Development of Chlorophyll-Meter-Index-Based Dynamic Models for Evaluation of High-Yield Japonica Rice Production in Yangtze River Reaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sites and Experimental Design
2.2. Plant Sampling and Measurement; Shoot Biomass, Nitrogen Concentration, and the NNI
2.3. SPAD Measurements
2.4. Data Analysis
2.4.1. Nitrogen Nutrition Index
2.4.2. Calibration of Dynamic-Critical Curve Models
2.4.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
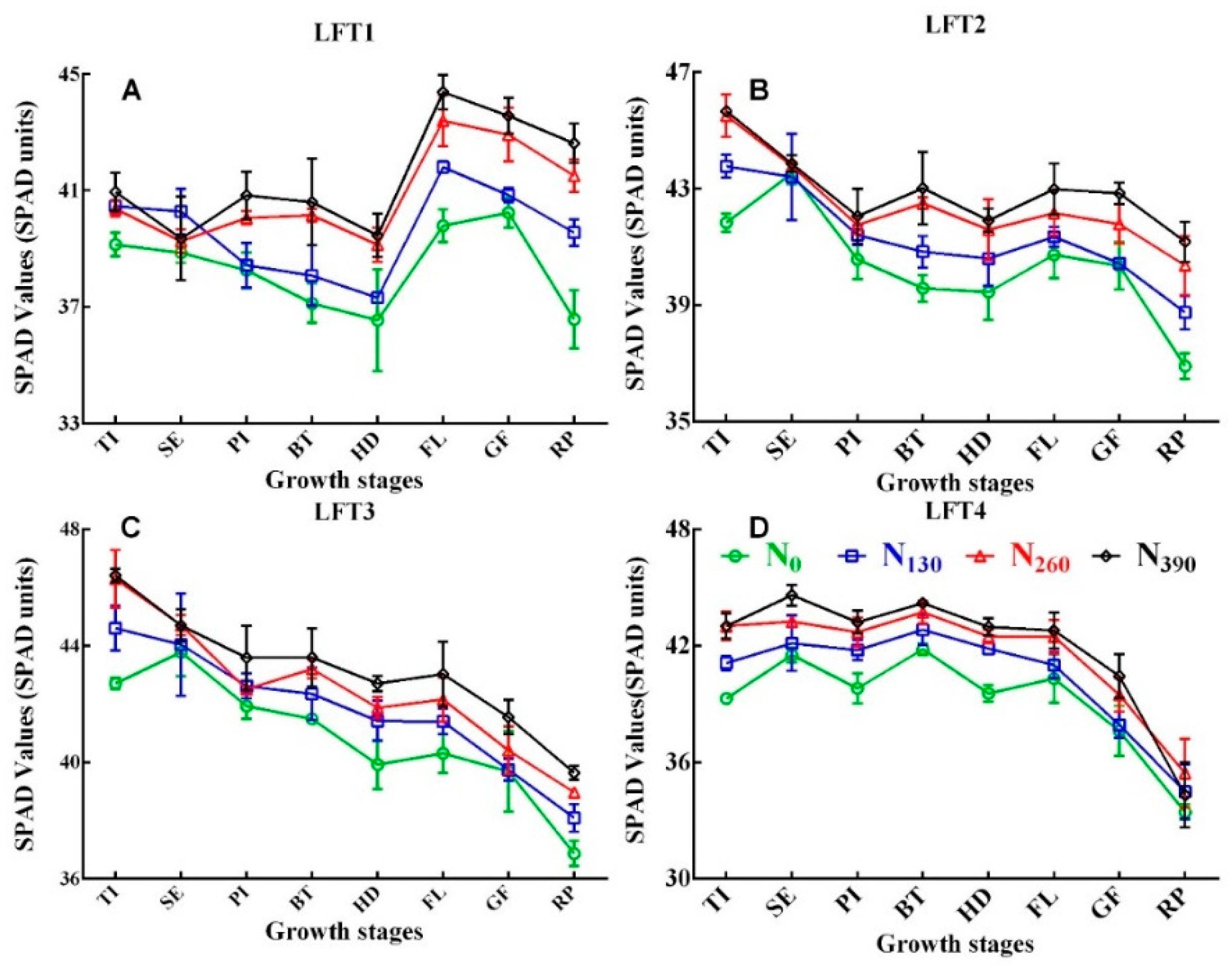
3.1. SPAD Readings of Different Leaves
3.2. Differences in the Normalized SPAD Indices
3.3. The Relationship between the NDSILi,j and Leaf N Concentration
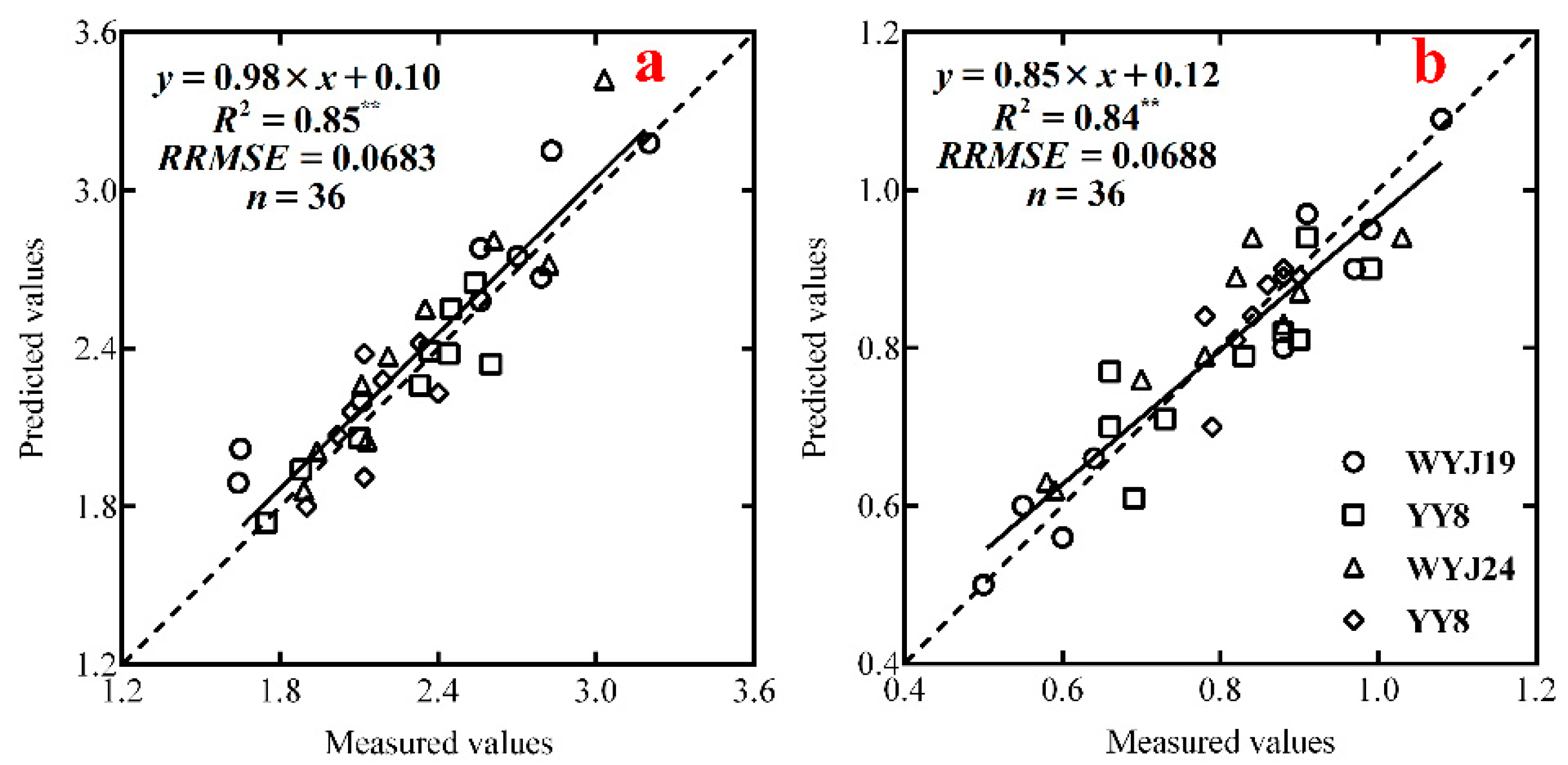
3.4. Relationships between the NDSILi,j and N Nutrition Index
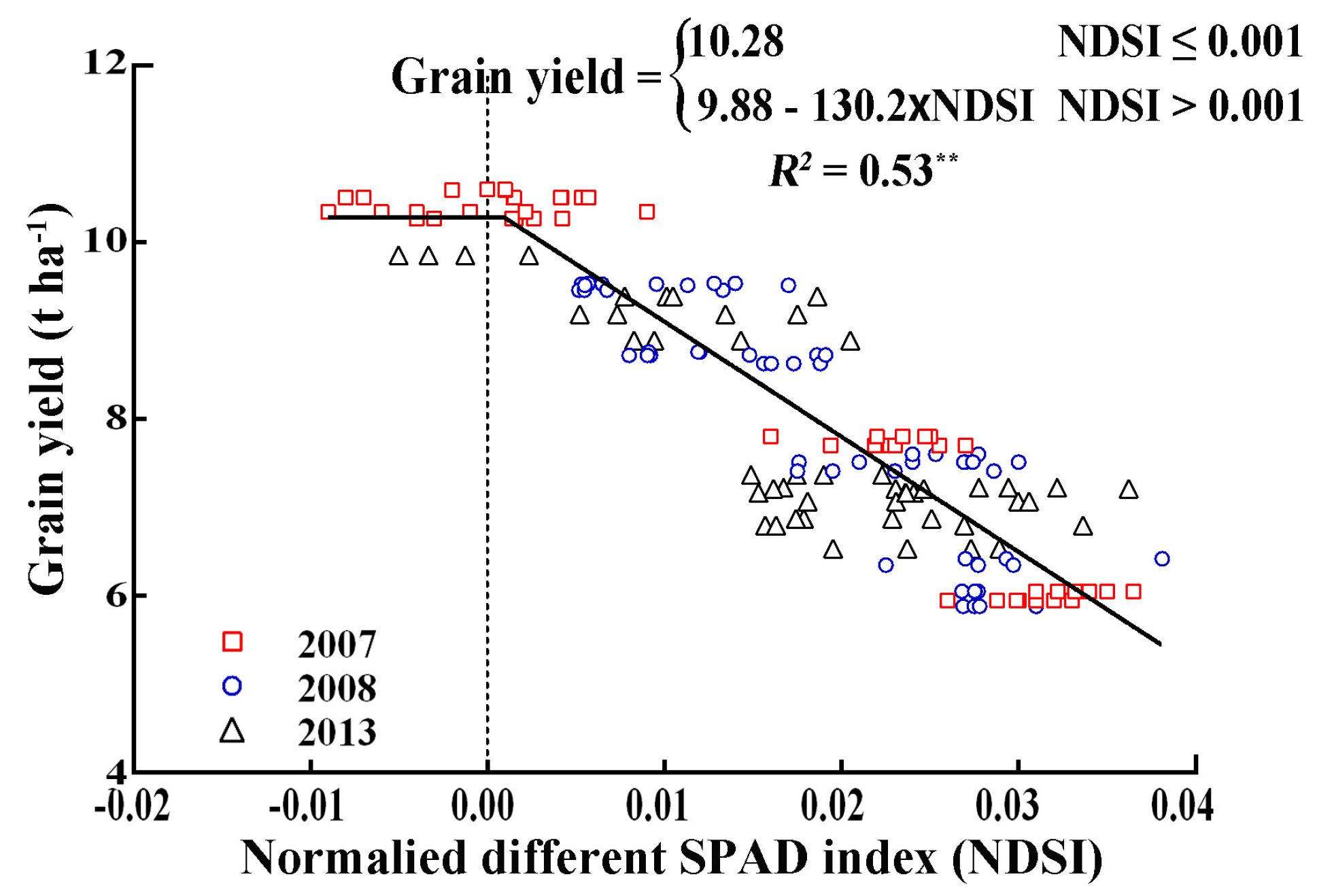
3.5. The Relationship between NDSIL3,4 and Grain Yield
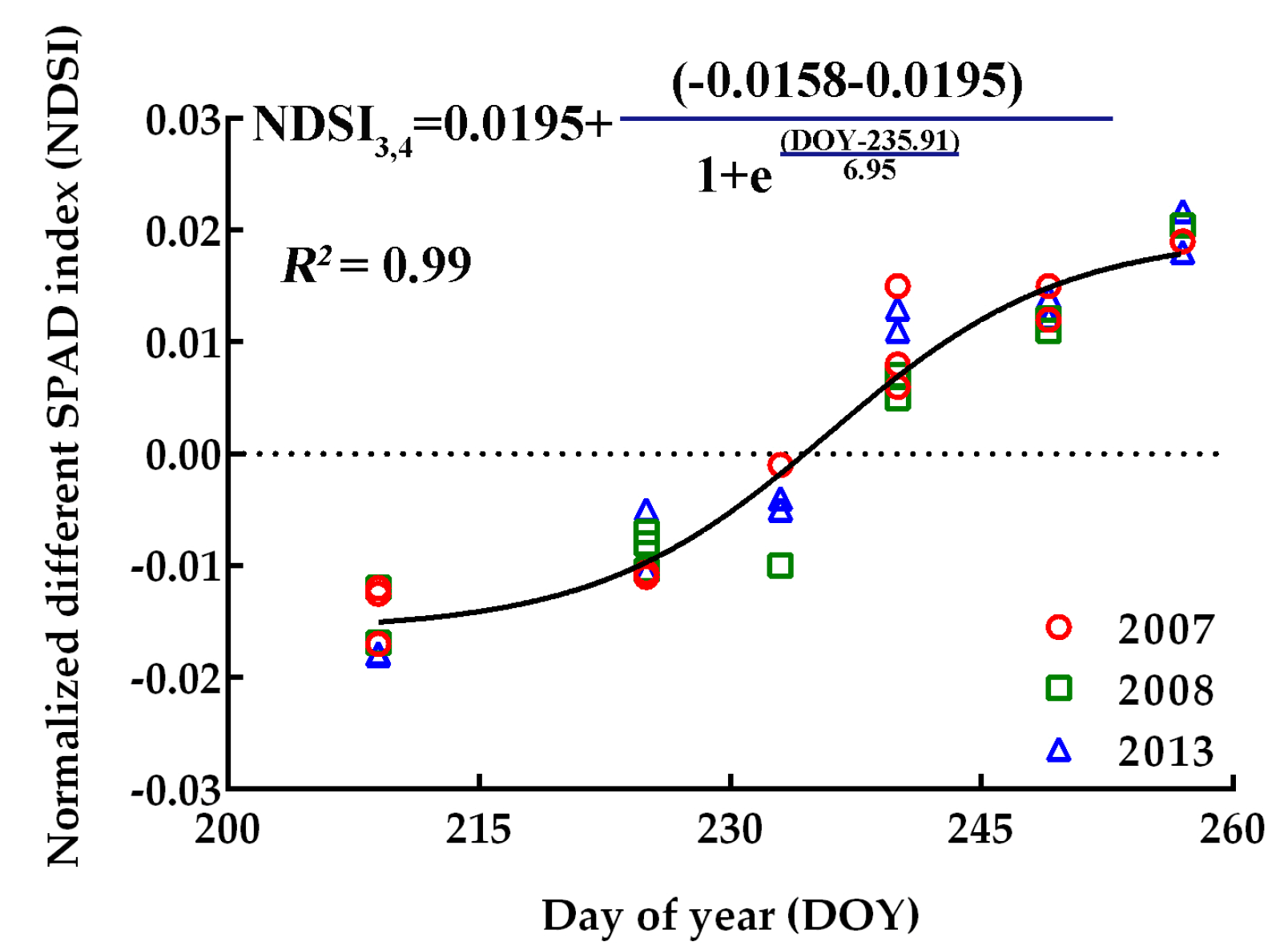
3.6. Use of the NDSIL3,4 Curve for N Management
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TI | Tillering |
| RP | Ripening period |
| BT | Booting |
| HD | Heading |
| SE | Stem elongation |
| PI | Panicle initiation |
| FL | Flowering |
| GF | Grain filling |
| SPAD | Soil and plant analysis development |
| NDSI | Normalized Different SPAD values |
| RSI | Relative SPAD index |
| DSI | Difference SPAD index |
| RDSI | Relative difference SPAD index |
| NNI | Nitrogen Nutrition Index |
| LNC | Leaf Nitrogen concentration |
| LAI | Leaf Area Index |
| DW | Dry matter weight |
| SSNM | Site-Specific Nitrogen Management |
| NUE | Nitrogen Use Efficiency |
| DAT | Day after Transplanting |
| RRMSE | Relative root mean square error |
| LSD | Least significant difference |
| LFT | The position on upper fully expanded Leaf From the rice Top |
References
- Zhao, B.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Duan, A.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Z.; Qin, A.; Ning, D.; Zhang, W. Determination of critical nitrogen concentration and dilution curve based on leaf area index for summer maize. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 228, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Zheng, H.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Estimation of nitrogen fertilizer requirement for rice crop using critical nitrogen dilution curve. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 201, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W. Comparison of different critical nitrogen dilution curves for nitrogen diagnosis in rice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataulkarim, S.T.; Liu, X.; Lu, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Yan, Z.; Cao, W. In-season estimation of rice grain yield using critical nitrogen dilution curve. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 195, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, H.X.; Zhang, H.S.; Zhang, H.; Cai, X.H.; Song, Y.; Kang, L. The characteristics of methane flux from an irrigated rice farm in East China measured using the eddy covariance method. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2018, 249, 228–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousaf, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Shah, F.; Shah, A.N.; Lu, J. Nitrogen fertilizer management for enhancing crop productivity and nitrogen use efficiency in a rice-oilseed rape rotation system in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Tang, L.; Rehmani, M.I.; Cao, W. Non-destructive assessment of plant nitrogen parameters using leaf chlorophyll measurements in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yao, X.; Yao, X.F.; Tian, Y.C.; Liu, X.J.; Ni, J.; Cao, W.X.; Zhu, Y. Estimating leaf nitrogen concentration with three-band vegetation indices in rice and wheat. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 129, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markwell, J.; Osterman, J.C.; Mitchell, J.L. Calibration of the Minolta SPAD-502 leaf chlorophyll meter. Photosynth. Res. 1995, 46, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Qiang, C.; Ke, Z.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Tian, Y.; Yan, Z.; Cao, W.; Liu, X. Optimal leaf positions for spad meter measurement in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Huerta, R.F.; Guevara-Gonzalez, R.G.; Contreras-Medina, L.M.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Prado-Olivarez, J.; Ocampo-Velazquez, R.V. A review of methods for sensing the nitrogen status in plants: Advantages, disadvantages and recent advances. Sensors 2013, 13, 10823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, S.; García, F.V.; Laza, R.C.; Cassman, K.G. Adjustment for specific leaf weight improves chlorophyll meter’s estimate of rice leaf nitrogen concentration. Agron. J. 1993, 85, 987–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, D.; Shi, P.; Omasa, K. Estimating rice chlorophyll content and leaf nitrogen concentration with a digital still color camera under natural light. Plant Methods 2014, 10, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gitelson, A.A.; Viña, A.; Ciganda, V.; Rundquist, D.C.; Arkebauer, T.J. Remote estimation of canopy chlorophyll content in crops. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, 93–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ge, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Cao, Q.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. Evaluation of the chlorophyll meter and GreenSeeker for the assessment of rice nitrogen status. In Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Precision Agriculture (ECPA 2017), Edinburgh, UK, 16–20 July 2017; Volume 8, pp. 359–363. [Google Scholar]
- Sudduth, K.A.; Kitchen, N.R.; Drummond, S.T. Nadir and oblique canopy reflectance sensing for n application in corn. Liccosec 2011, 7, 162–172. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Cao, Q.; Lu, Z.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X. Indicators for diagnosing nitrogen status of rice based on chlorophyll meter readings. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 185, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cao, W. Positional differences in nitrogen and sugar concentrations of upper leaves relate to plant N status in rice under different N rates. Field Crop. Res. 2006, 96, 224–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziadi, N.; Bélanger, G.; Claessens, A.; Lefebvre, L.; Tremblay, N.; Cambouris, A.N.; Nolin, M.C.; Parent, L.