Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Samples and Measurement
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
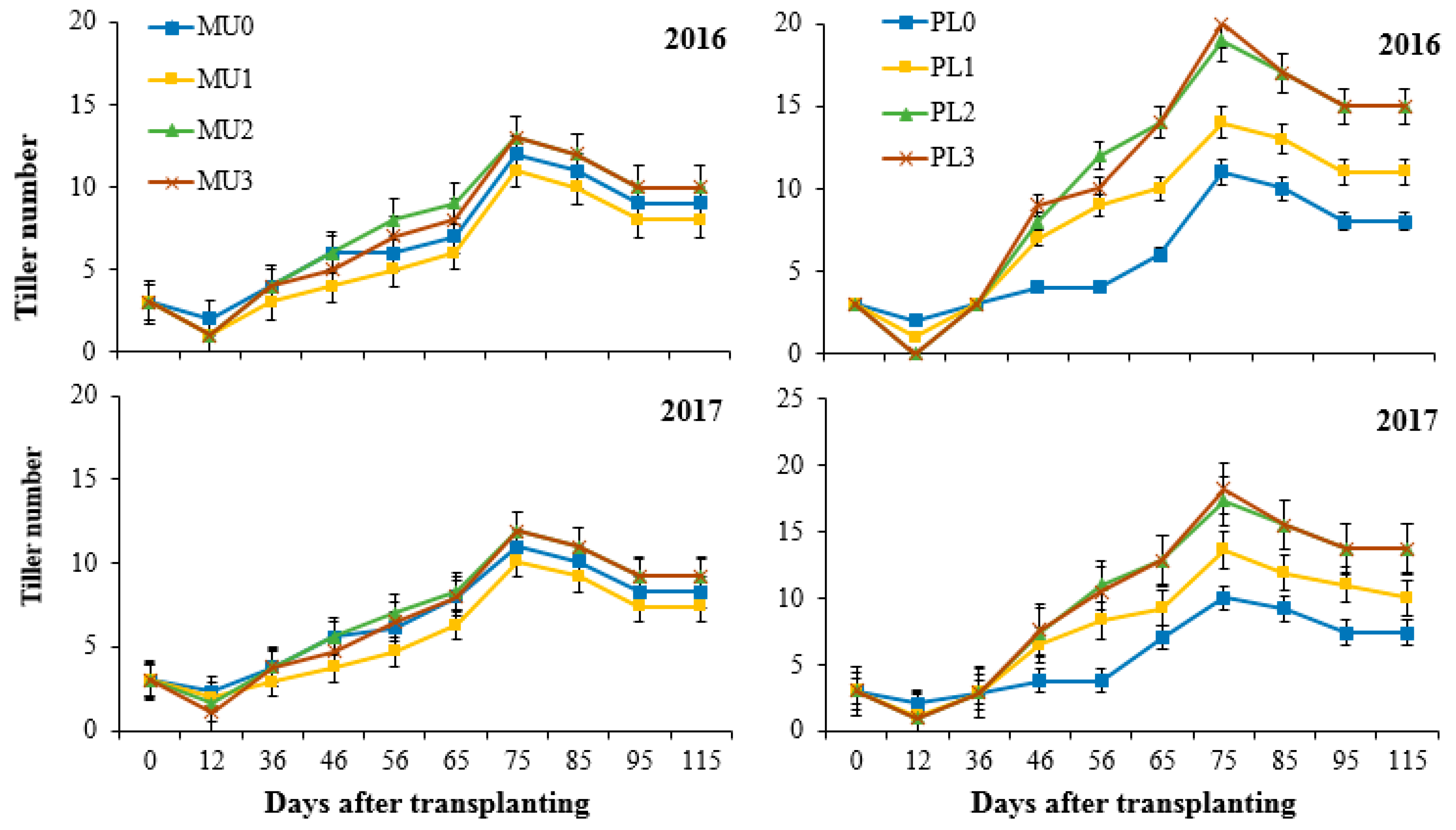
3.1. Impacts of Straw Incorporation on the Tillering Dynamics of Rice
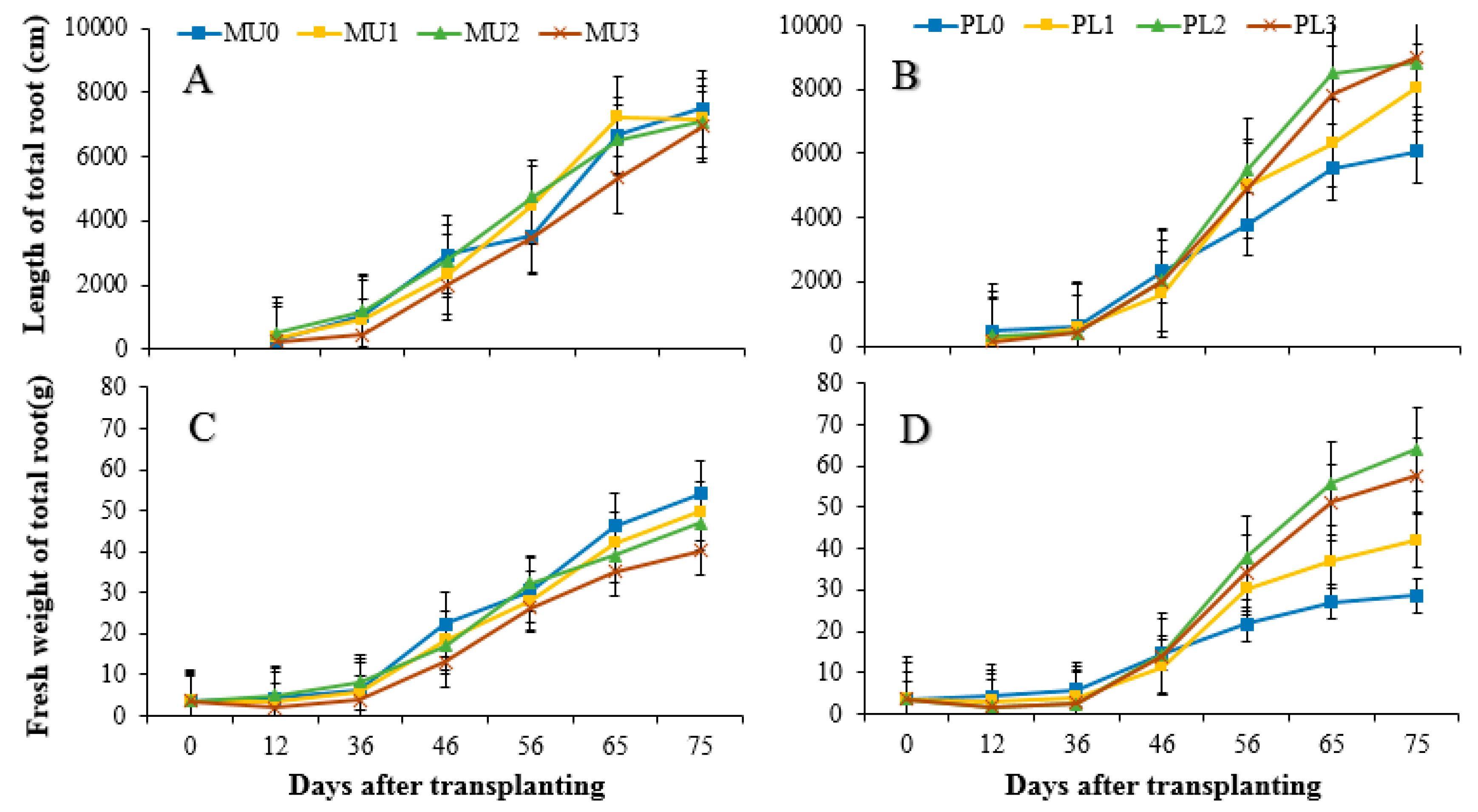
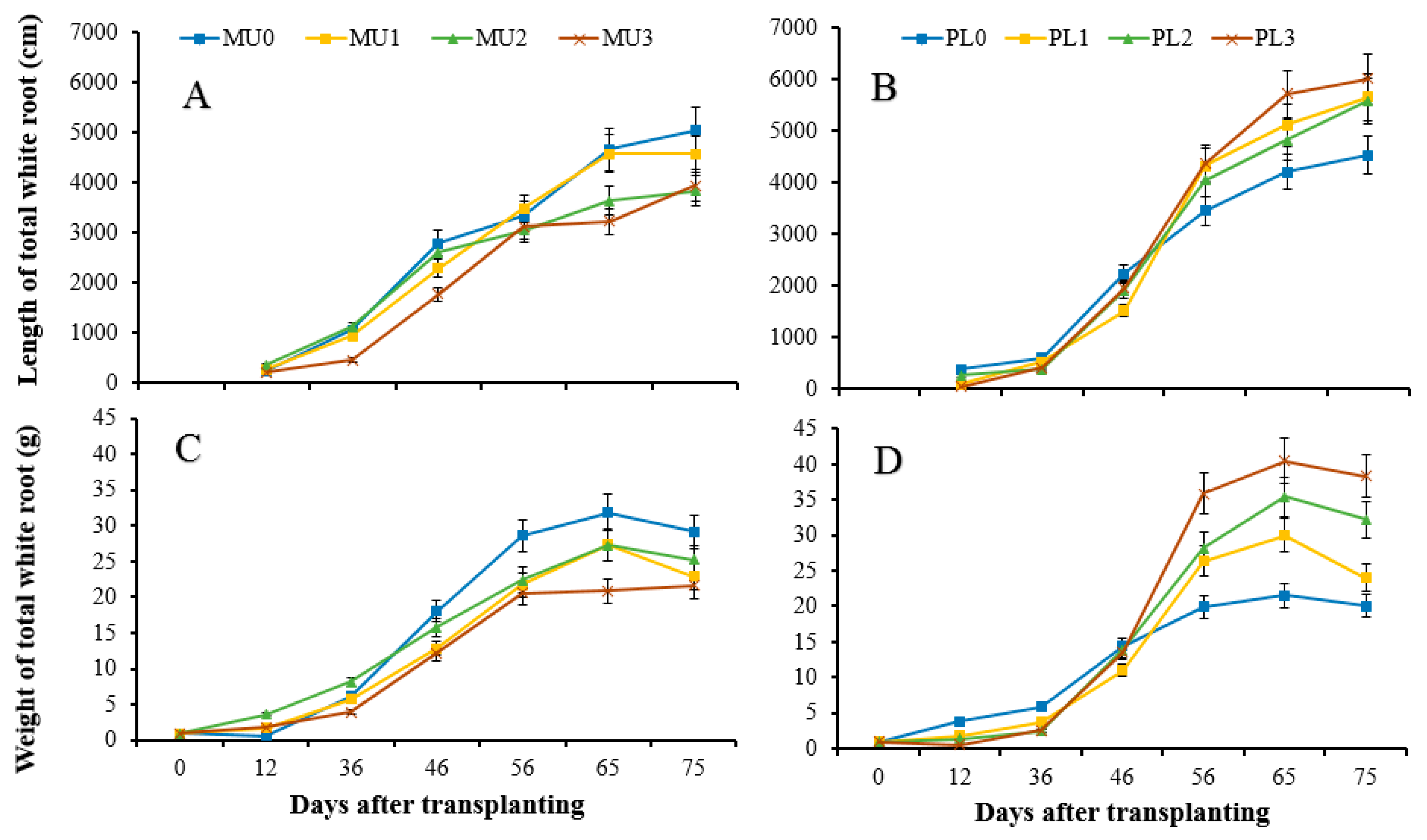
3.2. Impacts of Straw Incorporation on the Dynamics of White Root
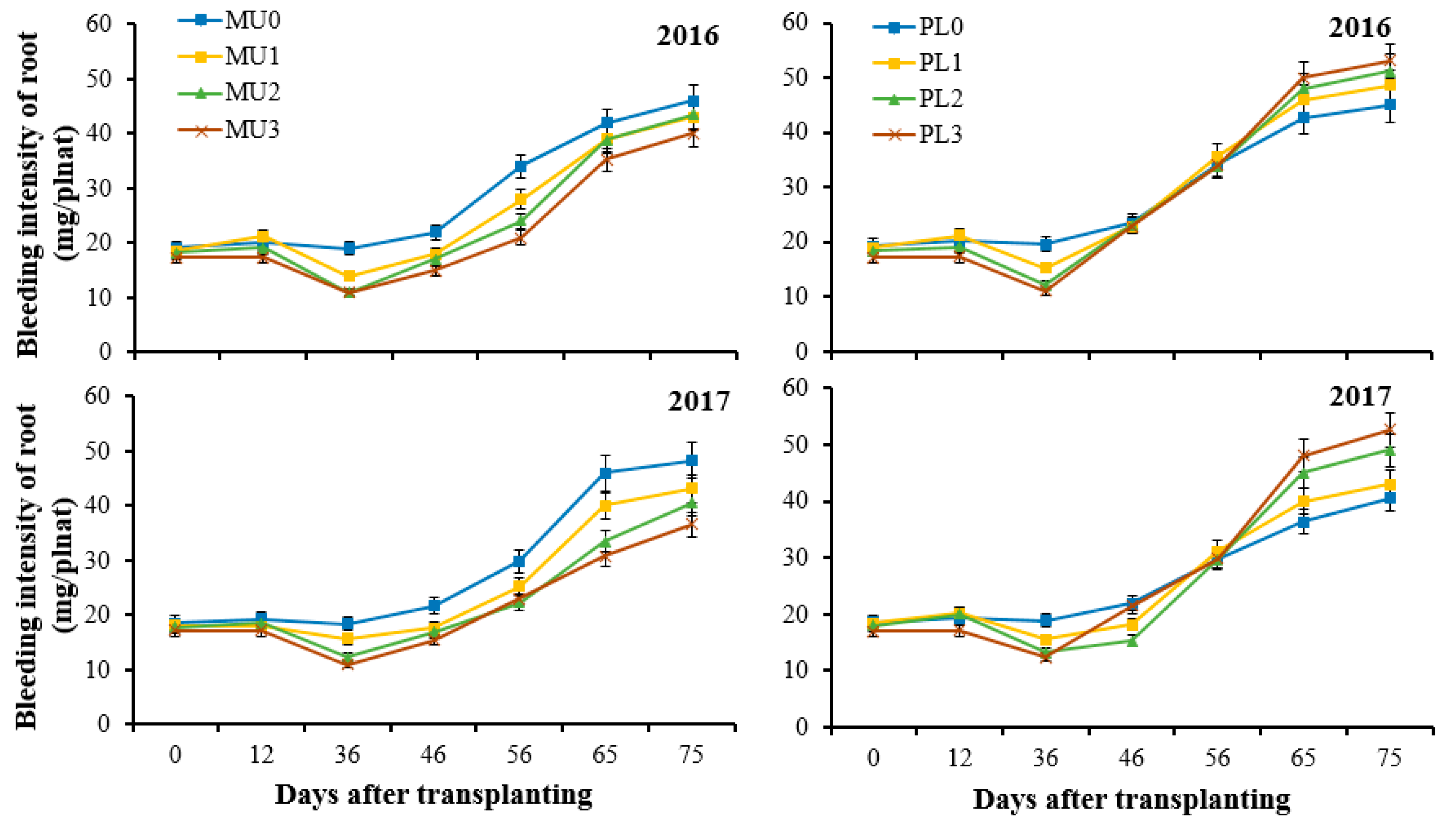
3.3. Impacts of Straw Incorporation on Root Bleeding
3.4. Impacts of Straw Returning on Rice Yield and Its Component
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Impacts of Straw Returning on Root Growth
4.2. Impacts of Straw Returning on Tiller Growth and Yield of Hybrid Rice
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Dai, M.; Dai, S.; Dong, X. Current status and environment impact of direct straw return in China’s cropland—A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.; Cao, X.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, L. Responses of rice production, milled rice quality and soil properties to various nitrogen inputs and rice straw incorporation under continuous plastic film mulching cultivation. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 155, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totin, E.; Stroosnijder, L.; Agbossou, E. Mulching upland rice for efficient water management: A collaborative approach in Benin. Agric. Water Manag. 2013, 125, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Lu, J.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Ren, T.; Cong, R. Influence of rice straw mulching on seed yield and nitrogen use efficiency of winter oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in intensive rice-oilseed rape cropping system. Field Crop. Res. 2014, 159, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, H.; Zhao, W.; Li, T.; Cheng, X.; Liu, Q. Balancing straw returning and chemical fertilizers in China: Role of straw nutrient resources. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 2695–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Köbke, S.; Pfeiffer, B.; Senbayram, M.; Dittert, K.; Nacke, H. Post-harvest N2O and CO2 emissions related to plant residue incorporation of oilseed rape and barley straw depend on soil NO3-content. Soil. Till. Res. 2018, 179, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupnik, T.J.; Shennan, C.; Rodenburg, J. Yield, water