Abstract
Background: Microsatellite instability (MSI) testing is important for the classification of Lynch syndrome, as a prognostic marker and as a guide for adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer (CRC). The gold standard for determining MSI status has traditionally been fluorescent multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE). However, its use in the clinical setting has diminished and has been replaced by immunohistochemical (IHC) detection of loss of mismatch repair protein expression due to practicability and cost. The aim of this study was to develop a simple, cost-effective and accurate MSI assay based on CGE. Method: After amplification of microsatellites by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using the National Cancer Institute (NCI) panel (BAT 25, BAT26, D5S346, D2S123, D17S250) of MSI markers, parallel CGE was utilized to classify colorectal cancers as MSI-H, MSI-L and MSS using the 5200 Fragment Analyzer System. Cell lines and patient cancer specimens were tested. DNA from 56 formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded cancer specimens and matched normal tissue were extracted and CGE was performed. An automated computational algorithm for MSI status determination was also developed. Results: Using the fragment analyser, MSI status was found to be 100% concordant with the known MSI status of cell lines and was 86% and 87% concordant with immunohistochemistry (IHC) from patient cancer specimens using traditional assessment and our MSI scoring system, respectively, for MSI determination. The misclassification rate was mainly attributed to IHC, with only one (1.8%) sampling error attributed to CGE testing. CGE was also able to distinguish MSI-L from MSI-H and MSS, which is not possible with IHC. An MSI score based on total allelic variability that can accurately determine MSI status was also successfully developed. A significant reduction in cost compared with traditional fluorescent multiplex PCR and CGE was achieved with this technique. Conclusions: A simple, cost-effective and reliable method of determining MSI status and an MSI scoring system based on an automatic computational algorithm to determine MSI status, as well as degree of allelic instability in colorectal cancer, has been developed using the 5200 Fragment Analyzer System.
1. Introduction
Microsatellite instability (MSI) testing for colorectal cancer has become universal in many countries worldwide. The main utility of MSI testing has been to aid with the diagnosis of Lynch syndrome [1]. In 2016, the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) called for universal MSI testing to guide further testing for Lynch syndrome for people with colorectal cancer [2]. Microsatellite instability status has also been used to guide adjuvant therapy [3,4,5], although the use of MSI status to guide adjuvant treatment for colorectal cancer remains controversial [6,7]. Arguably, MSI tumours may not respond as well to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) based chemotherapy [3,8,9], but may respond better to irinotecan [10] or oxaliplatin therapy [11]. Furthermore, the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) guidelines suggest that patients with Stage II colon cancer with high-risk adverse features in the absence of MSI may benefit from chemotherapy [12,13]. Several meta-analyses have shown that MSI status may be useful in guiding prognosis [14,15,16] as well as predicting the risk of dissemination [16,17]. Furthermore, MSI status alongside stage and other clinically relevant biomarkers may be used to provide patients with a more accurate prognosis as well as guide the optimal surveillance regimen post cancer resection. Finally, in the era of immunotherapy, MSI status has become an important biomarker to guide the selection of colorectal cancer patients suitable for immunotherapy [18], with the CheckMate study by Overman et al. demonstrating a durable response and disease control with Nivolumab in patients with metastatic MSI-H colorectal cancer [19].
Since 1997, an international consensus has supported the use of the Bethesda panel of five markers to detect MSI [20]. This panel of markers consists of two mononucleotide repeats BAT-25 and BAT-26 and three dinucleotides D5S346, D2S123 and D17S250. The test requires DNA extraction, PCR and resolution of the amplification products by capillary gel electrophoresis (CGE). It is commonly performed using costly fluorescent primer sets and the PCR products separated using an expensive genetic analyser instrument. Colorectal cancers with high-level microsatellite instability (MSI-H) have insertion/deletion mutations in repeats of short non-coding microsatellites (1–6 bp) [21], and as such, are characterised by alterations in nucleotide length in DNA sequences. Capillary gel electrophoresis can detect alterations in nucleotide length in DNA sequences as this test separates PCR products of different sizes, thereby enabling the characterisation of instability at different microsatellite loci. Tumours with instability at two or more of the markers are considered to be MSI-H; at one marker, they are considered to be microsatellite instability low (MSI-L) and those without instability are considered to be microsatellite stable (MSS).
While still regarded as the gold standard, molecular-based determination of MSI has fallen out of favour for clinical utilisation, mainly due to assay workflow and instrument expense. In 2009, Palomaki et al. performed an evidence review for the Evaluation of Genomic Applications in Practice and Prevention (EGAPP) working group (EQG), reviewing the cost of MSI testing by both CGE (which traditionally requires expensive fluorescent primer sets) and by immunohistochemistry (IHC) for mismatch repair deficiency (MMRD) and determined the cost to be USD 457 and USD 261, respectively [22]. While the economics of these tests have changed with time, MSI status determination for colorectal cancer for clinical purposes is still largely performed using IHC in most institutions.
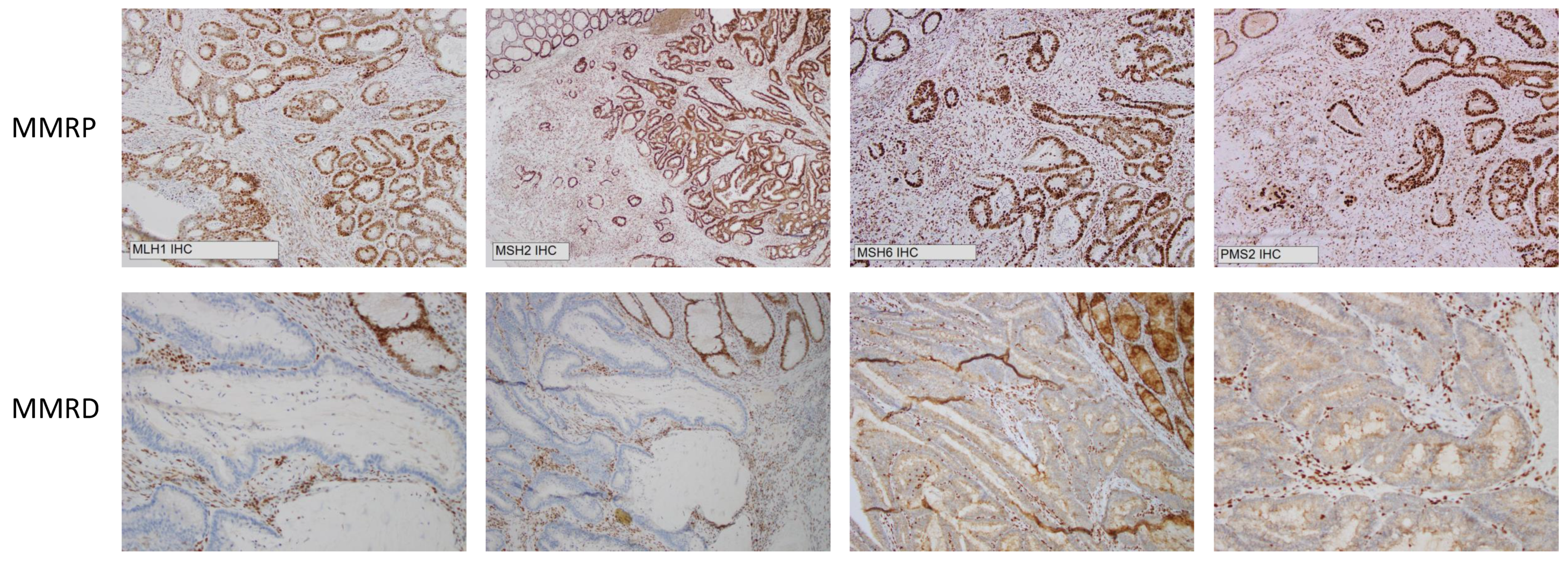
It is evident that IHC has worked well as a surrogate measure for determining MSI status and has been the workhorse for evaluating MSI status on a clinical basis in the era of universal MSI testing. It is practicable, cost-effective and can be applied widely [23]. However, it does not directly identify changes in DNA, but rather identifies loss of mismatch repair protein expression, specifically MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2 (Figure 1). One limitation of IHC is that it can only classify colorectal cancer as either MSI-H or MSS. It cannot determine MSI-L, nor can it assess the degree of allelic instability. Further, approximately 5% of MSI-H tumours have normal levels of mismatch repair (MMR) proteins and are potentially be missed by IHC (these MMR proteins have retained expression but are functionally defective). Therefore, this 5% of MSI-H tumours would be misclassified as MSS [24]. A study by Cheah et al. estimated the accuracy of IHC to be 89–95% [25], whereas fluorescent multiplex PCR and CGE can achieve up to 100% accuracy [26].
