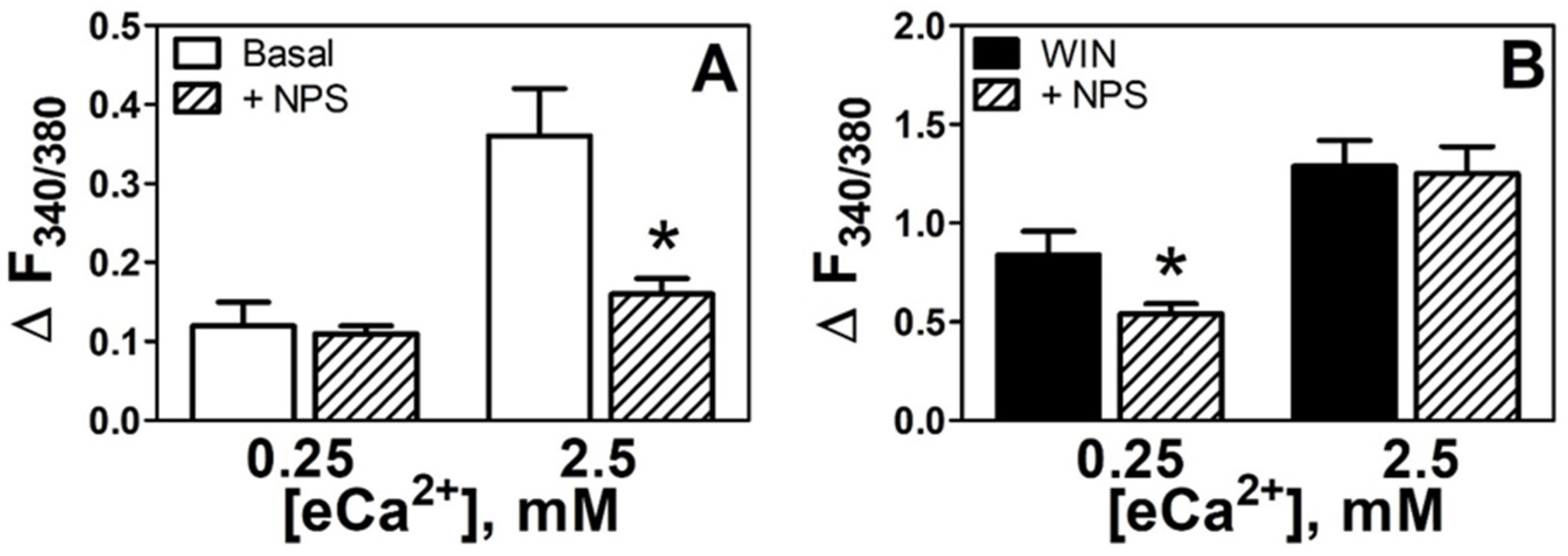
3.2. CaSR Mediates Increases in eCa2+-Induced [Ca2+]i in N18TG2 Cells
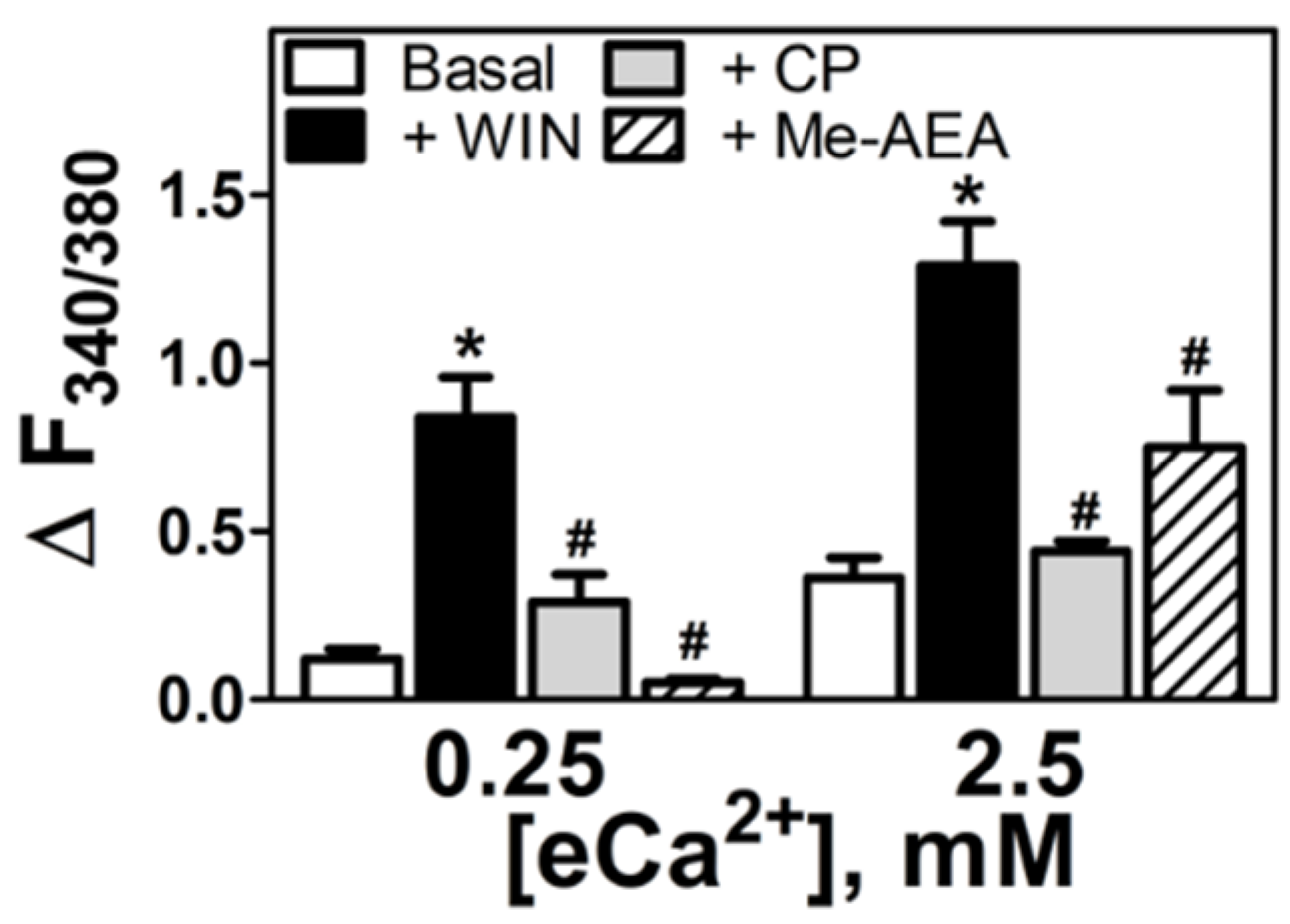
3.3. Aminoalkylindole-Specific Potentiation of the eCa2+-Mediated Increase in [Ca2+]i
3.4. WIN55212-2-Stimulated Increases in [Ca2+]i Require Operational Store Operated Calcium Entry (SOCE)
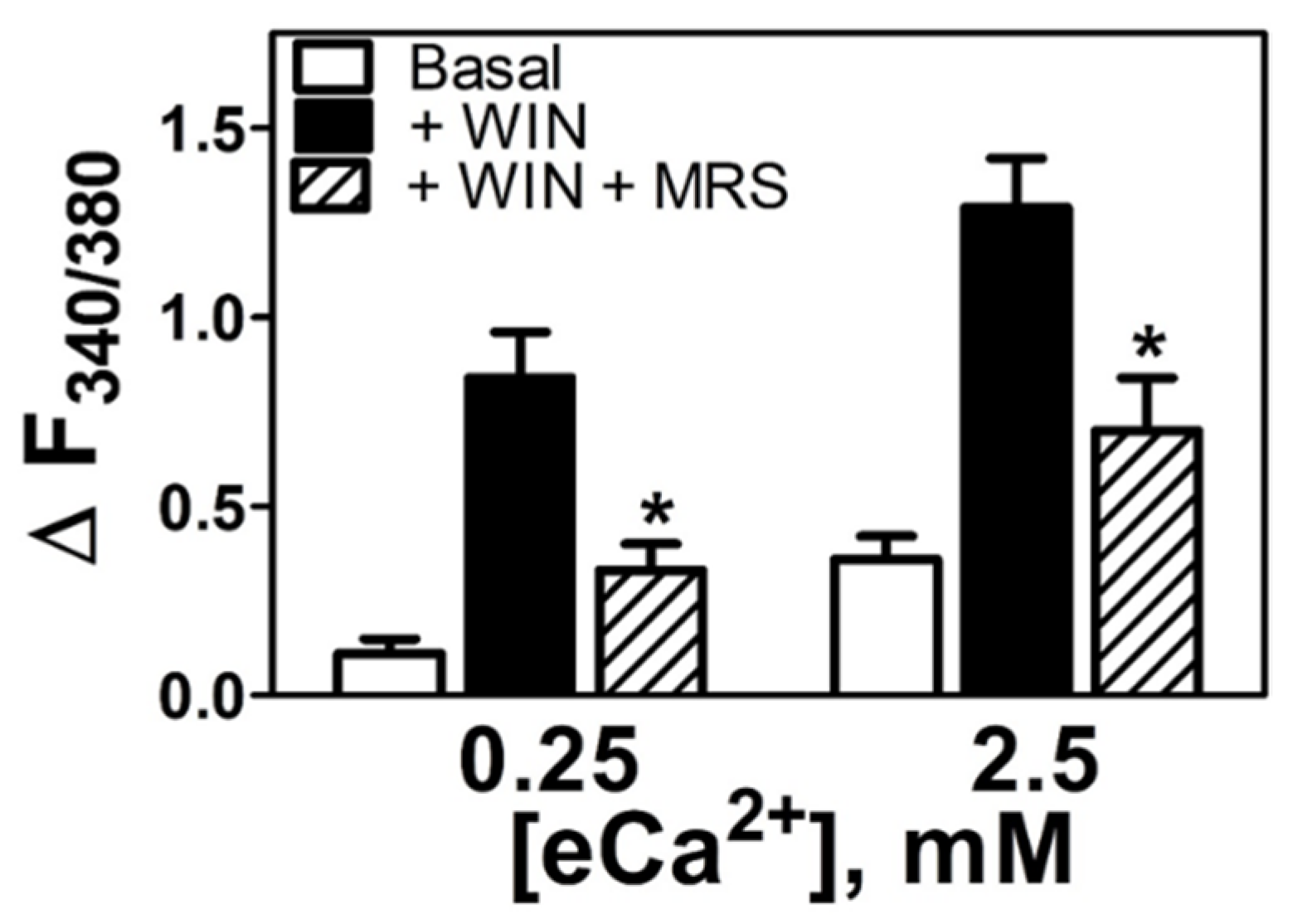
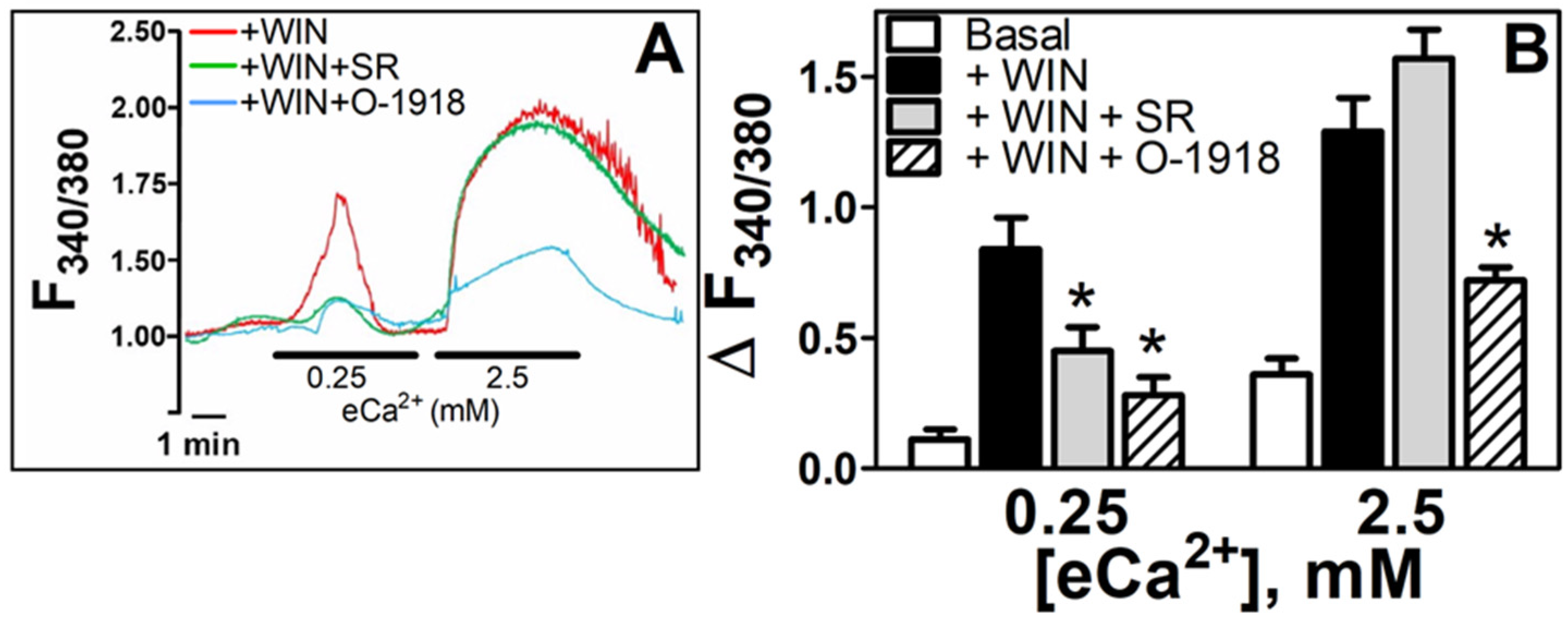
3.5. WIN55212-2-Dependent Increases in [Ca2+]i Are Mediated by either CB1R or a nonCB1/CB2 Receptor as a Function of the eCa2+ Stimulus
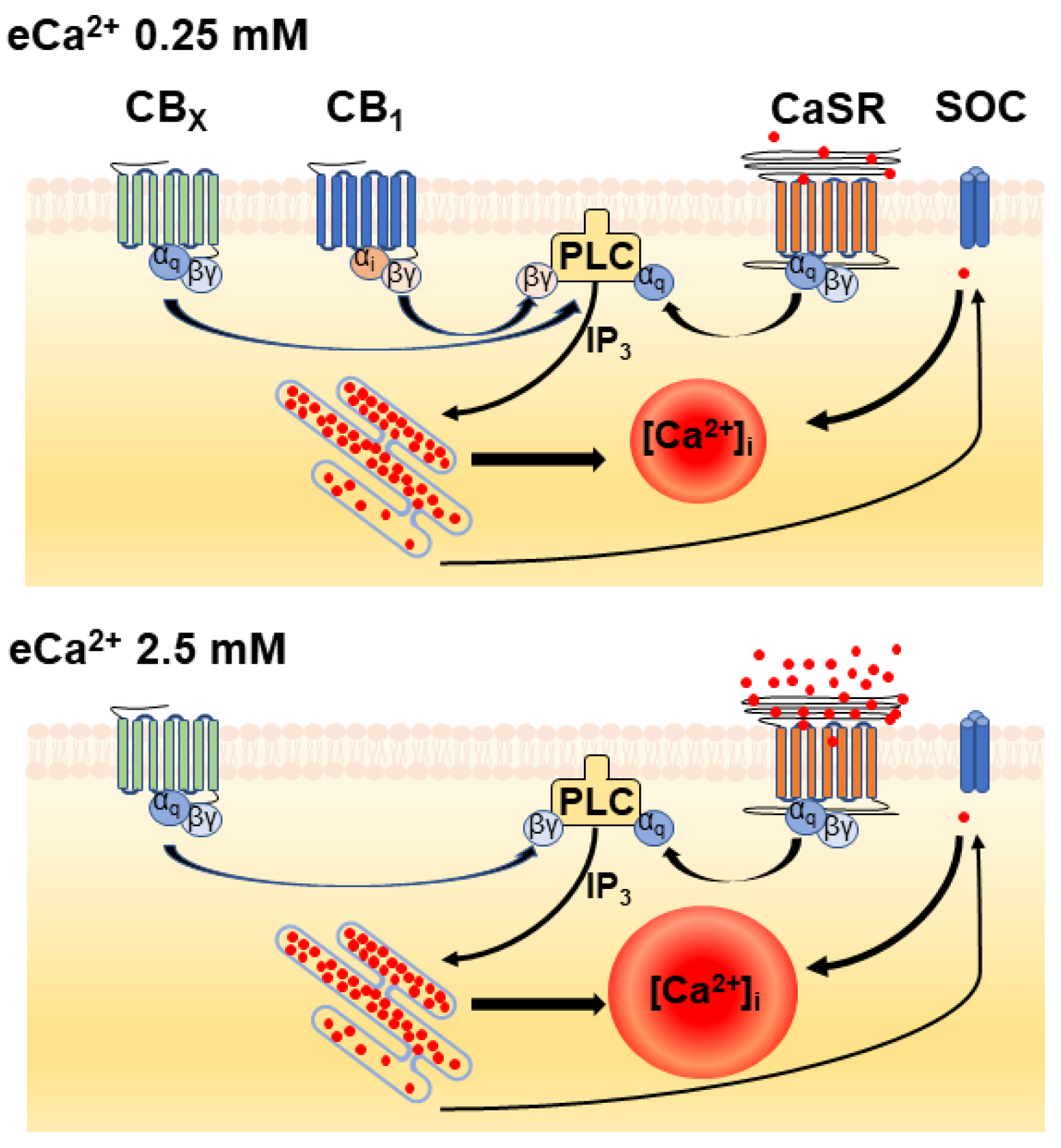
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Felder, C.C.; Veluz, J.S.; Williams, H.L.; Briley, E.M.; Matsuda, L.A. Cannabinoid agonists stimulate both receptor- and non-receptor-mediated signal transduction pathways in cells transfected with and expressing cannabinoid receptor clones. Mol. Pharmacol. 1992, 42, 838–845. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carney, S.T.; Lloyd, M.L.; MacKinnon, S.E.; Newton, D.C.; Jones, J.D.; Howlett, A.C.; Norford, D.C. Cannabinoid regulation of nitric oxide synthase I (nNOS) in neuronal cells. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2009, 4, 338–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felder, C.C.; Joyce, K.E.; Briley, E.M.; Mansouri, J.; Mackie, K.; Blond, O.; Lai, Y.; Ma, A.L.; Mitchell, R.L. Comparison of the pharmacology and signal transduction of the human cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Mol. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugiura, T.; Kondo, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Miyashita, T.; Nakane, S.; Kodaka, T.; Suhara, Y.; Takayama, H.; Waku, K. Evidence that 2-arachidonoylglycerol but not N-palmitoylethanolamine or anandamide is the physiological ligand for the cannabinoid CB2 receptor. Comparison of the agonistic activities of various cannabinoid receptor ligands in HL-60 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 605–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, T.; Kodaka, T.; Kondo, S.; Tonegawa, T.; Nakane, S.; Kishimoto, S.; Yamashita, A.; Waku, K. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol, a putative endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand, induces rapid, transient elevation of intracellular free Ca2+ in neuroblastoma × glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 229, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. The cannabinoid agonist WIN55,212-2 increases intracellular calcium via CB1 receptor coupling to Gq/11 G proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19144–19149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Jensen, J.B.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. GPR55 is a cannabinoid receptor that increases intracellular calcium and inhibits M current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berridge, M.J. The inositol trisphosphate/calcium signaling pathway in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2016, 96, 1261–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerbino, A.; Colella, M. The different facets of extracellular calcium sensors: Old and new concepts in calcium-sensing receptor signalling and pharmacology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neves, S.R.; Ram, P.T.; Iyengar, R. G protein pathways. Science 2002, 296, 1636–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorkhali, R.; Tian, L.; Dong, B.; Bagchi, P.; Deng, X.; Pawar, S.; Duong, D.; Fang, N.; Seyfried, N.; Yang, J. Extracellular calcium alters calcium-sensing receptor network integrating intracellular calcium-signaling and related key pathway. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 20576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sesay, J.S.; Gyapong, R.N.; Najafi, L.T.; Kabler, S.L.; Diz, D.I.; Howlett, A.C.; Awumey, E.M. Gαi/o-dependent Ca2+ mobilization and Gαq-dependent PKCα regulation of Ca2+-sensing receptor-mediated responses in N18TG2 neuroblastoma cells. Neurochem. Int. 2015, 90, 142–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awumey, E.M.; Howlett, A.C.; Putney, J.W.; Diz, D.I.; Bukoski, R.D. Ca2+ mobilization through dorsal root ganglion Ca2+-sensing receptor stably expressed in HEK293 cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1895–C1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddad, M. The impact of CB1 receptor on nuclear receptors in skeletal muscle cells. Pathophysiology 2021, 28, 457–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boczek, T.; Zylinska, L. Receptor-dependent and independent regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels and Ca2+-permeable channels by endocannabinoids in the brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, K.; Leone-Kabler, S.; Howlett, A.C. Mouse neuroblastoma CB1 cannabinoid receptor-stimulated [35S]GTPγS binding: Total and antibody-targeted Gα protein-specific scintillation proximity assays. Methods Enzymol. 2017, 593, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grynkiewicz, G.; Poenie, M.; Tsien, R.Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemeth, E.F.; Delmar, E.G.; Heaton, W.L.; Miller, M.A.; Lambert, L.D.; Conklin, R.L.; Gowen, M.; Gleason, J.G.; Bhatnagar, P.K.; Fox, J. Calcilytic compounds: Potent and selective Ca2+ receptor antagonists that stimulate secretion of parathyroid hormone. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2001, 299, 323–331. [Google Scholar]
- Harper, J.L.; Camerini-Otero, C.S.; Li, A.H.; Kim, S.A.; Jacobson, K.A.; Daly, J.W. Dihydropyridines as inhibitors of capacitative calcium entry in leukemic HL-60 cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoi, P.M.; Hiley, C.R. Vasorelaxant effects of oleamide in rat small mesenteric artery indicate action at a novel cannabinoid receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 147, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey, A.E.; Leach, K.; Valant, C.; Conigrave, A.D.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A. Positive and negative allosteric modulators promote biased signaling at the calcium-sensing receptor. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 1232–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, T.; Wang, Z.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Lu, X.; Xing, Y.; Lu, J.; Chang, S.