The Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Losartan Sensitizes Human Liver Cancer Cells to Lenvatinib-Mediated Cytostatic and Angiostatic Effects
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Compounds and Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.3. Measurement of Cleaved Caspase-3
2.4. Measurement of VEGF-A, IL-8, and FGF2 Levels
2.5. In Vitro Endothelial Tubular Formation
2.6. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription-quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-qPCR)
2.7. Human Liver Cancer-Derived Xenograft
2.8. Histological and Immunohistochemical Analyses
2.9. Measurement of AT1R Protein Levels
2.10. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Effects of Lenvatinib and Losartan on in vitro Human Liver Cancer Cell Growth.
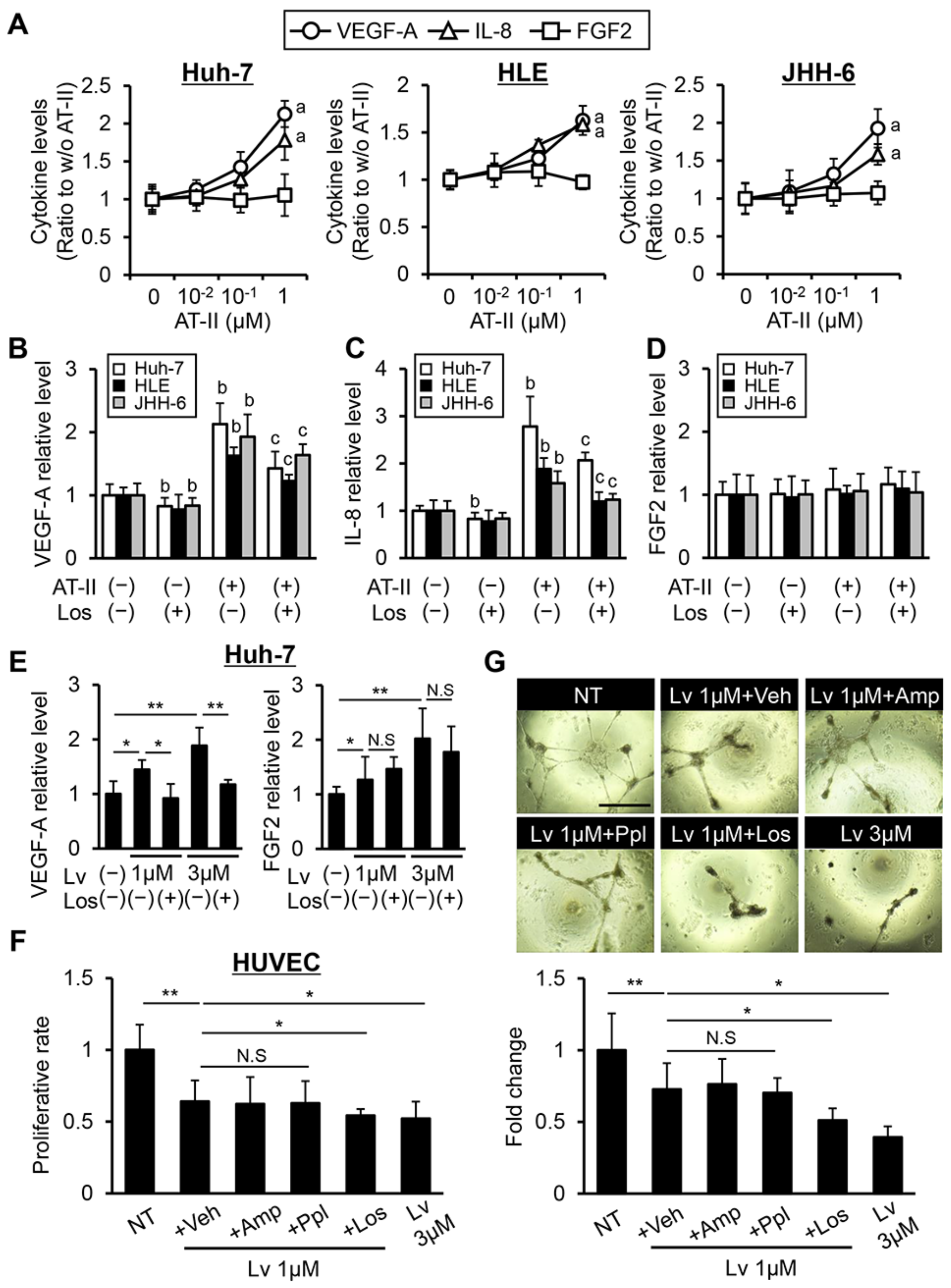
3.2. Effects of Lenvatinib and Losartan on Angiogenic Activity in Human Liver Cancer Cells and HUVECs.
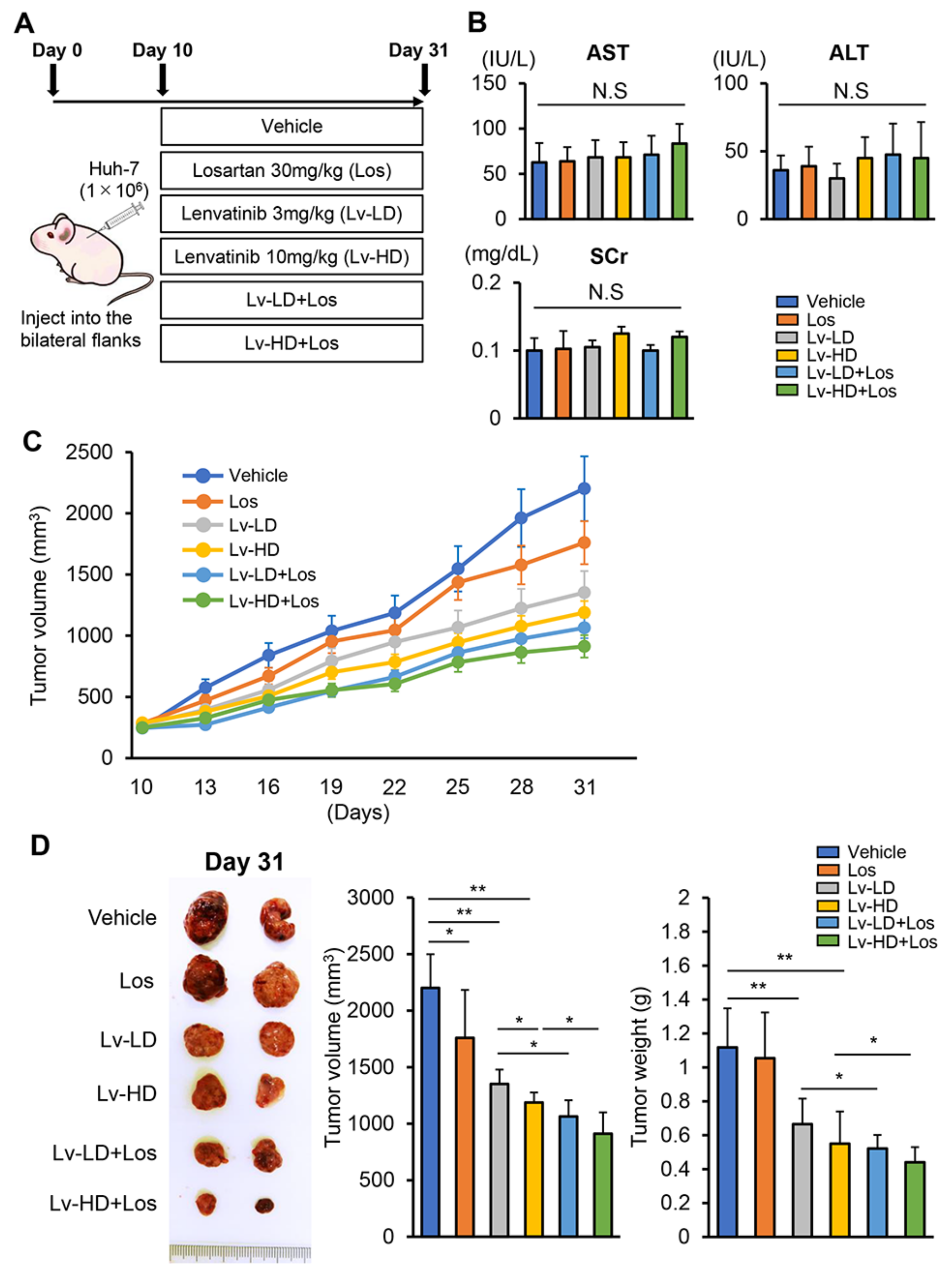
3.3. Losartan Augments the Reduction in Xenograft Tumor Burden Mediated by Lenvatinib in Liver Cancer Cells
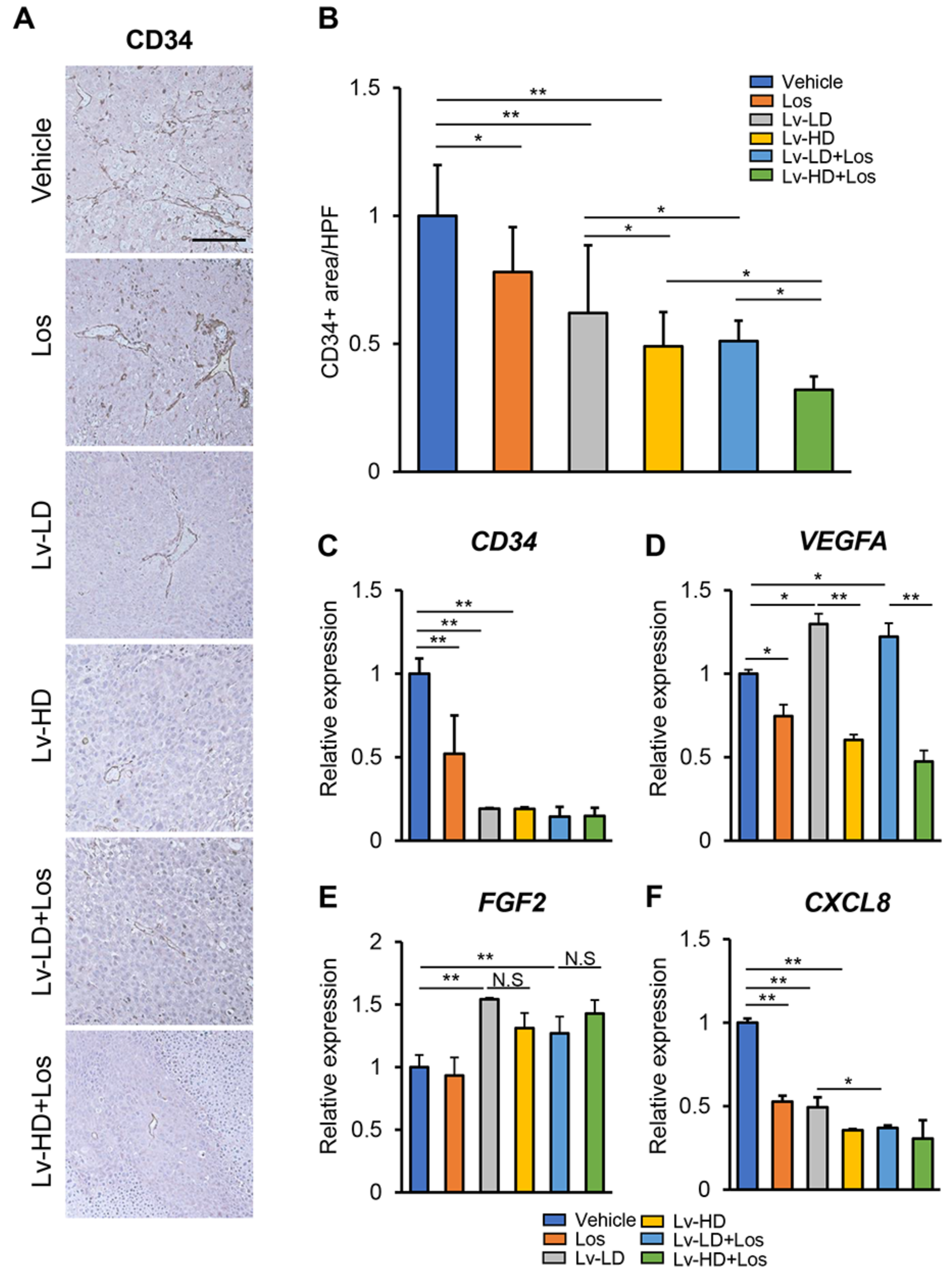
3.4. Combined Effects of Lenvatinib and Losartan on Intratumor Angiogenesis in Liver Cancer Cells
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TKI | Tyrosine kinase inhibitors |
| AT1R | Angiotensin II Receptor Type 1 |
| AT2R | Angiotensin II Receptor Type 2 |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein endothelial cell |
| CCND1 | Cyclin D1 |
| CDK4 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| CCNE1 | Cyclin E1 |
| CDK2 | Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 |
| BCL2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| BAX | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| MCL1 | Myeloid cell leukemia 1 |
| Amp | Amlodipine |
| Ppl | Propranolol |
| Los | Losaltan |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| SCr | Serum creatinine |
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akinyemiju, T.; Abera, S.; Ahmed, M.; Alam, N.; Alemayohu, M.A.; Allen, C.; Al-Raddadi, R.; Alvis-Guzman, N.; Amoako, Y.; Artaman, A.; et al. The Burden of Primary Liver Cancer and Underlying Etiologies From 1990 to 2015 at the Global, Regional, and National Level. JAMA Oncol. 2017, 3, 1683–1691. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Omata, M.; Cheng, A.L.; Kokudo, N.; Kudo, M.; Lee, J.M.; Jia, J.; Tateishi, R.; Han, K.H.; Chawla, Y.K.; Shiina, S.; et al. Asia-Pacific clinical practice guidelines on the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: A 2017 update. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 317–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütte, K.; Bornschein, J.; Malfertheiner, P. Hepatocellular carcinoma—Epidemiological trends and risk factors. Dig. Dis. 2009, 27, 80–92. [Google Scholar]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Splan, M.F.; Weiss, N.S.; McDonald, G.B.; Beretta, L.; Lee, S.P. Incidence and Predictors of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Cirrhosis. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 5, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sangiovanni, A.; Prati, G.M.; Fasani, P.; Ronchi, G.; Romeo, R.; Manini, M.; Del Ninno, E.; Morabito, A.; Colombo, M. The natural history of compensated cirrhosis due to hepatitis C virus: A 17-year cohort study of 214 patients. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1303–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Chung, H.; Haji, S.; Osaki, Y.; Oka, H.; Seki, T.; Kasugai, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Matsunaga, T. Validation of a new prognostic staging system for hepatocellular carcinoma: The JIS score compared with the CLIP score. Hepatology 2004, 40, 1396–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, J.D.; Kennedy, E.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Beg, M.S.; Brower, S.T.; Gade, T.P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Harris, W.P.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 4317–4345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tohyama, O.; Matsui, J.; Kodama, K.; Hata-Sugi, N.; Kimura, T.; Okamoto, K.; Minoshima, Y.; Iwata, M.; Funahashi, Y. Antitumor Activity of Lenvatinib (E7080): An Angiogenesis Inhibitor That Targets Multiple Receptor Tyrosine Kinases in Preclinical Human Thyroid Cancer Models. J. Thyroid Res. 2014, 2014, 638747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, M.; Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Han, K.H.; Ikeda, K.; Piscaglia, F.; Baron, A.; Park, J.W.; Han, G.; Jassem, J.; et al. Lenvatinib versus sorafenib in first-line treatment of patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A randomised phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 