Abstract
Hypoxia in cancer is a thoroughly studied phenomenon, and the logical cause of the reduction in oxygen tension is tumor growth itself. While sustained hypoxia leads to death by necrosis in cells, there is an exquisitely regulated mechanism that rescues hypoxic cells from their fatal fate. The accumulation in the cytoplasm of the transcription factor HIF-1α, which, under normoxic conditions, is marked for degradation by a group of oxygen-sensing proteins known as prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) in association with the von Hippel-Lindau anti-oncogene (VHL) is critical for the cell, as it regulates different mechanisms through the genes it induces. A group of microRNAs whose expression is regulated by HIF, collectively called hypoxaMIRs, have been recognized. In this review, we deal with the hypoxaMIRs that have been shown to be expressed in colorectal cancer. Subsequently, using data mining, we analyze a panel of hypoxaMIRs expressed in both normal and tumor tissues obtained from TCGA. Finally, we assess the impact of these hypoxaMIRs on cancer hallmarks through their target genes.
Keywords:
hypoxaMIR; angiogenesis; HIF-1α; microRNAs; metastasis; transcription factor; miRNA network; miRNA regulation 1. Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer, and represents the fourth leading cause of cancer mortality worldwide. In 2018, more than 1.8 million cases were diagnosed, and 880 thousand death cases were reported worldwide [1]. The most common risk factors associated with CRC development include genetic predisposition, diet, alcohol and tobacco consumption, age, and inflammatory bowel disease. Molecular mechanisms related to CRC progression are microsatellite and chromosomal instability, CpG island methylator phenotype, oncogene and tumor suppressor gene mutations [2]. Furthermore, variations in microRNA expression profiles [3] promote the formation of aberrant crypt foci and polyps [4], changes in the tissue microenvironment [5], the establishment of carcinoma [6], angiogenesis [7], and, finally, metastasis [8,9].
Although the multistep progression and the main mutated oncogenes are widely known, the molecular events that underly each step of CRC progression are not yet completely understood due to the high rates of genomic instability and intra-tumoral heterogeneity that characterize this type of cancer [10]. Therefore, several groups are actively searching for gene expression profiles in CRC from different perspectives; for instance, response to therapy [11], pathway analysis [12], and miRNA profiles [13]. Among these, we encounter hypoxia-regulated genes, given the importance of hypoxia in the induction of proliferation, cell invasion, and angiogenesis [14,15].
Hypoxia itself is an extensively studied phenomenon [16] whose response is coordinated by a family of transcription factors, collectively known as hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs) [17]. These factors are overexpressed in multiple types of tumors, and both local and distant metastases [18]; consequently, genes under transcriptional control are overexpressed [19]. HIFs are relevant in maintaining malignancy, particularly in CRC [20]. However, the prognostic value of HIF expression by itself does not seem to be as relevant as the gene network regulated by HIF activity. For instance, HIF overexpression and high VEGF protein detection are associated with the vascular invasion of colorectal carcinoma and tongue squamous cell carcinoma [21], serving as prognosis biomarkers [22], while others disregard its importance as a biomarker [23,24]. However, some HIF-α hypoxia-regulated genes, such as VEGF-A, Smad7, Jun, IL-8, CXCR-4, PDGF-A, TGF-A, or ANGPTL-4, are considered markers of CRC metastasis and poor prognosis [14]. Therefore, even though the relevant role of HIF-α activation in cancer development is not a bona fide molecular marker, genes that are under its transcriptional control, such as those formerly mentioned, may be valid as biomarkers or new therapeutic targets. Therefore, in this work, we focus on describing the role of HIF-1α in regulating through the transcription of microRNAs called hypoxaMIRs, each representing the hallmarks of CRC, providing a broader picture of how these types of non-coding RNAs are involved in the multistep progression of this type of cancer.
2. Hypoxia-Inducible Transcription Factors
HIFs are a family of heterodimeric transcription factors conformed by one of three possible isoforms of an O2-labile α subunit (HIF-1α, 2α, and 3α), and a second stable HIF-1β subunit. HIF-1α is ubiquitously expressed in all human cells; HIF-1α subunits dimerize with HIF-1β through their HLH (helix–loop–helix) and PAS (Per–Arnt–Sim) domains to play a role as a transcription factor. The HIF-1α subunit contains an N-TAD (N-terminal transactivation domain) that overlaps with the ODD domain (oxygen-dependent degradation) associated with protein stability, while C-TAD interacts with the transactivator protein CBP/P300. In normoxic environments, conserved proline residues of HIF-1α (Pro 402 and Pro 564 localized in ODD domain) are hydroxylated by prolyl-4-hydroxylases (PHDs) through molecular oxygen and 2-oxoglutarate as substrates for their activity [25]. Once HIF-1α is hydroxylated, it is recognized and marked for proteasome degradation by Von Hippel-Lindau (pVHL) tumor suppressor protein, an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Conversely, under hypoxic conditions, PHD activity is diminished, so they cannot hydroxylate HIF-1α and, as a consequence, HIF-1α is stabilized and translocated into the nucleus, where it heterodimerizes with the HIF-1β subunit. HIF-1α recognizes and binds to the consensus sequence G/ACGTG, better known as HRE (hypoxia response elements) [26], which is present in the promoter region of genes that promote the maintenance of cancer hallmarks, such as the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), angiogenesis, metastasis, and drug resistance (Figure 1).
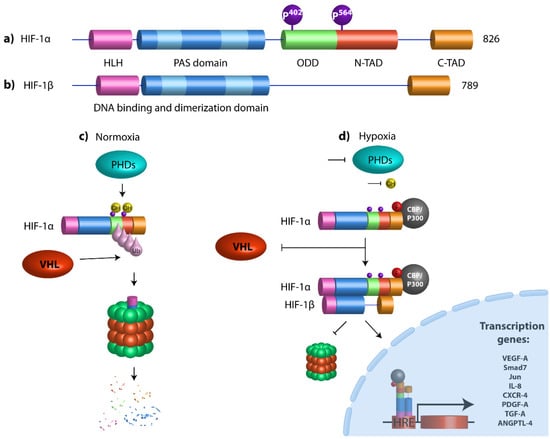
Figure 1.
Structural domains of HIF-1α and HIF-1β and schematic diagram of HIF pathway. (a) HIF-1α contains a basic helix–loop–helix (HLH) system and two dimerization domains (PAS-A and PAS-B) that mediate DNA binding and dimerization, respectively. An oxygen-dependent degradation domain (ODD) is required for oxygen-dependent hydroxylation and degradation under normoxia conditions. The transactivation domains (N-and C-Terminal TADs) are both responsible for the transcriptional activity. N-TAD domain is located within the ODD domain and C-TAD domain at the C-terminal region of the protein. Prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) hydroxylate HIF-1α proline residues 402 and 564. (b) HIF-1β is the aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT), which has a bHLH domain, PAS-A and PAS-B domains, and only one C-terminal transactivation domain. (c) Under normoxic conditions, HIF-1α undergoes hydroxylation by prolyl-4-hydroxylases (PHDs) at proline residues 402 and 564, which promotes the destabilization of the HIF-1α protein, which allows the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) protein to bind it, resulting in polyubiquitination, leading to proteasome-mediated degradation. (d) Under hypoxic conditions, PHDs are inactivated, promoting HIF-1α stabilization. HIF-1α dimerizes with its partner HIF-1β (ARNT), they are translocated to the nucleus, and, in combination with the transcriptional coactivator CBP/P300, they bind to genomic DNA at hypoxia response elements (HREs) to activate the transcription of target genes.
EMT is one of the central mechanisms for the induction of invasion and metastasis [27]. In the EMT process, polarized epithelial cells lose their polarity and acquire migrating and invasive properties. HIF-1α mediates EMT by down-regulating epithelial markers (E-cadherin), and increasing the expression of mesenchymal markers (such as N-cadherin and Vimentin) [28]. HIF-1α transcribes ZEB1 (zinc finger E-box binding homeobox 1), which can bind to the E-cadherin promoter, and inhibits its transcription in CRC cell lines, suggesting a relevant role of HIF-1α in CRC [29].
Moreover, regulating the expression of many genes involved in tumor maintenance, it has been described that HIF-1α is able to promote drug resistance through metabolic reprogramming by increasing the transactivation of PDK1, LDHA, and BNIP3-L to switch from oxidative to glycolytic metabolism, an event known as the Warburg effect [17]. It has been reported that this metabolic rewiring prevents mitochondrial production of reactive oxygen species, thereby reducing the DNA damage and attenuating the antitumor effect of TKIs (tyrosin–kinase inhbitors) in several types of cancer [30,31,32,33]. Furthermore, in CRC cells treated with 5-FU (5-fluoruracil), the damage of mitochondria promotes the loss of their main source of energy, and, consequently, cell death is induced. In this scenario, HIF-1α, through the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin and PI3K pathways, stimulates the transcription of glycolytic genes, such as GLUT1, HK2, PKM2, and LDHA, restoring the lost energy, and promoting drug resistance to 5-FU [34].
