Effects of Droughting Stress on Leaf Physiological Characteristics of Machilus thunbergii Seedlings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Determination of Relative Moisture Content of Matrix
2.4. Observation on Anatomical Structure of Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings
2.5. Determination of Physiological Indexes
2.5.1. Relative Water Content of Leaves
2.5.2. Relative Electrical Conductivity
2.5.3. MDA Content
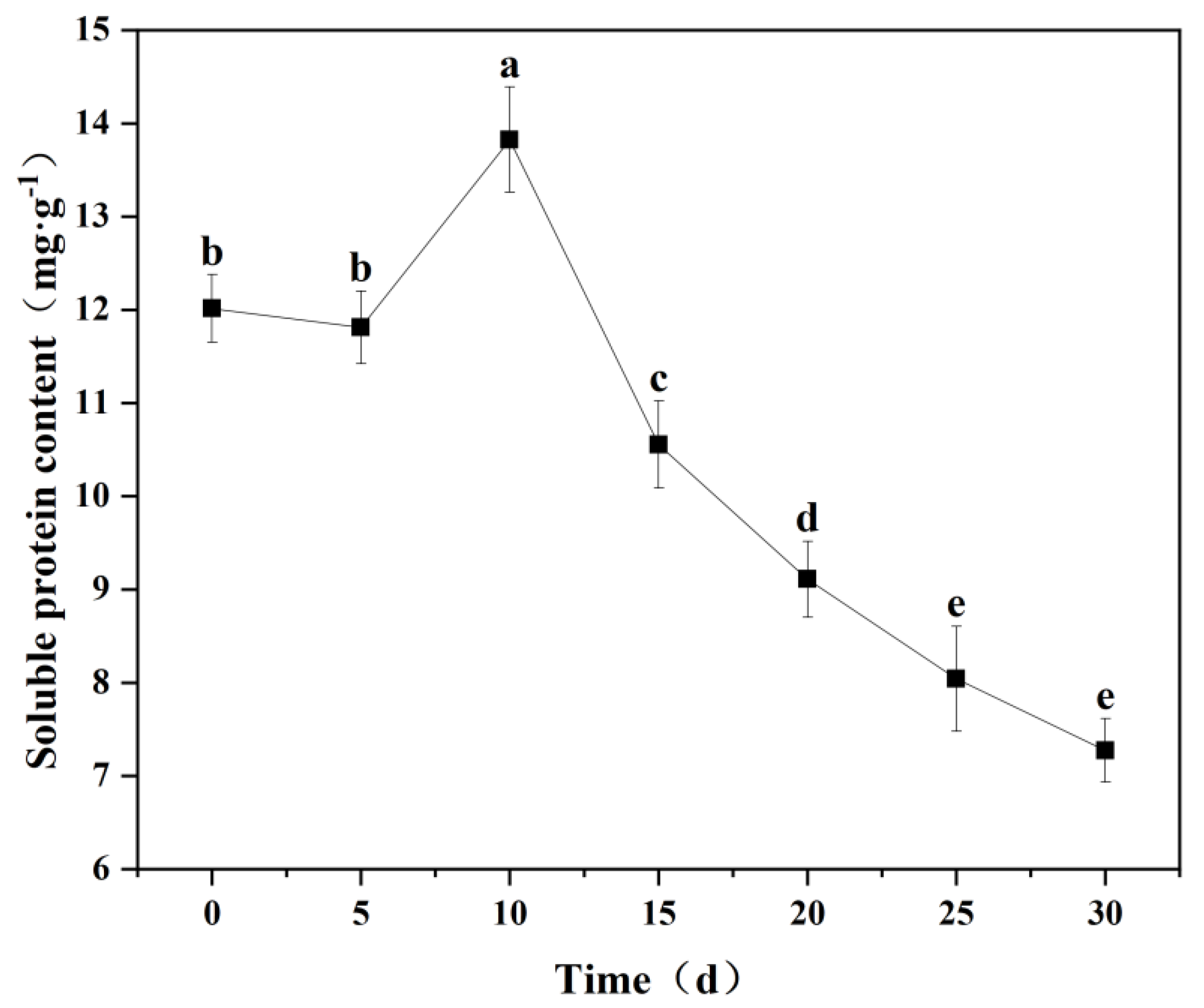
2.5.4. Soluble Protein Content
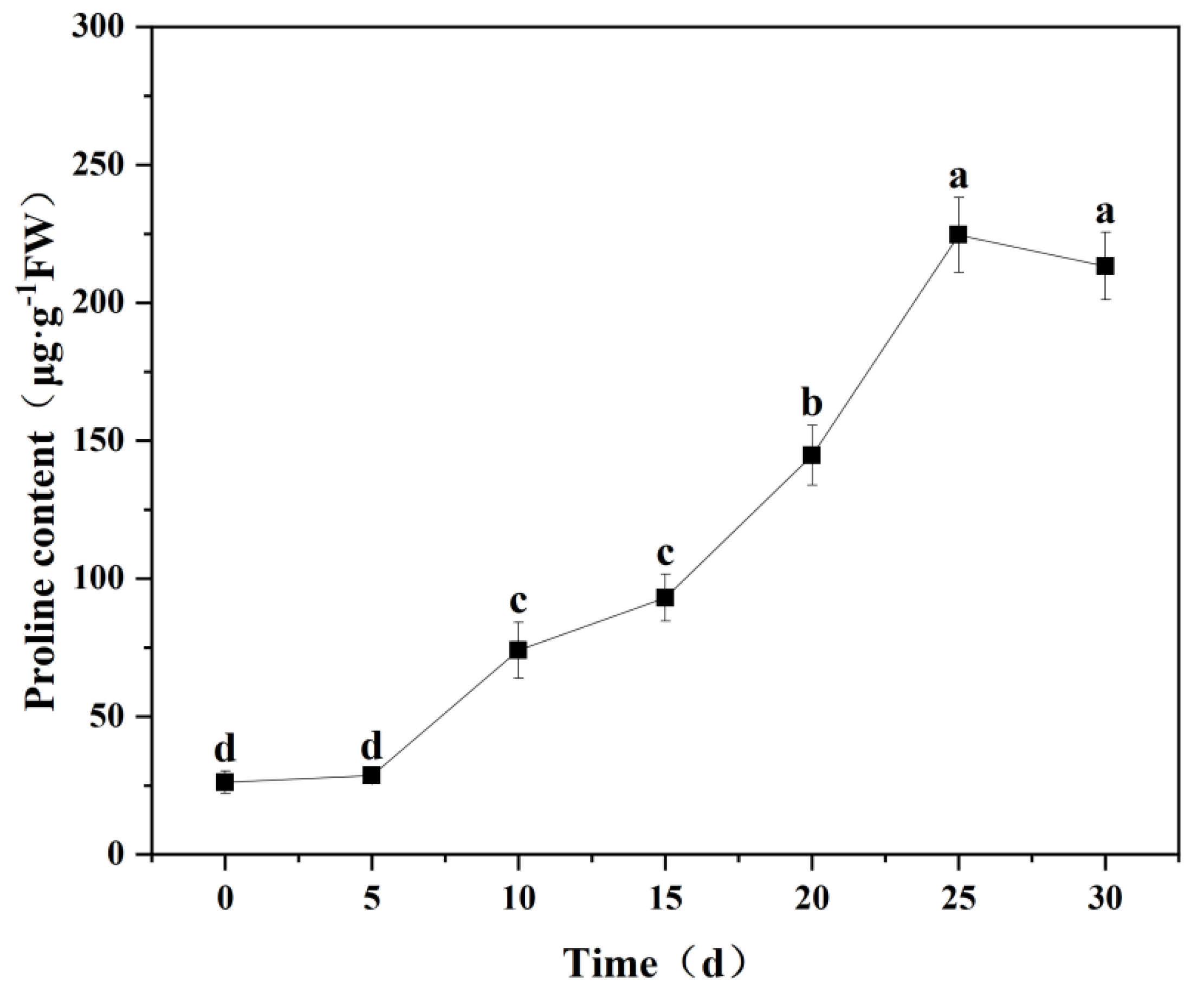
2.5.5. Pro Content
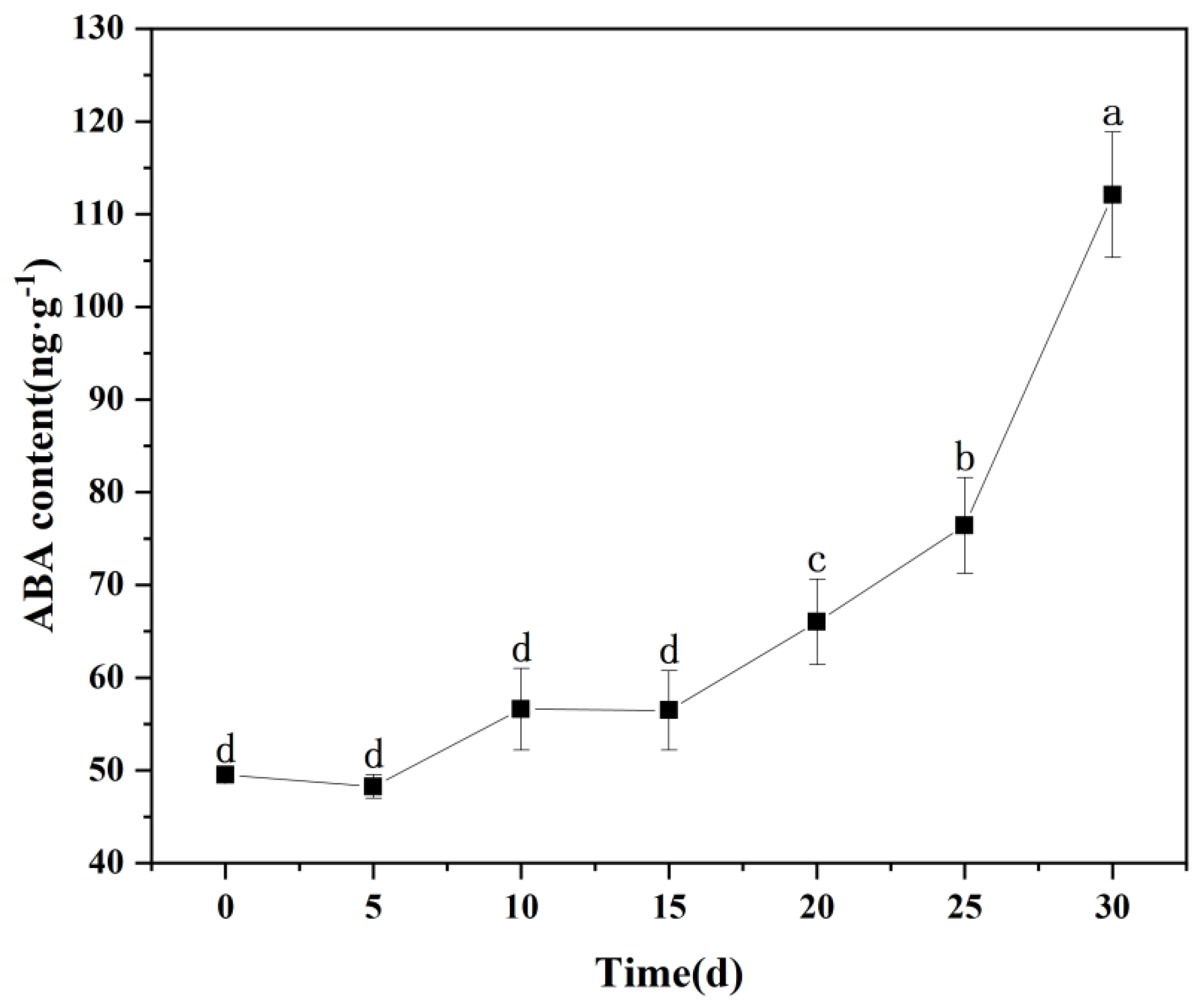
2.5.6. ABA Content
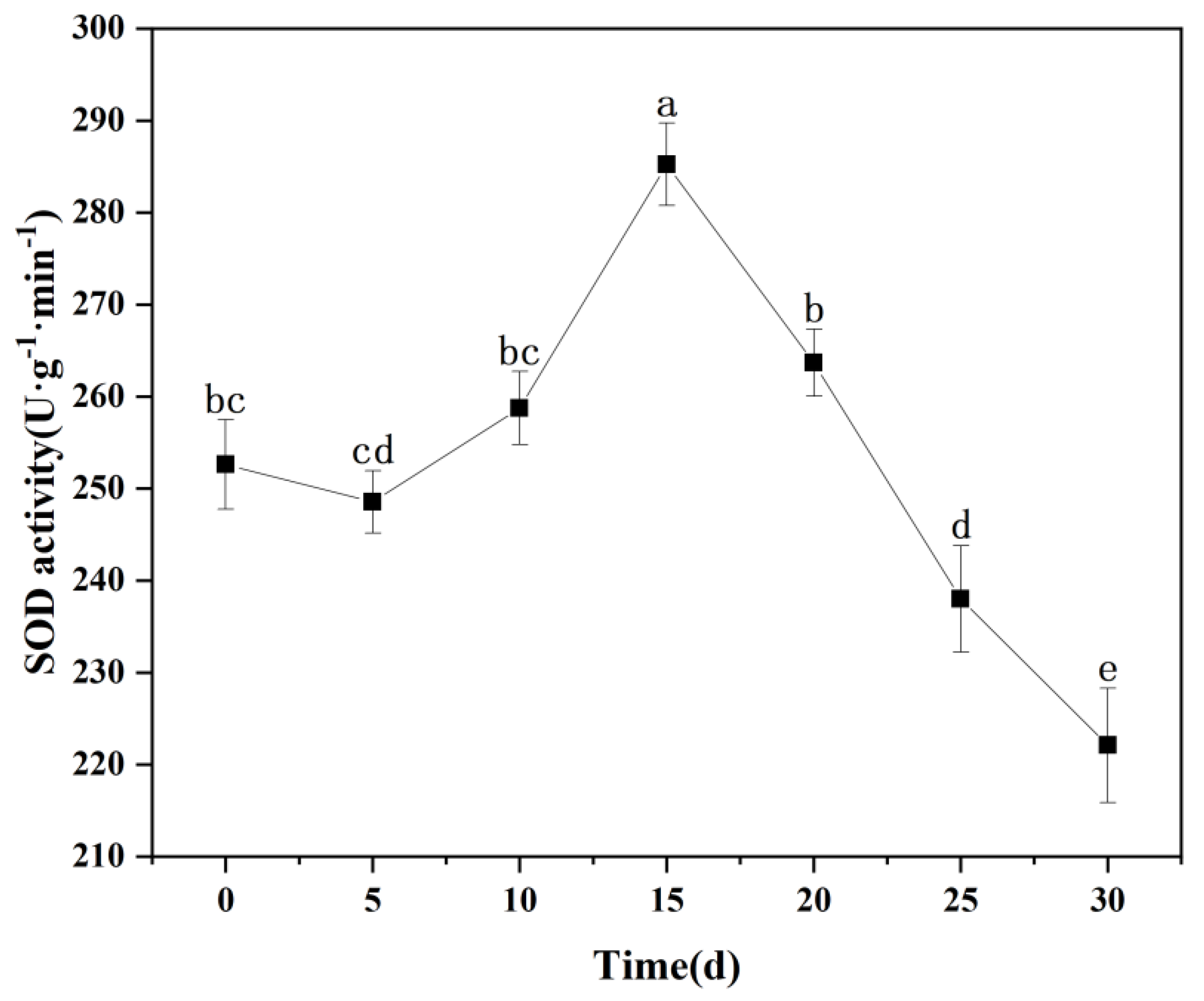
2.5.7. The Activity of SOD
2.5.8. The Activity of POD
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Changes in Relative Water Content in Seedling Culture Substrate During Drought Treatment
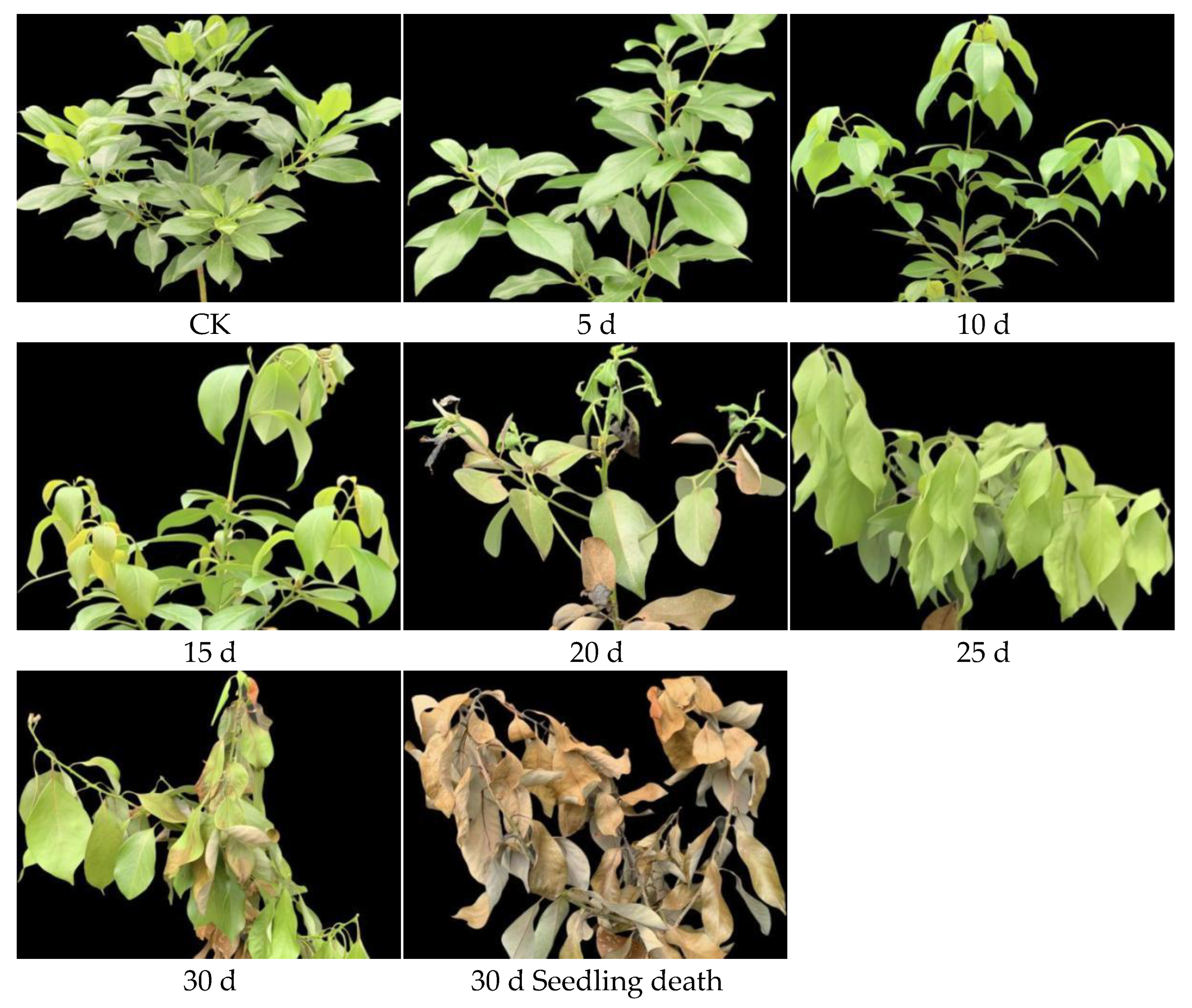
3.2. Changes in Seedling Morphology and Mortality During Drought Treatment
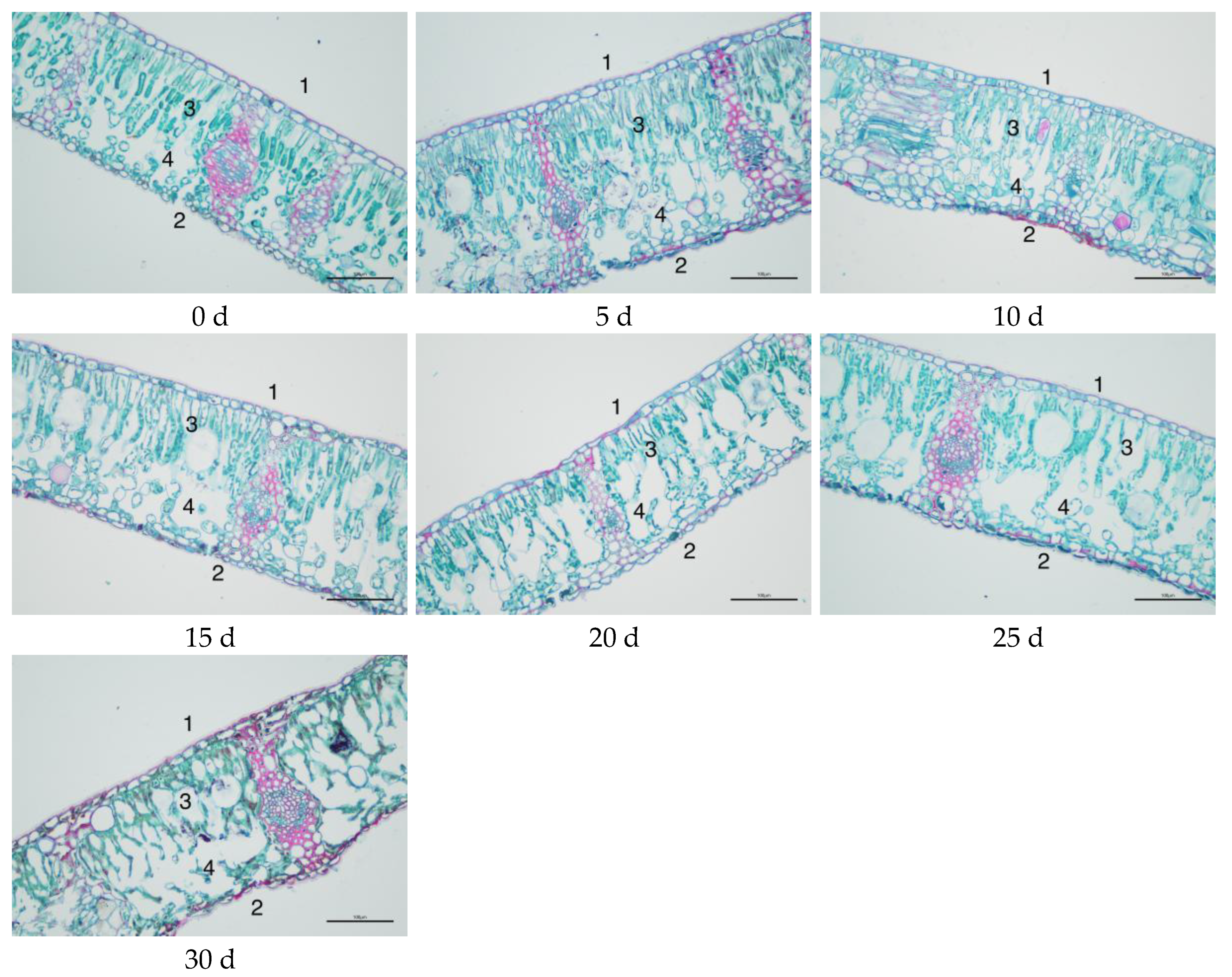
3.3. Changes in Leaf Structure of M. thunbergii Seedlings During Drought Treatment
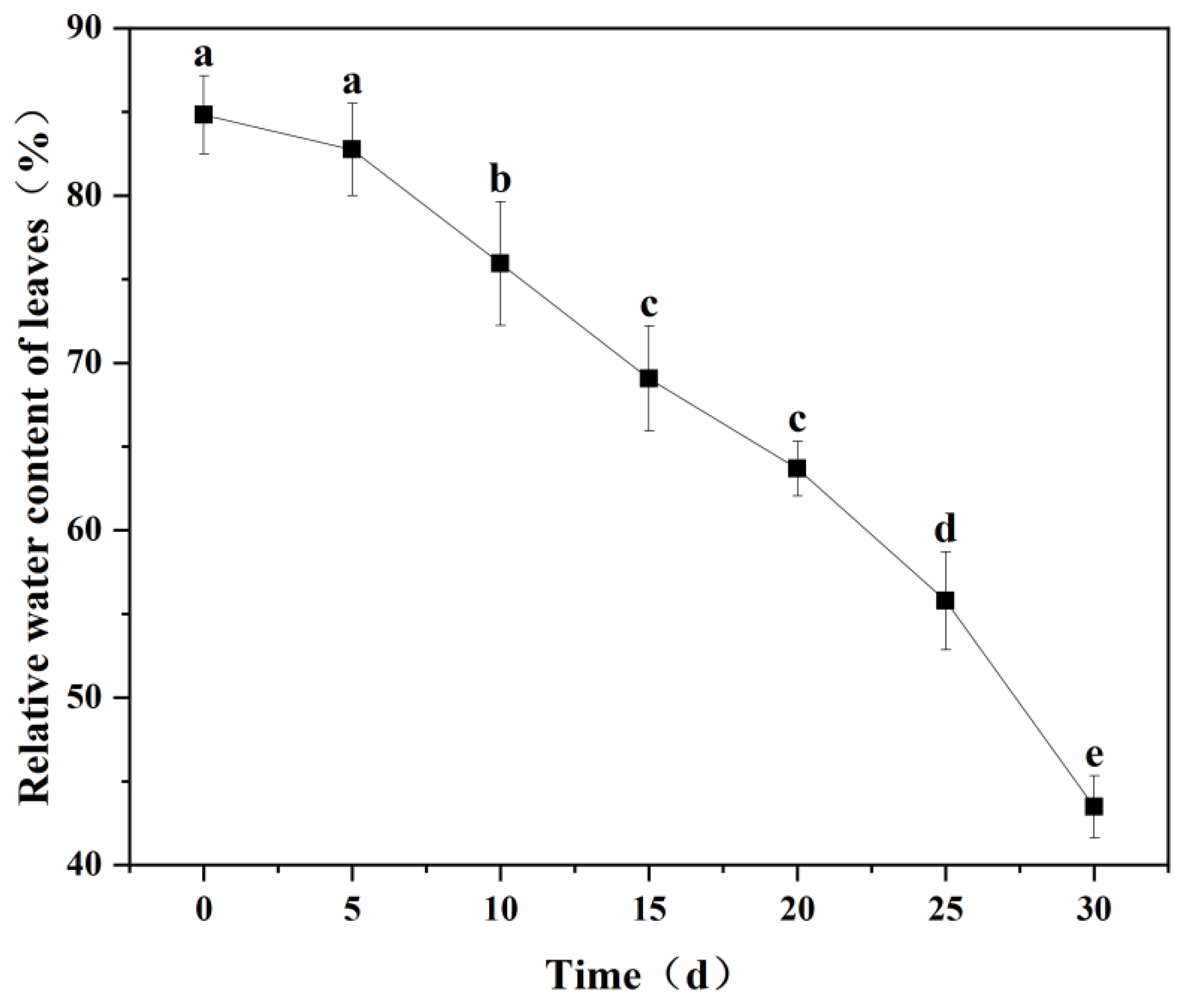
3.4. Changes in Relative Water Content in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings During Drought Treatment
| Index | Sum of Squares | Degree of Freedom | Mean Square | F Value | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative water content of leaves | 4001.855 | 6 | 666.976 | 91.022 ** | 0.00 |
| Relative conductivity | 3137.472 | 20 | 434.629 | 11.487 ** | 0.00 |
| MDA content | 8.025 | 20 | 202.846 | 202.846 ** | 0.00 |
| Soluble protein content | 102.819 | 20 | 16.661 | 81.841 ** | 0.00 |
| PRO content | 121,422.891 | 20 | 20021.026 | 216.154 ** | 0.00 |
| ABA content | 8984.470 | 6 | 225.020 | 78.335 ** | 0.00 |
| SOD activity | 7156.003 | 6 | 1192.667 | 53.426 ** | 0.00 |
| POD activity | 4384.378 | 6 | 6730.730 | 84.696 ** | 0.00 |
3.5. Changes in Cell Membrane Stability in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings During Drought Treatment
