Comparison of Main Agronomic Traits and Identification of Important Genes in Japonica Rice Cultivars Grown in the Jianghuai Region
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Field Trials
2.3. Data Collection
2.4. Analysis of Molecular Markers
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
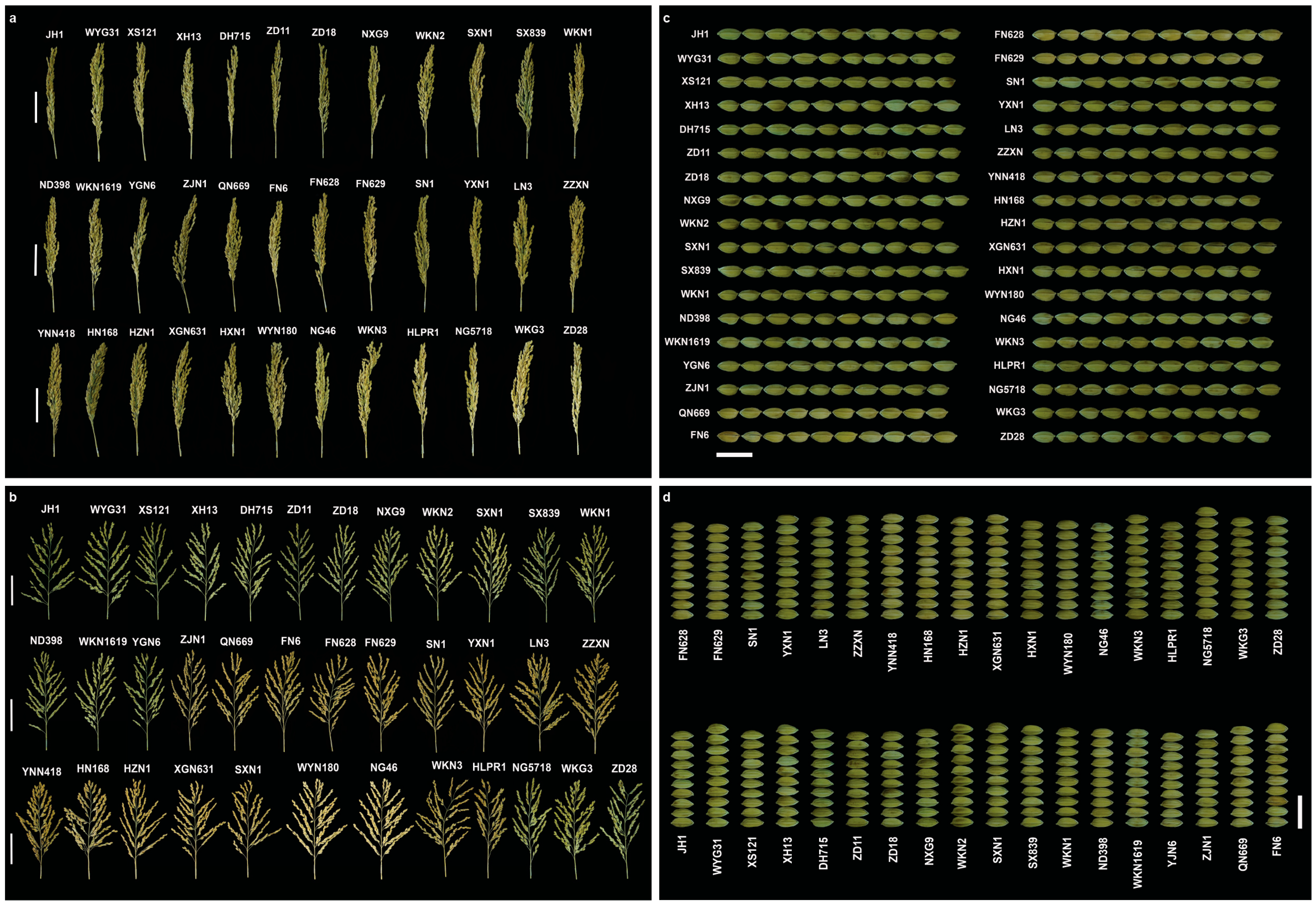
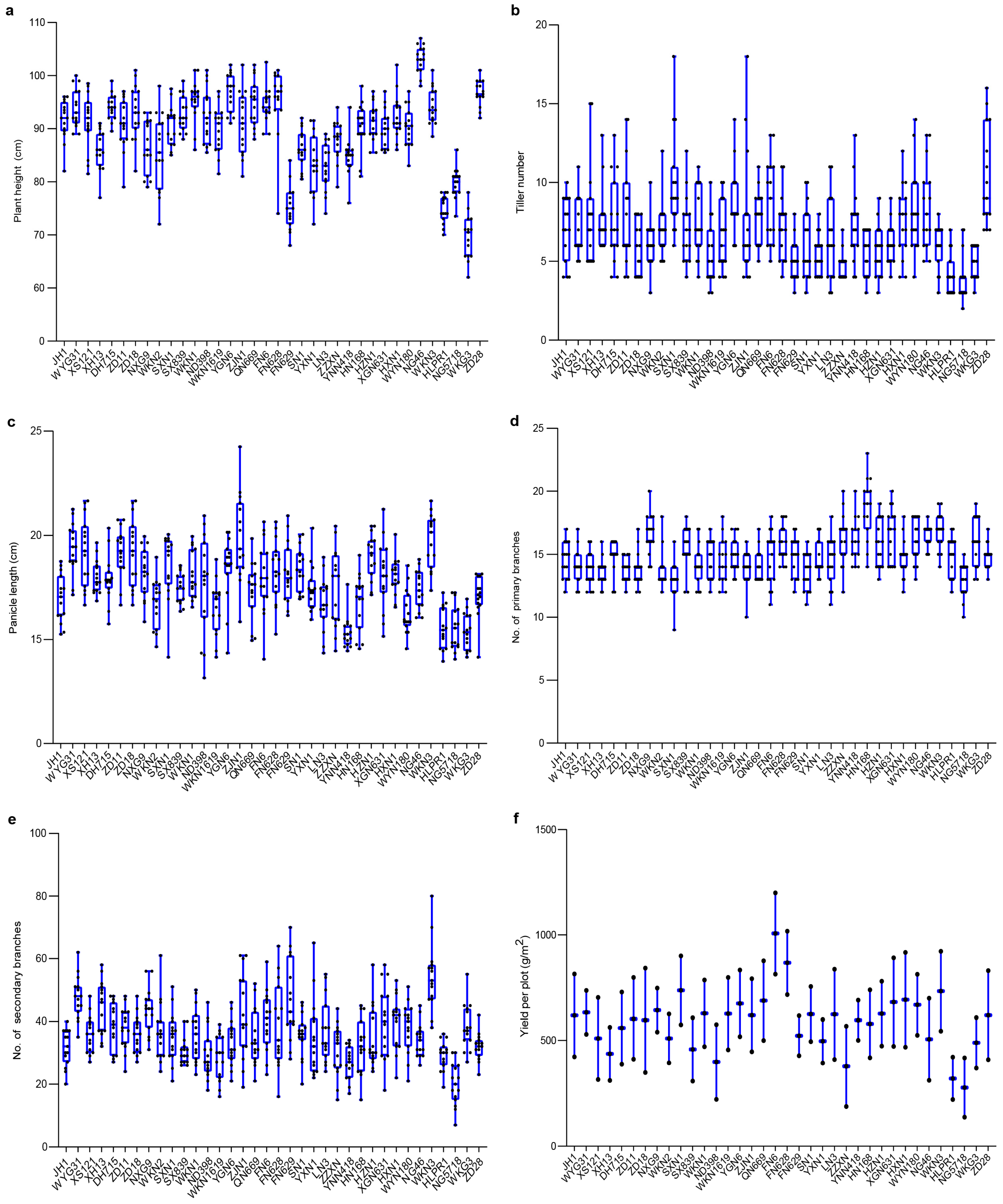
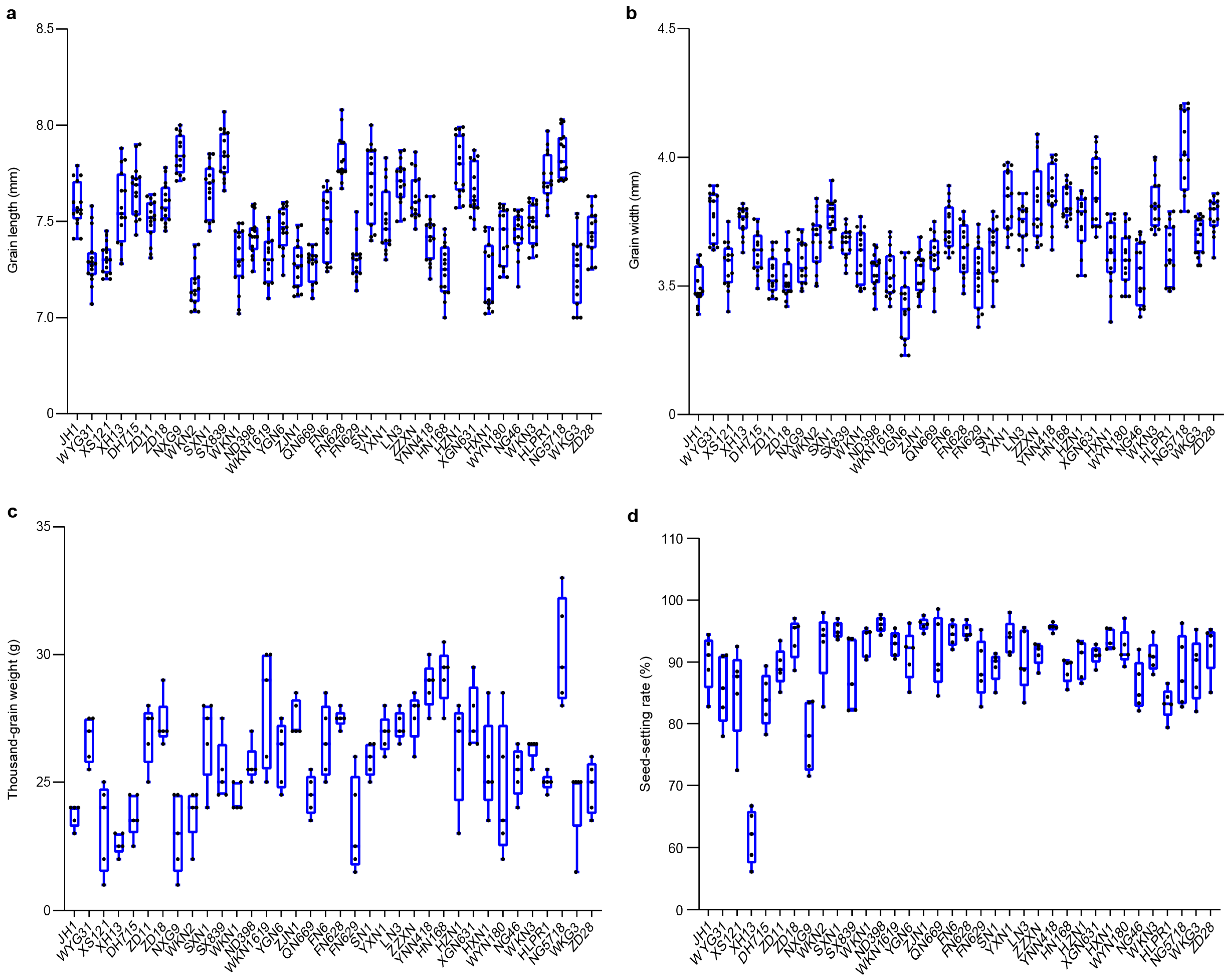
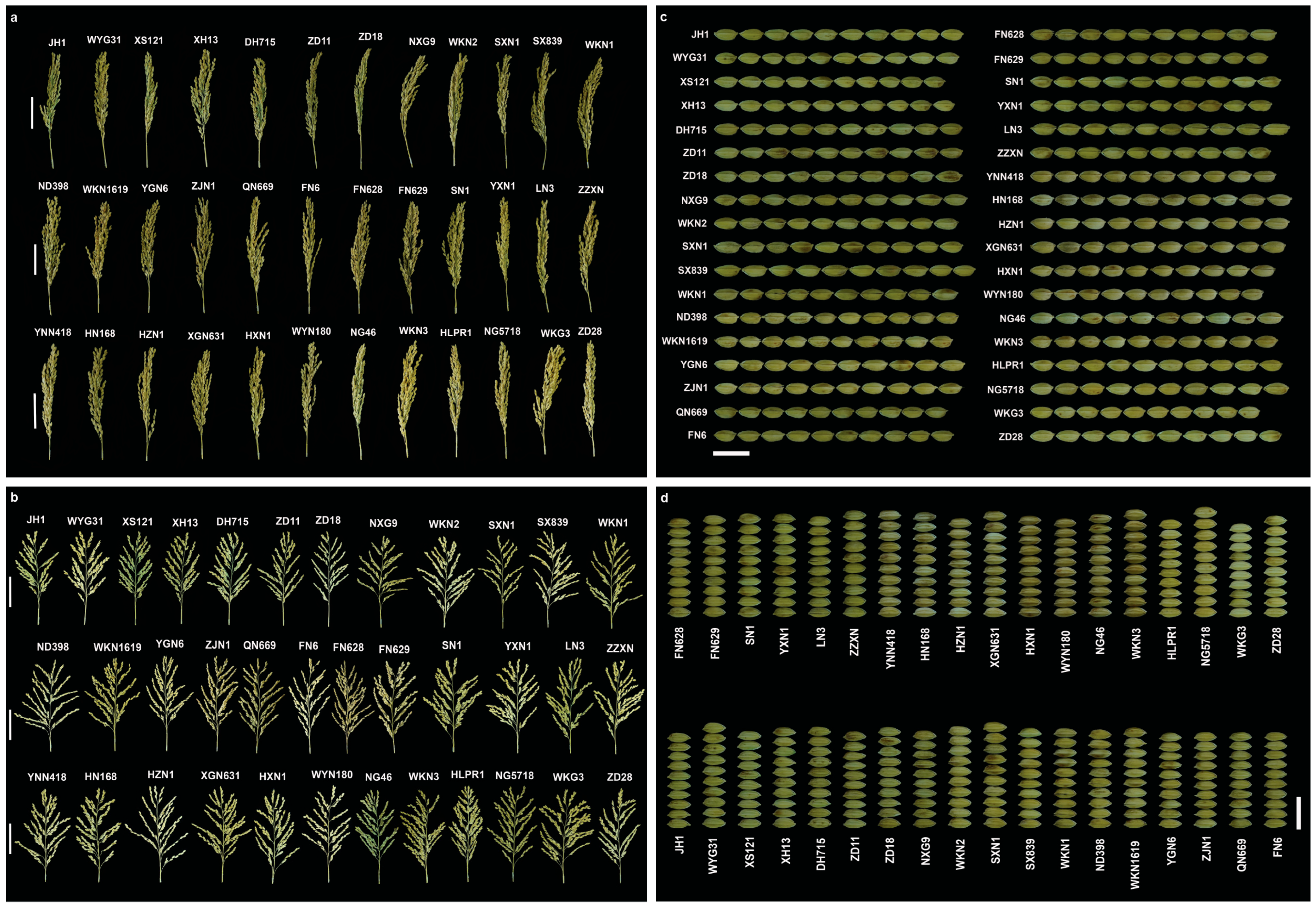
3.1. Variation in Agronomic Traits Under Different Environmental Conditions
3.1.1. Variation in Agronomic Traits in Fengyang
3.1.2. Variation in Agronomic Traits in Hexian Rice Fields
3.2. Trait Variation and Distribution Patterns in Fengyang and Hexian
3.3. Comparative Analysis of Agronomic Traits Between Fengyang and Hexian Rice Fields
3.4. Trait Relationships Between Fengyang and Hexian
3.5. PCR Analysis of Japonica Cultivars
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of Trait Variability and Distribution
4.2. Influence of Environment on Trait Expression
4.3. Correlation Analysis
4.4. Molecular Characterization and Gene Detection
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mather, K.A.; Caicedo, A.L.; Polato, N.R.; Olsen, K.M.; McCouch, S.; Purugganan, M.D. The Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 2007, 177, 2223–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proceedings of the FAO Rice Conference. Available online: https://www.fao.org/4/y5682e/y5682e0f.htm (accessed on 18 November 2024).
