Soil Calcium Gradients Drive Divergent Responses in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Brassica Rhizosphere
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
2.3. Physical and Chemical Properties of Soil
2.4. Soil DNA Isolation
2.5. Data Analysis and Calculation
2.5.1. Analysis of Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
2.5.2. Analysis of Microbiological
2.5.3. Calculation of Microbial Function Prediction
3. Results
3.1. Physicochemical Properties of Soil
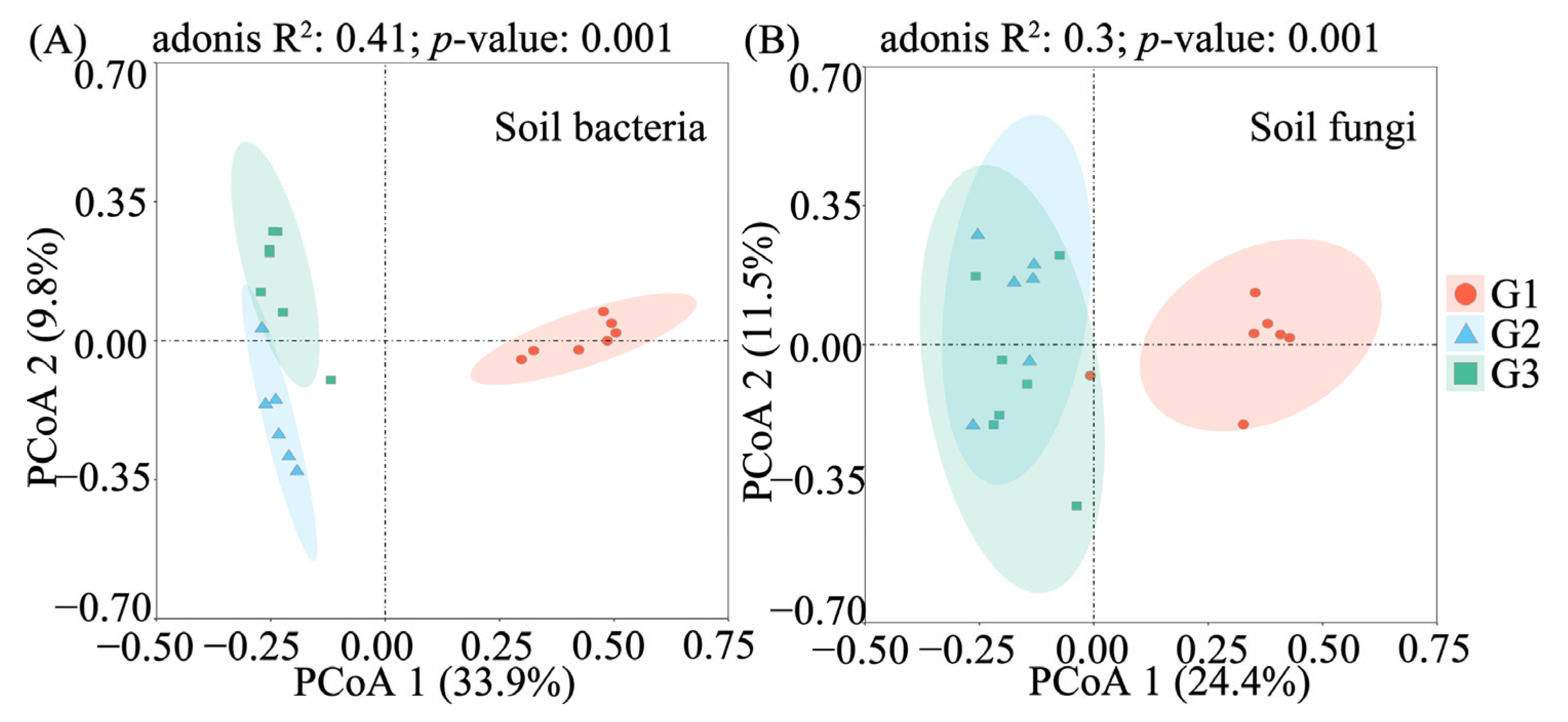
3.2. Taxonomic and Compositional Differences in Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities on a Soil Ca Gradient
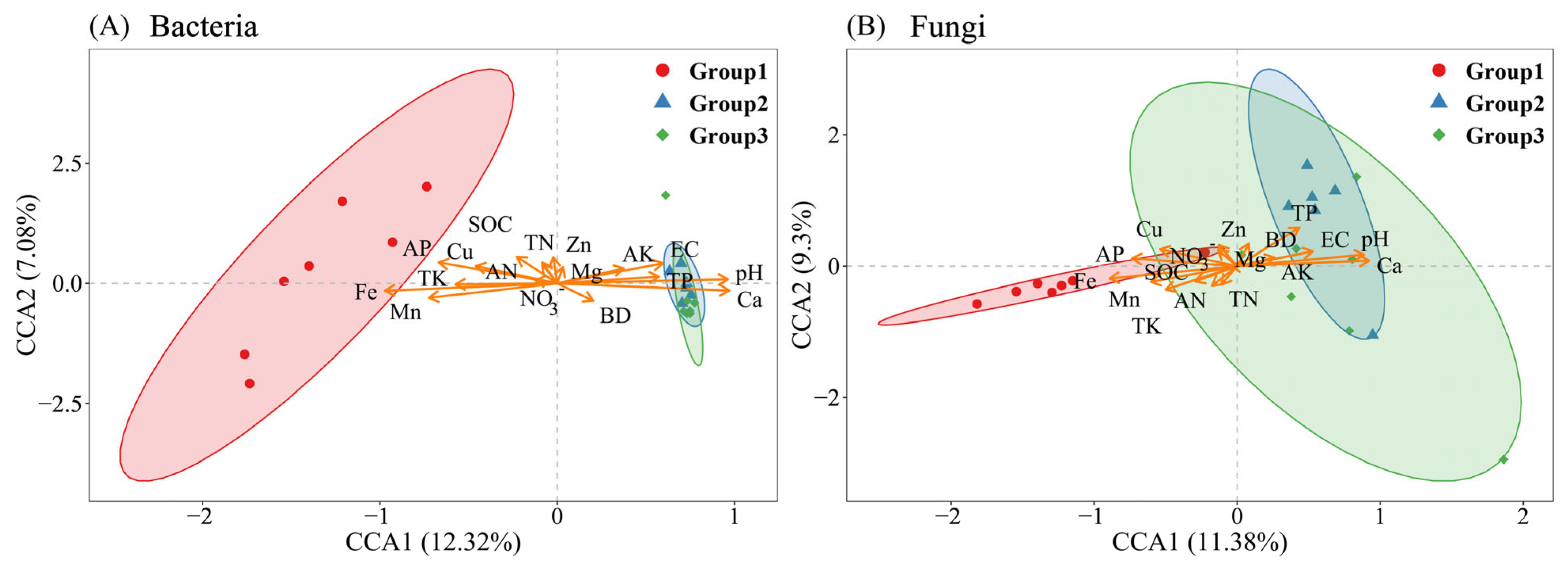
3.3. Alpha Diversity and CCA of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Communities Across a Ca Gradient
3.4. Drivers of Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Alpha Diversity
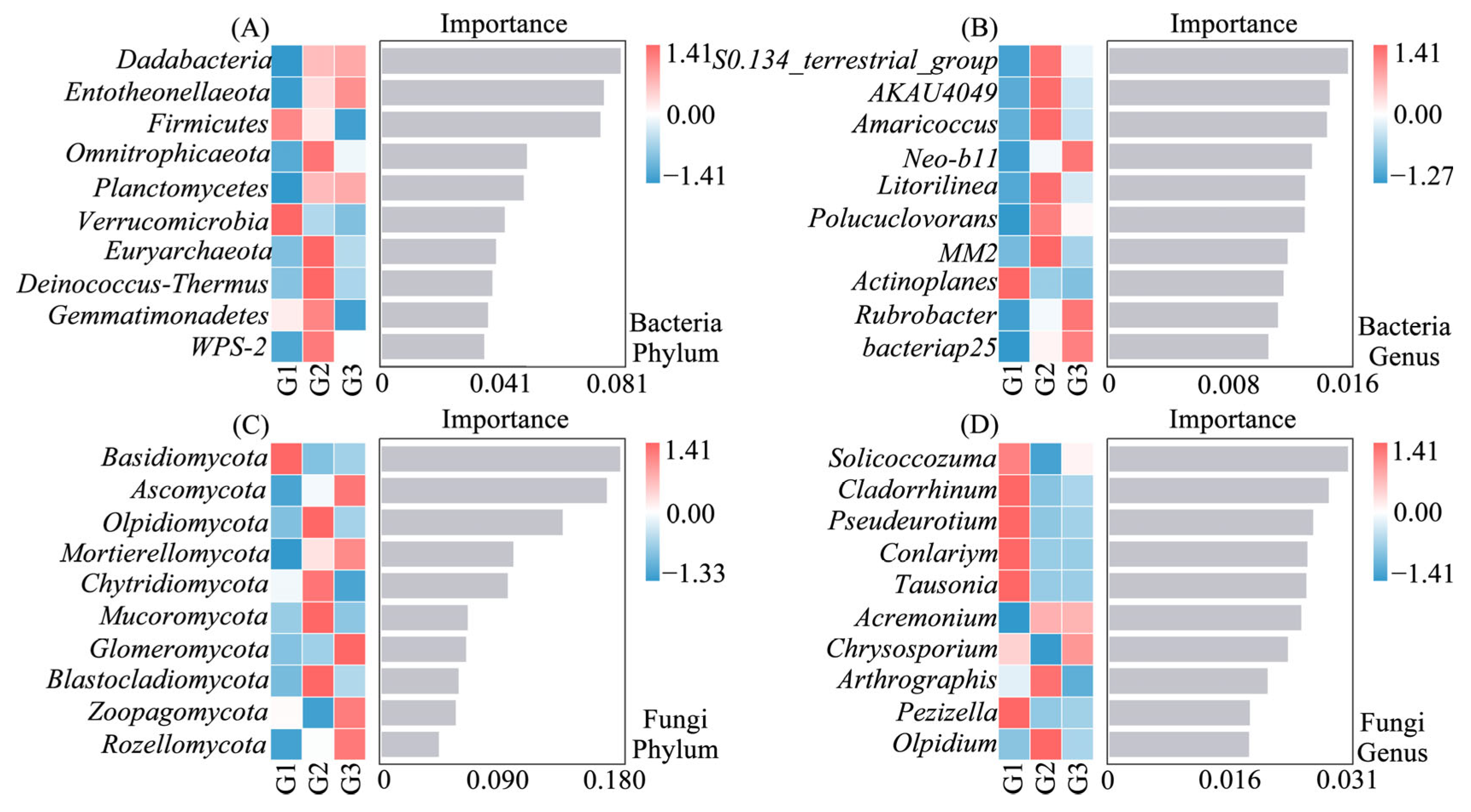
3.5. Important Species for Differences in Bacterial and Fungal Community Composition Along Soil Ca Gradient
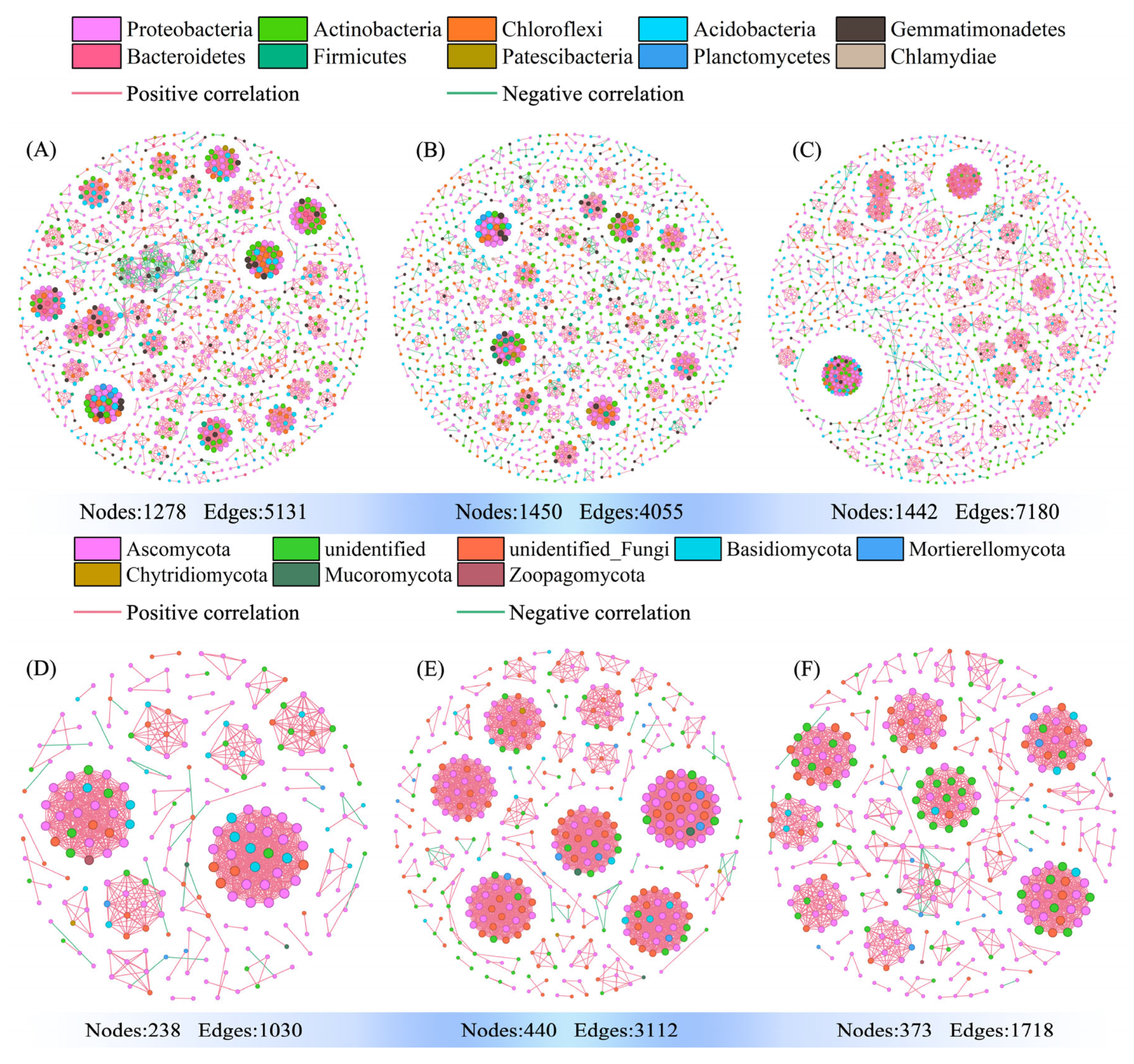
3.6. Effects on Soil Bacterial and Fungal Community Networks of Ca Gradients
3.7. Annotating and Analyzing KEGG in Soil Bacterial Communities and FUNGuild Function in Fungal Communities Along Ca Gradients
4. Discussion
4.1. Changes in the Structural Composition of Microbial Communities Along Ca Gradients and Their Drivers
4.2. Driving Mechanisms for Changes in Microbial Network Stability and Complexity and Metabolic Pathway Dynamics Along Ca Gradients
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lima, D.P.; Junior, E.D.S.P.; de Menezes, A.V.; de Souza, D.A.; de Sao Jose, V.P.B.; da Silva, B.P.; de Almeida, A.Q.; de Carvalho, I.M.M. Chemical composition, minerals concentration, total phenolic compounds, flavonoids content and antioxidant capacity in organic and conventional vegetables. Food Res. Int. 2024, 175, 113684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Guo, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, R.; Li, M.; Ma, F.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. Effects of nitrogen fertilizer and water management practices on nitrogen leaching from a typical open field used for vegetable planting in northern China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 213, 913–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X.; Ji, M. Pesticide residues in greenhouse leafy vegetables in cold seasons and dietary exposure assessment for consumers in Liaoning Province, Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugavel, D.; Rusyn, I.; Solorza-Feria, O.; Kamaraj, S.K. Sustainable SMART fertilizers in agriculture systems: A review on fundamentals to in-field applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 