productivity and nutrient balances under the System of Rice Intensification and Recommended Management Practices in the Sahel. Field Crop. Res. 2012, 130, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hu, K.; Li, K.; Zheng, C.; Li, B. Simulating the effects of long-term discontinuous and continuous fertilization with straw return on crop yields and soil organic carbon dynamics using the DNDC model. Soil. Till. Res. 2017, 165, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, C.A.; O’Donovan, J.T.; Blackshaw, R.E.; Harker, K.N.; Johnson, E.N.; Gan, Y.; Lafond, G.P.; May, W.E.; Turkington, T.K.; Lupwayi, N.Z.; et al. Residual effects of preceding crops and nitrogen fertilizer on yield and crop and soil N dynamics of spring wheat and canola in varying environments on the Canadian prairies. Field Crop. Res. 2016, 192, 86–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Jalota, S.K.; Singh, Y. Manuring and residue management effects on physical properties of a soil under the rice-wheat system in Punjab, India. Soil. Till. Res. 2007, 94, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Nie, L.; Buresh, R.J.; Huang, J.; Cui, K.; Xu, B.; Gong, W.; Peng, S. Agronomic performance of late-season rice under different tillage, straw, and nitrogen management. Field Crop. Res. 2010, 115, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawe, D.; Dobermann, A.; Ladha, J.K.; Yadav, R.L.; Bao, L.; Gupta, R.K.; Lal, P.; Panaullah, G.; Sariam, O.; Singh, Y.; et al. Do organic amendments improve yield trends and profitability in intensive rice systems? Field Crop. Res. 2003, 83, 191–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, M.; Asch, F.; Maskey, S.L.; Pande, K.R.; Shah, S.C.; Shrestha, S. Effects of transition season management on soil N dynamics and system N balances in rice-wheat rotations of Nepal. Field Crop. Res. 2007, 103, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hang, X.; Lamine, S.M.; Jiang, Y.; Afreh, D.; Qian, H.; Feng, X.; Zheng, C.; Deng, A.; Song, Z.; et al. Interactive effects of straw incorporation and tillage on crop yield and greenhouse gas emissions in double rice cropping system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 250, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.Y.; Jia, J.X.; Xiong, Z.Q.; Khalil, M.A.K.; Xing, G.X. Water regime-nitrogen