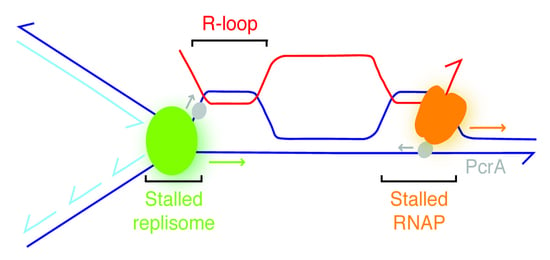
Bacillus subtilis PcrA Helicase Removes Trafficking Barriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Plasmids
2.2. Viability and Survival Assays
2.3. Fluorescence Microscopy and Data Analysis
2.4. Enzymes, Reagents, Protein, and DNA Purification
2.5. DNA Binding Assays
2.6. Nucleotide Hydrolysis Assays
2.7. DNA Unwinding Assays
3. Results
3.1. Experimental Rationale
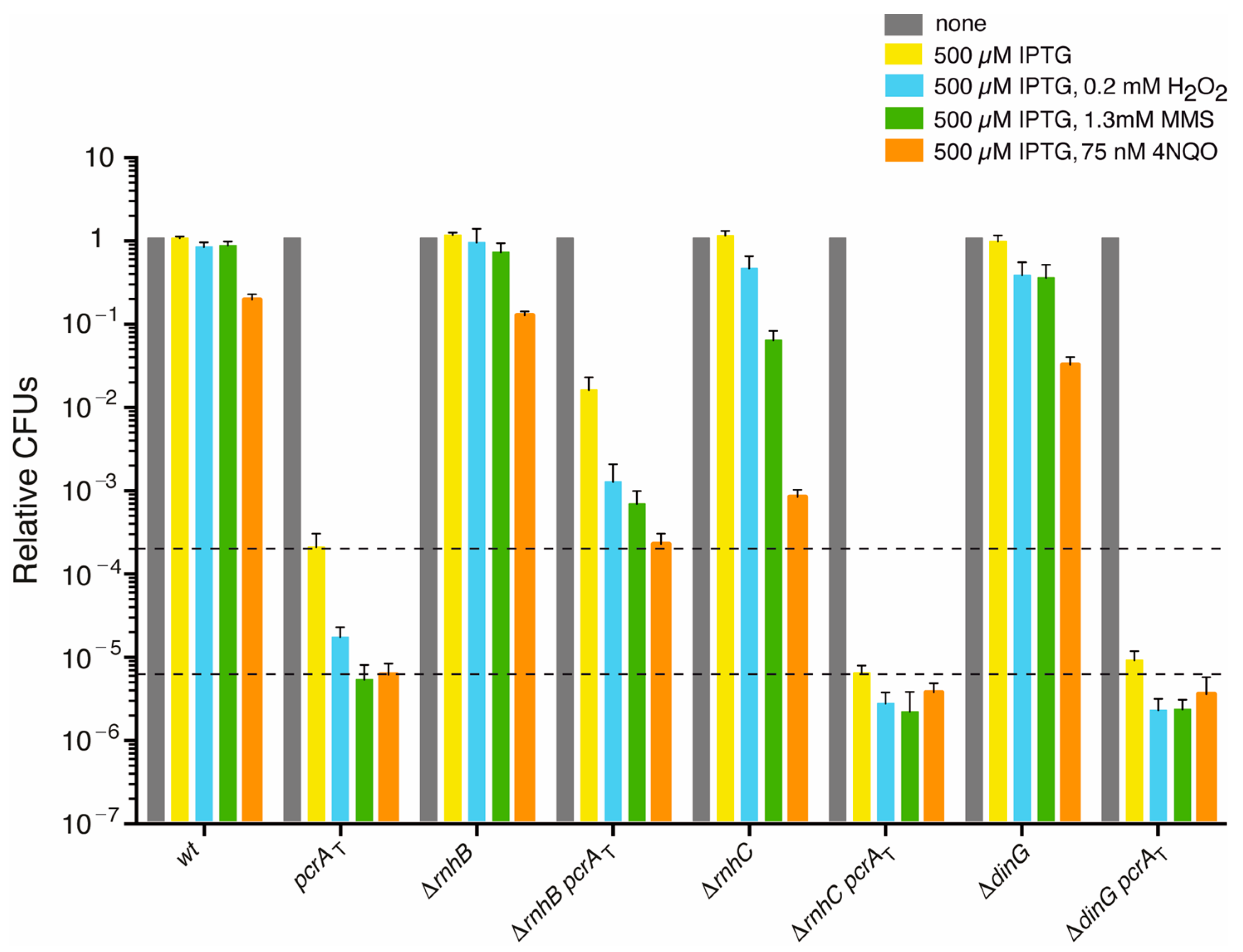
3.2. PcrA Lethality Is Partially Suppressed by rnhB Inactivation
3.3. PcrA Is Required to Overcome a Replicative Stress
3.4. PcrA Inviability Does Not Require RnhC or DinG
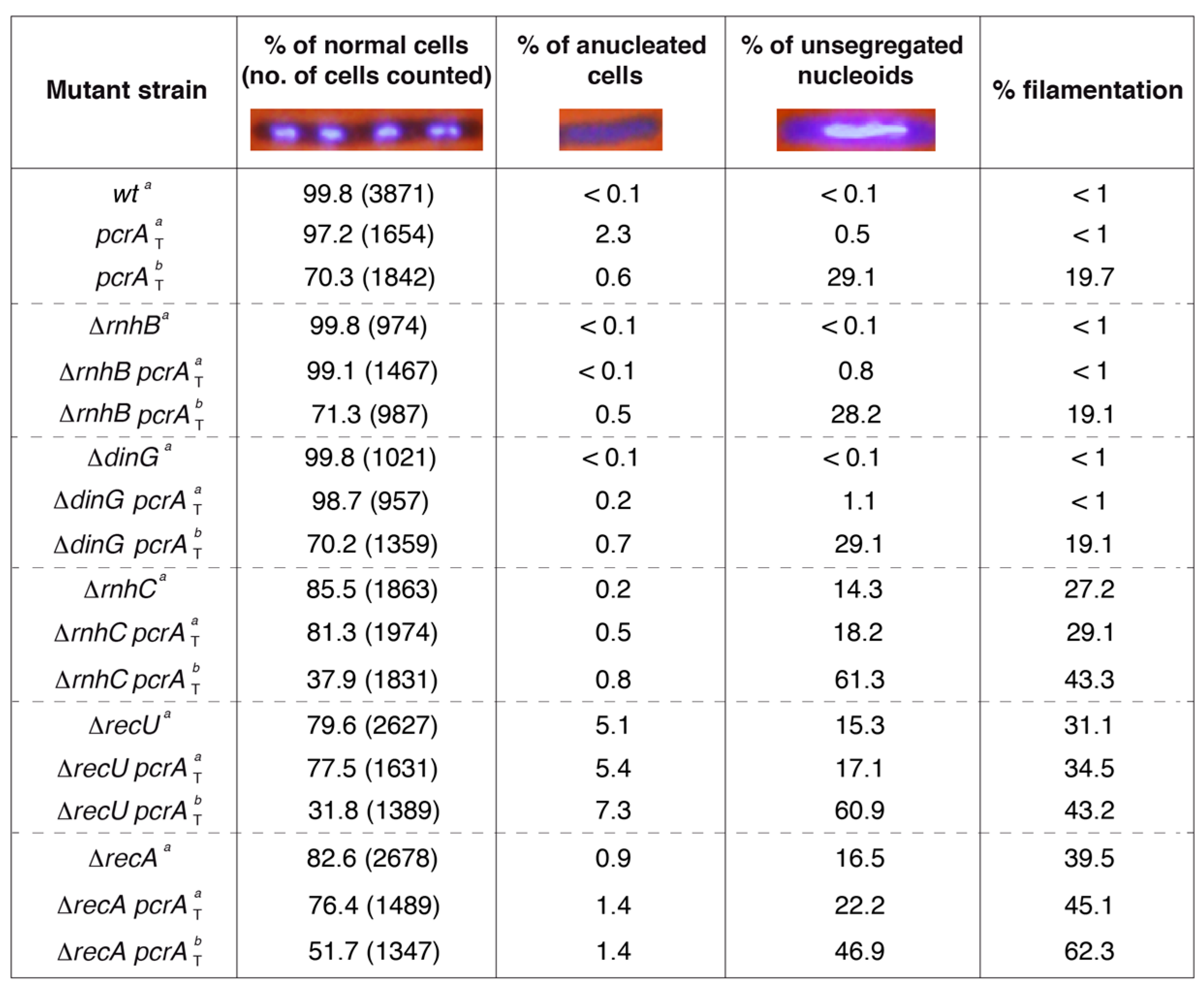
3.5. PcrA Depletion Leads to Unsegregated Chromosomes in the ΔrnhC Context
3.6. The ΔrecA Mutation Is Synthetically Lethal in the ΔrnhC Context
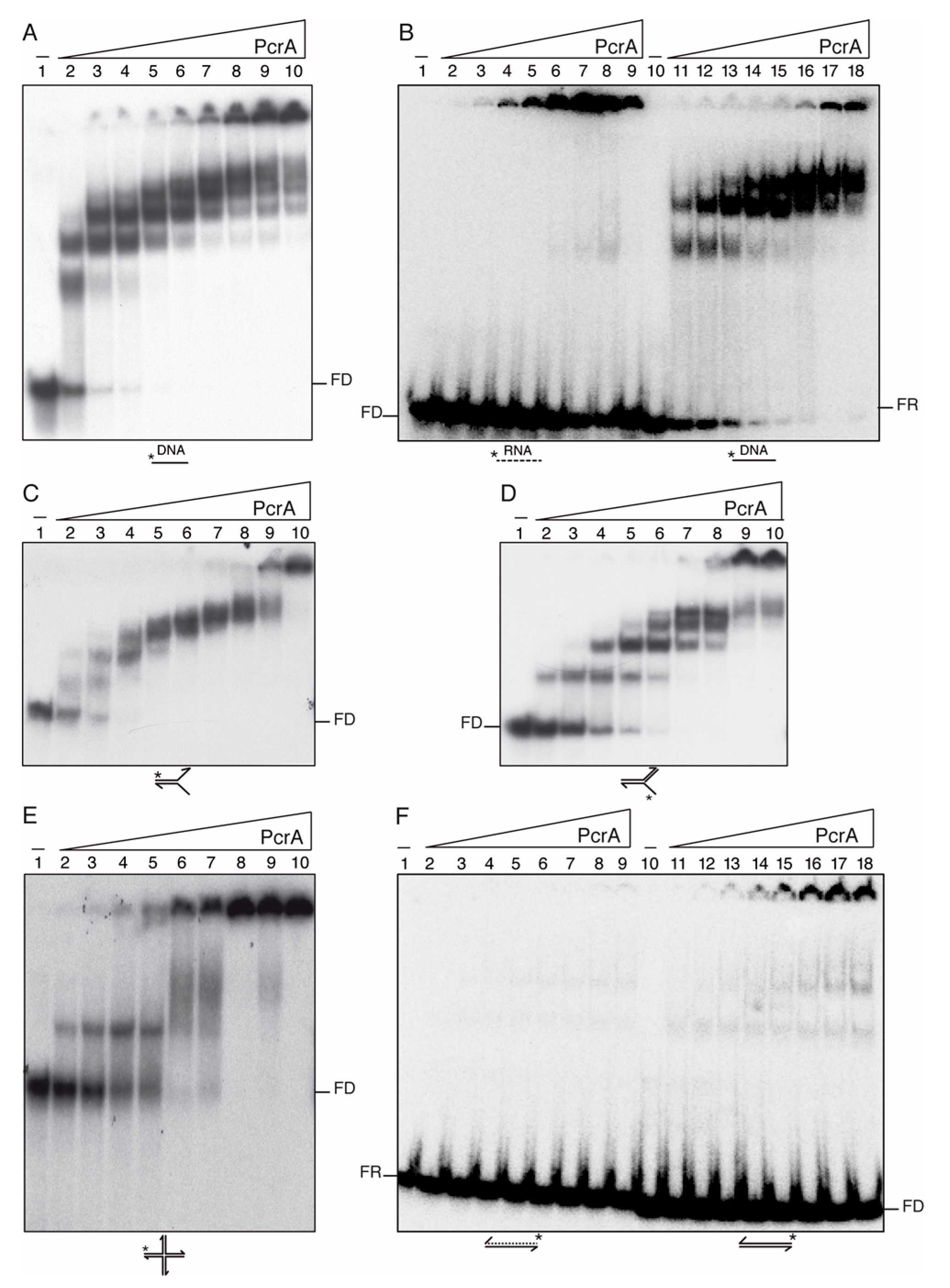
3.7. PcrA Preferentially Binds ssDNA and RNA
3.8. PcrA Is an ssDNA-Dependent ATPase
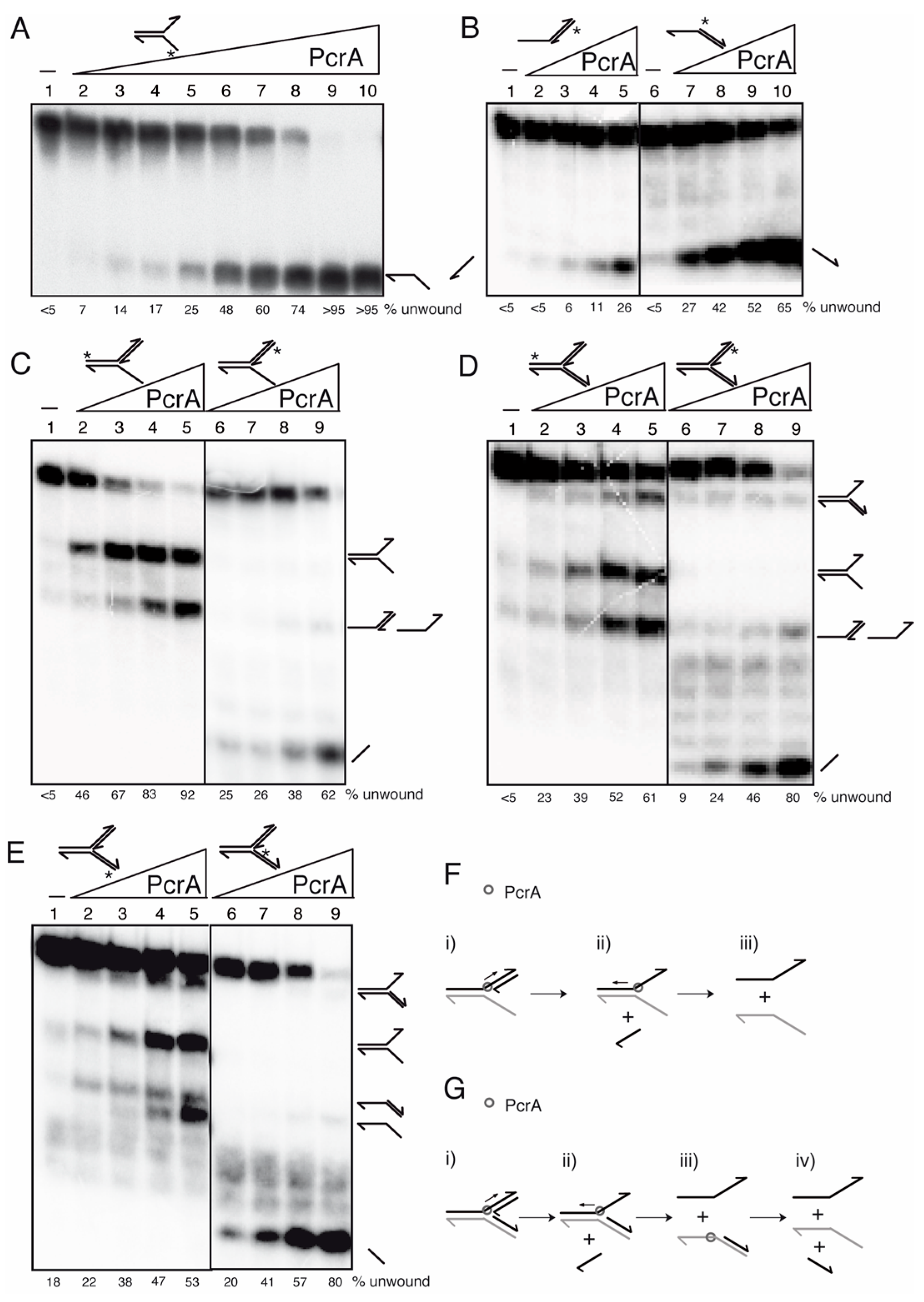
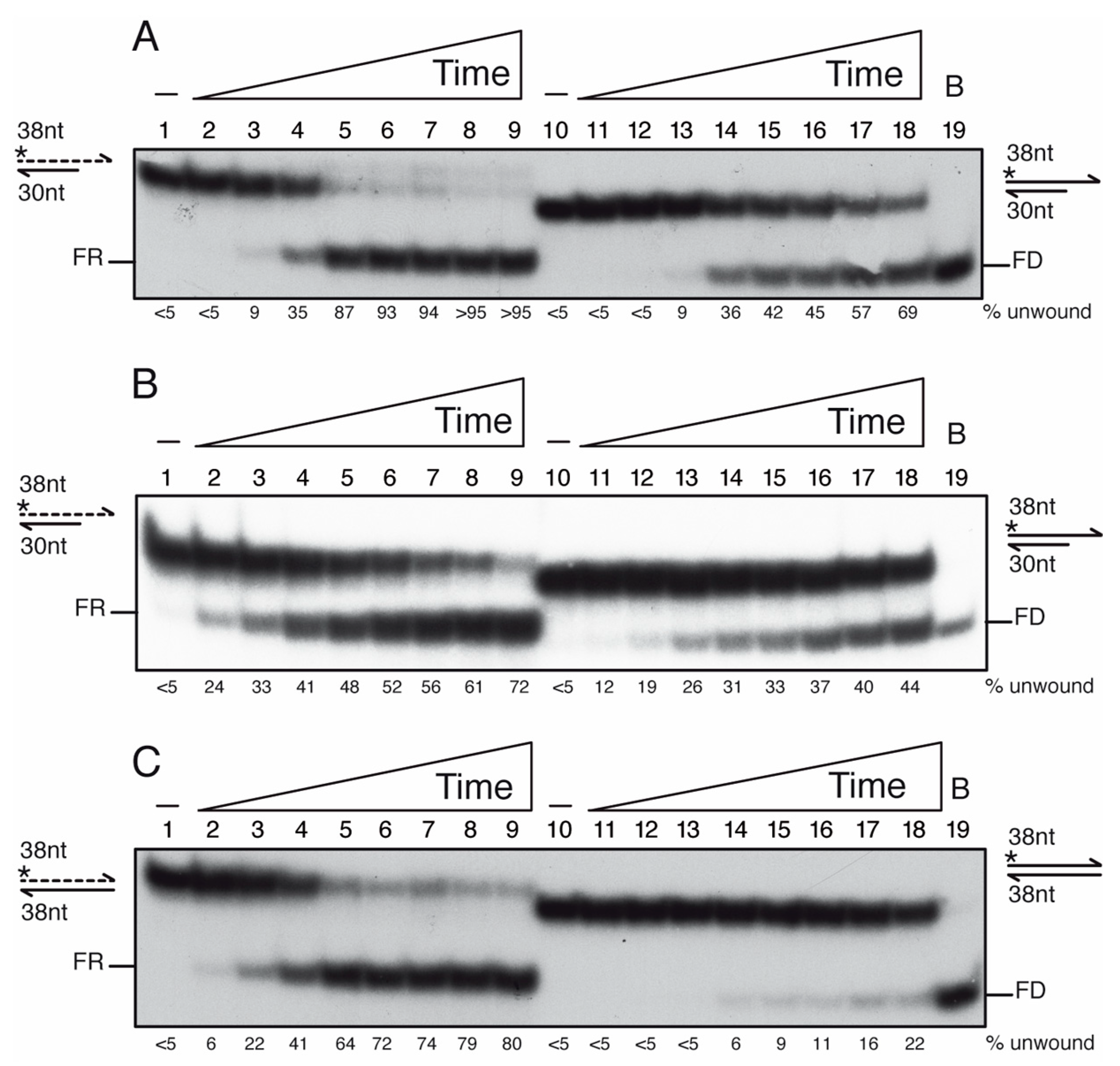
3.9. PcrA Preferentially Unwinds ssDNA in the 3′→ 5′ Direction
3.10. PcrA Unwinds RNA-DNA Hybrids
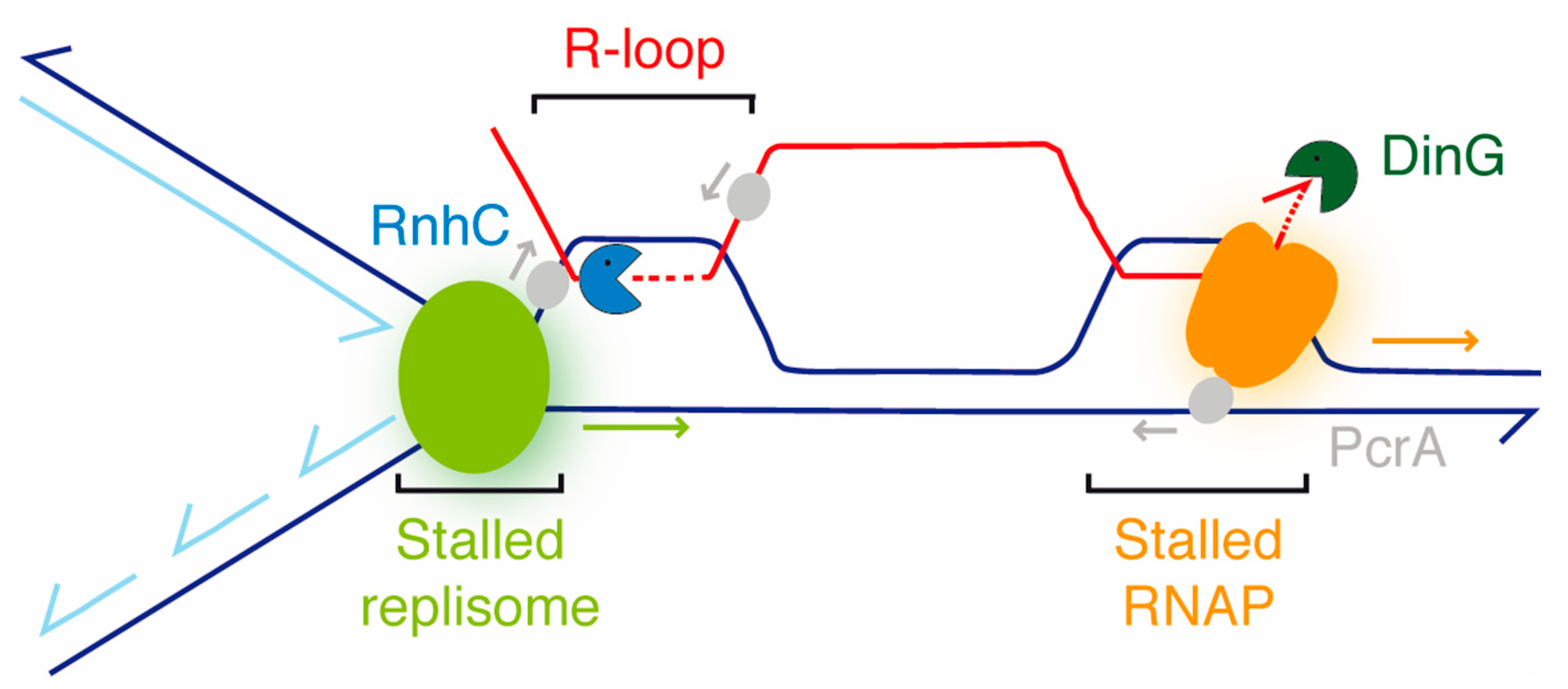
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Note Added in Proof
References
- Mirkin, E.V.; Mirkin, S.M. Replication fork stalling at natural impediments. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2007, 71, 13–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilera, A.; Garcia-Muse, T. R loops: From transcription byproducts to threats to genome stability. Mol. Cell. 2012, 46, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, H.; Aguilera, A. Transcription as a threat to genome integrity. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2016, 85, 291–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.S.; Merrikh, H. The clash of macromolecular titans: Replication-transcription conflicts in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 72, 71–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamperl, S.; Cimprich, K.A. Conflict resolution in the genome: How transcription and replication make it work. Cell 2016, 167, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crossley, M.P.; Bocek, M.; Cimprich, K.A. R-Loops as cellular regulators and genomic threats. Mol. Cell. 2019, 73, 398–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, D.; Shatalin, K.; Epshtein, V.; Gottesman, M.E.; Nudler, E. Linking RNA polymerase backtracking to genome instability in E. coli. Cell 2011, 146, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masukata, H.; Tomizawa, J. Effects of point mutations on formation and structure of the RNA primer for ColE1 DNA replication. Cell 1984, 36, 513–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viguera, E.; Hernandez, P.; Krimer, D.B.; Boistov, A.S.; Lurz, R.; Alonso, J.C.; Schvartzman, J.B. The ColE1 unidirectional origin acts as a polar replication fork pausing site. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 22414–22421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubakri, H.; de Septenville, A.L.; Viguera, E.; Michel, B. The helicases DinG, Rep and UvrD cooperate to promote replication across transcription units in vivo. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrikh, H.; Machon, C.; Grainger, W.H.; Grossman, A.D.; Soultanas, P. Co-directional replication-transcription conflicts lead to replication restart. Nature 2011, 470, 554–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrikh, C.N.; Brewer, B.J.; Merrikh, H. The B. subtilis accessory helicase PcrA facilitates DNA replication through transcription units. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1005289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, K.S.; Hall, A.N.; Merrikh, C.N.; Ragheb, M.; Tabakh, H.; Pollock, A.J.; Woodward, J.J.; Dreifus, J.E.; Merrikh, H. Replication-transcription conflicts generate R-Loops that orchestrate bacterial stress survival and pathogenesis. Cell 2017, 170, 787–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlasic, I.; Mertens, R.; Seco, E.M.; Carrasco, B.; Ayora, S.; Reitz, G.; Commichau, F.M.; Alonso, J.C.; Moeller, R. Bacillus subtilis RecA and its accessory factors, RecF, RecO, RecR and RecX, are required for spore resistance to DNA double-strand break. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, M.R.; Dillingham, M.S.; Wigley, D.B. Structure and mechanism of helicases and nucleic acid translocases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2007, 76, 23–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petit, M.A.; Dervyn, E.; Rose, M.; Entian, K.D.; McGovern, S.; Ehrlich, S.D.; Bruand, C. PcrA is an essential DNA helicase of Bacillus subtilis fulfilling functions both in repair and rolling-circle replication. Mol. Microbiol. 1998, 29, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Del Alamo, M.; Torres, R.; Manfredi, C.; Ruiz-Maso, J.A.; Del Solar, G.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis PcrA couples DNA replication, transcription, recombination and segregation. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2020, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit, M.A.; Ehrlich, D. Essential bacterial helicases that counteract the toxicity of recombination proteins. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3137–3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guy, C.P.; Atkinson, J.; Gupta, M.K.; Mahdi, A.A.; Gwynn, E.J.; Rudolph, C.J.; Moon, P.B.; van Knippenberg, I.C.; Cadman, C.J.; Dillingham, M.S.; et al. Rep provides a second motor at the replisome to promote duplication of protein-bound DNA. Mol. Cell. 2009, 36, 654–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baharoglu, Z.; Lestini, R.; Duigou, S.; Michel, B. RNA polymerase mutations that facilitate replication progression in the rep uvrD recF mutant lacking two accessory replicative helicases. Mol. Microbiol. 