CRC cells develop drug resistance by different mechanisms; in patients bearing the G12V mutation in the KRAS gene, it has been shown that high levels of HIF-1α are associated with resistance to Cetuximab. When a HIF inhibitor is used (PX-478), the cells were drug-sensitized, abating proliferation [35]. In addition, CRC-derived cell lines treated with DNMTs inhibitors indirectly diminished HIF-1α activity, leading to loss of resistance to oxaliplatin treatment [36]. Therefore, due to the large number of mechanisms involved in cancer establishment regulated by HIF-1α, it is important to describe their relevance in colorectal cancer.
3. HIF-1α and Its Relevance in CRC Development
HIF-1α is highly overexpressed in CRC at mRNA and protein levels; it is detected in adenomas and adenocarcinomas, and is frequently correlated with VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) overexpression, tumor vascularization, lymphatic invasion, disease stage, and overall survival. Immunostaining assays by several groups have shown that HIF-1α is present in 70–77% of CRC tumor cells, perinecrotic tissue, and blood vessels [37,38]. Current studies have shown the multiple roles that HIF-1α plays in CRC development and maintenance. HIF-1α promotes JMJD2B oncoprotein transcription in colorectal cancer-derived tumor cells, triggering a significant increase in cell proliferation and invasion through the overexpression of SLC2A1, SLC2A3, ELF3, UCA1, MET, NOV by removing trimethylation of H3K9 on their promoters [39]. Conversely, the inhibition of HIF-1α with sh-RNAs and lncRNAs avoids vasculogenic mimicry (a process in which cancer cells mimic endothelial cells by forming blood vessels), reducing their metastatic capabilities, and restoring E-cadherin expression in Lovo and HCT116 cells [40,41]. HIF-1α also promotes survival and chemoresistance in CRC through the direct modulation of survivin [42] and EZH2 [43]. In addition, mTOR/PP2A promotes cell survival via PHD2 inhibition, resulting in HIF-1α stabilization [44].
Wnt/β-catenin, another commonly overactive pathway in CRC that stimulates proliferation and migration, could be indirectly regulated by HIF-1α. In this pathway, the APC protein induces β-catenin degradation via the proteasome. Interestingly, the APC promoter contains an HRE element; thus, hypoxia levels allow HIF-1α to bind to this site, causing direct transcriptional repression in APC mRNA [45]. Moreover, HIF-1α overexpression induces β-catenin nuclear location, leading to high rates of proliferation, tumor growth, and radioresistance [46]. The mechanism by which HIF-1α promotes transcriptional repression is currently unknown; nevertheless, it has been reported that HIF-1α overexpression promotes transcriptional repression of several DNA repair genes, such as MSH2, MSH6, and NBS1, by promoter occupancy [47].
These examples demonstrate the relevance of HIF-1α in the hallmarks of colorectal cancer. However, the scope of this regulation is amplified due to the capability of HIF-1α activation of microRNAs transcription as direct targets, a process which will be discussed in depth in the following sections.
4. HypoxaMIRs, miRNAs Regulated by HIF-1α
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are non-coding short RNAs that target the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of mRNAs, and cause their silencing by recruiting proteins that induce translational repression, mRNA deadenylation, and mRNA decay [48]. Approximately 1% of the transcriptome in eukaryotic organisms consists of miRNAs; thus, they play a key role as post-transcriptional regulators of gene expression [49]. miRNAs could regulate tumor suppressor genes, allowing the development of cancer; as such, they have been designated as oncomirs; their counterparts, miRNAs that regulate oncogenes negatively, are called miRNA tumor suppressors, or anti-oncomirs [50]. Several reviews concerning biogenesis, maturation, and their role in multistep carcinogenesis have been published.
Furthermore, HIF-1α plays a major role in the miRNAs’ biogenesis and maturation [51,52,53]. Previous reports have demonstrated that hypoxia activation decreases the levels of several proteins involved in microRNAs biogenesis, such as DGCR8, Exportin 5, DICER, TRBP, AGO1, and AGO2 [52], as well as modulating microRNA expression of mir-200 family [54] and mir-630 [55].
One of the main targets of HIF-1α is DICER, a key protein in microRNA processing. In colon tumors and HCT116 cells, HIF-1α recruits the ubiquitin ligase E3 parkin, forming a heterodimer that binds and ubiquitinates DICER, inducing its degradation by autophagosomes, thereby decreasing the expression of mir-200b [56]. In addition, in breast cancer cell lines under hypoxic conditions, DICER promoter can be hypermethylated by KDMA6A/B and EZH2, resulting in a mir-200b decrease, as well as EMT activation [57]. These findings are worth exploring to establish a putative role of HIF-1α participation.
Hypoxic conditions not only regulate DICER, but also play a crucial role in the maintenance of Argonaut proteins. HIF-1α promotes the expression of EIF2C4, which positively regulates Argonaut 4 (AGO4), inducing mir-18a, mir 107, mir-155, and mir-210 overexpression and angiogenesis induction [58]. Moreover, HIF-1α transcribes collagen type I prolyl-4-hydroxylase (cP4HI), which enhances the prolylhydroxylation and endonuclease activity of AGO2. Once AGO2 is hydroxylated, the processing of numerous microRNAs, such as mir-210, mir-21, mir-24, mir-221, mir-222, mir-25, mir-100, mir-15b, mir-23a, among others, is increased [59]. These data support the role of HIF-1α as a key regulator of miRNAs biogenesis in cancer (Figure 2).
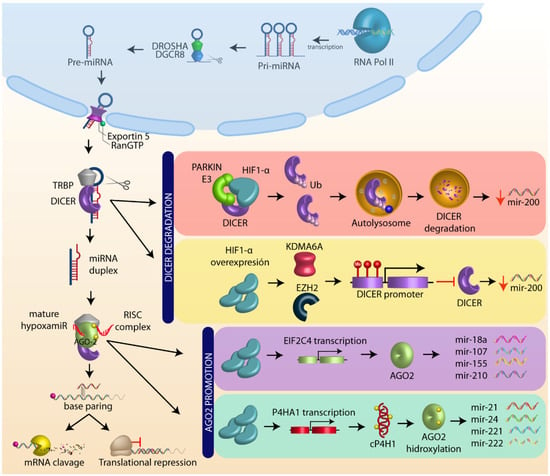
Figure 2.
MicroRNA biogenesis and HIF-1α role. MicroRNA (miRNA) are transcribed as primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) in the nucleus. The pri-miRNAs are cleaved by the endonuclease DROSHA/DGCR8 (DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8) to a shorter pre-miRNA hairpin structure (60–70 nucleotides). The pre-miRNAs are exported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by exportin-5-Ran-GTP (XPO5), and are processed by DICER1/TRBP, a ribonuclease III (RIII) enzyme that produces miRNA duplex (~21-nucleotide). The final step of miRNA maturation is the selective functional strand of small RNA duplex into RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), which includes DICER, TRPB, and Argonaut (AGO). One strand of the mature miRNA (the guide strand) is loaded with Argonaut (AGO2) to form a miRNA-induced silencing complex (miRISC) that targets mRNAs by a complementary sequence leading to mRNA degradation and translational repression. HIF-1α negatively regulates DICER through autolysosome degradation and promoter methylation, whereas HIF1-α positively regulates AGO by target transcription and promotes AGO hydroxilation (see text).
HIF-1α plays a dual role in the regulation of miRNAs. HIF-1α directly regulates their biogenesis, and promotes the transcriptional activity of miRNAs with HRE sequences in their promoters as a transcription factor. This group of miRNAs is called “hypoxaMIRs” [60]. The best-characterized hypoxaMIR is mir-210, and it is considered to be the master of hypoxaMIRs [61]. Mir-210 has an HRE element 400 bp upstream from its core promoter. The HRE is highly conserved across species, suggesting that HIF-1α regulation has an important phylogenetic role. The evidence so far proves that mir-210 overexpression via HIF-1α favors cancer development [62]. In breast cancer, mir-210 expression is considered a biomarker of cancer progression, with a direct correlation to metastatic capability [63,64]. Another study showed that mir-210 is expressed in different cancer tissues (breast, lung, colon, pancreatic, head, and neck), and correlates with HIF-1α stabilization. Moreover, mir-210 can repress the expression of genes involved in the maintenance of normoxia, promoting hypoxic conditions in the tumor microenvironment [65]. Furthermore, mir-210 overexpression enhances proliferation and inhibits apoptosis in ovarian cancer [66], promoting vascular endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis in the brain [67]. Furthermore, it shifts the cancer cell metabolism, enhancing cell survival by driving tumor growth initiation [68]. These facts confer a pivotal relevance to mir-210, which acts as an oncomir, and highlights the importance of HIF-1α in cancer progression.
