Synergistic Effects of Silicon and Ferrous Sulfate on Reducing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice from Co-Contaminated Soil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Hydroponic Experiment
2.1.1. Rice Seedling Preparation
2.1.2. Experimental Treatments
2.1.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2. Soil Pot Experiment
2.2.1. Soil Collection and Treatment
2.2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2.3. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. Dry Weight of Rice Plant Exposed to As and Cd
3.2. Dynamic Accumulation of As and Cd in Rice Tissues
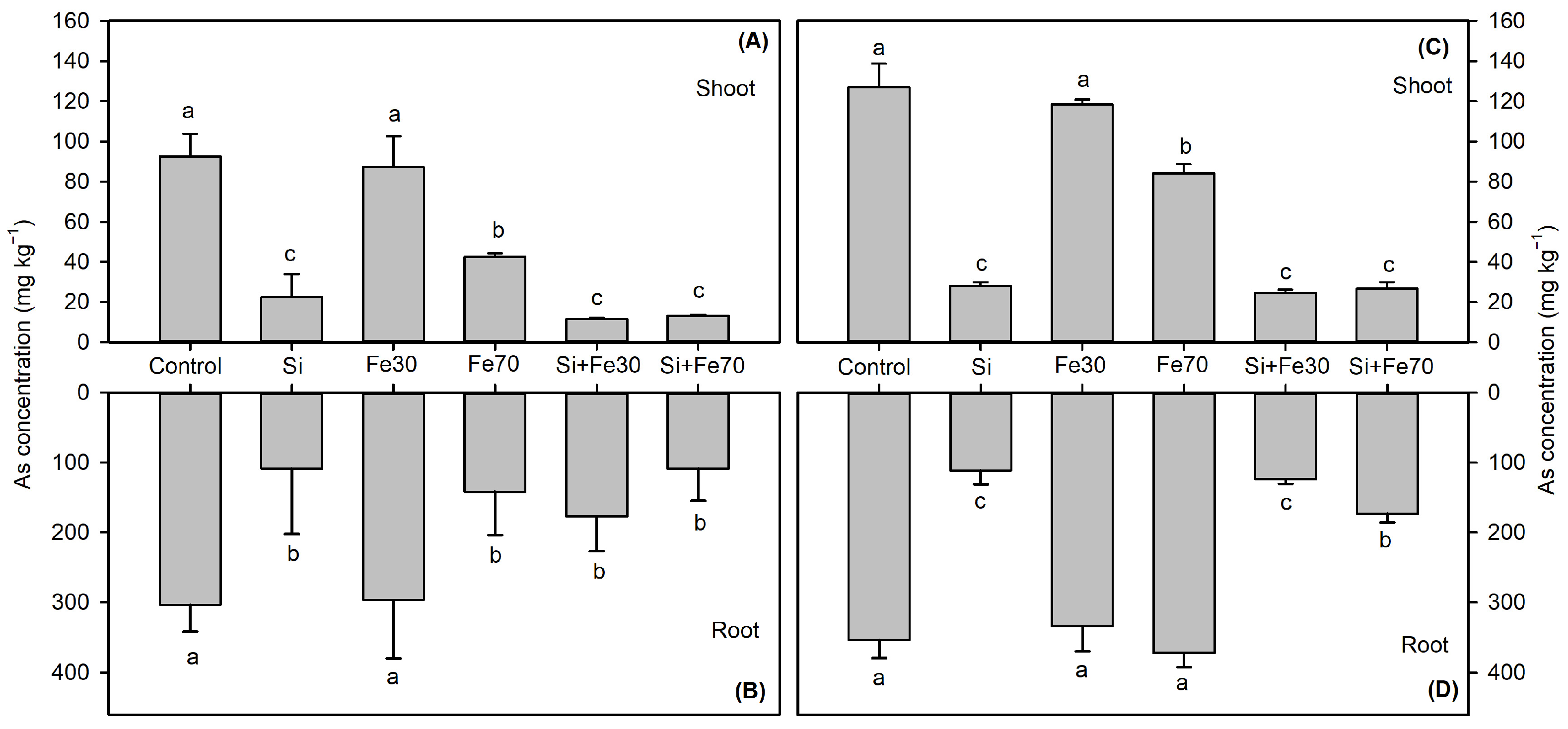
3.2.1. As Sequestration Patterns
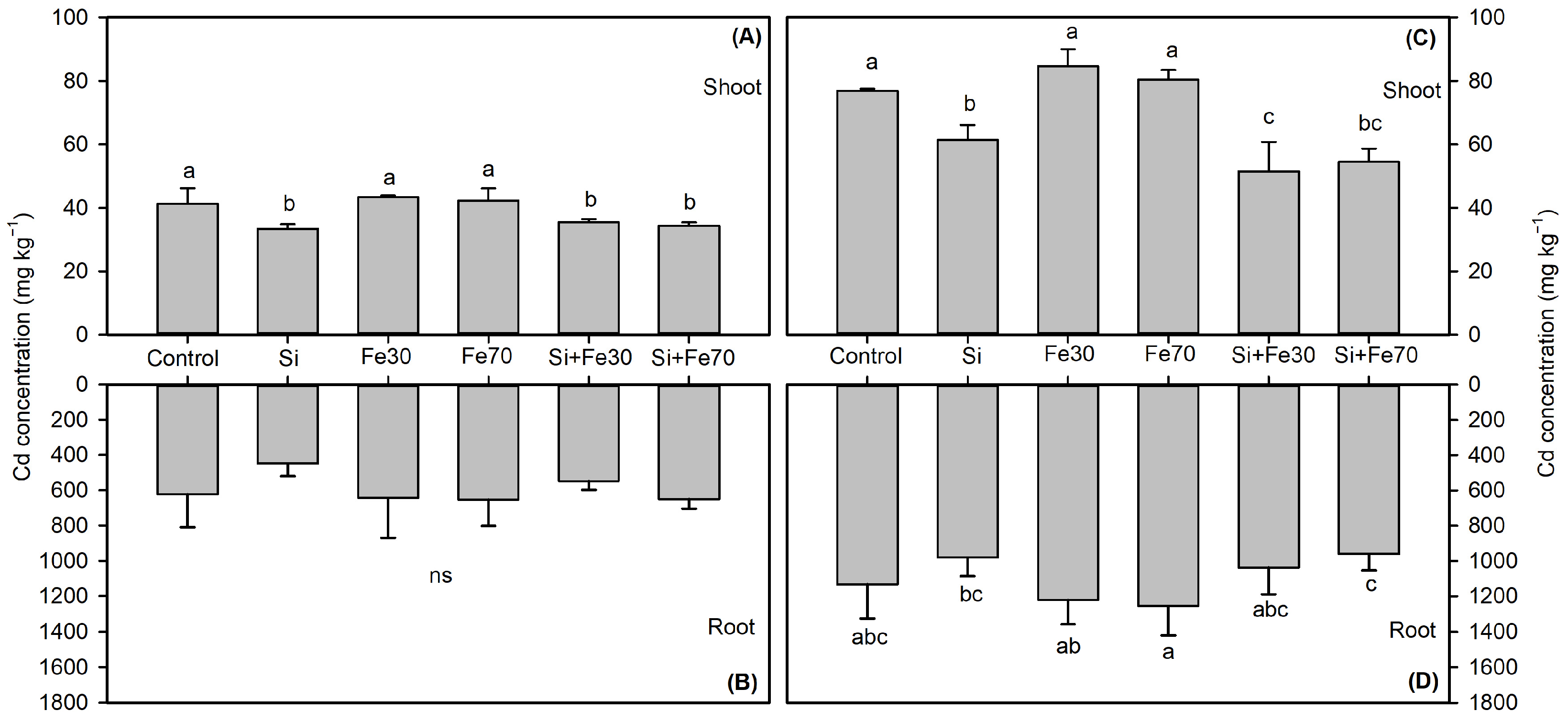
3.2.2. Cd Accumulation Heterogeneity
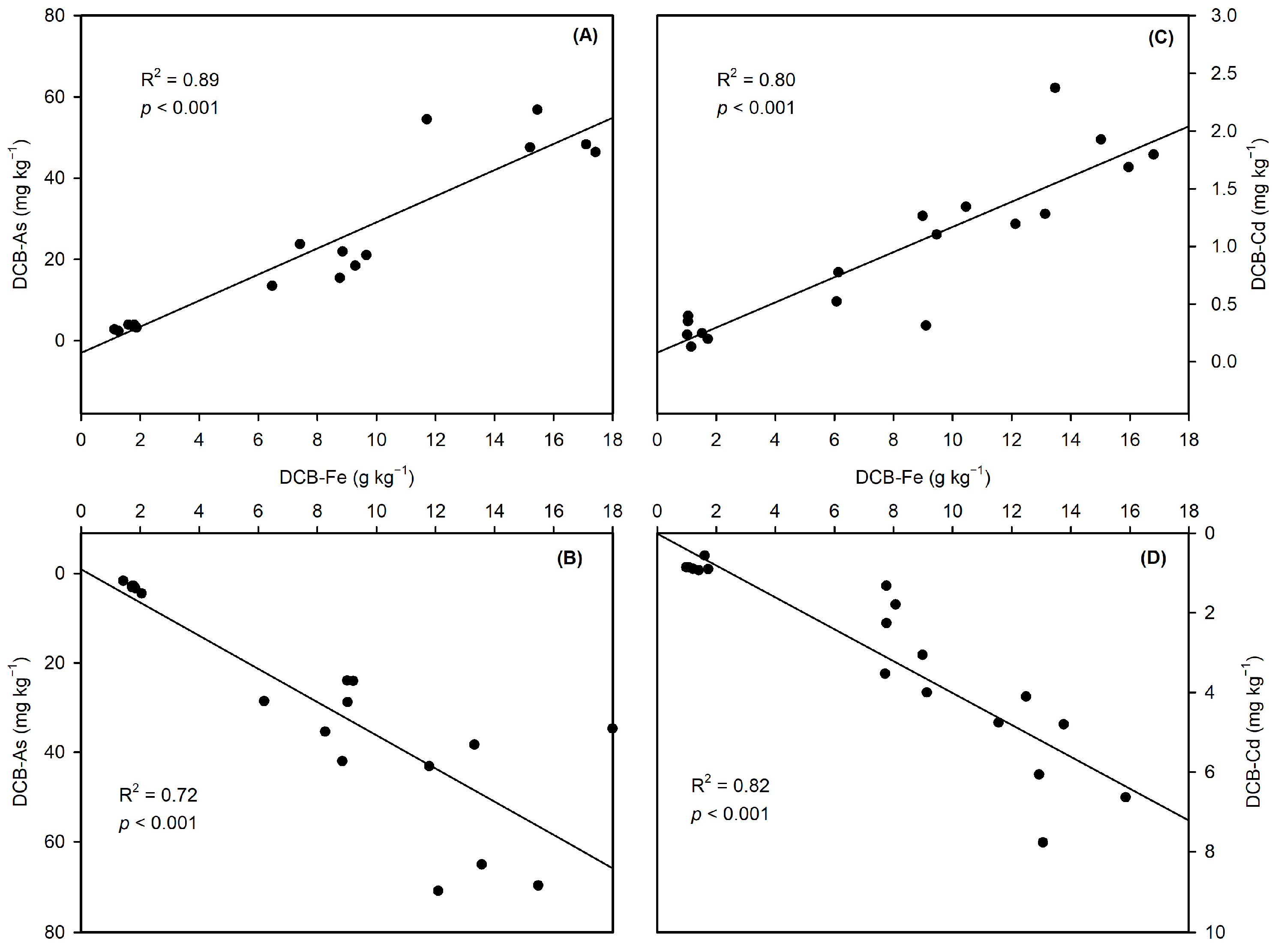
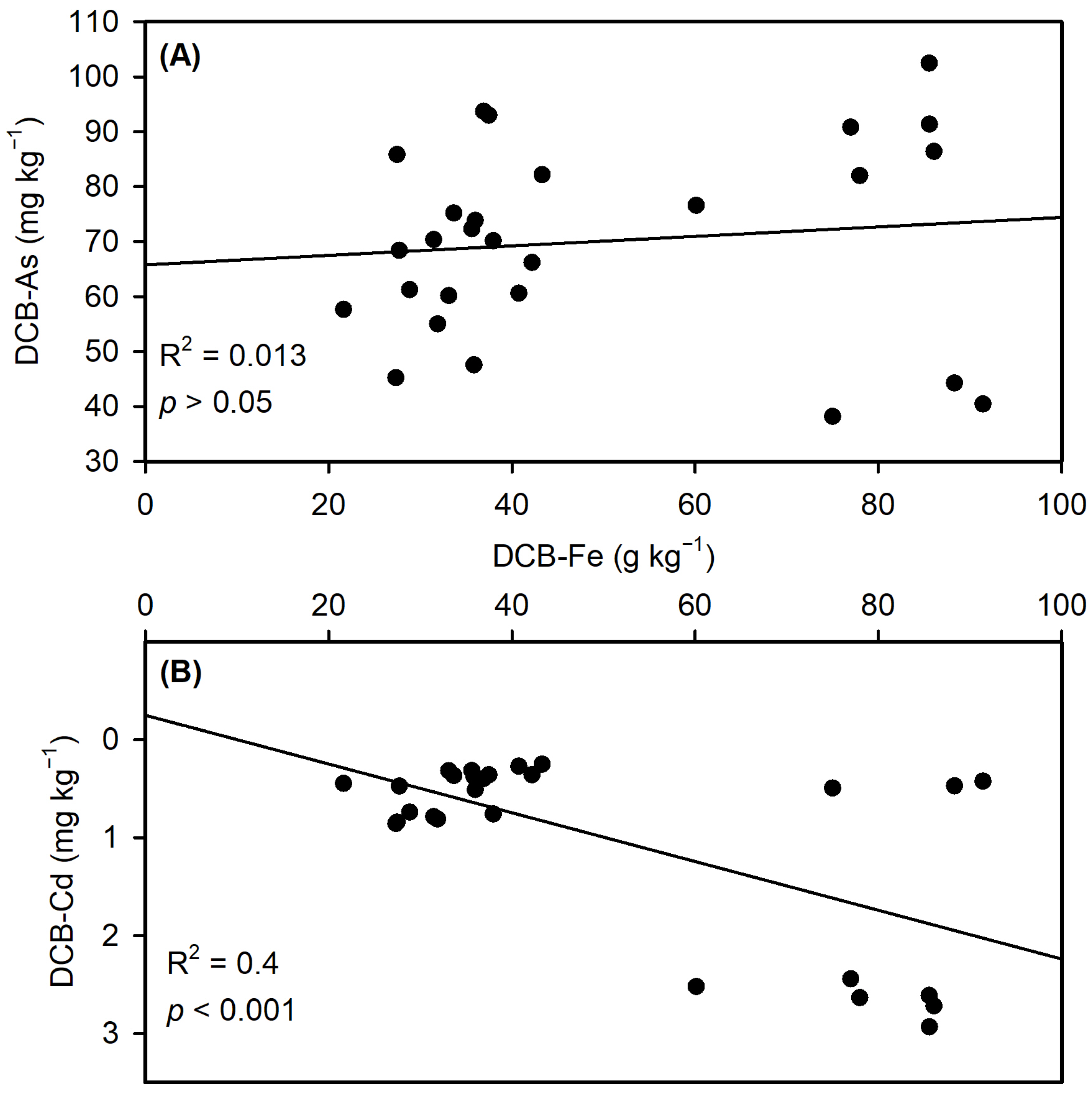
3.2.3. Iron Plaque-Mediated Metal(loid) Binding
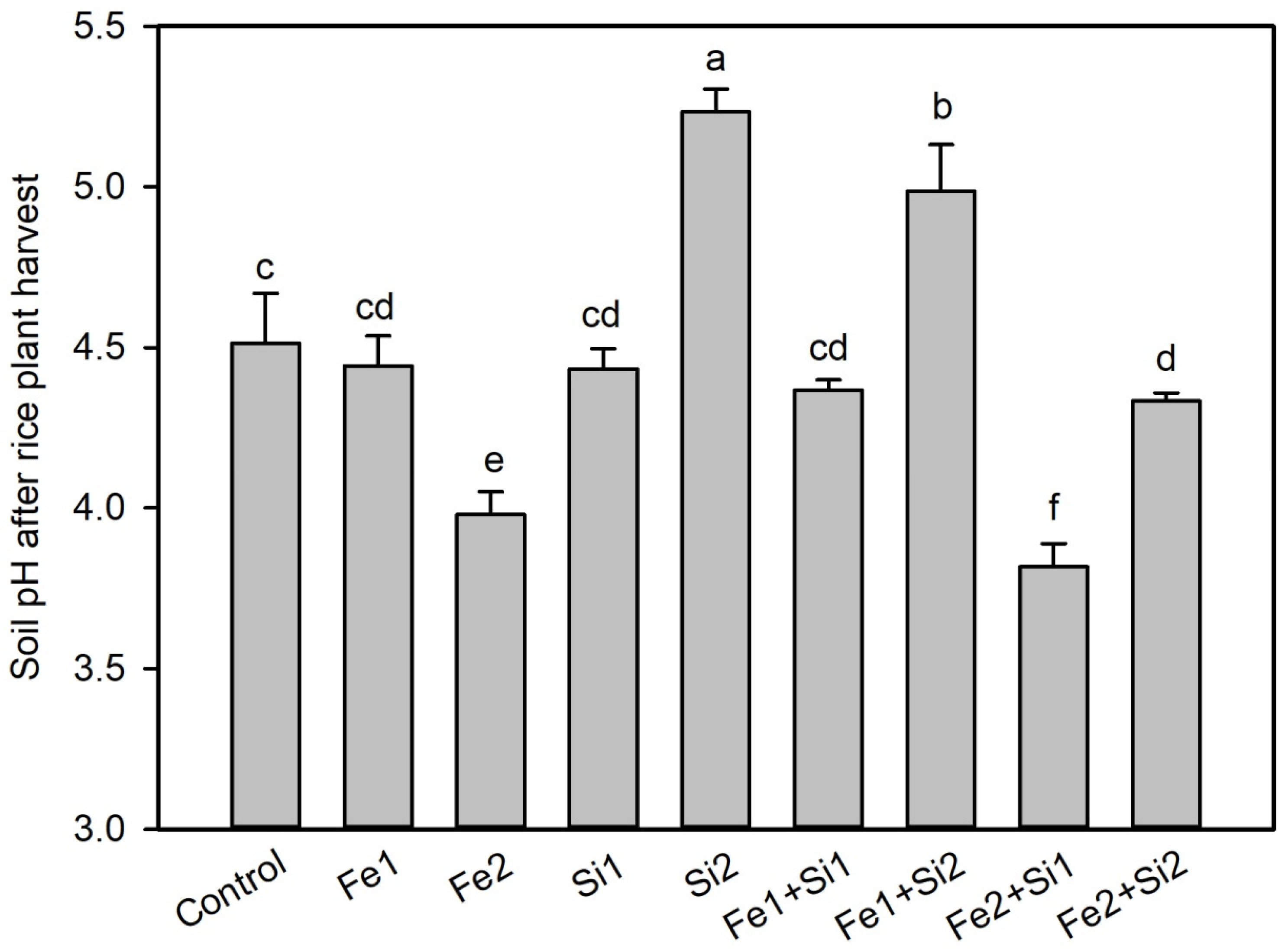
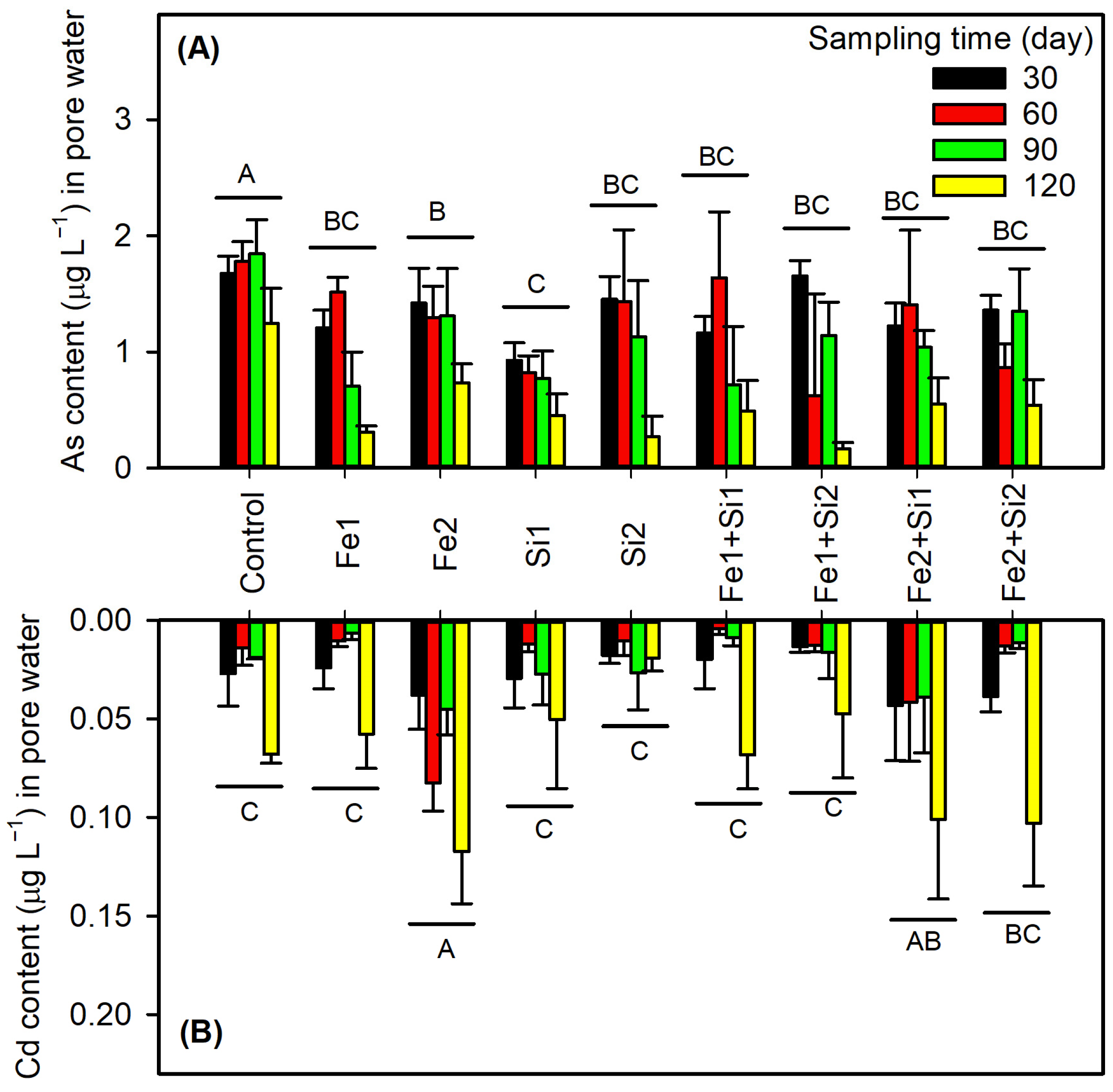
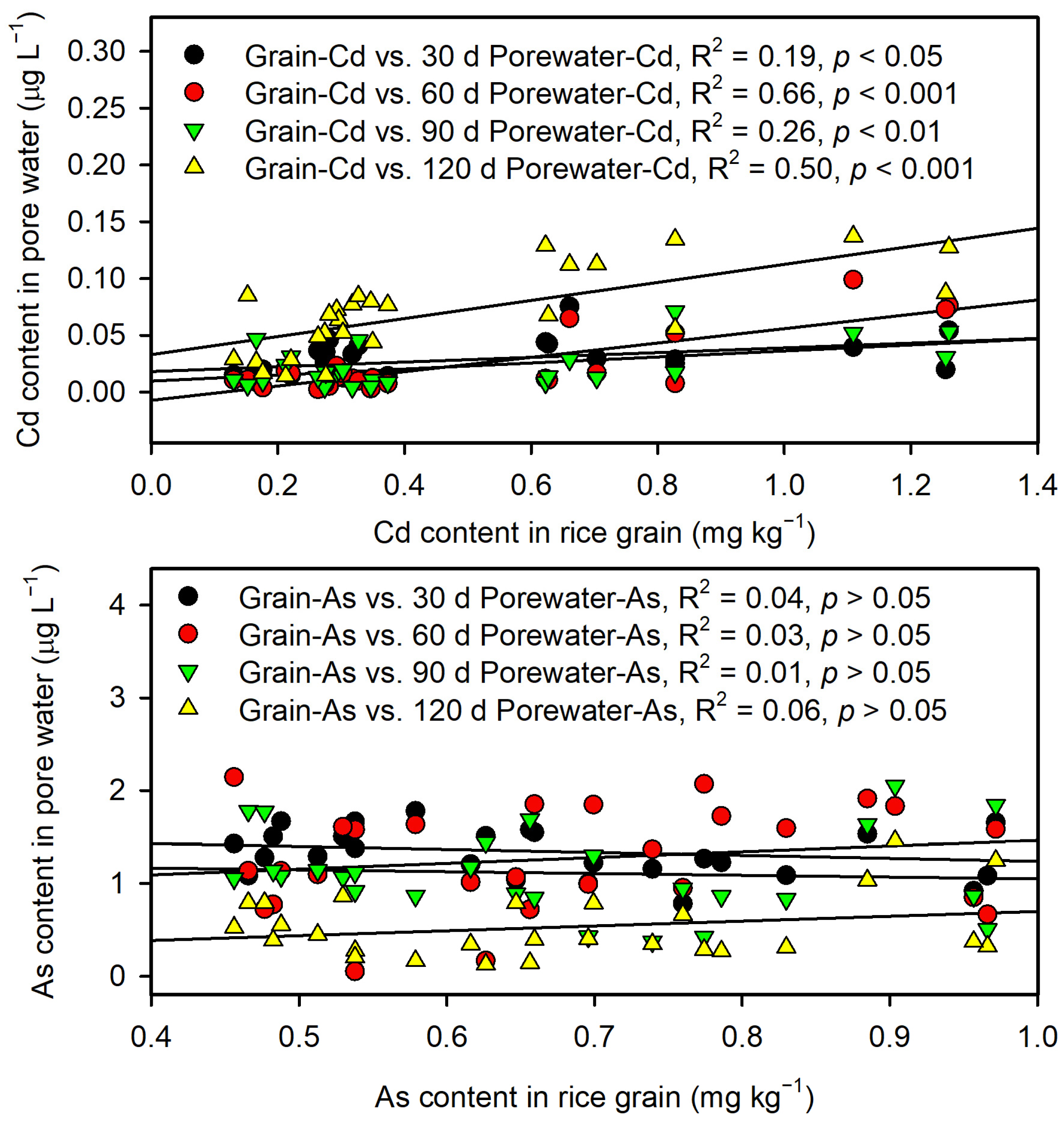
3.3. Changes in Soil pH and As and Cd in Pore Water
3.3.1. Dose-Dependent pH Regulation
3.3.2. Contrasting As/Cd Solubility Dynamics
4. Discussion
4.1. Interactive Effects of Si and Fe on Rice Growth Under As and Cd Stress
4.1.1. Phytotoxic Impacts of As/Cd Contamination
4.1.2. Si/Fe-Mediated Stress Alleviation Mechanisms
4.2. Si-Fe Interactions in Regulating As/Cd Accumulation
4.2.1. Si’s Tripartite Detoxification Pathway
4.2.2. FeSO4’s Dual-Phase Modulation of Element Mobility
4.2.3. Synergistic Si-Fe Effects and Nutritional Homeostasis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharafi, S.; Salehi, F. Comprehensive assessment of heavy metal (HMs) contamination and associated health risks in agricultural soils and groundwater proximal to industrial sites. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, D.; Jia, X.; Wang, L.; McGrath, S.P.; Zhu, Y.G.; Hu, Q.; Zhao, F.J.; Bank, M.S.; O’Connor, D.; Nriagu, J. Global soil pollution by toxic metals threatens agriculture and human health. Science 2025, 388, 316–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, T.; Wu, T.; Zhou, T.; Li, Z.; Ouyang, Y.; Jiang, J.; Zhu, D.; Hou, J.