fertilizer-straw incorporation interaction: Field study on nitrous oxide emissions from a rice agroecosystem in Nanjing, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2011, 141, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Turner, D.; Duan, Y.H.; Wang, D.S.; Shen, Q.R. Root Physiological and Morphological Characteristics of Two Rice Cultivars with Different Nitrogen-Use Efficiency. Pedosphere 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Fang, C.; Lu, L.; Hu, Z.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, Z. Determination of soluble sugar profile in rice. J. Chromatogr. B 2017, 1058, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sax, S.M.; Moore, J.J.; Nino, H.V.; Edwards, D.J.; Annino, J.S. Glutamic Oxalacetic Transaminase (Colorimetric); MacDonald, R.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Cao, X.; Bai, Z.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, L.; Huang, J.; Jin, Q. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry Nitrogen metabolism correlates with the acclimation of photosynthesis to short-term water stress in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.Z.; Zhang, F.Z. Activities of nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase in rice seedlings during cyanide metabolism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 225–226, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wang, B.; Gu, Z.; Tao, B.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, S.; Zhu, L.; Meng, Y. Effects of different straw returning modes on greenhouse gas emissions and crop yields in a rice-wheat rotation system. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 223, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, J.; Zheng, J.; Chang, A. Changes in greenhouse gas evolution in heavy metal polluted paddy soils with rice straw return: A laboratory incubation study. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2014, 63, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.S.; Guo, L.J.; Liu, T.Q.; Li, C.F.; Cao, C.G. Effects of tillage practices and straw returning methods on greenhouse gas emissions and net ecosystem economic budget in rice-wheat cropping systems in central China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 636–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Lu, D.; Zhou, J.; Li, C. Changes in soil microbial community and organic carbon fractions under short-term straw return in a rice–wheat cropping system. Soil. Till. Res. 2017, 165, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Pang, D.; Chen, J.