Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Novel Loci for Susceptibility of Scrub Typhus and Highlights Immune-Related Signaling Pathways in Its Pathogenesis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Statement
2.2. Subjects
2.3. GWAS
2.4. In Silico Analysis of Scrub Typhus-Related Candidate Genes and Signaling Pathways
3. Results
3.1. Subjects
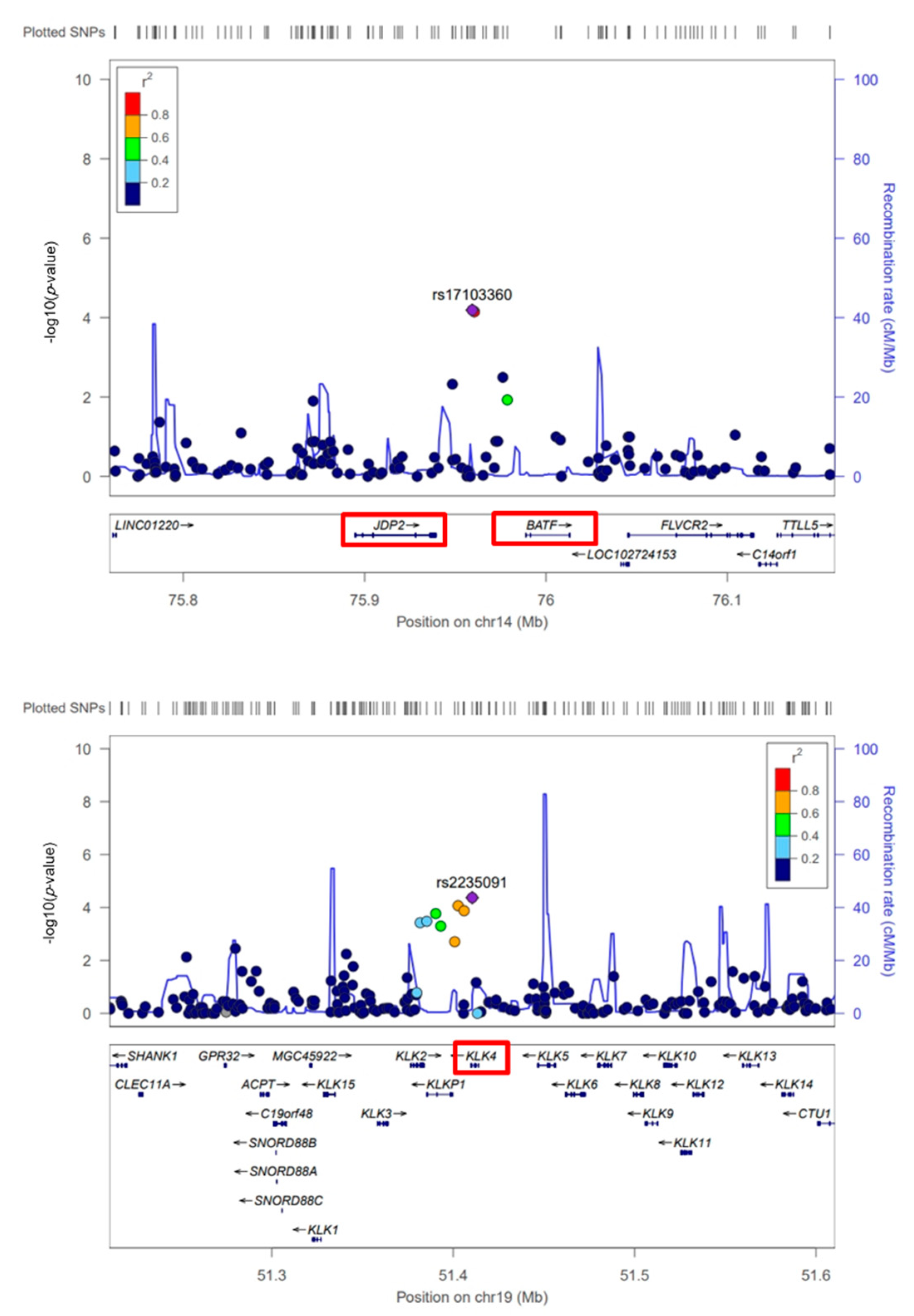
3.2. GWAS for Scrub Typhus
3.3. In Silico Analysis of Scrub Typhus-Related Candidate Genes and Signaling Pathways
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GWAS | Genome-wide association study |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| TLR4 | Toll-like receptor 4 |
| PRMT6 | Protein arginine methyltransferase 6 |
| ONECUT1 | One cut homeobox 1 |
| WDR72 | WD repeat domain 72 |
| BATF | Basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor |
| JDP2 | Jun dimerization protein 2 |
| KLK4 | Kallikrein-related peptidase 4 |
| MAP3K7 | Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 |
| TGFBR2 | TGF-beta receptor type-2 |
| ILF2 | Interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 |
| OAS1 | 2’-5’-oligoadenylate synthetase 1 |
| IFI35 | Interferon-induced protein 35 |
| HLA-DRA | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha |
References
- Luce-Fedrow, A.; Lehman, M.L.; Kelly, D.J.; Mullins, K.; Maina, A.N.; Stewart, R.L.; Ge, H.; John, H.S.; Jiang, J.; Richards, A.L. A Review of Scrub Typhus (Orientia tsutsugamushi and Related Organisms): Then, Now, and Tomorrow. Trop. Med. Infect. Dis. 2018, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, I.; Pearson, I.; Dahal, P.; Thomas, N.V.; Roberts, T.; Newton, P.N. Scrub typhus ecology: A systematic review of Orientia in vectors and hosts. Parasites Vectors 2019, 12, 513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.J.; Fuerst, P.A.; Ching, W.M.; Richards, A.L. Scrub typhus: The geographic distribution of phenotypic and genotypic variants of Orientia tsutsugamushi. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48 (Suppl. 3), S203–S230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Walker, D.H.; Jupiter, D.; Melby, P.C.; Arcari, C.M. A review of the global epidemiology of scrub typhus. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11, e0006062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.S.; Hwang, J.H. IMAGES IN CLINICAL MEDICINE. Scrub Typhus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, G.C.; Maude, R.J.; Paris, D.H.; Newton, P.N.; Blacksell, S.D. Diagnosis of scrub typhus. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2010, 82, 368–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, S.; Weeratunga, P.; Sivayoganathan, S.; Fernando, S.D. Clinical manifestations of scrub typhus. Trans. R Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2017, 111, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Roberts, T.; Homsana, A.; Myat, T.O.; Crump, J.A.; Lubell, Y.; Newton, P.N. Febrile illness in Asia: Gaps in epidemiology, diagnosis and management for informing health policy. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2018, 24, 815–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Sayed, I.; Liu, Q.; Wee, I.; Hine, P. Antibiotics for treating scrub typhus. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 9, CD002150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watt, G.; Chouriyagune, C.; Ruangweerayud, R.; Watcharapichat, P.