Optimizing the Light Intensity, Nutrient Solution, and Photoperiod for Speed Breeding of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Under Full-Spectrum LED Light
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Design
2.2.1. Light Intensity Treatments
2.2.2. Nutrient Solution Treatments
2.2.3. Photoperiod Treatments
2.2.4. Validation of Rapid Breeding Conditions in Alfalfa with Varying Fall Dormancy Levels
2.3. Data Acquisition
2.3.1. Plant Morphology Parameters
2.3.2. Photosynthetic Parameters and Photosynthetic Pigment Measurement
2.3.3. Determination of Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and Oxidative Stress Markers
2.4. Data Analysis
3. Results
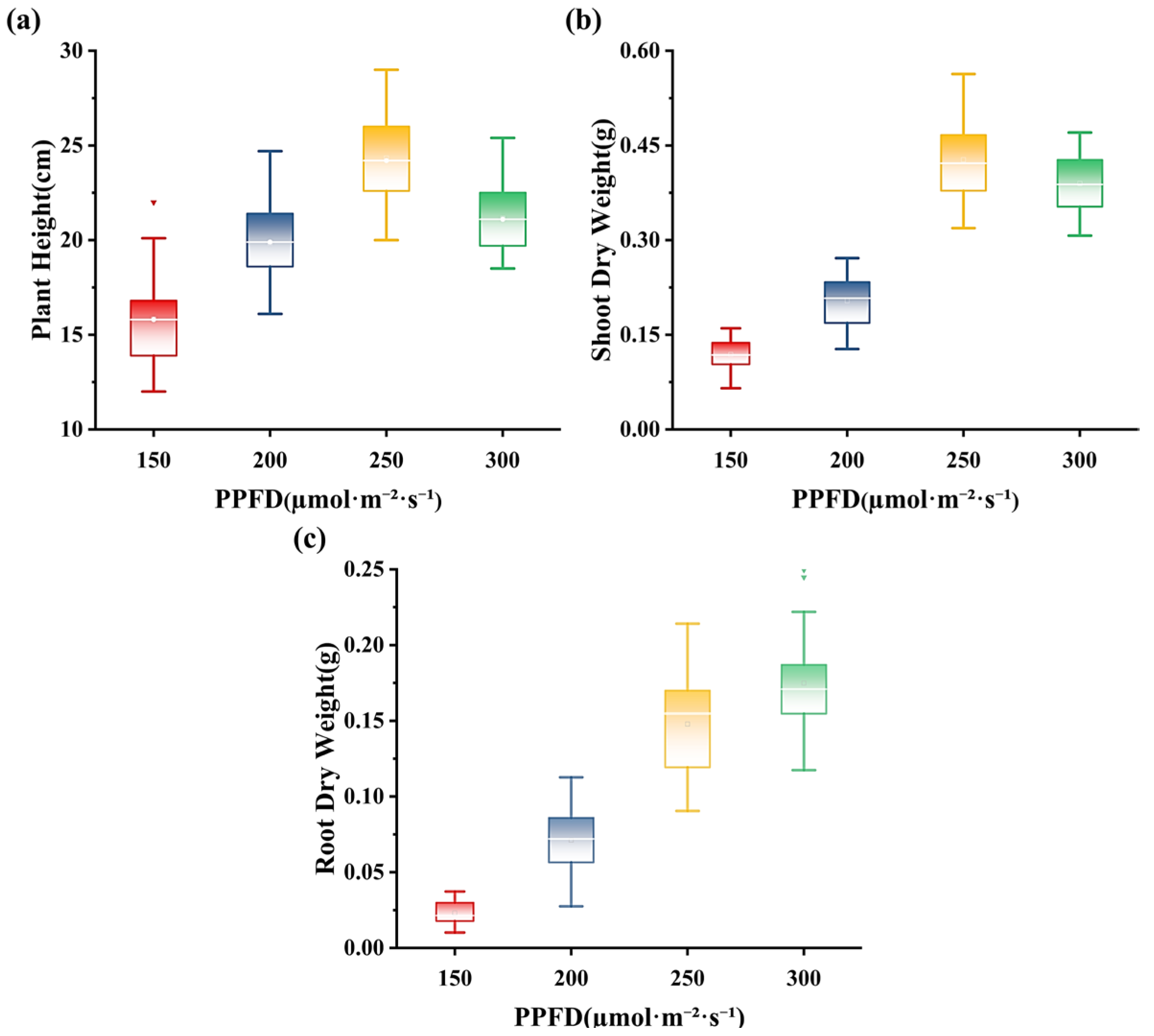
3.1. Effects of Light Intensity on Plant Growth and the Biomass of Alfalfa Seedlings
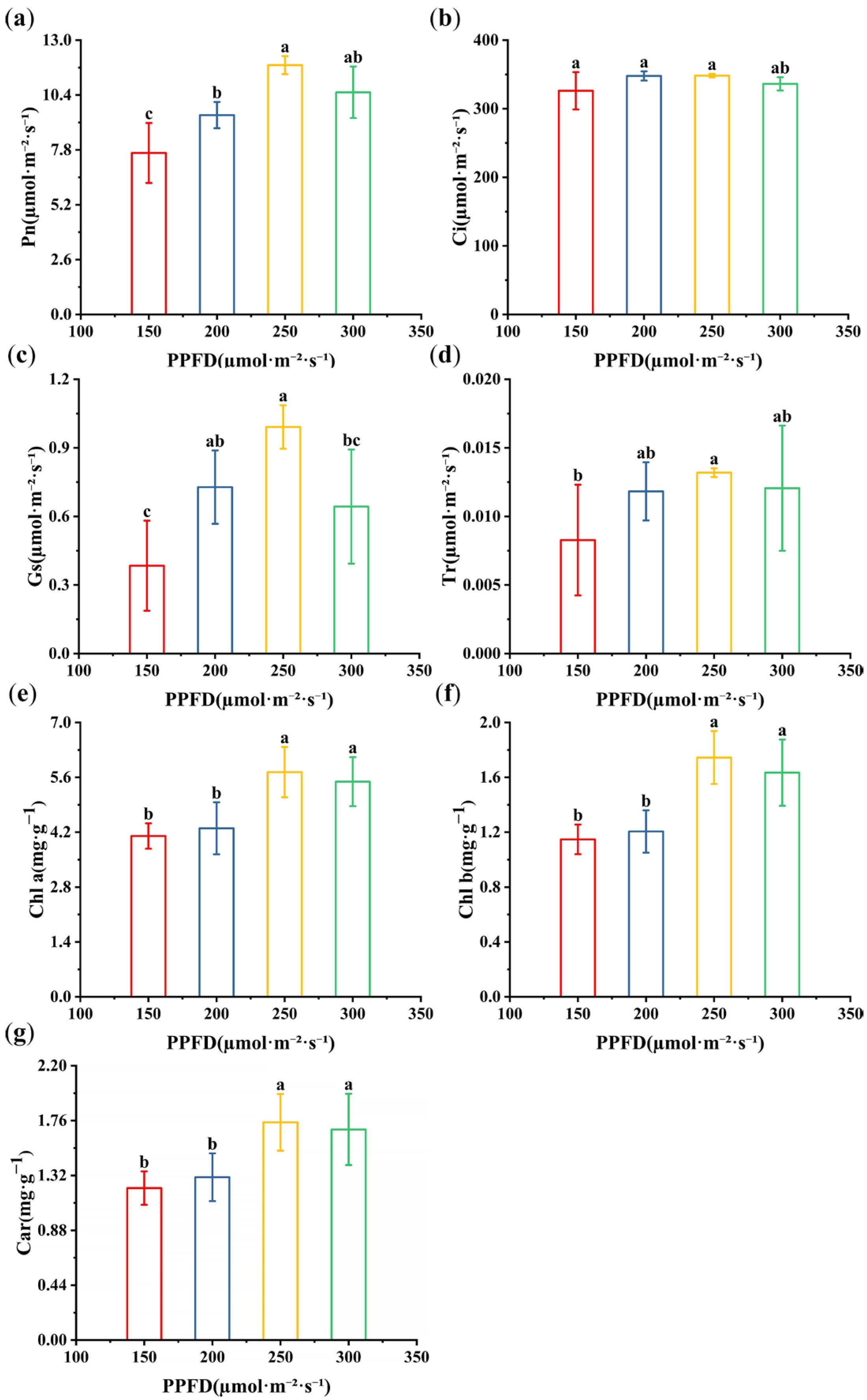
3.2. Effects of Light Intensity on the Photosynthetic Parameters and Photosynthetic Pigments of Alfalfa Seedlings
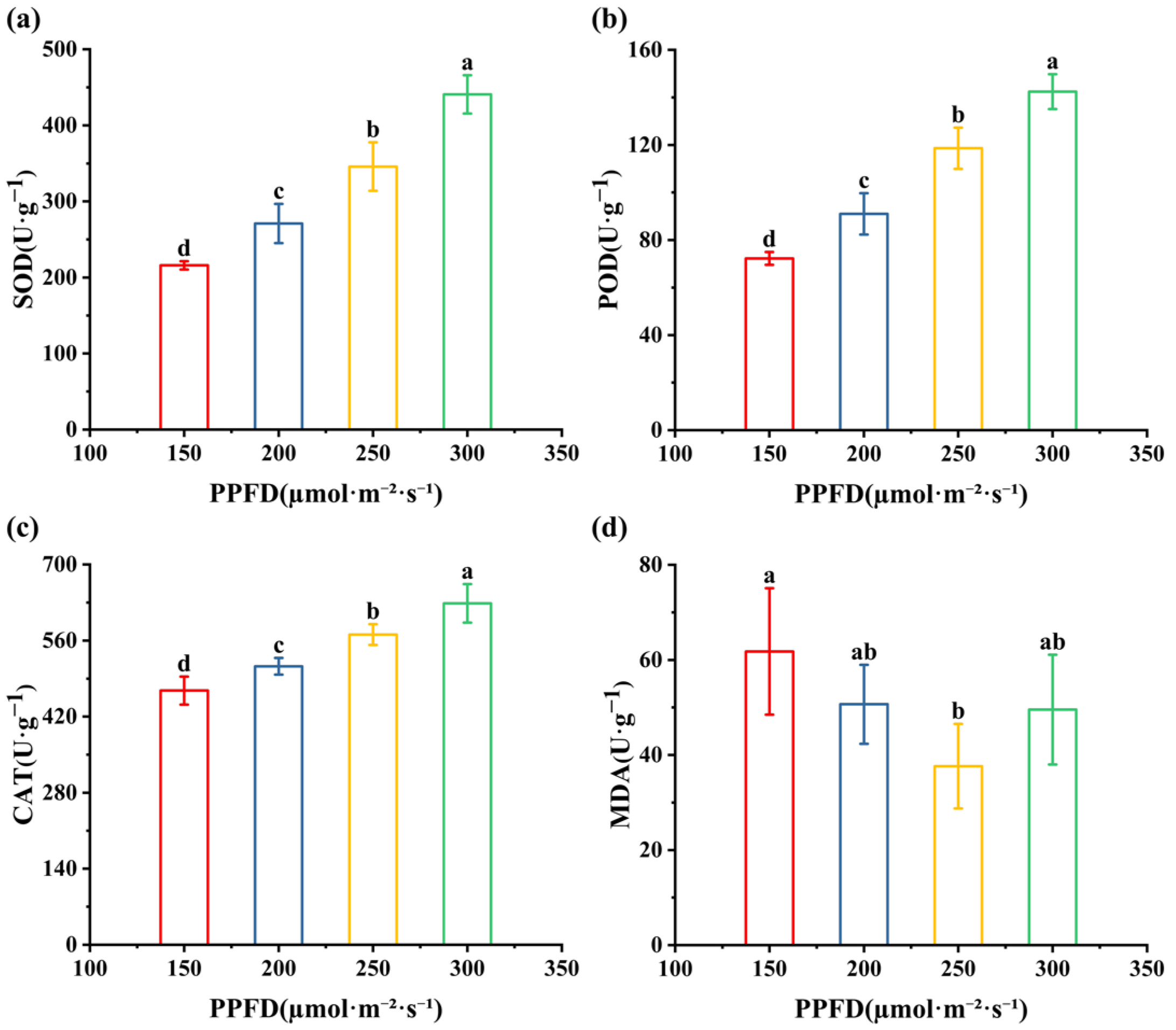
3.3. Effects of Light Intensities on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities and MDA in Alfalfa Seedlings
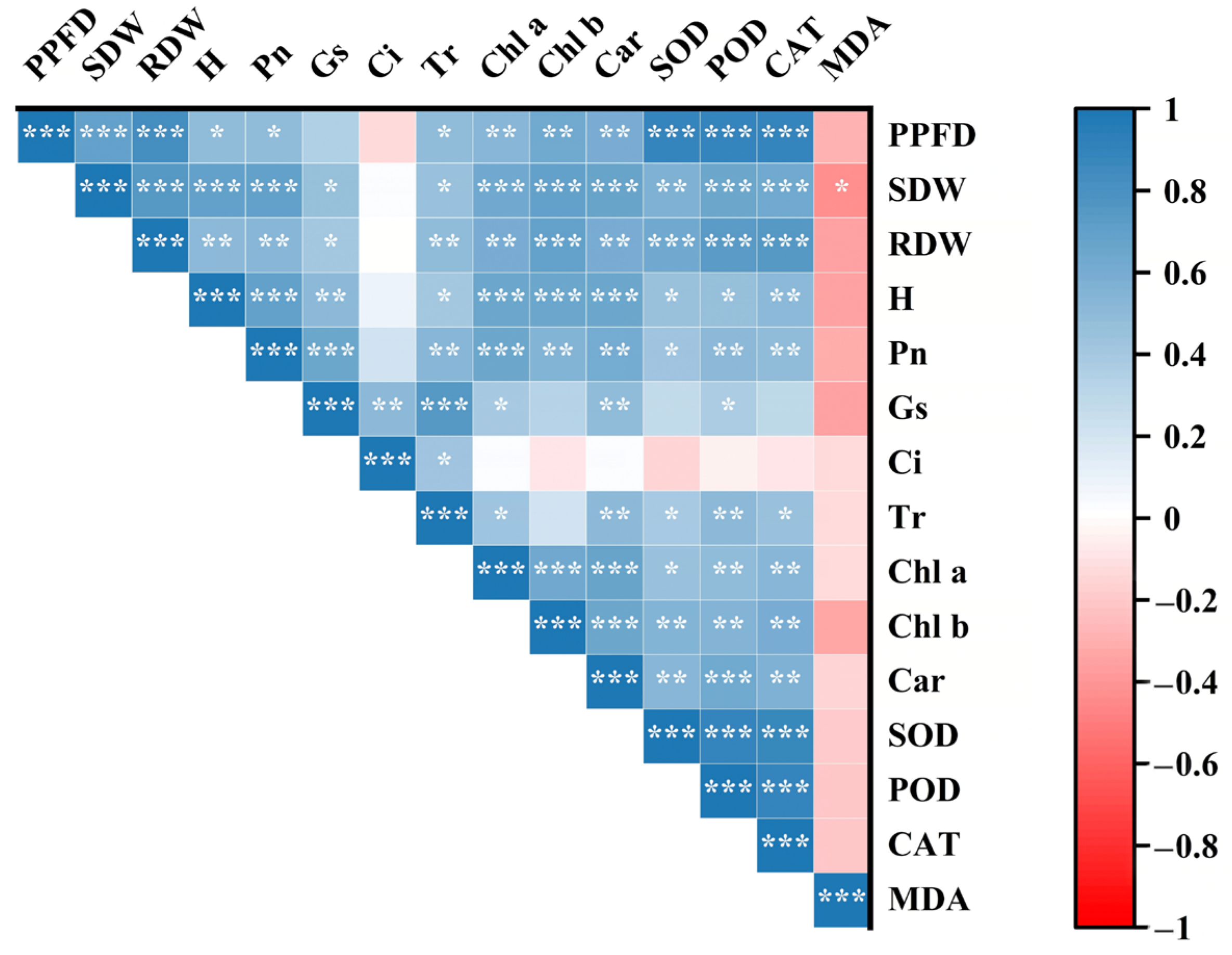
3.4. Result Evaluation Through Pearson Correlation Analysis
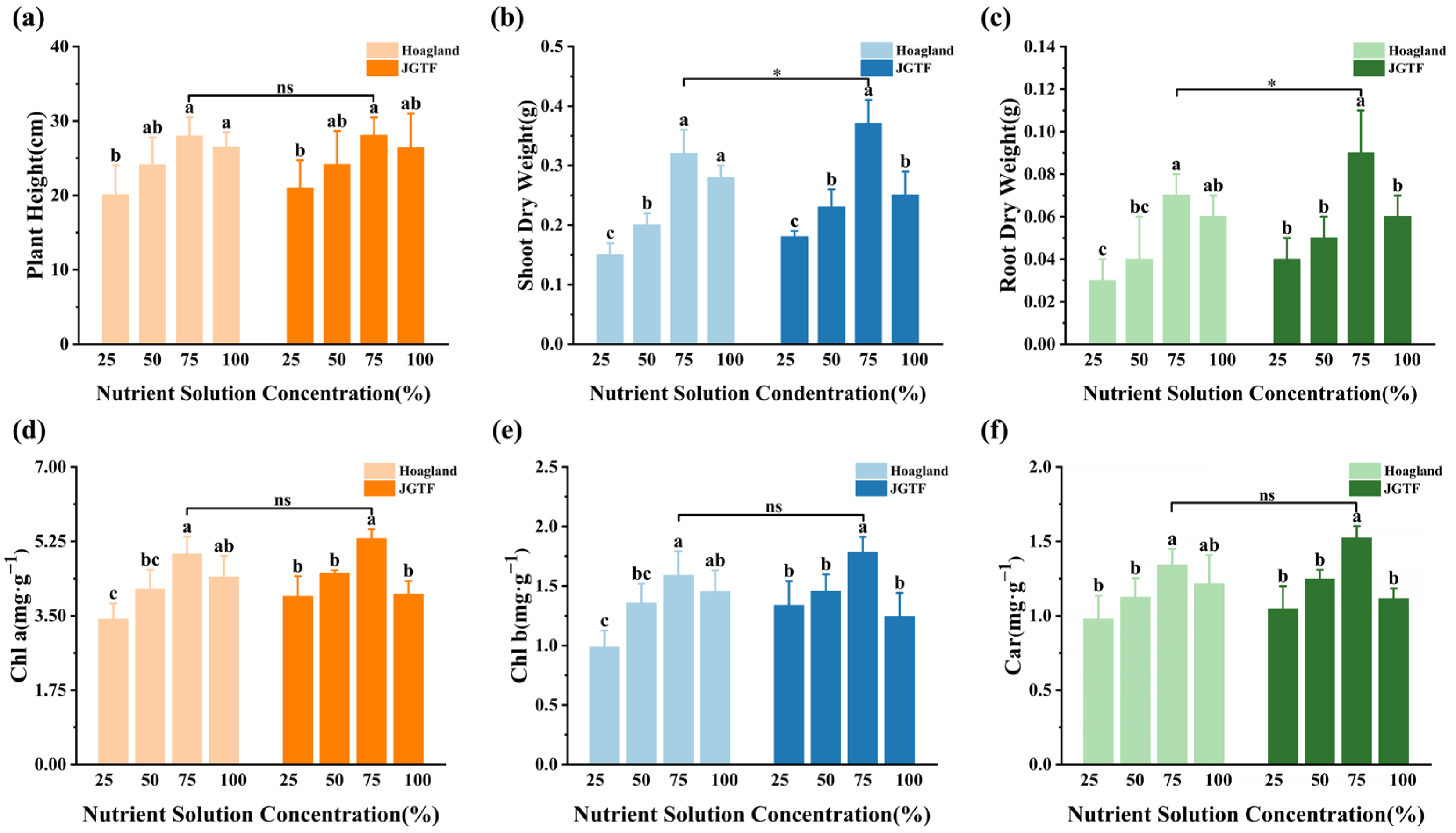
3.5. Effects of Nutrient Solution on the Growth and Photosynthetic Pigments of Alfalfa Seedlings
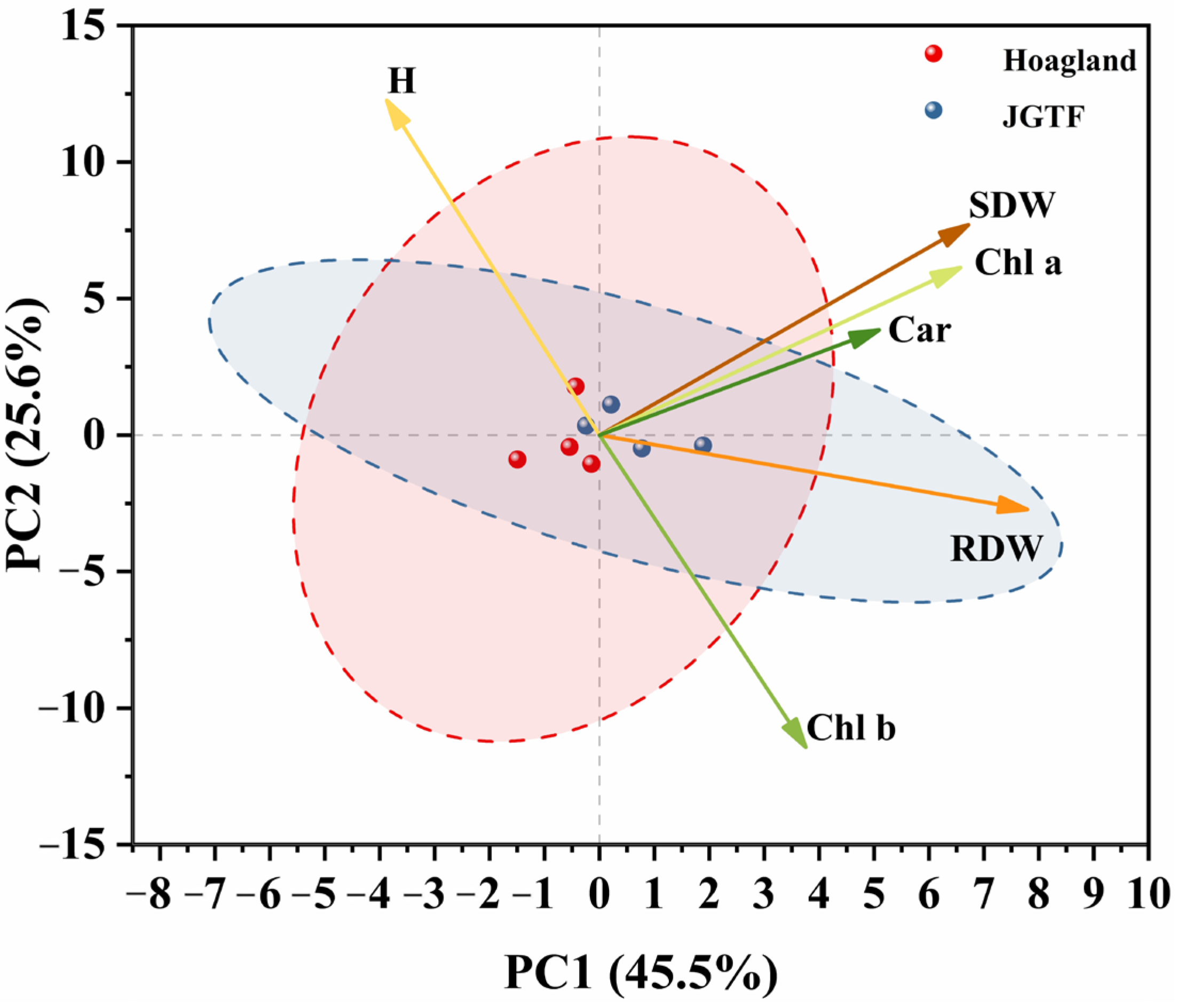
3.6. Result Evaluation Through Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
3.7. Effects of Photoperiods on Biomass and Flowering Time of Alfalfa Plant
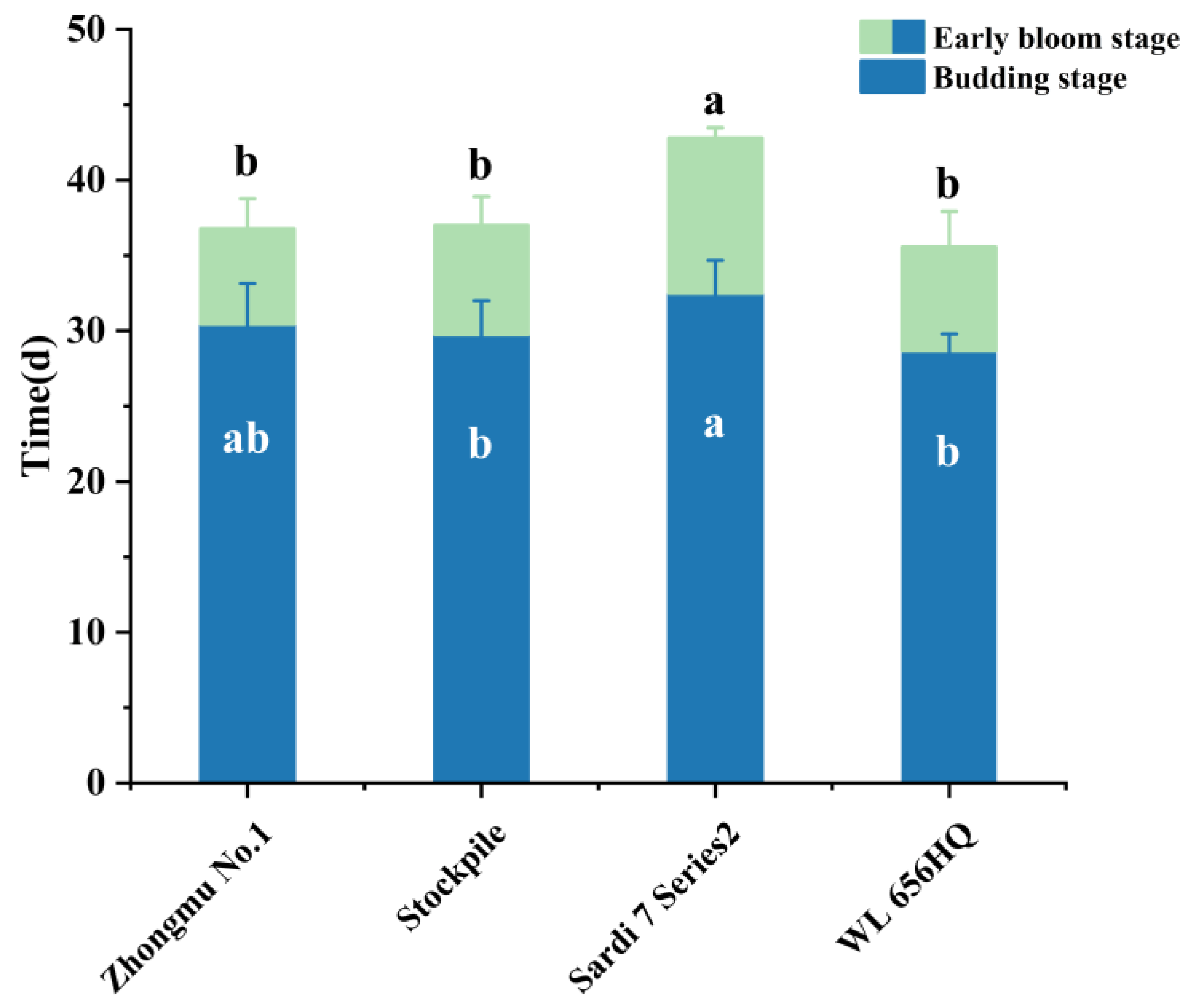
3.8. Flowering Time of Different Fall Dormancy Levels of Alfalfa Under Optimized Conditions
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Capstaff, N.M.; Miller, A.J. Improving the yield and nutritional quality of forage crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmar, S.; Gill, R.A.; Jung, K.H.; Faheem, A.; Qasim, M.U.; Mubeen, M.; Zhou, W. Conventional and molecular techniques from simple breeding to speed breeding in crop plants: Recent advances and future outlook. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdallah, N.A.; Hamwieh, A.; Radwan, K.; Fouad, N.; Prakash, C. Genome editing techniques in plants: A comprehensive review and future prospects toward zero hunger. GM Crops Food. 2021, 12, 601–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nerkar, G.; Devarumath, S.; Purankar, M.; Kumar, A.; Valarmathi, R.; Devarumath, R.; Appunu, C. Advances in crop breeding through precision genome editing. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 880195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Lai, M.; Ghouri, F.; Nawaz, M.A.; Ali, F.; Baloch, F.S.; Nadeem, M.A.; Aasim, M.; Shahid, M.Q. Modern plant breeding techniques in crop improvement and genetic diversity: From molecular markers and gene editing to artificial intelligence—A critical review. Plants 2024, 13, 2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kigoni, M.; Choi, M.; Arbelaez, J.D. Single-seed-speedbulks: A protocol that combines ‘speed breeding’ with a cost-efficient modified single-seed descent method for rapid-generation-advancement in oat (Avena sativa L.). Plant Methods 2023, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Luo, H.; Zhang, H.; Yung, W.S.; Li, M.W.; Lam, H.M.; Huang, C. Feeding the world using speed breeding technology. Trends Plant Sci. 2023, 28, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Li, S.; Zha, L.; He, J.; Zhang, J.; Bao, H. Significantly enhanced energy efficiency through reflective materials integration in plant factories with artificial light. Appl. Energy 2025, 377, 124587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Back, S.; Kim, G.; Lee, K.; Venkatesh, J.; Lee, H.; Kwon, J.K.; Kang, B.C. Development of a speed breeding protocol with flowering gene investigation in pepper (Capsicum annuum). Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1151765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Lin, H.; Debernardi, J.M.; Zhang, C.; Dubcovsky, J. GIGANTEA accelerates wheat heading time through gene interactions converging on FLOWERING LOCUS T1. Plant J. 2024, 118, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, R.; Ju, J.; Liu, K.; Song, J.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, M.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, H. Technology of plant factory for vegetable crop speed breeding. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1414860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Z.G.; Cheng, H.; Yang, X.; Li, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Gan, R.Y.; Yang, Q.C. Plant factory speed breeding significantly shortens rice generation time and enhances metabolic diversity. Engineering 2025, 50, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razzak, M.A.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Tanaka, H.; Asao, T. Effects of supplementing green light to red and blue light on the growth and yield of lettuce in plant factories. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 305, 111429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitache, M.; Baidani, A.; Bencharki, B.; Idrissi, O. Exploring the impact of light intensity under speed breeding conditions on the development and growth of lentil and chickpea. Plant Methods 2024, 20, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabade, P.G.; Dixit, S.; Singh, U.M.; Alam, S.; Bhosale, S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, S.K.; Badri, J.; Varma, N.R.G.; Chetia, S.; et al. SpeedFlower: A comprehensive speed breeding protocol for indica and japonica rice. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 1051–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, A.; Ghosh, S.; Williams, M.J.; Cuddy, W.S.; Simmonds, J.; Rey, M.D.; Asyraf Md Hatta, M.; Hinchliffe, A.; Steed, A.; Reynolds, D.; et al. Speed breeding is a powerful tool to accelerate crop research and breeding. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majidi, A.; Shahhoseini, R.; Salehi, H.; Roosta, H.R. Effect of hoagland’s nutrient solution strengths and sodium silicate on growth, yield and biochemical parameters of carla (Momordica charantia L.) under hydroponic conditions. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Acharya, S.; Kumar, K.; Singh, N.; Chaurasia, O. Hydroponics as an advanced technique for vegetable production: An overview. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 17, 364–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, K.M.A.; Zhang, D. Effects of fertilizer broadcasting on the excessive use of inorganic fertilizers and environmental sustainability. Sustainability 2018, 10, 759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, L. Advances in basic biology of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): A comprehensive overview. Hortic. Res. 2025, 