2010, 77, 324–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myka, K.K.; Hawkins, M.; Syeda, A.H.; Gupta, M.K.; Meharg, C.; Dillingham, M.S.; Savery, N.J.; Lloyd, R.G.; McGlynn, P. Inhibiting translation elongation can aid genome duplication in Escherichia coli. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, 2571–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, M.M. Regulation of bacterial RecA protein function. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2007, 42, 41–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bell, J.C.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. RecA: Regulation and Mechanism of a Molecular Search Engine. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2016, 41, 491–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasahara, M.; Clikeman, J.A.; Bates, D.B.; Kogoma, T. RecA protein-dependent R-loop formation in vitro. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 360–365. [Google Scholar]
- Zaitsev, E.N.; Kowalczykowski, S.C. A novel pairing process promoted by Escherichia coli RecA protein: Inverse DNA and RNA strand exchange. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 740–749. [Google Scholar]
- Krejci, L.; Van Komen, S.; Li, Y.; Villemain, J.; Reddy, M.S.; Klein, H.; Ellenberger, T.; Sung, P. DNA helicase Srs2 disrupts the Rad51 presynaptic filament. Nature 2003, 423, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veaute, X.; Jeusset, J.; Soustelle, C.; Kowalczykowski, S.C.; Le Cam, E.; Fabre, F. The Srs2 helicase prevents recombination by disrupting Rad51 nucleoprotein filaments. Nature 2003, 423, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veaute, X.; Delmas, S.; Selva, M.; Jeusset, J.; Le Cam, E.; Matic, I.; Fabre, F.; Petit, M.A. UvrD helicase, unlike Rep helicase, dismantles RecA nucleoprotein filaments in Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Zheng, H.; Bianco, P.R.; Leuba, S.H.; Khan, S.A. DNA helicase activity of PcrA is not required for the displacement of RecA protein from DNA or inhibition of RecA-mediated strand exchange. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 4502–4509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Park, J.; Myong, S.; Niedziela-Majka, A.; Lee, K.S.; Yu, J.; Lohman, T.M.; Ha, T. PcrA helicase dismantles RecA filaments by reeling in DNA in uniform steps. Cell 2010, 142, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delumeau, O.; Lecointe, F.; Muntel, J.; Guillot, A.; Guedon, E.; Monnet, V.; Hecker, M.; Becher, D.; Polard, P.; Noirot, P. The dynamic protein partnership of RNA polymerase in Bacillus subtilis. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2992–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, K.; Lin, C.L.; Smith, A.J.; Cronin, N.; Fisher, G.; Eftychidis, V.; McGlynn, P.; Savery, N.J.; Wigley, D.B.; Dillingham, M.S. The structure and function of an RNA polymerase interaction domain in the PcrA/UvrD helicase. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3875–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogoma, T. Stable DNA replication: Interplay between DNA replication, homologous recombination, and transcription. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 1997, 61, 212–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, F.; Alonso, J.C. The β recombinase of plasmid pSM19035 binds to two adjacent sites, making different contacts at each of them. Nucl. Acids Res. 1995, 23, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rojo, F.; Alonso, J.C. The β recombinase from the Streptococcal plasmid pSM19035 represses its own transcription by holding the RNA polymerase at the promoter region. Nucl. Acids Res. 1994, 22, 1855–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso, J.C.; Ayora, S.; Canosa, I.; Weise, F.; Rojo, F. Site-specific recombination in Gram-positive θ-replicating plasmids. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 1996, 142, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, R.; Romero, H.; Rodríguez-Cerrato, V.; Alonso, J.C. Interplay between Bacillus subtilis RecD2 and the RecG or RuvAB helicase in recombinational repair. DNA Repair 2017, 55, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keiler, K.C.; Waller, P.R.; Sauer, R.T. Role of a peptide tagging system in degradation of proteins synthesized from damaged messenger RNA. Science 1996, 271, 990–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, K.L.; Grossman, A.D. Inducible protein degradation in Bacillus subtilis using heterologous peptide tags and adaptor proteins to target substrates to the protease ClpXP. Mol. Microbiol. 2008, 70, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, J.C.; Lüder, G.; Tailor, R.H. Characterization of Bacillus subtilis recombinational pathways. J. Bacteriol. 1991, 173, 3977–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, B.; Cozar, M.C.; Lurz, R.; Alonso, J.C.; Ayora, S. Genetic recombination in Bacillus subtilis 168: Contribution of Holliday junction processing functions in chromosome segregation. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 5557–5566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGregor, N.; Ayora, S.; Sedelnikova, S.; Carrasco, B.; Alonso, J.C.; Thaw, P.; Rafferty, J. The structure of Bacillus subtilis RecU Holliday junction resolvase and its role in substrate selection and sequence-specific cleavage. Structure 2005, 13, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zecchi, L.; Lo Piano, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Cañas, C.; Takeyasu, K.; Ayora, S. Characterization of the Holliday junction resolving enzyme encoded by the Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPP1. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadav, T.; Carrasco, B.; Myers, A.R.; George, N.P.; Keck, J.L.; Alonso, J.C. Genetic recombination in Bacillus subtilis: A division of labor between two single-strand DNA-binding proteins. Nucl. Acids Res. 2012, 40, 5546–5559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Del Alamo, M.; Tabone, M.; Muñoz-Martinez, J.; Valverde, J.R.; Alonso, J.C. Toxin ζ reduces the ATP and modulates the uridine diphosphate-N-acetylglucosamine pool. Toxins 2019, 11, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayora, S.; Weise, F.; Mesa, P.; Stasiak, A.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis bacteriophage SPP1 hexameric DNA helicase, G40P, interacts with forked DNA. Nucl. Acids Res. 2002, 30, 2280–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, R.; Serrano, E.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis RecA interacts with and loads RadA/Sms to unwind recombination intermediates during natural chromosomal transformation. Nucl. Acids Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selby, C.P.; Sancar, A. Mechanisms of transcription-repair coupling and mutation frequency decline. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisker, C.; Kuper, J.; Van Houten, B. Prokaryotic nucleotide excision repair. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a012591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, O.N.; Vanevski, F.; Khil, P.P.; Camerini-Otero, R.D. Characterization of the DNA damage-inducible helicase DinG from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 28284–28293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voloshin, O.N.; Camerini-Otero, R.D. The DinG protein from Escherichia coli is a structure-specific helicase. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 18437–18447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goranov, A.I.; Kuester-Schoeck, E.; Wang, J.D.; Grossman, A.D. Characterization of the global transcriptional responses to different types of DNA damage and disruption of replication in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 5595–5605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McRobbie, A.M.; Meyer, B.; Rouillon, C.; Petrovic-Stojanovska, B.; Liu, H.; White, M.F. Staphylococcus aureus DinG, a helicase that has evolved into a nuclease. Biochem. J. 2012, 442, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, Q.; Mahdi, A.A.; Briggs, G.S.; Sharples, G.J.; Lloyd, R.G. Conservation of RecG activity from pathogens to hyperthermophiles. DNA Repair 2005, 4, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochiwa, H.; Tomita, M.; Kanai, A. Evolution of ribonuclease H genes in prokaryotes to avoid inheritance of redundant genes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2007, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itaya, M.; Omori, A.; Kanaya, S.; Crouch, R.J.; Tanaka, T.; Kondo, K. Isolation of RNase H genes that are essential for growth of Bacillus subtilis 168. J. Bacteriol. 