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; et al. Geographical variation in arsenic, cadmium, and lead of soils and rice in the major rice producing regions of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 677, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Islam, M.S.; Islam, A.R.M.T.; Phoungthong, K.; Ustaoğlu, F.; Tokatli, C.; Ahmed, R.; Ibrahim, K.A.; Idris, A.M. Potentially toxic elements in vegetable and rice species in Bangladesh and their exposure assessment. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 106, 104350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Shin, D.Y.; Jang, Y.; Han, J.P.; Cho, E.M.; Seo, Y.R. Cadmium-induced carcinogenesis in respiratory organs and the prostate: Insights from three perspectives on toxicogenomic approach. J. Cancer Prev. 2023, 28, 150–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasmi, S.; Moser, L.; Gonvers, S.; Dormond, O.; Demartines, N.; Labgaa, I. Carcinogenic effect of arsenic in digestive cancers: A systematic review. Environ. Health Glob. 2023, 22, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, F.; Sun, Z.; You, L.; Müller, D. Determinants of changes in harvested area and yields of major crops in China. Food Secur. 2024, 16, 339–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.J.; Zhou, D.M. Foreword. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2018, 37, 1316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J.P. Efforts to build a modernization with harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. Xinchangzheng 2022, 9, 4–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhou, T.; Wu, Y.; Tan, Z. A Review of the electrochemical coupled leaching technique: An effective solution for remediation of heavy metal contaminated soils. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 262, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Chen, B.; Yang, F.; Han, T.; Zeng, R.; Lei, L.; Liu, S. A review of research progress on prevention and control technologies for arsenic and cadmium composite pollution in paddy soil. Environ. Sci. Adv. 2025, 4, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.M.; Wang, S.Q.; Xie, S.T.; Li, G.; Sun, G.X. Optimal soil Eh, pH for simultaneous decrease of bioavailable Cd, As in co-contaminated paddy soil under water management strategies. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.Y.; McGrath, S.P.; Meharg, A.A.; Zhao, F.J. Growing rice aerobically markedly decreases arsenic accumulation. Environ Sci Technol 2008, 42, 5574–5579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, C.; Zhou, Z.; Tang, X.; He, L.; Li, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, X. Impact of iron and sulfur cycling on the bioavailability of cadmium and arsenic in co-contaminated paddy soil. J Hazard Mater 2024, 465, 133408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, M.; Guo, L.; Yang, D.; He, N.; Ying, B.; Wang, Y. Influence of silicon on cadmium availability and cadmium uptake by rice in acid and alkaline paddy soils. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2343–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mišúthová, A.; Slováková, Ľ.; Kollárová, K.; Vaculík, M. Effect of silicon on root growth, ionomics and antioxidant performance of maize roots exposed to As toxicity. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2021, 168, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.X.; Zhang, L.; Chen, P.; Yao, B.M. Silicon fertilizers mitigate rice cadmium and arsenic uptake in a 4-year field trial. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Huang, H.H.; Syu, C.H.; Lin, T.H.; Lee, D.Y. Increase of As release and phytotoxicity to rice seedlings in As-contaminated paddy soils by Si fertilizer application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.; Seshadri, B.; Bolan, N.; Saint, C.P.; Kirkham, M.B.; Chowdhury, S.; Yamaguchi, N.; Lee, D.Y.; Li, G.; Kunhikrishnan, A.; et al. Root iron plaque on wetland plants as a dynamic pool of nutrients and contaminants. Adv. Agron. 2016, 138, 1–96. [Google Scholar]
- Panthri, M.; Gupta, M. An insight into the act of iron to impede arsenic toxicity in paddy agro-system. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 316, 115289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X.; Luo, T.; Chen, Y. Removal of cadmium and arsenic from Cd-As-Pb-bearing dust based on peroxide leaching and coprecipitation. Hydrometallurgy 2022, 209, 105839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.J.; Crowder, A.A. Use of the DCB technique for extraction of hydrous iron-oxides from roots of wetland plants. Am. J. Bot. 1983, 70, 1254–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.Y.; Guo, X.D.; Luo, Z.Q.; Ding, J.; Xu, B.; Chen, H.Y.; Zheng, C.