12, uhaf081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, Y.; Lin, K.; Ding, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, S. Growth, quality, and nitrogen metabolism of medicago sativa under continuous light from red–blue–green leds responded better to high nitrogen concentrations than under red–blue leds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 13116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Guo, H.; Baskin, C.C.; Xiong, W.; Yang, C.; Li, Z.; Song, H.; Wang, T.; Yin, J.; Wu, X. Effect of light intensity on morphology, photosynthesis and carbon metabolism of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) seedlings. Plants 2022, 11, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, J.; Liu, W. Enhancing growth, quality, and metabolism of nitrogen of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) by high red–blue light intensity. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2023, 186, 661–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.; Zhang, M.; Du, L.; Zhang, L.; Li, B. Effects of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens QST713 on photosynthesis and antioxidant characteristics of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) under drought stress. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, A.; Singh, J.; Kant, R. Comparative study of estimation methods for efficient extraction of chlorophyll a and carotenoids using different solvents. Bull. Pure Appl. Sci.- Bot. 2022, 41, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandy, N.E.; Di Giulio, R.T.; Richardson, C.J. Assay and electrophoresis of superoxide dismutase from red spruce (Picea rubens Sarg.), loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.), and scotch pine (Pinus sylvestris L.): A method for biomonitoring. Plant Physiol. 1989, 90, 742–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyaya, A.; Sankhla, D.; Davis, T.D.; Sankhla, N.; Smith, B.N. Effect of paclobutrazol on the activities of some enzymes of activated oxygen metabolism and lipid peroxidation in senescing soybean leaves. J. Plant Physiol. 1985, 121, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Havir, E.A.; McHale, N.A. Biochemical and developmental characterization of multiple forms of catalase in tobacco leaves. Plant Physiol. 