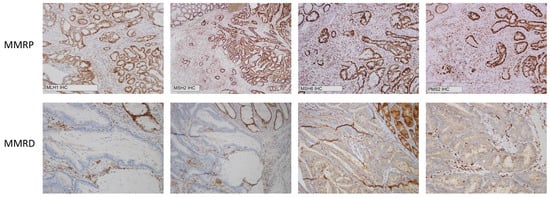
Figure 1.
Immunohistochemistry demonstrating mismatch repair proficiency (MMRP) and mismatch repair deficiency (MMRD) at MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2.
Several studies have already reported different CGE based assays for MSI testing (Suraweera et al. (2002) [27], Shemirani et al. (2011) [28], Murphy et al. (2006) [29], Goel et al. (2009) [30] and Buhard et al. (2004) [31], but to the best of our knowledge, this is the first study using the Fragment Analyzer System to determine MSI status in colorectal cancer.
The primary objective of this study was to develop a molecular MSI test based on CGE (which is still considered a gold standard) [23] that is cost-effective, practicable, with rapid reporting of results; preferably with a computational algorithm that can accurately determine MSI status automatically based on the NCI panel of markers without the need for a technician/scientist/medical professional to inspect the electropherogram or digital gels to determine MSI status. The secondary objective of this study was to develop an MSI score based on allelic variability (which represents the degree of alterations in nucleotide lengths within the microsatellites) and to use this score as an alternative computational method to determine MSI status, as well as to use it as a means to further characterise MSI-H colorectal cancers.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Culture
Twelve colorectal cancer cell lines including RKO, LS174T, HT116, LIM1215, LIM2033, LISP1, DLD1 and LOVO (representing MSI-H cell lines) and SW1222, HT29, SW620 and SW480 (representing MSS cell lines) were grown in an RPMI medium containing 10% foetal bovine serum (FBS; Gibco) and 2 mM L-glutamine (Gibco) at 37 °C and 5% CO2. All cell lines were harvested at 80–90% confluence using 0.05% Trypsin-EDTA (Gibco) and genomic DNA was extracted from the cell pellets for use as MSI-H and MSS controls.
2.2. Patient Samples
Seventy-two colorectal cancer patients with available BRAF and MSI status information (see Table 1) were identified from the Concord Colorectal Cancer Resection Database (Institutional Ethics approval: Sydney Local Health District Ethics CH62/62011-136 HREC/11/CRGH206). All patients included in this study provided written consent for the use of their information for research. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) tumour and matched normal tissue samples comprising 19 MSI-H and BRAF mutant, 23 MSI-H and BRAF wild type and 30 MSS specimens were retrieved from the Concord anatomical pathology department. Nineteen matched samples were randomly selected from each subgroup (a total of 57 samples). Routine pathologic review of all samples was performed by an expert pathologist, and after retrieval, tissue sufficiency was reviewed by JWTT and KJS. For one of the MSI-H and BRAF mutant samples, insufficient tumour material was available for DNA extraction and was excluded from the study. The remaining 56 tumour blocks were randomly assigned a study identification number (ID) and the investigators were then blinded to MSI status and patient demographics associated with each sample.

Table 1.
Patient and tumour characteristics based on MSI and BRAF status.
2.3. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
Immunohistochemical analysis for MMR protein (MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2) expression was routinely performed on 4 µm FFPE tumour sections and stained using an automated IHC Stainer. An experienced pathologist reviewed the IHC results and confirmed MMR protein expression status for all samples used in this study, with the absence of staining within tumour regions indicating loss of MMR protein expression (MMRD).
2.4. DNA Extraction and Quantitation
Genomic DNA was extracted from all cell lines using the Isolate II Genomic DNA Kit (Bioline, London, UK) in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions. After elution, the DNA was quantified using a NanoDrop spectrophotometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA). For the tissue samples, five 10µm scrolls were taken from the FFPE blocks and DNA extraction was performed using the QIAamp DNA FFPE Tissue Kit (Qiagen, Hilden, Germany) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. All tissue DNA samples were quantified as per the cell line DNA.