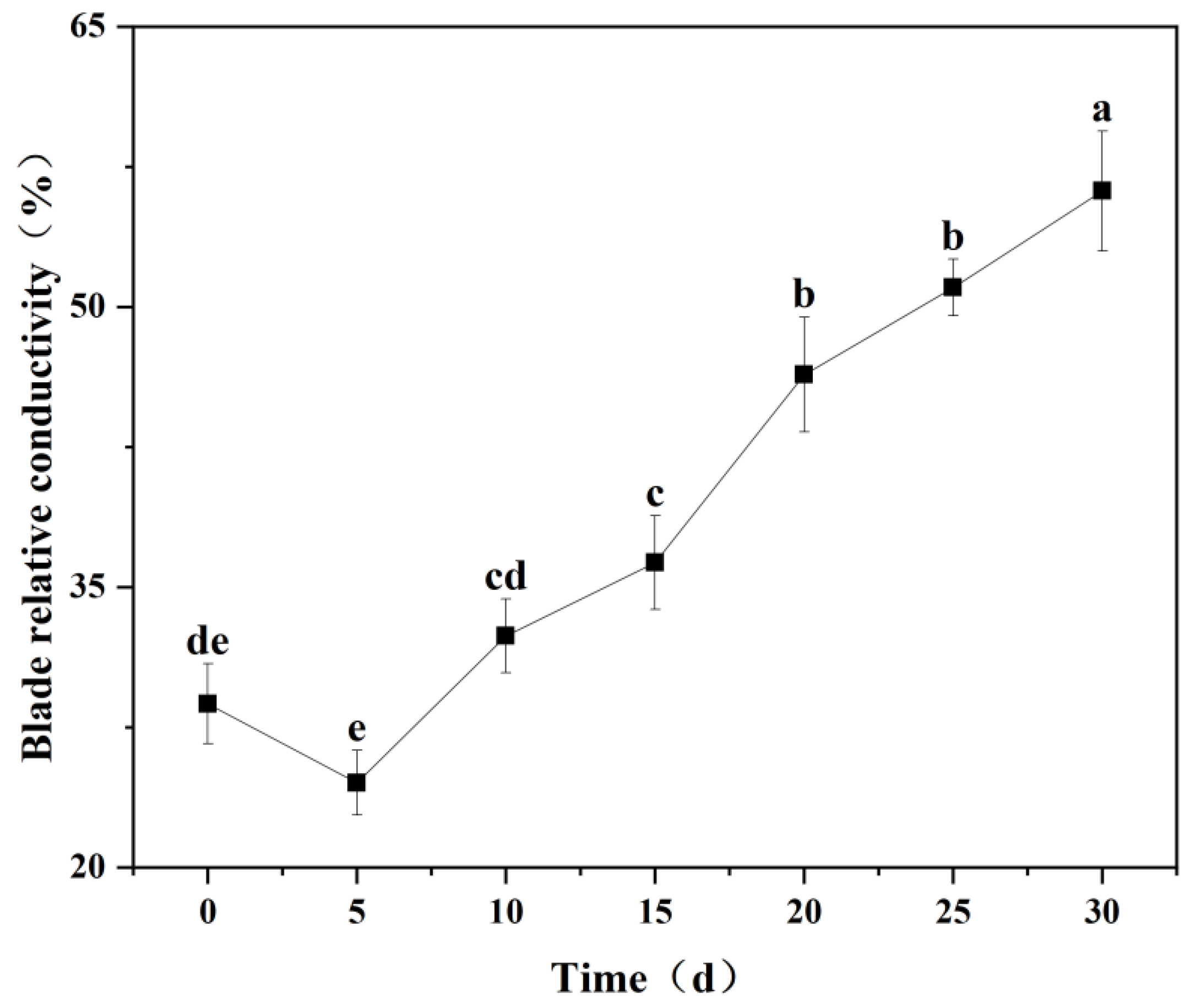
3.5.1. Changes in Relative Conductivity of Seedling Leaves
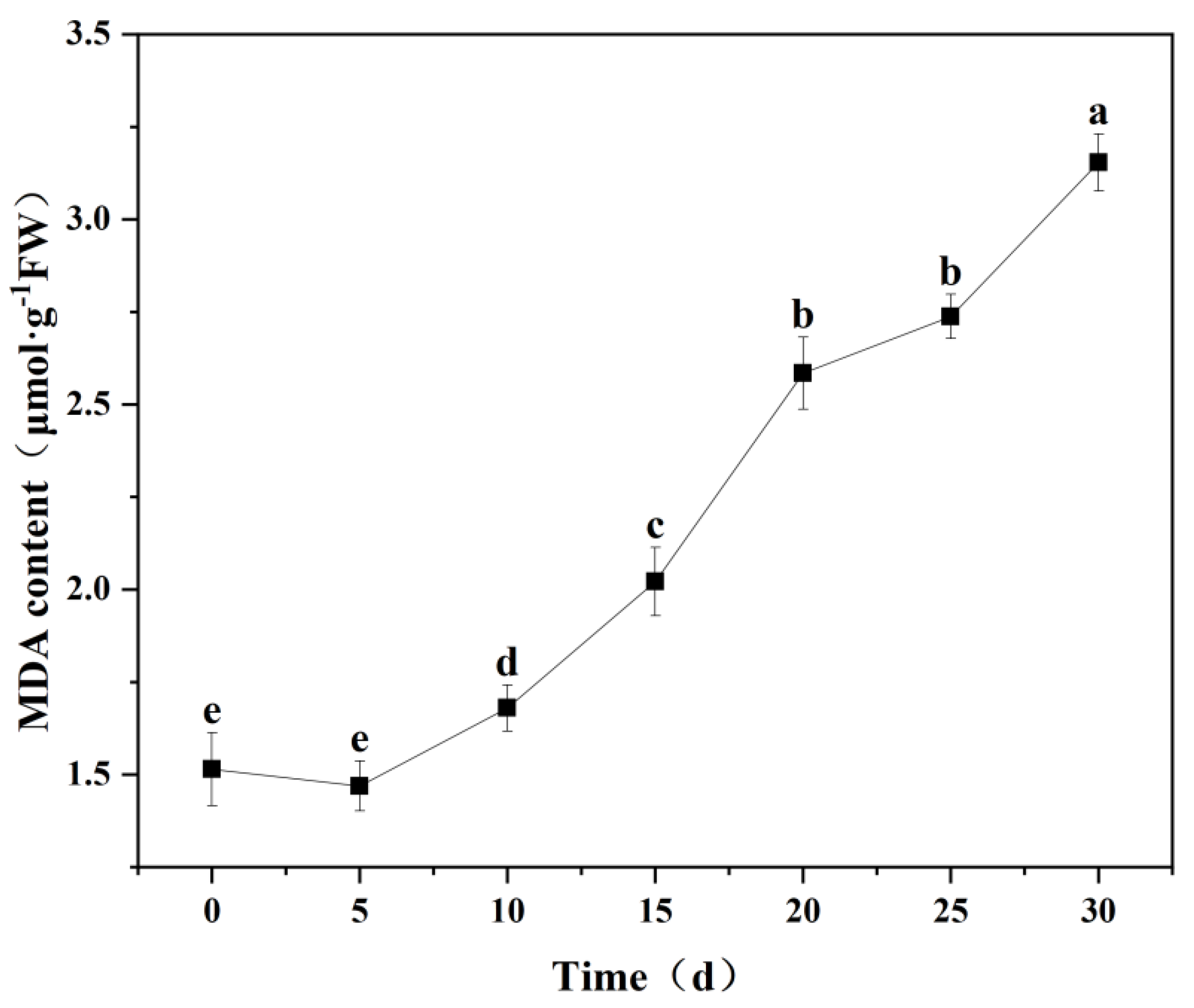
3.5.2. Changes in MDA Content in Seedling Leaves
3.6. Changes in Osmotic Adjustment Substance Content in Seedling Leaves During Drought Treatment
3.6.1. Changes in Soluble Protein Content in Seedling Leaves
3.6.2. Changes in Proline Content in Seedling Leaves
3.7. Changes in ABA Content in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings During Drought Treatment
3.8. Changes in Protective Enzyme System in Seedling Leaves During Drought Treatment
3.8.1. Changes in SOD Activity in Seedling Leaves
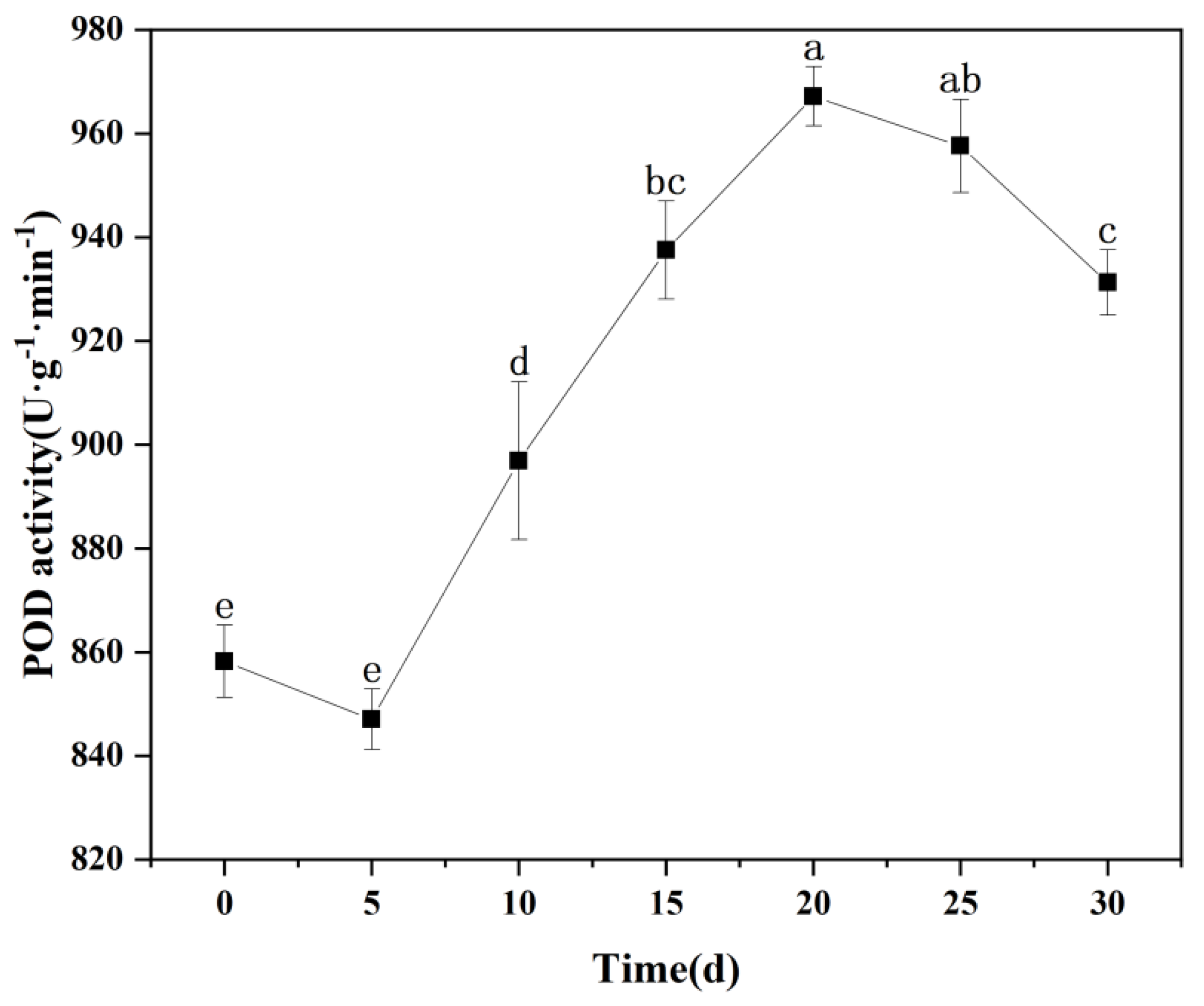
3.8.2. Changes in POD Activity in Seedling Leaves
3.9. Correlation Analysis of Drought Tolerance of M. thunbergii Seedlings
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Anatomical Structure of M. thunbergii Seedlings
4.2. Effects of Drought Stress on Leaf Water Content of M. thunbergii Seedlings
4.3. Effects of Drought Stress on the Stability of the Cell Membrane in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings
4.4. Response of Osmotic Adjustment Substances in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings to Drought Treatment
4.5. Response of ABA in Leaves of M. thunbergii Seedlings to Drought Treatment
4.6. Response of Enzyme Protection System of M. thunbergii Seedlings to Drought Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.Q.; Gao, Y.; Tang, Z.H.; Zhang, J.Y.; Li, Z.Y.; Liu, J.R. Effect of soil drought stress on photosynthrsis and yield of sweetpotato. J. Jiangsu Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2019, 37, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.; Shang, Z.H.; Shen, Z.G.; Ding, X. Research progress in palnt response mechanism to drought stress. J. Henan For. Sci. Tech. 2019, 39, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, F.L.; Ma, Y.H. Effect of drought stress on plants and their response mechanism. J. Ningxia Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2022, 43, 391–399. [Google Scholar]