1987, 84, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buege, J.A.; Aust, S.D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzym. 1978, 52, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.S.; Li, L.; Li, L.; Wei, X.; Xu, F.; Xu, P.; Wang, W.; Xu, P.; Cao, X.; Miao, L.; et al. Photoexcited cryptochrome2 interacts directly with TOE1 and TOE2 in flowering regulation. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 487–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanoue, J.; Leonardos, E.D.; Grodzinski, B. Effects of light quality and intensity on diurnal patterns and rates of photo-assimilate translocation and transpiration in tomato leaves. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, S.; Liu, W.; Huang, S.; Xie, Y.; Meng, X.; Li, Z.; Jin, N.; Jin, L.; Lyu, J.; et al. Different spatial configurations of LED light sources enhance growth in tomato seedlings by influencing photosynthesis, CO2 assimilation, and endogenous hormones. Plants 2025, 14, 1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.X.; Xu, Z.G.; Liu, X.Y.; Tang, C.M.; Wang, L.W.; Han, X. Effects of light intensity on the growth and leaf development of young tomato plants grown under a combination of red and blue light. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 153, 50–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Zou, J.; Lin, S.; Jin, C.; Shi, M.; Yang, B.; Yang, Y.; Jin, D.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; et al. Effects of different light intensity on the growth of tomato seedlings in a plant factory. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0294876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Grimm, B. Connecting chlorophyll metabolism with accumulation of the photosynthetic apparatus. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 484–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Li, Q.M.; Liu, B.B.; Li, S.H.; Ai, X.Z.; Wei, M.; Zhang, D.L. Effects of light quality ratio on photosynthetic characteristics and quality of purple lettuce. J. Appl. Ecol. 2018, 29, 3649–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Lee, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Min, C.W.; Woo, J.H.; Choi, B.R.; Rahman, M.M.; Lee, K.W. Light quality plays a crucial role in regulating germination, photosynthetic efficiency, plant development, reactive oxygen species production, antioxidant enzyme activity, and nutrient acquisition in alfalfa. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, Y.; Kuroda, H.; Ozawa, S.I.; Saito, K.; Dogra, V.; Scholz, M.; Zhang, G.; De Vitry, C.; Ishikita, H.; Kim, C.; et al. Characterization of tryptophan oxidation affecting D1 degradation by FtsH in the photosystem II quality control of chloroplasts. Elife 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmitrieva, V.A.; Tyutereva, E.V.; Voitsekhovskaja, O.V. Singlet oxygen in plants: Generation, detection, and signaling roles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanuzzaman, M.; Bhuyan, M.; Zulfiqar, F.; Raza, A.; Mohsin, S.M.; Mahmud, J.A.; Fujita, M.; Fotopoulos, V. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant defense in plants under abiotic stress: Revisiting the crucial role of a universal defense regulator. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umićević, S.; Kukavica, B.; Maksimović, I.; Gašić, U.; Milutinović, M.; Antić, M.; Mišić, D. Stress response in tomato as influenced by repeated waterlogging. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1331281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coulombier, N.; Nicolau, E.; Le Déan, L.; Antheaume, C.; Jauffrais, T.; Lebouvier, N. Impact of light intensity on antioxidant activity of tropical microalgae. Mar. Drugs 2020, 18, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.G.; Van Iersel, M. Nutrient solution concentration affects shoot: Root ratio, leaf area ratio, and growth of subirrigated salvia (Salvia splendens). HortScience 2004, 39, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ajlouni, M.G.; Othman, Y.A.; Abu-Shanab, N.S.; Alzyoud, L.F. Evaluating the performance of cocopeat and volcanic tuff in soilless cultivation of roses. Plants 2024, 13, 2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, M.; Suzuki, T. Effect of nutrient solution concentration on the growth of hydroponic sweetpotato. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, D.; He, L.; Liu, F.; Zhou, Q.; Nandwani, D.; Hui, D.; Yu, J. Electrical conductivity of nutrient solution influenced photosynthesis, quality, and antioxidant enzyme activity of pakchoi (Brassica campestris L. ssp. Chinensis) in a hydroponic system. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0202090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, N.N.; Kitaya, Y.; Shibuya, T.; Endo, R. Development of an in vitro hydroponic culture system for wasabi nursery plant production—Effects of nutrient concentration and supporting material on plantlet growth. Sci. Hortic. 2019, 245, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgharably, A.; Benes, S. Alfalfa biomass yield and nitrogen fixation in response to applied mineral nitrogen under saline soil conditions. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 744–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.K.; Brouder, S.M.; Cunningham, S.M.; Volenec, J.J. Potassium and phosphorus fertilizer impacts on alfalfa taproot carbon and nitrogen reserve accumulation and use during fall acclimation and initial growth in spring. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 715936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carré, I.A. Day-Length perception and the photoperiodic regulation of flowering in arabidopsis. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2001, 16, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.H.; Shim, J.S.; Kinmonth, H.A.; Imaizumi, T. Photoperiodic flowering: Time measurement mechanisms in leaves. Annu. Rev. Plant. Biol. 2015, 66, 441–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D. Photoperiodic inhibition of potato tuberization: An update. Plant Growth Regul. 2010, 62, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.D. Plant responses to photoperiod. New Phytol. 2009, 181, 517–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Svystun, T.; AlDahmash, B.; Jönsson, A.M.; Bhalerao, R.P. Photoperiod and temperature mediated control of phenology in trees a molecular perspective. New Phytol. 2017, 213, 511–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeber, V.M.; Schmülling, T.; Cortleven, A. The photoperiod: Handling and causing stress in plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 781988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Barrios, P.; Bhatta, M.; Halley, M.; Sandro, P.; Gutiérrez, L. Speed breeding and early panicle harvest accelerates oat (Avena sativa L.) breeding cycles. Crop Sci. 2020, 61, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, K.; Subramani, M.; Lofton, L.W.; Penney, M.; Todd, A.; Ozbay, G. Tools and techniques to accelerate crop breeding. Plants 2024, 13, 1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nutrient Solution Formulation | Ca(NO3)2·4H2O (mg/L) | KNO3 (mg/L) | NH4H2PO4 (mg/L) | MgSO4·7H2O (mg/L) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hoagland | 945 | 607 | 115 | 493 |