2.5. PCR Amplification and Capillary Electrophoresis Detection of MSI
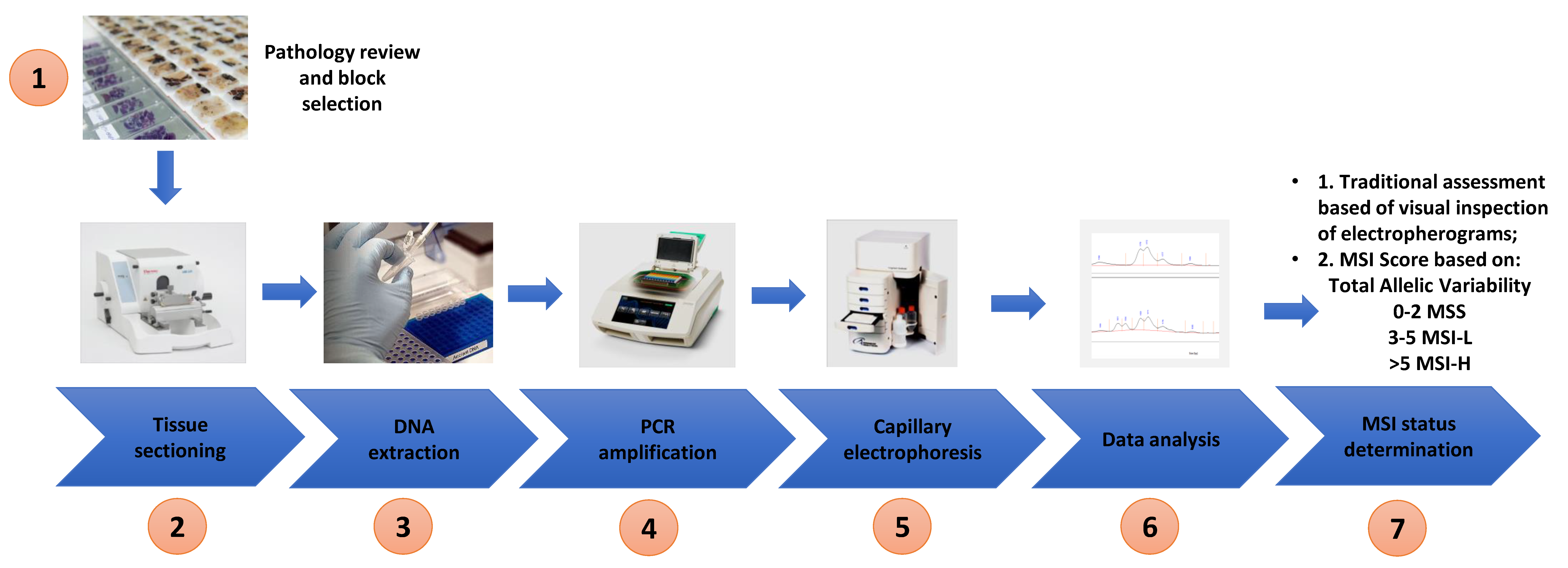
Extracted DNA from both cell lines and tissue was used for MSI analysis. The optimised Bethesda panel of 5 microsatellite markers (BAT 25, BAT 26, D2S123, D5S346 and D17S250) described by Umetani et al. was used in this study and the primer sequences are shown in Table 2 [32]. PCR amplification was performed using a Bio-Rad C1000 Touch Thermal Cycler (Bio-Rad Laboratories) in 10 µL reaction mixtures containing 20 ng of genomic DNA, 0.4 µM of each primer and 1× MyTaq Mix following the recommendations of the manufacture (Bioline). The following PCR cycling conditions were used: 3 min initial denaturation at 95 °C and 40 cycles at 95 °C for 30 s, 56 °C for 30 s and 72 °C for 20 s and a final extension at 72 °C for 2 min. The PCR products were then subjected to parallel CGE using a 1–500 bp (DNF-905) DNA kit on a 5200 Fragment Analyzer System (Agilent) according to the manufactures instructions (see Figure 2 for the workflow).

Table 2.
Bethesda panel primer sequences for microsatellite analysis.
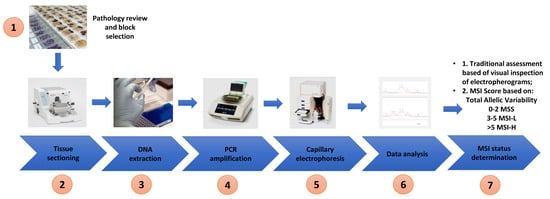
Figure 2.
Workflow of study—pathology review and tumour block selection, tissue sectioning into scrolls, DNA extraction, polymerase chain reaction, capillary electrophoresis, inspection of electropherogram/data analysis and determination of MSI status based on allelic variability and MSI score.
2.6. Microsatellite Analysis
Analysis of microsatellite instability was performed by the following two approaches. Firstly, electropherograms of all samples were visually inspected and MSI status was based on the observed number of markers that displayed instability. If two or more markers were unstable, then the sample was classified as MSI-H; if there was no instability in any of the markers, then the sample was classified as MSS. If instability was found in one marker, the sample was considered to be MSI-L. Secondly, a computational algorithm based on the RFU signals assigned to tumour and normal tissue electropherogram fragment peaks was developed to automatically detect differences in DNA products without visual inspection of the electropherogram and accurately call samples as MSI-H, MSI-L or MSS. In order to achieve this, for each peak size at each position, the proportion of the signal (RFU) assigned to that position and whether the peak was ‘novel’ in the sample compared to the matched sample control. A peak was deemed ‘novel’ if it was at least 2 bases from the nearest peak in the matched normal, not more than 10 bases outside of the entire range of peak sizes observed in the normal, and if it accounted for more than 2% of the total signal in the sample (peaks with less than 2% were filtered as potential noise). This noise level may be easily adjusted in the computational method as required depending on the calibration values at each laboratory. The sum of the proportion of the signal that was assigned to novel peaks for each position for each tumour sample is then reported.
For each marker, a percentage allelic variability was calculated by this computational method. An allelic variability of >2% for any marker was considered unstable, ≤2% was considered stable. Using the traditional assessment of the NCI panel of markers, if none of the markers were unstable, the tumour was considered MSS; if one marker was unstable, MSI-L and if two or more markers were unstable, then the tumour was considered MSI-H. The maximum allelic variability of any marker (%) for each sample was assessed and an MSI score based on total allelic variability was created. An MSI score of 1–2 was considered MSS; 3–5 MSI-L; ≥5 MSI-H. A Total high-level MSI (Toh) score (/500) was attributed to each MSI-H colorectal cancer. Finally, the MSI status calculated by visual assessment of NCI markers, automatically by % allelic variability (≤2%/>2%) and by MSI score based on total allelic variability was compared to the MSI status reported by pathologist-based assessment of IHC.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using STATA (Stata MP, Version 15; StataCorp LP) and GraphPad Prism.
3. Results
3.1. MSI Assessment of Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines
The microsatellite status of twelve colorectal cancer cell lines was analysed by CGE using the Fragment Analyzer System and the electropherograms were visually inspected (JWTT and KJS). There was 100% sensitivity and specificity in the comparative analysis of MSI status determined by CGE and the known MSI status of the cancer cell line (Table 3).

Table 3.
Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive value of high-resolution capillary electrophoresis of colorectal cancer cell lines by visual inspection of high-resolution capillary electrophoresis signatures.
3.2. Limit of Detection of MSI
In order to determine the potential lower limit of tumour cellularity that MSI is able to be accurately detected in a specimen by Fragment Analyser-based CGE, a cell line mixing experiment was performed. RKO (MSI-H cell line) genomic DNA was proportionally mixed with HT-29 (MSS cell line) to 5%, 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and 100% in a total of 20 ng of genomic material. Using allelic variability scoring of >2%/≤2% for each marker, MSI was detected even at 5% of MSI-H genomic material (Table 4). This suggested that CGE using the Fragment Analyser can detect MSI at very low concentrations and laborious micro-dissection of tumour tissue from each block may not be required.

Table 4.
Limit of microsatellite instability detection analysis in cell lines. MSI dilution series (5%, 10%, 20%, 40%, 60%, 80%, 100%) using RKO (MSI-H) and HT29 (MSS) cell line DNA.