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, M.; Yin, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Z. Straw return accompany with low nitrogen moderately promoted deep root. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 221, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Zhong, H.; Wu, J. Chemosphere Incorporating rice residues into paddy soils affects methylmercury accumulation in rice. Chemosphere 2016, 152, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Mandal, K.G.; Mohanty, R.K.; Ambast, S.K. Rice root growth, photosynthesis, yield and water productivity improvements through modifying cultivation practices and water management. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 206, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linh, T.B.; Sleutel, S.; Vo Thi, G.; Le Van, K.; Cornelis, W.M. Deeper tillage and root growth in annual rice-upland cropping systems result in improved rice yield and economic profit relative to rice monoculture. Soil. Till. Res. 2015, 154, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, L.; Yang, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Rice root growth and nutrient uptake as influenced by organic manure in continuously and alternately flooded paddy soils. Agric. Water Manag. 2004, 70, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Huang, L.; Huang, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Effects of organic carbon and iron oxides on soil aggregate stability under different tillage systems in a rice–rape cropping system. Catena 2019, 177, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhai, S.; Li, Y.; Zhou, J.; He, R.; Liu, J.; Xue, Y.; Meng, Y. Waterlogging reduction and wheat yield increase through long-term ditch-buried straw return in a rice—Wheat rotation system. Field Crop. Res. 2017, 209, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Yang, B.; Dai, Y.; Xu, M.; Koide, R.T.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Bian, X. Soil nitrogen retention is increased by ditch-buried straw return in a rice-wheat rotation system. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 69, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.L.; Wang, L.; Lu, Y.L.; Yang, L.P.; Zhou, L.P.; Ni, L.; Cheng, M.F. Effects of long-term full straw return on yield and potassium response in wheat-maize rotation. J. Integr. Agric. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, J.; Du, C.; Wang, H. Effect of Long-Term Rice Straw Return on Soil Glomalin, Carbon and Nitrogen. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 295–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chico-Santamarta, L.; Humphries, A.C.; Chaney, K.; White, D.R.; Magan, N.; Godwin, R.J. Microbial changes during the on-farm storage of canola (oilseed rape) straw bales and pellets. Biomass Bioenergy 2011, 35, 2939–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimber, R. Phytotoxicity from plant residues. I. The influence of rotted wheat straw on seedling growth. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Li, G.; Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Yang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ding, C.; Liu, Z.; Ding, Y. Methane emissions from rice fields under continuous straw return in the middle-lower reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Environ. Sci-China 2013, 25, 1874–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Bai, J.; Zeng, N.; Zhou, X.; Liao, Y.; Lu, Y.; Rees, R.M.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Diazotroph abundance and community structure are reshaped by straw return and mineral fertilizer in rice-rice-green manure rotation. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 136, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.R.; Dong, J.X.; Han, L.L.; Zheng, Y.M.; He, J.Z. Influence of rice straw amendment on mercury methylation and nitrification in paddy soils. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 209, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wu, M.; Petropoulos, E.; Zhang, J.; Nie, J.; Liao, Y.; Li, Z.; Lin, X.; Feng, Y. Responses of paddy soil bacterial community assembly to different long-term fertilizations in southeast China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 656, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azam, F.; Lodhi, A.; Ashraf, M. Availability of soil and fertilizer nitrogen to wetland rice following wheat straw amendment. Biol. Fert. Soils. 1991, 11, 97–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Han, S.; Du, Y.; Liu, H.; Nie, H.