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, G. Do brassinosteroids and iron plaque affect the accumulation of As and Cd in rice (Oryza sativa L.)? Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 23, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Chen, J.Y.; Yu, J.Y.; Guo, Y.Y.; Cai, Q.Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Xie, T.H.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, G. Effects of 24-epibrassinolide and 28-homobrassinolide on iron plaque formation and the uptake of As and Cd by rice seedlings (Oryza sativa L.) in solution culture. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 101660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.H.; Sun, H.H.; Wang, S.F.; Luo, J.; Ma, L.N.Q. Interactive effects of mercury and arsenic on their uptake, speciation and toxicity in rice seedling. Chemosphere 2014, 117, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Gao, M.; Song, Z.; Qiu, W. Microplastic particles increase arsenic toxicity to rice seedlings. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 259, 113892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Lin, L.; Li, F.J.; Han, Y.; Song, Z.G. Reduction of arsenic toxicity in two rice cultivar seedlings by different nanoparticles. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Nhung, N.T.H.; Dodbiba, G.; Fujita, T. Mitigation of arsenic accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings by oxygen nanobubbles in hydroponic cultures. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 268, 115700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yang, X.; Shen, H. Root iron plaque alleviates cadmium toxicity to rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 161, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, G.; Fang, Q.; Lu, H.; Hu, H. Calcium Decreases Cadmium concentration in root but facilitates cadmium translocation from root to shoot in rice. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, U.; Zhong, M.; Shar, T.; Fiaz, S.; Xie, L.; Jiao, G.; Ahmad, S.; Sheng, Z.; Tang, S.; Wei, X.; et al. The influence of pH on cadmium accumulation in seedlings of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 930–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wairich, A.; Aung, M.S.; Ricachenevsky, F.K.; Masuda, H. You can’t always get as much iron as you want: How rice plants deal with excess of an essential nutrient. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1381856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavinsky, A.O.; Detmann, K.C.; Reis, J.V.; Ávila, R.T.; Sanglard, M.L.; Pereira, L.F.; Sanglard, L.M.V.P.; Rodrigues, F.A.; Araújo, W.L.; DaMatta, F.M. Silicon improves rice grain yield and photosynthesis specifically when supplied during the reproductive growth stage. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 206, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Feng, A.; Liu, N.; Jiang, Z.; Wei, S. Silicon application improved the yield and nutritional quality while reduced cadmium concentration in rice. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 20370–20379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, M.S.; Sanglard, L.M.V.P.; Barbosa, M.L.; Namorato, F.A.; de Melo, D.C.; Franco, W.C.G.; Pérez-Molina, J.P.; Martins, S.C.V.; DaMatta, F.M. Silicon nutrition mitigates the negative impacts of iron toxicity on rice photosynthesis and grain yield. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 189, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaga, G.; Edema RAsea, G. Tolerance of rice germplasm to iron toxicity stress and the relationship between tolerance, Fe2+, P and K content in the leaves and roots. Arch. Agron. Soil. Sci. 2013, 59, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, J.L.; Christie, P.; Zhang, F.S. Influence of iron plaque on uptake and accumulation of Cd by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings grown in soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 394, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, F.; Zhang, Q.H.; Lan, Q.Q.; Liu, C.Y.; Guo, X.; Cai, Q.Y.; Chen, Y.H.; Wang, G.; Ding, J. Influence of iron plaque on the uptake and accumulation