3.3. Patient Tumour Specimens
Of the 72 patient specimens with known MSI and BRAF status (MSS n = 30, MSI-H:BRAF mutant n = 19 and MSI-H:BRAF wild type n = 23), 19 patients from each subgroup were selected for analysis and of these 57 patients, 56 patient tumour specimens were analysed by CGE.
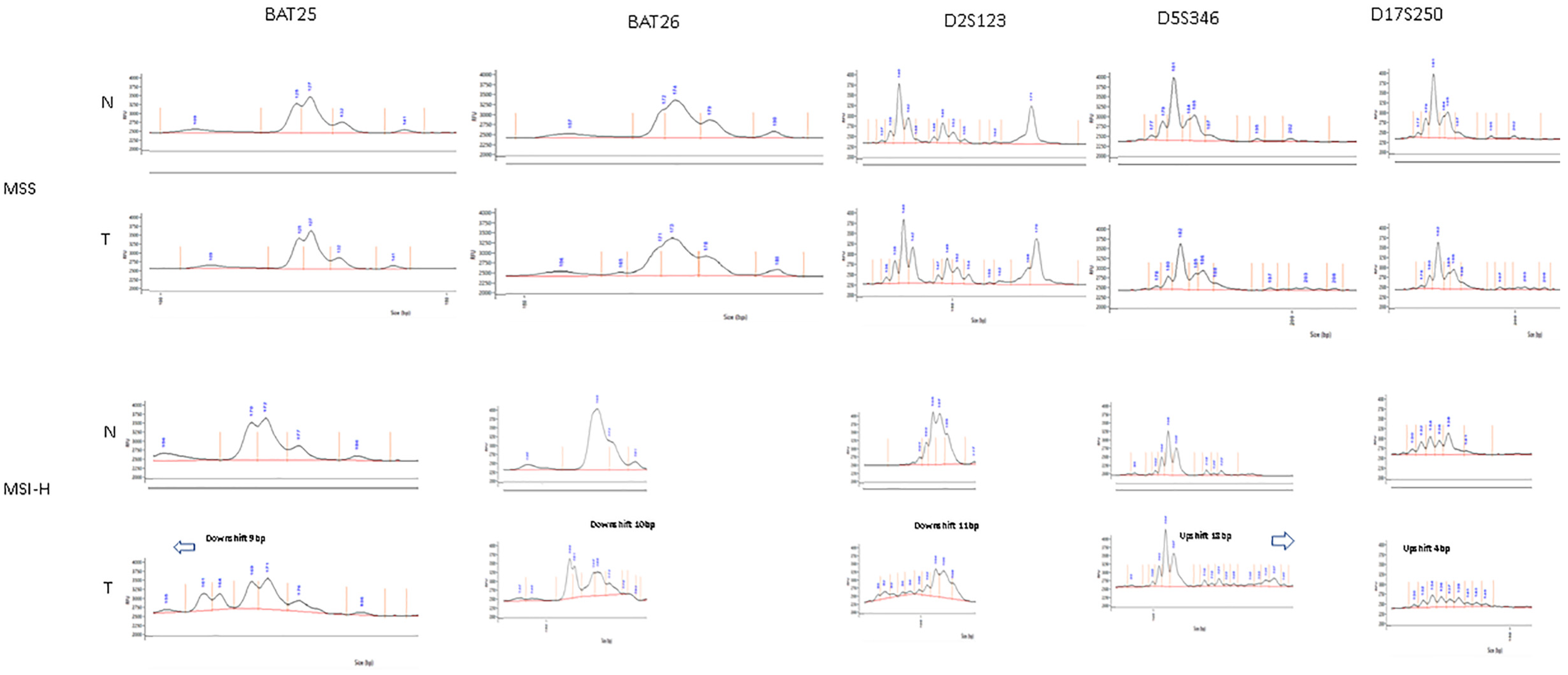
The tumour specimens were classified as MSS, MSI-L or MSI-H by assessment of the NCI panel of markers based on visual inspection of the digital gel view or electropherogram (Figure 3) and by using the automatic computational method developed in this study (Figure 4). There was 100% concordance with visual inspection and allelic variability scoring in determining if any one of the five markers displayed instability.
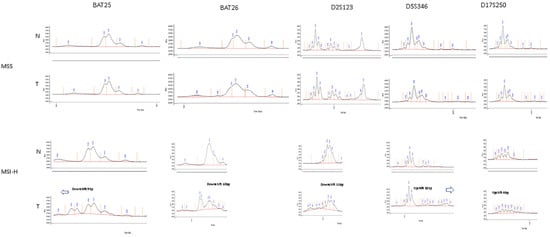
Figure 3.
Example of visual inspection of electropherogram for tumour specimens—above (MSS) showing identical electropherograms between tumour and matched normal tissue, below (MSI-H) showing allelic shift between tumour and matched normal tissue on electropherogram.
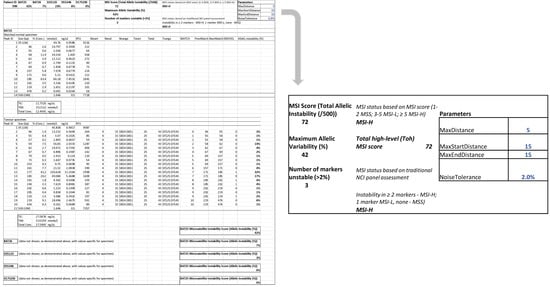
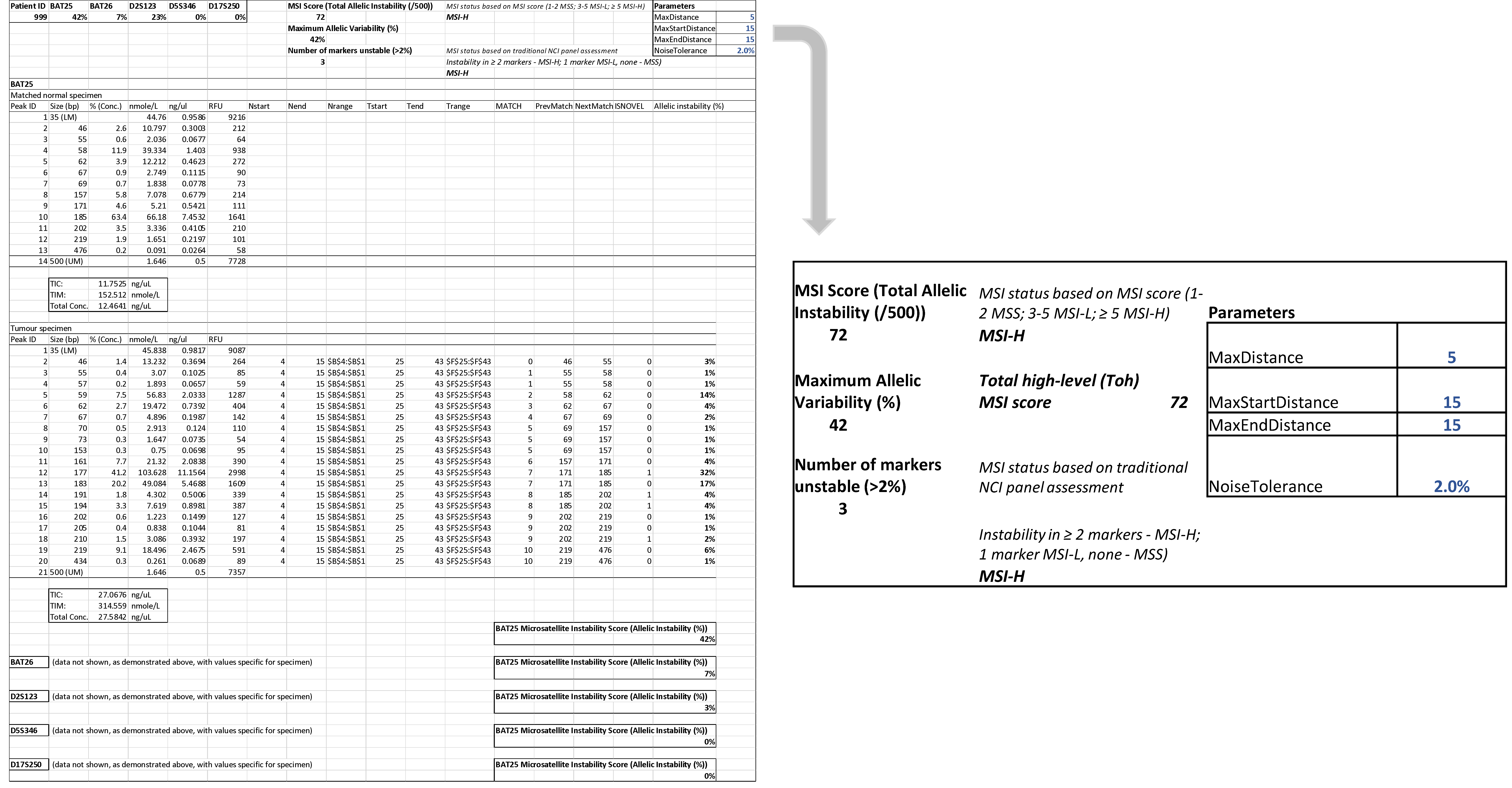
Figure 4.
Automatic computation methods for MSI status determination based on allelic instability using both a traditional assessment of NCI panel (0/1/≥2 markers unstable corresponding to MSS/MSI-L and MSI-H respectively) and an MSI scoring system (total allelic variability 1–2/3–5/>5 corresponding to MSS/MSI-L and MSI-H). This tumour specimen was considered MSI-H with a Total high-level (Toh) MSI score of 72.
As IHC cannot determine MSI-L, these were excluded from correlation analysis with IHC. There was a 93% (14/15), 85% (11/13) and 79% (11/14) correlation with IHC based on an assessment of the NCI panel of markers using the allelic variability score of >2%/≤2% for each marker for MSI-H:BRAF mutant, MSI-H:BRAF wild type and MSS subgroups, respectively. In total, for the assessment of the NCI panel of markers by both computational methods of allelic variability and by visual inspection the correlation with IHC was 86%.