In the same way that mir-210 has been described as the main hypoxaMIR in several types of cancer, there are other microRNAs reported as hypoxaMIRs. RNA sequencing technologies have revealed a considerable amount of information concerning miRNA profiles from a broad variety of cellular contexts, describing miRNAs regulated by HIF-1α [69]. Their understanding could contribute to developing new therapeutic strategies in cancer prognosis and treatment. Thus, we compiled a set of hypoxaMIRs regulated by the hypoxic response under some pathological conditions. These miRNAs were selected from 10 previous studies focused on hypoxaMIR identification, employing microarrays, RNA deep sequencing, and ChIP-seq. [58,61,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77]. Subsequently, we created a list with all miRNAs obtained from these studies, and we investigated their role in the hallmarks of CRC (Table 1).

Table 1.
microRNAs regulated by HIF-1α in hypoxic response. This table represents those microRNAs that were regulated under hypoxic conditions (upregulated or downregulated). We selected those microRNAs that appeared in previously mentioned studies. The asterisk represents the miRNA presence in each of the articles reviewed; thus, a miRNA with six asterisks mean that this molecule was present in six of the articles reviewed, and so on. On the other hand, a miRNA without asterisk means that was present in just one report.
5. HypoxaMIRs Involved in CRC Hallmarks
5.1. Cell Cycle, Proliferation, and Apoptosis
The control of cell proliferation has been linked to hypoxaMIR function in CRC samples. mir-21, mir-26a, mir-181a, and mir-103 promote tumor growth and enhance proliferation by downregulating PTEN expression; these microRNAs are also associated with clinicopathological features of CRC patients, being significantly overexpressed in patients with advanced clinical TNM stage. Interestingly, mir-103 regulates DICER and modifies the expression of microRNA profiles, increasing the proliferation rate in HCT116 cells. Therefore, restoring DICER and PTEN expression inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase [78,79,80,81]. In addition, mir-103 also regulates proliferation by targeting LATS2 [82]. Meanwhile, mir-21 regulates tumor growth to alter protein traffic between the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus via Sec23A [83]. Functional experiments demonstrated that locked nucleic acid treatment and overexpression of the long non-coding RNA LINC00312 directed against mir-21 reduce cell viability and decrease the invasive behavior in the LS174T cell line and in an in vivo nude mice model, respectively [84,85]. Another hypoxaMIR which is well-described in CRC development is mir-155, the expression of which increases the proliferation rate [86], thereby activating the PI3K-AKT pathway in HCT116 cells through PPP2CA (protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit alpha) and PTPRJ (protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor J) degradation, both negative regulators of this pathway [87,88]. In cancer cells, E2F2 binds to Rb1 protein in order to promote cell cycle progression, functioning as an oncogene. However, in colorectal cancer, it was reported for the first time that the E2F2 oncoprotein has a tumor suppressor role, but is negatively regulated by mir-155, having a direct impact on the proliferation of these cells [89,90]. Even though many earlier studies have described mir-181, mir-21, and mir-155 as direct targets of HIF-1α, we found reports that prove that these miRNAs also can be transcribed by NF-κB in CRC, which, in turn, can be positively regulated by HIF-1α during hypoxia and ischemia events, suggesting a key feedback loop that enhances cell proliferation and tumor growth [91,92,93].
Another hallmark of critical importance in the progression of cancer is the evasion of cell death. Apoptosis is necessary to maintain tissue homeostasis. In colon cancer cells, apoptosis participates in intestinal exchange, and its depletion promotes tumor transformation and progression [94]. Prior studies have indicated that multiple hypoxaMIRs reduce apoptosis via several mechanisms. mir-21 and mir-10b-5 repress RhoB [95] and PTEN expression [79,96] in HCT116, SW480, and HT29 cells, resulting in a significant decrease in apoptosis rates by annexin V detection, highlighting that mir-21 and mir-10b-5p increase cell proliferation through apoptosis inhibition. Similarly, mir-181b suppresses apoptosis through PDCD4 degradation [97] and the reduction in the NF-κB signaling pathway [98], leading to the modulation of a battery of key genes for the promotion of this cell death (Bax, caspase-3, and IκBα). Moreover, mir-27a-3p, which is highly expressed in both colon tissue and cell lines, abrogates apoptosis by targeting multiple genes involved in ERK/ MEK [99], Wnt/β-catenin [100], and apoptosome formation pathways (BTG1, RXRα and Apaf-1, respectively) [101]. In addition, other studies have shown that miR-155 exerts its oncogenic function by regulating the tumor suppressor gene FOXO3a, which transcribes caspase 3 and 7 [102]. Similarly, evidence supports that miR-107 contributes to the pathogenesis of human CRC by directly targeting Par4 [103], which increases Fas/FasL to the plasma membrane, and interacts with FADD activating caspase 8 and extrinsic apoptosis [104]. Therefore, reducing the expression of hypoxaMIRs involved in apoptosis is of potential interest in the search for chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agents. Although extensive research is ongoing, the specific mechanism by which hypoxaMIR-mediated apoptosis is impaired remains unclear. All of the above provides a promising avenue for research.
5.2. Angiogenesis, Migration, and Invasion
HIF-1α mediates the transcription of VEGF to promote angiogenesis. The overexpression and activity of both are associated with tumor vascularization in CRC [37,105]. Nevertheless, at the time of writing, there is still not enough information regarding the regulation of angiogenesis via HIF-1α/hypoxaMIRs. The only related hypoxaMIR is mir-181, which has a critical role in the tube formation of endothelial cells, triggering VEGF secretion in HT29 and SW480 cancer cell lines [106]. Cancer progression depends on the metastatic and migratory potential of cancer cells, which relies on their expressing invasion and migration genes, and mir-21 appears to regulate this process [79,84,107]. Interestingly, different mir-21 isoforms have been found in CRC; there are 10 and 30 isoforms for mir-21-3p (passenger strand) and mir-21-5p, respectively. Due to this, mir-21 is also considered as an “isomir”, with each isoform showing different migration and invasion regulation abilities as a consequence of their different targets [108]. On the other hand, mir-155 enhances the invasion behavior of CRC cells increasing β-catenin mRNA and protein expression [109]. Moreover, mir-155 shows an interesting activity due to its sequence: it can increase RNA translation by binding AU-rich elements (AREs) in the 3′ UTR of its targets, effectively upregulating the expression of its targets. In this way, mir-155 regulates HuR (human antigen R) and RhoA expression positively to promote proliferation, migration, and invasion in CRC [110,111]. Another feature that allows cancer cells to migrate is filopodia formation. In CRC cells, the overexpression of mir-23a promotes the transition from indolent to invasive cancer through FBXW7 regulation. This gene induces the proteasomal degradation of c-MYC and c-Jun transcription factors. The downregulation of mir-23a via lentivirus transduction represses tumor formation and lung metastasis in a mouse model, and abolishes the presence of filopodia in CCSC cells [112]. Other studies have shown that mir-10b is upregulated in CRC patients with advanced clinicopathological features, and it was also found to be markedly elevated in lymph node and serum. Furthermore, the overall survival of CRC patients with high mir-10b levels is significantly shorter than that of patients with low mir-10b expression [113,114]. This hypoxaMIR acquires its function of increasing RhoC by targeting HoxD10; overexpression of RhoC enhances migration through the degradation and reconstruction of the extracellular matrix [115,116]. Hypoxia can lead to metastasis through specific mRNA translation control; PDCD4 functions as an eIF4A-dependent protein translation suppressor, and is recognized as a tumor suppressor protein. However, its function is inhibited by mir-181 overexpression. Interestingly, mir-181 is also transcribed by STAT3, suggesting that proinflammatory stimuli play a crucial role in metastasis signaling in correlation with HIF-1α activity.
5.3. Metabolism and Inflammation
To maintain a high proliferation rate and growth, cancer cells have developed strategies to supply energetic requirements by changing their metabolism. In the presence of oxygen, normal cells process glucose in pyruvate via glycolysis. Thereafter, pyruvate is processed in the mitochondria via the tricarboxylic acid cycle, generating enough energy to maintain homeostasis. Nevertheless, cancer cells oxidize pyruvate in lactate, producing energy 100 times faster than normal cells. This phenomenon is known as the Warburg effect [117]. Under hypoxia conditions, RAS oncoprotein increases HIF-1α and HIF-2α transcription factors; in this manner, HIF-1α transcribes glucose transporters and multiple enzymes of the glycolysis pathway, enhancing the Warburg effect. Another mechanism that involves lactate production is mediated by mir-26a. This hypoxaMIR regulates pyruvate dehydrogenase protein X complex (PDHX), avoiding pyruvate entrance in the tricarboxylic acid cycle; therefore, whole pyruvate production is metabolized in lactate [118]. Changes in metabolism are also associated with chemoresistance. In CRC hypoxic microenvironments, HIF-1α overexpresses mir-21 and mir-30d, altering amino acid metabolism. As a consequence, CRC cells treated with 5-FU obtained chemoresistance; as such, the inhibition of these hypoxaMIRs brings them back to drug sensitivity [119]. Moreover, metabolism is a pivotal regulator of gene expression due to the metabolites produced by these metabolic pathways being used as cofactors, regulating epigenetic processes, such as DNA and histone methylation. Folate is the key methyl group donor, and it is related to mir-21 overexpression in serum, serving as a CRC biomarker [120]. Moreover, aberrant metabolism can influence changes in the inflammatory process. For example, high levels of glucose uptake trigger pro-inflammatory activation of macrophages through the production of reactive oxygen species.