1163–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, R.; Fukushima, M.; Haraguchi, M.; Miuma, S.; Miyaaki, H.; Hidaka, M.; Eguchi, S.; Matsuo, S.; Tajima, K.; Matsuzaki, T.; et al. Response to Lenvatinib Is Associated with Optimal Relative Dose Intensity in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Experience in Clinical Settings. Cancers 2019, 11, 1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, H.M.; White, C.M.; White, W.B. The Comparative Efficacy and Safety of the Angiotensin Receptor Blockers in the Management of Hypertension and Other Cardiovascular Diseases. Drug Saf. 2015, 38, 33–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrario, C.M.; Mullick, A.E. Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Inhibition in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 125, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maschio, G.; Alberti, D.; Janin, G.; Locatelli, F.; Mann, J.F.; Motolese, M.; Ponticelli, C.; Ritz, E.; Zucchelli, P. The Angiotensin-Converting-Enzyme Inhibition in Progressive Renal Insufficiency Study Group: Effect of the angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor benazepril on the progression of chronic renal insufficiency. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 939–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol. Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Noguchi, R.; Namisaki, T.; Moriya, K.; Kitade, K.; Aihara, Y.; Douhara, A.; Kawaratani, H.; Nishimura, N.; Fukui, H. Combination of sorafenib and angiotensin-II receptor blocker attenuates preneoplastic lesion development in a non-diabetic rat model of steatohepatitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, E.; Kim, J.Y.; Cho, Y.; An, H.; Lee, N.; Jo, H.; Ban, C.; Seo, J.H. Overexpression of angiotensin II type 1 receptor in breast cancer cells induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1863, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saikawa, S.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Seki, K.; Sato, S.; Nakanishi, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Kawaratani, H.; Kitade, M.; Moriya, K.; et al. Angiotensin receptor blockade attenuates cholangiocarcinoma cell growth by inhibiting the oncogenic activity of Yes-associated protein. Cancer Lett. 2018, 434, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshiji, H.; Kuriyama, S.; Kawata, M.; Yoshii, J.; Ikenaka, Y.; Noguchi, R.; Nakatani, T.; Tsujinoue, H.; Fukui, H. The angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril suppresses tumor growth and angiogenesis: Possible role of the vascular endothelial growth factor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, R.; Lei, C.G.; Bai, Y.X.; Tang, N.; Xing, X. The AT1/Raf/ERK1/2 signaling pathway is involved in Angiotensin II-enhanced proliferation of hepatic carcinoma cells. Neoplasma 2019, 66, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, M.; Weinmann, A.; Wörns, M.A.; Hucke, F.; Bota, S.; Marquardt, J.U.; Duda, D.G.; Jain, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Trauner, M.; et al. Use of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system is associated with longer survival in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa-Almeida, R.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Ramalho, C.; Granja, P.L.; Soares, R.; Guerreiro, S.G. Fibroblast-Endothelial Partners for Vascularization Strategies in Tissue Engineering. Tissue Eng. Part A 2015, 21, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoshi, T.; Miyano, S.W.; Watanabe, H.; Sonobe, R.M.K.; Seki, Y.; Ohta, E.; Nomoto, K.; Matsui, J.; Funahashi, Y. Lenvatinib induces death of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells harboring an activated FGF signaling pathway through inhibition of FGFR–MAPK cascades. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 513, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, S.; Mihara, Y.; Kondo, R.; Kusano, H.; Akiba, J.; Yano, H. Antiproliferative Effect of Lenvatinib on Human Liver Cancer Cell Lines In Vitro and In Vivo. Anticancer Res. 2019, 39, 5973–5982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Adjei, A.A. Targeting Angiogenesis in Cancer Therapy: Moving Beyond Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor. Oncologist 2015, 20, 660–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casanovas, O.; Hicklin, D.J.; Bergers, G.; Hanahan, D. Drug resistance by evasion of antiangiogenic targeting of VEGF signaling in late-stage pancreatic islet tumors. Cancer Cell 2005, 8, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, A.