904, 166729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, F.; Siddique, A.B.; Shabala, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, C. Phosphorus plays key roles in regulating plants’ physiological responses to abiotic stresses. Plants 2023, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuronuma, T.; Watanabe, H. Identification of the causative genes of calcium deficiency disorders in horticulture crops: A systematic review. Agriculture 2021, 11, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saure, M.C. Causes of the tipburn disorder in leaves of vegetables. Sci. Hortic. 1998, 76, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadarajah, K.; Abdul Rahman, N.S.N. Plant-Microbe Interaction: Aboveground to Belowground, from the Good to the Bad. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Lan, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Yue, K. Effects of soil exchangeable calcium in promoting the accumulation of soil organic carbon by karst vegetation restoration. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 24, 843–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabtai, I.A.; Wilhelm, R.C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Hoschen, C.; Buckley, D.H.; Lehmann, J. Calcium promotes persistent soil organic matter by altering microbial transformation of plant litter. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, T.; Li, J.; He, Y.; Shankar, A.; Saxena, A.; Tiwari, A.; Maturi, K.C.; Solanki, M.K.; Singh, V.; Eissa, M.A.; et al. Role of calcium nutrition in plant Physiology: Advances in research and insights into acidic soil conditions—A comprehensive review. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2024, 210, 108602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walton, C.R.; Ewens, S.; Coates, J.D.; Blake, R.E.; Planavsky, N.J.; Reinhard, C.; Ju, P.C.; Hao, J.H.; Pasek, M.A. Phosphorus availability on the early Earth and the impacts of life. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.; Dai, Z.; He, Z.; Qiu, Y.; Alharbi, S.A.; Wei, F.; Wei, L.; Ahmed, W.; et al. Pre-soil fumigation with ammonium bicarbonate and lime modulates the rhizosphere microbiome to mitigate clubroot disease in Chinese cabbage. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1376579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.L.; Xu, J.; Xu, H.M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.X.; Wang, Z.K. Analysis of growth resistance mechanisms and causes in tea plants (Camellia sinensis) in high-pH regions of Northern China. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1131380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.-W.; Jin, J.-Y.; Yang, L.-P.; Bai, Y.