- Saud, S.; Wang, D.; Fahad, S.; Alharby, H.F.; Bamagoos, A.A.; Mjrashi, A.; Alabdallah, N.M.; AlZahrani, S.S.; AbdElgawad, H.; Adnan, M.; et al. Comprehensive Impacts of Climate Change on Rice Production and Adaptive Strategies in China. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 926059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.Z. The Conservation of Chinese Rice Biodiversity: Genetic Erosion, Ethnobotany and Prospects. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2003, 50, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panesar, P.S.; Kaur, S. Rice: Types and Composition. In Encyclopedia of Food and Health; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 646–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Shi, J.; Quan, S.; Cui, B.; Kleessen, S.; Nikoloski, Z.; Tohge, T.; Alexander, D.; Guo, L.; Lin, H.; et al. Metabolic Variation between Japonica and Indica Rice Cultivars as Revealed by Non-Targeted Metabolomics. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordero-Lara, K.I.; Cordero-Lara, K.I. Temperate Japonica Rice (Oryza sativa L.) Breeding: History, Present and Future Challenges. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 80, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Z.; Wu, H.; Wang, P. Spatiotemporal Variability in Precipitation Extremes in the Jianghuai Region of China and the Analysis of Its Circulation Features. Sustainability 2022, 14, 6680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Liu, C.; Cai, J.; Cao, N.; Liao, X.; Su, Q.; Jin, L.; Zheng, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L. The North–South Shift of the Ridge Location of the Western Pacific Subtropical High and Its Influence on the July Precipitation in the Jianghuai Region from 1978 to 2021. Front. Earth Sci. 2023, 11, 1251294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, N.; Ling, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fahad, S.; Peng, S.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, J. Influence of Temperature and Solar Radiation on Grain Yield and Quality in Irrigated Rice System. Eur. J. Agron. 2015, 64, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Zhu, S.; Cui, S.; Hou, H.; Wu, H.; Hao, B.; Cai, L.; Xu, Z.; Liu, L.; Jiang, L.; et al. Transcriptional and Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Heading Date in Rice. New Phytol. 2021, 230, 943–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molla, K.A. Flowering Time and Photoperiod Sensitivity in Rice: Key Players and Their Interactions Identified. Plant Cell 2022, 34, 3489–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jang, S.; Kim, B.; Piao, Z.; Redona, E.; Koh, H.-J. Evaluating Genotype × Environment Interactions of Yield Traits and Adaptability in Rice Cultivars Grown under Temperate, Subtropical and Tropical Environments. Agriculture 2021, 11, 558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Li, D.; Zhang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, L. Identification of Traits Contributing to High and Stable Yields in Different Soybean Varieties Across Three Chinese Latitudes. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Ma, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, X.; Liu, G.; Hu, Q.; Xu, F.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Quality Characteristics of Japonica Rice in Southern and Northern China and the Effect of Environments on Its Quality. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Xu, R.; Li, Y. Molecular Networks of Seed Size Control in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2019, 70, 435–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, S.; Asch, F.; Dusserre, J.; Ramanantsoanirina, A.; Brueck, H. Climate Effects on Yield Components as Affected by Genotypic Responses to Variable Environmental Conditions in Upland Rice Systems at Different Altitudes. Field Crops Res. 2012, 134, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Q.; Jia, Q.; Yin, W.; Wang, Y.; Rao, Y.; Mao, Y. Advances in Cloning Functional Genes for Rice Yield Traits and Molecular Design Breeding in China. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1206165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, B.L.; Zhao, Z. Archaeological and Genetic Insights into the Origins of Domesticated Rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 6190–6197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subudhi, P.K. Molecular Research in Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IRRI. The Standard Evaluation System for Rice; International Rice Research Institute: Luguna, Philippines, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, G.C.; Flores-Vergara, M.A.; Krasynanski, S.; Kumar, S.; Thompson, W.F. A Modified Protocol for Rapid DNA Isolation from Plant Tissues Using Cetyltrimethylammonium Bromide. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2320–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Qian, Q.; Liu, Z.; Sun, H.; He, S.; Luo, D.; Xia, G.; Chu, C.; Li, J.; Fu, X. Natural Variation at the DEP1 Locus Enhances Grain Yield in Rice. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 494–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Xing, Y.; Weng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Yu, S.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; et al. Natural Variation in Ghd7 Is an Important Regulator of Heading Date and Yield Potential in Rice. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Tian, Z.; Rao, Y.; Dong, G.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Leng, Y.; Xu, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, G.; et al. Rational Design of High-Yield and Superior-Quality Rice. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Fan, C.; Xing, Y.; Yun, P.; Luo, L.; Yan, B.; Peng, B.; Xie, W.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; et al. Chalk5 Encodes a Vacuolar H+-Translocating Pyrophosphatase Influencing Grain Chalkiness in Rice. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Luo, W.; Zheng, X.; Zeng, D.; Pan, Y.; Lin, X.; Liu, H.; Zhang, D.; et al. COLD1 Confers Chilling Tolerance in Rice. Cell 2015, 160, 1209–1221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.Y.; Chao, D.Y.; Gao, J.P.; Zhu, M.Z.; Shi, M.; Lin, H.X. A Previously Unknown Zinc Finger Protein, DST, Regulates Drought and Salt Tolerance in Rice via Stomatal Aperture Control. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1805–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Fu, B.; Yang, H.; Xu, C.; Li, Z.; Sanchez, A.; Park, Y.J.; Bennetzen, J.L.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S. Targeting Xa13, a Recessive Gene for Bacterial Blight Resistance in Rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 112, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fan, F.; He, S.; Guo, Y.; Chen, G.; Li, N.; Li, N.; Yuan, H.; Si, F.; Yang, F.; et al. Creation of Elite Rice with High-Yield, Superior-Quality and High Resistance to Brown Planthopper Based on Molecular Design. Rice 2022, 15, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Hassan, M.A.; Xu, E.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhan, X.; Ni, D.; Zhang, P. Evaluation of Breeding Progress and Agronomic Traits for Japonica Rice in Anhui Province, China (2005–2024). Agronomy 2024, 14, 2957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.-F.; Tang, F.-F.; Shao, Y.-F.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tong, C.; Bao, J.-S. Genotype × Environment Interactions for Agronomic Traits of Rice Revealed by Association Mapping. Rice Sci. 2014, 21, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Geng, X.; Xia, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q. Deciphering the Environmental Impacts on Rice Quality for Different Rice Cultivated Areas. Rice 2018, 11, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, M.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, X.; Peng, C.; Lu, X.; Zhang, M.; Jin, J. Effect of Drought on Agronomic Traits of Rice and Wheat: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig-Valiente, J.L.; Marqués, L.; Talón, M.; Domingo, C. Genome-Wide Association Study of Agronomic Traits in Rice Cultivated in Temperate Regions 06 Biological Sciences 0604 Genetics. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.R.; Mahmud, A.; Islam, M.N.; Ghosh, U.K.; Hossain, M.S. Genetic Variability and Agronomic Performances of Rice Genotypes in Different Growing Seasons in Bangladesh. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.J. Phenotypic Plasticity: From Theory and Genetics to Current and Future Challenges. Genetics 2020, 215, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitali, A.; Moretti, B.; Bertora, C.; Miniotti, E.F.; Tenni, D.; Romani, M.; Facchi, A.; Martin, M.; Fogliatto, S.; Vidotto, F.; et al. The Environmental and Agronomic Benefits and Trade-Offs Linked with the Adoption Alternate Wetting and Drying in Temperate Rice Paddies. Field Crops Res. 2024, 317, 109550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Ramón, H.; Ulzurrum, J.; Lidon, A.; Sanjuán, N. Assessing the Environmental Impacts of Rice in an Anthropized Mediterranean Wetland: Towards Carbon Farming. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2024, 45, 476–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muraleedharan, A. Utilizing Genetic Traits Distributions to Enhance Rice Breeding Programs: A Study of Skewness and Kurtosis in Segregating Generations. J. Exp. Agric. Int. 2024, 46, 741–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napier, J.D.; Heckman, R.W.; Juenger, T.E. Gene-by-Environment Interactions in Plants: Molecular Mechanisms, Environmental Drivers, and Adaptive Plasticity. Plant Cell 2022, 35, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aty, M.S.A.; Abo-Youssef, M.I.; Sorour, F.A.; Salem, M.; Gomma, M.A.; Ibrahim, O.M.; Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M.; Al-Qahtani, W.H.; Abdel-Maksoud, M.A.; El-Tahan, A.M. Performance and Stability for Grain Yield and Its Components of Some Rice Cultivars under Various Environments. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovi, M.R.; Bai, X.; Mao, D.; Xing, Y. Impact of Seasonal Changes on Spikelets per Panicle, Panicle Length and Plant Height in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 2011, 179, 319–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, R.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, S.; Zhang, H.; Wu, M.; Ye, M.; Zhang, Z. The Formation of Rice Tillers and Factors Influencing It. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Matsue, Y.; Xu, Q. Effects of Genetic Background and Environmental Conditions on Texture Properties in a Recombinant Inbred Population of an Inter-Subspecies Cross. Rice 2019, 12, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Zhang, T.; Lei, X.Y.; Cui, X.W.; Lu, Y.X.; Fan, P.F.; Long, S.P.; Huang, J.; Gao, J.S.; Zhang, Z.H.; et al. Improvement of Soil Fertility and Rice Yield after Long-Term Application of Cow Manure Combined with Inorganic Fertilizers. J. Integr. Agric. 2023, 22, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Mo, Z.; Lin, Q.; Pan, S.; Duan, M.; Tian, H.; Wang, S. Relationships between Grain Yield and Agronomic Traits of Rice in Southern China. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2019, 80, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbuma, N.W.; Gerrano, A.S.; Lebaka, N.; Labuschagne, M. Interrelationship between Grain Yield Components and Nutritional Quality Traits in Cowpea Genotypes. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2022, 150, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Khush, G.S.; Virk, P.; Tang, Q.; Zou, Y. Progress in Ideotype Breeding to Increase Rice Yield Potential. Field Crops Res. 2008, 108, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Eixarch, M.; del Mar Català, M.; Tomàs, N.; Pla, E.; Zhu, D. Tillering and Yield Formation of a Temperate Japonica Rice Cultivar in a Mediterranean Rice Agrosystem. Span. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 13, e0905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, W.; Abliz, B.; Xue, X. Increased Number of Spikelets per Panicle Is the Main Factor in Higher Yield of Transplanted vs. Direct-Seeded Rice. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.S.; Khaskheli, M.A.; Uzair, M.; Xu, Y.; Wattoo, F.M.; Rehman, O.U.; Amatus, G.; Fatima, H.; Khan, S.A.; Fiaz, S.; et al. Inquiring the Inter-Relationships amongst Grain-Filling, Grain-Yield, and Grain-Quality of Japonica Rice at High Latitudes of China. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 988256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Shan, S.; Cao, J.; Fang, S.; Tian, A.; Liu, Y.; Cao, F.; Yin, X.; Zou, Y. Primary-Tiller Panicle Number Is Critical to Achieving High Grain Yields in Machine-Transplanted Hybrid Rice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaitzidis, A.; Kadoglidou, K.; Mylonas, I.; Ghoghoberidze, S.; Ninou, E. Investigating the Impact of Tillering on Yield and Yield-Related Traits in European Rice Cultivars. Agriculture 2025, 15, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Łyskowski, A.; Jaremko, Ł.; Jaremko, M. Genetic and Molecular Factors Determining Grain Weight in Rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 605799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Z.; Xu, Q. The DENSE AND ERECT PANICLE 1 (DEP1) Gene Offering the Potential in the Breeding of High-Yielding Rice. Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, J.; Hu, Y.; Du, H.; Xu, C.; Xing, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Zhang, Q. Grain Number, Plant Height, and Heading Date7 Is a Central Regulator of Growth, Development, and Stress Response. Plant Physiol. 2014, 164, 735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gong, R.; Yang, Y.; Yu, S. Ghd8 controls rice photoperiod sensitivity by forming a complex that interacts with Ghd7. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Huang, M.; Zong, W.; Xiao, D.; Lei, C.; Luo, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, S.; Hao, Y.; Luo, W.; et al. Hd1, Ghd7, and DTH8 Synergistically Determine the Rice Heading Date and Yield-Related Agronomic Traits. J. Genet. Genom. 2022, 49, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, X.; Zheng, M.; Hu, R.; Dong, J.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Liu, D.; Yang, W. Genes Controlling Grain Chalkiness in Rice. Crop J. 2024, 12, 979–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, T.; Hua, Y.; Yan, X.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, R.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Assessment of the Characteristics of Waxy Rice Mutants Generated by CRISPR/Cas9. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 881964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Jiang, J.; Long, Y.; Wang, R.; Liang, F.; Liu, H.; Xu, J.; Qiu, X.; Li, Z. Generation of Two-Line Restorer Line with Low Chalkiness Using Knockout of Chalk5 through CRISPR/Cas9 Editing. Biology 2024, 13, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gann, P.J.I.; Dharwadker, D.; Cherati, S.R.; Vinzant, K.; Khodakovskaya, M.; Srivastava, V. Targeted Mutagenesis of the Vacuolar H+ Translocating Pyrophosphatase Gene Reduces Grain Chalkiness in Rice. Plant J. 2023, 115, 1261–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Aisha, S.; Malakar, A.; Perveen, K.; Alfagham, A.T.; Nisha Khanam, M.; Adawiyah Ahmad, R.; Pramanik, B.; Ahmed Mohammed, Y. Understanding the Cross-Talk of Major Abiotic-Stress-Responsive Genes in Rice: A Computational Biology Approach. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2023, 35, 102786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manishankar, P.; Kudla, J. Cold Tolerance Encoded in One SNP. Cell 2015, 160, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Wu, D.; Zhao, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, X.; Ouyang, Y.; Cai, B.; Liu, X.; Jing, S.; et al. Bph6 Encodes an Exocyst-Localized Protein and Confers Broad Resistance to Planthoppers in Rice. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
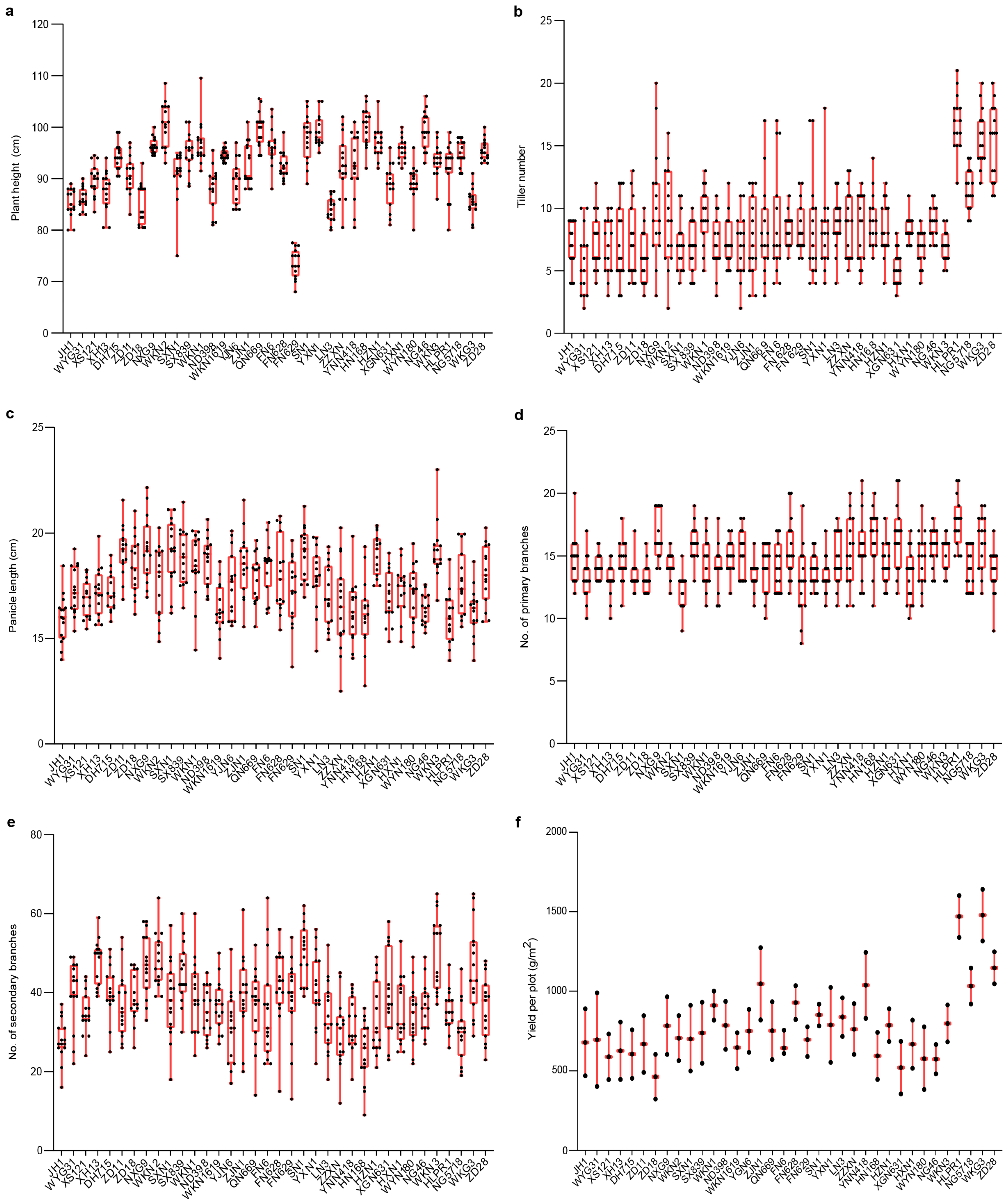
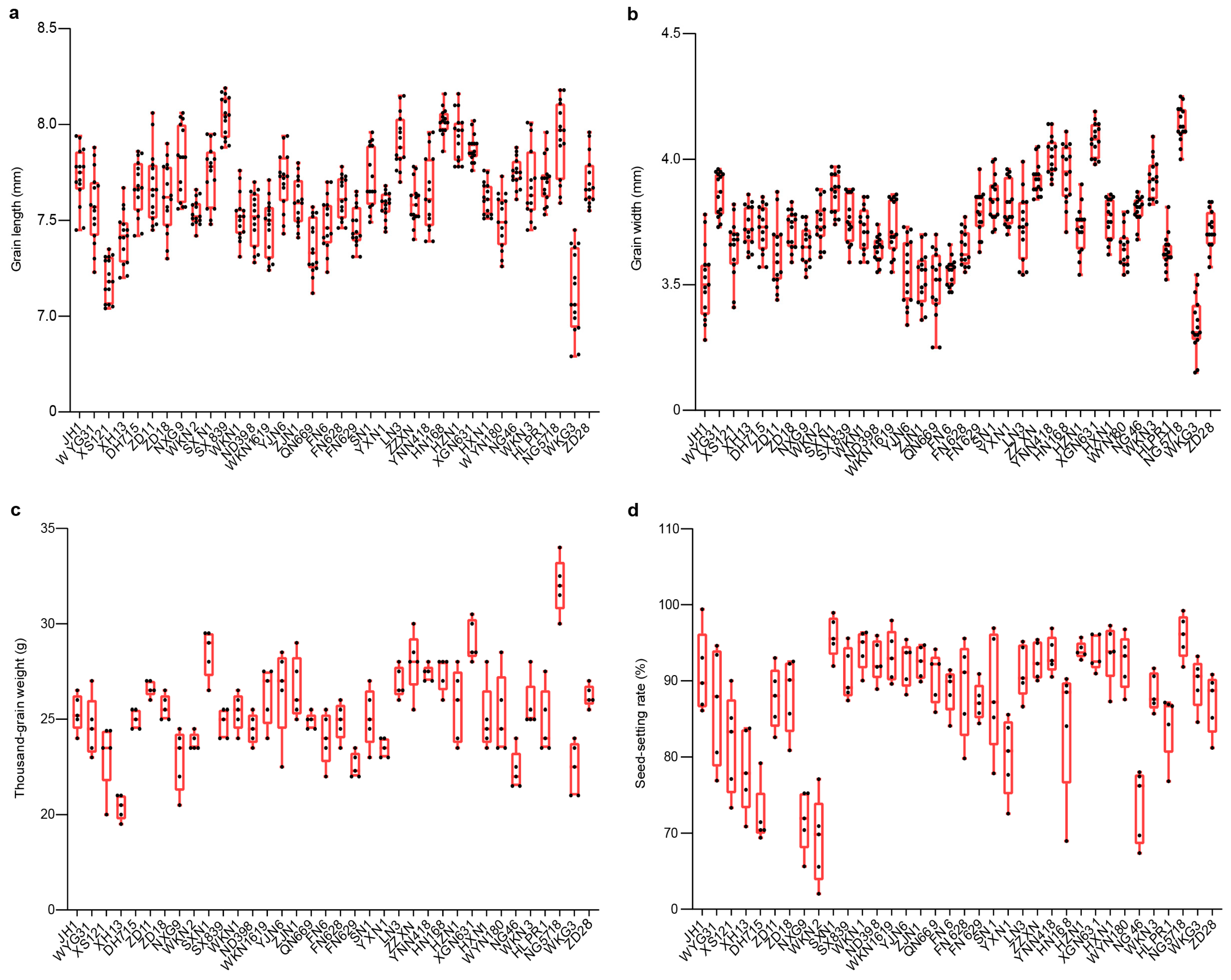
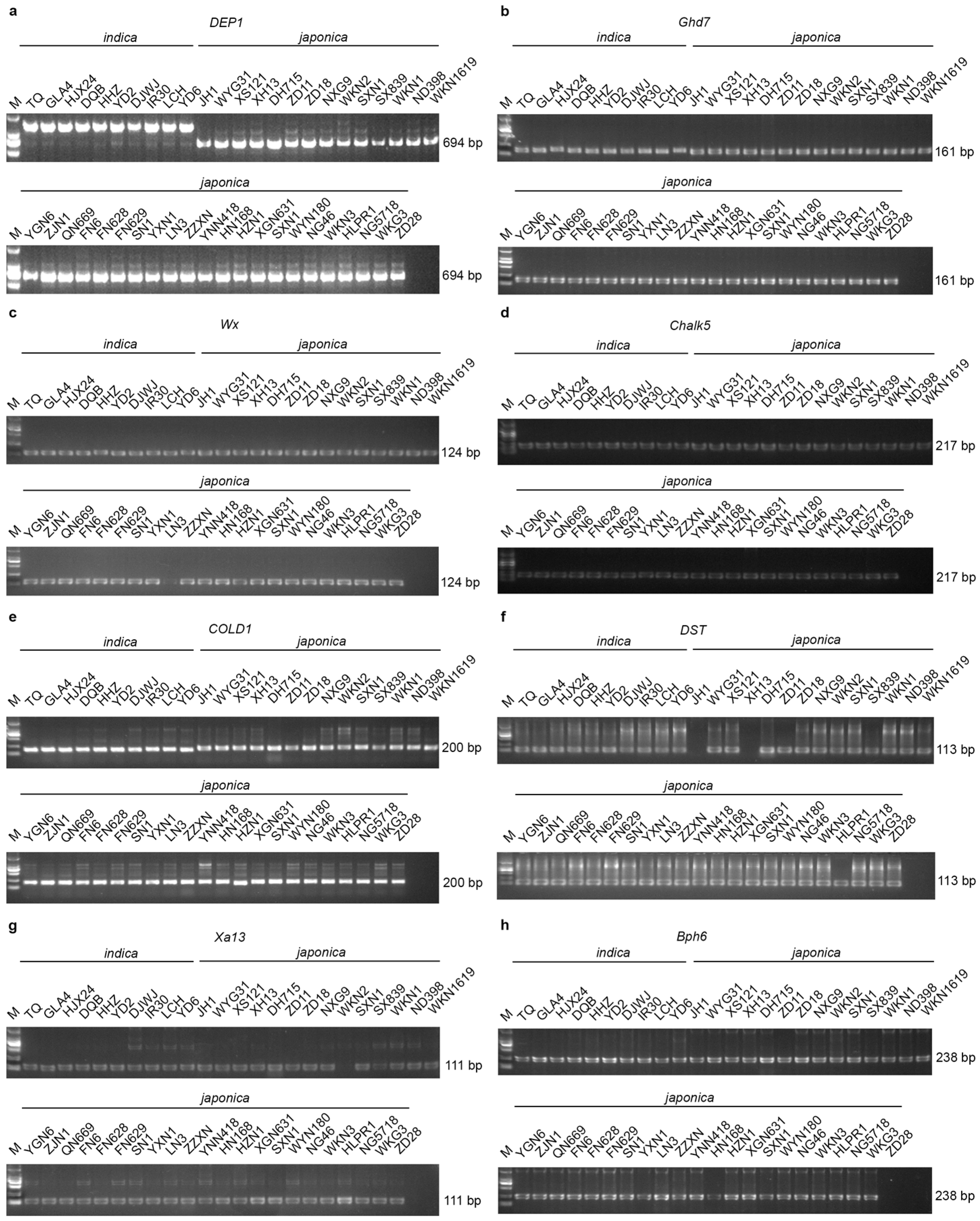
| Traits | Env. | Mean ± SD | Range | CV (%) | Skewness | Kurtosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH/cm | FY | 89.44 ± 4.12 | 69.63–103.13 | 4.60 | −1.07 | 1.63 |
| HX | 92.32 ± 3.47 | 73.53–100.68 | 3.76 | −0.10 | 1.90 | |
| TN | FY | 6.8 ± 2.1 | 3.9–10.3 | 30.70 | 0.16 | −0.02 |
