A Rare Mutation in LMNB2 Associated with Lipodystrophy Drives Premature Cell Senescence
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient
2.2. Molecular Studies
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Cell Proliferation ELISA and SA-Beta-Galactosidase Assays
2.5. Immunofluorescence, Imaging, and Analysis
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
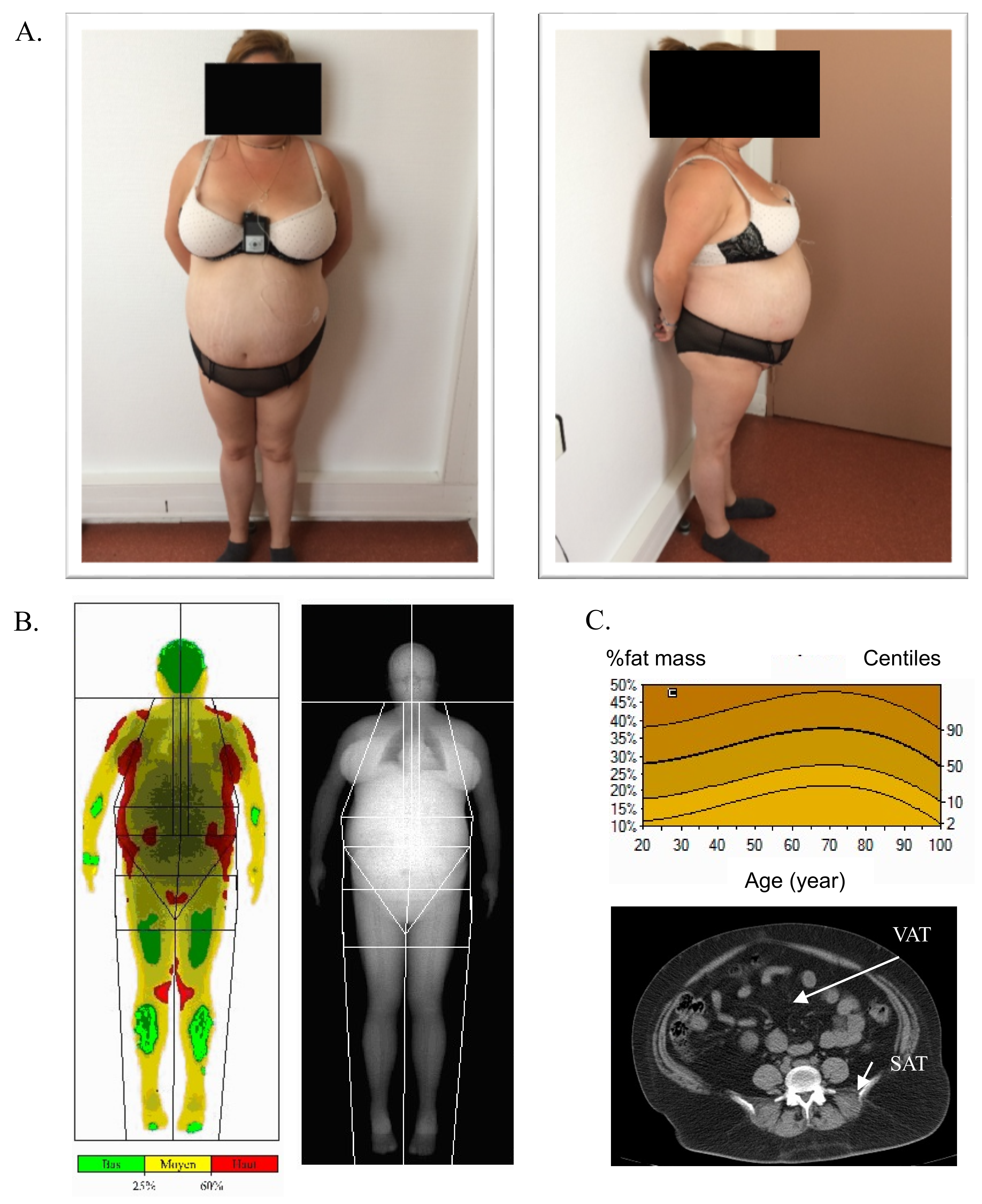
3.1. Patient Description
3.2. Molecular Findings
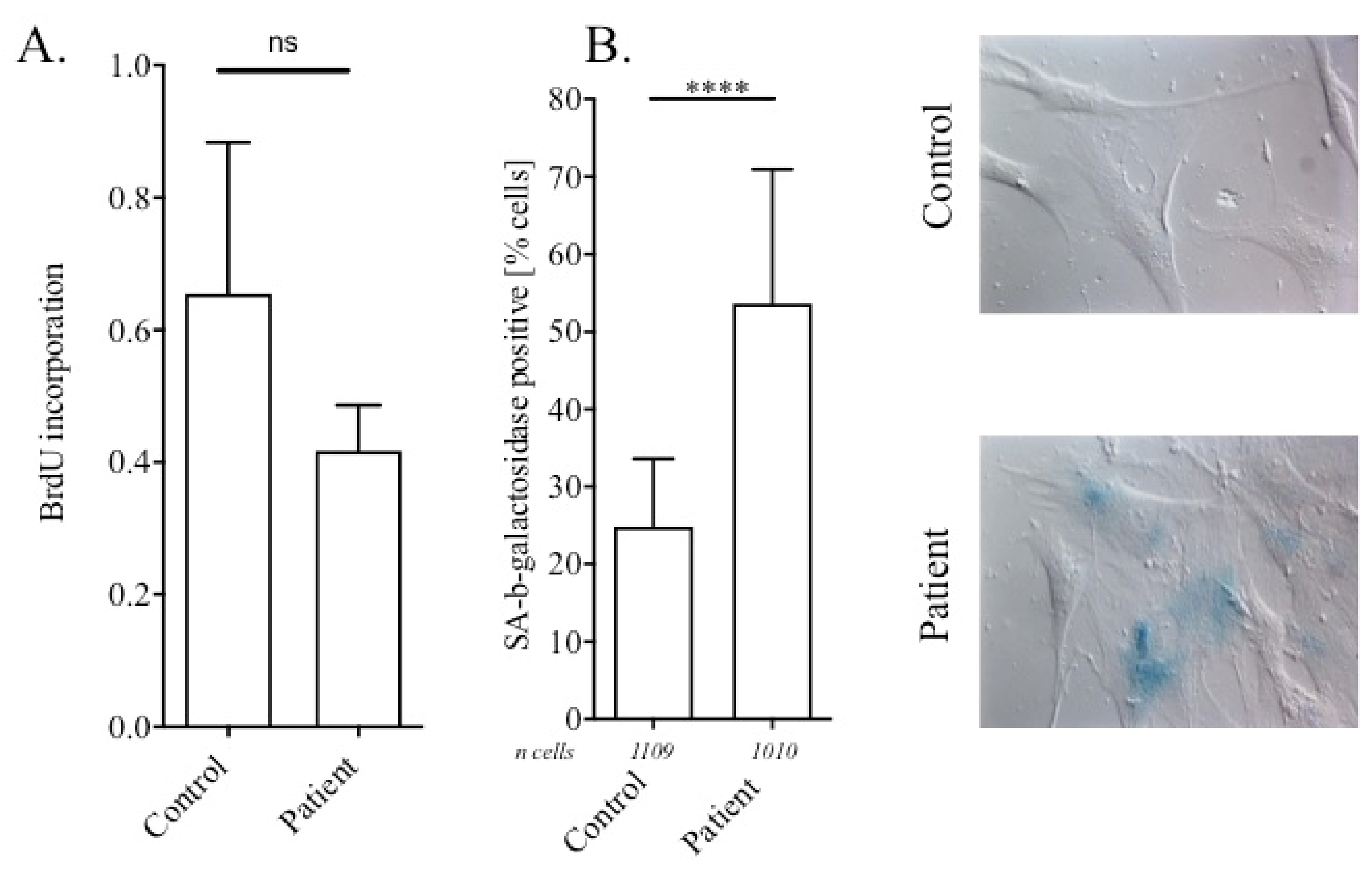
3.3. Nuclear Abnormalities and Cellular Senescence Assays
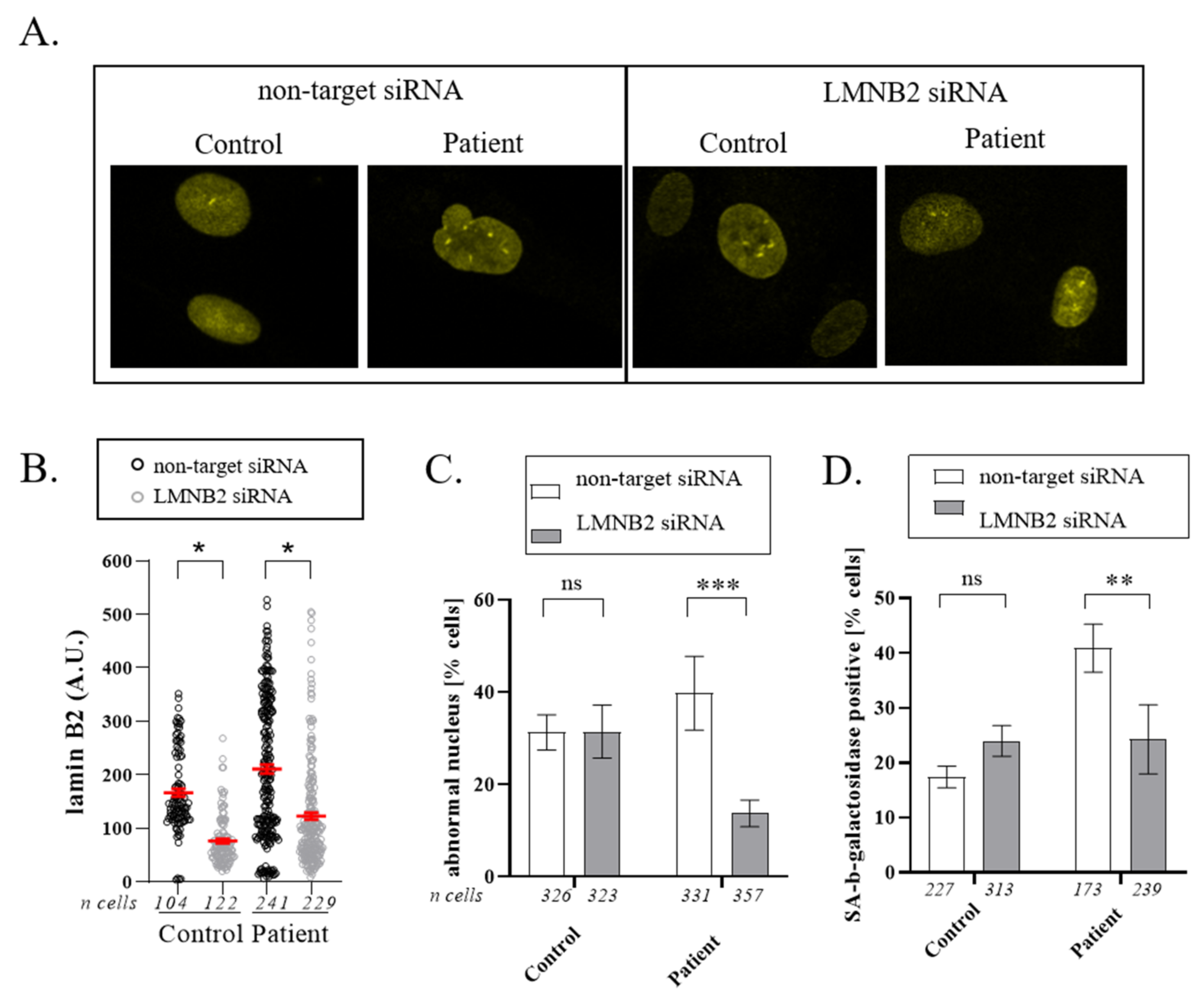
3.4. Downregulation of Lamin B2
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fiorenza, C.G.; Chou, S.H.; Mantzoros, C.S. Lipodystrophy: Pathophysiology and advances in treatment. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capeau, J.; Magré, J.; Lascols, O.; Caron, M.; Béréziat, V.; Vigouroux, C. Primary lipodystrophies. Ann. Endocrinol. (Paris) 2007, 68, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ben-Shahar, T.R.; Riemer, D.; Treinin, M.; Spann, P.; Weber, K.; Fire, A.; Gruenbaum, Y. Essential Roles for Caenorhabditis elegans Lamin Gene in Nuclear Organization, Cell Cycle Progression, and Spatial Organization of Nuclear Pore Complexes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 3937–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lammerding, J.; Fong, L.G.; Ji, J.Y.; Reue, K.; Stewart, C.L.; Young, S.G.; Lee, R.T. Lamins A and C but Not Lamin B1 Regulate Nuclear Mechanics. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 25768–25780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gupta, A.S.; Sengupta, K. Lamin B2 Modulates Nucleolar Morphology, Dynamics, and Function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2017, 37, e00274-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegele, R.A.; Cao, H.; Liu, D.M.; Costain, G.A.; Charlton-Menys, V.; Rodger, N.W.; Durrington, P.N. Sequencing of the reannotated LMNB2 gene reveals novel mutations in patients with acquired partial lipodystrophy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Li, Y.; Fu, X.; Luo, X. A Chinese patient with acquired partial lipodystrophy caused by a novel mutation with LMNB2 gene. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 25, 375–377. [Google Scholar]
- Akinci, B.; Onay, H.; Demir, T.; Savas-Erdeve, Ş.; Gen, R.; Simsir, I.Y.; Keskin, F.E.; Erturk, M.S.; Uzum, A.K.; Yaylali, G.F.; et al. Clinical presentations, metabolic abnormalities and end-organ complications in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy. Metabolism 2017, 72, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonello-Palot, N.; Laine, M.; Cuisset, T.; Ronchard, T.; Desgrouas, C.; Merono, F.; Ibrahim-Kosta, M.; Cerino, M.; Blanchard, A.; Bourgeois, P.; et al. High prevalence of mutations in perilipin 1 in patients with precocious acute coronary syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2020, 293, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desvignes, J.-P.; Bartoli, M.; Delague, V.; Krahn, M.; Miltgen, M.; Beroud, C.; Salgado, D. VarAFT: A variant annotation and filtration system for human next generation sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W545–W553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Gerasimova, A.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salgado, D.; Desvignes, J.