Abstract
Organic amendments, such as straw, biochar, and animal manure, have been demonstrated to enhance soil phosphorus (P) availability effectively; however, the long-term impacts and underlying mechanisms require further study. Based on a long-term field experiment, this research systematically analyzed the effects of biochar (BIO), biochar-based fertilizer (BF), straw-returning (CS), and pig manure compost (PMC) on soil phosphorus transformation and crop phosphorus uptake. Results showed that biochar significantly boosted soil available phosphorus (AP) by releasing soluble phosphorus, raising soil pH, reducing phosphorus fixation by iron and aluminum oxides, and enhancing soil cation exchange capacity (CEC) to promote phosphorus dissolution and transformation. Notably, biochar increased the proportion of NaOH-P, facilitating phosphorus accumulation in peanut grains and improving the phosphorus harvest index and utilization efficiency. Straw-returning primarily elevated soil AP by promoting organic phosphorus mineralization and inorganic phosphorus release; however, its acidification of the soil impaired phosphorus translocation to grains, resulting in lower phosphorus-use efficiency compared to biochar. Pig manure compost reduced soil phosphorus fixation and increased soil total organic carbon (TOC), thereby boosting phosphorus transformation. Despite enhancing phosphorus dry-matter production in plants, most phosphorus remained in stems and leaves, with limited translocation to grains, leading to lower phosphorus-use efficiency than biochar. In conclusion, biochar was most effective in enhancing soil phosphorus availability and crop phosphorus-use efficiency, highlighting its potential in sustainable soil fertility management and optimized crop production.
1. Introduction
Phosphorus is an essential nutrient for crop growth and development and a critical factor influencing agricultural productivity. Although increasing the application of phosphorus fertilizers can enhance soil phosphorus fertility and crop yield, phosphorus availability is often limited due to its adsorption and fixation by soil colloids and metal cations [1]. Peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.), a major oilseed crop and nutrient-dense food, has a high phosphorus requirement throughout its life cycle. Phosphorus is not only directly involved in the assembly of the photosynthetic apparatus and carbon assimilation but also critically modulates the biosynthesis and accumulation of lipids, proteins, phospholipids, fatty acids, and nucleotides, ultimately determining seed yield and quality [2]. Therefore, enhancing the efficiency of phosphorus fertilizer utilization and extending the lifespan of phosphate rock resources have become critical scientific issues in the fields of agriculture and environmental science [3]. Driven by the concept of agricultural sustainability, the use of organic materials, such as straw, biochar, and animal manure, has been optimized over time. These materials are now key for enhancing soil phosphorus-use efficiency and mitigating environmental risks; however, the mechanisms by which different types of organic materials affect phosphorus availability vary notably, and the long-term effects of their application require further in-depth research and exploration. This study aims to elucidate the impacts of long-term fertilization with different organic materials (crop straw, biochar, biochar-based fertilizer, and pig manure) on soil phosphorus pools, phosphorus speciation transformations, and availability characteristics, thereby providing a comprehensive analysis of their underlying mechanisms.
The mechanisms by which direct straw incorporation affects soil phosphorus availability are multifaceted. First, the decomposition of straw releases a significant amount of low-molecular-weight organic acids and dissolved organic matter, which can markedly reduce phosphorus fixation in the soil [4]. These organic acids compete with iron, aluminum oxides, or calcium ions in the soil for phosphate adsorption, thereby decreasing phosphate precipitation or fixation and increasing the proportion of labile phosphorus [5]. Studies have shown that long-term straw incorporation can significantly improve soil structure and enhance the stability of soil aggregates [6,7]. This structural improvement not only aids in phosphorus retention but also reduces phosphorus leaching losses, particularly in the topsoil, where the accumulation of readily available phosphorus is more pronounced [8]. However, due to the slow decomposition rate of straw, its short-term phosphorus release effect is limited, often necessitating co-application with other organic or inorganic fertilizers to compensate for the short-term phosphorus supply deficit.
As a carbon-rich material produced through biomass pyrolysis [9], biochar can directly provide a phosphorus source to the soil. The high surface area and porous structure of biochar provide a physical basis for phosphorus adsorption and slow release. Additionally, biochar can influence phosphorus availability by improving soil physicochemical properties, such as increasing soil pH, cation exchange capacity, and organic matter content [10]. These changes facilitate phosphorus dissolution and transformation. For instance, in acidic soils, biochar neutralizes soil acidity, inhibiting the binding of phosphate with iron and aluminum oxides, thereby significantly enhancing phosphorus availability [11]. Furthermore, the positive regulation of soil microbial communities and enzyme activities by biochar is another important mechanism. Studies have shown that biochar can enhance the activity of phosphorus-solubilizing and -mineralizing microorganisms in the soil and promote alkaline phosphatase activity, thereby accelerating the conversion of organic phosphorus to inorganic phosphorus and improving soil phosphorus supply capacity [12]. Biochar-based fertilizers, which are produced by combining fertilizers with biochar matrices, represent an effective slow-release fertilizer. In this system, biochar acts as a carrier, binding nutrients from the fertilizer and releasing them slowly into the soil, thereby improving soil quality and fertilizer-use efficiency. Meanwhile, the fertilizer component supplements nutrients and promotes crop production [13].
Livestock manure, rich in available phosphorus and organic matter, exhibits more direct effects and mechanisms upon application [14]. Livestock manure contains a significant amount of inorganic phosphorus, such as orthophosphate, which can rapidly replenish the soil’s available phosphorus pool and meet the phosphorus demands of crops [15]. Simultaneously, the organic matter in livestock manure provides a rich carbon source and energy for soil microorganisms during decomposition, significantly enhancing microbial phosphorus mineralization and improving the conversion efficiency of organic phosphorus to inorganic phosphorus [16]. Additionally, the dissolved organic matter released from manure decomposition binds to soil mineral surfaces, increasing the soil’s phosphorus adsorption capacity and aiding in phosphorus retention [17,18]. However, the long-term application of livestock manure also carries certain risks. Studies have shown that excessive long-term application of manure can lead to an over-accumulation of phosphorus in the soil, particularly in soils with high phosphorus saturation, significantly increasing the risk of phosphorus loss through runoff or leaching and potentially triggering eutrophication in water bodies [19]. The effect of livestock manure on soil pH varies depending on multiple factors. Most studies indicate that manure application increases soil pH, primarily due to components such as CaCO3, HCO3−, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in the manure, as well as the neutralization of H+ by organic acid anions [20]; however, some studies have found that long-term application of cattle or poultry manure may lead to a decrease in soil pH, likely due to the acidifying effect of nitrification and the increased cation exchange caused by elevated electrical conductivity [21].
