Simple and Rapid Non-Enzymatic Procedure Allows the Isolation of Structurally Preserved Connective Tissue Micro-Fragments Enriched with SVF
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
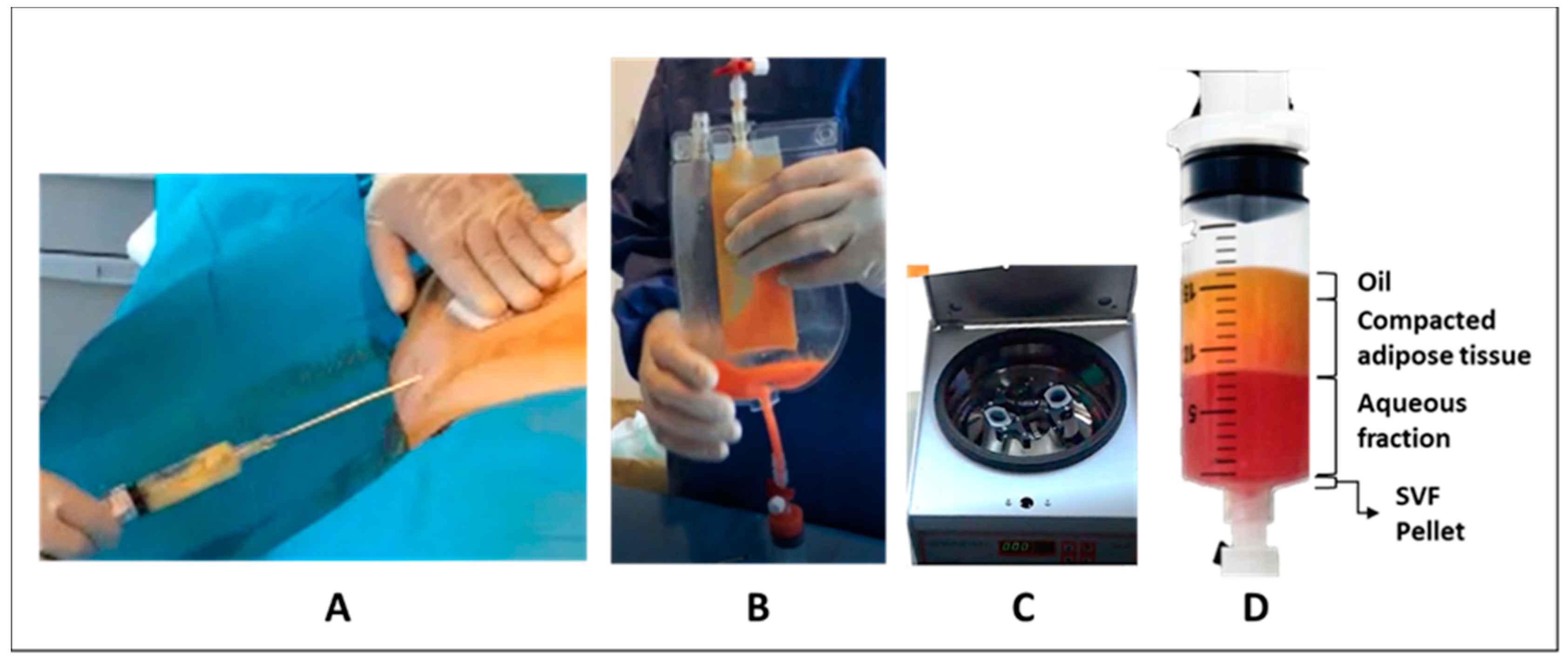
2.1. Adipose Tissue Collection
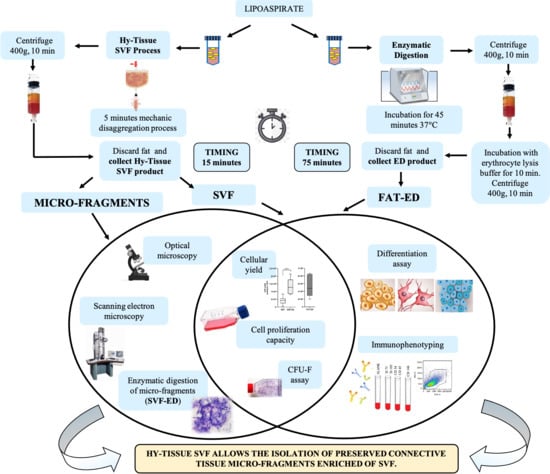
2.2. Procedure for SVF Production
2.3. Enzymatic Digestion of the Fat
2.4. Enzymatic Digestion of the SVF
2.5. Cell Counting and Yield
2.6. Cell Proliferation Capacity
2.7. Colony Forming Unit Assay
2.8. Optical Microscopy
2.9. SEM Analysis
2.10. Immunophenotyping
2.11. In Vitro Differentiation Assays
2.12. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
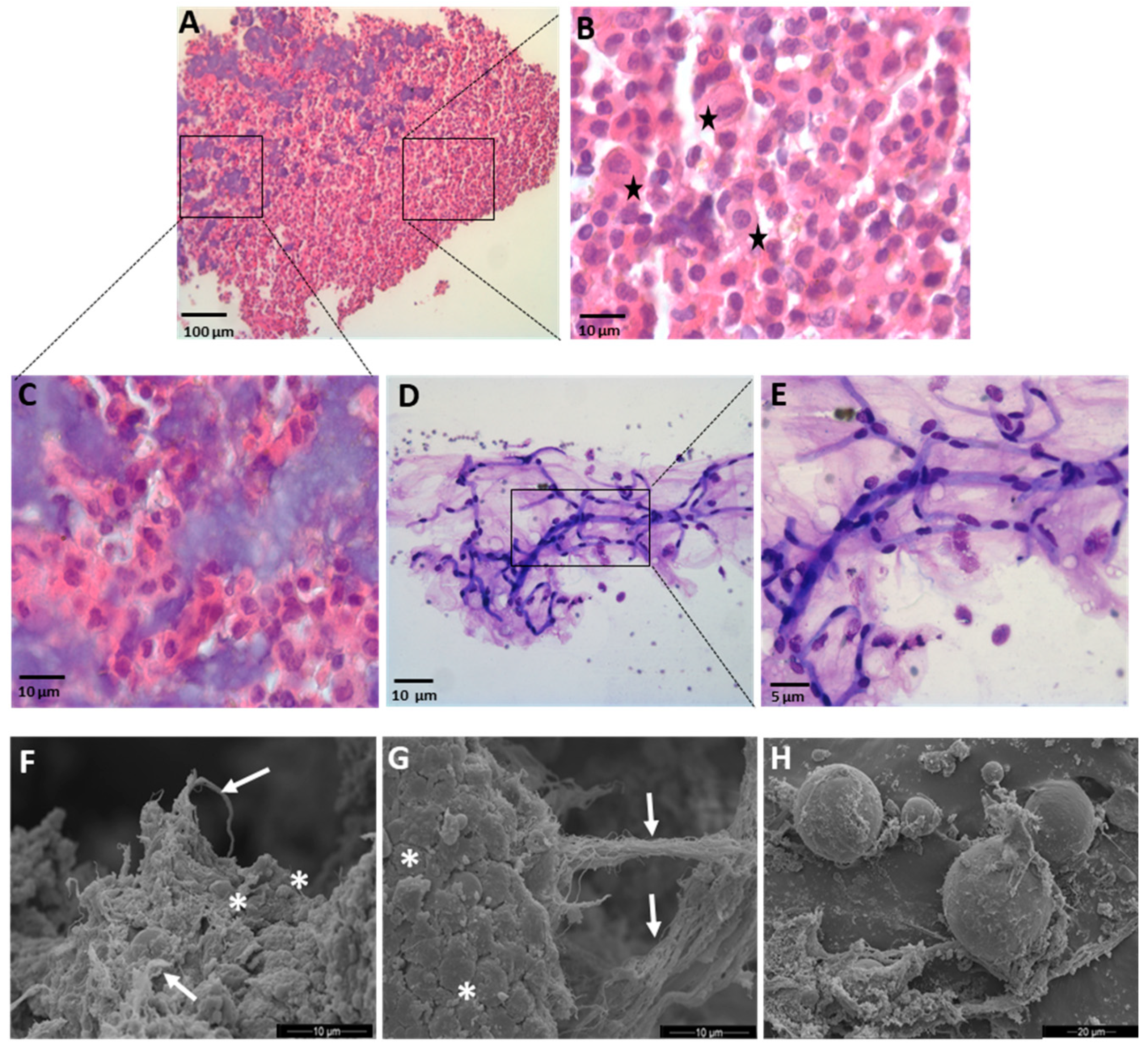
3.1. Microscopical Analysis of the SVF
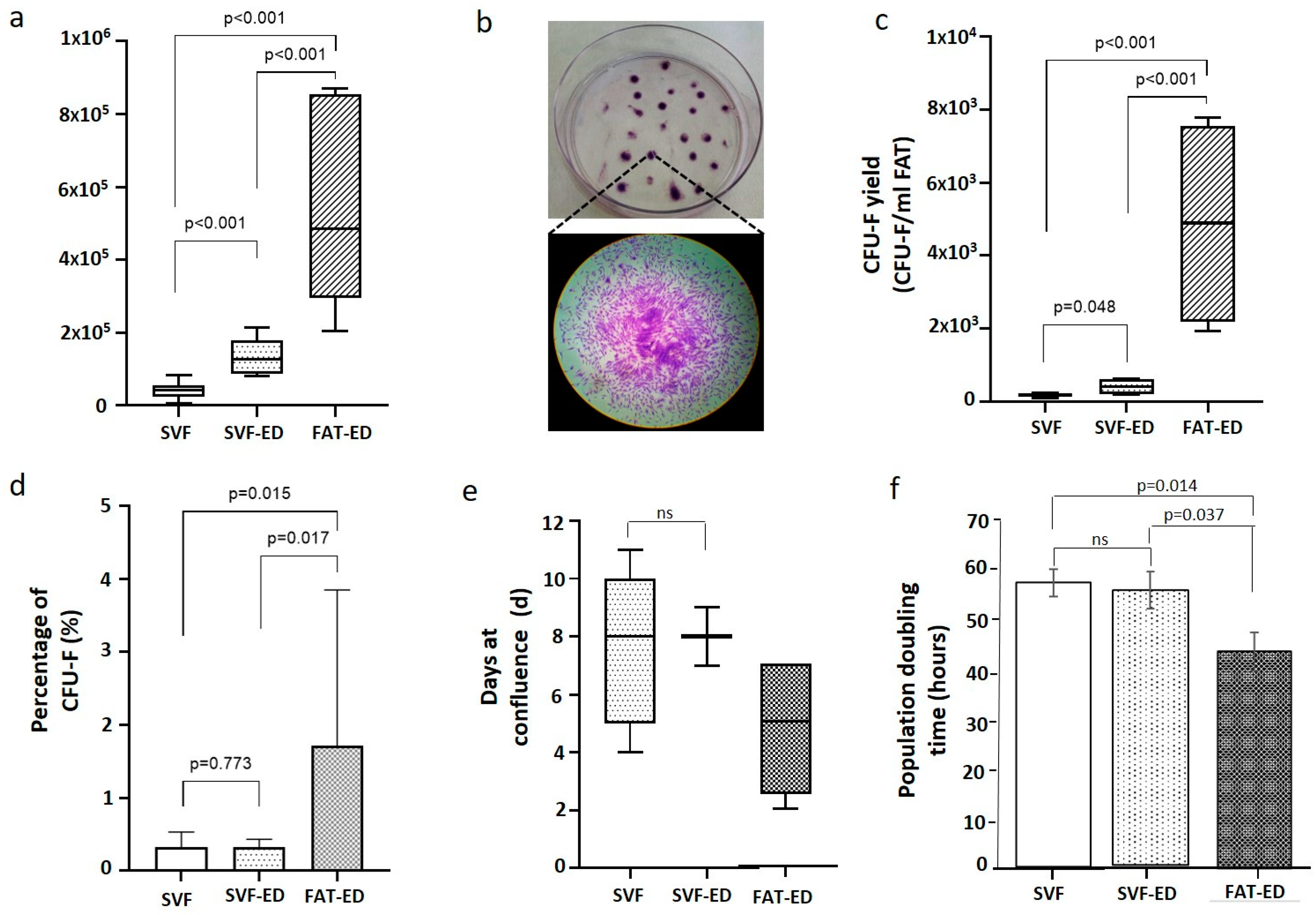
3.2. In Vitro Characterization of the SVF
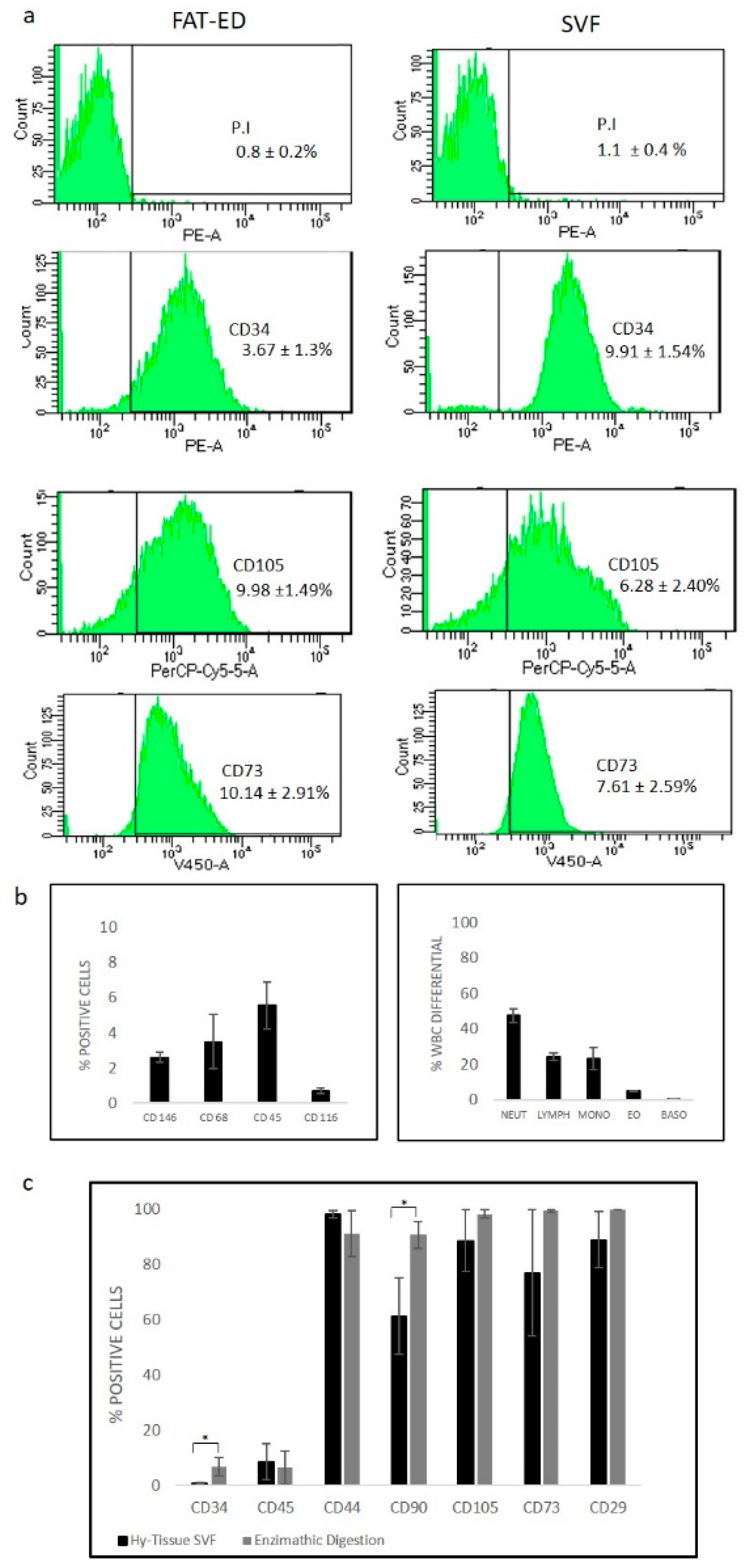
3.3. Immunophenotypic Analysis
3.4. Analysis of Multipotency of SVF Product
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zuk, P.A.; Zhu, M.; Ashjian, P.; De Ugarte, D.A.; Huang, J.I.; Mizuno, H.; Alfonso, Z.C.; Fraser, J.K.; Benhaim, P.; Hedrick, M.H. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 4279–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bora, P.; Majumdar, A.S. Adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction in regenerative medicine: A brief review on biology and translation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2017, 8, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourin, P.; Bunnell, B.A.; Casteilla, L.; Dominici, M.; Katz, A.J.; March, K.L.; Redl, H.; Rubin, J.P.; Yoshimura, K.; Gimble, J.M. Stromal cells from the adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction and culture expanded adipose tissue-derived stromal/stem cells: A joint statement of the International Federation for Adipose Therapeutics and Science (IFATS) and the International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Majors, A.K.; Boehm, C.A.; Nitto, H.; Midura, R.J.; Muschler, G.F. Characterization of human bone marrow stromal cells with respect to osteoblastic differentiation. J. Orthop. Res. 1997, 15, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Q.; Bai, Y.; Wang, G.; Song, Q.; Guo, C.