- Mang, L.Y.; Huang, J.J. Research progress and development prospect of indigenous species Machilus thunbergii. Protec. For. Sci. Tech. 2019, 06, 66–68. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D. The Population Structure of Machilus thunbergii and Effect of Animals on Its Seed Dispersal. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- He, W.Z.; Li, T.T.; Chen, B.; Gao, D.H.; Yuan, W.H. Influences of root-controlling containers on root architecture and survival rate of seedling for 2 speciesin Lauraceae in Zhoushan. J. For. Eng. 2015, 29, 56–59. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.S.; Kim, J.W.; Yu, Y.U.; Kim, Y.C. Inhibition of phospholipase Cgamma1 and cancer cell proliferation by lignans and flavans from Machilus thunbergill. Arch. Phar. Res. 2004, 27, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Oktavia, D.; Jin, G. Variations in leaf morphological and chemical traits in response to life stages, plant functional types, and habitat types in an old-growth temperate forest. Basic Appl. Ecol. 2020, 49, 22–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.M. Investigation on the inhabitation environments and growth conditions of Machilus thunbergii community in Pyonsanbando. Kor. J. Env. Eco. 1998, 12, 242–252. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.J.; Cang, J. Guide of Plant Physiological Experiments; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- GB/T 32136-2015; Agrometeorology (SAC/TC 539). Grade of Agricultural Drought. Standard Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Cui, Y.T. The Effection of Drought Stress on Structure and Physiology of four Potentilla Olants. Master’s Thesis, Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, Q.; Bai, H.R.; Bian, F.H.; Pang, Y.J.; Li, L.X. Effects of drought stress on anatomical structure and physiological characteristics of leaves of cultivated and wild Glehnia littoralis. J. Yantai Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2023, 36, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, K.Y. Research on Drought Resistance and Waterlogging Resistance of Koelreuteria bipinnata var. integrifoliola Seedlings; Zhejiang A&F University: Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.R. Effects of Soil Environment Regulation on Water Absorptionand Utlilzation of Lycium barbarum L. in Arid Regions; Gansu Agricultural University: Lanzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jian, L.C.; Wang, H. Plant Cell Biology of Stress; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Parkhey, S.; Naithani, S.C.; Keshavkant, S. ROS production and lipid catabolism in desiccating Shorea robusta seeds during aging. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2012, 57, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blum, A. Osmotic adjustment is a prime drought stress adaptive engine in support of plant production. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.M.; Li, C.N.; Liu, X.L.; Bu, Z.Y.; Huang, Z.W. Effect of shading on leaf growth and primary metabolism of Camellia azalea seedlings. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident. Sin. 2019, 39, 294–301. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Z.J.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Zhang, C. The seedling growth and root physiological traits of Fagopyrum tataricum cultivars under drought stress. Acta Bot. Boreal. Occident. Sin. 2018, 38, 112–120. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, J.M.; Huang, X.L.; Liang, Z.F.; Li, C.D.; Lan, J.X.; Li, B.C.; Liang, W.H. Content changes of endogenous hormones under drought stress of Carya illinoensis seedlings. Guangxi For. Sci. 2020, 49, 511–517. [Google Scholar]
