Genomic Architecture of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta) and Insights into the Differential Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes During Floral Organ Specification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Identification, Physicochemical Property Analysis, and Subcellular Localization of AP2/ERF Genes in Marigold
2.3. Phylogenetic Analysis of AP2/ERF Genes
2.4. Gene Structure Analysis and Motif Identification
2.5. Chromosomal Mapping and Synteny Analysis
2.6. RNA Extraction from Various Tissues and Organs
2.7. Expression Analysis of AP2 Family Genes
2.8. Protein–Protein Interaction Network Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Classification of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of AP2/ERF Superfamily Members in Marigold
3.3. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis
3.4. Chromosomal Distribution and Duplication Analysis
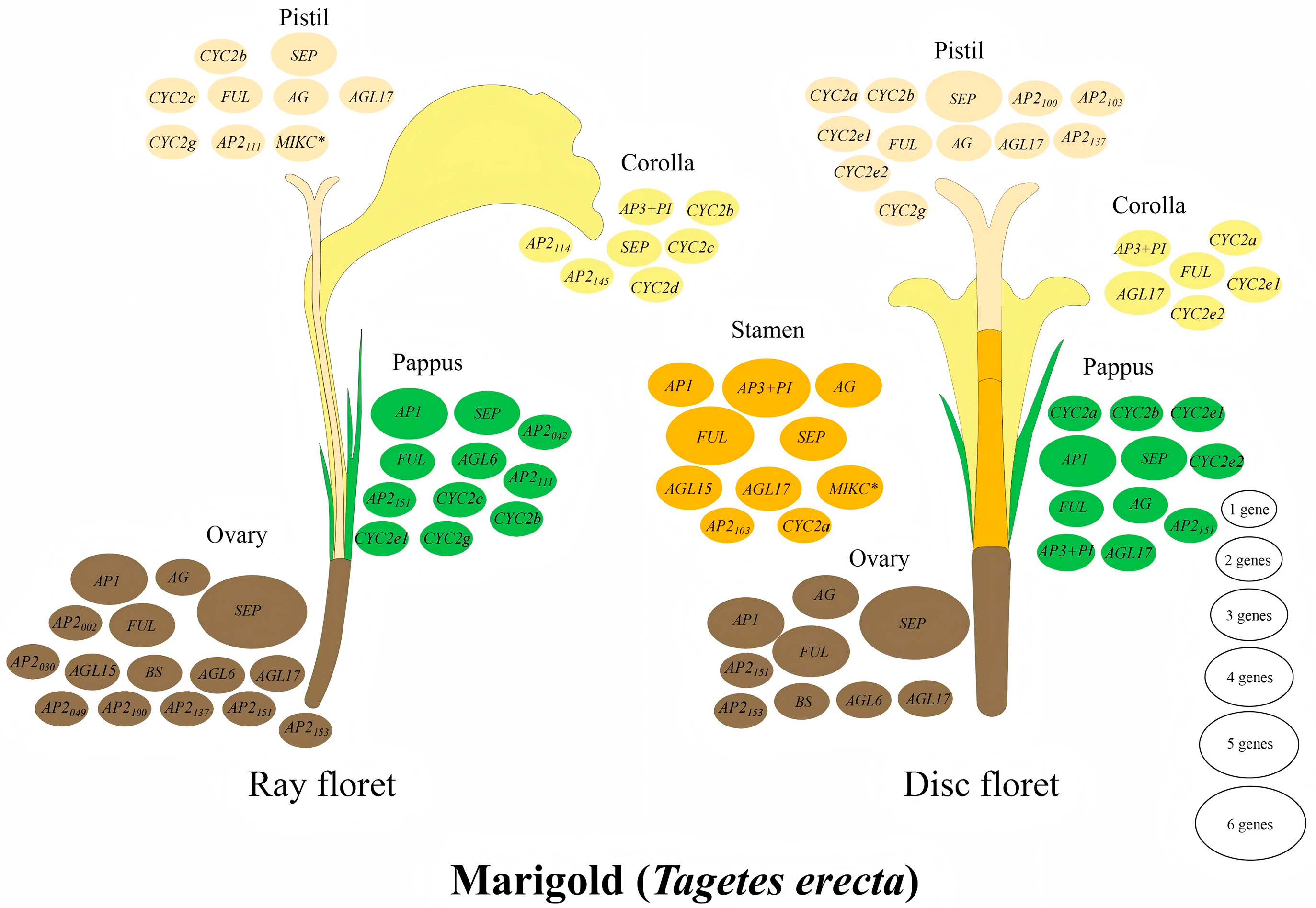
3.5. Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes Reveal Their Roles in Tissue-Specific and Floral Organ Development
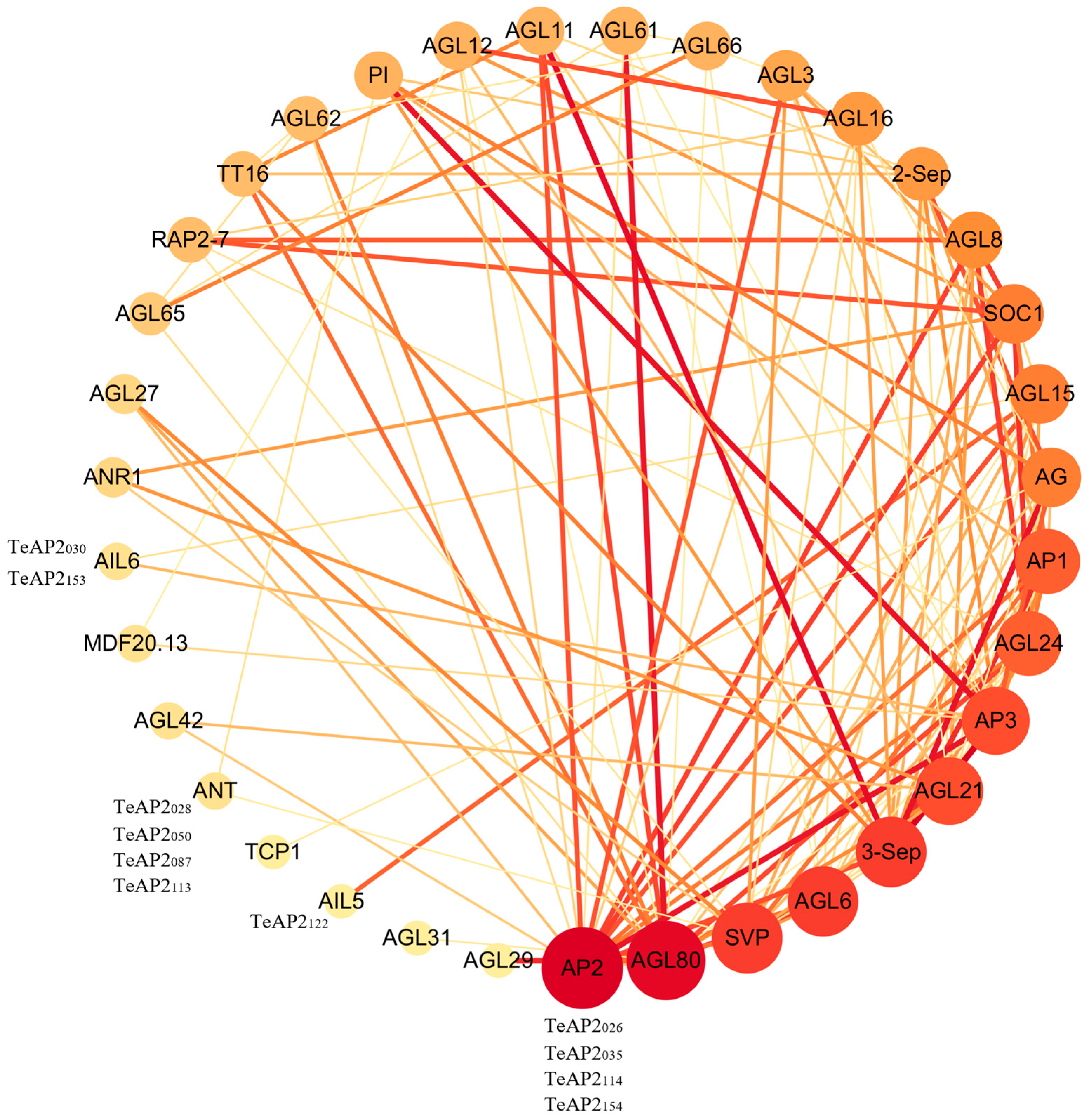
3.6. Protein Interaction Network Analysis of AP2 Family, MADS-Box, and TCP Family Transcription Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Evolutionary Relationships and Structural Features of AP2/ERF Genes in Marigold
4.2. Diverse Expression Patterns Reveal Functional Specialization of AP2 Family Genes in Marigold
4.3. Integration of AP2 Family, MADS-Box, and CYC2 Protein Regulatory Networks in Marigold Floral Development
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Riechmann, J.L.; Heard, J.; Martin, G.; Reuber, L.; Jiang, C.Z.; Keddie, J.; Adam, L.; Pineda, O.; Ratcliffe, O.J.; Samaha, R.R.; et al. Arabidopsis Transcription Factors: Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis Among Eukaryotes. Science 2000, 290, 2105–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; White, M.J.; Macrae, T.H. Transcription factors and their genes in higher plants. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 262, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Perata, P. APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttner, M.; Singh, K.B. Arabidopsis thaliana ethylene-responsive element binding protein (AtEBP), an ethylene-inducible, GCC box DNA-binding protein interacts with an ocs element binding protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 5961–5966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohme-Takagi, M.; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.; Cai, B.; Peng, R.H.; Zhu, B.; Jin, X.F.; Xue, Y.; Gao, F.; Fu, X.Y.; Tian, Y.S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizek, B. AINTEGUMENTA and AINTEGUMENTA-LIKE6 act redundantly to regulate Arabidopsis floral growth and patterning. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1916–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, R.J.; Bailey, L.J.; Mai, Q.A.; Wu, S.L.; Hon, C.T.; Chapman, E.J.; Ditta, G.S.; Estelle, M.; Yanofsky, M.F. microRNA regulation of fruit growth. Nat. Plants 2015, 1, 15036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.Y.; Catinot, J.; Zimmerli, L. Ethylene response factors in Arabidopsis immunity. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matias-Hernandez, L.; Aguilar-Jaramillo, A.E.; Marin-Gonzalez, E.; Suarez-Lopez, P.; Pelaz, S. RAV genes: Regulation of floral induction and beyond. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1459–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, R.; Liang, Y.; Gao, B.; Li, S.; Bai, W.; Oliver, M.J.; Zhang, D. The ScAPD1-like gene from the desert moss Syntrichia caninervis enhances resistance to Verticillium dahliae via phenylpropanoid gene regulation. Plant J. 2023, 113, 75–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.M.; Zhou, M.L.; Dan-Wang; Tang, Y.X.; Lin, M.; Wu, Y.M. Overexpression of the Lotus corniculatus Soloist Gene LcAP2/ERF107 Enhances Tolerance to Salt Stress. Protein Pept. Lett. 2016, 23, 442–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeble, L.; van Benthem, K.J.; Weigelt, P.; Kreft, H.; Knope, M.L.; Mandel, J.R.; Vargas, P.; Etienne, R.S.; Valente, L. Island biogeography of the megadiverse plant family Asteraceae. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 7276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panero, J.L.; Crozier, B.S. Macroevolutionary dynamics in the early diversification of Asteraceae. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2016, 99, 116–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandel, J.R.; Dikow, R.B.; Siniscalchi, C.M.; Thapa, R.; Watson, L.E.; Funk, V.A. A fully resolved backbone phylogeny reveals numerous dispersals and explosive diversifications throughout the history of Asteraceae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 14083–14088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Elomaa, P. Development and evolution of the Asteraceae capitulum. New Phytol. 2024, 242, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elomaa, P.