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q. Delivery of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obese Mice Through Remodeling Macrophage Phenotypes. Stem Cells Dev. 2015, 24, 2052–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, T.; Masutani, R.; Suzuka, T.; Oda, K.; Makino, S.; Ii, M. Anti-inflammatory and anti-fibrotic effects of intravenous adipose-derived stem cell transplantation in a mouse model of bleomycin-induced interstitial pneumonia. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Prasai, A.; El Ayadi, A.; Mifflin, R.C.; Wetzel, M.D.; Andersen, C.R.; Redl, H.; Herndon, D.N.; Finnerty, C.C. Characterization of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Following Burn Injury. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2017, 13, 781–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lapuente, J.P.; Dos-Anjos, S.; Blázquez-Martínez, A. Intra-articular infiltration of adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction cells slows the clinical progression of moderate-severe knee osteoarthritis: Hypothesis on the regulatory role of intra-articular adipose tissue. J. Orthop. Surg. Res. 2020, 15, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, C.; Bi, M.; Chen, X.; Bi, Q. Intra-articular injection of autologous adipose-derived stromal vascular fractions for knee osteoarthritis: A double-blind randomized self-controlled trial. Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, J.; Lee, J.H.; Park, K.S.; Park, M.; Kang, L.W.; Lee, S.H. Current use of autologous adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction cells for orthopedic applications. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chu, D.-T.; Nguyen Thi Phuong, T.; Tien, N.L.B.; Tran, D.K.; Minh, L.B.; Thanh, V.V.; Gia Anh, P.; Pham, V.H.; Thi Nga, V. Adipose Tissue Stem Cells for Therapy: An Update on the Progress of Isolation, Culture, Storage, and Clinical Application. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Oberbauer, E.; Steffenhagen, C.; Wurzer, C.; Gabriel, C.; Redl, H.; Wolbank, S. Enzymatic and non-enzymatic isolation systems for adipose tissue-derived cells: Current state of the art. Cell Regen. 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aronowitz, J.A.; Ellenhorn, J.D. Adipose stromal vascular fraction isolation: A head-to-head comparison of four commercial cell separation systems. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 932e–939e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crisan, M.; Yap, S.; Casteilla, L.; Chen, C.W.; Corselli, M.; Park, T.S.; Andriolo, G.; Sun, B.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.; et al. A perivascular origin for mesenchymal stem cells in multiple human organs. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vezzani, B.; Shaw, I.; Lesme, H.; Yong, L.; Khan, N.; Tremolada, C.; Péault, B. Higher Pericyte Content and Secretory Activity of Microfragmented Human Adipose Tissue Compared to Enzymatically Derived Stromal Vascular Fraction. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2018, 7, 876–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nava, S.; Sordi, V.; Pascucci, L.; Tremolada, C.; Ciusani, E.; Zeira, O.; Cadei, M.; Soldati, G.; Pessina, A.; Parati, E.; et al. Long-Lasting Anti-Inflammatory Activity of Human Microfragmented Adipose Tissue. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2019, 5901479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudetz, D.; Borić, I.; Rod, E.; Jeleč, Ž.; Kunovac, B.; Polašek, O.; Vrdoljak, T.; Plečko, M.; Skelin, A.; Polančec, D.; et al. Early results of intra-articular micro-fragmented lipoaspirate treatment in patients with late stages knee osteoarthritis: A prospective study. Croat. Med. J. 2019, 60, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolbe, M.; Xiang, Z.; Dohle, E.; Tonak, M.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Fuchs, S. Paracrine effects influenced by cell culture medium and consequences on microvessel-like structures in cocultures of mesenchymal stem cells and outgrowth endothelial cells. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, T.; Zhu, L.; Gao, W.; Gong, M.; Ren, J.; Yao, H.; Wang, K.; Shi, D. Coculture of endothelial progenitor cells and mesenchymal stem cells enhanced their proliferation and angiogenesis through PDGF and Notch signaling. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 7, 1722–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loibl, M.; Binder, A.; Herrmann, M.; Duttenhoefer, F.; Richards, R.G.; Nerlich, M.; Alini, M.; Verrier, S. Direct cell-cell contact between mesenchymal stem cells and endothelial progenitor cells induces a pericyte-like phenotype in vitro. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 395781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Q.; Zhang, H.; Hou, J.; Wan, L.; Cheng, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, D.; Chen, C.; Xia, J.; Guo, J.; et al. VEGF secreted by mesenchymal stem cells mediates the differentiation of endothelial progenitor cells into endothelial cells via paracrine mechanisms. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 1667–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyldig, K.; Riis, S.; Pennisi, C.P.; Zachar, V.; Fink, T. Implications of Extracellular Matrix Production by Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells for Development of Wound Healing Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Z.Q.; Chen, Y.; Chai, M.; Tao, R.; Lei, Y.H.; Jia, Y.Q.; Shu, J.; Ren, J.; Li, G.; Wei, W.X.; et al. Adipose extracellular matrix promotes skin wound healing by inducing the differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells into fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2019, 43, 890–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vilaboa, S.D.A.; Navarro-Palou, M.; Llull, R. Age influence on stromal vascular fraction cell yield obtained from human lipoaspirates. Cytotherapy 2014, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadel, L.; Viana, B.R.; Feitosa, M.L.; Ercolin, A.C.; Roballo, K.C.; Casals, J.B.; Pieri, N.C.; Meirelles, F.V.; Martins Ddos, S.; Miglino, M.A.; et al. Protocols for obtainment and isolation of two mesenchymal stem cell sources in sheep. Acta Cir. Bras. 2011, 26, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mojallal, A.; Auxenfans, C.; Lequeux, C.; Braye, F.; Damour, O. Influence of negative pressure when harvesting adipose tissue on cell yield of the stromal-vascular fraction. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2008, 18, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aronowitz, J.A.; Lockhart, R.A.; Hakakian, C.S. Mechanical versus enzymatic isolation of stromal vascular fraction cells from adipose tissue. SpringerPlus 2015, 4, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trivisonno, A.; Di Rocco, G.; Cannistra, C.; Finocchi, V.; Torres Farr, S.; Monti, M.; Toietta, G. Harvest of superficial layers of fat with a microcannula and isolation of adipose tissue-derived stromal and vascular cells. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2014, 34, 601–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jang, Y.; Koh, Y.G.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.H.; Yoon, D.S.; Lee, M.; Lee, J.W. Characterization of adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular fraction for clinical application to cartilage regeneration. Vitr. Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2015, 51, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aust, L.; Devlin, B.; Foster, S.J.; Halvorsen, Y.D.; Hicok, K.; du Laney, T.; Sen, A.; Willingmyre, G.D.; Gimble, J.M. Yield of human adipose-derived adult stem cells from liposuction aspirates. Cytotherapy 2004, 6, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Pratta, A.S.; Abbassi, N.; Fabre, H.; Rodriguez, F.; Debard, C.; Adobati, J.; Boucher, F.; Mallein-Gerin, F.; Auxenfans, C.; et al. Evaluation of Three Devices for the Isolation of the Stromal Vascular Fraction from Adipose Tissue and for ASC Culture: A Comparative Study. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 9289213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Doi, K.; Tanaka, S.; Iida, H.; Eto, H.; Kato, H.; Aoi, N.; Kuno, S.; Hirohi, T.; Yoshimura, K. Stromal vascular fraction isolated from lipo-aspirates using an automated processing system: Bench and bed analysis. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2013, 7, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurgens, W.J.; Oedayrajsingh-Varma, M.J.; Helder, M.N.; Zandiehdoulabi, B.; Schouten, T.E.; Kuik, D.J.; Ritt, M.J.; van Milligen, F.J. Effect of tissue-harvesting site on yield of stem cells derived from adipose tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Cell Tissue Res. 2008, 332, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Markarian, C.F.; Frey, G.Z.; Silveira, M.D.; Chem, E.M.; Milani, A.R.; Ely, P.B.; Horn, A.P.; Nardi, N.B.; Camassola, M. Isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: A comparison among different methods. Biotechnol. Lett. 2014, 36, 693–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, L.S.; do Amaral, R.J.; Carias, R.B.; Aniceto, M.; Claudio-da-Silva, C.; Borojevic, R. An alternative method for the isolation of mesenchymal stromal cells derived from lipoaspirate