Although numerous studies have explored the effects of organic materials on phosphorus speciation transformation and availability, most of these studies have focused on short-term experiments and lack support from long-term field trial data. Moreover, research on the synergistic effects of combined applications of organic materials on phosphorus availability remains limited, and their potential advantages have yet to be fully explored. This study, based on a long-term field trial platform, systematically analyzes the long-term effects of different organic materials on soil phosphorus pool accumulation, speciation transformation, and availability, and investigates their regulatory mechanisms on soil phosphorus cycling. Specifically, it aims to reveal the patterns of soil phosphorus pool dynamics and phosphorus speciation transformation under long-term application of different organic materials, such as biochar, biochar-based fertilizer, straw, and pig manure. By examining changes in soil phosphorus fractions and crop phosphorus uptake, this study explores how different organic materials, such as biochar, biochar-based fertilizer, straw, and pig manure, influence soil phosphorus dynamics under equal phosphorus conditions. The findings provide valuable theoretical insights and practical guidance for enhancing phosphorus fertilizer management and efficiency.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
A long-term field experiment was initiated in 2009 at the Soil and Fertilizer Long-term Positioning Experimental Base of the National Peanut Industry Technology System, Shenyang Agricultural University (40°48′ N, 123°33′ E). The region has a temperate humid-to-semi-humid monsoon climate, with an average annual temperature of 7.0–8.1 °C, and average annual precipitation of 574–684 mm. The soil type in the experimental area is Haplic Luvisols (Typical Brown Earth), with a sandy clay loam texture, consisting of 51% sand, 28% silt, and 21% clay. The basic physicochemical properties of the soil prior to the experiment are presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Basic physical and chemical properties of soil before the experiment.
2.2. Experimental Design
Four treatments were arranged in a completely randomized design with three replicates per treatment; individual plot dimensions were 1 m × 2 m. The treatments were as follows: (i) BF, biochar-based fertilizer; (ii) BIO, biochar plus NPK; (iii) CS, maize straw plus NPK; and (iv) PMC, pig manure compost plus NPK. For CS, PMC, and BIO, the mineral fertilizer component was calculated by subtracting the N, P, and K supplied by the annually applied organic amendments from the total nutrient requirement, thereby equalizing total NPK inputs across all treatments to match those in the BF treatment. Urea, calcium superphosphate, and potassium sulfate were used to supply the balance of minerals N, P2O5, and K2O, respectively; application rates of both organic amendments and mineral fertilizers are given in Table 2. This moderate nutrient input level was selected to balance economic considerations while ensuring stable peanut yield [22].

Table 2.
Application rates of different experiment plots (kg ha−1 year−1).
Each year, before sowing, the organic materials and fertilizers were uniformly applied to the 0–20 cm soil layer and thoroughly mixed before ridging. The biochar was produced by pyrolyzing corn cobs at 450 °C, which were sieved through an 80–100 mesh and then pelletized. The biochar-based fertilizer was produced by co-pelletizing biochar derived from maize straw pyrolyzed at 450–550 °C with inorganic nutrients, resulting in an analysis of 11% N, 11% P2O5, and 13% K2O. The straw consisted of corn stalks crushed to 2–3 cm in length. The peanut variety used in the experiment was “Fuhua 12” (150GY), planted in a double-row ridge system with a plant spacing of approximately 11 cm and three plants per hole.
2.3. Sample Collection and Analytical Methods
At the annual peanut harvest, a composite surface soil (0–25 cm) sample was collected from the center of each plot by pooling five cores taken in an “S-shaped” pattern; visible stones and root fragments were removed, and the sample was placed in a polyethylene bag. After air-drying, soils were passed through 2 mm and then 0.15 mm sieves for subsequent physicochemical analyses.
Concurrently, two representative plants per plot were partitioned into leaves, stems, roots, pods (shells), and kernels. All tissues were first deactivated at 120 °C for 30 min, dried to constant mass at 60 °C, weighed, and analyzed for P concentration.
The present study focuses on samples collected at the 2021 harvest, with selected data from 2015 included for comparative purposes.
2.3.1. Soil Properties Determination and Plant Sample Analysis
Soil physicochemical properties closely related to phosphorus were analyzed, including pH, cation exchange capacity (CEC), total organic carbon (TOC), available phosphorus (AP), total phosphorus (TP), total nitrogen (TN), and soil acid phosphatase activity (ACP). Soil pH was measured using a pH meter. Total carbon and nitrogen in the soil were determined using an elemental analyzer. Cation exchange capacity was measured by extracting the soil with cobalt hexamine trichloride and determining the absorbance using a microplate reader. Soil acid phosphatase activity was assessed using the disodium phenyl phosphate colorimetric method, where soil samples were incubated for 24 h, and the released phenol content was measured as an indicator of enzyme activity, with re-distilled phenol used as the standard.
Total Soil Phosphorus Determination: A 0.25 g soil sample (<0.15 mm) was mixed with 2 g of solid sodium hydroxide (NaOH) in a nickel crucible and fused in a muffle furnace at 450 °C for 30 min. The cooled melt was dissolved in 0.5 M H2SO4, and the extract was analyzed for phosphorus concentration using the molybdenum blue method (Murphy and Riley, 1962) [23]. Absorbance was measured at 880 nm with a microplate reader (Epoch2TM, BioTek Instruments, Winooski, VT, USA).
Available Soil Phosphorus Determination: A 2.50 g air-dried soil sample (<2 mm) was extracted with 50 mL of 0.5 mol L−1 sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3, pH 8.5) by shaking for 30 min at 25 ± 1 °C. The extract was filtered through Whatman No. 42 filter paper, and the phosphorus concentration was determined using the ascorbic acid–molybdenum blue method (Olsen, 1954) [24].Absorbance was measured at 880 nm with a microplate reader(Biotek Instruments. Inc, Winooski, VT, USA).
For plant samples, after drying to a constant weight, they were ground and digested with H2SO4-H2O2 at high temperature. The phosphorus content in different plant parts was determined using the vanadate–molybdate yellow colorimetric method. Phosphorus harvest index, phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency, and grain phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency were calculated as follows:
Phosphorus accumulation in a specific plant part (mg/plant) = Phosphorus concentration in that part × Dry matter weight of that part.
Total phosphorus accumulation in the whole peanut plant (mg/plant) = Root phosphorus accumulation + Stem phosphorus accumulation + Leaf phosphorus accumulation + Shell phosphorus accumulation + Kernel phosphorus accumulation.