Chronic inflammation is one of the principal etiopathological features that promote CRC development; ulcerative colitis is considered a premalignant condition. Inflammatory stimuli produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) that damage DNA, leading to DNA mutations. In addition, chronic inflammation allows cytokine, chemokine, and growth factor production, which cause oxidative damage and epigenetic silencing of tumor suppressor genes [9]. Moreover, miRNAs have been implicated in the innate immune response and adaptive immunity, since they control T- and B-cell maturation [121]. The AOM/DSS CRC inflammation model represents the best model symptoms associated with this disease. mir-26b was found to be overexpressed in the serum of AOM/DSS-treated mice, as compared to controls. The results showed that, when mir-26b was coimmunoprecipitated with AGO2, there was significant enrichment of DIP1, MDM2, BRCA1, PTEN, and CREBBP mRNAs. Such mRNAs are involved in apoptosis induction, avoiding proliferation, and stopping pro-inflammation processes, suggesting that mir-26b may coordinate cross-talk of different pathways [122]. Associated with the inflammatory process, it has been reported that overexpression of mir-21, IL6, and IL-8 in peripheral blood-derived plasma is negatively associated with relapse-free periods and overall survival in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer [123]. Another critical event in CRC development is the evasion of the immune response. This process depends on antigen processing and the presentation by of histocompatibility complex 1 (MHC1); downward activation of MHC1 is also detected in 74% of cases of CRC. For MHC1 to exert its function, it must be exposed to the cell surface, but in order for this molecular event to happen, it is necessary for it to be assembled with calnexin and calreticulin protein chaperones. However, it has been reported that mir-27a directly regulates these mRNAs, thereby preventing MHC1 exposure [124].
MicroRNAs are also expressed in many immune cells; the imbalance in the expression of microRNA profiles changes their behavior and function. One example is mir-24; its overexpression in natural killer cells downregulates Paxilin levels, altering their killing effect to CRC cells [125], despite documented evidence that macrophages M2 can promote cell migration and invasion in CRC through microRNA delivery via exosomes [126]. These facts show us how hypoxaMIRs modulate the immune response in CRC. Figure 3 summarizes the role of hypoxaMIRs in colorectal cancer.
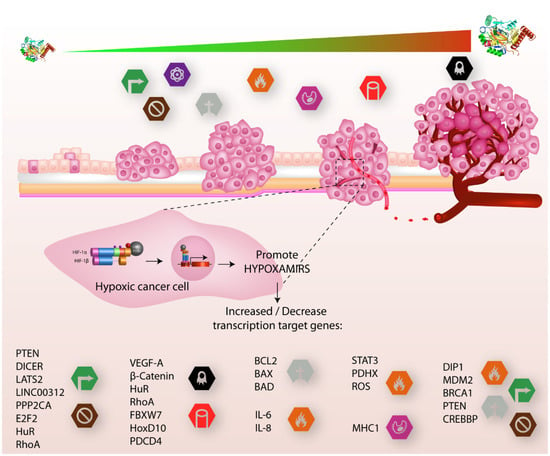
Figure 3.
HIF-α involved in cancer progression. In the early stages of tumor growth, cells acquire distinctive hallmarks that promote cancer progression, such as sustaining proliferative signals, evasion growth suppression, reprogramming energy metabolism, and resistance to cell death, while in the final stages of tumor growth, hallmarks which are added include inflammation, avoiding immune destruction, and, finally, metastasis and angiogenesis. These features are regulated by different genes (lower part) that are activated or inhibited by different hypoxaMIRs, which are regulated positively and negatively by the transcription factor HIF1-α, which, in turn, increases the concentration of proteins as tumor progression increases.
With all of the evidence described above, we can demonstrate the potential value of hypoxaMIRs as master regulators of each hallmark in CRC, as well as evidence of the major tumor suppressor genes that are affected by hypoxia. Furthermore, by means of data mining of CRC patients and analysis of interaction networks, which are described in detail in the following subtopic, we corroborated that HIF-1α has a high clinical value in colon tumor progression.
6. HypoxaMIR Expression in TCGA Database and Its Correlation with the Hallmarks of Cancer
With the attempt to understand the biological impact of hypoxaMIRs on the molecular mechanism involved in CRC, we analyzed the expression levels of hypoxaMIRs in the TCGA database (Table 1). miRNA-seq reads data were obtained using the Bioconductor TCGA biolinks package [127], and differential expression analysis between normal and tumoral tissues was assessed using the DESeq2 package [128], considering only miRNAs with an FDR < 0.05 as statistically significant (Figure 4). These data show that hypoxaMIRs are highly expressed in colorectal cancer tissue (red), compared with normal samples (light blue).
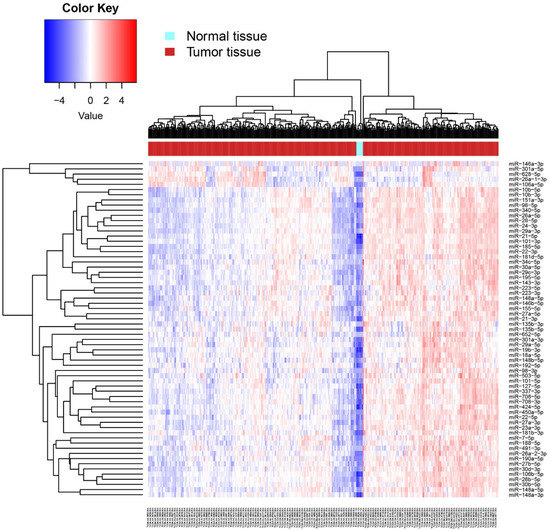
Figure 4.
Heat map of differential expression of hypoxaMIRs in human normal and tumor tissues. Differential expression of hypoxaMIRs was identified in normal tissue and tumor tissue by a miRNA body map along with the hierarchical cluster analysis. Expression of hypoxaMIRs is represented as blue (downregulated), red (upregulated), and white colors (no significant change or absence of data).
We randomly selected six hypoxaMIRs (mir-19b, mir-21, mir-24, mir-26b, mir-101, and mir-106b), and their targets were predicted using the multiMiR package [129]. Next, we took targets that were present in the Catalogue of Somatic Mutations (COSMIC) database [130]. We found that all of these miRNAs mainly have target genes involved in the suppression of growth, escaping of programmed cell death, and invasion and metastasis (Figure 5), thereby supporting the relevance of hypoxaMIRs expression in colorectal cancer progression and development.
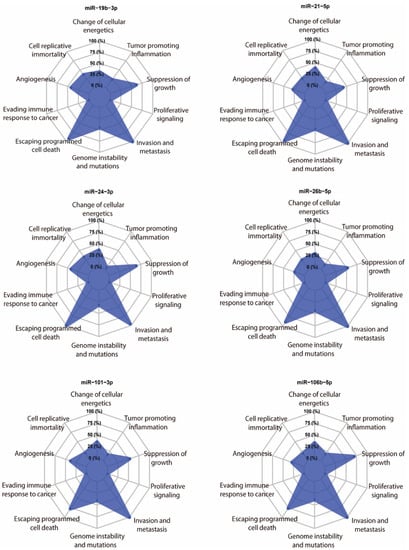
Figure 5.
In silico analysis. Radar chart of the relevant hallmarks of cancer simultaneously modulated by the selected hypoxaMIRs after analysis. The levels show the proportion of the number of putative gene targets for each class.