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q. The shift of sulfate-reducing bacterial communities from the upland to the paddy stage in a rapeseed-rice rotation system, and the e ff ect from the long- term straw returning. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.; Xu, X.; He, P.; Ullah, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, W. Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency through alternative fertilization options for rice in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crop. Res. 2018, 227, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.J.; Li, L.Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Pan, G.X.; Qaiser, H.; Liu, Y.Z. Impact of Long-Term Fertilization on Community Structure of Ammonia Oxidizing and Denitrifying Bacteria Based on amoA and nirK Genes in a Rice Paddy from Tai Lake Region, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 2286–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, G.; Zhou, P.; Li, Z.; Smith, P.; Li, L.; Qiu, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Shen, S.; Chen, X. Combined inorganic/organic fertilization enhances N efficiency and increases rice productivity through organic carbon accumulation in a rice paddy from the Tai Lake region, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 131, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, X.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.; Li, J.; Wan, Y.; Gao, Q.; Fan, F.; Liao, Y. Long-term effect of biochar application on yield-scaled greenhouse gas emissions in a rice paddy cropping system: A four-year case study in south China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 570, 1390–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
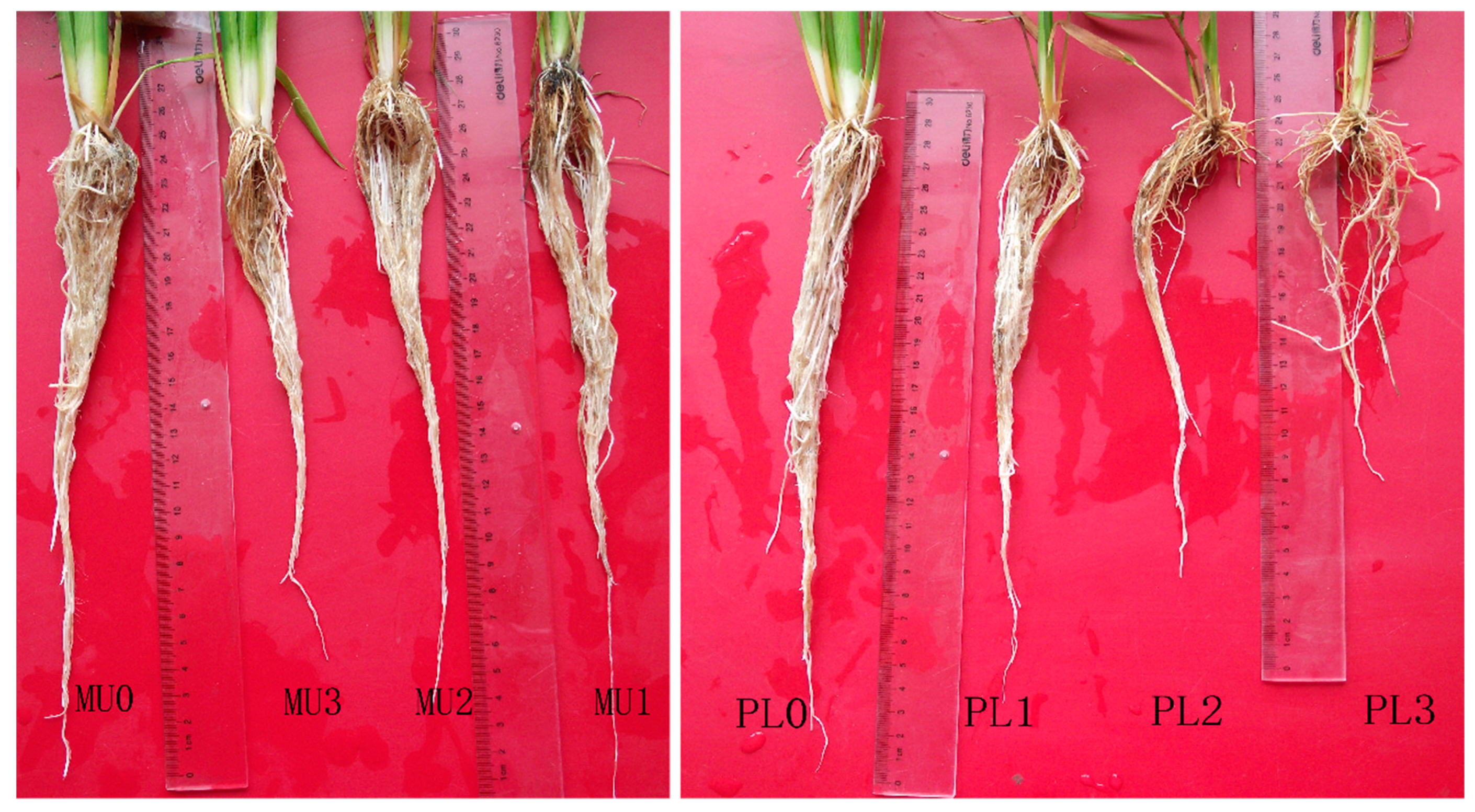


| MU0 | MU1 | MU2 | MU3 | PL0 | PL1 | PL2 | PL3 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Straw returning amount | 0.0 t/hm2 | 1.5 t/hm2 | 3.0 t/hm2 | 4.5 t/hm2 | 0.0 t/hm2 | 1.5 t/hm2 | 3.0 t/hm2 | 4.5 t/hm2 |
| 12 d | 56 d | 75 d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MU0 | 0.34 ± 0.04 | a | 0.44 ± 0.04 | b | 0.21 ± 0.01 | d |
| MU1 | 0.33 ± 0.02 | b | 0.43 ± 0.02 | c | 0.22 ± 0.02 | c |
| MU2 | 0.32 ± 0.02 | c | 0.44 ± 0.02 | b | 0.27 ± 0.02 | b |
| MU3 | 0.30 ± 0.01 | d | 0.45 ± 0.01 | a | 0.29 ± 0.02 | a |
| PL0 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | a | 0.51 ± 0.02 | a | 0.22 ± 0.03 | d |