Phosphorus harvest index (PHI) (mg/mg) = (Kernel phosphorus accumulation + Shell phosphorus accumulation)/Total phosphorus accumulation in the whole plant.
Grain phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (GP-DPE) (mg/mg) = Grain dry-matter accumulation/Total phosphorus accumulation in the whole plant.
Phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE) (mg/mg) = Total dry-matter accumulation of the whole plant/Total phosphorus accumulation in the whole plant.
2.3.2. Phosphorus Fractionation
Soil samples were ground and passed through a 0.15 mm sieve. Phosphorus fractionation was performed using the Hedley sequential extraction method [25]. The soil samples were sequentially extracted to obtain the following fractions: Resin-P, NaHCO3-P, NaOH-P, Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P. Initially, 1.5 g of soil sample (<0.015 mm) was mixed with 0.4 g of ion-exchange resin and 50 mL of 0.5 M NaCl solution, followed by 16 h of shaking. The first leachate was collected to determine Resin-P. Subsequently, 30 mL of 0.05 M NaHCO3 solution was added, and the mixture was shaken for another 16 h to extract NaHCO3-P. Next, NaOH-P was extracted using 30 mL of 0.1 M NaOH under 16 h of shaking. For Sonic-P, an additional 30 mL of 0.1 M NaOH was introduced, followed by 10 min of ultrasonication and 16 h shaking. HCl-P was then extracted by shaking the sample with 30 mL of 1 M HCl for 16 h. Finally, the residual soil was digested with 5 mL of H2SO4 at 360 °C for 3 h to determine Residual-P, representing the most recalcitrant phosphorus fraction in the soil pool. All extracts were analyzed colorimetrically at 880 nm using the Mo-Sb antimony–molybdate method in a microplate reader. During the sequential extraction process, organic matter was continuously released, resulting in a reddish-brown color in the extracts. Therefore, when using dinitrophenol as an indicator to adjust the pH, color interference occurred. To address this, a pH meter (Shanghai Instrument Electric Scientific Instruments Co., Ltd. Shanghai, China) was used to accurately adjust the pH for optimal color development.
2.4. Data Analysis
All datasets were tested for normality (Shapiro–Wilk test) and homogeneity of variance (Levene’s test) prior to analysis. Statistical comparisons among treatment means were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan’s multiple range test (p < 0.05) in IBM SPSS Statistics 25.0. Principal component analysis (PCA) was conducted to evaluate relationships among soil physicochemical properties. All graphical representations were generated using Origin 2022 (OriginLab Corporation, Northampton, MA, USA) and GraphPad Prism 8 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA).
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Properties
Following long-term applications of different organic amendments, soil chemical properties exhibited significant alterations (Figure 1). Soil acid phosphatase (ACP) activity under CS and PMC treatments was markedly higher than that in the biochar-amended soil (BIO). No significant difference in ACP activity was observed between CS and PMC treatments. Soil total nitrogen (TN) followed a trend identical to ACP, i.e., PMC ≈ CS > BIO > BF. The mean cation exchange capacity (CEC) across all treatments was 43.33 cmol kg−1, with BF exhibiting a significantly greater CEC than the other treatments. The soil C/P ratio in BIO and BF exceeded that of the remaining treatments, following the order BF > BIO > CS ≈ PMC.
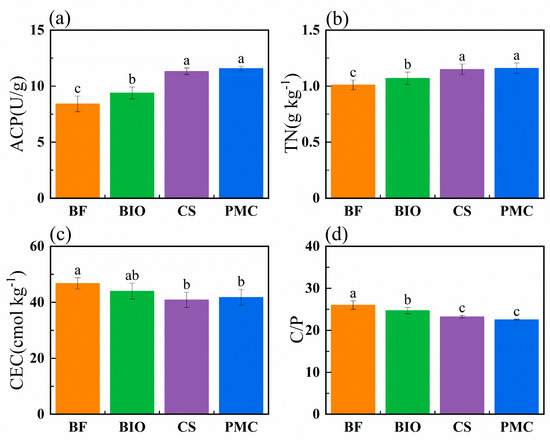
Figure 1.
Soil chemical properties under different fertilization treatments. soil acid phosphatase activity (ACP) (a), total nitrogen content (TN) (b), cation-exchange capacity (CEC) (c), and C:P content ratio (C/P) (d). Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05). (BF: biochar-based fertilizer; BIO: biochar; CS: straw return; PMC: pig manure compost; error bars represent standard error).
3.2. Soil Phosphorus Availability
Soil phosphorus availability was strongly governed by soil pH. Over the fertilization period, soil pH under the BIO treatment followed a distinct trajectory compared to the other treatments, displaying a unique pattern of initial decline followed by a subsequent increase, whereas the other treatments generally exhibited a continuous decrease (Figure 2a). Notably, the PMC treatment consistently maintained the highest total phosphorus (TP) and available phosphorus (AP) contents throughout the entire fertilization period, following a trend of initial increase followed by a subsequent decrease. Meanwhile, AP contents under BIO, BF, and CS treatments showed a steady upward trend, with the magnitude ranked as BIO > BF > CS (Figure 2b,c). Additionally, soil total organic carbon (TOC) across all treatments exhibited a stable, progressive increase with prolonged fertilization duration (Figure 2d).
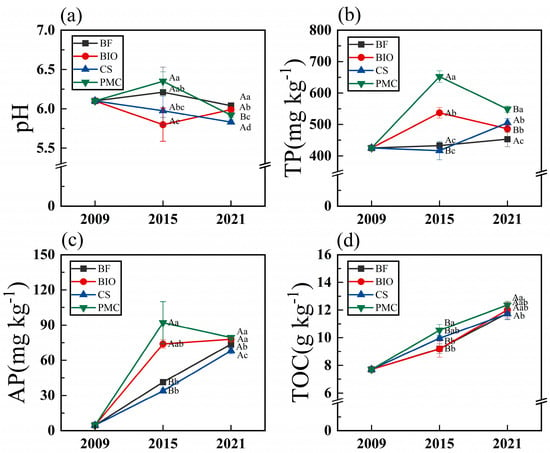
Figure 2.
Soil pH (a), total P (TP) (b), available P (AP) (c), and total organic C (TOC) (d) under different organic amendments across fertilization years. Uppercase letters indicate significant differences among fertilization years within the same treatment; lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments within the same fertilization year. (BF: biochar-based fertilizer; BIO: biochar; CS: straw return; PMC: pig manure compost; error bars represent standard error).