É. Plant-based diagnostic tools for evaluating wheat nitrogen status. Crop Sci. 2010, 50, 2580–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, F.; Bronson, K.F.; Singh, Y.; Singh, B.; Peng, S. Use of chlorophyll meter sufficiency indices for nitrogen management of irrigated rice in Asia. Agron. J. 2000, 92, 875–879. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.Z.; Ding, Y.F.; Wang, Q.S.; Huang, P.S.; Ling, Q.H. Relationship between leaf color and nitrogen uptake of rice. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2006, 39, 916–921. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.H.; Cao, W.X.; Wang, Q.S.; Ding, Y.F.; Huang, P.S.; Ling, Q.H. Positional distribution of leaf color and diagnosis of nitrogen nutrition in rice plant. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2002, 192, 45–51. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.Q.; Wang, K.; Zhu, J.Y. Preliminary study on diagnosis of the nitrogen status of two rice varieties using the chlorophyll meter. Bull. Sci. Technol. 2002, 18, 174–176. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, F.F.; Qiu, L.F.; Deng, J.S.; Shi, Y.Y.; Chen, L.S.; Ke, W. Investigation of SPAD meter-based indices for estimating rice nitrogen status. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2010, 71, S60–S65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Rehmani, M.I.A.; Cao, W.; Tang, L. In-season assessment of rice protein and amylose content using critical nitrogen dilution curve. Eur. J. Agron. 2017, 90, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, D.J.; Lemaire, G.; Gosse, G.; Cruz, P.; Draycott, A.; Neeteson, J.J. Decline in percentage n of c3 and c4 crops with increasing plant mass. Ann. Bot. 1990, 66, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Yang, J.P.; Lv, Y.M.; He, J.J. SPAD values and nitrogen nutrition index for the evaluation of rice nitrogen status. Plant Prod. Sci. 2014, 17, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Noura, Z.; Marianne, B.; Gilles, B.; Annie, C.; Nicolas, T.; Athynan, C.; Michelc, N.; Léonétienne, P. Chlorophyll measurements and nitrogen nutrition index for the evaluation of corn nitrogen status. Agron. J. 2010, 100, 2275–2279. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, B.; Liu, Z.; Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Z.; Qi, A.; Ning, D.; Nan, J.; Duan, A. Rapid and nondestructive estimation of the nitrogen nutrition index in winter barley using chlorophyll measurements. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 185, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, Q.; Lv, Z.; Yuan, Z.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Canopy chlorophyll density based index for estimating nitrogen status and predicting grain yield in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ferguson, R.B.; Zheng, H.; Cao, Q.