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; et al. Structural basis for activation and allosteric modulation of full-length calcium-sensing receptor. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabg1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khajehali, E.; Malone, D.T.; Glass, M.; Sexton, P.M.; Christopoulos, A.; Leach, K. Biased agonism and biased allosteric modulation at the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Mol. Pharmacol. 2015, 88, 368–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.S. Store-Operated Calcium Channels: From function to structure and back again. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2020, 12, a035055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prakriya, M.; Lewis, R.S. Store-Operated Calcium Channels. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1383–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, G.S.; Putney, J.W., Jr. Pharmacology of store operated calcium entry channels. In Calcium Entry Channels in Non-Excitable Cells; Kozak, J.A., Putney, J.W., Eds.; CRC Press/Taylor & Francis Group, LLC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2018; pp. 311–324. [Google Scholar]
- Putney, J.W. Forms and functions of store-operated calcium entry mediators, STIM and Orai. Adv. Biol. Regul. 2018, 68, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, J.J.; Albarran, L.; Gómez, L.J.; Smani, T.; Salido, G.M.; Rosado, J.A. Molecular modulators of store-operated calcium entry. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1863, 2037–2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomben, V.C.; Sontheimer, H. Disruption of transient receptor potential canonical channel 1 causes incomplete cytokinesis and slows the growth of human malignant gliomas. Glia 2010, 58, 1145–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, K.; Ganjiwale, A.D.; Chandrashekaran, I.R.; Padgett, L.W.; Burgess, J.; Howlett, A.C.; Cowsik, S.M. CB1 cannabinoid receptor-phosphorylated fourth intracellular loop structure-function relationships. Pept. Sci. 2019, 111, e24104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Das, S.; Williams, E.A.; Moore, D.; Jones, J.D.; Zahm, D.S.; Ndengele, M.M.; Lechner, A.J.; Howlett, A.C. Lipopolysaccharide