Slope Construction on Croplands in Reclaimed Tidal Flats of Korea Improved Surface Drainage but Not Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
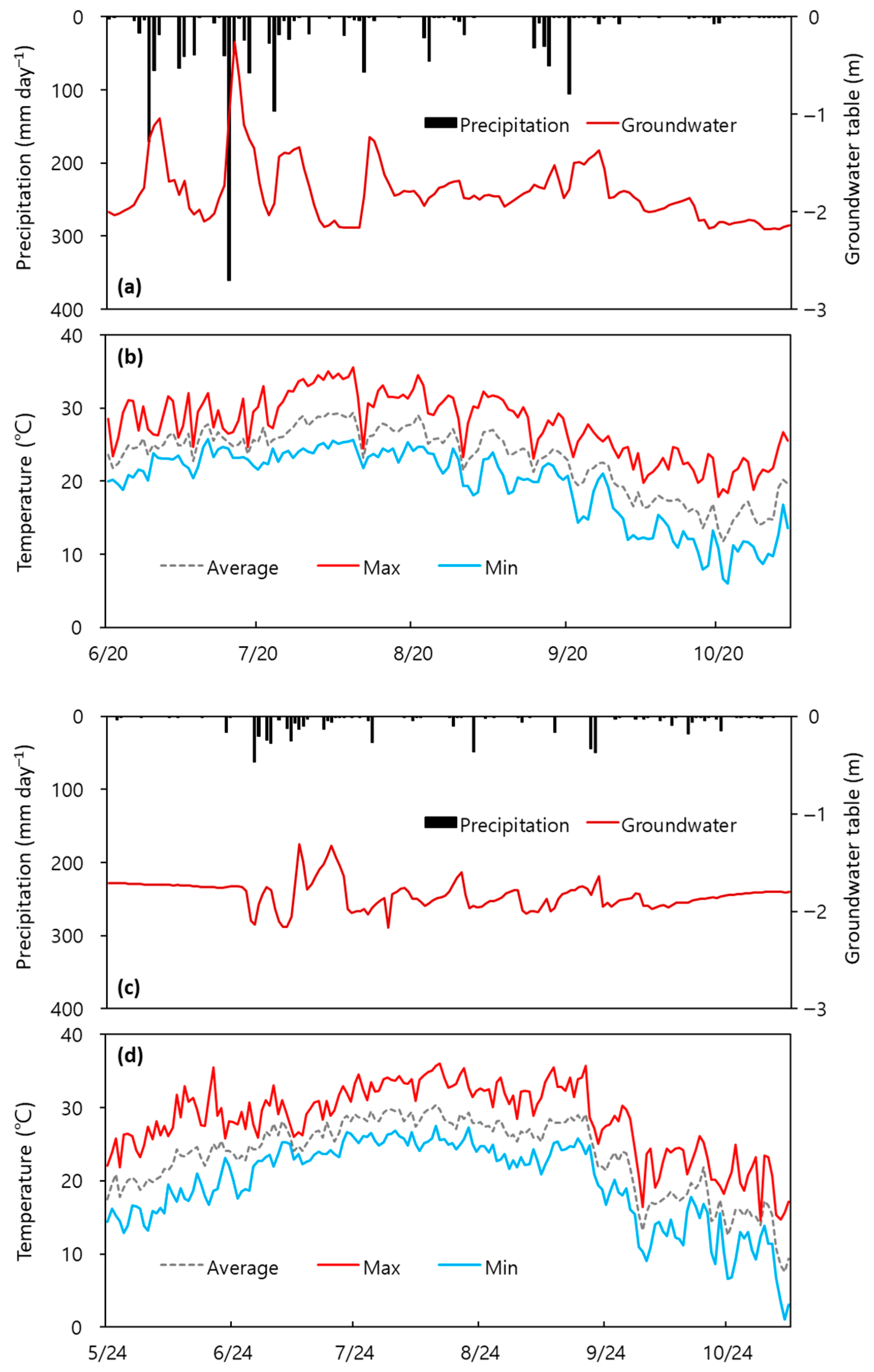
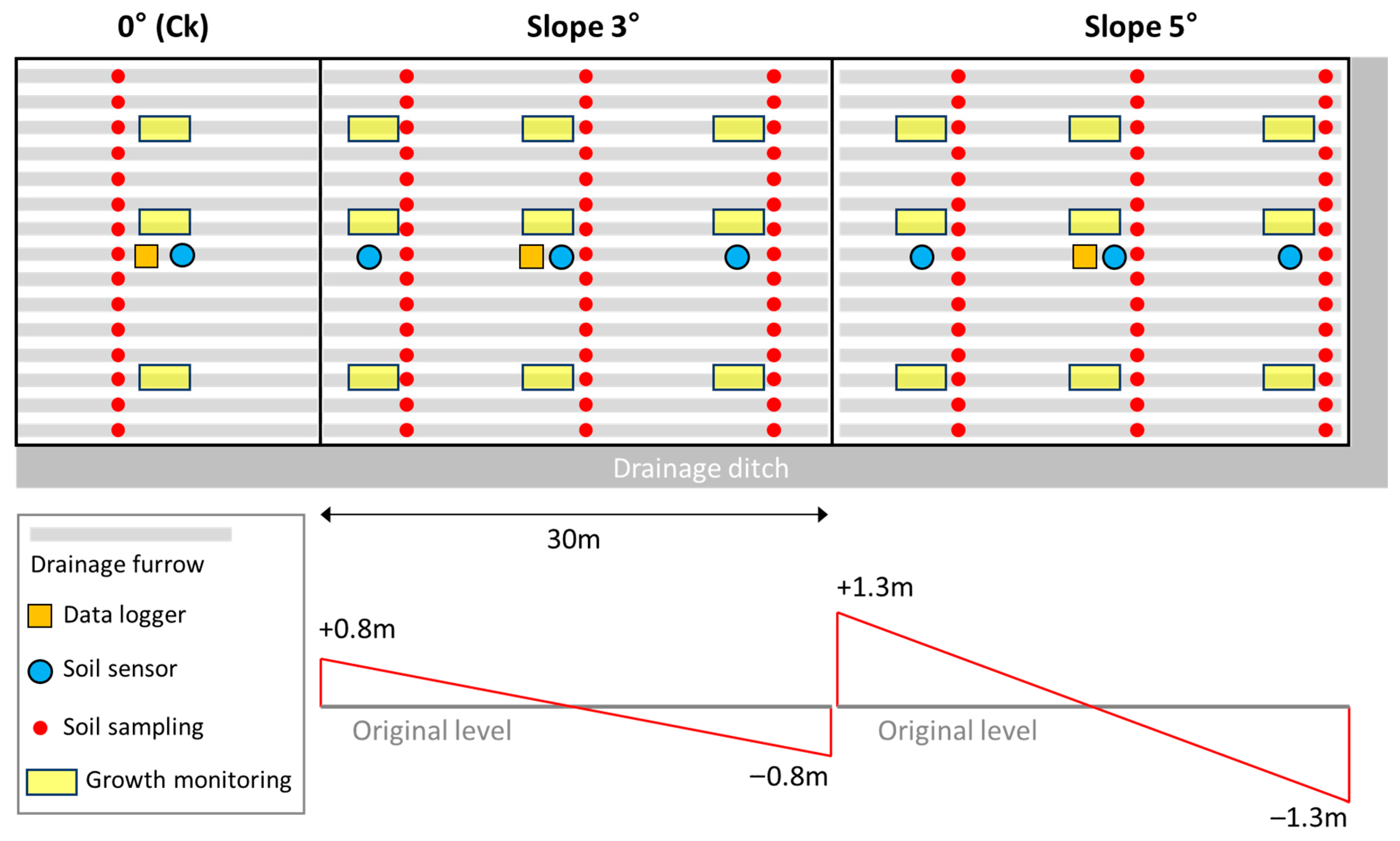
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Soil and Plant Monitoring
2.3. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
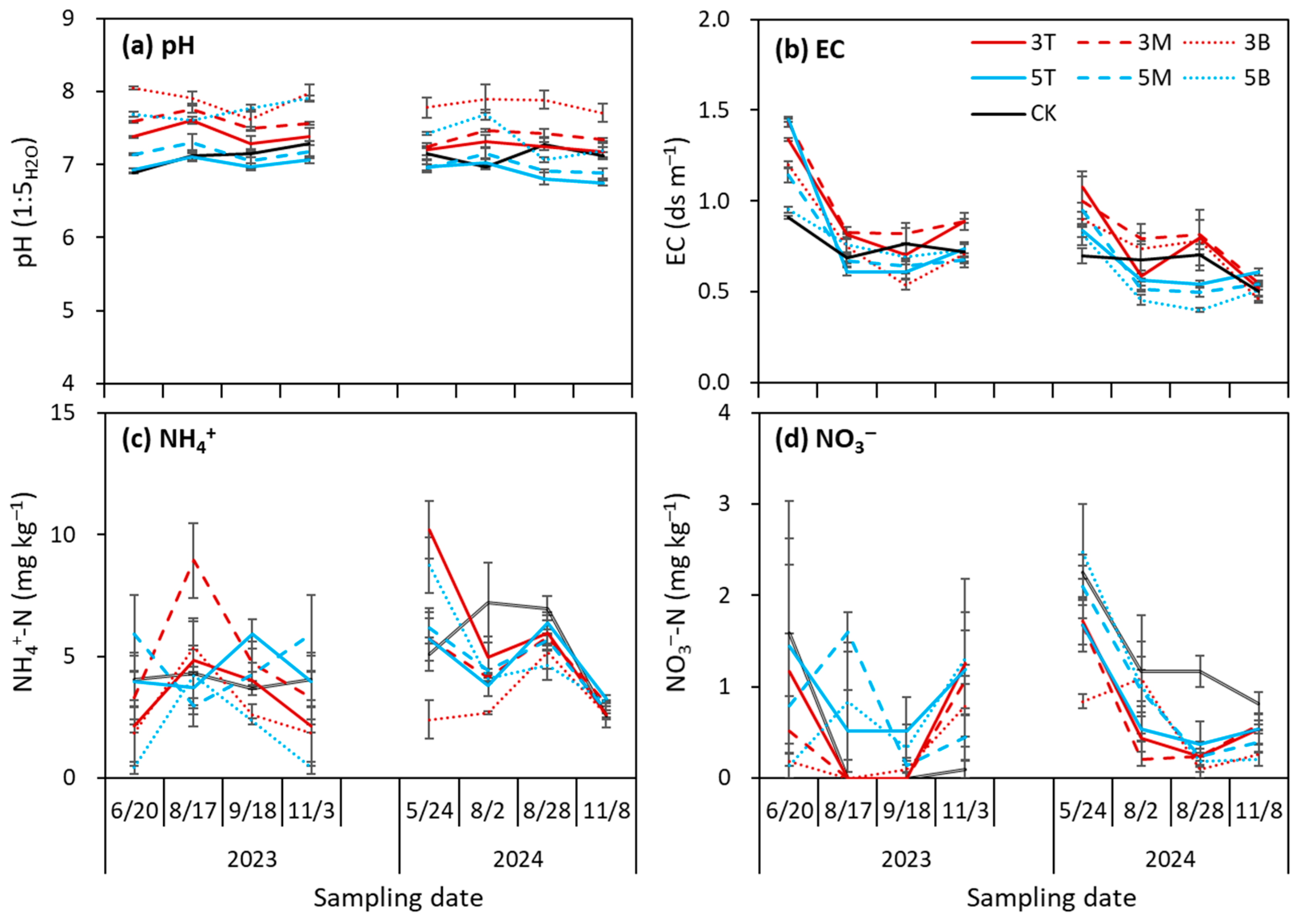
3.1. Initial Soil Properties Changed by Slope Construction
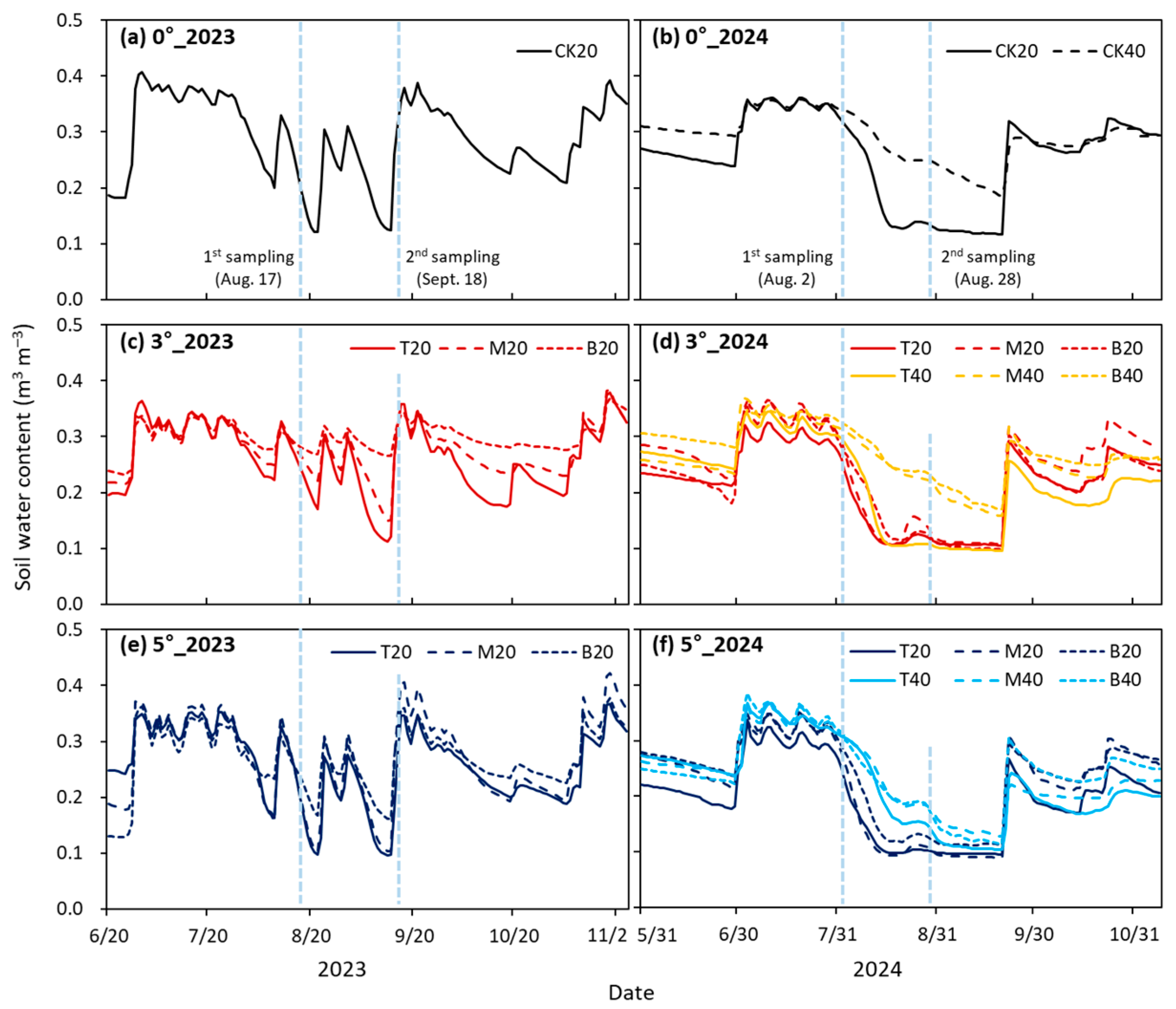
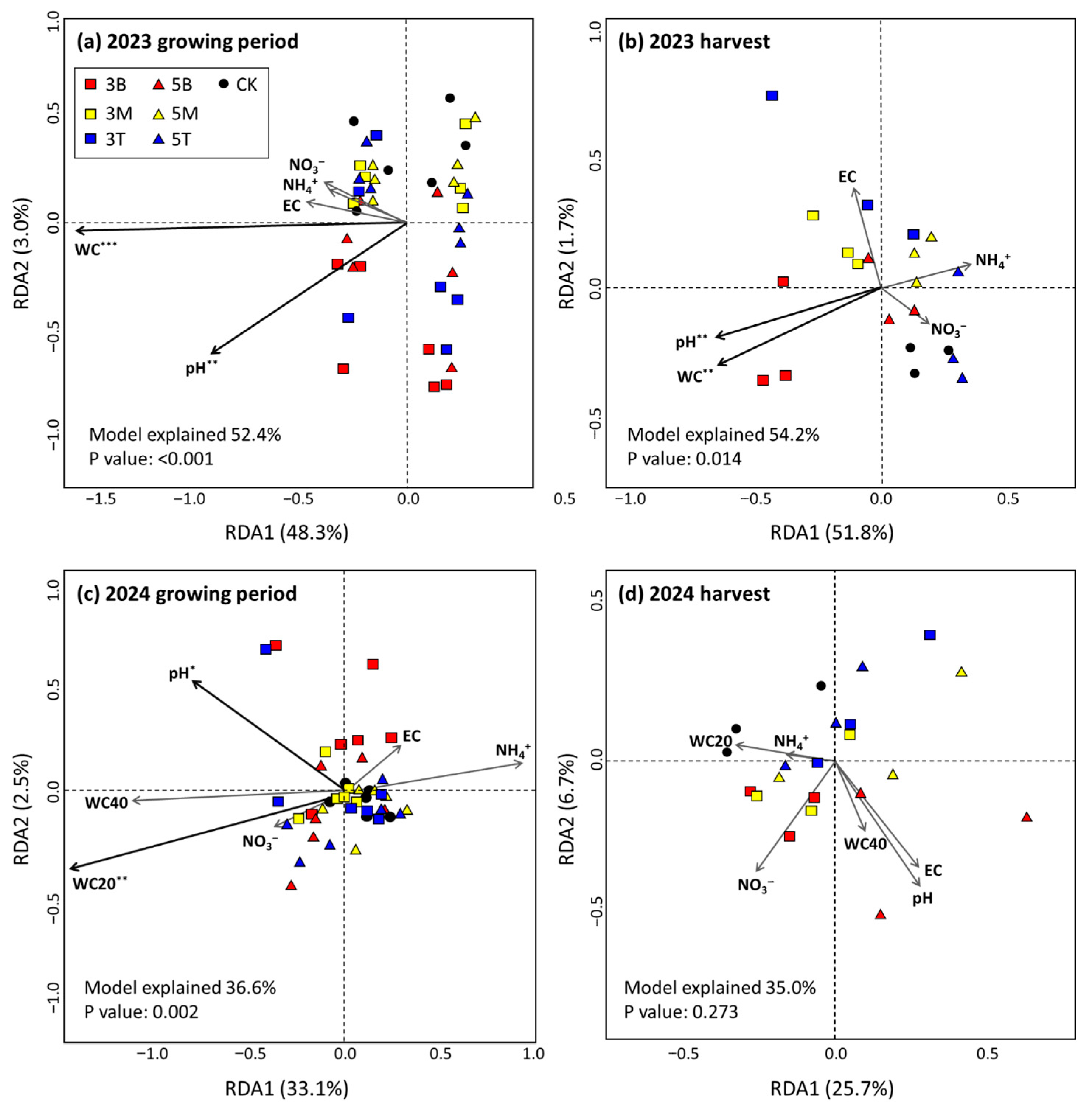
3.2. Changes in Soil Properties During Soybean Growing Experiments
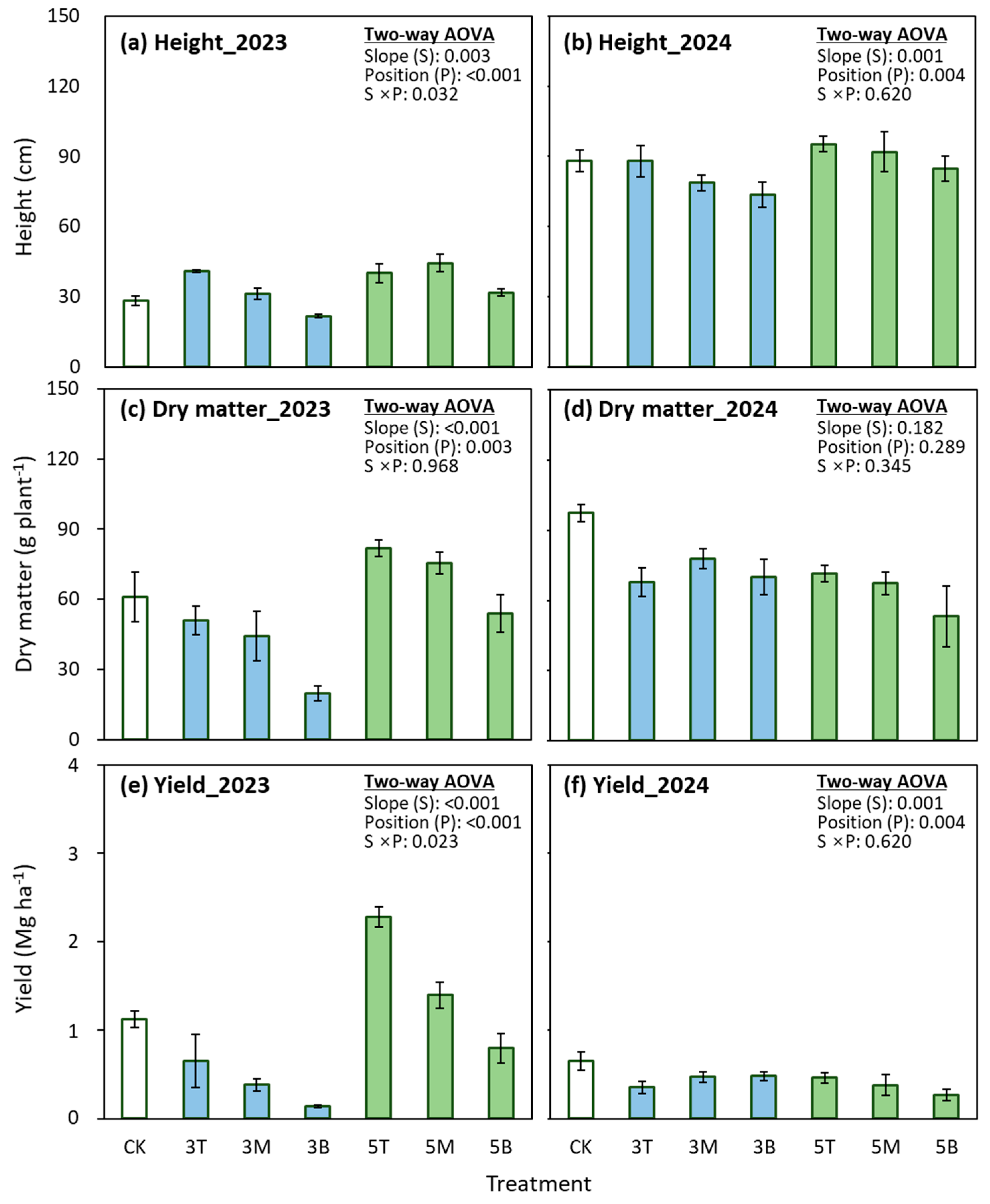
3.3. Soybean Growth
4. Discussion
4.1. Slope Construction Increased Surface Drainage and Changed Soil Properties
4.2. Slope Construction Did Not Consistently Improve Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RTL | Reclaimed coastal tidelands |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| NH4+ | Ammonium |
| NO3− | Nitrate |
| TC | Total carbon |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
Appendix A