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Using an active-optical sensor to develop an optimal NDVI dynamic model for high-yield rice production (Yangtze, China). Sensors 2017, 17, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debaeke, P.; Rouet, P.; Justes, E. Relationship between the normalized spad index and the nitrogen nutrition index: Application to Durum Wheat. J. Plant Nutr. 2006, 29, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Guo, Z.Q.; Hou, L.B.; Dong, Z.Q.; Zhao, M. Establishment of dry matter accumulation dymamic simulation model and analysis of growth charateristc for high-yielding population of spring maize. J. Maize Sci. 2008, 16, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.R.; Haque, K.M.S.; Akter, N.; Karim, M.A. Leaf chlorophyll dynamics in wheat based on SPAD meter reading and its relationship with grain yield. Sci. Agric. 2014, 4, 13–18. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Cheng, T.; Yao, X.; Deng, X.; Tian, Y.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Detection of rice phenology through time series analysis of ground-based spectral index data. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 198, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Xia, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, W.; Yan, Z. Development of critical nitrogen dilution curve of Japonica rice in Yangtze River Reaches. Field Crop. Res. 2013, 149, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ata-Ul-Karim, S.T.; Zhu, Y.; Yao, X.; Cao, W. Determination of critical nitrogen dilution curve based on leaf area index in rice. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 167, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bijay-Singh; Varinderpal-Singh; Yadvinder-Singh; Thind, H.S.; Kumar, A.; Gupta, R.K.; Kaul, A.; Vashistha, M. Fixed-time adjustable dose site-specific fertilizer nitrogen management in transplanted irrigated rice (Oryza sativa L.) in South Asia. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 126, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yazhen, L.I.; Huiwen, H.U. Estimating the effect of urease inhibitor on rice yield based on NDVI at key growth stages. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2014, 1, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, P.S.A.; Atzberger, C.; Høgda, K.A.; Johansen, B.; Skidmore, A.K. Improved monitoring of vegetation dynamics at very high latitudes: A new method using MODIS NDVI. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 100, 321–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prost, L.; Jeuffroy, M.H. Replacing the nitrogen nutrition index by the chlorophyll meter to assess wheat N status. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2007, 27, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dente, L.; Satalino, G.; Mattia, F.; Rinaldi, M. Assimilation of leaf area index derived from ASAR and MERIS data into CERES-Wheat model to map wheat yield. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1395–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Zhi-Jun, J.I.; Liu, S.H.; Ding, Y.F.; Cao, W.X. Relationships between balance of nitrogen supply-demand and nitrogen translocation and senescence of different position leaves on rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2003, 2, 747–751. [Google Scholar]