| HX | 8.5 ± 2.4 | 5.3–16.9 | 28.69 | 2.03 | 4.22 | |
| PL/cm | FY | 17.71 ± 1.29 | 15.33–19.86 | 7.28 | −0.28 | −0.42 |
| HX | 17.63 ± 1.34 | 15.94–19.23 | 7.60 | 0.03 | −1.20 | |
| PB | FY | 14.95 ± 1.54 | 12.93–18.67 | 10.30 | 0.76 | 0.74 |
| HX | 14.60 ± 1.79 | 12.33–17. 67 | 12.26 | 0.47 | −0.31 | |
| SB | FY | 36.20 ± 8.16 | 20.00–54.20 | 22.53 | 0.34 | 1.46 |
| HX | 37.94 ± 7.18 | 24.93–50.53 | 21.61 | 0.31 | −0.14 | |
| GL/mm | FY | 7.50 ± 0.13 | 7.16–7.85 | 1.73 | 0.18 | −0.9 |
| HX | 7.64 ± 0.14 | 7.12–8.04 | 1.83 | −0.25 | 0.58 | |
| GW/mm | FY | 3.67 ± 0.10 | 3.43–4.21 | 2.72 | 0.46 | 0.03 |
| HX | 3.74 ± 0.09 | 3.29–4.14 | 2.41 | 0.24 | 0.53 | |
| TGW/g | FY | 25.89 ± 1.15 | 22.60–30.10 | 4.44 | 0.15 | −0.50 |
| HX | 25.36 ± 1.15 | 20.40–32.10 | 4.53 | 0.54 | 1.75 | |
| SR/% | FY | 89.69 ± 3.46 | 61.77–96.08 | 3.86 | −2.83 | 11.18 |
| HX | 87.69 ± 4.06 | 69.09–95.88 | 4.63 | −1.31 | 0.95 | |
| YD/g/m2 | FY | 590 ± 161 | 277–1006 | 15.95 | 0.30 | 1.72 |
| HX | 786 ± 151 | 462–1478 | 12.89 | 1.84 | 3.60 |
| Traits | No. of Cultivars | Sig. Diff. (%) | FY (%) | HX (%) | p-Value Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | 36 | 52.77 | 16.66 | 36.11 | 0.0001 < 0.0460 |
| TN | 36 | 44.44 | 5.55 | 38.89 | 0.0001 < 0.0455 |
| PL | 36 | 30.77 | 19.44 | 11.11 | 0.0001–0.0443 |
| PB | 36 | 12.12 | 8.33 | 2.78 | 0.0004–0.0473 |
| SB | 36 | 25.00 | 5.55 | 19.44 | 0.0001 < 0.0362 |
| GL | 36 | 61.11 | 8.33 | 52.78 | 0.0001 < 0.0126 |
| GW | 36 | 72.22 | 27.78 | 44.44 | 0.0001 < 0.0448 |
| TGW | 36 | 36.11 | 25.00 | 11.11 | 0.0004–0.0393 |
| SR | 36 | 22.22 | 16.67 | 5.55 | 0.0009–0.0492 |
| YD | 36 | 61.11 | 11.11 | 50.00 | 0.0001 < 0.0165 |
| Traits | Env. | PH | TN | PL | PB | SB | GL | GW | TGW | SR | YD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PH | FY | - | |||||||||
| HX | - | ||||||||||
| TN | FY | 0.65 **** | - | ||||||||
| HX | 0.15 | - | |||||||||
| PL | FY | 0.50 *** | 0.27 | - | |||||||
| HX | 0.20 | −0.23 | - | ||||||||
| PB | FY | 0.06 | −0.21 | −0.18 * | - | ||||||
| HX | 0.19 | 0.35 * | −0.40 * | - | |||||||
| SB | FY | 0.08 | 0.14 | 0.62 **** | 0.11 | - | |||||
| HX | 0.07 | −0.01 | 0.46 ** | −0.06 | - | ||||||
| GL | FY | −0.05 | −0.20 | 0.01 | 0.02 | −0.20 | - | ||||
| HX | 0.14 | −0.09 | 0.19 | 0.27 | −0.22 | - | |||||
| GW | FY | −0.24 | −0.25 | −0.26 | 0.17 | −0.11 | 0.23 | - | |||
| HX | 0.14 | −0.21 | −0.03 | 0.01 | −0.09 | 0.51 *** | - | ||||
| TGW | FY | 0.04 | −0.22 | −0.09 | 0.14 | −0.38 * | 0.15 | 0.48 ** | - | ||
| HX | 0.10 | −0.06 | 0.03 | 0.05 | −0.49 *** | 0.53 *** | 0.53 *** | - | |||
| SR | FY | 0.18 | 0.08 | −0.01 | 0.02 | −0.25 | −0.22 | −0.04 | 0.48 ** | - | |
| HX | −0.25 | −0.11 | 0.08 | −0.12 | −0.40 * | 0.09 | 0.09 | 0.59 *** | - | ||
| YD | FY | 0.47 ** | 0.57 *** | 0.40 * | 0.07 | 0.44 ** | −0.07 | −0.14 | 0.07 | 0.35 * | - |
| HX | −0.02 | 0.87 **** | −0.13 | 0.29 | 0.08 | −0.12 | −0.23 | 0.03 | 0.14 | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Owusu, E.A.; Sun, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, D.; Fan, H.; Ai, H.; Huang, X. Comparison of Main Agronomic Traits and Identification of Important Genes in Japonica Rice Cultivars Grown in the Jianghuai Region. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061409
Owusu EA, Sun Z, Liu S, Xu D, Fan H, Ai H, Huang X. Comparison of Main Agronomic Traits and Identification of Important Genes in Japonica Rice Cultivars Grown in the Jianghuai Region. Agronomy. 2025; 15(6):1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061409
Chicago/Turabian StyleOwusu, Edwin Afriyie, Zhanglun Sun, Shengqin Liu, Dachao Xu, Huailin Fan, Hao Ai, and Xianzhong Huang. 2025. "Comparison of Main Agronomic Traits and Identification of Important Genes in Japonica Rice Cultivars Grown in the Jianghuai Region" Agronomy 15, no. 6: 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061409
APA StyleOwusu, E. A., Sun, Z., Liu, S., Xu, D., Fan, H., Ai, H., & Huang, X. (2025). Comparison of Main Agronomic Traits and Identification of Important Genes in Japonica Rice Cultivars Grown in the Jianghuai Region. Agronomy, 15(6), 1409. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15061409