Effects | 20 June 2023 | 17 August 2023 | 18 September 2023 | 3 November 2023 | 24 May 2024 | 2 August 2024 | 28 August 2024 | 8 November 2024 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | ||||||||
| Slope (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.014 | 0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Position (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| S × P | 0.044 | 0.393 | 0.010 | 0.120 | 0.753 | 0.299 | 0.05 | 0.818 |
| EC | ||||||||
| S | <0.001 | 0.006 | 0.323 | 0.006 | 0.055 | 0.005 | <0.001 | 0.058 |
| P | <0.001 | 0.621 | 0.094 | 0.115 | 0.253 | 0.527 | 0.600 | 0.015 |
| S × P | <0.001 | 0.073 | 0.015 | 0.033 | 0.41 | 0.157 | 0.719 | 0.218 |
| NH4+-N | ||||||||
| S | 0.272 | 0.017 | 0.365 | 0.272 | 0.941 | 0.777 | 0.859 | 0.211 |
| P | 0.019 | 0.412 | 0.001 | 0.019 | 0.047 | 0.346 | 0.084 | 0.958 |
| S × P | 0.167 | 0.118 | 0.063 | 0.167 | 0.001 | 0.241 | 0.678 | 0.225 |
| NO3−-N | ||||||||
| S | 0.105 | 0.006 | 0.062 | 0.105 | 0.027 | 0.413 | 0.511 | 0.402 |
| P | 0.815 | 0.147 | 0.565 | 0.815 | 0.761 | 0.284 | 0.525 | 0.033 |
| S × P | 0.677 | 0.147 | 0.565 | 0.677 | 0.061 | 0.493 | 0.881 | 0.685 |