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Le, X. Angiotensin II Enhances Proliferation and Inflammation through AT1/PKC/NF-κB Signaling Pathway in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabre, S.; Mahmoud, A.A.A.; Goda, R.; Helal, N.S.; El-Ahwany, E.; Abdelghany, R.H. Perindopril, fosinopril and losartan inhibited the progression of diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in mice via the inactivation of nuclear transcription factor kappa-B. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 295, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oura, K.; Tadokoro, T.; Fujihara, S.; Morishita, A.; Chiyo, T.; Samukawa, E.; Yamana, Y.; Fujita, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Nomura, T.; et al. Telmisartan inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation in vitro by inducing cell cycle arrest. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2825–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Wang, Y.; Peng, H.; Chen, D.; Shen, S.; Peng, B.; Chen, M.; Lencioni, R.; Kuang, M. Autocrine vascular endothelial growth factor signaling promotes cell proliferation and modulates sorafenib treatment efficacy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary 2014, 60, 1264–1277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.S.; Xu, J.; Kong, L.C.; Wei, P. Celastrol Enhances the Anti-Liver Cancer Activity of Sorafenib. Med. Sci. Monit. 2019, 25, 4068–4075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, F.; Tian, C.; Tao, L.; Wu, H.; Liu, Z.; Shen, C.; Jiang, G.; Lu, Y. Candesartan attenuates angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating AT1R/VEGF pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 704–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, T.; Kumada, T.; Hiraoka, A.; Michitaka, K.; Atsukawa, M.; Hirooka, M.; Tsuji, K.; Ishikawa, T.; Takaguchi, K.; Kariyama, K.; et al. Safety and efficacy of lenvatinib in elderly patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A multicenter analysis with propensity score matching. Hepatol. Res. 2020, 50, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maruta, S.; Ogasawara, S.; Ooka, Y.; Obu, M.; Inoue, M.; Itokawa, N.; Haga, Y.; Seki, A.; Okabe, S.; Azemoto, R.; et al. Potential of Lenvatinib for an Expanded Indication from the REFLECT Trial in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2020, 9, 382–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogushi, K.; Chuma, M.; Uojima, H.; Hidaka, H.; Numata, K.; Kobayashi, S.; Hirose, S.; Hattori, N.; Fujikawa, T.; Nakazawa, T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Lenvatinib Treatment in Child–Pugh A and B Patients with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Clinical Practice: A Multicenter Analysis. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Chen, H.; Gow, W.; Ma, L.; Jin, Y.; Hui, B.; Yang, Z.; Wang, Z. Potential biomarkers Ang II/AT1R and S1P/S1PR1 predict the prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, M.; Hou, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, L.; Luo, Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, D.; Zhou, H.; et al. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors have adverse effects in anti-angiogenesis therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2021, 501, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takagi, H.; Kaji, K.; Nishimura, N.; Ishida, K.; Ogawa, H.; Takaya, H.; Kawaratani, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Akahane, T.; et al. The Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Losartan Sensitizes Human Liver Cancer Cells to Lenvatinib-Mediated Cytostatic and Angiostatic Effects. Cells 2021, 10, 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030575
Takagi H, Kaji K, Nishimura N, Ishida K, Ogawa H, Takaya H, Kawaratani H, Moriya K, Namisaki T, Akahane T, et al. The Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Losartan Sensitizes Human Liver Cancer Cells to Lenvatinib-Mediated Cytostatic and Angiostatic Effects. Cells. 2021; 10(3):575. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030575
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakagi, Hirotetsu, Kosuke Kaji, Norihisa Nishimura, Koji Ishida, Hiroyuki Ogawa, Hiroaki Takaya, Hideto Kawaratani, Kei Moriya, Tadashi Namisaki, Takemi Akahane, and et al. 2021. "The Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Losartan Sensitizes Human Liver Cancer Cells to Lenvatinib-Mediated Cytostatic and Angiostatic Effects" Cells 10, no. 3: 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030575
APA StyleTakagi, H., Kaji, K., Nishimura, N., Ishida, K., Ogawa, H., Takaya, H., Kawaratani, H., Moriya, K., Namisaki, T., Akahane, T., Mitoro, A., & Yoshiji, H. (2021). The Angiotensin II Receptor Blocker Losartan Sensitizes Human Liver Cancer Cells to Lenvatinib-Mediated Cytostatic and Angiostatic Effects. Cells, 10(3), 575. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030575