- Krishnan, S.; Merewitz, E.B. Drought stress and trinexapac-ethyl modify phytohormone content within Kentucky Bluegrass leaves. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 34, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moller, I.M.; Jensen, P.M.; Hansson, A. Oxidative modification to cellular components in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, D.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, H.; Chen, R.; Li, C.W. Effects of drought stress on SOD, POD and PAL activity in tomato seedling leaves. J. Jilin Agric. Sci. 2015, 40, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Hannachi, S.; Signore, A.; Adnan, M.; Mechi, L. Single and associated effects of drought and heat stresses on physiological, biochemical and antioxidant machinery of four eggplant cultivars. Plants 2022, 11, 2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Zhang, B.; Jia, J.Q.; Feng, M.C.; Zhang, M.J.; Yang, W.D. Effects of drought and rewatering on root growth and anatomical structure of Oat in early growth stage. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2021, 49, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Q.H.; Mubareke, A.Y.P.; Xu, P.Y.; Gong, P.; Dilixiati, H.S.M. Drought tolerance evaluation of almond cultivars and comparison on stem xylem natural embolism degree and anatomical structure under drought stress. J. Plant Resour. Environ. 2022, 31, 15–24. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Yuan, H.M.; Chen, D.S.; Wang, X.L.; Kang, L.; He, J.S. Advances in studies on physiological and biochemical indexes and QTL for drought resistance in wheat. Agric. Res. Arid. Areas 2015, 33, 139–148. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, X.Z.; Mu, H.X.; Sun, X.; He, H.Y.; Yang, K.W.; Dan, Y.Y.; Li, C.Y. Effect of drought stress on the water physiological characteristics and the osmotic regulation substances of Xanthoceras sorbifolia seedings from different provenances. J. Northeast. For. Univ. 2017, 45, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Priyanandhini, L.; Kalarani, M.K.; Senthil, A.; Senthil, N.; Pazhanivelan, S.; Karthikeyan, R.; Umapathi, M.; Vanitha, G. Effect of gas exchange, antioxidative enzyme activities and yield characteristics of maize inbred lines under drought stress. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2024, 71, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, F.; Naeem, M.; Zulfiqar, B. Understanding brassinosteroid-regulated mechanisms to improve stress tolerance in plants: A critical review. Enviro. Sci. Pol. 2017, 24, 15959–15975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.T.; Yao, A.B.; Li, J.X.; Zhou, L.P.; Wei, L.; Zhang, J.X. Water stress tolerance of four roses varieties. Northern Hortic. 2021, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.J. Research progress on osmotic adjustment material under water stress. J. Anhui Agri. Sci. 2010, 38, 7750–7753, 7760. [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney, J.M. Response of a hybrid poplar to water Table decline in different substrates. For. Ecol. Manage 1992, 54, 141–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. Effects of drought stress on soluble protein of Hordeum vulgare seedlings. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2015, 43, 124–126. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.J.; Yang, C.X.; Tan, S.C.; Gu, Z.J.; Tang, S.; Yu, F.Y. Effects of drought stress on proline and endogenous hormones contentin Pinus massoniana seedlings from different provenances. South China For. Sci. 2020, 48, 24–28, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.M.; Guan, S.Y.; Guo, X.M. Effects of NaCl stress on antioxidant enzymes activities and soluble protein content in 3 kinds of sweet potatoes (Dioscorea esculenta). J. Anhui Agri. Sci. 2012, 40, 9228–9229. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Yang, A.; Yin, H. Influence of water stress on endogenous hormone contents and cell damage of maize seedlings. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2008, 50, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H. Study on the Relationship Between Endogenous Hormone Changes and Green Holding and Drought Resistance in Green-Holding Wheat. Master’s Thesis, Northwest A&F University, Xianyang, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, M.J.; Meng, Y.; Meng, X.Z. Effects