Circulating miRNA Fingerprint and Endothelial Function in Myocardial Infarction: Comparison at Acute Event and One-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
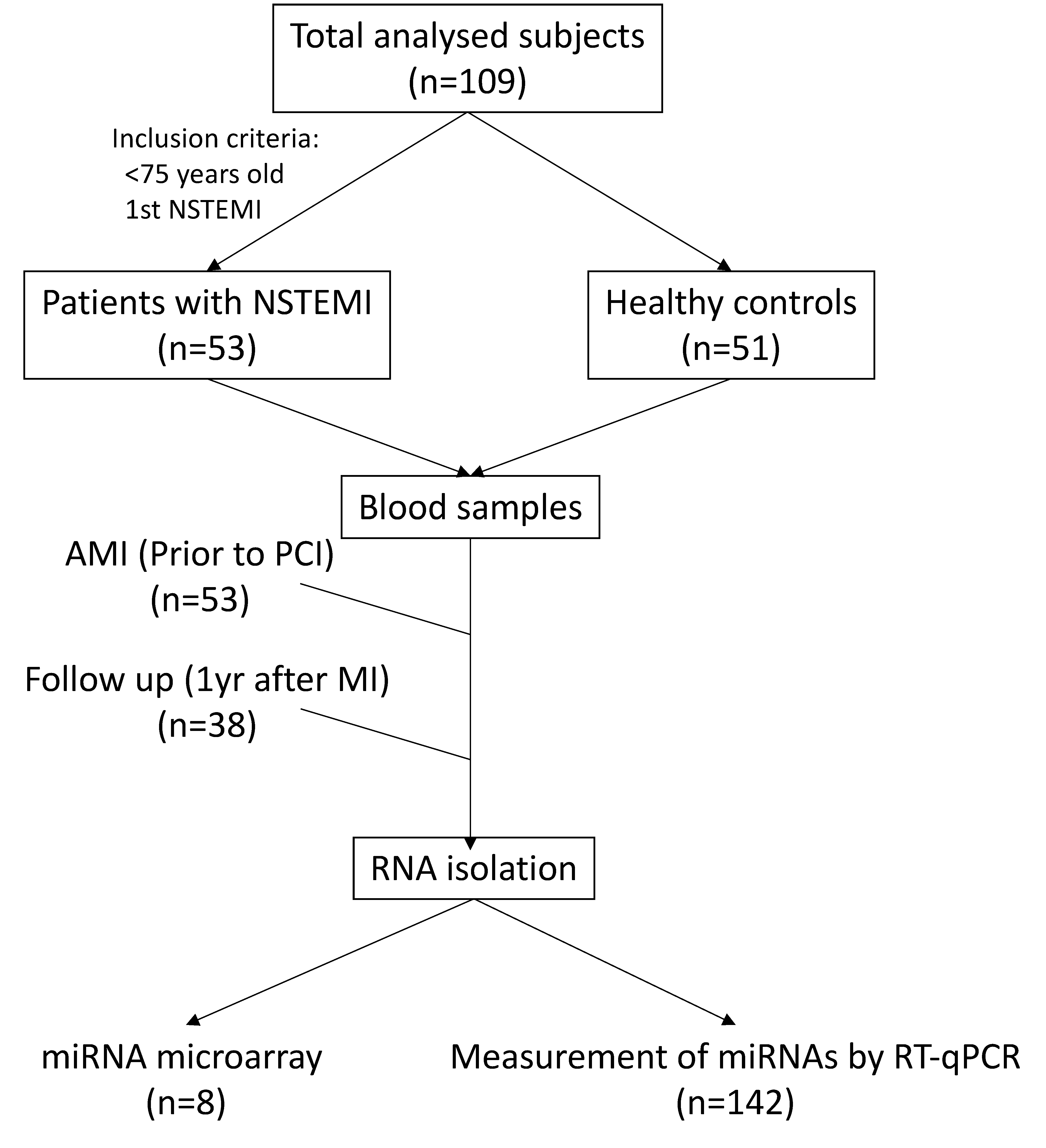
2.1. Study Population and Blood Sampling
2.2. miRNA Isolation and Expression Profile
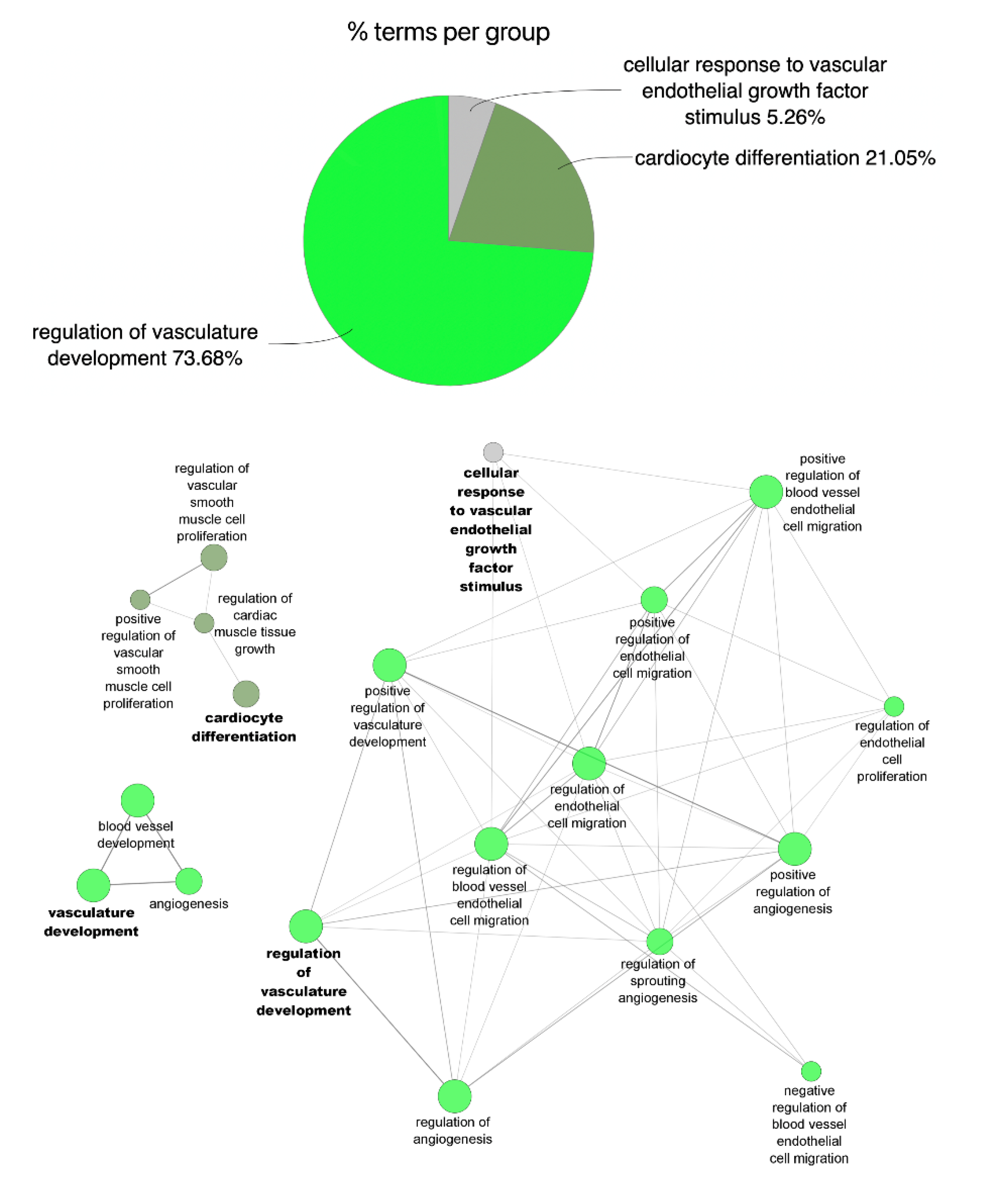
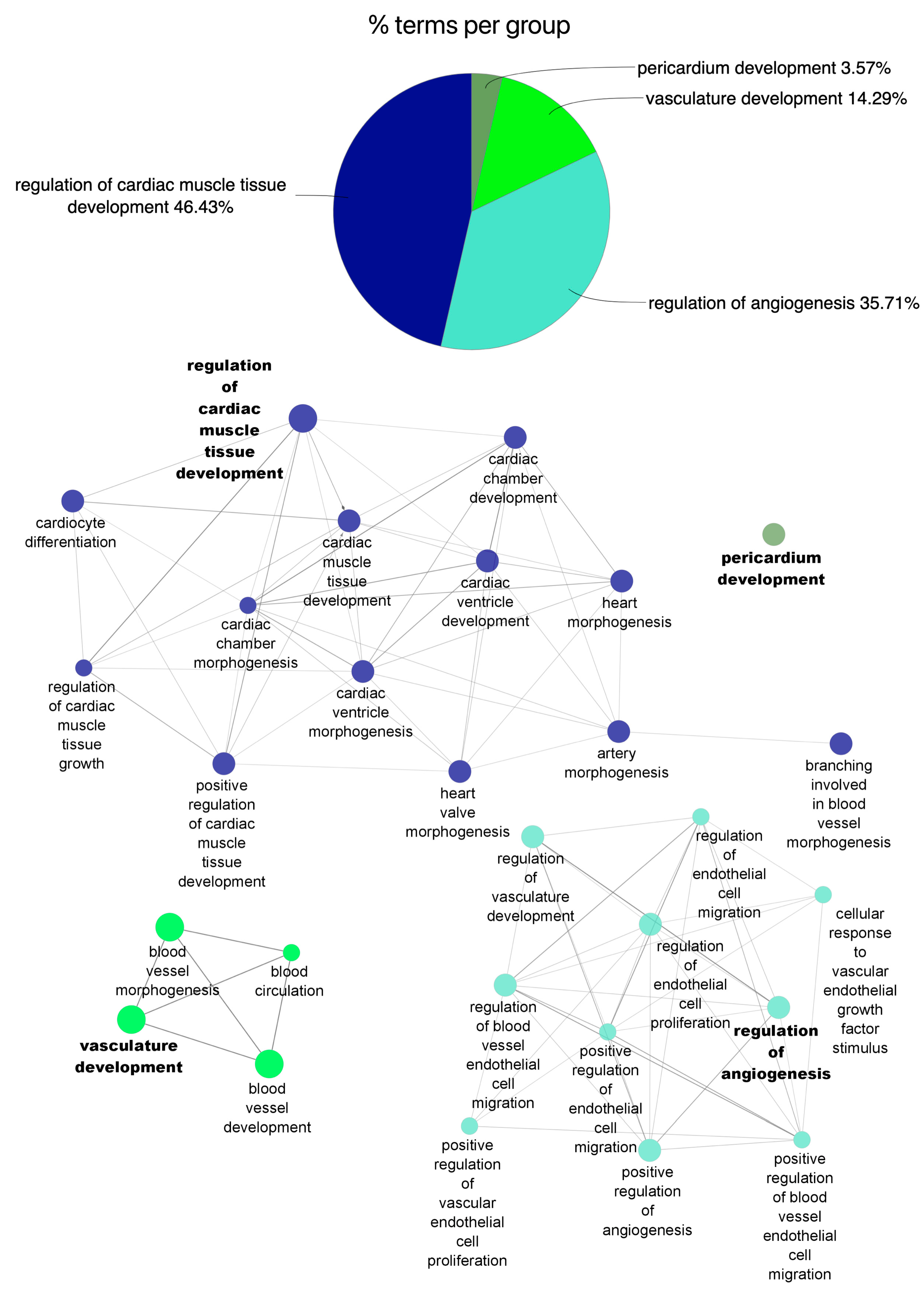
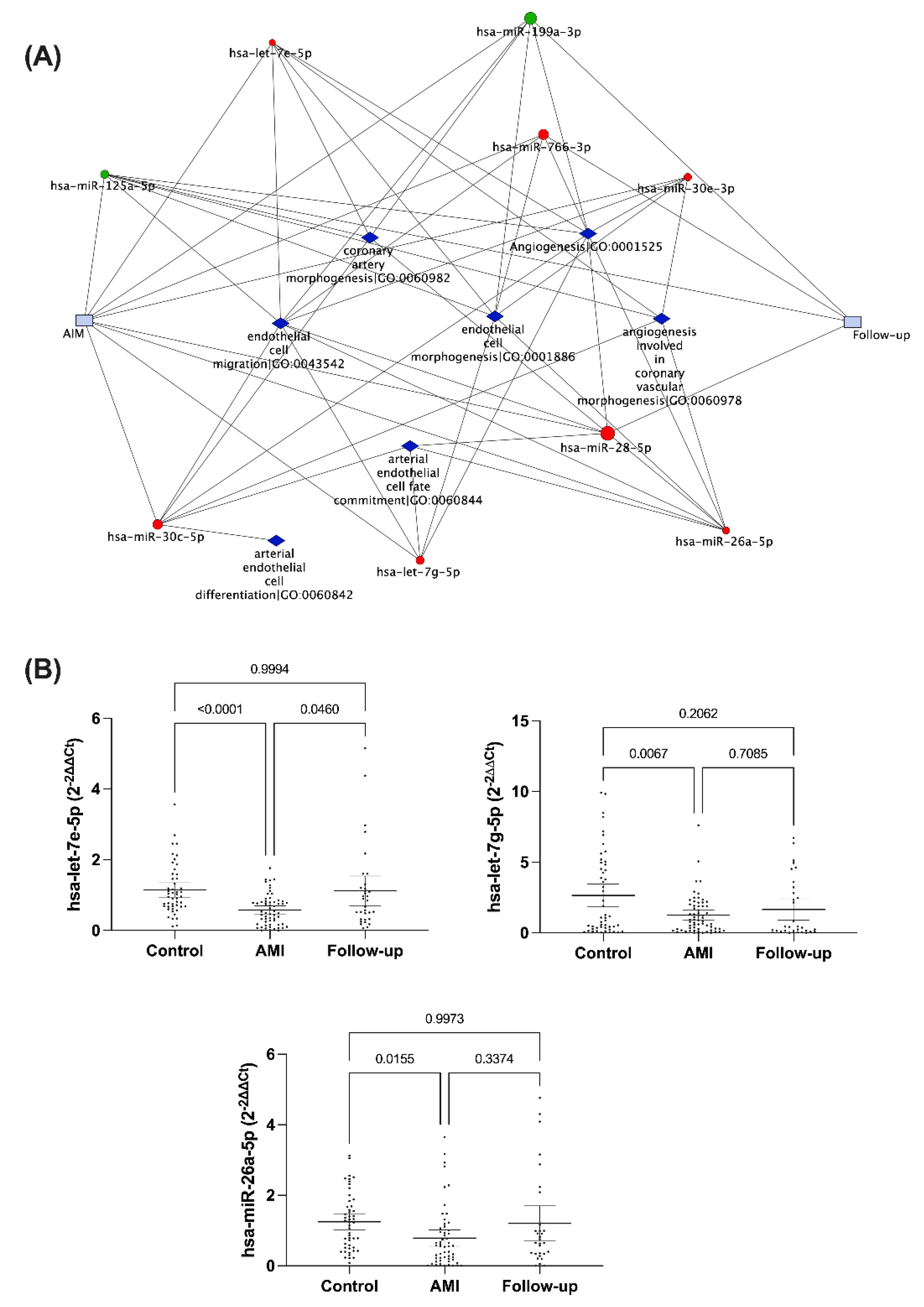
2.3. Functional Enrichment of miRNA Profile
2.4. miRNA Validation by Quantitative Real-Time PCR Assay (qRT-PCR)
2.5. Endothelial Cell Culture
2.6. miRNA Transfection
2.7. Endothelial Cell Adhesion and Proliferation Assays
2.8. Angiogenesis Assay In Vitro
2.9. Multiplex Cytokine Assay
2.10. Data Analysis and Statistics
3. Results
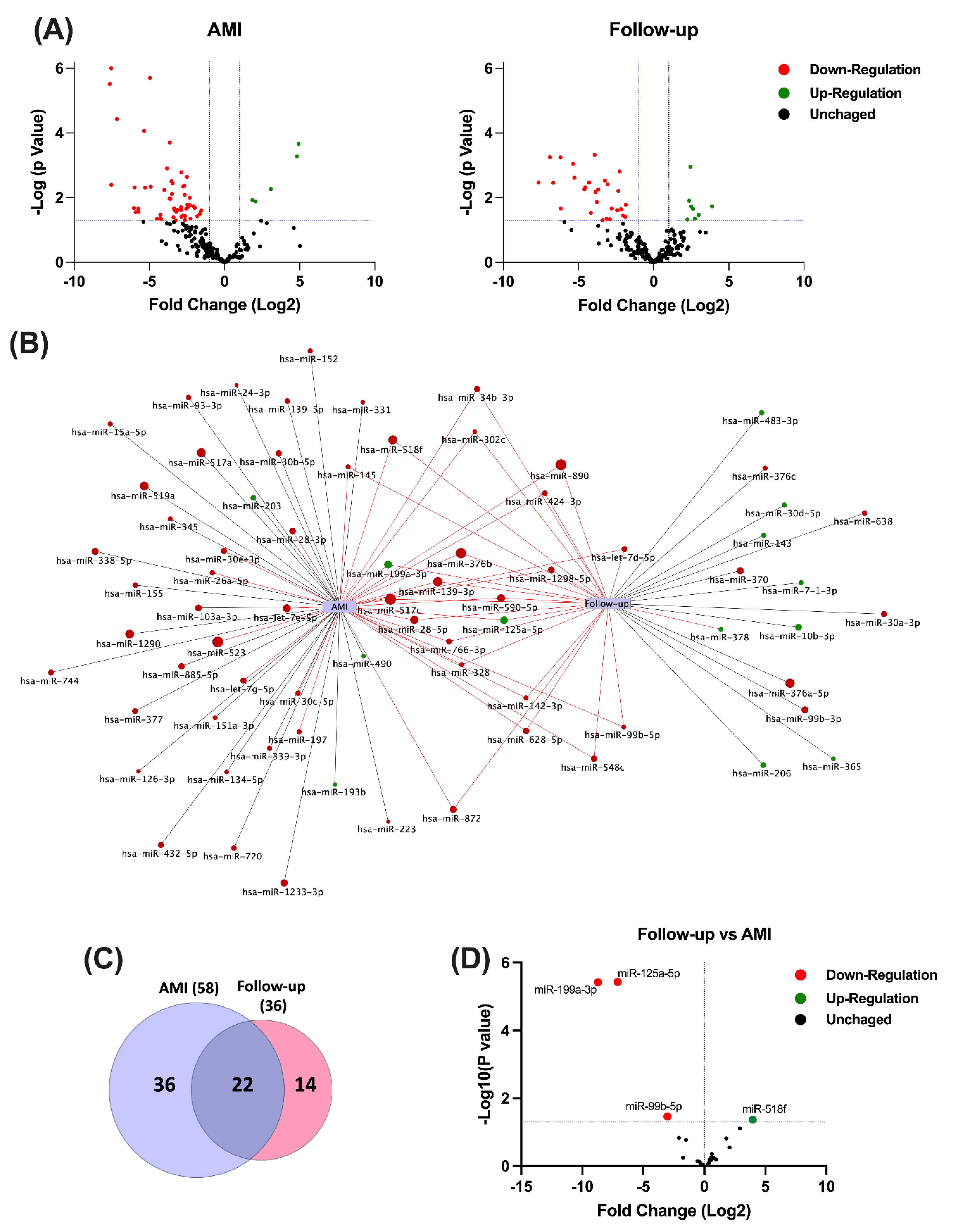
3.1. Circulating miRNA Expression Profile during AMI and at One-Year Follow-Up
3.2. Validation of Circulating miRNA Expression in the Study Population
3.3. Correlation of Circulating miRNA with Serum Levels of Cytokines and Chemokines
3.4. The Role of Let-7e-5p in Modulating Endothelial Cell Function
4. Discussion
Study Limitation
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thomas, M.R.; Lip, G.Y. Novel Risk Markers and Risk Assessments for Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Tabas, I.; Fredman, G.; Fisher, E.A. Inflammation and its resolution as determinants of acute coronary syndromes. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 1867–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alpert, J.S.; Thygesen, K.; Antman, E.; Bassand, J.P. Myocardial infarction redefined—A consensus document of The Joint European Society of Cardiology/American College of Cardiology Committee for the redefinition of myocardial infarction. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2000, 36, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrow, D.A.; Cannon, C.P.; Jesse, R.L.; Newby, L.K.; Ravkilde, J.; Storrow, A.B.; Wu, A.H.; Christenson, R.H. National Academy of Clinical Biochemistry Laboratory Medicine Practice Guidelines: Clinical characteristics and utilization of biochemical markers in acute coronary syndromes. Circulation 2007, 115, e356–e375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, C. Biomarkers and acute coronary syndromes: An update. Eur. Heart J. 2014, 35, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, M.S.; Mosterd, A.; van ‘t Hof, A.W.; Hoes, A.W. Novel biochemical markers in suspected acute coronary syndrome: Systematic review and critical appraisal. Heart 2010, 96, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanindi, A.; Cemri, M. Troponin elevation in conditions other than acute coronary syndromes. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2011, 7, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Viereck, J.; Thum, T. Circulating Noncoding RNAs as Biomarkers of Cardiovascular Disease and Injury. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondkar, A.A.; Abu-Amero, K.K. Utility of circulating microRNAs as clinical biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 821823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navickas, R.; Gal, D.; Laucevičius, A.; Taparauskaitė, A.; Zdanytė, M.; Holvoet, P. Identifying circulating microRNAs as biomarkers of cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 111, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viereck, J.; Bang, C.; Foinquinos, A.; Thum, T. Regulatory RNAs and paracrine networks in the heart. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 102, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.K.; Zhu, J.Q.; Zhang, J.T.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; He, J.; Qin, Y.W.; Jing, Q. Circulating microRNA: A novel potential biomarker for early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction in humans. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 659–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widera, C.; Gupta, S.K.; Lorenzen, J.M.; Bang, C.; Bauersachs, J.; Bethmann, K.; Kempf, T.; Wollert, K.C.; Thum, T. Diagnostic and prognostic impact of six circulating microRNAs in acute coronary syndrome. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2011, 51, 872–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandra, Y.; Devanna, P.; Limana, F.; Straino, S.; Di Carlo, A.; Brambilla, P.G.; Rubino, M.; Carena, M.C.; Spazzafumo, L.; De Simone, M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs are new and sensitive biomarkers of myocardial infarction. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 2765–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devaux, Y.; Vausort, M.; Goretti, E.; Nazarov, P.V.; Azuaje, F.; Gilson, G.; Corsten, M.F.; Schroen, B.; Lair, M.L.; Heymans, S.; et al. Use of circulating microRNAs to diagnose acute myocardial infarction. Clin. Chem. 2012, 58, 559–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Fan, Z.; Zhao, T.; Cao, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Xie, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wang, B. Plasma miR-1, miR-208, miR-499 as potential predictive biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction: An independent study of Han population. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 72, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oerlemans, M.I.; Mosterd, A.; Dekker, M.S.; de Vrey, E.A.; van Mil, A.; Pasterkamp, G.; Doevendans, P.A.; Hoes, A.W.; Sluijter, J.P. Early assessment of acute coronary syndromes in the emergency department: The potential diagnostic value of circulating microRNAs. EMBO Mol. Med. 2012, 4, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, J.V.; Heintz-Buschart, A.; Ghosal, A.; Wampach, L.; Etheridge, A.; Galas, D.; Wilmes, P. Sources and Functions of Extracellular Small RNAs in Human Circulation. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2016, 36, 301–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Urbich, C.; Kuehbacher, A.; Dimmeler, S. Role of microRNAs in vascular diseases, inflammation, and angiogenesis. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 79, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, M.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, E.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, Y.; Yang, L.; Wu, B.; Yi, G.; Mao, X.; et al. Circulating myocardial microRNAs from infarcted hearts are carried in exosomes and mobilise bone marrow progenitor cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barile, L.; Lionetti, V.; Cervio, E.; Matteucci, M.; Gherghiceanu, M.; Popescu, L.M.; Torre, T.; Siclari, F.; Moccetti, T.; Vassalli, G. Extracellular vesicles from human cardiac progenitor cells inhibit cardiomyocyte apoptosis and improve cardiac function after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc. Res. 2014, 103, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, Z.; Qin, S.; Li, W.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Chu, M.; Li, X.; Huo, Y.; Schaer, G.L.; Wang, S.; et al. An Endocrine Genetic Signal Between Blood Cells and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells: Role of MicroRNA-223 in Smooth Muscle Function and Atherogenesis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 65, 2526–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, Y.J.; Li, Y.S.; Wu, C.C.; Wang, K.C.; Huang, T.C.; Chen, Z.; Chien, S. Extracellular MicroRNA-92a Mediates Endothelial Cell-Macrophage Communication. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 2492–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Treguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mompeón, A.; Ortega-Paz, L.; Vidal-Gómez, X.; Costa, T.J.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Garcia-Blas, S.; Brugaletta, S.; Sanchis, J.; Sabate, M.; Novella, S.; et al. Disparate miRNA expression in serum and plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction: A systematic and paired comparative analysis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Siklenka, K.; Arora, S.K.; Ribeiro, P.; Kimmins, S.; Xia, J. miRNet-dissecting miRNA-target interactions and functional associations through network-based visual analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 2016, 44, W135–W141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape plug-in to decipher functionally grouped gene ontology and pathway annotation networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, T.P.; Lee, C.Y.; Tsai, M.H.; Chiu, Y.C.; Hsiao, C.K.; Lai, L.C.; Chuang, E.Y. miRSystem: An integrated system for characterizing enriched functions and pathways of microRNA targets. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuehbacher, A.; Urbich, C.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Role of Dicer and Drosha for endothelial microRNA expression and angiogenesis. Circ. Res. 2007, 101, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCall, M.N.; Kent, O.A.; Yu, J.; Fox-Talbot, K.; Zaiman, A.L.; Halushka, M.K. MicroRNA profiling of diverse endothelial cell types. BMC Med. Genom. 2011, 4, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Icli, B.; Dorbala, P.; Feinberg, M.W. An emerging role for the miR-26 family in cardiovascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2014, 24, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Icli, B.; Wara, A.K.M.; Moslehi, J.; Sun, X.; Plovie, E.; Cahill, M.; Marchini, J.F.; Schissler, A.; Padera, R.F.; Shi, J.; et al. MicroRNA-26a regulates pathological and physiological angiogenesis by targeting BMP/SMAD1 signaling. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, S.; Zhu, W.; Liu, D.; Su, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chang, Q.; Li, P. Circulating miR-26a-1, miR-146a and miR-199a-1 are potential candidate biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. Mol. Med. 2019, 25, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, A.; Chen, S.J.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, H.C.; Chu, P.H. Systemic approach to identify serum microRNAs as potential biomarkers for acute myocardial infarction. BioMed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 418628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, X.; Huang, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, L. Clinical impact of circulating miR-26a, miR-191, and miR-208b in plasma of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2015, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, Y.C.; Wang, Y.S.; Guo, Y.C.; Lin, W.L.; Chang, M.H.; Juo, S.H. Let-7g improves multiple endothelial functions through targeting transforming growth factor-beta and SIRT-1 signaling. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 1685–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Ge, J.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J.; Wang, X.; Xiong, H.; Gao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q. Let-7e modulates the inflammatory response in vascular endothelial cells through ceRNA crosstalk. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Tao, G.; Liu, Q.; Liu, K.; Yang, X. MicroRNA let-7g alleviates atherosclerosis via the targeting of LOX-1 in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brennan, E.; Wang, B.; McClelland, A.; Mohan, M.; Marai, M.; Beuscart, O.; Derouiche, S.; Gray, S.; Pickering, R.; Tikellis, C.; et al. Protective Effect of let-7 miRNA Family in Regulating Inflammation in Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis. Diabetes 2017, 66, 2266–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Varga, Z.V.; Zvara, A.; Faragó, N.; Kocsis, G.F.; Pipicz, M.; Gáspár, R.; Bencsik, P.; Görbe, A.; Csonka, C.; Puskás, L.G.; et al. MicroRNAs associated with ischemia-reperfusion injury and cardioprotection by ischemic pre- and postconditioning: ProtectomiRs. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2014, 307, H216–H227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. An epigenetic switch involving NF-kappaB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009, 139, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kong, L.; Du, X.; Hu, N.; Li, W.; Wang, W.; Wei, S.; Zhuang, H.; Li, X.; Li, C. Downregulation of let-7e-5p contributes to endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in deep vein thrombosis via targeting FASLG. Thromb. Res. 2016, 138, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Heiden, K.; Gijsen, F.J.; Narracott, A.; Hsiao, S.; Halliday, I.; Gunn, J.; Wentzel, J.J.; Evans, P.C. The effects of stenting on shear stress: Relevance to endothelial injury and repair. Cardiovasc. Res. 2013, 99, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, S.; Jiang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, K.; Yang, C. MicroRNA-let-7e regulates the progression and development of allergic rhinitis by targeting suppressor of cytokine signaling 4 and activating Janus kinase 1/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway. Exp. Med. 2018, 15, 3523–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, Y.; He, H.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L.; Ye, R.D.; et al. MK2 mediates macrophage activation and acute lung injury by regulating let-7e miRNA. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2018, 315, L371–L381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Gui, L.; Cai, Y.; Deng, X.; Li, C.; Guo, Q.; He, X.; Huang, J. Let-7e inhibits TNF-α expression by targeting the methyl transferase EZH2 in DENV2-infected THP-1 cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 8605–8616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Gelfond, J.A.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Reproducibility of quantitative RT-PCR array in miRNA expression profiling and comparison with microarray analysis. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pritchard, C.C.; Cheng, H.H.; Tewari, M. MicroRNA profiling: Approaches and considerations. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, L.; Batte, K.E.; Trgovcich, J.; Wisler, J.; Marsh, C.B.; Piper, M. Methodological challenges in utilizing miRNAs as circulating biomarkers. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2014, 18, 371–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva, S.; Agbulut, O. MiRroring the Multiple Potentials of MicroRNAs in Acute Myocardial Infarction. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2017, 4, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lippi, G.; Mattiuzzi, C.; Cervellin, G. Circulating microRNAs (miRs) for diagnosing acute myocardial infarction: Meta-analysis of available studies. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulte, C.; Barwari, T.; Joshi, A.; Theofilatos, K.; Zampetaki, A.; Barallobre-Barreiro, J.; Singh, B.; Sörensen, N.A.; Neumann, J.T.; Zeller, T.; et al. Comparative Analysis of Circulating Noncoding RNAs Versus Protein Biomarkers in the Detection of Myocardial Injury. Circ. Res. 2019, 125, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, J.A.; Esa, N.; Pidikiti, R.; Freedman, J.E.; Keaney, J.F.; Tanriverdi, K.; Vitseva, O.; Ambros, V.; Lee, R.; McManus, D.D. Circulating Cell and Plasma microRNA Profiles Differ between Non-ST-Segment and ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Fam. Med. Med. Sci. Res. 2013, 2, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Lan, C.; Pei, H.; Duan, G.; Huang, L.; Li, L. Expression of circulating miR-486 and miR-150 in patients with acute myocardial infarction. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2015, 15, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuwabara, Y.; Ono, K.; Horie, T.; Nishi, H.; Nagao, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Watanabe, S.; Baba, O.; Kojima, Y.; Shizuta, S.; et al. Increased microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a levels in serum of patients with cardiovascular disease indicate myocardial damage. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Antonicelli, R.; Lorenzi, M.; D’Alessandra, Y.; Lazzarini, R.; Santini, G.; Spazzafumo, L.; Lisa, R.; La Sala, L.; Galeazzi, R.; et al. Diagnostic potential of circulating miR-499-5p in elderly patients with acute non ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 531–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, S.M.; El-Shal, A.S.; Shoukry, A.; Khedr, M.H.; Abdelraheim, N. Serum miRNA-499 and miRNA-210: A potential role in early diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome. IUBMB Life 2016, 68, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zong, R.; Zhou, T.; Lin, Z.; Bao, X.; Xiu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Ma, J.X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y. Down-Regulation of MicroRNA-184 Is Associated With Corneal Neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1398–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, A.; Kwee, L.C.; Grass, E.; Neely, M.L.; Gregory, S.G.; Fox, K.A.A.; Armstrong, P.W.; White, H.D.; Ohman, E.M.; Roe, M.T.; et al. Whole blood sequencing reveals circulating microRNA associations with high-risk traits in non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2017, 261, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brieger, D.; Fox, K.A.; Fitzgerald, G.; Eagle, K.A.; Budaj, A.; Avezum, A.; Granger, C.B.; Costa, B.; Anderson, F.A., Jr.; Steg, P.G. Predicting freedom from clinical events in non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndromes: The Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events. Heart 2009, 95, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomou, T.; Mori, M.A.; Dreyfuss, J.M.; Konishi, M.; Sakaguchi, M.; Wolfrum, C.; Rao, T.N.; Winnay, J.N.; Garcia-Martin, R.; Grinspoon, S.K.; et al. Adipose-derived circulating miRNAs regulate gene expression in other tissues. Nature 2017, 542, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abels, E.R.; Maas, S.L.N.; Nieland, L.; Wei, Z.; Cheah, P.S.; Tai, E.; Kolsteeg, C.J.; Dusoswa, S.A.; Ting, D.T.; Hickman, S.; et al. Glioblastoma-Associated Microglia Reprogramming Is Mediated by Functional Transfer of Extracellular miR-21. Cell Rep. 2019, 28, 3105–3119.e3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Martin, R.; Wang, G.; Brandão, B.B.; Zanotto, T.M.; Shah, S.; Kumar Patel, S.; Schilling, B.; Kahn, C.R. MicroRNA sequence codes for small extracellular vesicle release and cellular retention. Nature 2021, 601, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosar, J.P.; Gámbaro, F.; Sanguinetti, J.; Bonilla, B.; Witwer, K.W.; Cayota, A. Assessment of small RNA sorting into different extracellular fractions revealed by high-throughput sequencing of breast cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5601–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife 2016, 5, e19276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zernecke, A.; Bidzhekov, K.; Noels, H.; Shagdarsuren, E.; Gan, L.; Denecke, B.; Hristov, M.; Koppel, T.; Jahantigh, M.N.; Lutgens, E.; et al. Delivery of microRNA-126 by apoptotic bodies induces CXCL12-dependent vascular protection. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Rosa, S.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Lehmann, R.; Assmus, B.; Dimmeler, S.; Zeiher, A.M. Transcoronary concentration gradients of circulating microRNAs. Circulation 2011, 124, 1936–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fichtlscherer, S.; De Rosa, S.; Fox, H.; Schwietz, T.; Fischer, A.; Liebetrau, C.; Weber, M.; Hamm, C.W.; Röxe, T.; Müller-Ardogan, M.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in patients with coronary artery disease. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Control Group (n = 51) | AMI Group (n = 53) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 60 (46–64) | 65 (56–71) | <0.001 |