7. HypoxaMIRs and Its Relevance as Biomarkers in CRC Clinical Outcomes
The necessity of novel markers or therapeutic targets in cancer has brought hypoxaMIRs forward as excellent candidates. Since 2012, before being considered, several HIF-regulated miRNAs have been used as biomarkers; for example, let-7i was found to be differentially expressed in several CRC monolayer cell lines [131]. Moreover, mir-155 was measured by stem-loop qPCR in 109 pair-matched human CRC samples and the corresponding normal mucosa, showing the same findings as let-7i [132]. One of the main molecular events in CRC development is K-RAS overexpression. As such, Ota and collaborators developed a K-RAS variable expression model in 3D culture, and their results indicated that mir-181a and mir-210 were significantly overexpressed in a DLD-1 3D culture versus a DLD-1 monolayer culture, as well as in human CRC tissues [133]. These results suggested that hypoxaMIR expression variates even in the same CRC cell lines and, most likely, in a human sample. Over time, various hypoxaMIRs have been selected as reliable markers; they have been measured in different histological cancer stages, and have also been associated with clinical outcomes. Such a finding allowed for new miRNA signatures (mir-193a, mir-23a, mir-338-5p, and mir-10b) to be involved in cancer progression [134,135]. Furthermore, the prognostic value of hypoxaMIRs in chemotherapy response has been successfully tested. For example, in a cohort of 78 CRC patients, low mir-429 expression was associated with a positive response to 5-FU treatment; in contrast, high mir-429 expression was correlated with poor prognosis, metastatic phenotype, and non-5-FU response [136]. Moreover, many studies have matched hypoxaMIR availability in different fluids with clinicopathological features. For example, they have been isolated from circulating plasma, and associated with treatment response [137] and poor prognosis [138], as well as having been isolated from serum in association with CRC development [139]. All of these lines of evidence support the value of hypoxaMIRs as a prognostic marker during colorectal cancer progression in each of the cancer hallmarks (Figure 6).
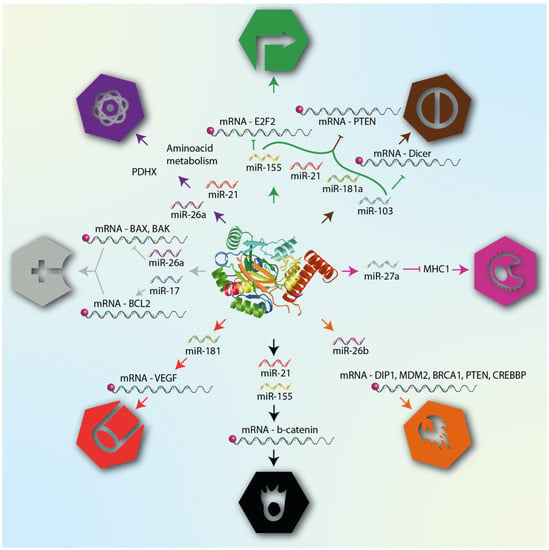
Figure 6.
HypoxaMIRs associated with their corresponding cancer hallmark. The figure lists some hypoxaMIRs (previously described in this review) that regulate genes involved in the different hallmarks of cancer, as defined by Hanahan and Weinberg. These hallmarks are cellular mechanisms acquired during tumor transformation, and include proliferation, apoptosis, angiogenesis, invasion, and metastasis.
8. Concluding Remarks
Here, we have analyzed a group of microRNAs, known as hypoxaMIRs, that are directly transcribed by the transcription factor HIF-1α. Together, these hypoxaMIRs which are overexpressed in CRC participate in different hallmarks of cancer. Furthermore, by analyzing their expression and participation in the establishment of the tumor phenotype, we show that a select group of them (miR-19b-3p, -21-5p, -24-3p, -26b-5p, -101-3p, and -106b-5p) mainly regulate invasion and metastasis, key events in advanced clinical stage tumors.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.C.-H. and C.P.-P.; Software, I.D.-W. and R.R.-P.; Investigation, J.C.-H., N.J.-H., C.L.-C. and C.P.-P.; Writing—Review and Editing, J.C.-H., N.J.-H., D.C.d.L. and C.P.-P.; Supervision, C.P.-P.; Project Administration, C.P.-P.; Funding Acquisition, C.P.-P. and C.L.-C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnologia (CONACYT), Mexico, Grant Programa Presupuestal F003, proyecto CF 2019/51207. J. Coronel-Hernández received the catedratic support COMECYT EDOMÉX CAT2021-0024.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Grady, W.M. Colorectal cancer molecular biology moves into clinical practice. Gut 2011, 60, 116–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Belaguli, N.; Berger, D.H. MicroRNA and Colorectal Cancer. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 638–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, N.; Kim, H.; Talcott, S.; Mertens-Talcott, S. Pomegranate polyphenolics suppressed azoxymethane-induced colorectal aberrant crypt foci and inflammation: Possible role of miR-126/VCAM-1 and miR-126/PI3K/AKT/mTOR. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2814–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.; Tian, Y.; Niu, G.; Cao, C. Role of microRNAs in remodeling the tumor microenvironment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2020, 56, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Lan, Z.; Xiong, X.; Ao, H.; Feng, Y.; Gu, H.; Yu, M.; Cui, Q. The Dual Role of MicroRNAs in Colorectal Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zong, S.; Zeng, H.; Ruan, X.; Yao, L.; Han, S.; Hou, F. MicroRNAs and angiogenesis: A new era for the management of colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, S.; Kaur, K.; Huang, R.; Zhang, Q.; Kaur, P.; Yazdani, H.O.; Bilal, M.U.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, X.-S. MicroRNAs in colorectal cancer: Role in metastasis and clinical perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 17011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terzić, J.; Grivennikov, S.; Karin, E.; Karin, M. Inflammation and Colon Cancer. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 2101–2114.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markowitz, S.D.; Bertagnolli, M.M. Molecular Basis of Colorectal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 361, 2449–2460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez-Garcia, P.; Rivera, F.; Molina-Pinelo, S.; Benavent, M.; Gómez, J.; Limón, M.L.; Pastor, M.D.; Martínez-Pérez, J.; Paz-Ares, L.; Carnero, A.; et al. Gene expression profile predictive of response to chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6151–6159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Bao, Y.; Ma, M.; Yang, W. Identification of Key Candidate Genes and Pathways in Colorectal Cancer by Integrated Bioinformatical Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, B.; Xiao, Z. Colorectal cancer characterization and therapeutic target prediction based on microRNA expression profile. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Li, W.; Li, H.; Han, S.; Liu, S.; Shi, Q.; Hou, F. Identification of hypoxia-regulated angiogenic genes in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De La Cruz, O.N.H.; López-González, J.S.; García-Vázquez, R.; Salinas-Vera, Y.M.; Muñiz-Lino, M.A.; Aguilar-Cazares, D.; López-Camarillo, C.; Carlos-Reyes, A. Regulation Networks Driving Vasculogenic Mimicry in Solid Tumors. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierson, D.J. Pathophysiology and clinical effects of chronic hypoxia. Respir. Care 2000, 45, 39–53. [Google Scholar]
- Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors in Physiology and Medicine. Cell 2012, 148, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, H.; De Marzo, A.M.; Laughner, E.; Lim, M.; Hilton, D.A.; Zagzag, D.; Buechler, P.; Isaacs, W.B.; Semenza, G.L.; Simons, J.W. Overexpression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in Common Human Cancers and Their Metastases. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 5830–5835. [Google Scholar]
- Lal, A.; Peters, H.; Croix, B.S.; Haroon, Z.A.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Strausberg, R.L.; Kaanders, J.H.A.M.; van der Kogel, A.J.; Riggins, G.J. Transcriptional Response to Hypoxia in Human Tumors. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001, 93, 1337–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraju, G.P.; Bramhachari, P.V.; Raghu, G.; El-Rayes, B.F. Hypoxia inducible factor-1α: Its role in colorectal carcinogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2015, 366, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, F.-W.; Gao, Y.; Que, L.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.-L. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α overexpression indicates poor clinical outcomes in tongue squamous cell carcinoma. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fillies, T.; Werkmeister, R.; Van Diest, P.J.; Brandt, B.; Joos, U.; Buerger, H. HIF1-alpha overexpression indicates a good prognosis in early stage squamous cell carcinomas of the oral floor. BMC Cancer 2005, 5, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulkowska, M.; Wincewicz, A.; Sulkowski, S.; Koda, M.; Kanczuga-Koda, L. Relations of TGF-β1 with HIF-1α, GLUT-1 and longer survival of colorectal cancer patients. Pathology 2009, 41, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berk, V.; Deniz, K.; Bozkurt, O.; Ozaslan, E.; Karaca, H.; Inanc, M.; Duran, A.O.; Ozkan, M. Predictive Significance of VEGF and HIF-1? Expression in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer Receiving Chemotherapy Combinations with Bevacizumab. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 6149–6154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-W.; Bae, S.-H.; Jeong, J.-W.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, K.-W. Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1)α: Its protein stability and biological functions. Exp. Mol. Med. 2004, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wigerup, C.; Påhlman, S.; Bexell, D. Therapeutic targeting of hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in cancer. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 164, 152–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; Weinberg, R.A. The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 1420–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, H.; Ye, J.; Wei, X.; Liu, S.; Wang, R. HIF-1α/Ascl2/MiR-200b Regulatory Feedback Circuit Modulated the Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) in Colorectal Cancer Cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 360, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Shi, X.; Peng, Y.; Wu, M.; Zhang, P.; Xie, R.; Wu, Y.; Yan, Q.; Liu, S.; Wang, J. HIF-1α Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis through Direct Regulation of ZEB1 in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0129603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.H.