We also assessed MSI status using an MSI score based on total allelic variability (/500). An MSI score of 1–2 was considered MSS; 3–5 MSI-L; >5 MSI-H. Again, MSI-L was excluded from correlation analysis with IHC. Based on the MSI score, there was a 94% (17/18), 87% (13/15) and 77% (10/13) correlation with IHC. In total, the correlation between MSI score with IHC was 87%.
The correlation between CGE and IHC determination of MSI status is shown in Table 5, Table 6 and Table 7. The original MSI status (determined by IHC) on the anatomical pathology report was used for comparison and representative IHC staining for MMRP and MMRD is shown in Figure 1.

Table 5.
Correlation between MSI status detection using high-resolution capillary electrophoresis with (a) traditional analysis and (b) MSI score based on total allelic variability, compared to immunohistochemistry (IHC) for MSI-H BRAF mutant tumours from patient specimens.

Table 6.
Correlation between MSI status detection using high-resolution capillary electrophoresis with (a) traditional analysis and (b) MSI score based on total allelic variability, compared to immunohistochemistry (IHC) for MSI-H:BRAF wild type tumours from patient specimens.

Table 7.
Correlation between MSI status detection using high-resolution capillary electrophoresis with (a) traditional analysis and (b) MSI score based on total allelic variability, compared to immunohistochemistry (IHC) for MSS tumours from patient specimens.
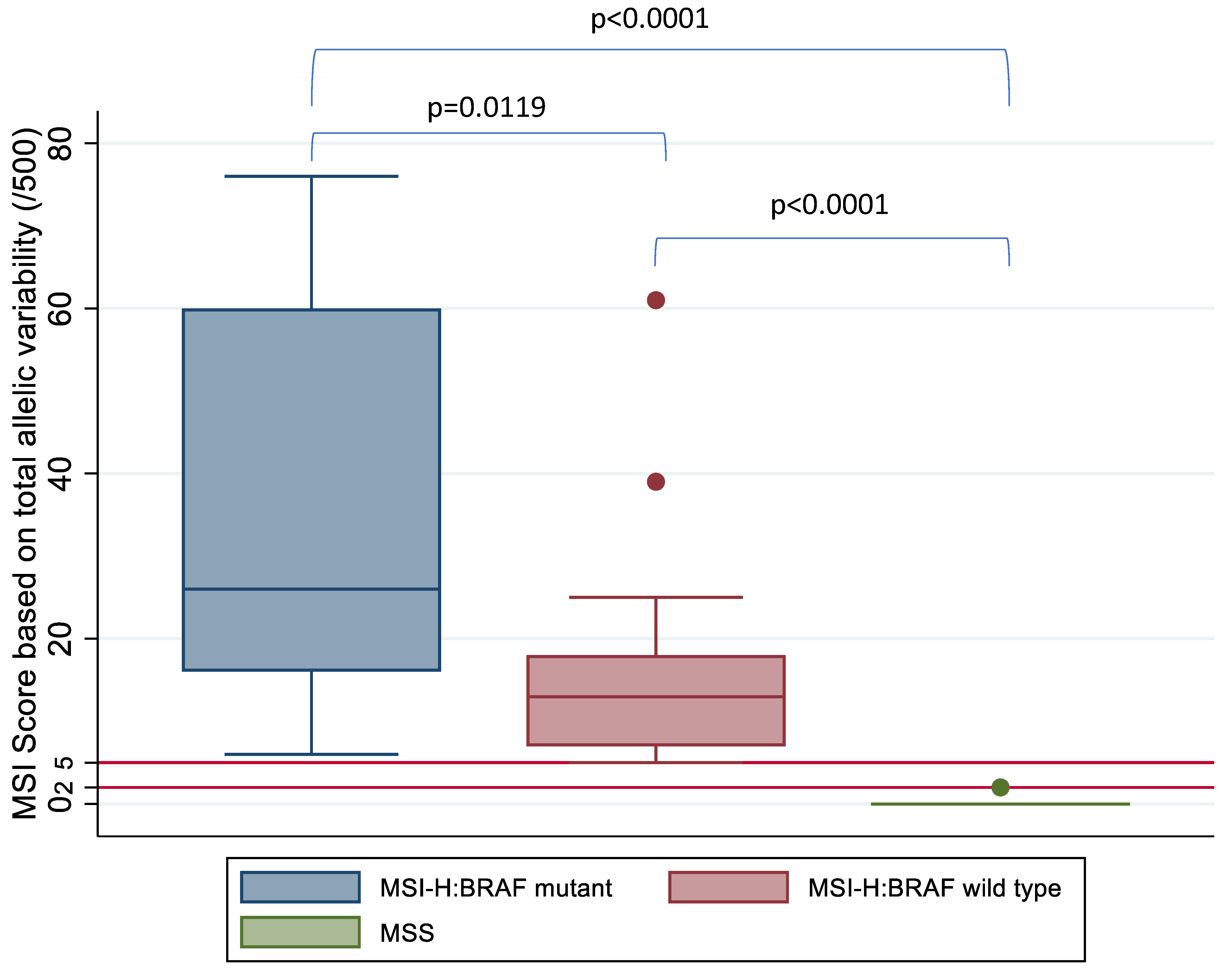
A Student t-test and Kruskal–Wallis test was used to compare the mean and median MSI score between the three groups based on MSI and BRAF status, respectively, and this demonstrated a statistically significant difference in MSI score between the MSI-H:BRAF mutant, MSI-H:BRAF wild type and MSS subgroups (Figure 5).