-P.; Rai, G.; Blanchard, A.; Miltgen, M.; Pinard, A.; Levy, N.; Collod-Beroud, G.; Beroud, C. UMD-Predictor: A High-Throughput Sequencing Compliant System for Pathogenicity Prediction of any Human cDNA Substitution. Hum. Mutat. 2016, 37, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Desgrouas, C.; Varlet, A.-A.; Dutour, A.; Galant, D.; Merono, F.; Bonello-Palot, N.; Bourgeois, P.; Lasbleiz, A.; Petitjean, C.; Ancel, P.; et al. Unraveling LMNA Mutations in Metabolic Syndrome: Cellular Phenotype and Clinical Pitfalls. Cells 2020, 9, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gruenbaum, Y.; Foisner, R. Lamins: Nuclear Intermediate Filament Proteins with Fundamental Functions in Nuclear Mechanics and Genome Regulation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2015, 84, 131–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiano, J.A.; Afawi, Z.; Bahlo, M.; Mauermann, M.; Misk, A.; Arsov, T.; Oliver, K.L.; Dahl, H.-H.M.; Shearer, A.E.; Smith, R.J.H.; et al. Mutation of the nuclear lamin gene LMNB2 in progressive myoclonus epilepsy with early ataxia. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4483–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soleimanipour, F.; Razmara, E.; Rahbarizadeh, F.; Fallahi, E.; Khodaeian, M.; Tavasoli, A.R.; Garshasbi, M. A novel missense variant in the LMNB2 gene causes progressive myoclonus epilepsy. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parry, D.A.; Martin, C.