- Escobar-Gutiérrez, A.J.; Combe, L. Senescence in field-grown maize: From flowering to harvest. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 134, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Yang, L. Recommendations for nitrogen fertilizer topdressing rates in rice using canopy reflectance spectra. Biosyst. Eng. 2008, 100, 524–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Experiment No. | Transplanting/Harvesting Date | Location | Cultivar | N Rate (kg N ha−1) | Soil Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EXP. 1 2007 | 20-Jun; 21-Oct | Jiangning, E 118.98°, N 31.93° | 9915, 27123 (Japonica) | N0 (0) | Soil type = Fe-leachic -stagnic Anthrosols |
| N1 (130) | Soil pH = 6.5 | ||||
| N4 (260) | OM = 13.5 g·kg−1 | ||||
| N7 (390) | Total N = 1.13 g·kg−1 | ||||
| Available P = 45 mg·g−1 | |||||
| Available K = 82.6 mg·g−1 | |||||
| EXP. 2 2008 | 25-Jun; 27-Oct | Jiangning, E 118.98°, N 31.93° | WXJ14, 27123 (Japonica) | N0 (0) | Soil type = Fe-leachic -stagnic Anthrosols |
| N1 (130) | Soil pH = 6.9 | ||||
| N4 (260) | OM = 13.5 g·kg−1 | ||||
| N7 (390) | Total N = 1.38 g·kg−1 | ||||
| Available P = 43 mg·g−1 | |||||
| Available K = 80 mg·g−1 | |||||
| EXP. 3 2009 | 19-Jun; 20-Oct | Jiangning, E 118.98°, N 31.93° | WYJ19, YY8, WXJ14, WYJ24 (Japonica) | N0 (0) | Soil type = Gley- stagnic Anthrosols |
| N1(130) | Soil pH = 6.9 | ||||
| N4 (260) | OM = 26.15 g·kg−1 | ||||
| N7 (390) | Total N = 1.65 g·kg−1 | ||||
| Available P = 38 mg·g−1 | |||||
| Available K = 70 mg·g−1 | |||||
| EXP. 4 2013 | 19-Jun; 20-Oct | Wujiang, E 121.28°, N 31°33′ | WYJ19, WXJ19 (Japonica) | N0 (0) | Soil type = Typic Endoaquepts |
| N2(150) | Soil pH = 6.75 | ||||
| N3 (225) | OM = 26.15 g·kg−1 | ||||
| N5 (300) | Total N = 2.15 g·kg−1 | ||||
| N6 (375) | Available P = 45.5 mg·g−1 | ||||
| Available K = 115.3 mg·g−1 |
| Index | Description | Algorithm | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DSIL1-L3 | The difference SPAD between 1LFT and 3LFT | S1LFT − S3LFT | [24] |
| SPADL3-L4 | The difference SPAD between 3LFT and 4LFT | S3LFT − S4LFT | [18] |
| RSIL1/L3 | The relative SPAD index between 1LFT and 3LFT | S1LFT/S3LFT | [23] |
| RDSIL1,3 | The relative difference SPAD index between 1LFT and 3LFT | S1LFT/(S1LFT + S3LFT) | [25] |
| NDSIL1,3 | The normalized differences SPAD and index between 1LFT and 3LFT | (S1LFT − S3LFT)/(S1LFT + S3LFT) | [28] |
| NDSI | The normalized differences SPAD and index between i LFT and j LFT, the range of i, j values is from 1 to 4, i < j | (SiLFT − SjLFT)/(SiLFT + SjLFT) | [29] |
| SPAD Indicator | Variety | Year | Treatment | Growth Stage | Residual | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| df | MS | F-Value | df | MS | F-Value | df | MS | F-Value | df | MS | F-Value | df | MS | |
| NDSIL1,2 | 6 | 0.00612 ** | 12.016 | 2 | 0.016 * | 30.025 | 3 | 0.0001 ** | 0.064 | 5 | 0.16 ns | 53.7 | 271 | 0.0001 |
| NDSIL1,3 | 6 | 0.013 ns | 11.288 | 2 | 0.032 ns | 27.303 | 3 | 0.0001 ns | 0.184 | 5 | 0.04 * | 81.014 | 271 | 0.001 |