3.3. Soil Phosphorus Fractionation
Long-term application of different organic materials significantly altered the soil phosphorus pool, with variations in phosphorus fractions among treatments (Figure 3). The Resin-P content in the PMC treatment was significantly higher than in other treatments, followed by the BIO and BF treatments, which showed no significant difference between them. The NaHCO3-P content in the PMC treatment was significantly higher than in other treatments. The NaOH-P content in the BF and BIO treatments was significantly higher than in other treatments, with no significant difference between BF and BIO. The trends for Sonic-P and HCl-P contents were similar, with the order PMC > CS > BIO > BF. The Residual-P content in the PMC and CS treatments was significantly higher than in biochar-amended treatments.
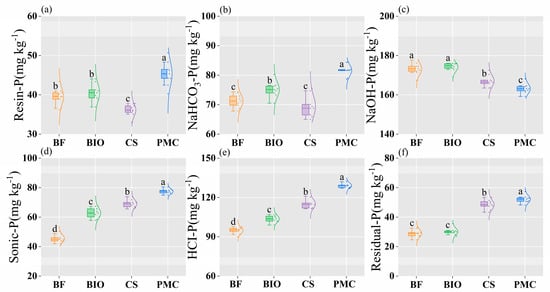
Figure 3.
Distribution of soil phosphorus fractions under different fertilization treatments. Resin-P (a), NaHCO3-P (b), NaOH-P (c), Sonic-P (d), HCI-P (e), and Residual-P (f). Lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments within the same fertilization year. (BF: biochar-based fertilizer; BIO: biochar; CS: straw return; PMC: pig manure compost; error bars represent standard error).
In the soil phosphorus pool, NaOH-P accounted for the highest proportion (Figure 4), approximately 34.23% of the total phosphorus, while Residual-P accounted for the lowest proportion at 7.91%. Under long-term combined application of organic fertilizers and chemical fertilizers, the proportions of different phosphorus forms in the soil phosphorus pool were ranked as follows: NaOH-P > HCl-P > NaHCO3-P > Sonic-P > Resin-P > Residual-P. The average proportion of Resin-P across treatments was 8.11% of the total phosphorus, with the BF treatment showing a significantly higher proportion than other treatments. The proportion of NaHCO3-P ranged from 13.73% to 15.72%, averaging 14.94% of the total phosphorus, with significant differences among treatments in the order BF > BIO > PMC > CS (p < 0.05). The proportion of NaOH-P accounted for approximately 29.72% to 38.26% of the total phosphorus, ranked as BF > BIO > CS > PMC (p < 0.05). The proportions of Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P in the CS and PMC treatments were significantly higher than in biochar-amended treatments. The proportions of HCl-P and Sonic-P in the soil phosphorus pool were ranked as PMC > CS > BIO > BF.
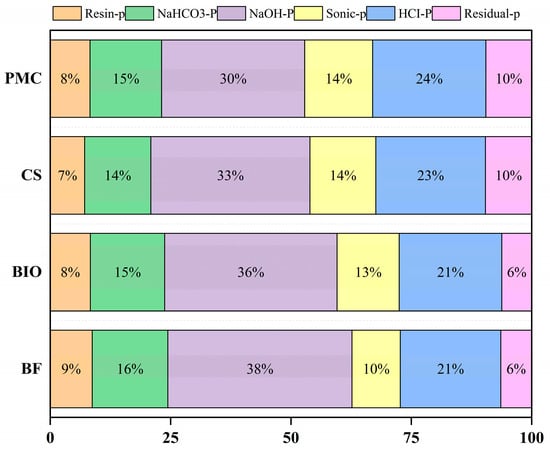
Figure 4.
Stacked bar chart showing the percentage distribution of soil phosphorus forms under different fertilization treatments. (BF: biochar-based fertilizer; BIO: biochar; CS: straw return; PMC: pig manure compost).
3.4. The Analysis of the Correlation Between Soil Phosphorus Fractionation and Soil Chemical Properties
Long-term application of different organic materials altered soil properties, thereby influencing the distribution of various phosphorus fractions in brown soil. Most soil phosphorus fractions showed significant correlations with soil chemical indicators (Figure 5). Resin-P and NaHCO3-P contents were significantly positively correlated with soil available phosphorus (AP) and total organic carbon (TOC). NaOH-P content was highly significantly positively correlated with soil pH and cation exchange capacity (CEC) but significantly negatively correlated with soil acid phosphatase activity (ACP). Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P contents were highly significantly positively correlated with soil total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), and ACP but negatively correlated with CEC.
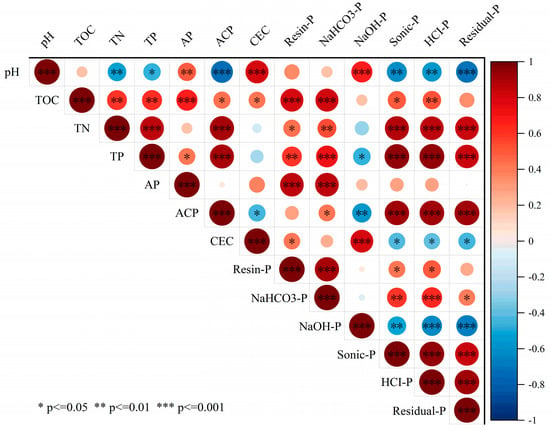
Figure 5.
Pearson’s correlation analysis between soil properties and phosphorus content in surface soil (0–25 cm).
3.5. Soil Phosphorus Fractionation and Peanut Phosphorus Uptake
The linear regression analysis between soil phosphorus fractions and phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels under different fertilization modes is shown in Figure 6. Soil phosphorus fractions were highly correlated with phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels, with determination coefficients (r2) of 0.1151, 0.2595, 0.9676, 0.6898, 0.9201, and 0.7413, respectively. The higher r2 values for non-labile phosphorus fractions (NaOH-P, Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P) indicate that these fractions significantly influenced phosphorus uptake in peanut kernels. Among these, NaOH-P showed a strong positive correlation with phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels. In contrast, labile phosphorus fractions (Resin-P and NaHCO3-P) exhibited weak positive correlations with phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels.