1999, 181, 2118–2123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtani, N.; Haruki, M.; Morikawa, M.; Crouch, R.J.; Itaya, M.; Kanaya, S. Identification of the genes encoding Mn2+-dependent RNase HII and Mg2+-dependent RNase HIII from Bacillus subtilis: Classification of RNases H into three families. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 605–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, S.; Itaya, M.; Kato, H.; Ogasawara, N.; Yoshikawa, H. Reassessment of the in vivo functions of DNA polymerase I and RNase H in bacterial cell growth. J. Bacteriol. 2007, 189, 8575–8583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Chatterjee, D.; Glickman, M.S.; Shuman, S. Division of labor among Mycobacterium smegmatis RNase H enzymes: RNase H1 activity of RnhA or RnhC is essential for growth whereas RnhB and RnhA guard against killing by hydrogen peroxide in stationary phase. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, N.Y.; Schroeder, J.W.; Yurieva, O.; Simmons, L.A.; O’Donnell, M.E. Cost of rNTP/dNTP pool imbalance at the replication fork. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12942–12947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.W.; Randall, J.R.; Matthews, L.A.; Simmons, L.A. Ribonucleotides in bacterial DNA. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 50, 181–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vaisman, A.; Woodgate, R. Redundancy in ribonucleotide excision repair: Competition, compensation, and cooperation. DNA Repair 2015, 29, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Randall, J.R.; Hirst, W.G.; Simmons, L.A. Substrate specificity for bacterial RNases HII and HIII is influenced by metal availability. J. Bacteriol. 2018, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, A.; McDonald, J.P.; Huston, D.; Kuban, W.; Liu, L.; Van Houten, B.; Woodgate, R. Removal of misincorporated ribonucleotides from prokaryotic genomes: An unexpected role for nucleotide excision repair. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imlay, J.A.; Linn, S. Bimodal pattern of killing of DNA-repair-defective or anoxically grown Escherichia coli by hydrogen peroxide. J. Bacteriol. 1986, 166, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedberg, E.C.; Walker, G.C.; Siede, W.; Wood, R.D.; Schultz, R.A.; Ellenberger, T. DNA Repair and Mutagenesis; ASM Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sedgwick, B. Repairing DNA-methylation damage. Nature Rev Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 5, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, H.; Shen, Y.; Huang, F.; Patel, M.; Yang, T.; Ashley, K.; Mazin, A.V.; Storici, F. Transcript-RNA-templated DNA recombination and repair. Nature 2014, 515, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidane, D.; Sánchez, H.; Alonso, J.C.; Graumann, P.L. Visualization of DNA double-strand break repair in live bacteria reveals dynamic recruitment of Bacillus subtilis RecF, RecO and RecN proteins to distinct sites on the nucleoids. Mol. Microbiol. 