| PL1 | 0.28 ± 0.03 | b | 0.48 ± 0.03 | c | 0.25 ± 0.01 | c |
| PL2 | 0.26 ± 0.03 | c | 0.48 ± 0.03 | c | 0.27 ± 0.01 | b |
| PL3 | 0.24 ± 0.05 | d | 0.49 ± 0.05 | b | 0.28 ± 0.02 | a |
| DFP | TRT | SS (%) | GPT (μmol/(g·h)) | GOT (μmol/(g·h)) | GS (μmol/(g·h)) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36 | MU0 | 1.84 ± 0.08a | 2.53 ± 0.07a | 5.71 ± 0.06a | 17.64 ± 0.09a |
| MU1 | 1.72 ± 0.11b | 2.48 ± 0.06ab | 5.64 ± 0.05b | 15.21 ± 0.08b | |
| MU2 | 1.61 ± 0.09bc | 2.46 ± 0.06b | 5.02 ± 0.08c | 13.62 ± 0.07c | |
| MU3 | 1.52 ± 0.09c | 2.31 ± 0.09c | 4.87 ± 0.07d | 11.54 ± 0.07d | |
| PL0 | 1.86 ± 0.09a | 2.51 ± 0.07a | 5.73 ± 0.09a | 17.65 ± 0.09a | |
| PL1 | 1.76 ± 0.08b | 2.45 ± 0.08a | 5.51 ± 0.07b | 16.28 ± 0.11b | |
| PL2 | 1.51 ± 0.07c | 2.35 ± 0.07b | 5.26 ± 0.08c | 14.02 ± 0.09c | |
| PL3 | 1.44 ± 0.08c | 2.27 ± 0.08c | 4.95 ± 0.07d | 13.15 ± 0.10d | |
| 56 | MU0 | 2.05 ± 0.08a | 3.04 ± 0.07a | 5.86 ± 0.08a | 18.18 ± 0.12a |
| MU1 | 1.99 ± 0.06ab | 2.98 ± 0.08ab | 5.72 ± 0.08b | 18.02 ± 0.09a | |
| MU2 | 1.95 ± 0.08b | 2.95 ± 0.05b | 5.65 ± 0.07bc | 17.98 ± 0.12ab | |
| MU3 | 1.86 ± 0.07c | 2.73 ± 0.06c | 5.59 ± 0.07c | 17.84 ± 0.09b | |
| PL0 | 2.08 ± 0.06b | 3.01 ± 0.08d | 5.78 ± 0.08c | 18.24 ± 0.08b | |
| PL1 | 2.10 ± 0.08b | 3.14 ± 0.06c | 5.86 ± 0.09bc | 18.58 ± 0.07b | |
| PL2 | 2.16 ± 0.06ab | 3.27 ± 0.07b | 5.94 ± 0.08ab | 18.75 ± 0.11ab | |
| PL3 | 2.23 ± 0.06a | 3.46 ± 0.08a | 5.98 ± 0.07a | 19.02 ± 0.12a |
| Year | Treatment | Panicle per Plant | 1000 Grain Weight (g) | Spikelet Fertility | Spikelet per Panicle | Yield (t/hm2) | Yield per Plot (kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016 | MU0 | 9.74a | 29.26b | 0.92b | 255.54b | 7.54b | 29.94c |
| MU1 | 7.38b | 29.24b | 0.94a | 258.15b | 7.98ab | 31.18b | |
| MU2 | 10.19a | 29.99a | 0.94a | 284.97a | 8.82a | 34.34a | |
| MU3 | 10.38a | 29.54ab | 0.93ab | 283.62a | 8.49a | 33.21a | |
| PL0 | 9.82b | 29.27b | 0.93ab | 254.91b | 7.67b | 31.38b | |
| PL1 | 11.20b | 29.23b | 0.94a | 261.48b | 7.98ab | 31.18b | |
| PL2 | 13.37a | 29.90a | 0.94a | 286.68a | 8.95a | 34.79a | |
| PL3 | 13.65a | 29.56ab | 0.92b | 285.87a | 8.67a | 33.82a | |
| 2017 | MU0 | 9.65a | 29.24b | 0.91c | 254.55b | 7.40b | 29.46b |
| MU1 | 7.75b | 29.24b | 0.94a | 256.26b | 7.54ab | 29.94ab | |
| MU2 | 10.74a | 29.92a | 0.93ab | 283.17a | 8.34a | 32.69a | |