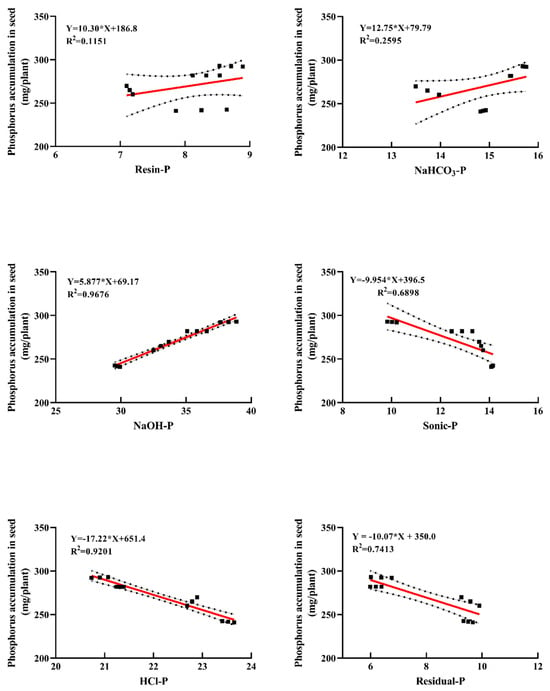
Figure 6.
Linear regression equations between soil phosphorus fractions and phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels. The * here denotes multiplication.
Figure 7 presents the linear regression analysis between soil phosphorus (P) fractions and peanut yield under different fertilization treatments. Significant correlations were observed between soil P fractions and peanut yield, with determination coefficients (R2) of 0.3986, 0.3396, 0.04936, 0.1772, 0.02768, and 0.1842 for the respective P fractions. Notably, many P fractions showed positive correlations with peanut yield, except for Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P, which exhibited negative correlations. The strongest positive correlation was observed with Resin-P (R2 = 0.3986), suggesting that increasing Resin-P content in soil may enhance peanut yield. Conversely, elevated levels of non-labile P fractions (Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P) appeared to negatively affect peanut yield.
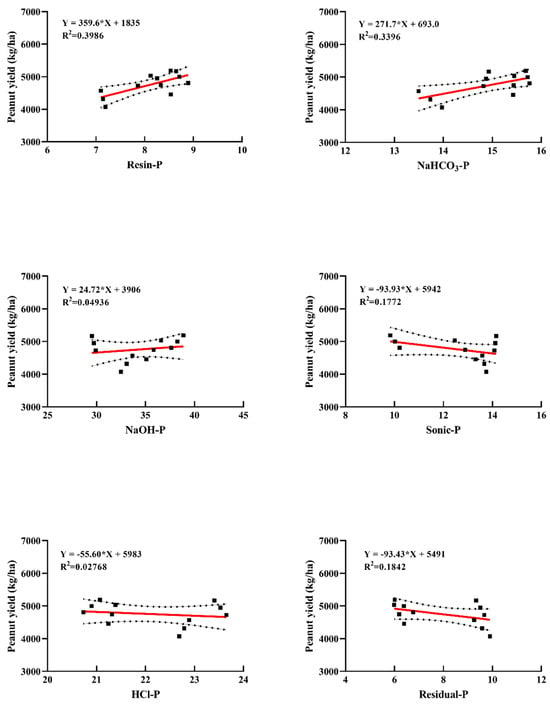
Figure 7.
Linear regression equations between soil phosphorus fractions and peanut yield. The * here denotes multiplication.
Under different fertilization modes, the phosphorus harvest index (PHI) in the BF treatment was significantly higher than in other treatments (Figure 8a). The grain phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (GP-DPE) in both biochar treatments (BF and BIO) was significantly higher than in the CS and PMC treatments (Figure 8b). The phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE) in the PMC treatment was significantly higher than in other treatments (Figure 8c).
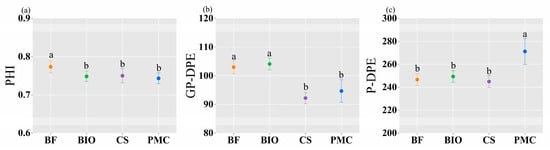
Figure 8.
Panels (a–c) represent the phosphorus harvest index (PHI), grain phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (GP-DPE), and phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE) under different fertilization treatments, respectively. lowercase letters indicate significant differences among treatments within the same fertilization year. (BF: biochar-based fertilizer; BIO: biochar; CS: straw return; PMC: pig manure compost; error bars represent standard error).
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of Long-Term Biochar Application on Soil Phosphorus Availability
The results of this study indicate that continuous application of biochar significantly increases soil available phosphorus (AP) content. This phenomenon can be explained by two mechanisms: Firstly, during the carbonization process of corn cob, the content of soluble phosphorus in biochar is increased. After biochar is applied to the soil, it can directly release phosphorus elements, thereby significantly increasing the available phosphorus content in the soil. Secondly, during the pyrolysis of corn cob, the volatilization of carbon elements and the cleavage of organic phosphorus chemical bonds lead to the release of phosphate salts from organic phosphorus compounds, further enhancing the availability of phosphorus in the soil [26]. Therefore, biochar application is a direct approach to improving soil AP content. The increase in soil pH caused by biochar application may also be a significant factor influencing soil phosphorus availability. In acidic soils, the increase in soil pH promotes the desorption of phosphorus (P) bound to Al3+ and Fe3+, thereby releasing the immobilized P into the soil solution [27,28].
In soil, phosphatase promotes the hydrolysis of organic phosphorus into plant-available forms [29]. Compared to the CS treatment, the lower acid phosphatase activity (ACP) in BIO and BF treatments may be attributed to the biochar protecting enzyme reaction sites, thereby inhibiting enzyme activity [30]. The higher C/P ratio in BF and BIO treatments facilitates the conversion of non-labile phosphorus to labile phosphorus, enhancing phosphorus availability [31]. However, some studies have demonstrated non-significant effects of biochar on phosphorus (P) availability, with observed variations depending on the soil types and biochar characteristics [32,33]. Mohan et al. reported that biochar application significantly enhanced the availability of Na+, K+, Ca2+, and Mg2+ in soils [34]. Further analysis demonstrated that the cation exchange capacity (CEC) could increase by up to 362% under higher biochar application rates compared to unamended soils [35]. These findings reveal the pH-dependent nature of CEC, where elevated soil pH promotes CEC enhancement—a phenomenon consistently observed in our study, with both the BF and BIO treatments exhibiting higher CEC values than the CS and PMC treatments. Prior studies have confirmed that biochar improves soil physicochemical properties, including CEC [36]. The high CEC of biochar contributes to phosphorus (P) availability through two key mechanisms: (1) electrostatic repulsion: this reduces phosphate-calcium contact, thereby decreasing Ca-P precipitation risk; (2) porous adsorption: the porous structure of biochar may locally adsorb Ca2+, further mitigating Ca-P precipitation [37].