of drought stress on photosynthetic pigments, protective enzyme activities and active oxygen metabolism of Sweet Sorghum Seedlings. Tianjin Agric. Sci. 2021, 27, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Bu, L.D.; Zhang, R.h.; Han, M.M.; Xue, J.Q.; Chang, Y. The physiological mechanism of compensation effect in maize leaf by re-watering after draught Stress. Acta Agric. Bor.-Occid. Sin. 2009, 18, 88–92. [Google Scholar]

| Treatment Time (d) | Matrix Moisture Content (%) | Drought Degree |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 71.13 Aa | Normal level |
| 5 | 65.42 Aa | Normal level |
| 10 | 56.87 Bb | Mild drought |
| 15 | 50.66 Cc | Mild drought |
| 20 | 33.85 Dd | Moderate drought |
| 25 | 17.64 Ee | Severe drought |
| 30 | 14.33 Ee | Severe drought |
| Treatment Time (d) | Blade Thickness (μm) | Upper Epidermal Cells (μm) | Lower Epidermal Cells Thickness (μm) | Palisade Tissue Thickness (μm) | Spongy Tissue Thickness (μm) | Palisade Tissue Thickness/Spongy Tissue Thickness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 232.81 ± 5.78 A | 16.05 ± 2.09 A | 10.16 ± 0.45 A | 88.62 ± 4.64 D | 105.70 ± 8.72 A | 0.84 ± 0.93 C |
| 5 | 230.05 ± 6.62 AB | 15.19 ± 0.17 AB | 9.94 ± 1.15 A | 95.86 ± 2.28 BCD | 103.49 ± 7.31 A | 0.92 ± 0.68 C |
| 10 | 219.71 ± 3.95 BC | 14.64 ± 0.69 ABC | 9.21 ± 0.56 AB | 93.97 ± 4.40 CD | 95.30 ± 3.23 AB | 0.98 ± 0.66 BC |
| 15 | 214.92 ± 1.42 CD | 14.18 ± 0.79 ABC | 8.83 ± 0.66 ABC | 97.53 ± 1.49 BC | 88.59 ± 1.59 BC | 1.10 ± 0.33 B |
| 20 | 204.93 ± 8.09 D | 13.45 ± 1.26 BC | 8.21 ± 0.81 BC | 97.20 ± 2.16 BC | 76.70 ± 6.87 D | 1.27 ± 0.11 A |
| 25 | 207.11 ± 5.40 D | 13.15 ± 0.55 C | 7.96 ± 0.35 BC | 102.44 ± 5.40 AB | 79.76 ± 1.39 CD | 1.28 ± 0.09 A |
| 30 | 203.58 ± 6.33 D | 12.58 ± 0.60 C | 7.48 ± 0.41 C | 106.16 ± 4.65 A | 75.40 ± 3.62 D | 1.40 ± 0.07 A |
| Index | Relative Moisture Content of Matrix | Blade Thickness | Relative Water Content | Relative Conductivity | MDA Content | Proline Content | Soluble Protein Content | ABA Content | SOD Activity | POD Activity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Relative moisture content of matrix | 1.000 | |||||||||