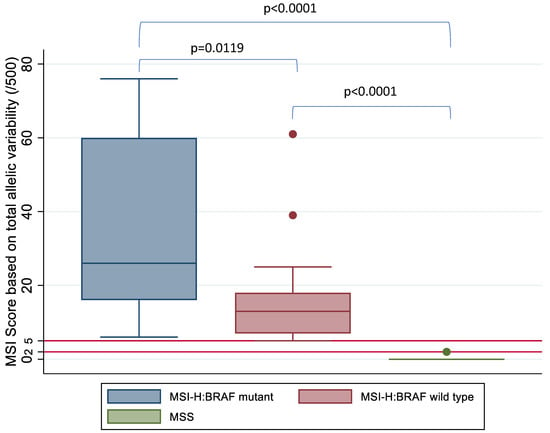
Figure 5.
MSI score based on allelic instability (/500) by MSI and BRAF status confirmed on IHC and high-resolution capillary electrophoresis. Kruskal–Wallis test shows a statistically significant difference between the three subgroups based on MSI status. Horizontal red lines mark the tiers between MSS, MSI-L and MSI-H based on MSI score.
3.4. Analysis of Discordant IHC and DNA Based MSI Status
Where the MSI status reported by IHC and CGE were different, both were re-examined. There were several misclassifications by IHC. Three MSI-H colorectal cancers identified by CGE were classified as MSS by IHC. One MSI-H:BRAF mutant and two MSI-H:BRAF wild-type colorectal cancers identified by IHC were classified as MSS using CGE. There was one sampling error (re-examination of the tumour block and the H&E section revealed <5% tumour in the specimen where the MSI-H colorectal cancer was incorrectly classified as MSS on CGE). In total, compared to IHC, which had a misclassification rate of 8.9% (5/56), there was only one misclassification due to a sampling error using CGE (1.8%) (1/56).
Furthermore, 13/56 (23%) of the specimens had only one marker displaying instability based on assessment of the NCI panel using CGE and 10/56 (18%) by MSI total allelic variability score of 3–5/500. These cancer specimens were considered MSI-L by CGE, but IHC classification was not able to distinguish MSI-L from MSS and MSI-H.
4. Discussion
Approximately 15% of colorectal cancers are microsatellite unstable [14,15,16,33], 3% are associated with Lynch syndrome and 12% due to other causes, including epigenetic silencing of MLH1. Colorectal cancer is the third most common cancer with >1.9 million cases (representing 1 in 10 cancers) worldwide and the second most common cause of cancer death (9.4% of cancer deaths) [34]. With IHC, there may be a 5–11% misclassification rate of MSI status in colorectal cancer [24,25]. This means that approximately 95,000–209,000 colorectal cancers are incorrectly classified into the wrong MSI subgroup. Furthermore, IHC fails to distinguish MSI-L from MSI-H and MSS, as IHC only classifies cancers into MSI-H/MSS. Thus, the use of only one detection method alone may lead to misdiagnosis of mismatch repair deficiency status in a small number of cases [35]. This is because IHC examines protein expression rather than DNA microsatellite sequences. In cases where MMR proteins have retained expression despite being functionally defective, IHC cannot detect MMRD.
However, most institutions perform IHC due to the significant expense and practicability issues with the complex techniques associated with DNA based testing [22], despite CGE being the gold standard [23]. With this in mind, the aim of our study was to develop a simple, accurate and cost-effective MSI test using CGE and utilizing (i) basic assessment and (ii) development of an MSI score to represent the total allelic variability of the tumour.
Currently, several different MSI analysis systems based on CGE are being used [26,27,28,29,30,31]. The strength of the MSI assay we have developed using the Fragment Analyzer System is that it is accurate, simple, practicable, automated and cost-effective. In this study, a sensitivity and specificity of 100% in determining MSI status in cancer cell lines was observed. This was similar to the study by Arulananda et al., which also reported 100% accuracy with fluorescent multiplex PCR and CGE [26]. On patient specimens, when using a basic assessment of the NCI panel of markers using both automatic computational methods and visual inspection of the electropherogram, the correlation with IHC was 86%. When using the MSI score, the correlation with IHC was 87%. This is in line with other IHC studies, with the reported accuracy of IHC being 89–95% [25]. There was only one error attributed to CGE, and this was noted to be an error with tumour sampling rather than an error with the testing regimen. CGE was able to detect allelic variability within 2 bp for fragments between 1–500 bp [36].
In terms of practicability, micro-dissection prior to DNA extraction was not required. With the 5200 Fragment Analyzer System, up to 24 cancer specimens may be tested per run (10 wells/1 row for each specimen (tumour and matched normal for each of the five markers and one well for the ladder) as each tray has 96 wells (8 rows × 12 columns) and three trays may be accommodated for each run). Furthermore, an accurate computational method to determine MSI status without visual inspection of the electropherogram has been developed in this study, requiring less user intervention and ensuring rapid reporting.
The cost of the assay developed in this study was approximately $25, compared to IHC, which costs > $100. We have thus achieved a significant cost reduction. Unlike traditional fluorescent multiplex PCR and CGE, expensive fluorescent labelled primers were not required with this test.
While techniques other than IHC and CGE for MSI status determination exist, including NGS techniques (which targets known genes for genome sequencing) [37], single-molecule molecular inversion probes (snMIPs) (which do not need matched normal tissue) [38] and the MANTIS calculation method (which requires comparisons with tumour cell detection and stained histological section images to predict MSI status) [39], these techniques have their own limitations and disadvantages [23].