| NDSIL1,4 | 6 | 0.034 ns | 11.751 | 2 | 0.079 ** | 27.068 | 3 | 0.003 ns | 0.863 | 5 | 0.1 ** | 81 | 271 | 0.002 |
| NDSIL2,3 | 6 | 0.002 * | 1.706 | 2 | 0.003 ns | 2.84 | 3 | 0.016 * | 17.755 | 5 | 0.009 ** | 10.771 | 271 | 0.001 |
| NDSIL2,4 | 6 | 0.016 ** | 8.448 | 2 | 0.035 * | 17.932 | 3 | 0.006 ns | 2.62 | 5 | 0.048 ns | 44.103 | 271 | 0.002 |
| NDSIL3,4 | 6 | 0.004 ns | 6.65 | 2 | 0.009 ns | 13.945 | 3 | 0.006 ** | 10.29 | 5 | 0.017 ** | 60.636 | 271 | 0.0001 |
| Year | SPAD Index | Quantitative Relationship | R2 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | SPADL3-L4 | LNC = 2.243 × e−0.053SPAD | 0.21 ns | 0.37 |
| RSIL1/L3 | LNC = 2.12 × e−2.66RSI | 0.56 * | 0.27 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | LNC = 11.909 × e−1.75DSI | 0.53 * | 0.33 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | LNC = 2.054 × e−0.049RDSI | 0.35 * | 0.29 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | LNC = 2.193 × e−11.38NDSI | 0.77 ** | 0.31 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | LNC = 2.137 × e−5.072NDSI | 0.61 * | 0.33 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | LNC = 2.205 × e−2.229NDSI | 0.36 * | 0.46 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | LNC = 2.16 × e−7.467NDSI | 0.36 * | 0.23 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | LNC = 2.257 × e−2.681NDSI | 0.19 ns | 0.25 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | LNC = 2.249 × e−10.58NDSI | 0.83 ** | 0.23 | |
| 2008 | SPADL3-L4 | LNC = 2.195 × e−0.042SPAD | 0.11 ns | 0.27 |
| RSIL1/L3 | LNC = 1.863 × e−6.747RSI | 0.58 * | 0.31 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | LNC = 4.131 × e−0.688DSI | 0.56 * | 0.33 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | LNC = 1.862 × e−0.163RDSI | 0.59 * | 0.24 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | LNC = 1.896 × e−14.87NDSI | 0.61 ** | 0.21 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | LNC = 1.898 × e−14.84NDSI | 0.61 ** | 0.21 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | LNC = 2.092 × e−3.476NDSI | 0.18 ns | 0.48 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | LNC = 2.019 × e−0.4133NDSI | - | 0.54 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | LNC = 2.201 × e−1.895NDSI | 0.06 ns | 0.49 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | LNC = 2.208 × e−14.71NDSI | 0.81 ** | 0.16 | |
| 2013 | SPADL3-L4 | LNC = 1.974 × e−0.045SPAD | 0.16 ns | 0.41 |
| RSIL1/L3 | LNC = 1.979 × e−0.037RSI | 0.49 * | 0.34 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | LNC = 8.39 × e−1.43DSI | 0.17 ns | 0.52 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | LNC = 1.998 × e−1.434RDSI | 0.57 * | 0.36 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | LNC = 2.167 × e−3.556NDSI | 0.56 ** | 0.34 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | LNC = 2.219 × e−2.401NDSI | 0.57 ** | 0.29 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | LNC = 2.324 × e−1.706NDSI | 0.18 ns | 0.39 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | LNC = 2.363 × e−2.673NDSI | 0.07 ns | 0.15 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | LNC = 2.385 × e−0.121NDSI | - | 0.24 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | LNC = 2.246 × e−10.56NDSI | 0.82 ** | 0.18 |