of chromium by rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings: Insights from hydroponic and soil cultivation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 162, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talukdar, P.; Hartley, S.E.; Travis, A.J.; Price, A.H.; Norton, G.J. Genotypic differences in shoot silicon concentration and the impact on grain arsenic concentration in rice. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2019, 182, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, J.F.; Che, J.; Yamaji, N.; Shen, R.F.; Ma, J.F. Silicon reduces cadmium accumulation by suppressing expression of transporter genes involved in cadmium uptake and translocation in rice. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 5641–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Chai, G.; Lu, M.; Xiao, R.; Xie, Q.; Luo, L. A new insight into the role of iron plaque in arsenic and cadmium accumulation in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 254, 114714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Yin, G.; Chen, Z.; Lin, Q.; Huang, R.; Liu, D.; Peng, H.; Huang, L.; Wang, X.; Jiang, X. Influencing mechanism of Eh, pH and iron on the release of arsenic in paddy soil (in Chinese). Environ. Sci. 2017, 38, 2530–2537. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Wang, P.-M.; Gu, Y.; Kopittke, P.M.; Zhao, F.-J.; Wang, P. Iron–Manganese (Oxyhydro)oxides, Rather than Oxidation of Sulfides, Determine Mobilization of Cd during Soil Drainage in Paddy Soil Systems. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 2500–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixit, S.; Hering, J.G. Comparison of arsenic(V) and arsenic(III) sorption onto iron oxide minerals: implications for arsenic mobility. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4182–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Ji, X.; Chen, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ji, S.; Wang, X.; Pan, S. Silicon facilitated the physical barrier and adsorption of cadmium of iron plaque by changing the biochemical composition to reduce cadmium absorption of rice roots. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 256, 114879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, M.A.; James, B.; Chen, Y.H.; Ahmed Saqib, H.S.; Li, H.H.; Jayasuriya, P.; Guo, W. Uptake, translocation, and accumulation of Cd and its interaction with mineral nutrients (Fe, Zn, Ni, Ca, Mg) in upland rice. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 916–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabagala, F.S.; Zhang, T.; Zeng, X.; He, C.; Shan, H.; Qiu, C.; Gao, X.; Zhang, N.; Su, S. A review of amendments for simultaneously reducing Cd and As availability in paddy soils and rice grain based on meta-analysis. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchelt, A.C.; Teixeira, G.C.M.; Oliveira, K.S.; Rocha, A.M.S.; de Mello Prado, R.; Caione, G. Silicon contribution via nutrient solution in forage plants to mitigate nitrogen, potassium, calcium, magnesium, and sulfur deficiency. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2020, 20, 1532–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Treatments | Root (g pot−1) | Straw (g pot−1) | Grain (g pot−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.48 ± 1.03 cd | 44.8 ± 22.8 cd | 4.17 ± 1.45 bc |
| Fe1 | 1.36 ± 0.60 cd | 43.7 ± 13.0 cd | 2.75 ± 0.53 c |
| Fe2 | 1.43 ± 0.46 cd | 45.2 ± 9.74 cd | 3.02 ± 0.35 c |
| Si1 | 2.23 ± 0.11 abc | 63.3 ± 6.18 abc | 6.94 ± 1.59 a |
| Si2 | 2.63 ± 0.14 ab | 66.6 ± 8.43 ab | 5.56 ± 1.27 ab |
| Fe1 + Si1 | 1.41 ± 0.45 cd | 41.6 ± 7.74 d | 3.24 ± 0.27 c |
| Fe1 + Si2 | 2.79 ± 0.98 a | 73.1 ± 15.5 a | 6.41 ± 1.78 a |
| Fe2 + Si1 | 1.69 ± 0.26 bcd | 52.5 ± 8.22 d | 2.79 ± 0.15 c |
| Fe2 + Si2 | 1.19 ± 0.18 d | 36.5 ± 4.25 bcd | 2.48 ± 0.15 c |
| F value | 3.24 | 3.44 | 7.97 |
| P | <0.05 | <0.05 | <0.0005 |
| Treatments | Root (mg kg−1) | Straw (mg kg−1) | Grain (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 211 ± 48.1 a | 19.5 ± 4.38 a | 0.92 ± 0.05 a |
| Fe1 | 147 ± 57.3 ab | 16.2 ± 2.30 ab | 0.70 ± 0.15 bc |
| Fe2 | 138 ± 56.8 ab | 11.8 ± 1.12 cd | 0.49 ± 0.03 d |
| Si1 | 109 ± 69.0 b | 14.5 ± 1.90 bc | 0.89 ± 0.12 a |
| Si2 | 179 ± 47.9 ab | 12.8 ± 1.12 bcd | 0.70 ± 0.07 bc |
| Fe1 + Si1 | 130 ± 28.4 b | 19.4 ± 2.22 a | 0.72 ± 0.04 b |
| Fe1 + Si2 | 148 ± 33.3 ab | 12.2 ± 0.49 bcd | 0.58 ± 0.04 cd |
