Phosphorus and Microbial Degradation Mediate Vegetation-Induced Macroaggregate Dynamics on the Loess Plateau, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Sites and Sampling
2.2. Soil Physical Fractionation for Aggregate Studies
2.3. Soil Measurements
2.4. Microbial Diversity Determination
2.5. Data Processing and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
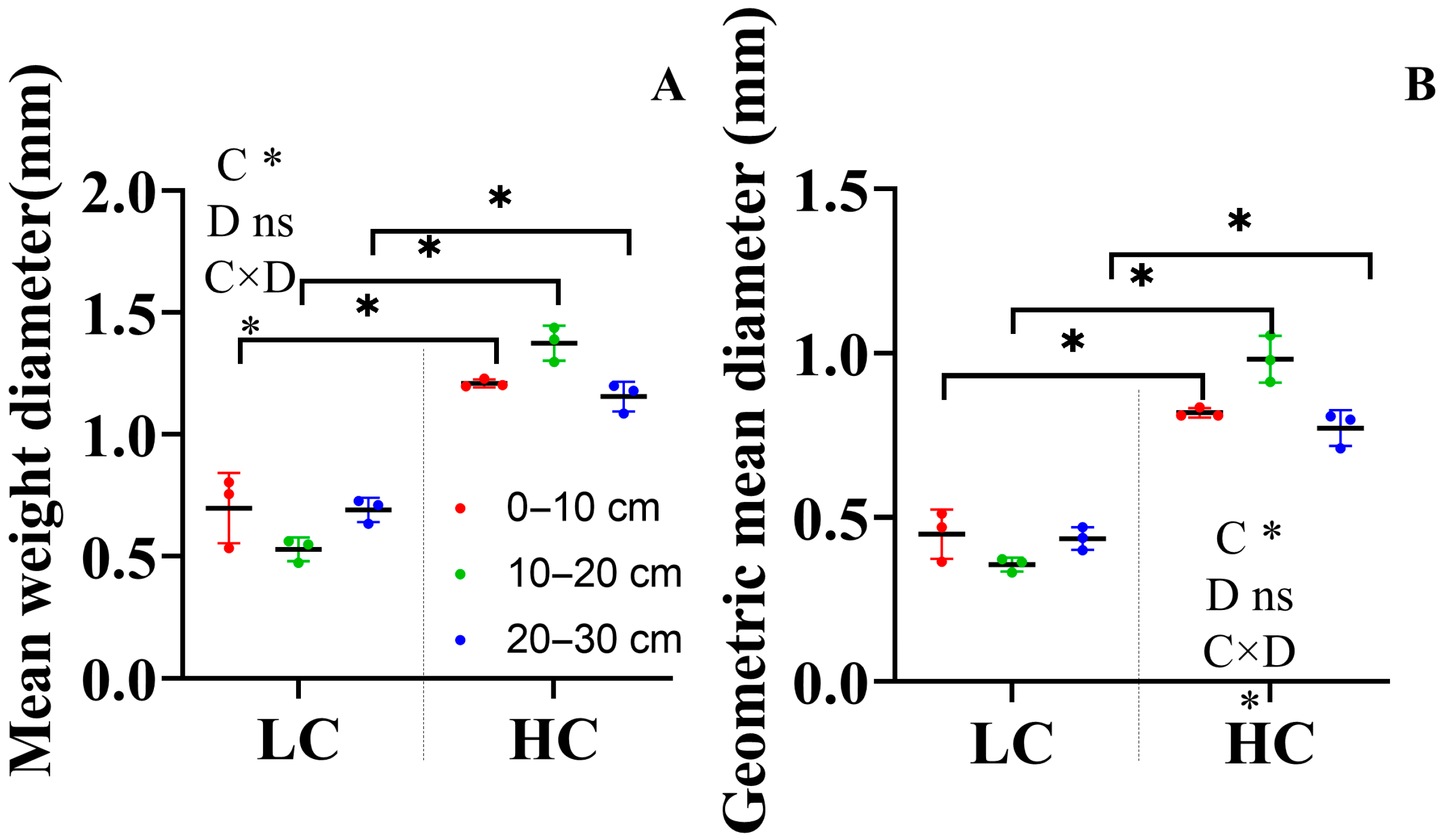
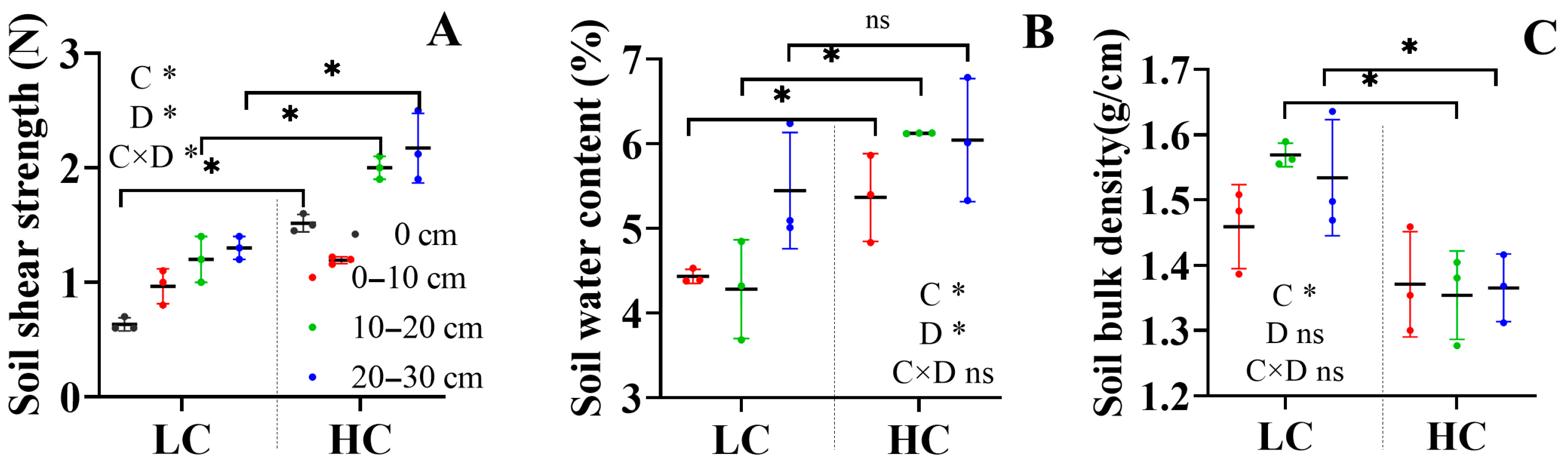
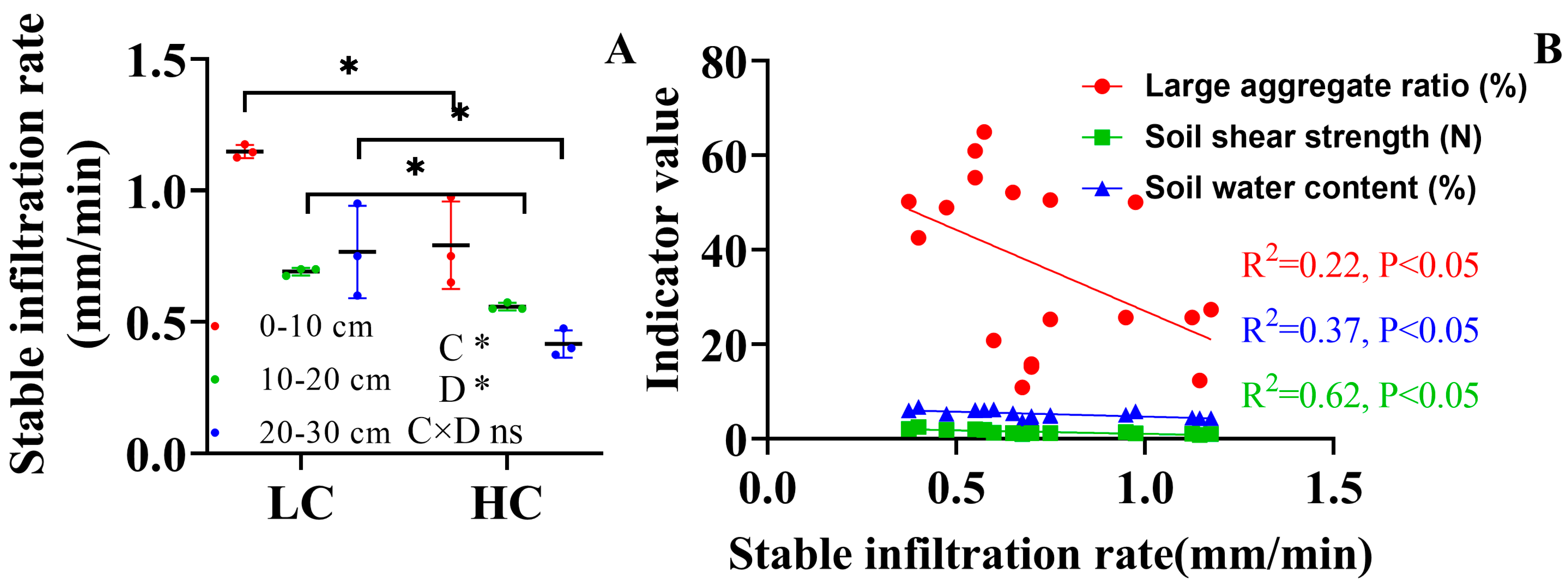
3.1. Soil Aggregate and Soil Stability Indices
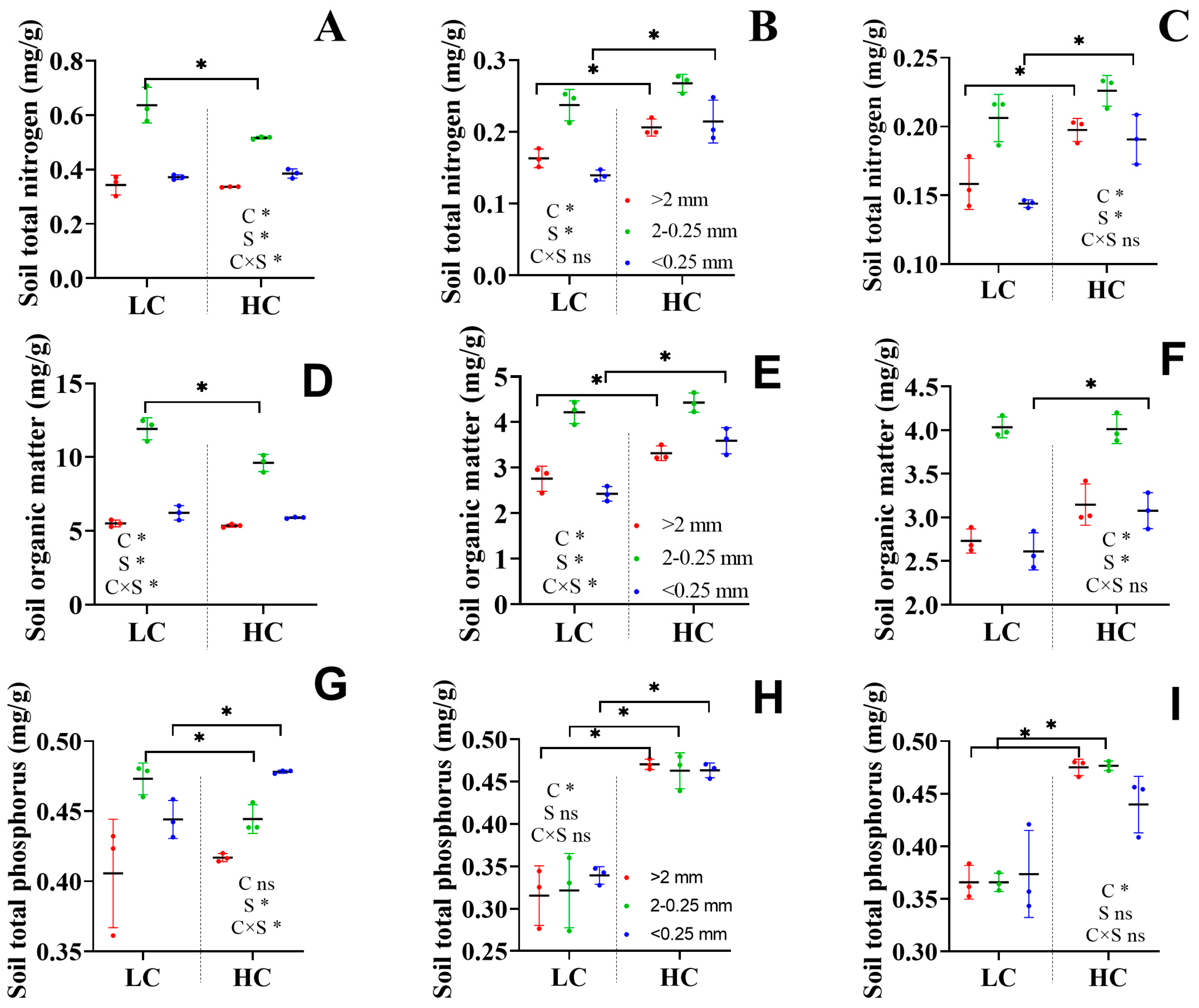
3.2. Soil Nutrient Content
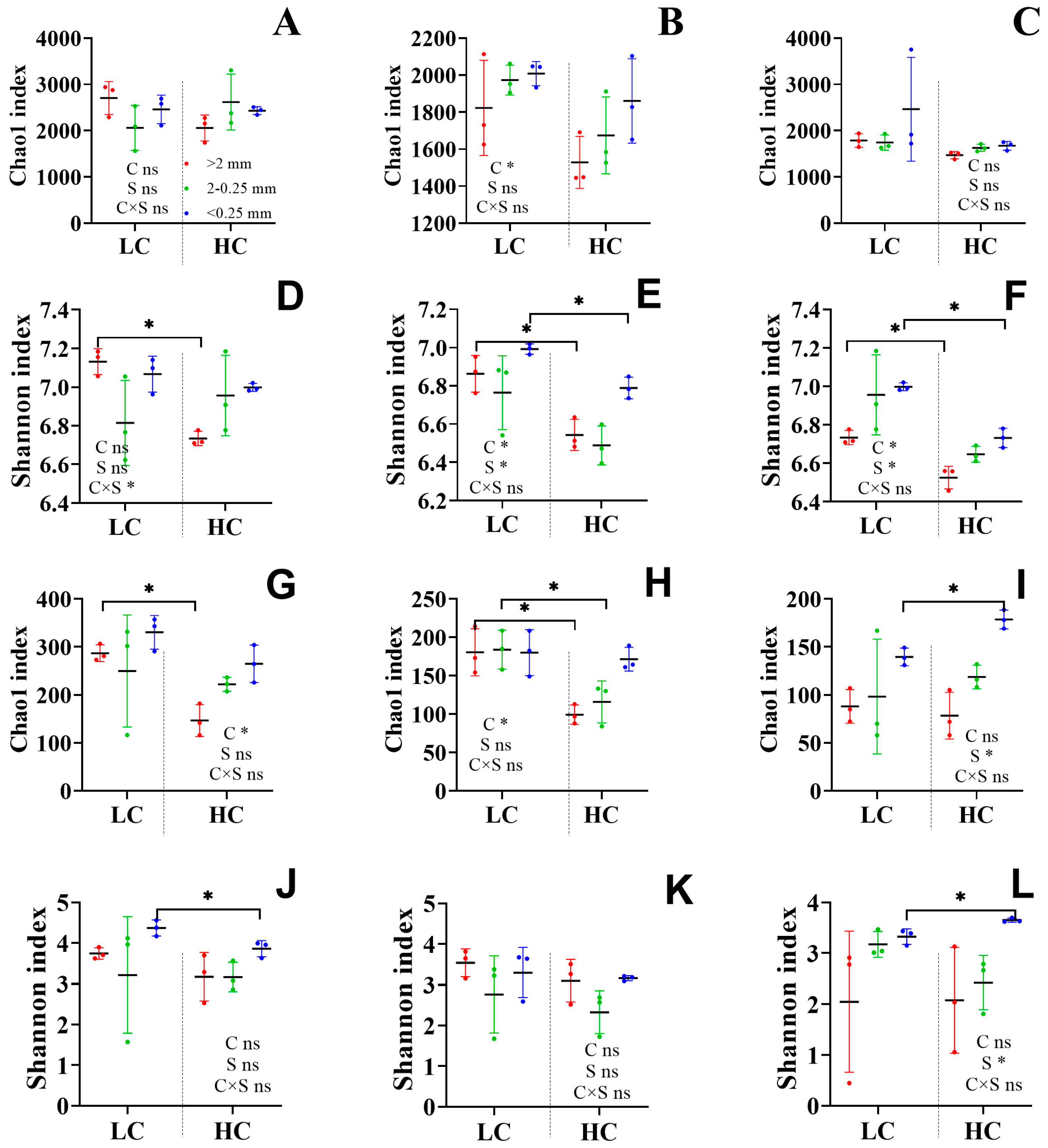
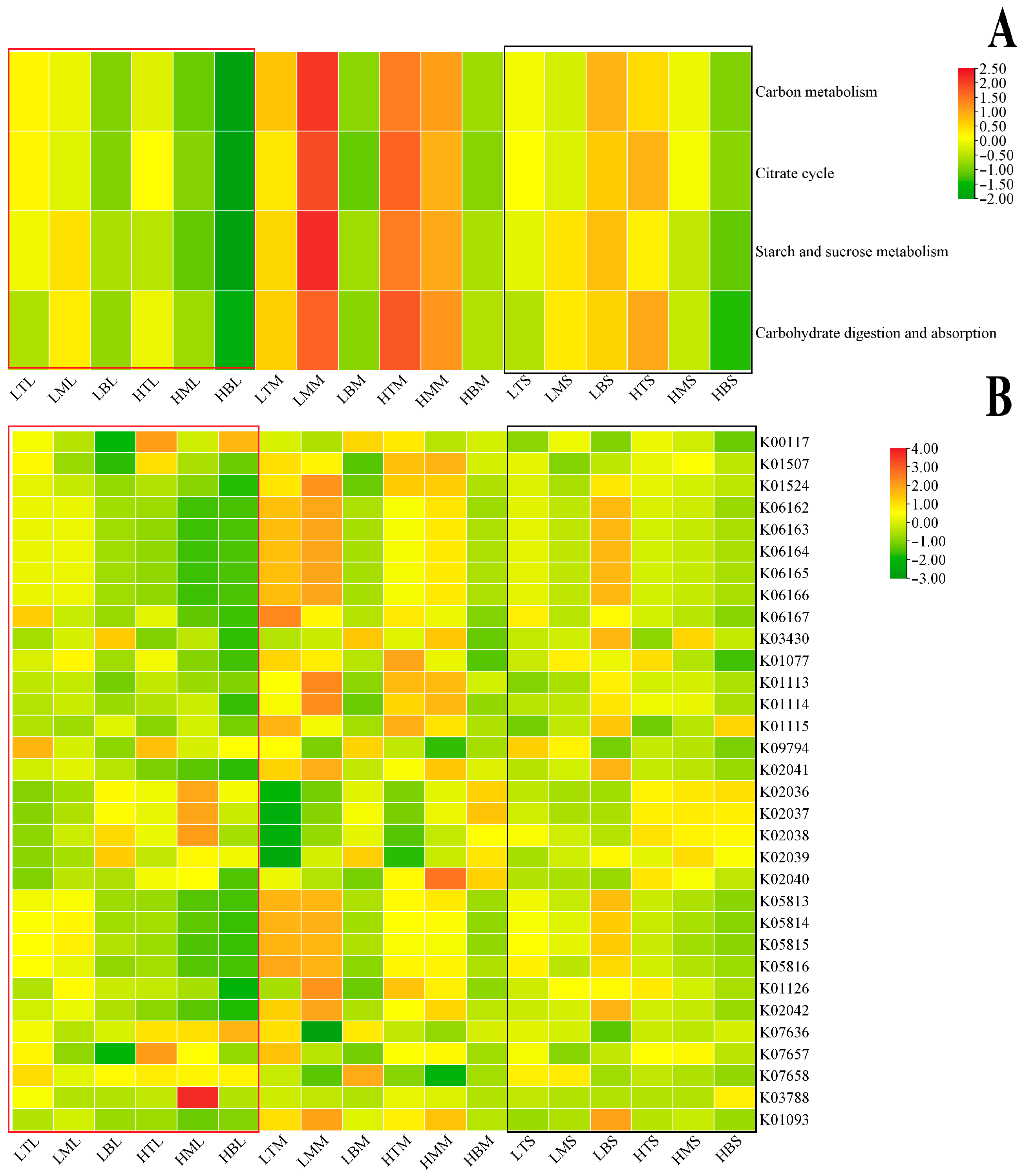
3.3. Microbial Diversity and Function
4. Discussion
4.1. Land Cover Increased the Formation of Macroaggregates but Not Small Macroaggregates
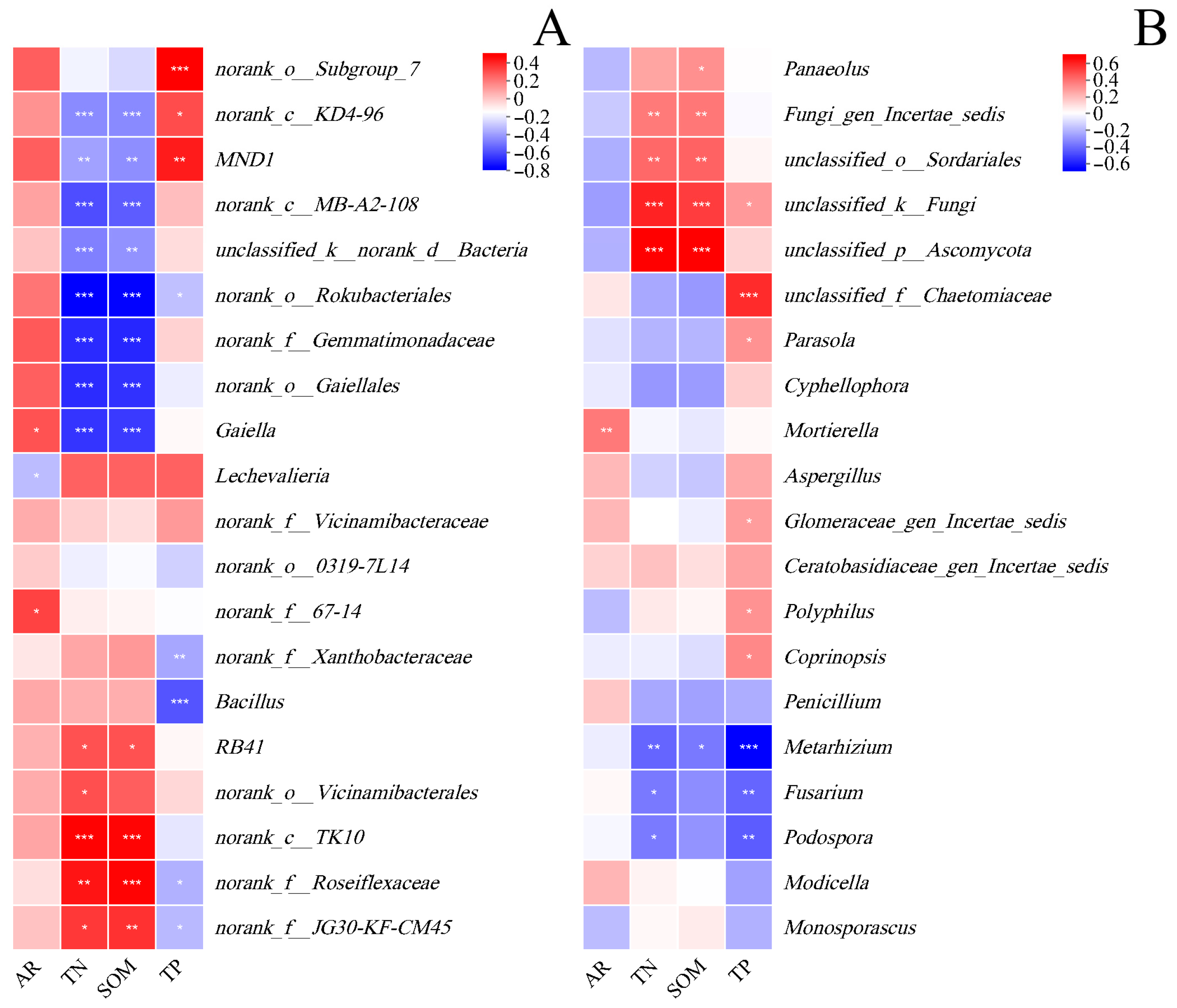
4.2. Variation in SOM Content of Different Aggregate Sizes Changes Soil Microbial Diversity and Taxa
4.3. Aggregates Affect Soil Microbes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Henderson, M.; Chen, M.; Dou, Z.; Zhou, W.; Huang, W.; Liu, B. Effects of terracing on soil aggregate stability and erodibility in sloped farmland in black soil (Mollisols) region of China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Panagos, P.; Lugato, E.; Yang, J.E.; Alewell, C.; Wuepper, D.; Montanarella, L.; Ballabio, C. Land use and climate change impacts on global soil erosion by water (2015–2070). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 21994–22001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Hu, W.; Jia, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhang, C.; Huang, B.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shukla, M.K.; et al. Soil degradation: A global threat to sustainable use of black soils. Pedosphere 2025, 35, 264–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, F.A.L.; Sanches Fernandes, L.F.; Valle Junior, R.F.; Valera, C.A.; Pissarra, T.C.T. Land degradation: Multiple environmental consequences and routes to neutrality. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sci. Health 2018, 5, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Wan, S.; Zhang, K.; Hong, S.; Xia, J.; Piao, S.; Wang, Y.P.; Chen, J.; Hui, D.; Luo, Y.; et al. Ecological restoration enhances dryland carbon stock by reducing surface soil carbon loss due to wind erosion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2416281121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Jiang, X.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cai, W. Spatiotemporal evolution characteristics of soil erosion and its driving mechanisms—A case Study: Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2024, 242, 108075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torri, D.; Ciampalini, R.; Gil, P.A. The role of soil aggregates in soil erosion processes. In Modelling Soil Erosion by Water; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, R.; Hu, F.; Xu, C.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Liu, G.; Zhao, S.; Zheng, F. Vegetation restoration enhances soil erosion resistance through decreasing the net repulsive force between soil particles. Catena 2023, 226, 107085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Bossuyt, H.; Degryze, S.; Denef, K. A history of research on the link between (micro)aggregates, soil biota, and soil organic matter dynamics. Soil Till. Res. 2004, 79, 7–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Minggang, X.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Nan, S.; Baoren, W.; Zejiang, C.; Saeed, Q.; Naveed, M.; Mehmood, K.; et al. Soil aggregation and soil aggregate stability regulate organic carbon and nitrogen storage in a red soil of southern China. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 270, 110894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Liu, W.; Yuan, X.; Chen, C.; Zhu, K.; Zhang, W.; Yang, B. Aggregate stability and size distribution regulate rainsplash erosion: Evidence from a humid tropical soil under different land-use regimes. Geoderma 2022, 420, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Hao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Qin, F.; Xu, M.; Cai, P.; Chen, W.; Huang, Q. Soil aggregate modulates microbial ecological adaptations and community assemblies in agricultural soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2022, 172, 108769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jesús Melej, M.; Acevedo, S.E.; Contreras, C.P.; Giraldo, C.V.; Maurer, T.; Calderón, F.J.; Bonilla, C.A. Changes in macroaggregate stability as a result of wetting/drying cycles of soils with different organic matter and clay contents. Geoderma 2024, 448, 116965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totsche, K.U.; Amelung, W.; Gerzabek, M.H.; Guggenberger, G.; Klumpp, E.; Knief, C.; Lehndorff, E.; Mikutta, R.; Peth, S.; Prechtel, A.; et al. Microaggregates in soils. J. Plant Nut. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 104–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Luo, X.; Liu, Y.; Van Nostrand, J.D.; Chen, W.; Zhou, J.; Huang, Q. Soil aggregate size-dependent relationships between microbial functional diversity and multifunctionality. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 154, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhu, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, R. Response of organic carbon fractions and microbial community composition of soil aggregates to long-term fertilizations in an intensive greenhouse system. J. Soils Sed. 2020, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Han, X.; You, M.; Yan, J.; Lu, X.; Horwath, W.R.; Zou, W. Soil macroaggregates and organic-matter content regulate microbial communities and enzymatic activity in a Chinese Mollisol. J. Integr. Agric. 2019, 18, 2605–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Munkholm, L.J.; Liu, X.; An, T.; Xu, Y.; Ge, Z.; Xie, N.; Li, A.; Dong, Y.; Peng, C.; et al. Soil aggregate microstructure and microbial community structure mediate soil organic carbon accumulation: Evidence from one-year field experiment. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackerman, D.; Millet, D.B.; Chen, X. Global estimates of inorganic nitrogen deposition across four decades. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycl. 2019, 33, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, R.; Li, Q.; Liu, J.; Ma, X.; Xu, W.; Tang, A.; Collett, J.L.; Li, H.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variations of nitrogen and phosphorus deposition across China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154740. [Google Scholar]
- Han, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, L.; Tian, S.; Liang, T.; Liu, Y. Identification of areas vulnerable to soil erosion and risk assessment of phosphorus transport in a typical watershed in the Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 758, 143661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, F.; Xia, Y.; Li, W.; Tan, X.; Jiang, L.; Dai, Q.; Yan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Pu, J. Long-term abandoned farmland enhanced soil aggregate-associated total carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus storage under different rocky desertification grades in a karst trough valley. Catena 2025, 259, 109326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Peng, X.; Dai, Q.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Liu, T. Storage infiltration of rock-soil interface soil on rock surface flow in the rocky desertification area. Geoderma 2023, 435, 116512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Olga, V.T.; Jason, M.U.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Wei, G.; Chen, C. Pristine and sulfidized zinc oxide nanoparticles promote the release and decomposition of organic carbon in the Legume rhizosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 8943–8953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Ou, Y.; Liu, H.; Hou, X.; Yan, L.; Li, X. The various effect of cow manure compost on the degradation of imazethapyr in different soil types. Chemosphere 2023, 337, 139325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Varma, A.; Choudhary, D.K. Perspectives on