| Nitrogen Indicator | Parameter | Impact Factor | Mean Square (MS) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NDSIL1,2 | NDSIL1,3 | NDSIL1,4 | NDSIL2,3 | NDSIL2,4 | NDSIL3,4 | |||
| LNC | a | Year | 0.27 * | 0.27 ns | 0.15 ns | 0.0355 ns | 0.09 ns | 0.001 ns |
| variety | 0.104 ns | 0.035 ns | 0.021 ns | 0.0178 ns | 0.26 ns | 0.0252 ns | ||
| b | Year | 42.67 ns | 42.88 ns | 0.83 ns | 12.97 ns | 1.72 ns | 5.71 ns | |
| variety | 36.58 ns | 41.24 ns | 0.61 ns | 8.73 ns | 1.22* | 3.07 ns | ||
| Residual | 0.051 | 0.061 | 0.021 | 0.035 | 0.014 | 0.023 | ||
| NNI | a | Year | 0.02 ns | 0.01 ns | 0.01 ns | - | - | 0.02 ns |
| variety | 0.21 ns | 0.04 ns | 0.09 * | 0.17 ns | 0.06 ns | 0.51 ns | ||
| b | Year | 5.51 ns | 5.58 ns | 0.54 ns | 8.45 ns | 5.91 ns | 5.62 ns | |
| variety | 1.39 ns | 6.71 ns | 0.91 ns | 4.27 ns | 6.53 ns | 4.98 ns | ||
| Residual | 0.27 | 0.39 | 0.17 | 0.32 | 0.21 | 0.04 | ||
| Year | SPAD Index | Quantitative Relationship | R2 | SD |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | SPADL3-L4 | NNI = 0.780 × e−0.028SPAD | 0.16 ns | 0.49 |
| RSIL1/L3 | NNI = 0.739 × e−0.012RSI | 0.35 * | 0.38 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | NNI = 1.017 × e−0.322DSI | 0.26 ns | 0.32 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.746 × e−0.627RDSI | 0.56 * | 0.27 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | NNI = 0.776 × e−5.84NDSI | 0.76 ** | 0.31 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.759 × e−2.35NDSI | 0.53 * | 0.33 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | NNI = 0.766 × e−1.06NDSI | 0.15 ns | 0.46 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | NNI = 0.755 × e−2.89NDSI | 0.61 * | 0.23 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | NNI = 0.773 × e−1.32NDSI | 0.14 ns | 0.25 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | NNI = 0.809 × e−8.85NDSI | 0.83 ** | 0.23 | |
| 2008 | SPADL3-L4 | NNI = 0.764 × e−0.36SPAD | 0.14 ns | 0.51 |
| RSIL1/L3 | NNI = 0.713 × e−2.91RSI | 0.21 ns | 0.34 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | NNI = 0.498 × e0.41DSI | 0.43 * | 0.40 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.707 × e−0.07RDSI | 0.67 * | 0.26 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | NNI = 0.709 × e−5.99NDSI | 0.71 * | 0.21 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.710 × e−6.05NDSI | 0.62 * | 0.21 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | NNI = 0.749 × e0.50NDSI | - | 0.48 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | NNI = 0.746 × e−2.11NDSI | 0.68 * | 0.54 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | NNI = 0.742 × e1.48NDSI | 0.07 ns | 0.49 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | NNI = 0.821 × e−11.96NDSI | 0.85 ** | 0.16 | |
| 2013 | SPADL3-L4 | NNI = 0.653 × e−0.02SPAD | 0.15 ns | 0.39 |
| RSIL1/L3 | NNI = 0.610 × e−0.03RSI | 0.32 * | 0.28 | |
| DSIL1-L3 | NNI = 2.492 × e−1.40DSI | 0.51 * | 0.36 | |
| RDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.615 × e−1.40RDSI | 0.60 * | 0.26 | |
| NDSIL1,2 | NNI = 0.708 × e−1.85NDSI | 0.57 * | 0.34 | |