-L. Spatial variability of soil nutrients and influencing factors in a vegetable production area of Hebei Province in China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2006, 75, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bontpart, T.; Weiss, A.; Vile, D.; Gerard, F.; Lacombe, B.; Reichheld, J.P.; Mari, S. Growing on calcareous soils and facing climate change. Trends Plant Sci. 2024, 29, 1319–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olle, M.; Bender, I. Causes and control of calcium deficiency disorders in vegetables: A review. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 84, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, R.; Shivay, Y.S. Agronomic biofortification of plant foods with minerals, vitamins and metabolites with chemical fertilizers and liming. J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1534–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritonga, F.N.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, F.; Gao, J.; Li, C.; Li, J. Exploiting Brassica rapa L. subsp. pekinensis genome research. Plants 2024, 13, 2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wu, S.; Xia, L.; Sun, J.; Zha, Y.; Yang, P. Retrieval of chromium and mercury concentrations in agricultural soils: Using spectral information, environmental covariates, or a fusion of both? Ecol. Indic. 2024, 167, 112594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meersmans, J.; Van Wesemael, B.; Van Molle, M. Determining soil organic carbon for agricultural soils: A comparison between the Walkley & Black and the dry combustion methods (north Belgium). Soil Use Manag. 2009, 25, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goidts, E.; van Wesemael, B.; Crucifix, M. Magnitude and sources of uncertainties in soil organic carbon (SOC) stock assessments at various scales. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2009, 60, 723–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adhikari, B.K.; Barrington, S.; Martinez, J.; King, S. Characterization of food waste and bulking agents for composting. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 795–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsfold, P.J.; Gimbert, L.J.; Mankasingh, U.; Omaka, O.N.; Hanrahan, G.; Gardolinski, P.C.; Haygarth, P.M.; Turner, B.L.; Keith-Roach, M.J.; McKelvie, I.D. Sampling, sample treatment and quality assurance issues for the determination of phosphorus species in natural waters and soils. Talanta 2005, 66, 273–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.K.R.; Bailey, J.; Wingwafi, R.W. Comparison of three digestion methods for total soil potassium estimation in soils of papua new guinea derived from varying parent materials. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2011, 42, 1259–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kachurina, O.M.; Zhang, H.; Raun, W.R.; Krenzer, E.G. Simultaneous determination of soil aluminum, ammonium- and nitrate-nitrogen using 1 M potassium chloride extraction. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2008, 31, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayment, G.E.; Lyons, D.J. New, Comprehensive Soil Chemical Methods Book for Australasia. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, M.R.; Cornish, P.S. Comparison of bicarbonate-extractable soil phosphorus measured by ICP-AES and colourimetry in soils of south-eastern New South Wales. Aust. J. Soil Res. 2009, 47, 742–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, G.L.; Pettygrove, G.S.; Southard, R.J. Estimating Plant-Available Potassium in Potassium-Fixing Soils. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 741–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez, S.; Moreno, E.; Carpena, R.O. Bioavailability of metals and As from acidified multicontaminated soils: Use of white lupin to validate several extraction methods. Environ. Geochem. Health 2008, 30, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.G.; Xiao, M.; Dong, Y.H.; Jiang, Y. Determination of Soil Exchangeable Base Cations by Using Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometer and Extraction with Ammonium Acetate. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2012, 32, 2242–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Fabregat-Santiago, F.; Ferriols, N.S.; Garcia-Belmonte, G.; Bisquert, J. Determination of the humidity of soil by monitoring the conductivity with indium tin oxide glass electrodes. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 80, 2785–2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; An, S. Identifying the biogeographic patterns of rare and abundant bacterial communities using different primer sets on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coyer, J.A.; Hoarau, G.; Kuo, J.; Tronholm, A.; Veldsink, J.; Olsen, J.L. Phylogeny and temporal divergence of the seagrass family Zosteraceae using one nuclear and three chloroplast loci. Syst. Biodivers. 2013, 11, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lepš, J.; Šmilauer, P. Multivariate Analysis of Ecological Data Using CANOCO; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’hara, R.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. Package ‘vegan’. Community Ecol. Package Version 2013, 2, 1–295. [Google Scholar]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langfelder, P.; Horvath, S. WGCNA: An R package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wemheuer, F.; Taylor, J.A.; Daniel, R.; Johnston, E.; Meinicke, P.; Thomas, T.; Wemheuer, B. Tax4Fun2: Prediction of habitat-specific functional profiles and functional redundancy based on 16S rRNA gene sequences. Environ. Microbiome 2020, 15, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, G.; Xie, T.; Wang, X.; Bai, J.; Tang, L.; Zhao, H.; Wei, W.