-A.; Greene, P.; Marsh, J.A.; Genomics England Research Consortium; Blyth, M.; Cox, H.; Donnelly, D.; Greenhalgh, L.; Greville-Heygate, S.; et al. Heterozygous lamin B1 and lamin B2 variants cause primary microcephaly and define a novel laminopathy. Genet. Med. 2021, 23, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvarani, N.; Crasto, S.; Miragoli, M.; Bertero, A.; Paulis, M.; Kunderfranco, P.; Serio, S.; Forni, A.; Lucarelli, C.; Ferro, M.D.; et al. The K219T-Lamin mutation induces conduction defects through epigenetic inhibition of SCN5A in human cardiac laminopathy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roncarati, R.; Anselmi, C.V.; Krawitz, P.; Lattanzi, G.; von Kodolitsch, Y.; Perrot, A.; di Pasquale, E.; Papa, L.; Portararo, P.; Columbaro, M.; et al. Doubly heterozygous LMNA and TTN mutations revealed by exome sequencing in a severe form of dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Refgene | Mutation | SNP Ref | GnomAD | UMD Score | Mutation Taster |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SYNE1: NM_182961 | Exon 24: c.2882G > A p.(Arg961Gln) | rs76646638 | 0.001423 | 68/100 | Polymorphism |
| LMNB2: NM_032737.4 | Exon 5: c.700C > T p.(Arg234Trp) | rs148936043 | 0.0001351 | 100/100 | Disease causing |
| Our Publication | Gao et al., 2012 | Hegele et al., 2006 | Hegele et al., 2006 | Akinci et al., 2017 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LMNB2 mutation | p.(Arg234Trp) | p.(Tyr252His) | p.(Arg235Gln) | p.(Arg235Gln) | p.(Arg235Gln) |
| Age when fat loss began (years) | - | 12 | 5 | 16 | 13 |
| Age at APL diagnosis (years) | NA | NA | 9 | 30 | NR |
| Diabetes, age at onset (years) | Yes, 19 | No At 26: increased insulin level | Yes, 19 | Yes, 37 | Yes |
| Extent of fat loss | Limbs | Symmetrical, face and upper body | Symmetrical, upper body to knees | Symmetrical, upper body to upper thigh | Limbs, trunk, gluteal |
| Excess of fat | Face, neck, trunk | NR | NR | NR | Face, neck |