| Treatment | Flowering Stage | Pod-Filling Stage | Harvest | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | No. of Pod | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Yield (kg ha−1) | |
| CK | 46.5 (4.4) | 3.3 (0.3) | 5.5 (0.9) | 46.7 (3.3) | 2.3 (0.3) | 20.8 (2.5) | 28.3 (2.0) | 7.3 (1.2) | 61.0 (10.5) | 33.7 (4.1) | 20.0 (1.6) | 1128.5 (95.4) |
| 3T | 43.0 (1.5) | 3.0 (0.6) | 4.0 (1.6) | 54.7 (1.2) | 2.7 (0.3) | 11.3 (1.6) | 41.0 (0.6) | 3.3 (0.3) | 50.8 (6.1) | 26.0 (5.6) | 19.1 (1.3) | 654.5 (296.7) |
| 3M | 39.8 (0.8) | 0.7 (0.3) | 4.5 (0.2) | 40.0 (4.8) | 1.7 (0.3) | 19.6 (4.1) | 31.3 (2.4) | 2.7 (0.3) | 44.3 (10.6) | 17.3 (1.7) | 18.1 (1.0) | 385.6 (68.6) |
| 3B | 50.0 (4.2) | 4.3 (0.7) | 1.3 (0.4) | 53.0 (2.3) | 1.7 (0.3) | 6.5 (0.5) | 21.7 (0.7) | 2.7 (0.3) | 19.7 (3.3) | 9.0 (1.7) | 18.6 (0.8) | 140.0 (12.8) |
| 5T | 58.3 (2.7) | 3.0 (0.1) | 6.9 (0.7) | 56.3 (3.7) | 3.7 (0.3) | 22.1 (3.2) | 40.0 (4.0) | 5.3 (0.7) | 81.7 (3.4) | 38.0 (2.6) | 25.4 (0.8) | 2277.6 (114.5) |
| 5M | 60.7 (4.9) | 3.7 (0.3) | 7.6 (1.1) | 56.0 (4.0) | 3.0 (0.6) | 28.5 (4.1) | 44.3 (3.7) | 7.0 (1.0) | 75.5 (4.5) | 41.0 (4.0) | 21.0 (0.5) | 1401.9 (148.7) |