nitrogen-fixing bacillus species. In Soil Nitrogen Ecology; Soil Biology; Cruz, C., Vishwakarma, K., Choudhary, D.K., Varma, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Zhang, W.; Hu, P.; Xiao, D.; Yang, R.; Ye, Y.; Wang, K. The formation of large macroaggregates induces soil organic carbon sequestration in short-term cropland restoration in a typical karst area. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 801, 149588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Wang, C.; Gao, J.; Ma, H.; Li, Z.; Hao, Y.; Qiu, X.; Ru, J.; Song, J.; Wan, S. Changes in plant litter and root carbon inputs alter soil respiration in three different forests of a climate transitional region. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2024, 358, 110212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucetaite, M.; Persson, P.; Parker, J.; Johansson, U.; Hammer, E.C. Visualization of soil aggregate structures provides insights into their formation mechanisms induced by litter inputs. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 202, 109686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Even, R.J.; Francesca Cotrufo, M. The ability of soils to aggregate, more than the state of aggregation, promotes protected soil organic matter formation. Geoderma 2024, 442, 116760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Zhu, H.; Shutes, B.; Rousseau, A.N.; Feng, W.D.; Hou, S.N.; Ou, Y.; Yan, B.X. Soil aggregate-driven changes in nutrient redistribution and microbial communities after 10-year organic fertilization. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 348, 119306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Yang, W.; Yu, B.; Li, Z.; Cai, C.; Ma, R. Estimating the influence of related soil properties on macro- and micro-aggregate stability in ultisols of south-central China. Catena 2016, 137, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Mao, Y.; Gao, S.; Lu, C.; Pan, C.; Li, X. Organic carbon accumulation and aggregate formation in soils under organic and inorganic fertilizer management practices in a rice–wheat cropping system. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amelung, W.; Meyer, N.; Rodionov, A.; Knief, C.; Aehnelt, M.S.; Bauke, L.; Biesgen, D.; Dultz, S.; Guggenberger, G.; Jaber, M.; et al. Process sequence of soil aggregate formation disentangled through multi-isotope labelling. Geoderma 2023, 429, 116226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabinejad, N.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Jalalian, A.; Chavoshi, E. The fractionation of soil aggregates associated with primary particles influencing wind erosion rates in arid to semiarid environments. Geoderma 2019, 356, 113936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Lv, J.; Shi, J.; Shang, J.; Wang, X. Effects of erosion on macroaggregation, aggregate associated organic carbon sources and compositions in a Mollisol agricultural landscape. Catena 2024, 240, 107994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Feng, G.; Huang, Y.; Adeli, A.; Jenkins, J.N. Soil aggregate stability and erodibility as influenced by soil amendments and winter cover crop in upland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2025, 89, e70022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Liu, C.; Wang, J.; Meng, Q.; Yuan, Y.; Ma, X.; Liu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Ding, G.; Zhang, J.; et al. Soil aggregates stability and storage of soil organic carbon respond to cropping systems on Black Soils of Northeast China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fan, H.; Jiang, Y.; Ma, R. Evaluation of soil macro-aggregate characteristics in response to soil macropore characteristics investigated by X-ray computed tomography under freeze-thaw effects. Soil Till. Res. 2023, 225, 105559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.P.; Fornara, D.; Yang, H.; Yu, R.P.; Callaway, R.M.; Li, L. Plant litter strengthens positive biodiversity–ecosystem functioning relationships over time. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2023, 38, 473–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urbanek, E.; Horn, R.; Smucker, A.J.M. Tensile and erosive strength of soil macro-aggregates from soils under different management system. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2014, 62, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, P.; Yin, Z.; Li, A.; Zhou, X.; Qi, Z.; Wang, B. Soil Aggregates and Water Infiltration Performance of Different Water and Soil Conservation Measures on Phaeozems Sloping Farmland in Northeast China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y.; Shi, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, H. Soil P components and soil fungi community traits in poplar shelterbelts and neighboring farmlands in northeastern China: Total alterations and complex associations. Catena 2022, 218, 106531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Jia, X.; Li, T.; Shao, M.; Yu, Q.; Wei, X. Decreased soil total phosphorus following artificial plantation in the Loess Plateau of China. Geoderma 2021, 385, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, E.; Guseva, K.; Darcy, S.; Alteio, L.; Pjevac, P.; Schmidt, H.; Jenab, K.; Ranits, C.; Kaiser, C. Distinct microbial communities are linked to organic matter properties in millimetre-sized soil aggregates. ISME J. 2024, 18, wrae156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Song, X.; Wu, X.; Zheng, F.; Li, S.; Zhuang, Y.; Man, X.; Degré, A. Microbial regulation of aggregate stability and carbon sequestration under long-term conservation tillage and nitrogen application. Sust. Prod. Consum. 2024, 44, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Xin, X.; Zhu, A.; Yang, W.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S.; Mu, L.; Shao, L. Linking macroaggregation to soil microbial community and organic carbon accumulation under different tillage and residue managements. Soil Till. Res. 2018, 178, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhu, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Chen, K.; Xue, S. Stable Aggregate Formation and Microbial Diversity Resilience in Soil Formation of Bauxite Residue: Roles of Extracellular Polymeric Substances Secreted by Penicillium oxalicum. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 1758–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Chenu, C.; Kappler, A.; Rillig, M.C.; Fierer, N. The interplay between microbial communities and soil properties. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2024, 22, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Liu, N.; Zhang, Y. Soil aggregates regulate the impact of soil bacterial and fungal communities on soil respiration. Geoderma 2019, 337, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, G.; Miller, R.; Deng, S. Dynamic relationships between microbial community, enzyme activity, and soil properties across global ecosystems. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, E.D.; Grandy, A.S.; Geyer, K.M.; Morrison, E.W.; Frey, S.D. Microbial trait multifunctionality drives soil organic matter formation potential. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 10209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, N.; Cao, P.; Wang, Z.; Yan, J. Phosphorus and Microbial Degradation Mediate Vegetation-Induced Macroaggregate Dynamics on the Loess Plateau, China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15082011
Zhang N, Cao P, Wang Z, Yan J. Phosphorus and Microbial Degradation Mediate Vegetation-Induced Macroaggregate Dynamics on the Loess Plateau, China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(8):2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15082011
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Ningning, Pandeng Cao, Zhi Wang, and Jiakun Yan. 2025. "Phosphorus and Microbial Degradation Mediate Vegetation-Induced Macroaggregate Dynamics on the Loess Plateau, China" Agronomy 15, no. 8: 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15082011
APA StyleZhang, N., Cao, P., Wang, Z., & Yan, J. (2025). Phosphorus and Microbial Degradation Mediate Vegetation-Induced Macroaggregate Dynamics on the Loess Plateau, China. Agronomy, 15(8), 2011. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15082011