| NDSIL1,3 | NNI = 0.711 × e−1.52NDSI | 0.41 * | 0.29 | |
| NDSIL1,4 | NNI = 0.721 × e−1.96NDSI | 0.25 * | 0.39 | |
| NDSIL2,3 | NNI = 0.733 × e−2.96NDSI | 0.58 * | 0.15 | |
| NDSIL2,4 | NNI = 0.764 × e−3.36NDSI | 0.16 ns | 0.24 | |
| NDSIL3,4 | NNI = 0.734 × e−13.51NDSI | 0.84 ** | 0.18 |
| Year | Variety | Growth Stage | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TI | SE | PI | BT | HD | FL | ||
| 2007 | 9915 | 0.26 * | 0.73 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.68 * | 0.68 * | 0.32 * |
| 27123 | 0.21 * | 0.48 * | 0.62 * | 0.75 ** | 0.51 * | 0.43 * | |
| 2008 | 27123 | 0.20 * | 0.68 * | 0.73 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.65 * | 0.40 * |
| WXJ14 | 0.26 * | 0.75 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.72 ** | 0.54 * | 0.37 * | |
| 2013 | WYJ19 | 0.22 * | 0.57 * | 0.63 * | 0.61 * | 0.52 * | 0.34 * |
| YY8 | 0.19 ns | 0.74 ** | 0.62 * | 0.47 * | 0.62 * | 0.42 * | |
| Regression Model | Equation | R2 | RRMSE (%) | F-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| linear model | y = a + b × x | 0.899 | 23.5 | 213.8 |
| Boltzmann model | y = A2 + (A1 − A2)/(1 + e((x − x0)/dx)) | 0.975 | 16.8 | 265.9 |
| Polynomial model | y = A + B × x + C × x2+D × x3+… | 0.927 | 25.2 | 113.91 |
| Exponential model | y = a−b × cx | 0.894 | 28.5 | 99.9 |
| Bradley model | y = a × ln(−b × ln(x)) | 0.889 | 28.95 | 142.5 |
| Power model | y = a × xb | 0.453 | 48.3 | 15.3 |
| Nelder model | y = (x + a)/(b0 + b1 × (x + a) + b2 × (x + a)2) | 0.929 | 24.4 | 116.9 |
| DoseResp model | y = A1 + (A2 − A1)/(1 + 10((LOGx0 − x) × p)) | 0.931 | 23.4 | 119.8 |
| Hyperbola model | - | - | - | - |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, K.; Liu, X.; Tahir Ata-Ul-Karim, S.; Lu, J.; Krienke, B.; Li, S.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Cao, W.; Tian, Y. Development of Chlorophyll-Meter-Index-Based Dynamic Models for Evaluation of High-Yield Japonica Rice Production in Yangtze River Reaches. Agronomy 2019, 9, 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020106
Zhang K, Liu X, Tahir Ata-Ul-Karim S, Lu J, Krienke B, Li S, Cao Q, Zhu Y, Cao W, Tian Y. Development of Chlorophyll-Meter-Index-Based Dynamic Models for Evaluation of High-Yield Japonica Rice Production in Yangtze River Reaches. Agronomy. 2019; 9(2):106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020106
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ke, Xiaojun Liu, Syed Tahir Ata-Ul-Karim, Jingshan Lu, Brian Krienke, Songyang Li, Qiang Cao, Yan Zhu, Weixing Cao, and Yongchao Tian. 2019. "Development of Chlorophyll-Meter-Index-Based Dynamic Models for Evaluation of High-Yield Japonica Rice Production in Yangtze River Reaches" Agronomy 9, no. 2: 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020106
APA StyleZhang, K., Liu, X., Tahir Ata-Ul-Karim, S., Lu, J., Krienke, B., Li, S., Cao, Q., Zhu, Y., Cao, W., & Tian, Y. (2019). Development of Chlorophyll-Meter-Index-Based Dynamic Models for Evaluation of High-Yield Japonica Rice Production in Yangtze River Reaches. Agronomy, 9(2), 106. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9020106