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Jongsakul, K.; Teja-Isavadharm, P.; Bhodhidatta, D.; Corcoran, K.D.; Dasch, G.A.; et al. Scrub typhus infections poorly responsive to antibiotics in northern Thailand. Lancet 1996, 348, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollars, T.M., Jr.; Bodhidatta, D.; Phulsuksombati, D.; Tippayachai, B.; Coleman, R.E. Short report: Variation in the 56-kD type-specific antigen gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi isolated from patients in Thailand. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2003, 68, 299–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangrangsimakul, T.; Phuklia, W.; Newton, P.N.; Richards, A.L.; Day, N.P.J. Scrub Typhus and the Misconception of Doxycycline Resistance. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 70, 2444–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wangrangsimakul, T.; Phuklia, W.; Newton, P.N.; Richards, A.L.; Day, N.P.J. Reply to Watt. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2020, 71, 1580–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trent, B.; Fisher, J.; Soong, L. Scrub Typhus Pathogenesis: Innate Immune Response and Lung Injury During Orientia tsutsugamushi Infection. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janardhanan, J.; Joseph Martin, S.; Astrup, E.; Veeramanikandan, R.; Aukrust, P.; Abraham, O.C.; Varghese, G.M. Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in Toll-like receptor (TLR)-2, TLR4 and heat shock protein 70 genes and susceptibility to scrub typhus. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 58, 707–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Jeong, B.H. Strong association of regulatory single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of the IFITM3 gene with influenza H1N1 2009 pandemic virus infection. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2020, 17, 662–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Won, S.Y.; Jeong, B.H. Potential scrapie-associated polymorphisms of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in Korean native black goats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Kim, S.K.; Jeong, B.H. Scrapie susceptibility-associated indel polymorphism of shadow of prion protein gene (SPRN) in Korean native black goats. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Won, S.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Kim, K.; Kim, A.D.; Jeong, B.H. The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bush, W.S.; Moore, J.H. Chapter 11: Genome-wide association studies. Plos Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, V.; Patel, N.; Turcotte, M.; Bosse, Y.; Pare, G.; Meyre, D. Benefits and limitations of genome-wide association studies. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Cho, N.; Lee, S.K.; Han, B.G.; Sull, J.W.; Jee, S.H.; Shin, C. Identification of FAM13A gene associated with the ratio of FEV1 to FVC in Korean population by genome-wide association studies including gene-environment interactions. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 60, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Vinayagam, A.; Nand, A.; Comjean, A.; Chung, V.; Hao, T.; Mohr, S.E.; Perrimon, N. Molecular Interaction Search Tool (MIST): An integrated resource for mining gene and protein interaction data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D567–D574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Thomas, P.D. PANTHER-PSEP: Predicting disease-causing genetic variants using position-specific evolutionary preservation. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 2230–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.S.; Choi, J.S.; Lim, H.S.; Kim, J.R.; Kim, K.Y.; Ryu, S.Y.; Yoo, H.S.; Park, O. Rapid increase of scrub typhus, South Korea, 2001–2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1127–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jan, R.H.; Chen, C.J.; Hong, Y.R.; Lin, Y.L.; Chen, L.K. A surface antigen of Orientia tsutsugamushi activates human monocyte-derived dendritic cells via nuclear factor-kB and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Indian J. Med. Res. 2018, 148, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Case | Control | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 74 | 74 | |
| Sex | Female | 43 | 42 |
| Male | 31 | 32 | |
| p value | 0.87 | ||
| Mean age of diagnosis (years ± *STD) | 64.4 ± 7.6 | ||
| Mean age at sample collection (years ± *STD) | 64.4 ± 7.6 | ||
| p value | 1.0 |
| p Value * | Count | Cumulative |
|---|---|---|
| <1 × 10−6 | 2 | 2 |
| <1 × 10−5 | 2 | 4 |
| <1 × 10−4 | 35 | 39 |
| <1 × 10−3 | 791 | 830 |
| <0.01 | 4219 | 5049 |
| <0.05 | 17,303 | 22,352 |
| NS** | 454,741 | 477,093 |
| Gene | Gene Full Name | Function | Related Candidate Gene of Scrub Typhus |
|---|---|---|---|
| ILF2 | Interleukin enhancer binding factor 2 | Transcription factor required for T-cell expression of the interleukin 2 gene | PRMT6 |
| OAS1 | 2’-5’-oligoadenylate synthetase 1 | Interferon-induced, dsRNA-activated antiviral enzyme which plays a critical role in cellular innate antiviral response | PRMT6 |
| BATF | Basic leucine zipper ATF-like transcription factor | AP-1 family transcription factor that controls the differentiation of lineage-specific cells in the immune system | − |
| IFI35 | Interferon induced protein 35 | IFI35 involved in interferon gamma signaling and innate immune system | BATF, JDP2 |
| HLA-DRA | Major histocompatibility complex, class II, DR alpha | HLA-DRA plays a central role in the immune system by presenting peptides derived from extracellular proteins | KLK4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-K.; Lee, Y.; Shin, C.; Lee, C.-S.; Jeong, B.-H. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Novel Loci for Susceptibility of Scrub Typhus and Highlights Immune-Related Signaling Pathways in Its Pathogenesis. Cells 2021, 10, 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030570
Kim Y-C, Kim S, Kim H-K, Lee Y, Shin C, Lee C-S, Jeong B-H. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Novel Loci for Susceptibility of Scrub Typhus and Highlights Immune-Related Signaling Pathways in Its Pathogenesis. Cells. 2021; 10(3):570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030570
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Yong-Chan, Soriul Kim, Hee-Kwon Kim, Yi Lee, Chol Shin, Chang-Seop Lee, and Byung-Hoon Jeong. 2021. "Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Novel Loci for Susceptibility of Scrub Typhus and Highlights Immune-Related Signaling Pathways in Its Pathogenesis" Cells 10, no. 3: 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030570
APA StyleKim, Y.-C., Kim, S., Kim, H.-K., Lee, Y., Shin, C., Lee, C.-S., & Jeong, B.-H. (2021). Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Eight Novel Loci for Susceptibility of Scrub Typhus and Highlights Immune-Related Signaling Pathways in Its Pathogenesis. Cells, 10(3), 570. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10030570