The BF and BIO treatments differentially affected soil phosphorus fractions, indicating that biochar utilization methods impact soil phosphorus transformation. Resin-P and NaHCO3-P, which are highly active and prone to adsorption, primarily determine short-term phosphorus availability. NaOH-P, a key available phosphorus source in soil, was the most abundant fraction in this study. Its strong positive correlation with soil pH suggests that in alkaline conditions, phosphorus bound to iron and aluminum oxides is more readily released [38], increasing weakly bound phosphorus. Biochar-based fertilizer, a blend of biochar and chemical fertilizer formed into granules, slowly releases phosphorus and inhibits the rapid adsorption of phosphorus by soil clay particles [39]. It significantly increases the proportions of Resin-P, NaHCO3-P, and NaOH-P, making it suitable for long-term phosphorus management. In contrast, biochar primarily affects stable phosphorus forms (e.g., HCl-P) through pH regulation and mineral adsorption. Short-term phosphorus management should focus on rapidly fixing unstable phosphorus, while long-term effectiveness depends on biochar’s sustained regulation of the phosphorus adsorption–desorption balance.
The influence of different phosphorus forms on phosphorus uptake in peanut kernels varied. Labile phosphorus fractions (Resin-P and NaHCO3-P) showed weak positive correlations with phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels, although some studies have reported a stronger influence of labile phosphorus pools on crop phosphorus accumulation [40]. NaOH-P exhibited a significant positive correlation with phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels, consistent with previous findings [41]. As an important source of soil available phosphorus, NaOH-P can stably supply phosphorus to crops, promoting continuous phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels. This demonstrates that long-term biochar application can enhance crop phosphorus uptake by increasing moderately labile phosphorus fractions (NaOH-P). Although the phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE) in the BF and BIO treatments was lower than in the PMC treatment, the higher phosphorus harvest index (PHI) in biochar-amended treatments indicates a stronger ability to translocate absorbed nutrients to the kernels, resulting in higher phosphorus-use efficiency in the BF and BIO treatments. Resin-P showed the strongest correlation with peanut yield (R2 = 0.3986), while stable phosphorus components (Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P) were negatively related to yield. This underscores the importance of enhancing soil active phosphorus for crop production and suggests excessive non-active phosphorus accumulation may adversely affect plant growth.
4.2. Effects of Long-Term Straw Incorporation on Soil Phosphorus Availability
The soil pH in the CS treatment remained at a relatively low level, showing only a slight increase compared to the initial conditions. Limei Chen suggested that straw incorporation has a limited impact on soil pH [14]. Long-term straw incorporation increased soil total phosphorus (TP) and available phosphorus (AP) contents. This is attributed to the fact that straw incorporation provides a substantial substrate for soil enzymes, enhancing enzyme activity. The higher acid phosphatase activity (ACP) in the CS treatment indicates that increased soil organic carbon (SOC) content promotes soil phosphatase activity, thereby improving the mineralization rate of organic phosphorus. Additionally, organic anions released during straw decomposition can reduce the fixation of fertilizer phosphorus or induce the activation of adsorbed phosphorus by competing for phosphorus adsorption sites [42], ultimately increasing soil AP content. The main components of straw (cellulose and lignin) enhance soil phosphorus availability through different mechanisms [43]. Studies have shown that cellulose improves soil phosphorus availability by increasing microbial biomass phosphorus, while lignin enhances phosphorus availability by competitively adsorbing iron and aluminum oxides through its functional groups [44]. Furthermore, the increase in SOC content under straw incorporation stimulates microbial proliferation, enhances the diversity of bacteria and fungi involved in phosphorus cycling, and improves soil phosphorus turnover rates [45]. However, the lower soil pH in the CS treatment compared to other treatments may negatively affect the survival of certain bacteria, resulting in a smaller increase in AP content relative to other treatments.
Under the CS treatment, the contents of Resin-P and NaHCO3-P were relatively low, and these phosphorus forms are readily absorbed by plants. This may explain the lower phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE) in the CS treatment. The results of this study indicate a highly significant negative correlation between soil pH and the contents of Sonic-P, HCl-P, and Residual-P. This suggests that the lower soil pH in the CS treatment leads to an increase in these three phosphorus fractions. This further supports the conclusion that the P-DPE in the CS treatment is relatively low. Compared to biochar treatments, straw incorporation significantly increased Residual-P content but reduced NaOH-P content. In the short term, straw decomposition rapidly releases unstable phosphorus; however, as phosphate diesterase is activated, it promotes the conversion of organic to inorganic phosphorus, followed by the long-term release of hard-to-decompose organic phosphorus [46]. Crushed straw can enhance phosphodiesterase activity, promoting the transformation between organic and inorganic phosphorus pools, depleting moderately stable NaOH-P, and increasing Residual-P. Conversely, long-term biochar application promotes inorganic phosphorus transformation by boosting Ca-P solubility and stabilizing pH, maintaining higher levels of labile phosphorus (Resin-P and NaHCO3-P) and optimizing phosphorus continuous availability [5].
In this study, the P-DPE, phosphorus harvest index (PHI), and grain phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (GP-DPE) in the CS treatment were all at relatively low levels. This is because long-term straw incorporation results in lower phosphorus uptake by peanuts and weaker translocation of absorbed nutrients to the kernels, leading to lower phosphorus-use efficiency in the CS treatment.
4.3. Effects of Long-Term Pig Manure Application on Soil Phosphorus Availability
Due to the high amount of available phosphorus introduced into the soil with pig manure and the reduced application of chemical phosphorus fertilizers, the conversion of phosphorus to soluble forms was enhanced, thereby reducing phosphorus fixation in the soil [47]. As a result, the PMC treatment significantly increased soil available phosphorus (AP) content. Long-term application of pig manure provides abundant organic matter, offering carbon and energy for microorganisms, stimulating acid phosphatase (ACP) secretion. This facilitates the conversion of soil organic phosphorus to inorganic forms, thereby enhancing available phosphorus levels [48]. Both total phosphorus (TP) and AP contents in the PMC treatment were higher than in other treatments, indicating that long-term organic fertilizer application is the most effective approach for improving soil phosphorus fertility. The total organic carbon (TOC) content in the PMC treatment was significantly higher than in other treatments, likely due to the direct and indirect effects of pig manure on soil TOC. The high organic carbon content of pig manure, residual recalcitrant carbon compounds, the coupling effect of trace metal ions, and changes in microbial communities collectively enhance soil organic carbon levels [49,50,51]. In this study, the proportion of labile phosphorus fractions was positively correlated with soil TOC, consistent with previous findings [31], suggesting that TOC contributes to unstable phosphorus accumulation. Labile carbon fractions stimulate rapid microbial proliferation, while recalcitrant carbon sustains long-term microbial activity. This ongoing microbial activity enhances immediate phosphorus availability and optimizes phosphorus cycling efficiency through organic–mineral–microbial interactions.