| 5B | 35.3 (0.3) | 0.3 (0.3) | 2.8 (0.3) | 37.2 (2.4) | 1.3 (0.3) | 9.3 (1.8) | 31.7 (1.5) | 5.3 (0.9) | 53.9 (8.1) | 32.0 (5.3) | 19.4 (0.5) | 799.7 (169.4) |
| Treatment | Flowering Stage | Pod-Filling Stage | Harvest | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | Plant Height (cm) | No. Branches | Dry Weight (g) | No. of Pod | 100-Seed Weight (g) | Yield (kg ha−1) | |
| CK | 83.7 (1.5) | 2.7 (0.3) | 33.0 (2.7) | 93.7 (2.9) | 2.3 (0.9) | 42.4 (4.7) | 88.0 (4.0) | 3.0 (2.0) | 97.4 (3.7) | 69.9 (4.9) | 17.6 (1.7) | 658.5 (103.9) |
| 3T | 83.0 (5.3) | 1.3 (0.7) | 20.9 (8.6) | 103.3 (5.9) | 2.7 (0.3) | 50.5 (6.6) | 88.0 (1.7) | 3.7 (1.2) | 67.8 (6.2) | 45.4 (5.8) | 13.6 (1.1) | 357.8 (70.2) |
| 3M | 77.0 (3.8) | 2.0 (0.6) | 20.6 (3.2) | 91.3 (2.4) | 2.0 (0.1) | 34.8 (3.3) | 78.7 (3.2) | 4.0 (1.0) | 77.9 (4.3) | 53.4 (3.0) | 21.6 (0.5) | 476.0 (60.2) |
| 3B | 74.7 (5.4) | 1.0 (0.6) | 17.5 (3.1) | 74.3 (2.8) | 1.7 (0.3) | 29.2 (5.3) | 73.7 (2.0) | 2.3 (0.3) | 70.0 (7.7) | 36.9 (0.8) | 20.0 (1.2) | 483.6 (47.1) |