2004, 52, 1627–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savery, N.J. The molecular mechanism of transcription-coupled DNA repair. Trends Microbiol. 2007, 15, 326–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolak, C.; Ma, H.J.; Soubry, N.; Sandler, S.J.; Reyes-Lamothe, R.; Keck, J.L. Interaction with single-stranded DNA-binding protein localizes Ribonuclease HI to DNA replication forks and facilitates R-loop removal. Mol. Microbiol. 2020, 114, 495–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayora, S.; Carrasco, B.; Doncel, E.; Lurz, R.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis RecU protein cleaves Holliday junctions and anneals single-stranded DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahba, L.; Gore, S.K.; Koshland, D. The homologous recombination machinery modulates the formation of RNA-DNA hybrids and associated chromosome instability. Elife 2013, 2, e00505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimude, J.U.; Stockum, A.; Midgley-Smith, S.L.; Upton, A.L.; Foster, H.A.; Khan, A.; Saunders, N.J.; Retkute, R.; Rudolph, C.J. The Consequences of replicating in the wrong orientation: Bacterial chromosome duplication without an active replication origin. mBio 2015, 6, e01294-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrasco, B.; Yadav, T.; Serrano, E.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis RecO and SsbA are crucial for RecA-mediated recombinational DNA repair. Nucl. Acids Res. 2015, 43, 5984–5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.; Barroso, S.I.; Garcia-Rubio, M.L.; Tumini, E.; Herrera-Moyano, E.; Aguilera, A. BRCA2 prevents R-loop accumulation and associates with TREX-2 mRNA export factor PCID2. Nature 2014, 511, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.P.; Khan, S.A. Structure-specific DNA binding and bipolar helicase activities of PcrA. Nucl. Acids Res. 2004, 32, 3190–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Matson, S.W. Escherichia coli DNA helicase II (uvrD gene product) catalyzes the unwinding of DNA.RNA hybrids in vitro. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1989, 86, 4430–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, L.E.; Brannigan, J.A.; Subramanya, H.S.; Wigley, D.B. Characterisation of Bacillus stearothermophilus PcrA helicase: Evidence against an active rolling mechanism. Nucl. Acids Res. 1998, 26, 2686–2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soultanas, P.; Dillingham, M.S.; Velankar, S.S.; Wigley, D.B. DNA binding mediates conformational changes and metal ion coordination in the active site of PcrA helicase. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 290, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrutia-Irazabal, I.; Ault, J.R.; Sobott, F.; Savery, N.J.; Dillingham, M.S. Analysis of the PcrA-RNA polymerase complex reveals a helicase interaction motif and a role for PcrA/UvrD helicase in the suppression of R-loops. bioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epshtein, V.; Kamarthapu, V.; McGary, K.; Svetlov, V.; Ueberheide, B.; Proshkin, S.; Mironov, A.; Nudler, E. UvrD facilitates DNA repair by pulling RNA polymerase backwards. Nature 2014, 505, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Runyon, G.T.; Bear, D.G.; Lohman, T.M. Escherichia coli helicase II (UvrD) protein initiates DNA unwinding at nicks and blunt ends. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6383–6387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, K.S.; Merrikh, H. Topological stress is responsible for the detrimental outcomes of head-on replication-transcription conflicts. Cell Rep. 2021, 34, 108797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Strains a | Relevant Genotype | Source/Reference |
| BG214 | wt | Laboratory strain |
| BG1525 | +pcrA-ssrA sspB (pcrAT) | [37] |
| BG1873 | +∆recA | [17] |
| BG1877 | +pcrAT ∆recA | [17] |
| BG1711 | +pcrAT ∆recU | [17] |
| BG1749 | +∆rnhB | This work |
| BG1751 | +∆rnhC | This work |
| BG1605 | +∆dinG | This work |
| BG1867 | +pcrAT ∆dinG | This work |
| BG1863 | +pcrAT ∆rnhB | This work |
| BG1865 | +pcrAT ∆rnhC | This work |
| BG1753 | +∆rnhB ∆recA | This work |
| BG1757 | +∆rnhB ∆recO | This work |
| BG1671 | +∆dinG ∆recA | This work |
| Plasmid b | Relevant Genotype | Source/Reference |
| pCB1229 | +pcrA, AmpR, oriEco | [17] |
| pCB1230 | +pcrA K37A, AmpR, oriEco | [17] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreno-del Álamo, M.; Carrasco, B.; Torres, R.; Alonso, J.C. Bacillus subtilis PcrA Helicase Removes Trafficking Barriers. Cells 2021, 10, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040935
Moreno-del Álamo M, Carrasco B, Torres R, Alonso JC. Bacillus subtilis PcrA Helicase Removes Trafficking Barriers. Cells. 2021; 10(4):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040935
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreno-del Álamo, María, Begoña Carrasco, Rubén Torres, and Juan Carlos Alonso. 2021. "Bacillus subtilis PcrA Helicase Removes Trafficking Barriers" Cells 10, no. 4: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040935
APA StyleMoreno-del Álamo, M., Carrasco, B., Torres, R., & Alonso, J. C. (2021). Bacillus subtilis PcrA Helicase Removes Trafficking Barriers. Cells, 10(4), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040935