samples. Cytotherapy 2009, 11, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, F.S.; Wu, X.; Dietrich, M.; Rood, J.; Gimble, J.M. A non-enzymatic method for isolating human adipose tissue-derived stromal stem cells. Cytotherapy 2013, 15, 979–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raposio, E.; Caruana, G.; Bonomini, S.; Libondi, G. A novel and effective strategy for the isolation of adipose-derived stem cells: Minimally manipulated adipose-derived stem cells for more rapid and safe stem cell therapy. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2014, 133, 1406–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, S.; Dai Prè, E.; Conti, G.; Busato, A.; Mannucci, S.; Sbarbati, A. Comparative technical analysis of lipoaspirate mechanical processing devices. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 1213–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, S. Mechanical/physical methods of cell disruption and tissue homogenization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 424, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Du, H.; Dai, C.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Hunter, D.J.; Lu, L.; Bao, C. Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells for osteoarthritis: A pilot study with long-term follow-up and repeated injections. Regen. Med. 2018, 13, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pers, Y.M.; Rackwitz, L.; Ferreira, R.; Pullig, O.; Delfour, C.; Barry, F.; Sensebe, L.; Casteilla, L.; Fleury, S.; Bourin, P.; et al. Adipose Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Based Therapy for Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee: A Phase I Dose-Escalation Trial. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yokota, N.; Hattori, M.; Ohtsuru, T.; Otsuji, M.; Lyman, S.; Shimomura, K.; Nakamura, N. Comparative clinical outcomes after intra-articular injection with adipose-derived cultured stem cells or noncultured stromal vascular fraction for the treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Am. J. Sports Med. 2019, 47, 2577–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaput, B.; Bertheuil, N.; Escubes, M.; Grolleau, J.L.; Garrido, I.; Laloze, J.; Espagnolle, N.; Casteilla, L.; Sensebé, L.; Varin, A. Mechanically Isolated Stromal Vascular Fraction Provides a Valid and Useful Collagenase-Free Alternative Technique: A Comparative Study. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 138, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usuelli, F.G.; Grassi, M.; Maccario, C.; Vigano, M.; Lanfranchi, L.; Alfieri Montrasio, U.; de Girolamo, L. Intratendinous adipose-derived stromal vascular fraction (SVF) injection provides a safe, efficacious treatment for Achilles tendinopathy: Results of a randomized controlled clinical trial at a 6-month follow-up. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 2000–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, M.; Ghanbarvand, F.; Reza Behvarz, M.; Ejtemaei, M.; Ghadirkhomi, E. Comparison of mesenchymal stem cell markers in multiple human adult stem cells. Int. J. Stem Cells 2014, 7, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Busato, A.; De Francesco, F.; Biswas, R.; Mannucci, S.; Conti, G.; Fracasso, G.; Conti, A.; Riccio, V.; Riccio, M.; Sbarbati, A. Simple and Rapid Non-Enzymatic Procedure Allows the Isolation of Structurally Preserved Connective Tissue Micro-Fragments Enriched with SVF. Cells 2021, 10, 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010036
Busato A, De Francesco F, Biswas R, Mannucci S, Conti G, Fracasso G, Conti A, Riccio V, Riccio M, Sbarbati A. Simple and Rapid Non-Enzymatic Procedure Allows the Isolation of Structurally Preserved Connective Tissue Micro-Fragments Enriched with SVF. Cells. 2021; 10(1):36. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010036
Chicago/Turabian StyleBusato, Alice, Francesco De Francesco, Reetuparna Biswas, Silvia Mannucci, Giamaica Conti, Giulio Fracasso, Anita Conti, Valentina Riccio, Michele Riccio, and Andrea Sbarbati. 2021. "Simple and Rapid Non-Enzymatic Procedure Allows the Isolation of Structurally Preserved Connective Tissue Micro-Fragments Enriched with SVF" Cells 10, no. 1: 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010036
APA StyleBusato, A., De Francesco, F., Biswas, R., Mannucci, S., Conti, G., Fracasso, G., Conti, A., Riccio, V., Riccio, M., & Sbarbati, A. (2021). Simple and Rapid Non-Enzymatic Procedure Allows the Isolation of Structurally Preserved Connective Tissue Micro-Fragments Enriched with SVF. Cells, 10(1), 36. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10010036