| Sex [male, n (%)] | 30 (58.8) | 39 (73.6) | 0.147 |
| BMI, median (IQR) | 27.2 (24–29) | 27.4 (25–30) | 0.327 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 2 (3.9) | 21 (39.6) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 15 (29.4) | 45 (84.9) | <0.001 |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 10 (19.6) | 31 (58.5) | <0.001 |
| Smoking, n (%) | 18 (35.3) | 19 (35.8) | 0.953 |
| Cytokines (pg/mL) | Chemokines (pg/mL) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | IL-1β | IL-6 | TNF-α | VEGF-A | IL-10 | IL-8 | MIP-1α | MCP-3 | MDC | |
| let-7e-5p | r | −0.10 | −0.06 | −0.20 | −0.04 | 0.05 | 0.003 | −0.08 | −0.01 | −0.03 |
| p | 0.2634 | 0.5544 | 0.0265 | 0.6290 | 0.6128 | 0.9667 | 0.3717 | 0.8854 | 0.7374 | |
| let-7g-5p | r | −0.14 | −0.03 | −0.23 | −0.14 | −0.10 | 0.06 | 0.06 | −0.32 | −0.13 |
| p | 0.1329 | 0.7830 | 0.0111 | 0.1356 | 0.2943 | 0.4997 | 0.5236 | 0.0004 | 0.1663 | |
| miR-26a-5p | r | −0.03 | −0.03 | −0.16 | −0.005 | −0.02 | 0.04 | −0.04 | −0.15 | −0.22 |
| p | 0.7658 | 0.7493 | 0.079 | 0.9522 | 0.8668 | 0.6342 | 0.6698 | 0.1001 | 0.0134 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mompeón, A.; Pérez-Cremades, D.; Paes, A.B.; Sanchis, J.; Ortega-Paz, L.; Andrea, R.; Brugaletta, S.; Sabate, M.; Novella, S.; Dantas, A.P.; et al. Circulating miRNA Fingerprint and Endothelial Function in Myocardial Infarction: Comparison at Acute Event and One-Year Follow-Up. Cells 2022, 11, 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111823
Mompeón A, Pérez-Cremades D, Paes AB, Sanchis J, Ortega-Paz L, Andrea R, Brugaletta S, Sabate M, Novella S, Dantas AP, et al. Circulating miRNA Fingerprint and Endothelial Function in Myocardial Infarction: Comparison at Acute Event and One-Year Follow-Up. Cells. 2022; 11(11):1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111823
Chicago/Turabian StyleMompeón, Ana, Daniel Pérez-Cremades, Ana Belén Paes, Juan Sanchis, Luis Ortega-Paz, Rut Andrea, Salvatore Brugaletta, Manel Sabate, Susana Novella, Ana Paula Dantas, and et al. 2022. "Circulating miRNA Fingerprint and Endothelial Function in Myocardial Infarction: Comparison at Acute Event and One-Year Follow-Up" Cells 11, no. 11: 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111823
APA StyleMompeón, A., Pérez-Cremades, D., Paes, A. B., Sanchis, J., Ortega-Paz, L., Andrea, R., Brugaletta, S., Sabate, M., Novella, S., Dantas, A. P., & Hermenegildo, C. (2022). Circulating miRNA Fingerprint and Endothelial Function in Myocardial Infarction: Comparison at Acute Event and One-Year Follow-Up. Cells, 11(11), 1823. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11111823