-R.; Wong, C.C.-L. Hypoxia, Metabolic Reprogramming, and Drug Resistance in Liver Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Miao, X.-K.; Li, J.-Y.; Zhang, X.-W.; Xu, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Zhou, T.-X.; Hu, M.-N.; Yang, W.-L.; Mou, L.-Y. YC-1 potentiates the antitumor activity of gefitinib by inhibiting HIF-1α and promoting the endocytic trafficking and degradation of EGFR in gefitinib-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 874, 172961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.-M.; Liu, S.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Sun, G.-H.; Chang, S.-Y.; Huang, S.-M.; Cha, T.-L. HAF mediates the evasive resistance of anti-angiogenesis TKI through disrupting HIF-1α and HIF-2α balance in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 49713–49724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, S.; Wang, G.; Lu, Y.; Fan, Z. Functional cooperation between HIF-1α and c-Jun in mediating primary and acquired resistance to gefitinib in NSCLC cells with activating mutation of EGFR. Lung Cancer 2018, 121, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Liang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, M.; et al. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-catenin signalings activate HIF-1α-induced metabolic reprogramming to impart 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Lei, F.; Rong, W.; Zeng, Q. Positive feedback between oncogenic KRAS and HIF-1α confers drug resistance in colorectal cancer. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 8, 1229–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.-T.; Lin, Y.-T.; Tang, S.-P.; Luo, C.-K.; Tsai, C.-T.; Shun, C.-T.; Chen, C.-C. Metabolic targeting of HIF-1α potentiates the therapeutic efficacy of oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2020, 39, 414–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwai, T.; Kitadai, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Onogawa, S.; Matsutani, N.; Kaio, E.; Ito, M.; Chayama, K. Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is associated with tumor vascularization in human colorectal carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 105, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuomisto, A.; García-Solano, J.; Sirniö, P.; Väyrynen, J.; Pérez-Guillermo, M.; Mäkinen, M.J.; Conesa-Zamora, P. HIF-1α expression and high microvessel density are characteristic features in serrated colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch. 2016, 469, 395–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Chen, L.; Yang, J.; Ye, T.; Chen, Y.; Fang, J. HIF-1α-induced histone demethylase JMJD2B contributes to the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells via an epigenetic mechanism. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yuan, W.; Song, J.; Wang, S.; Gu, X. LncRNA CPS1-IT1 suppresses EMT and metastasis of colorectal cancer by inhibiting hypoxia-induced autophagy through inactivation of HIF-1α. Biochimie 2018, 144, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zong, S.; Shi, Q.; Li, H.; Xu, J.; Hou, F. Hypoxia-induced vasculogenic mimicry formation in human colorectal cancer cells: Involvement of HIF-1a, Claudin-4, and E-cadherin and Vimentin. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.-F.; Dong, W.-G.; Jiang, C.-Q.; Qian, Q.; Yu, Q.-F. Role of Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and Survivin in colorectal carcinoma progression. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2008, 23, 1057–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xing, J.; Wang, H.; Yu, E. The SLC34A2-ROS-HIF-1-induced up-regulation of EZH2 expression promotes proliferation and chemo-resistance to apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Biosci. Rep. 2019, 39, BSR20180268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Conza, G.; Cafarello, S.T.; Loroch, S.; Mennerich, D.; Deschoemaeker, S.; Di Matteo, M.; Ehling, M.; Gevaert, K.; Prenen, H.; Zahedi, R.; et al. The mTOR and PP2A Pathways Regulate PHD2 Phosphorylation to Fine-Tune HIF1α Levels and Colorectal Cancer Cell Survival under Hypoxia. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 1699–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newton, I.P.; Kenneth, N.S.; Appleton, P.L.; Näthke, I.; Rocha, S. Adenomatous Polyposis Coli and Hypoxia-inducible Factor-1α Have an Antagonistic Connection. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3630–3638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Li, M.; Zuo, X.; Basourakos, S.P.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, J.; Han, Y.; Lin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; et al. β-catenin nuclear translocation induced by HIF-1α overexpression leads to the radioresistance of prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1827–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- YYoo, Y.G.; Hayashi, M.; Christensen, J.; Huang, L.E. An Essential Role of the HIF-1α-c-Myc Axis in Malignant Progression. In Proceedings of the Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Malden, MA, USA, 2009; Volume 1177, pp. 198–204. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P.; Lee, R.; Feinbaum, R. MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism and Function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellis, M.; Wold, B.; Snyder, M.P.; Bernstein, B.E.; Kundaje, A.; Marinov, G.K.; Ward, L.D.; Birney, E.; Crawford, G.E.; Dekker, J.; et al. Defining Functional DNA Elements in the Human Genome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6131–6138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Getz, G.; Miska, E.A.; Alvarez-Saavedra, E.; Lamb, J.; Peck, D.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Ebert, B.L.; Mak, R.H.; Ferrando, A.A.; et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005, 435, 834–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Gao, H.; Xu, R.; Wang, H.; Mei, J.; Liu, C. The interplay between HIF-1α and noncoding RNAs in cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camps, C.; Saini, H.K.; Mole, D.R.; Choudhry, H.; Reczko, M.; Guerra-Assunção, J.A.; Tian, Y.-M.; Buffa, F.M.; Harris, A.L.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G.; et al. Integrated analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression and association with HIF binding reveals the complexity of microRNA expression regulation under hypoxia. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Xia, W.; Khotskaya, Y.B.; Huo, L.; Nakanishi, K.; Lim, S.-O.; Du, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chang, W.-C.; Chen, C.-H.; et al. EGFR modulates microRNA maturation in response to hypoxia through phosphorylation of AGO2. Nature 2013, 497, 383–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharpure, K.M.; Nagaraja, A.S.; Armaiz-pena, G.N.; Zand, B.; Dalton, H.J.; Filant, J.; Miller, J.B.; Lu, C.; Sadaoui, N.C.; Mangala, L.S.; et al. Hypoxia Mediated Downregulation of MiRNA Biogenesis Promotes Tumor Progression. Nat. Commun. 2015, 5, 5202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupaimoole, R.; Ivan, C.; Yang, D.; Gharpure, K.; Wu, S.Y.; Pecot, C.V.; Previs, R.A.; Nagaraja, A.; Armaiz-Pena, G.N.; McGuire, M.; et al. Hypoxia-upregulated microRNA-630 targets Dicer, leading to increased tumor progression. Oncogene 2016, 35, 4312–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.-H.; Li, J.-N.; Wang, M.-Y.; Huang, H.-Y.; Croce, C.M.; Sun, H.-L.; Lyu, Y.-J.; Kang, J.-W.; Chiu, C.-F.; Hung, M.-C.; et al. HIF-1α promotes autophagic proteolysis of Dicer and enhances tumor metastasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 625–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beucken, T.V.D.; Koch, E.; Chu, K.; Rupaimoole, R.; Prickaerts, P.; Adriaens, M.; Voncken, J.W.; Harris, A.; Buffa, F.; Haider, S.; et al. Hypoxia promotes stem cell phenotypes and poor prognosis through epigenetic regulation of DICER. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serocki, M.; Bartoszewska, S.; Janaszak-Jasiecka, A.; Ochocka, R.J.; Collawn, J.F.; Bartoszewski, R. miRNAs regulate the HIF switch during hypoxia: A novel therapeutic target. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 183–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, G.; Stewart, R.L.; Chen, J.; Gao, T.; Scott, T.L.; Samayoa, L.M.; O’Connor, K.; Lane, A.N.; Xu, R. Collagen prolyl 4-hydroxylase 1 is essential for HIF-1α stabilization and TNBC chemoresistance. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loscalzo, J. The cellular response to hypoxia: Tuning the system with microRNAs. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3815–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallamshetty, S.; Chan, S.Y.; Loscalzo, J. Hypoxia: A master regulator of microRNA biogenesis and activity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2013, 64, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, C.; Ba, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Bai, C.; Sun, Z.; Zhao, R.C. HIF-1α promotes the migration and invasion of cancer-associated fibroblasts by miR-210. Aging Dis. 2021, 12, 1794–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foekens, J.A.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Smid, M.; Look, M.P.; De Weerd, V.; Boersma, A.W.M.; Klijn, J.G.M.; Wiemer, E.A.C.; Martens, J.W. Four miRNAs associated with aggressiveness of lymph node-negative, estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 13021–13026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, C.; Buffa, F.M.; Colella, S.; Moore, J.; Sotiriou, C.; Sheldon, H.; Harris, A.; Gleadle, J.; Ragoussis, J. hsa-miR-210 Is Induced by Hypoxia and Is an Independent Prognostic Factor in Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2008, 14, 1340–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ding, L.; Bennewith, K.L.; Tong, R.T.; Welford, S.; Ang, K.K.; Story, M.; Le, Q.