| 5T | 91.7 (2.0) | 2.7 (0.3) | 23.5 (3.4) | 108.0 (4.2) | 3.0 (0.6) | 61.6 (3.4) | 95.3 (2.8) | 6.0 (1.5) | 71.4 (3.6) | 80.1 (5.6) | 13.5 (2.0) | 466.0 (58.9) |
| 5M | 84.3 (1.8) | 3.3 (0.9) | 30.5 (3.2) | 102.3 (2.0) | 2.7 (0.7) | 57.2 (8.4) | 92.0 (3.6) | 5.3 (1.2) | 67.3 (4.8) | 67.3 (5.9) | 16.5 (1.1) | 381.5 (118.6) |
| 5B | 82.3 (3.2) | 2.7 (0.7) | 20.8 (1.9) | 88.0 (3.1) | 1.7 (0.7) | 36.4 (5.3) | 84.7 (3.2) | 2.7 (0.7) | 53.2 (12.9) | 33.7 (3.5) | 20.9 (1.5) | 268.3 (64.3) |
References
- Lim, S.S.; Yang, H.I.; Park, H.J.; Park, S.I.; Seo, B.S.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, S.M.; Kim, H.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; et al. Land-use management for sustainable rice production and carbon sequestration in reclaimed coastal tideland soils of South Korea: A review. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 66, 60–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, B.S.; Jung, J.; Jung, K.; Kang, B.H. Soil physico-chemical properties and groundwater levels at the “Agricultural Life Science Sites” in Saemangeum reclaimed land. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2023, 56, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MOAF). Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs Statistics Yearbook; MOAF: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Bae, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Oh, Y.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Ko, J.C.; Hong, H.C.; Kim, Y.D.; Kim, S.L. Effect of subsurface drainage systems on soil salinity at Saemangeum reclaimed tidal land. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2015, 48, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bae, H.S.; Jang, H.; Hwang, J.B.; Park, T.S.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, D.S.; Chung, D.Y. Managing soil organic matter and salinity by crop cultivation in Saemangeum reclaimed tidal land. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2018, 51, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA). Medium and Long Term Development Plan of Upland Food Crop; MAFRA: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2016; Available online: http://www.mafra.go.kr (accessed on 1 May 2025).