and cyclic AMP regulation of CB2 cannabinoid receptor levels in rat brain and mouse RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 181, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.D.; Carney, S.T.; Vrana, K.E.; Norford, D.C.; Howlett, A.C. Cannabinoid receptor-mediated translocation of NO-sensitive guanylyl cyclase and production of cyclic GMP in neuronal cells. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E. CB1 and CB2 Receptor Pharmacology. Adv. Pharmacol. 2017, 80, 169–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, P.; Reggio, P.H. An update on non-CB1, non-CB2 cannabinoid related G-Protein-coupled receptors. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2017, 2, 265–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Cao, Z.; Wang, W.; Zhou, N. New insights in cannabinoid receptor structure and signaling. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2019, 12, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertwee, R.G.; Howlett, A.C.; Abood, M.E.; Alexander, S.P.; Di Marzo, V.; Elphick, M.R.; Greasley, P.J.; Hansen, H.S.; Kunos, G.; Mackie, K.; et al. International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology. LXXIX. Cannabinoid receptors and their ligands: Beyond CB1 and CB2. Pharmacol. Rev. 2010, 62, 588–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, P.; Lago-Fernandez, A.; Hurst, D.P.; Sotudeh, N.; Brailoiu, E.; Reggio, P.H.; Abood, M.E.; Jagerovic, N. Therapeutic exploitation of GPR18: Beyond the cannabinoids? J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 14216–14227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howlett, A.C.; Qualy, J.M.; Khachatrian, L.L. Involvement of Gi in the inhibition of adenylate cyclase by cannabimimetic drugs. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 29, 307–313. [Google Scholar]