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. Metagenomic analysis of microbial community and function involved in cd-contaminated soil. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.; Song, Z.; Bates, S.T.; Branco, S.; Tedersoo, L.; Menke, J.; Schilling, J.S.; Kennedy, P.G. FUNGuild: An open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol. 2016, 20, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Dai, H.C.; Zamanian, K.; Sun, Q.Q.; Wang, C.B.; Wu, Z.F.; Zheng, Y.M.; Li, L.; Wan, S.B.; Yu, T.Y. Liming shifts the chemical properties and microbial community structures of peanut soils with different initial pH values. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2023, 181, 104665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.M.; Yang, Z.F.; He, P.F.; Munir, S.; He, P.B.; Wu, Y.X.; Ho, H.H.; He, Y.Q. Fluazinam positively affected the microbial communities in clubroot cabbage rhizosphere. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 256, 108519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.L.; Fu, T.L.; He, G.; Zhong, Z.Y.; Yang, M.F.; Lou, F.; He, T.B. Characteristics of rhizosphere and bulk soil microbial community of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris) grown in Karst area. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1241436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goberna, M.; Verdú, M. Cautionary notes on the use of co-occurrence networks in soil ecology. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 166, 108534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wang, G.; Qian, X.; Wang, J. Optimized fertilization shifted soil microbial properties and improved vegetable growth in facility soils with obstacles. Horticulturae 2023, 9, 1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stimmler, P.; Prieme, A.; Elberling, B.; Goeckede, M.; Schaller, J. Arctic soil respiration and microbial community structure driven by silicon and calcium. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Dubey, S.K.; Kumar, D.; Toor, A.S.; Walia, S.S.; Randhawa, M.K.; Kaur, G.; Brar, S.K.; Khambalkar, P.A.; Shivey, Y.S. Enhanced organic carbon triggers transformations of macronutrients, micronutrients, and secondary plant nutrients and their dynamics in the soil under different cropping systems—A review. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 5272–5292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F.A. Ameliorating soil acidity with calcium carbonate and calcium hydroxide: Effects on carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus dynamics. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5270–5278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Lee, D.K.; Ali, M.A.; Kim, P.J. Effects of oyster shell on soil chemical and biological properties and cabbage productivity as a liming materials. Waste Manag. 2008, 28, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Morrissey, E.; Liu, Y.; Sun, L.; Qu, L.; Sang, C.; Zhang, H.; Li, G.; et al. Integrating microbial community properties, biomass and necromass to predict cropland soil organic carbon. ISME Commun. 2023, 3, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, P.; Xiao, L. Siltation of check dams alters microbial communities and thus limits organic carbon mineralization. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 236, 105949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.J.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q.Y.; Huang, Z.X.; Zhuang, G.Q. SOC bioavailability significantly correlated with the microbial activity mediated by size fractionation and soil morphology in agricultural ecosystems. Environ. Int. 2024, 186, 108588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, P.; Wang, X.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, S. Surface soil microbiome changes in Grain for Green Project accelerates organic carbon mineralization on the Loess Plateau in China. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2024, 49, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, L.; Wu, Q.; Zhou, G.; Ma, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, J. Calcium forms influence soil organic carbon by mediating labile organic carbon fractions, carbon pool management indices and microbial communities in calcareous alkaline soils. Plant Soil 2024, 512, 801–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Y.; Cai, G.; Yu, L. Exogenous carbon addition reduces soil organic carbon: The effects of fungi on soil carbon priming exceed those of bacteria on soil carbon sequestration. Forests 2023, 14, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Li, P. Biogeochemical mechanisms of iron (Fe) and manganese (Mn) in groundwater and soil profiles in the Zhongning section of the Weining Plain (northwest China). Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 939, 173506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Du, X.; Gao, C.; Yu, Z. Adsorption behavior of inorganic and organic phosphate by iron manganese plaques on reed roots in wetlands. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, W.-F.; Liu, F.; Li, Y.-H.; Hu, H.-Q.; Huang, Q.-Y. Elemental composition and geochemical characteristics of iron-manganese nodules in main soils of China. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, U.; Saqib, H.S.A.; Islam, W.; Prashant, P.; Patel, N.; Chen, W.; Yang, F.Y.; You, M.S.; He, W.Y. Landscape composition and soil physical-chemical properties drive the assemblages of bacteria and fungi in conventional vegetable fields. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.H.A.; Špánek, R.; Kasalický, V.; Ribas, D.; Vlková, D.; Řeháková, H.; Kejzlar, P.; Ševců, A. Different effects of nano-scale and micro-scale zero-valent iron particles on planktonic microorganisms from natural reservoir water. Environ. Sci. Nano 2018, 5, 1117–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan, J.; Moreno, D.F.; Yahya, G.; Moisa, M.; Ul Haq, I.; Krukiewicz, K.; Mosbah, R.; Metwally, K.; Cavalu, S. Regulatory and pathogenic mechanisms in response to iron deficiency and excess in fungi. Microb. Biotechnol. 2023, 16, 2053–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Xu, L.; Montoya, L.; Madera, M.; Hollingsworth, J.; Chen, L.; Purdom, E.; Singan, V.; Vogel, J.; Hutmacher, R.B.; et al. Co-occurrence networks reveal more complexity than community composition in resistance and resilience of microbial communities. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, F.T.; Griffiths, R.I.; Bailey, M.; Craig, H.; Girlanda, M.; Gweon, H.S.; Hallin, S.; Kaisermann, A.; Keith, A.M.; Kretzschmar, M.; et al. Soil bacterial networks are less stable under drought than fungal networks. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montoya, J.M.; Pimm, S.L.; Sole, R.V. Ecological networks and their fragility. Nature 2006, 442, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.J.; David, A.S.; Menges, E.S.; Searcy, C.A.; Afkhami, M.E. Environmental stress destabilizes microbial networks. ISME J. 2021, 15, 1722–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, O.; Park, J.M.; Lee, H.; Jin, E. De novo transcriptome profile of coccolithophorid alga Emiliania huxleyi CCMP371 at different calcium concentrations with proteome analysis. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0221938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mao, W.; Wang, C.; Yin, S. Functional potential differences between Firmicutes and Proteobacteria in response to manure amendment in a reclaimed soil. Can. J. Microbiol. 2020, 66, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Yin, Z.; Kang, J.; Tu, X.; Ao, G.; Ge, J.; Ping, W. Influence of community complexity and regulation by two-component system on community stability in aerobic composting in the presence of penicillin residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 465, 142836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Lu, L.; Tu, W.; Luo, T.; Fu, Z. Impacts of polystyrene microplastic on the gut barrier, microbiota and metabolism of mice. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 649, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; de Goede, R.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Creamer, R. Unlocking soil health: Are microbial functional genes effective indicators? Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 204, 109768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Variables | G1 | G2 | G3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| BD (g/cm3) | 1.3 ± 0.04 A | 1.4 ± 0.03 A | 1.32 ± 0.04 A |
| SOC (g/kg) | 11.85 ± 0.99 A | 9.65 ± 0.64 A | 11.02 ± 0.55 A |
| EC (μs/cm) | 86.33 ± 8.58 B | 125.55 ± 9.17 A | 100.17 ± 2.18 AB |
| TN (g/kg) | 1.41 ± 0.09 A | 1.21 ± 0.07 A | 1.44 ± 0.07 A |
| TP (g/kg) | 1.06 ± 0.08 B | 1.96 ± 0.19 A | 1.33 ± 0.09 AB |
| TK (g/kg) | 19.44 ± 0.3 A | 17.45 ± 0.17 B | 18.35 ± 0.49 AB |
| Ca (mg/kg) | 2056.54 ± 146.94 C | 6800.64 ± 191.61 B | 7804.32 ± 219 A |
| pH | 6.68 ± 0.17 B | 8.01 ± 0.06 A | 8.15 ± 0.05 A |
| AN (mg/kg) | 124.7 ± 7 A | 100.1 ± 7.16 A | 133.3 ± 12.17 A |
| AP (mg/kg) | 104.2 ± 14.01 A | 54.23 ± 8.7 B | 41.57 ± 7.81 B |
| AK (mg/kg) | 96.71 ± 11.93 A | 114.33 ± 15.33 A | 117.5 ± 7.41 A |
| NO3−-N (mg/kg) | 11.86 ± 1.86 A | 17.56 ± 4.13 A | 3.15 ± 0.65 B |
| Fe (mg/kg) | 48.64 ± 5.16 A | 10.67 ± 0.99 B | 9.29 ± 0.75 B |
| Mn (mg/kg) | 13.47 ± 2.48 A | 5.81 ± 0.34 A | 6.6 ± 0.65 A |
| Cu (mg/kg) | 3.33 ± 0.42 A | 2.18 ± 0.46 A | 2 ± 0.49 A |
| Zn (mg/kg) | 6.83 ± 1.44 A | 5.74 ± 1.34 A | 7.01 ± 2.1 A |
| Mg (mg/kg) | 256.95 ± 21.39 AB | 200.73 ± 11.96 B | 289.98 ± 30 A |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, R.; Shi, J.; Jiang, L.; Guo, L.; Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Wang, L. Soil Calcium Gradients Drive Divergent Responses in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Brassica Rhizosphere. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092212
Li J, Li R, Shi J, Jiang L, Guo L, Li Y, Jia Z, Wang L. Soil Calcium Gradients Drive Divergent Responses in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Brassica Rhizosphere. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092212
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jiawei, Ruonan Li, Jianshuo Shi, Longgang Jiang, Li Guo, Yihong Li, Zhou Jia, and Liying Wang. 2025. "Soil Calcium Gradients Drive Divergent Responses in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Brassica Rhizosphere" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092212
APA StyleLi, J., Li, R., Shi, J., Jiang, L., Guo, L., Li, Y., Jia, Z., & Wang, L. (2025). Soil Calcium Gradients Drive Divergent Responses in Bacterial and Fungal Communities in Brassica Rhizosphere. Agronomy, 15(9), 2212. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092212