-T.; Giaccia, A.J. Hypoxia-Inducible mir-210 Regulates Normoxic Gene Expression Involved in Tumor Initiation. Mol. Cell 2009, 35, 856–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Huang, K.; You, Y.; Fu, X.; Hu, L.; Song, L.; Meng, Y. Hypoxia-induced miR-210 in epithelial ovarian cancer enhances cancer cell viability via promoting proliferation and inhibiting apoptosis. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 2111–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, L.; He, X.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Cai, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Yang, G.-Y. MicroRNA-210 overexpression induces angiogenesis and neurogenesis in the normal adult mouse brain. Gene Ther. 2014, 21, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favaro, E.; Ramachandran, A.; McCormick, R.; Gee, H.; Blancher, C.; Crosby, M.; Devlin, C.; Blick, C.; Buffa, F.; Li, J.-L.; et al. MicroRNA-210 Regulates Mitochondrial Free Radical Response to Hypoxia and Krebs Cycle in Cancer Cells by Targeting Iron Sulfur Cluster Protein ISCU. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchand, A.; Roulland, I.; Semence, F.; Schröder, K.; Domergue, V.; Audran, M. Detection of Hypoxia-Regulated MicroRNAs in Blood as Potential Biomarkers of HIF Stabilizer Molidustat. MicroRNA 2019, 8, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Han, B.-M.; Liu, X.-B.; Yang, J.-J.; Wang, F.; Cong, X.-F.; Chen, X. Identification of MicroRNAs Involved in Hypoxia- and Serum Deprivation-Induced Apoptosis in Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voellenkle, C.; van Rooij, J.; Guffanti, A.; Brini, E.; Fasanaro, P.; Isaia, E.; Croft, L.; David, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Moles, A.; et al. Deep-sequencing of endothelial cells exposed to hypoxia reveals the complexity of known and novel microRNAs. RNA 2012, 18, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el Azzouzi, H.; Leptidis, S.; Doevendans, P.A.; De Windt, L.J. HypoxamiRs: Regulators of cardiac hypoxia and energy metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gee, H.; Ivan, C.; Calin, G.; Ivan, M. HypoxamiRs and Cancer: From Biology to Targeted Therapy. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1220–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mkrtchian, S.; Lee, K.L.; Kåhlin, J.; Ebberyd, A.; Poellinger, L.; Fagerlund, M.J.; Eriksson, L.I. Hypoxia regulates microRNA expression in the human carotid body. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 352, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.; Deng, L.; Su, D.; Xiao, J.; Ge, D.; Geng, Y.; Jing, H. Identification of crucial microRNAs and genes in hypoxia-induced human lung adenocarcinoma cells. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 4605–4616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, S.; Gaetano, C.; Martelli, F. HypoxamiR Regulation and Function in Ischemic Cardiovascular Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 21, 1202–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertero, T.; Rezzonico, R.; Pottier, N.; Mari, B. Impact of MicroRNAs in the Cellular Response to Hypoxia, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; Volume 333, ISBN 1937-6448. [Google Scholar]
- Geng, L.; Sun, B.; Gao, B.; Wang, Z.; Quan, C.; Wei, F.; Fang, X.-D. MicroRNA-103 Promotes Colorectal Cancer by Targeting Tumor Suppressor DICER and PTEN. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8458–8472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Song, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, K.; Han, B.; Bai, Y.; Liming, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, L. MicroRNA-21 (Mir-21) Promotes Cell Growth and Invasion by Repressing Tumor Suppressor PTEN in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 43, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, P.H.; Bo, T.F.; Li, L.; Hui, Y.N.; Hong, Z. IL-1β/NF-kb signaling promotes colorectal cancer cell growth through miR-181a/PTEN axis. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 604, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coronel-Hernández, J.; López-Urrutia, E.; Contreras-Romero, C.; Delgado-Waldo, I.; Figueroa-González, G.; Campos-Parra, A.D.; Salgado-García, R.; Martínez-Gutierrez, A.; Rodríguez-Morales, M.; Jacobo-Herrera, N.; et al. Cell migration and proliferation are regulated by miR-26a in colorectal cancer via the PTEN–AKT axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.-B.; Xiao, K.; Xiao, G.-C.; Tong, S.-L.; Ding, Y.; Wang, Q.-S.; Li, S.-B.; Hao, Z.-N. MicroRNA-103 promotes tumor growth and metastasis in colorectal cancer by directly targeting LATS2. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Y.; He, T.; Chen, X.; Mao, J.; Li, C.; Lyu, J.; Meng, Q.H. MicroRNA-21 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal cancer, and tumor growth associated with down-regulation of sec23a expression. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Sharifi, M.; Avan, A.; Kazemi, M.; Nabinejad, A.; Ferns, G.A.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Salehi, R. Inhibition of microRNA-21 via locked nucleic acid-anti-miR suppressed metastatic features of colorectal cancer cells through modulation of programmed cell death 4. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317692261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhang, W. LINC00312 represses proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells by regulation of miR-21. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 5565–5572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.-L.; Wang, H.-F.; Sun, Z.-Q.; Tang, Y.; Han, X.-N.; Yu, X.-B.; Liu, K. Up-Regulated MiR-155-5p Promotes Cell Proliferation, Invasion and Metastasis in Colorectal Carcinoma. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 6988–6994. [Google Scholar]
- Bakirtzi, K.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Karagiannides, I.; Polytarchou, C.; Jaeger, S.; Iliopoulos, D.; Pothoulakis, C. Neurotensin Signaling Activates MicroRNAs-21 and -155 and Akt, Promotes Tumor Growth in Mice, and Is Increased in Human Colon Tumors. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1749–1761.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tu, R.; Li, K.; Ye, P.; Cui, X. Tumor Suppressor PTPRJ Is a Target of miR-155 in Colorectal Cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 3391–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yang, J.; Lv, X.; Liu, K.; Gao, C.; Xing, Y.; Xi, T. miR-155 regulates the proliferation and cell cycle of colorectal carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 1743–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ma, X.; Yao, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wang, L.; Ma, M.; Lei, Z.; et al. miR-155 regulates the proliferation and invasion of clear cell renal cell carcinoma cells by targeting E2F2. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20324–20337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, P.; Li, J.; Samanta, S.; Mercurio, A.M. ERβ regulation of NF-κB activation in prostate cancer is mediated by HIF-1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40247–40254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.-B.; Liu, G.-H.; Chen, Z.-Y.; Mao, C.-Z.; Zhou, D.-C.; Wu, H.-Y.; Park, K.-S.; Zhao, H.; Kim, S.-K.; Cai, D.-Q.; et al. Hypoxia/ischemia promotes CXCL10 expression in cardiac microvascular endothelial cells by NFkB activation. Cytokine 2016, 81, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.-J.; Isaacs, J.S.; Lee, S.; Trepel, J.; Neckers, L. IL-1β mediated up-regulation of HIF-lα via an NFkB/COX-2 pathway identifies HIF-1 as a critical link between inflammation and oncogenesis. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 2115–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramesh, P.; Medema, J.P. BCL-2 family deregulation in colorectal cancer: Potential for BH3 mimetics in therapy. Apoptosis 2020, 25, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Tang, Q.; Qiu, M.; Lang, N.; Li, M.; Zheng, Y.; Bi, F. miR-21 targets the tumor suppressor RhoB and regulates proliferation, invasion and apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 2998–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Yu, C.; Li, W.; He, Y.; Bao, Y. Matrine Inhibits Proliferation, Invasion, and Migration and Induces Apoptosis of Colorectal Cancer Cells Via miR-10b/PTEN Pathway. In Cancer Biotherapy and Radiopharmaceuticals; Mary Ann Liebert, Inc.: Larchmont, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Guo, Y.; Liang, H.; Cheng, R.; Yang, F.; Hong, Y.; Zhao, C.; Liu, M.; Yu, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. miR-181b functions as an oncomiR in colorectal cancer by targeting PDCD4. Protein Cell 2016, 7, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Han, S. Downregulation of miR-181b inhibits human colon cancer cell proliferation by targeting CYLD and inhibiting the NF-κB signaling pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2020, 46, 1755–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, C.; Huang, D.; Liu, J.; Liu, W.; Cao, Y. miR-27a-3p regulates proliferation and apoptosis of colon cancer cells by potentially targeting BTG1. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 2825–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tang, J.; Shi, H.; Li, H.; Zhen, T.; Duan, J.; Kang, L.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Y.; Han, A. miR-27a-3p targeting RXRα promotes colorectal cancer progression by activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82991–83008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, J.; Zhao, J.; Bai, J. Knockdown of miR-27a sensitizes colorectal cancer stem cells to TRAIL by promoting the formation of Apaf-1-caspase-9 complex. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 45213–45223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapral, M.; Wawszczyk, J.; Węglarz, L. Regulation of MicroRNA-155 and Its Related Genes Expression by Inositol Hexaphosphate in Colon Cancer Cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 4153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Liu, S.; Ai, F.; Zhang, D.; Xiao, Z.; Nie, X.; Fu, Y. miR-107 Promotes Proliferation and Inhibits Apoptosis of Colon Cancer Cells by Targeting Prostate Apoptosis Response-4 (Par4). Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2017, 25, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebbar, N.; Wang, C.; Rangnekar, V.M. Mechanisms of apoptosis by the tumor suppressor Par-4. J. Cell. Physiol. 2012, 227, 3715–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, H.-C.; Kim, S.H.; Oh, S.Y.; Lee, S.; Kwon, K.A.; Choi, H.-J.; Park, K.-J.; Kim, H.-J.; Roh, M.S. Clinicopathological Significance of P53, Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1alpha, and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Expression in Colorectal Cancer Article. Anticancer. Res 2010, 30, 4163–4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; You, C.; Lu, P.; Feng, H.; Kong, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, R.; et al. MicroRNA-181a promotes angiogenesis in colorectal cancer by targeting SRCIN1 to promote the SRC/VEGF signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedaeinia, R.; Sharifi, M.; Avan, A.; Kazemi, M.; Rafiee, L.; Ghayour-Mobarhan, M.; Salehi, R. Locked nucleic acid anti-miR-21 inhibits cell growth and invasive behaviors of a colorectal adenocarcinoma cell line: LNA-anti-miR as a novel approach. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 246–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, W.; Leng, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wu, Y.; Sun, L.; Tan, Y.; Ni, H.; Dong, X.; Shen, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Different miR-21-3p isoforms and their different features in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 141, 2103–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Jiang, F.; Han, X.; Li, M.; Chen, W.; Liu, Q. MiRNA-155 Promotes the Invasion of Colorectal Cancer SW-480 Cells through Regulating the Wnt/β -Catenin. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Haidari, A.; Syk, I.; Thorlacius, H. MiR-155-5p positively regulates CCL17-induced colon cancer cell migration by targeting RhoA. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 14887–14896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haidari, A.; Algaber, A.; Madhi, R.; Syk, I.; Thorlacius, H. MiR-155-5p controls colon cancer cell migration via post-transcriptional regulation of Human Antigen R (HuR). Cancer Lett. 2018, 421, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahid, S.; Sun, J.; Edwards, R.A.; Dizon, D.; Panarelli, N.C.; Milsom, J.W.; Sikandar, S.S.; Gümüş, Z.H.; Lipkin, S.M. miR-23a Promotes the Transition from Indolent to Invasive Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 540–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmaksoud-Dammak, R.; Chamtouri, N.; Triki, M.; Saadallah-Kallel, A.; Ayadi, W.; Charfi, S.; Khabir, A.; Ayadi, L.; Sallemi-Boudawara, T.; Mokdad-Gargouri, R. Overexpression of miR-10b in colorectal cancer patients: Correlation with TWIST-1 and E-cadherin expression. Tumor Biol. 2017, 39, 1010428317695916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, C.; Li, B.; Hao, T. Up-regulation of mir-10b predicate advanced clinicopathological features and liver metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2932–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zuo, X.; Peng, Z. miR-10b promotes invasion by targeting HOXD10 in colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 488–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-F.; Li, Z.; Zhao, X.-H.; Zuo, X.-M.; Zhang, Y.; Xiao, Y.-H.; Li, J.; Peng, Z.-H. MicroRNA-10b is upregulated and has an invasive role in colorectal cancer through enhanced Rhoc expression. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 1275–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Liu, Y.; Jin, X.; Lu, W.; Liu, J.; Xia, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Zhao, X.; Xu, N.; Liang, S. MicroRNA-26a regulates glucose metabolism by direct targeting PDHX in colorectal cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijhuis, A.; Thompson, H.; Adam, J.; Parker, A.; Gammon, L.; Lewis, A.; Bundy, J.G.; Soga, T.; Jalaly, A.; Propper, D.; et al. Remodelling of microRNAs in colorectal cancer by hypoxia alters metabolism profiles and 5-fluorouracil resistance. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 1552–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckett, E.L.; Martin, C.; Choi, J.H.; King, K.; Niblett, S.; Boyd, L.; Duesing, K.; Yates, Z.; Veysey, M.; Lucock, M. Folate status, folate-related genes and serum miR-21 expression: Implications for miR-21 as a biomarker. BBA Clin. 2015, 4, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raisch, J.; Darfeuille-Michaud, A.; Nguyen, H.T.T. Role of microRNAs in the immune system, inflammation and cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2985–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benderska, N.; Dittrich, A.-L.; Knaup, S.; Rau, T.T.; Neufert, C.; Wach, S.; Fahlbusch, F.B.; Rauh, M.; Wirtz, R.M.; Agaimy, A.; et al. miRNA-26b Overexpression in Ulcerative Colitis-associated Carcinogenesis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2015, 21, 2039–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varkaris, A.; Katsiampoura, A.; Davis, J.S.; Shah, N.; Lam, M.; Frias, R.L.; Ivan, C.; Shimizu, M.; Morris, J.; Menter, D.; et al. Circulating inflammation signature predicts overall survival and relapse-free survival in metastatic colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2019, 120, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colangelo, T.; Polcaro, G.; Ziccardi, P.; Pucci, B.; Muccillo, L.; Galgani, M.; Fucci, A.; Milone, M.R.; Budillon, A.; Santopaolo, M.; et al. Proteomic screening identifies calreticulin as a miR-27a direct target repressing MHC class I cell surface exposure in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.-L.; Zhang, L.-F.; Shi, Y.-B. miR-24 inhibited the killing effect of natural killer cells to colorectal cancer cells by downregulating Paxillin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, J.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Liu, L.; Hu, F.; Song, D.; Hou, Z.; Wu, W.; Luo, X.; Wang, J.; et al. M2 Macrophage-Derived Exosomes Promote Cell Migration and Invasion in Colon Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 79, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colaprico, A.; Silva, T.C.; Olsen, C.; Garofano, L.; Cava, C.; Garolini, D.; Sabedot, T.S.; Malta, T.M.; Pagnotta, S.M.; Castiglioni, I.; et al. TCGAbiolinks: An R/Bioconductor package for integrative analysis of TCGA data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Kechris, K.J.; Tabakoff, B.; Hoffman, P.; Radcliffe, R.A.; Bowler, R.; Mahaffey, S.; Rossi, S.; Calin, G.; Bemis, L.; et al. The multiMiR R package and database: Integration of microRNA–target interactions along with their disease and drug associations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, e133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Ma, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, J.; Liu, Z.; Peng, J.; Qin, H. Comprehensive gene and microRNA expression profiling reveals the crucial role of hsa-let-7i and its target genes in colorectal cancer metastasis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, P.; Li, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhou, B.; Zhan, L.; Zhou, Z.; Sun, X. The quantitative analysis by stem-loop real-time PCR revealed the microRNA-34a, microRNA-155 and microRNA-200c overexpression in human colorectal cancer. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 3113–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, T.; Doi, K.; Fujimoto, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Matsuzaki, H.; Kuroki, M.; Miyamoto, S.; Shirasawa, S.; Tsunoda, T. KRAS up-regulates the expression of miR-181a, miR-200c and miR-210 in a three-dimensional-specific manner in DLD-1 colorectal cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2012, 32, 2271–2276. [Google Scholar]
- Yong, F.L.; Law, C.W.; Wang, C.W. Potentiality of a triple microRNA classifier: miR-193a-3p, miR-23a and miR-338-5p for early detection of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Song, Q.; Zhong, W.; Chen, Y.; Liang, L. MicroRNA-10b and the clinical outcomes of various cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Chim. Acta 2017, 474, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.-J.; Cai, X.-J.; Li, S.-J. The Clinical Significance of MiR-429 as a Predictive Biomarker in Colorectal Cancer Patients Receiving 5-Fluorouracil Treatment. Med. Sci. Monit. 2016, 22, 3352–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivi, P.; Canale, M.; Passardi, A.; Marisi, G.; Valgiusti, M.; Frassineti, G.L.; Calistri, D.; Amadori, D.; Scarpi, E. Circulating Plasma Levels of miR-20b, miR-29b and miR-155 as Predictors of Bevacizumab Efficacy in Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, C.-H.; Zhou, T.; Han, X.-L.; Zhuang, H.-J.; Qian, H.-X. Downregulation of mir-23b in plasma is associated with poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 4838–4844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Z.-C.; Fan, Y.-S.; Chen, H.-B.; Zhao, D.-W. Investigation of microRNA-155 as a serum diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Tumor Biol. 2014, 36, 1619–1625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).