| MU3 | 10.84a | 29.42ab | 0.92bc | 284.34a | 8.02a | 31.59a | |
| PL0 | 9.72b | 29.24b | 0.91b | 252.75b | 7.38b | 29.39b | |
| PL1 | 11.25b | 29.24b | 0.94a | 257.07b | 7.88ab | 31.11b | |
| PL2 | 13.43a | 29.80a | 0.93a | 285.78a | 8.82a | 34.34a | |
| PL3 | 13.65a | 29.51ab | 0.92ab | 283.80a | 8.58a | 33.52a |
| Year | Item | Total Root Length | Length of White Root | Nitrogen Invert-Ase | Root Bleeding | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36d | 65d | 36d | 65d | 36d | 65d | 36d | 65d | ||
| 2016 | Yield | −0.35 | 0.75 * | −0.40 | 0.07 | −0.49 | 0.77 * | 0.62 * | 0.21 |
| EPP | −0.54 | 0.61 * | −0.38 | 0.45 | −0.45 | 0.75 * | −0.48 | 0.69 * | |
| GW | 0.07 | 0.65 * | 0.01 | −0.23 | −0.39 | 0.08 | −0.07 | 0.63 * | |
| SPP | −0.32 | 0.32 | −0.66 * | 0.74 * | −0.90 * | 0.88 * | 0.91 * | 0.01 | |
| SPF | 0.30 | 0.49 | 0.26 | 0.25 | 0.00 | 0.18 | −0.24 | 0.19 | |
| 2017 | Yield | 0.26 | 0.81 * | −0.35 | 0.13 | −0.38 | 0.65 * | 0.66 * | 0.32 |
| EPP | −0.41 | 0.63 * | 0.15 | 0.37 | 0.12 | 0.71 * | −0.31 | 0.62 * | |
| GW | 0.15 | 0.66 * | −0.11 | 0.14 | −0.33 | −0.01 | 0.06 | 0.72 * | |
| SPP | −0.44 | 0.41 | −0.62 * | 0.71 * | −0.87 * | 0.88 * | 0.86 * | 0.13 | |
| SPF | 0.29 | 0.38 | 0.28 | 0.22 | −0.02 | 0.19 | 0.19 | 0.20 | |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Samo, N.; Zhao, C.; Wang, H.; Yang, G.; Hu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Rasul, F. Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area. Agronomy 2019, 9, 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110690
Wang X, Samo N, Zhao C, Wang H, Yang G, Hu Y, Peng Y, Rasul F. Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area. Agronomy. 2019; 9(11):690. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110690
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xuechun, Naseem Samo, Changkun Zhao, Hongni Wang, Guotao Yang, Yungao Hu, Youlin Peng, and Fahd Rasul. 2019. "Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area" Agronomy 9, no. 11: 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110690
APA StyleWang, X., Samo, N., Zhao, C., Wang, H., Yang, G., Hu, Y., Peng, Y., & Rasul, F. (2019). Negative and Positive Impacts of Rape Straw Returning on the Roots Growth of Hybrid Rice in the Sichuan Basin Area. Agronomy, 9(11), 690. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy9110690