The proportion of labile phosphorus fractions (Resin-P and NaHCO3-P) in the PMC treatment was higher than in the CS treatment, likely due to the substantial input of available phosphorus from pig manure. Heidi M. et al. found that manure application temporarily increases NaOH-P and HCl-P, attributed to the stimulation of microbial production and activity, which enhances the solubility of iron- and aluminum-associated phosphates [52]; however, these phosphorus fractions are easily converted into plant-available labile forms. In our study, long-term pig manure application significantly reduced NaOH-P while increasing the proportion of labile phosphorus fractions, indicating that pig manure promotes the transformation of NaOH-P into labile phosphorus forms.
The PMC treatment exhibited a lower proportion of NaOH-P, which was significantly positively correlated with phosphorus uptake in peanut kernels in this study. Although the PMC treatment showed the highest phosphorus dry-matter production efficiency (P-DPE), indicating that long-term pig manure application enhanced phosphorus uptake by peanuts, its phosphorus-use efficiency (PUE) was significantly lower than that of the two biochar treatments. This suggests that more phosphorus was retained in the stems and leaves of plants in the PMC treatment, and the ability to translocate absorbed phosphorus to the kernels was weaker compared to biochar treatments.
5. Conclusions
Long-term biochar application increased soil pH and cation exchange capacity (CEC), significantly enhancing soil available phosphorus (AP) content. It improved the soil C/P ratio, promoting phosphorus transformation, and stabilized NaOH-P supply, thereby facilitating phosphorus accumulation in peanut kernels. Biochar treatments exhibited a higher phosphorus-use efficiency (PUE) and phosphorus harvest index (PHI). Straw incorporation enhanced phosphatase activity, promoting the mineralization and transformation of organic phosphorus and increasing AP content; however, due to the lower soil pH under straw incorporation, the translocation of phosphorus to kernels was limited, resulting in lower phosphorus-use efficiency.
Pig manure application significantly increased soil AP and total organic carbon (TOC) content by reducing phosphorus fixation and promoting the transformation of labile phosphorus fractions; however, more phosphorus was retained in the stems and leaves, and the translocation of phosphorus to kernels was weaker, leading to lower phosphorus-use efficiency compared to biochar treatments.
Author Contributions
K.Z. Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing—Original Draft. H.L. and X.L. (Xiao Li): Methodology, Data Curation. B.Z. and X.W. Supervision and Project Administration. N.L., Y.W. and X.L. (Xue Li): Writing—Review and Editing. X.Z. and X.H.: Resources, Funding Acquisition, Supervision, Writing—Review. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (2024YFD1500100).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the authors upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank all the members of the Plant Nutrition and Fertilization Technical Team for their enthusiastic help and the availability of laboratory conditions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- Kolahchi, Z.; Jalali, M. Phosphorus Movement and Retention by Two Calcareous Soils. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2013, 22, 21–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Yang, L.; Liang, H.; Yin, L.; Chen, D.; Shen, P. Integrated analyses reveal the response of peanut to phosphorus deficiency on phenotype, transcriptome and metabolome. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, T.S.; Hinsinger, P.; Turner, B.L. Phosphorus in soils and plants—Facing phosphorus scarcity. Plant Soil 2016, 401, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.; Feng, G.; Gao, H.; Peng, C.; Zhu, P. Phosphorus Distribution within Aggregates in Long-Term Fertilized Black Soil: Regulatory Mechanisms of Soil Organic Matter and pH as Key Impact Factors. Agronomy 2024, 14, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Jiang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, L. Effects of various straw incorporation strategies on soil phosphorus fractions and transformations. GCB Bioenergy 2022, 15, 88–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, P.X.; Wang, H.X.; Zhao, Z.H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhan, X.M.; Han, X.R. Effects of Straw Addition on Soil Priming Effects Under Different Tillage and Straw Return Modes. Plants 2024, 13, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Geng, P.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Cai, P.X.; Zhan, X.M.; Han, X.R. Improvement of Active Organic Carbon Distribution and Soil Quality with the Combination of Deep Tillage and No-Tillage Straw Returning Mode. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, D.; Lan, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yang, X.; Chen, W.; Meng, J.; Wang, D.; Li, N. Maize straw and its biochar affect phosphorus distribution in soil aggregates and are beneficial for improving phosphorus availability along the soil profile. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2021, 72, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Qamar, S.A.; Qamar, M.; Bilal, M.; Iqbal, H.M.N. Sustainable remediation of hazardous environmental pollutants using biochar-based nanohybrid materials. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 300, 113762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, Z.H.; Zhou, K.Y.; Zhan, X.M.; Wang, Y.; Liu, N.; Han, X.R.; Li, X. Soil Organic Carbon and Humus Characteristics: Response and Evolution to Long-Term Direct/Carbonized Straw Return to Field. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Yuan, M.; Xu, R.; Bish, D.L. Mobilization of phosphate in variable-charge soils amended with biochars derived from crop straws. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 146, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Sui, L.; Tang, C.; Li, J.; Cheng, K.; Xue, Q. Sustainable advances on phosphorus utilization in soil via addition of biochar and humic substances. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 768, 145106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombel, A.; Krasucka, P.; Oleszczuk, P. Sustainable biochar-based soil fertilizers and amendments as a new trend in biochar research. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 816, 151588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Sun, S.; Yao, B.; Peng, Y.; Gao, C.; Qin, T.; Zhou, Y.; Sun, C.; Quan, W. Effects of straw return and straw biochar on soil properties and crop growth: A review. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 986763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.Y.; Shamsi, I.H.; Sun, D.S.; Ostermann, A.; Zhang, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.S.; Lin, X.Y. Impact of manure application on forms and quantities of phosphorus in a Chinese Cambisol under different land use. J. Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 837–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.; Liang, X.; He, M.; Liu, Y.; Tian, G.; Shi, J. Manure biochar influence upon soil properties, phosphorus distribution and phosphatase activities: A microcosm incubation study. Chemosphere 2016, 142, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.-F.; Li, K.-J.; Zheng, B.-X.; Liu, X.-P.; Li, H.-Z.; Jin, B.-J.; Ding, K.; Yang, X.-R.; Lin, X.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-G. Partial replacement of inorganic phosphorus (P) by organic manure reshapes phosphate mobilizing bacterial community and promotes P bioavailability in a paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, J.F.; Ohno, T.; He, Z.; Honeycutt, C.W.; Dail, D.B. Inhibition of phosphorus sorption to goethite, gibbsite, and kaolin by fresh and decomposed organic matter. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2007, 44, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, J.; Lan, Z.; Hyland, C.; Sato, S.; Solomon, D.; Ketterings, Q.M. Long-term dynamics of phosphorus forms and retention in manure-amended soils. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6672–6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokgolo, M.J.; Mzezewa, J.; Odhiambo, J.J.O. Poultry and cattle manure effects on sunflower performance, grain yield and selected soil properties in Limpopo Province, South Africa. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayne, N.; Aula, L. Livestock Manure and the Impacts on Soil Health: A Review. Soil Syst. 2020, 4, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Wang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zheng, X.; Liu, H.; Shi, P. Quantitative Estimation of the Nutrient Uptake Requirements of Peanut. Agronomy 2020, 10, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, J.; Riley, J.P. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 1962, 27, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, S.R. Estimation of Available Phosphorus in Soils by Extraction with Sodium Bicarbonate; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1954.