Prior to this study, the issues with using CGE or using two methods of MSI detection (IHC and CGE) were its high detection cost and high sample demand [35]. In this study, we have achieved an accurate, cost-effective CGE-based test capable of high throughput with ease of use and automatic computational methods for MSI status determination for colorectal cancer. While MSI is most commonly associated with colorectal cancer, MSI may also be found in gastric, endometrial, ovarian, urinary tract, hepatobiliary, brain and skin cancers. The CGE technique and automatic computational methods developed in this study may also be useful in the determination of MSI status in these other cancers.
Limitations
In most studies using CGE, tumour tissue is micro-dissected prior to DNA extraction [29]. In this study, micro-dissection of the tumour was not performed to keep the technique simple and practicable. Instead, H&E slides were microscopically examined and specimen blocks with greater than 10% tumour were used for DNA extraction. However, in this study, one tumour block with <5% tumour tissue was utilized, leading to a sampling error. While not performing micro-dissection may lead to errors if there is insufficient tumour in the block, this study showed in the mixing experiment with cell lines that the MSI status of samples with ≥5% MSI genomic material can be accurately classified even at low tumour content.
While this test was able to accurately determine allelic instability, the clinical significance of allelic instability remains unclear. It has been shown that tumour mutational burden is an emerging biomarker for response to checkpoint inhibitors [40], but it is unknown if allelic instability may also be a biomarker for response to checkpoint inhibition and this may be an area of interest in future research direction.
5. Conclusions
A simple, cost-effective and accurate test based on CGE using the Fragment Analyzer System linked with an automated computational method to call MSI status without the need for visual inspection of the electropherogram has been developed and potentially useful in both research and clinical settings. An MSI score based on total allelic instability, which can accurately determine MSI status, as well as correlate with the degree of genetic instability of the cancer, has also been developed in this study. Future research directions may include evaluating if this MSI score correlates with tumour mutational burden and response to checkpoint inhibitors.
Author Contributions
J.W.T.T. and K.J.S. conceptualised and designed the study experimental and analytical methods and were involved in experimental runs; J.W.T.T. performed the data analysis and data modelling; J.W.T.T. developed the computational methods used in this study; J.W.T.T. drafted the manuscript; P.S. and V.A.A.S.K.T. were involved in experimental runs; A.L. was involved in archival specimen retrieval and all authors were involved in critical revisions of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (RACS) Foundation for Surgery Small Projects Research Grant REA-RES-045.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board Sydney Local Health District Ethics CH62/62011-136 HREC/11/CRGH206.
Informed Consent Statement
All patients included in this study provided written consent for the use of their information for research. No identifiable patient information was included in this study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank P. Chapuis, who maintains the Concord Colorectal Cancer Resection Database and advises on entry of clinical and follow-up data as to occurrence, date and cause of death. The authors would also like to thank P. Priestley for his important contributions to this study, C. Chan for routine pathology review and E. Sinclair for her assistance with immunohistochemistry slides, L. Bokey and G. Ctercteko for their support in performing this study. The authors thank the Royal Australasian College of Surgeons (RACS) for the Foundation for Surgery Small Projects Research Grant (JWTT) and funding support by CONCERT Translational Cancer Research Centre ( JWTT and KJS). This study was presented at the RACS Annual Scientific Congress in 2016 and won the Mark Killingback prize for best colorectal research presentation and was invited as a podium presentation at the Tripartite meeting in Seattle in 2017. This study was presented and won the Colorectal Surgical Society Australia and New Zealand (CSSANZ) research prize in 2015.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aaltonen, L.A.; Salovaara, R.; Kristo, P.; Canzian, F.; Hemminki, A.; Peltomaki, P.; Chadwick, R.B.; Kaariainen, H.; Eskelinen, M.; Jarvinen, H.; et al. Incidence of hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer and the feasibility of molecular screening for the disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1481–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. NICE Recommends Wider Use of Tests to Detect Cancer-Causing Genetic Condition; National Institute for Health and Care Excellence: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Koenig, J.L.; Toesca, D.A.S.; Harris, J.P.; Tsai, C.J.; Haraldsdottir, S.; Lin, A.Y.; Pollom, E.L.; Chang, D.T. Microsatellite Instability and Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Stage II Colon Cancer. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 42, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Des Guetz, G.; Schischmanoff, O.; Nicolas, P.; Perret, G.Y.; Morere, J.F.; Uzzan, B. Does microsatellite instability predict the efficacy of adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer? A systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer (Oxf. Engl. 1990) 2009, 45, 1890–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Mahajan, H.; Chapuis, P.; Spring, K. Current status on microsatellite instability, prognosis and adjuvant therapy in colon cancer: A nationwide survey of medical oncologists, colorectal surgeons and gastrointestinal pathologists. Cancer Rep. 2021, 4, e1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, E.M.; Kauffman, T.L.; O’Connor, E.; Goddard, K.A. Systematic review of the predictive effect of MSI status in colorectal cancer patients undergoing 5FU-based chemotherapy. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romiti, A.; Rulli, E.; Pilozzi, E.; Gerardi, C.; Roberto, M.; Legramandi, L.; Falcone, R.; Pacchetti, I.; Marchetti, P.; Floriani, I. Exploring the Prognostic Role of Microsatellite Instability in Patients with Stage II Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Available online: http://www.journals.elsevier.com/clinical-colorectal-cancer; http://ovidsp.ovid.com/ovidweb.cgi?T=JS&PAGE=reference&D=emex&NEWS=N&AN=613354522 (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Elsaleh, H.; Joseph, D.; Grieu, F.; Zeps, N.; Spry, N.; Iacopetta, B. Association of tumour site and sex with survival benefit from adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. Lancet 2000, 355, 1745–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, G.H.J.; Chee, C.E. Making sense of adjuvant chemotherapy in colorectal cancer. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2019, 10, 1183–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertagnolli, M.M.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Compton, C.C.; Hahn, H.P.; Hall, M.; Damas, B.; Jewell, S.D.; Mayer, R.J.; Goldberg, R.M.; Saltz, L.B.; et al. Microsatellite instability predicts improved response to adjuvant therapy with irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin in stage III colon cancer: Cancer and Leukemia Group B Protocol 89803. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2009, 27, 1814–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.T.; Lee, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, J.O.; Lim, H.Y.; Kang, W.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Chang, D.K.; Rhee, P.L.; et al. Clinical impact of microsatellite instability in colon cancer following adjuvant FOLFOX therapy. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2010, 66, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labianca, R.; Nordlinger, B.; Beretta, G.D.; Mosconi, S.; Mandala, M.; Cervantes, A.; Arnold, D. Early colon cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med Oncol. ESMO 2013, 24 (Suppl. 6), 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ESMO Guidelines Committee eUpdate Early Colon Cancer Treatment Recommendations. 2019. Available online: https://www.esmo.org/guidelines/gastrointestinal-cancers/early-colon-cancer/eupdate-early-colon-cancer-treatment-recommendations (accessed on 30 April 2021).