- Chung, D.Y.; Kim, H.; Park, M.; Lee, S.E. Characteristics of a reclaimed tidal soil for effective resalization at Saemangum and Youngsan-River. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2012, 45, 1222–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, Y.Y.; Ryu, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Kang, B.H.; Ock, H.K.; Jung, K.H. Changes in soil salinity and upland crop productivity in reclaimed land as affected by groundwater table. Korean J. Soil Sci. Fertil. 2020, 53, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute of Crop Science (NICS). Look in the Reclaimed Tidal Land; NICS: Wanju, Republic of Korea, 2013; p. 102. [Google Scholar]
- Uni, N. Cropland soil salinization and associated hydrology: Trends, processes and examples. Water 2018, 10, 1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Bae, H.S.; Kim, H.K.; Noh, T.H.; Lee, G.H. Temporal variations on soil salinity and cation displacement at Saemangeum and Yeongsangang reclaimed tidal lands. J. Agric. Chem. Environ. 2014, 3, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bae, H.S.; Lee, S.H.; Hwang, J.B.; Park, H.K.; Lee, G.H.; Lee, G.B.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, D.S.; Hong, B.D.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Drainage effect on desalinization and crop growth on a poorly drained soil in the reclaimed tidal flat land. J. Korean Soc. Int. Agric. 2016, 28, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, X.H.; Chang, T.T.; Cai, F.; Wang, Z.Y.; Huang, M.Y. Effects of subsurface drainage design on soil desalinization in coastal resort of China. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2012, 10, 935–938. [Google Scholar]
- Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA). KMA Weather Data Service, Open MET Data Portal; KMA: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2025; Available online: https://data.kma.go.kr/cmmn/main.do (accessed on 15 May 2025).
- Keeney, D.R.; Nelson, D.W. Nitrogen-inorganic forms. In Methods of Soil Analysis; Agronomy Monograph 9, Part 2, 2nd ed.; Page, A.L., Ed.; ASA: San Antonio, TX, USA; SSSA: Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 1982; pp. 643–698. [Google Scholar]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology, 3rd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oksanen, J.; Blanchet, F.G.; Kindt, R.; Legendre, P.; Minchin, P.R.; O’Hara, B.; Simpson, G.L.; Solymos, P.; Stevens, M.H.H.; Wagner, H. VEGAN: Community Ecology Package, R package Version 2.0-9. 2012. Available online: https://researchportal.helsinki.fi/en/publications/vegan-community-ecology-package (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Nosetto, M.D.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B.; Sznaider, G.A. Reciprocal influence of crops and shallow groundwater in sandy landscapes of the inland Pampas. Field Crops Res. 2009, 113, 138–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayar, J.E.; Christen, E.W.; Soppe, R.W.; Meyer, W.S. The resource potential of in-situ shallow ground water use in irrigated agriculture: A review. Irrig. Sci. 2006, 24, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, R.E.; Kriz, G.J. Response of agricultural crops to flooding, depth-of-water table and soil gaseous composition. Trans. ASABE 1970, 13, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chae, S.; Shin, P.; Youn, J.; Sung, J.; Jeon, S. The effect of sowing date on soybean growth and yield under changing climate in the southern coastal region of Korea. Agriculture 2025, 15, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebre, M.G.; Earl, H.J. Effects of growth medium and water stress on soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] growth, soil water extraction and rooting profiles by depth in 1-m rooting columns. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katerji, N.; van Hoorn, J.W.; Hamdy, A.; Mastrorilli, M. Salt tolerance classification of crops according to soil salinity and to water stress day index. In Mediterranean Crop Responses to Water and Soil Salinity; International Centre for Advanced Mediterranean Agronomic Studies: Bari, Italy, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Chen, S.; Kurle, J.E. Interactive effects of soybean cyst nematode, arbuscular-mycorrhizal fungi, and soil pH on chlorophyll content and plant growth of soybean. Phytobiomes J. 2022, 6, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogovska, N.P.; Blackmer, A.M.; Mallarino, A.P. Relationships between soybean yield, soil pH, and soil carbonate concentration. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 38, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.J.; Seo, B.S.; Jeong, Y.J.; Yang, H.I.; Park, S.I.; Baek, N.; Kwak, J.H.; Choi, W.J. Soil salinity, fertility and carbon content, and rice yield of salt-affected paddy with different cultivation period in southwestern coastal area of South Korea. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 68, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.H.; Park, J.S.; Choi, M.S.; Jung, K.Y.; Chun, H.C.; Lee, S.H.; Gong, D.H.; Chae, S.E.; Jeon, S.H.; Yoon, D.K. Growth and yield response of soybean (Glycine max L.) in relation to sowing date in the southern region of South Korea. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chathurika, W.; Reddy, K.R.; Nacer, B. Soybean seed physiology, quality, and chemical composition under soil moisture stress. Food Chem. 2019, 278, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desouza, P.I.; Egli, D.B.; Bruening, W.P. Water stress during seed filling and leaf senescence in soybean. Agronomy 1997, 89, 807–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, W.G.; Baek, J.K.; Kwon, D.W.; Cho, J.I. Impact of climate change on yield and canopy photosynthesis of soybean. Korean J. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2022, 24, 275–284. [Google Scholar]
- Hatfield, J.L.; Boote, K.J.; Kimball, B.A.; Ziska, L.H.; Izaurralde, R.C.; Ort, D.; Thomson, A.M.; Wolfe, D. Climate impacts on agriculture: Implications for crop production. Agron. J. 2011, 103, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakurai, G.; Iizumi, T.; Yokozawa, M. Varying temporal and spatial effects of climate on maize and soybean affect yield prediction. Clim. Res. 2011, 49, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, M.A.; Murray, A.R.; Ward, A.R.; Konrad, C.E. Influence of growing season temperature and precipitation anomalies on crop yield in the southeastern United States. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2020, 291, 108053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Slope Degree | Position | pH1:5 | EC1:5 (dS m−1) | NH4+-N (mg kg−1) | NO3−-N (mg kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Total-N (g kg−1) | C/N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | NA a | 6.89 (0.01) | 0.91 (0.01) | 4.06 (1.09) | 0.09 (0.09) | 11.8 (1.28) | 0.65 (0.07) | 10.6 (0.30) |
| 3 | Top | 7.38 (0.01) | 1.34 (0.01) | 2.15 (0.23) | 1.26 (0.56) | 9.0 (0.62) | 0.47 (0.07) | 11.2 (0.47) |
| Middle | 7.59 (0.02) | 1.43 (0.02) | 3.31 (1.10) | 1.07 (0.05) | 7.4 (0.62) | 0.37 (0.02) | 11.6 (0.40) | |
| Bottom | 8.05 (0.02) | 1.20 (0.02) | 1.87 (1.35) | 0.79 (0.45) | 3.0 (0.22) | 0.20 (0.01) | 8.9 (0.31) | |
| 5 | Top | 6.92 (0.03) | 1.45 (0.01) | 3.97 (1.05) | 2.43 (0.94) | 9.2 (0.18) | 0.50 (0.02) | 10.8 (0.21) |
| Middle | 7.14 (0.01) | 1.14 (0.04) | 5.93 (1.58) | 1.63 (1.24) | 7.5 (1.24) | 0.39 (0.05) | 11.2 (0.25) | |
| Bottom | 7.69 (0.04) | 0.95 (0.02) | 0.42 (0.24) | 2.99 (1.74) | 3.8 (0.26) | 0.23 (0.01) | 9.7 (0.29) | |
| Effects | Probability > F | |||||||
| Slope (S) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.272 | 0.365 | 0.568 | 0.453 | 0.977 | |
| Position (P) | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.019 | 0.471 | <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| S × P | 0.044 | <0.001 | 0.167 | 0.607 | 0.904 | 0.988 | 0.128 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, S.-B.; Song, E.-S.; Lee, K.-S.; Kwak, J.-H.; Choi, W.-J. Slope Construction on Croplands in Reclaimed Tidal Flats of Korea Improved Surface Drainage but Not Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092177
Lee S-B, Song E-S, Lee K-S, Kwak J-H, Choi W-J. Slope Construction on Croplands in Reclaimed Tidal Flats of Korea Improved Surface Drainage but Not Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Seung-Beom, Eun-Su Song, Kwang-Seung Lee, Jin-Hyeob Kwak, and Woo-Jung Choi. 2025. "Slope Construction on Croplands in Reclaimed Tidal Flats of Korea Improved Surface Drainage but Not Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092177
APA StyleLee, S.-B., Song, E.-S., Lee, K.-S., Kwak, J.-H., & Choi, W.-J. (2025). Slope Construction on Croplands in Reclaimed Tidal Flats of Korea Improved Surface Drainage but Not Soybean Growth Due to Weather Variability. Agronomy, 15(9), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092177