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.; Lu, S. Does biochar affect the availability and chemical fractionation of phosphate in soils? Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 8725–8734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borges, B.M.M.N.; Strauss, M.; Camelo, P.A.; Sohi, S.P.; Franco, H.C.J. Re-use of sugarcane residue as a novel biochar fertilizer—Increased phosphorus use efficiency and plant yield. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 262, 121406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.-J.; Wang, M.K.; Fu, M.-L.; Ci, E. Enhancing phosphorus availability in phosphorus-fertilized zones by reducing phosphate adsorbed on ferrihydrite using rice straw-derived biochar. J. Soils Sediments 2011, 11, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Peñuelas, J.; Sardans, J.; Jin, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Fang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, W. Industrial and agricultural waste amendments interact with microorganism activities to enhance P availability in rice-paddy soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Yuan, J.; Chen, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Y. Animal manures promoted soil phosphorus transformation via affecting soil microbial community in paddy soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 831, 154917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, A.; Huang, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Bian, F.; Zhang, X. Effects of Long-Term Chemical and Organic Fertilizer Application on Soil Phosphorus Fractions in Lei Bamboo Plantations. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaser, B.; Lehr, V.-I. Biochar effects on phosphorus availability in agricultural soils: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 9338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Chang, L.; Liu, H.; de Jesús Puy Alquiza, M.; Li, Y. Biochar application to soils can regulate soil phosphorus availability: A review. Biochar 2025, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Abhishek, K.; Sarswat, A.; Patel, M.; Singh, P.; Pittman, C.U. Biochar production and applications in soil fertility and carbon sequestration—A sustainable solution to crop-residue burning in India. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 508–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyawade, S.O.; Karanja, N.N.; Gachene, C.K.K.; Gitari, H.I.; Schulte-Geldermann, E.; Parker, M.L. Short-term dynamics of soil organic matter fractions and microbial activity in smallholder potato-legume intercropping systems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2019, 142, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jien, S.-H.; Wang, C.-S. Effects of biochar on soil properties and erosion potential in a highly weathered soil. Catena 2013, 110, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.A.; Nkoh, J.N.; Xu, R.-K.; Jiang, J. Enhancing phosphorus availability in two variable charge soils by the amendments of crop straw biochars. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negassa, W.; Leinweber, P. How does the Hedley sequential phosphorus fractionation reflect impacts of land use and management on soil phosphorus: A review. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carneiro, J.S.d.S.; Ribeiro, I.C.A.; Nardis, B.O.; Barbosa, C.F.; Lustosa Filho, J.F.; Melo, L.C.A. Long-term effect of biochar-based fertilizers application in tropical soil: Agronomic efficiency and phosphorus availability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 760, 143955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Zhao, T.L.; Thu, N.; Zhao, H.M.; Zheng, Y.; Tang, L. The Synergistic Effects of Different Phosphorus Sources: Ferralsols Promoted Soil Phosphorus Transformation and Accumulation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, M.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Q.; Ahmed, W.; Mehmood, S.; Hui, X.; Wang, Z. Changes in Phosphorus Fractions and Its Availability Status in Relation to Long Term P Fertilization in Loess Plateau of China. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nziguheba, G.; Palm, C.A.; Buresh, R.J.; Smithson, P.C. Soil phosphorus fractions and adsorption as affected by organic and inorganic sources. Plant Soil 1997, 198, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Qiu, H.; Hu, Y.; Wei, X.; Chen, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Su, Y. Cellulose and lignin regulate partitioning of soil phosphorus fractions and alkaline phosphomonoesterase encoding bacterial community in phosphorus-deficient soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2018, 55, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.; Shen, J.; Sun, M.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Wu, J. Soil phosphorus availability and rice phosphorus uptake in paddy fields under various agronomic practices. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maarastawi, S.A.; Frindte, K.; Bodelier, P.L.E.; Knief, C. Rice straw serves as additional carbon source for rhizosphere microorganisms and reduces root exudate consumption. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 135, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damon, P.M.; Bowden, B.; Rose, T.; Rengel, Z. Crop residue contributions to phosphorus pools in agricultural soils: A review. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2014, 74, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wen, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, N.; Yang, J.; Romanyà, J.; Han, X. Long-term changes in organic and inorganic phosphorus compounds as affected by long-term synthetic fertilisers and pig manure in arable soils. Plant Soil 2022, 472, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Gu, D.; Yang, H.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Zhan, N.; Cui, X. Effect of Exogenous Organic Matter on Phosphorus Forms in Middle-High Fertility Cinnamon Soil. Plants 2024, 13, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, J.R.; Endelman, J.B.; Miller, B.E.; Hole, D.J. Residual Effects of Compost on Soil Quality and Dryland Wheat Yield Sixteen Years after Compost Application. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Singh, P.K.; Singh, R.; Bhadouria, R.; Singh, D.K.; Singh, S.; Afreen, T.; Tripathi, S.; Singh, P.; Singh, H.; et al. Relative availability of inorganic N-pools shifts under land use change: An unexplored variable in soil carbon dynamics. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 64, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangarajan, R.; Bolan, N.S.; Tian, G.; Naidu, R.; Kunhikrishnan, A. Role of organic amendment application on greenhouse gas emission from soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 465, 72–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldrip, H.M.; He, Z.; Erich, M.S. Effects of poultry manure amendment on phosphorus uptake by ryegrass, soil phosphorus fractions and phosphatase activity. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2011, 47, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).