| Fe2 + Si1 | 118 ± 29.5 b | 9.94 ± 1.35 d | 0.57 ± 0.10 cd |
| Fe2 + Si2 | 163 ± 28.2 ab | 15.0 ± 3.48 bc | 0.49 ± 0.02 d |
| F value | 1.38 | 6.00 | 11.3 |
| P | 0.27 | <0.001 | <0.0001 |
| Treatments | Root (mg kg−1) | Straw (mg kg−1) | Grain (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 1.88 ± 0.03 abc | 0.30 ± 0.02 b | 0.29 ± 0.01 d |
| Fe1 | 1.49 ± 0.24 bc | 0.19 ± 0.04 b | 0.31 ± 0.04 d |
| Fe2 | 2.59 ± 0.35 a | 0.91 ± 0.05 a | 1.21 ± 0.09 a |
| Si1 | 1.33 ± 0.35 bc | 0.26 ± 0.11 b | 0.30 ± 0.03 d |
| Si2 | 1.98 ± 0.43 ab | 0.28 ± 0.07 b | 0.18 ± 0.02 e |
| Fe1 + Si1 | 1.02 ± 0.06 c | 0.19 ± 0.05 b | 0.33 ± 0.06 d |
| Fe1 + Si2 | 1.33 ± 0.35 bc | 0.27 ± 0.08 b | 0.17 ± 0.05 e |
| Fe2 + Si1 | 2.63 ± 0.57 a | 1.19 ± 0.60 a | 0.77 ± 0.10 b |
| Fe2 + Si2 | 2.69 ± 1.18 a | 0.81 ± 0.44 a | 0.65 ± 0.05 c |
| F value | 4.67 | 6.65 | 118 |
| P | <0.005 | <0.0005 | <0.0001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, Y.; Guo, X.; Chen, J.; Liu, Z.; Cai, Q.; Yu, J.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, H.; Xu, B.; et al. Synergistic Effects of Silicon and Ferrous Sulfate on Reducing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice from Co-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061422
You Y, Guo X, Chen J, Liu Z, Cai Q, Yu J, Zhu W, Wang Y, Chen H, Xu B, et al. Synergistic Effects of Silicon and Ferrous Sulfate on Reducing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice from Co-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061422
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Yanlin, Xiaodong Guo, Jianyu Chen, Zhiqin Liu, Qiuying Cai, Jinyong Yu, Wanli Zhu, Yuna Wang, Hanyue Chen, Bo Xu, and et al. 2025. "Synergistic Effects of Silicon and Ferrous Sulfate on Reducing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice from Co-Contaminated Soil" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061422
APA StyleYou, Y., Guo, X., Chen, J., Liu, Z., Cai, Q., Yu, J., Zhu, W., Wang, Y., Chen, H., Xu, B., Chen, Y., & Wang, G. (2025). Synergistic Effects of Silicon and Ferrous Sulfate on Reducing Arsenic and Cadmium Accumulation in Rice from Co-Contaminated Soil. Agronomy, 15(6), 1422. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061422