| Blade thickness | 0.934 ** | 1.000 | ||||||||
| Relative water content | 0.974 ** | 0.919 ** | 1.000 | |||||||
| Relative conductivity | −0.979 ** | −0.936 ** | −0.973 ** | 1.000 | ||||||
| MDA content | −0.980 ** | −0.936 ** | −0.981 ** | 0.992 ** | 1.000 | |||||
| Proline content | −0.993 ** | −0.918 ** | −0.957 ** | 0.975 ** | 0.963 ** | 1.000 | ||||
| Soluble protein content | −0.896 ** | 0.793 * | 0.884 ** | −0.896 ** | −0.926 ** | −0.876 ** | 1.000 | |||
| ABA content | −0.837 ** | −0.762 * | −0.941 ** | 0.891 ** | 0.905 ** | 0.845 * | −0.803 * | 1.000 | ||
| SOD activity | 0.512 | 0.223 | 0.506 ** | −0.481 | −0.408 | −0.500 | 0.482 | −0.694 | 1.000 | |
| POD activity | −0.809 ** | −0.933 ** | −0.760 * | 0.824 ** | 0.806 * | 0.817* | −0.694 | 0.519 | 0.063 | 1.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shi, F.; Yan, K.; Zhu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Tong, B.; Lu, Y. Effects of Droughting Stress on Leaf Physiological Characteristics of Machilus thunbergii Seedlings. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092154
Shi F, Yan K, Zhu A, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Tong B, Lu Y. Effects of Droughting Stress on Leaf Physiological Characteristics of Machilus thunbergii Seedlings. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092154
Chicago/Turabian StyleShi, Fenghou, Kaili Yan, Aisheng Zhu, Yuhui Zhang, Yanan Bai, Boqiang Tong, and Yizeng Lu. 2025. "Effects of Droughting Stress on Leaf Physiological Characteristics of Machilus thunbergii Seedlings" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092154
APA StyleShi, F., Yan, K., Zhu, A., Zhang, Y., Bai, Y., Tong, B., & Lu, Y. (2025). Effects of Droughting Stress on Leaf Physiological Characteristics of Machilus thunbergii Seedlings. Agronomy, 15(9), 2154. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092154