| Dyslipidemia | Severe | Moderate | Type V | Type IV | Severe |
| Hypertension | No | No | No | Yes | NR |
| Polycystic ovarian syndrome | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
| Autoimmune disease | No | NR | No | Yes | NR |
| Hirsutism | NR | NR | No | Yes | NR |
| Other | CAD Osteoporosis Alopecia |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varlet, A.-A.; Desgrouas, C.; Jebane, C.; Bonello-Palot, N.; Bourgeois, P.; Levy, N.; Helfer, E.; Dubois, N.; Valero, R.; Badens, C.; et al. A Rare Mutation in LMNB2 Associated with Lipodystrophy Drives Premature Cell Senescence. Cells 2022, 11, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010050
Varlet A-A, Desgrouas C, Jebane C, Bonello-Palot N, Bourgeois P, Levy N, Helfer E, Dubois N, Valero R, Badens C, et al. A Rare Mutation in LMNB2 Associated with Lipodystrophy Drives Premature Cell Senescence. Cells. 2022; 11(1):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010050
Chicago/Turabian StyleVarlet, Alice-Anaïs, Camille Desgrouas, Cécile Jebane, Nathalie Bonello-Palot, Patrice Bourgeois, Nicolas Levy, Emmanuèle Helfer, Noémie Dubois, René Valero, Catherine Badens, and et al. 2022. "A Rare Mutation in LMNB2 Associated with Lipodystrophy Drives Premature Cell Senescence" Cells 11, no. 1: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010050
APA StyleVarlet, A.-A., Desgrouas, C., Jebane, C., Bonello-Palot, N., Bourgeois, P., Levy, N., Helfer, E., Dubois, N., Valero, R., Badens, C., & Beliard, S. (2022). A Rare Mutation in LMNB2 Associated with Lipodystrophy Drives Premature Cell Senescence. Cells, 11(1), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells11010050