- Rhee, S.G. Regulation of phosphoinositide-specific phospholipase C. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2001, 70, 281–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebres, R.A.; Roach, T.I.; Fraser, I.D.; Philip, F.; Moon, C.; Lin, K.M.; Liu, J.; Santat, L.; Cheadle, L.; Ross, E.M.; et al. Synergistic Ca2+ responses by Gαi- and Gαq-coupled G-protein-coupled receptors require a single PLCβ isoform that is sensitive to both Gβγ and Gαq. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 942–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kankanamge, D.; Ubeysinghe, S.; Tennakoon, M.; Pantula, P.D.; Mitra, K.; Giri, L.; Karunarathne, A. Dissociation of the G protein βγ from the Gq-PLCβ complex partially attenuates PIP2 hydrolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 296, 100702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, S.; Howlett, A.C. Chemically distinct ligands promote differential CB1 cannabinoid receptor-Gi protein interactions. Mol. Pharmacol. 2005, 67, 2016–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharir, H.; Abood, M.E. Pharmacological characterization of GPR55, a putative cannabinoid receptor. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 126, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Console-Bram, L.; Ciuciu, S.M.; Zhao, P.; Zipkin, R.E.; Brailoiu, E.; Abood, M.E. N-arachidonoyl glycine, another endogenous agonist of GPR55. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 1389–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sylantyev, S.; Jensen, T.P.; Ross, R.A.; Rusakov, D.A. Cannabinoid- and lysophosphatidylinositol-sensitive receptor GPR55 boosts neurotransmitter release at central synapses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 5193–5198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Petrocellis, L.; Di Marzo, V. Non-CB1, non-CB2 receptors for endocannabinoids, plant cannabinoids, and synthetic cannabimimetics: Focus on G-protein-coupled receptors and transient receptor potential channels. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2010, 5, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Console-Bram, L.; Brailoiu, E.; Brailoiu, G.C.; Sharir, H.; Abood, M.E. Activation of GPR18 by cannabinoid compounds: A tale of biased agonism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 3908–3917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Langmead, C.J.; Riddy, D.M. New advances in targeting the resolution of inflammation: Implications for specialized pro-resolving mediator GPCR drug discovery. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2020, 3, 88–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, S.; Cherry, A.E.; Xu, C.; Stella, N. Alkylindole-sensitive receptors modulate microglial cell migration and proliferation. Glia 2015, 63, 1797–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, N. Cannabinoid and cannabinoid-like receptors in microglia, astrocytes, and astrocytomas. Glia 2010, 58, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, S.; Pacheco, M.A.; Childers, S.R. Binding of aminoalkylindoles to noncannabinoid binding sites in NG108-15 cells. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 1997, 17, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breivogel, C.S.; Griffin, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Martin, B.R. Evidence for a new G protein-coupled cannabinoid receptor in mouse brain. Mol. Pharmacol. 2001, 60, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pulgar, V.M.; Howlett, A.C.; Eldeeb, K. WIN55212-2 Modulates Intracellular Calcium via CB1 Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma Cells. Cells 2022, 11, 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192947
Pulgar VM, Howlett AC, Eldeeb K. WIN55212-2 Modulates Intracellular Calcium via CB1 Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma Cells. Cells. 2022; 11(19):2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192947
Chicago/Turabian StylePulgar, Victor M., Allyn C. Howlett, and Khalil Eldeeb. 2022. "WIN55212-2 Modulates Intracellular Calcium via CB1 Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma Cells" Cells 11, no. 19: 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192947
APA StylePulgar, V. M., Howlett, A. C., & Eldeeb, K. (2022). WIN55212-2 Modulates Intracellular Calcium via CB1 Receptor-Dependent and Independent Mechanisms in Neuroblastoma Cells. Cells, 11(19), 2947. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11192947