| JGTF | 945 | 809 | 153 | 493 |
| Photoperiod (h/d) | Shoot Dry Weight (g) | Root Dry Weight (g) | Plant Height (cm) | Budding Stage (Day) | Budding Early Bloom Stage (Day) | Early Bloom Stage (Day) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8 | 0.42 ± 0.05 d | 0.04 ± 0.01 c | 44.70 ± 6.06 d | - | - | - |
| 13 | 2.97 ± 0.22 c | 0.67 ± 0.20 b | 66.43 ± 9.73 c | 48.50 ± 5.24 a | 9.13 ± 2.85 a | 57.63 ± 4.90 a |
| 16 | 5.76 ± 0.89 b | 1.08 ± 0.16 ab | 80.40 ± 8.64 a | 37.57 ± 1.99 b | 8.86 ± 3.89 b | 46.43 ± 4.24 b |
| 22 | 7.86 ± 1.52 a | 1.45 ± 0.33 a | 89.55 ± 9.68 a | 29.40 ± 2.01 c | 8.30 ± 0.67 c | 37.70 ± 2.00 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Gao, P.; Liang, Y.; Li, B. Optimizing the Light Intensity, Nutrient Solution, and Photoperiod for Speed Breeding of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Under Full-Spectrum LED Light. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092067
Han L, Lv Y, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Gao P, Liang Y, Li B. Optimizing the Light Intensity, Nutrient Solution, and Photoperiod for Speed Breeding of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Under Full-Spectrum LED Light. Agronomy. 2025; 15(9):2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092067
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Lingjuan, Yuanyuan Lv, Yifei Zhang, Xiaoyan Zhao, Peng Gao, Yinping Liang, and Bin Li. 2025. "Optimizing the Light Intensity, Nutrient Solution, and Photoperiod for Speed Breeding of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Under Full-Spectrum LED Light" Agronomy 15, no. 9: 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092067
APA StyleHan, L., Lv, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhao, X., Gao, P., Liang, Y., & Li, B. (2025). Optimizing the Light Intensity, Nutrient Solution, and Photoperiod for Speed Breeding of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) Under Full-Spectrum LED Light. Agronomy, 15(9), 2067. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15092067