- Popat, S.; Hubner, R.; Houlston, R.S. Systematic review of microsatellite instability and colorectal cancer prognosis. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 609–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guastadisegni, C.; Colafranceschi, M.; Ottini, L.; Dogliotti, E. Microsatellite instability as a marker of prognosis and response to therapy: A meta-analysis of colorectal cancer survival data. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 2788–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Phan, K.; Reza, F.; Chapuis, P.; Spring, K.J. Rate of dissemination and prognosis in early and advanced stage colorectal cancer based on microsatellite instability status: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toh, J.W.T.; Lim, S.H.; MacKenzie, S.; de Souza, P.; Bokey, L.; Chapuis, P.; Spring, K.J. Association Between Microsatellite Instability Status and Peri-Operative Release of Circulating Tumour Cells in Colorectal Cancer. Cells 2020, 9, 425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.W.; de Souza, P.; Lim, S.H.; Singh, P.; Chua, W.; Ng, W.; Spring, K.J. The Potential Value of Immunotherapy in Colorectal Cancers: Review of the Evidence for Programmed Death-1 Inhibitor Therapy. Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2016, 15, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, J.; Overman, S.K.; Raymond, S.M.; Leach, J.; Lonardi, S.; Lenz, H.; Michael, A.; Morse, J.D.; Andrew, H.; Michael, D.; et al. A Study of Nivolumab and Nivolumab Plus Ipilimumab in Recurrent and Metastatic Colon Cancer (CheckMate 142). J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Boland, C.R.; Thibodeau, S.N.; Hamilton, R.; Sidransky, D.; Eshleman, R.; Burt, W.; Meltzer, J.; Rodriguez-Bigas, A.; Fodde, R.; Ranzani, N.; et al. A National Cancer Institute workshop on microsatellite instability for cancer detection and familial predisposition: Development of international criteria for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 5248–5257. [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeau, S.N.; Bren, G.; Schaid, D. Microsatellite instability in cancer of the proximal colon. Science 1993, 260, 816–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palomaki, G.E.; McClain, M.R.; Melillo, S.; Hampel, H.L.; Thibodeau, S.N. EGAPP supplementary evidence review: DNA testing strategies aimed at reducing morbidity and mortality from Lynch syndrome. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med Genet. 2009, 11, 42–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Luo, H.; Huang, L.; Luo, H.; Zhu, X. Microsatellite instability: A review of what the oncologist should know. Cancer Cell Int. 2020, 20, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacher, J.W.; Flanagan, L.A.; Smalley, R.L.; Nassif, N.A.; Burgart, L.J.; Halberg, R.B.; Megid, W.M.; Thibodeau, S.N. Development of a fluorescent multiplex assay for detection of MSI-High tumors. Dis. Markers 2004, 20, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheah, P.L.; Li, J.; Looi, L.M.; Koh, C.C.; Lau, T.P.; Chang, S.W.; Teoh, K.H.; Mun, K.S.; Nazarina, A.R. Screening for microsatellite instability in colorectal carcinoma: Practical utility of immunohistochemistry and PCR with fragment analysis in a diagnostic histopathology setting. Malays. J. Pathol. 2019, 41, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arulananda, S.; Thapa, B.; Walkiewicz, M.; Zapparoli, G.V.; Williams, D.S.; Dobrovic, A.; John, T. Mismatch Repair Protein Defects and Microsatellite Instability in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2018, 13, 1588–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suraweera, N.; Duval, A.; Reperant, M.; Vaury, C.; Furlan, D.; Leroy, K.; Seruca, R.; Iacopetta, B.; Hamelin, R. Evaluation of tumor microsatellite instability using five quasimonomorphic mononucleotide repeats and pentaplex PCR. Gastroenterology 2002, 123, 1804–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shemirani, A.I.; Haghighi, M.M.; Zadeh, S.M.; Fatemi, S.R.; Taleghani, M.Y.; Zali, N.; Akbari, Z.; Kashfi, S.M.; Zali, M.R. Simplified MSI marker panel for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. APJCP 2011, 12, 2101–2104. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, K.M.; Zhang, S.; Geiger, T.; Hafez, M.J.; Bacher, J.; Berg, K.D.; Eshleman, J.R. Comparison of the microsatellite instability analysis system and the Bethesda panel for the determination of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancers. J. Mol. Diagn. JMD 2006, 8, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, A.; Nagasaka, T.; Hamelin, R.; Boland, C.R. An optimized pentaplex PCR for detecting DNA mismatch repair-deficient colorectal cancers. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buhard, O.; Suraweera, N.; Lectard, A.; Duval, A.; Hamelin, R. Quasimonomorphic mononucleotide repeats for high-level microsatellite instability analysis. Dis. Markers 2004, 20, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umetani, N.; Sasaki, S.; Watanabe, T.; Ishigami, H.; Ueda, E.; Nagawa, H. Diagnostic primer sets for microsatellite instability optimized for a minimal amount of damaged DNA from colorectal tissue samples. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2000, 7, 276–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, J.; Chapuis, P.H.; Bokey, L.; Chan, C.; Spring, K.J.; Dent, O.F. Competing risks analysis of microsatellite instability as a prognostic factor in colorectal cancer. Br. J. Surg. 2017, 104, 1250–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, R.; Hain, E.; Buhard, O.; Guilloux, A.; Bardier, A.; Kaci, R.; Bertheau, P.; Renaud, F.; Bibeau, F.; Fléjou, J.F.; et al. Association of Primary Resistance to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer with Misdiagnosis of Microsatellite Instability or Mismatch Repair Deficiency Status. JAMA Oncol. 2019, 5, 551–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Analytical, A. Impact of Accurate Qualification and Quantification of Fragments; MipTec: Basel, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, D.T.; Prasad, M.; Chekaluk, Y.; Benayed, R.; Sadowska, J.; Zehir, A.; Syed, A.; Wang, Y.E.; Somar, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Comprehensive detection of germline variants by MSK-IMPACT, a clinical diagnostic platform for solid tumor molecular oncology and concurrent cancer predisposition testing. BMC Med. Genom. 2017, 10, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waalkes, A.; Smith, N.; Penewit, K.; Hempelmann, J.; Konnick, E.Q.; Hause, R.J.; Pritchard, C.C.; Salipante, S.J. Accurate Pan-Cancer Molecular Diagnosis of Microsatellite Instability by Single-Molecule Molecular Inversion Probe Capture and High-Throughput Sequencing. Clin. Chem. 2018, 64, 950–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kautto, E.A.; Bonneville, R.; Miya, J.; Yu, L.; Krook, M.A.; Reeser, J.W.; Roychowdhury, S. Performance evaluation for rapid detection of pan-cancer microsatellite instability with MANTIS. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 7452–7463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalmers, Z.R.; Connelly, C.F.; Fabrizio, D.; Gay, L.; Ali, S.M.; Ennis, R.; Schrock, A.; Campbell, B.; Shlien, A.; Chmielecki, J.; et al. Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).