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T. Flower heads in Asteraceae-recruitment of conserved developmental regulators to control the flower-like inflorescence architecture. Hortic. Res. 2018, 5, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, V.; Susanna, A.; Stuessy, T.; Bayer, R. Systematics, Evolution, and Biogeography of Compositae; International Association for Plant Taxonomy: Vienna, Austria, 2009; ISBN 978-3-9501754-3-1. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Shen, C.Z.; Guo, Y.P.; Rao, G.Y. Patterning the Asteraceae Capitulum: Duplications and Differential Expression of the Flower Symmetry CYC2-Like Genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahtiharju, S.; Rijpkema, A.S.; Vetterli, A.; Albert, V.A.; Teeri, T.H.; Elomaa, P. Evolution and diversification of the CYC/TB1 gene family in Asteraceae—A comparative study in Gerbera (Mutisieae) and sunflower (Heliantheae). Mol. Biol. Evol. 2012, 29, 1155–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yu, Y.; Zhai, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Chen, S.; Chen, F.; Jiang, J. An ethylene-responsive transcription factor and a B-box protein coordinate vegetative growth and photoperiodic flowering in chrysanthemum. Plant Cell Environ. 2023, 46, 440–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broholm, S.K.; Tahtiharju, S.; Laitinen, R.A.; Albert, V.A.; Teeri, T.H.; Elomaa, P. A TCP domain transcription factor controls flower type specification along the radial axis of the Gerbera (Asteraceae) inflorescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fambrini, M.; Pugliesi, C. CYCLOIDEA 2 Clade Genes: Key Players in the Control of Floral Symmetry, Inflorescence Architecture, and Reproductive Organ Development. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 35, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, R.A.; Broholm, S.; Albert, V.A.; Teeri, T.H.; Elomaa, P. Patterns of MADS-box gene expression mark flower-type development in Gerbera hybrida (Asteraceae). BMC Plant Biol. 2006, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, Y.; Liao, M.; Li, J.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Z.; Song, X.; Dai, S. Floral Development Stage-Specific Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Formation Mechanism of Different Shapes of Ray Florets in Chrysanthemum. Genes 2023, 14, 766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Qi, S.; Huang, H.; Wu, X.; Zhang, B.; Fan, G.; Yang, L.; Hong, Y.; Dai, S. The expression and interactions of ABCE-class and CYC2-like genes in the capitulum development of Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium and C. × morifolium. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 88, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Broholm, S.K.; Wang, F.; Rijpkema, A.S.; Lan, T.; Albert, V.A.; Teeri, T.H.; Elomaa, P. TCP and MADS-Box Transcription Factor Networks Regulate Heteromorphic Flower Type Identity in Gerbera hybrida. Plant Physiol. 2020, 184, 1455–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang, Q.; Vayssieres, A.; O’Maoileidigh, D.S.; Yang, X.; Vincent, C.; Bertran, G.D.O.E.; Cerise, M.; Franzen, R.; Coupland, G. MicroRNA172 controls inflorescence meristem size through regulation of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2022, 235, 356–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Hu, S.; Feng, J.; Liu, Z.; Kang, C. The AP2 transcription factor BARE RECEPTACLE regulates floral organogenesis via auxin pathways in woodland strawberry. Plant Cell 2024, 36, 4970–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jofuku, K.D.; den Boer, B.G.; Van Montagu, M.; Okamuro, J.K. Control of Arabidopsis flower and seed development by the homeotic gene APETALA2. Plant Cell 1994, 6, 1211–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, S.; Kumar, R. Wild marigold (Tagetes minuta L.) an important industrial aromatic crop: Liquid gold from the Himalaya. J. Essent. Oil Res. 2020, 32, 373–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasudevan, P.; Kashyap, S.; Sharma, S. Tagetes: A multipurpose plant. Bioresour. Technol. 1997, 62, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, C.; Cao, Z.; Bao, M.; He, Y. Transcriptomic Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes during Flower Organ Development in Genetic Male Sterile and Male Fertile Tagetes erecta by Digital Gene-Expression Profiling. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Liu, C.; Dou, L.; Wei, L.; Cheng, W.; Bao, M.; Yi, Q.; et al. Identification and characterization of CYC2-like genes related to floral symmetric development in Tagetes erecta (Asteraceae). Gene 2023, 889, 147804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Ji, F.; Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Yi, C.; Zhao, S.; Cong, R.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z. Chromosome-scale genome assembly of marigold (Tagetes erecta L.): An ornamental plant and feedstock for industrial lutein production. Hortic. Plant J. 2023, 9, 1119–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, F.; Li, R.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, C.; He, Y. Marigold (Tagetes erecta) MADS-Box Genes: A Systematic Analysis and Their Implications for Floral Organ Development. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; He, Y.; Bao, M. Characterization and Functional Analysis of Five MADS-Box B Class Genes Related to Floral Organ Identification in Tagetes erecta. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Li, H.; Bao, M.; He, Y. Functional Conservation and Divergence of Five AP1/FUL-like Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta L.). Genes 2021, 12, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wei, L.; Wang, W.; Qi, W.; Cao, Z.; Li, H.; Bao, M.; He, Y. Identification, characterization and functional analysis of AGAMOUS subfamily genes associated with floral organs and seed development in Marigold (Tagetes erecta). BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Shi, A.; Meinhardt, L.W.; Mou, B. Genome-wide characterization and evolutionary analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in lettuce (Lactuca sativa). Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.; Guo, X.; Tian, S.; Chen, G. Genome-Wide Analysis of the MADS-Box Transcription Factor Family in Solanum lycopersicum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, W.; Huo, J.; Li, L.; Chen, B.; Guo, Z.; Ma, Z. Identification and expression analysis of citrate synthase 3 gene family members in apple. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 2024, 40, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiser, L.; Subramaniam, S.; Zhang, P.; Berardini, T. Using the Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) to Find Information About Arabidopsis Genes. Curr. Protoc. 2022, 2, e574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh, B.Q.; Schmidt, H.A.; Chernomor, O.; Schrempf, D.; Woodhams, M.D.; von Haeseler, A.; Lanfear, R. IQ-TREE 2: New Models and Efficient Methods for Phylogenetic Inference in the Genomic Era. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2020, 37, 1530–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.; von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, D.T.; Chernomor, O.; von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q.; Vinh, L.S. UFBoot2: Improving the Ultrafast Bootstrap Approximation. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Letunic, I.; Bork, P. Interactive Tree of Life (iTOL) v6: Recent updates to the phylogenetic tree display and annotation tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024, 52, W78–W82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, T.; Wan, S.; Tong, Y.; Wei, Y.; Li, P.; Hu, N.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Pan, X.; et al. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the SiCIN gene family in foxtail millet (Setaria italica L.). Gene 2024, 921, 148499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwa, K.; Subramani, B.; Lenka, G.; Chang, S. Sequence Motif Analysis of Phycobiliproteins in Cyanobacterial Genome. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Bioscience, Biochemistry and Bioinformatics, Singapore, 26–28 February 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, D.; Zeng, B.; He, Y.; Li, J.; Yu, Z. Genome-wide identification and comparative analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Prunus dulcis and Prunus tenella: Expression of PdAP2/ERF genes under freezing stress during dormancy. BMC Genom. 2025, 26, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Rashid, M.A.R.; Zafar, S.A.; Azhar, M.T.; Waqas, M.; Uzair, M.; Rana, I.A.; Azeem, F.; Chung, G.; Ali, Z.; et al. Genome-wide investigation and expression analysis of APETALA-2 transcription factor subfamily reveals its evolution, expansion and regulatory role in abiotic stress responses in Indica Rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica). Genomics 2021, 113, 1029–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, L.; Guo, C. Genome-Wide Analysis of the AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes and their Responses to Abiotic Stress in Medicago truncatula. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krizek, B.A. Aintegumenta and Aintegumenta-Like6 regulate auxin-mediated flower development in Arabidopsis. BMC Res. Notes 2011, 4, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yant, L.; Mathieu, J.; Dinh, T.T.; Ott, F.; Lanz, C.; Wollmann, H.; Chen, X.; Schmid, M. Orchestration of the floral transition and floral development in Arabidopsis by the bifunctional transcription factor APETALA2. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 2156–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, M.; Guangyuan, H.; Guangxiao, Y.; Hussain, J.; Xu, Y. AP2/ERF Transcription Factor in Rice: Genome-Wide Canvas and Syntenic Relationships between Monocots and Eudicots. Evol. Bioinform. Online 2012, 8, 321–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najafi, S.; Sorkheh, K.; Nasernakhaei, F. Characterization of the APETALA2/Ethylene-responsive factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factor family in sunflower. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, T.; Xu, X.; Jiang, J.; Li, J. Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of the ERF2 gene family in response to disease resistance against Stemphylium lycopersici in tomato. BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, X. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp. pekinensis). BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girardi, C.L.; Rombaldi, C.V.; Dal Cero, J.; Nobile, P.M.; Laurens, F.; Bouzayen, M.; Quecini, V. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in apple and transcriptional evidence of ERF involvement in scab pathogenesis. Sci. Hortic. 2013, 151, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, S.; Cheng, J.; Su, C.; Zhong, S.; Liu, Q.; Fang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Lv, H.; Zheng, Y.; et al. Intron Lariat RNA Inhibits MicroRNA Biogenesis by Sequestering the Dicing Complex in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1006422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.Y.; Ohta, M.; Usui, A.; Shinshi, H.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Arabidopsis ethylene-responsive element binding factors act as transcriptional activators or repressors of GCC box-mediated gene expression. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagaya, Y.; Ohmiya, K.; Hattori, T. RAV1, a novel DNA-binding protein, binds to bipartite recognition sequence through two distinct DNA-binding domains uniquely found in higher plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nole-Wilson, S.; Krizek, B.A. DNA binding properties of the Arabidopsis floral development protein AINTEGUMENTA. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 4076–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannon, S.B.; Mitra, A.; Baumgarten, A.; Young, N.D.; May, G. The roles of segmental and tandem gene duplication in the evolution of large gene families in Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Plant Biol. 2004, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, F.; Wu, J.; Fang, L.; Wang, X. Syntenic gene analysis between Brassica rapa and other Brassicaceae species. Front. Plant Sci. 2012, 3, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B.B.; Shang, G.D.; Pan, Y.; Xu, Z.G.; Zhou, C.M.; Mao, Y.B.; Bao, N.; Sun, L.; Xu, T.; Wang, J.W. AP2/ERF Transcription Factors Integrate Age and Wound Signals for Root Regeneration. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 226–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitomi, Y.; Ito, H.; Hobo, T.; Aya, K.; Kitano, H.; Inukai, Y. The auxin responsive AP2/ERF transcription factor CROWN ROOTLESS5 is involved in crown root initiation in rice through the induction of OsRR1, a type-A response regulator of cytokinin signaling. Plant J. 2011, 67, 472–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jofuku, K.D.; Omidyar, P.K.; Gee, Z.; Okamuro, J.K. Control of seed mass and seed yield by the floral homeotic gene APETALA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3117–3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohto, M.A.; Fischer, R.L.; Goldberg, R.B.; Nakamura, K.; Harada, J.J. Control of seed mass by APETALA2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3123–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, B.; He, X.; Tang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Zhang, C.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, W.; et al. Photoperiod controls plant seed size in a CONSTANS-dependent manner. Nat. Plants 2023, 9, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, M.A.; Alvarez, I.; Torices, R.; Fuertes-Aguilar, J. Floral development and evolution of capitulum structure in Anacyclus (Anthemideae, Asteraceae). Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 1597–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wollmann, H.; Mica, E.; Todesco, M.; Long, J.A.; Weigel, D. On reconciling the interactions between APETALA2, miR172 and AGAMOUS with the ABC model of flower development. Development 2010, 137, 3633–3642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogan, N.T.; Hogan, K.; Long, J.A. APETALA2 negatively regulates multiple floral organ identity genes in Arabidopsis by recruiting the co-repressor TOPLESS and the histone deacetylase HDA19. Development 2012, 139, 4180–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerstens, M.; Schranz, M.E.; Bouwmeester, K. Phylogenomic analysis of the APETALA2 transcription factor subfamily across angiosperms reveals both deep conservation and lineage-specific patterns. Plant J. 2020, 103, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Song, A.; Zhang, X.; Li, S.; Su, J.; Xia, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhao, W.; Guan, Y.; Fang, W.; et al. The core regulatory networks and hub genes regulating flower development in Chrysanthemum morifolium. Plant Mol. Biol. 2020, 103, 669–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Zhang, C.; Jiao, B.; Panero, J.L.; Cai, J.; Zhang, Z.R.; Gao, L.M.; Gao, T.; Ma, H. Nuclear phylogenomics of Asteraceae with increased sampling provides new insights into convergent morphological and molecular evolution. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
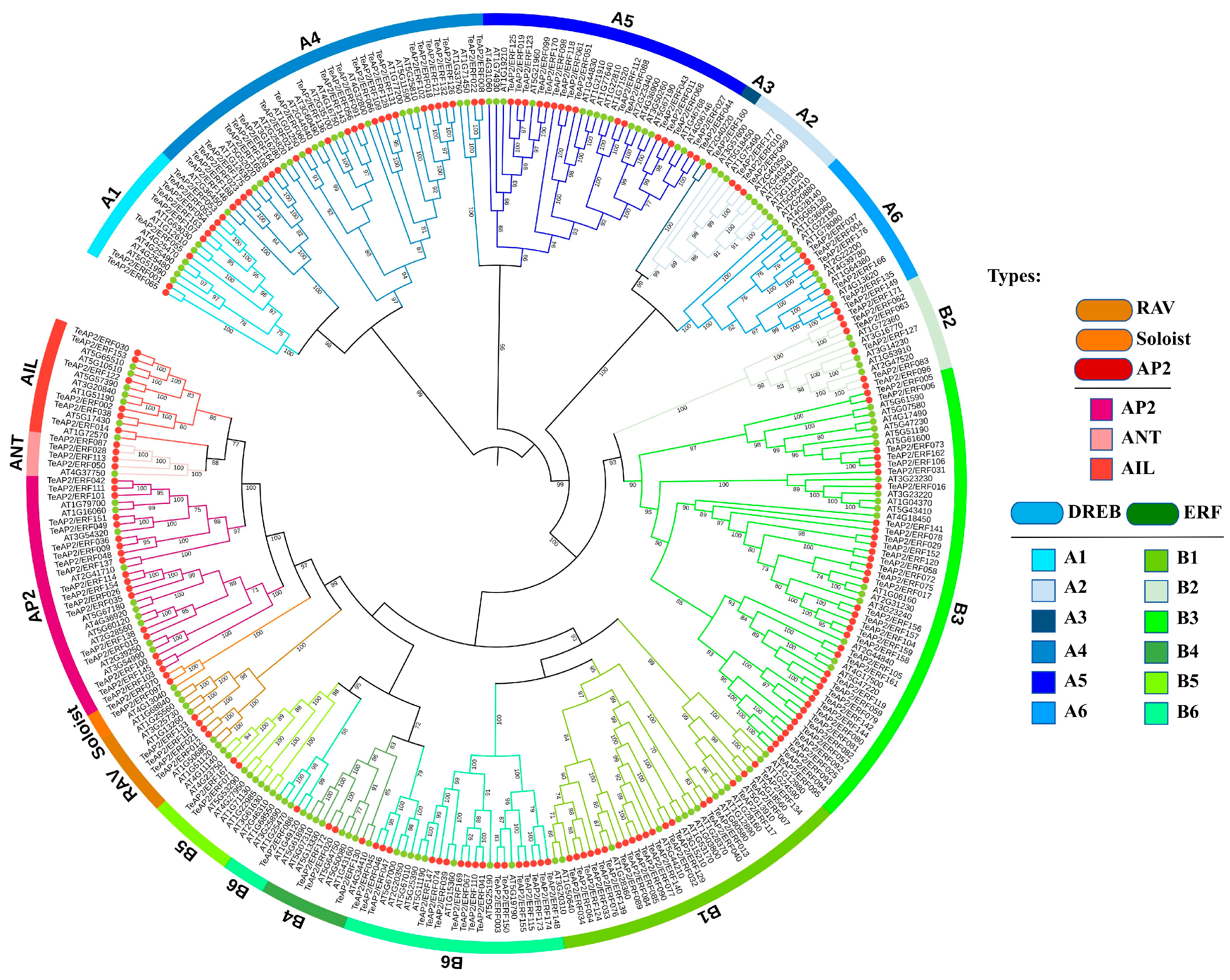
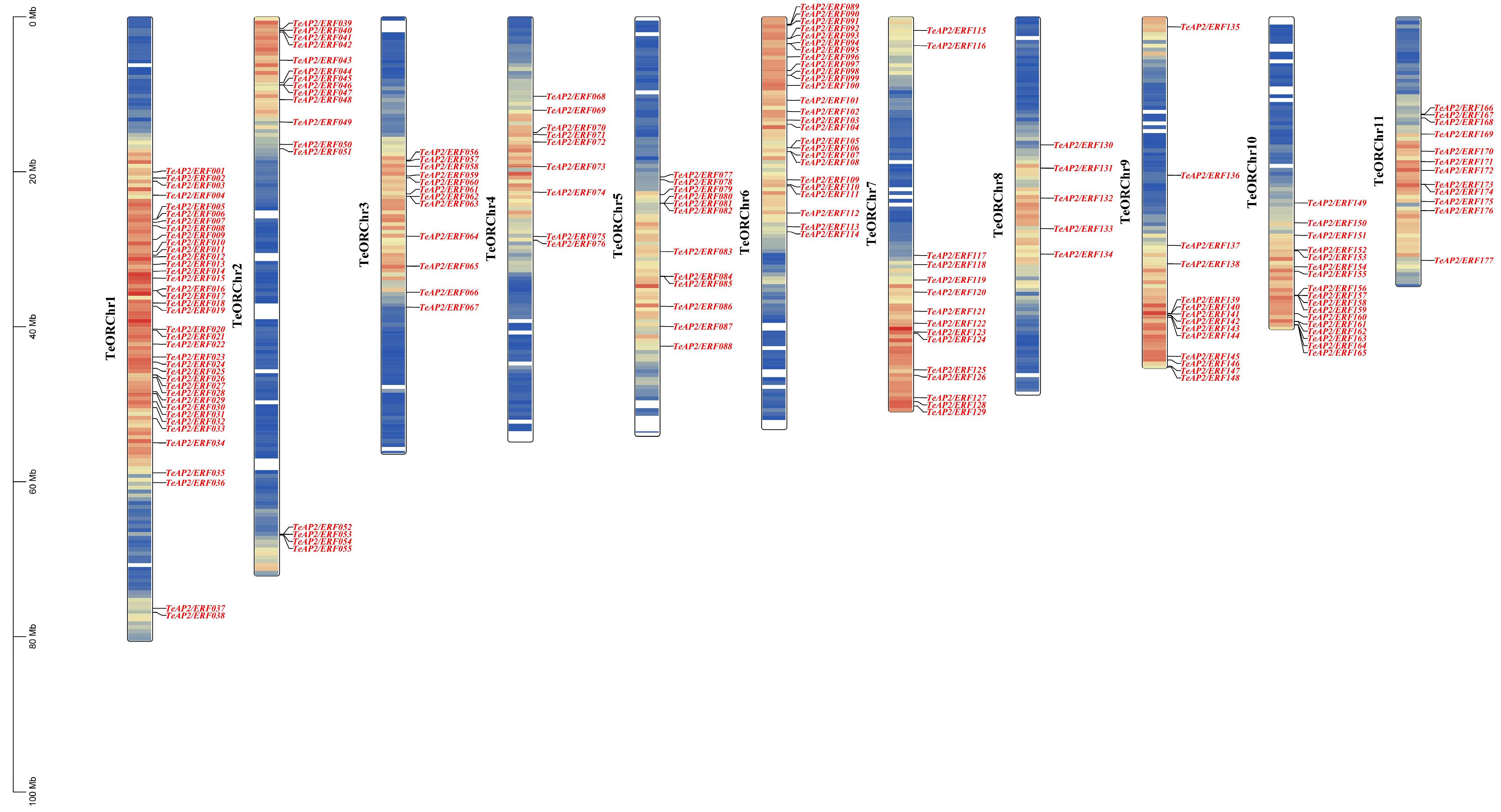

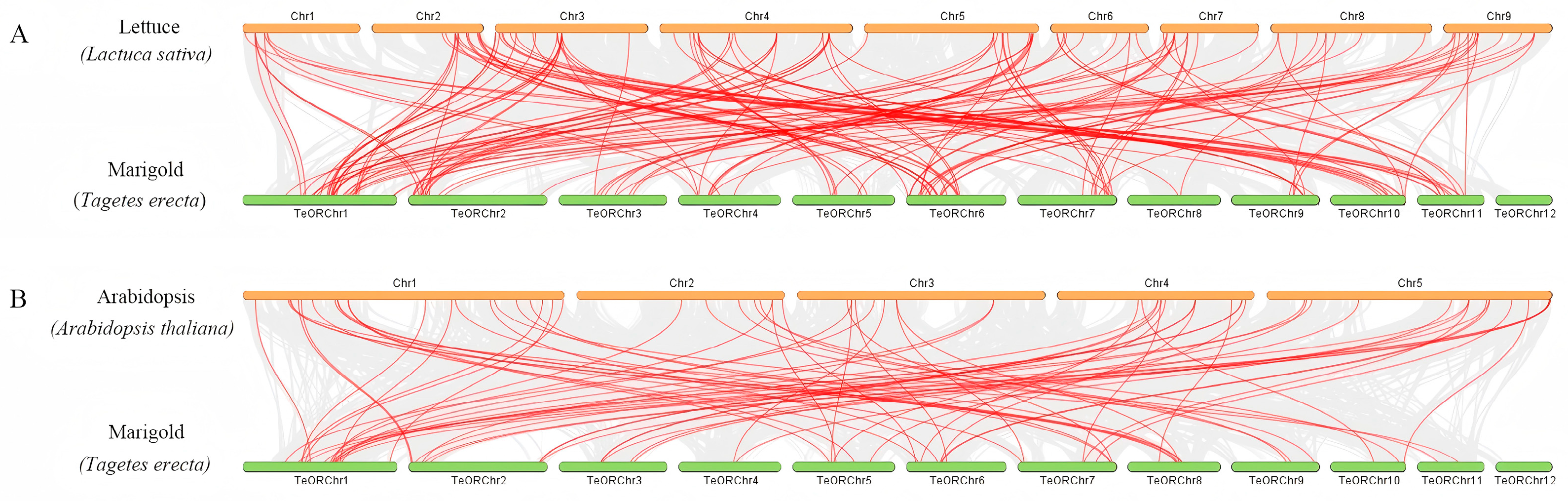
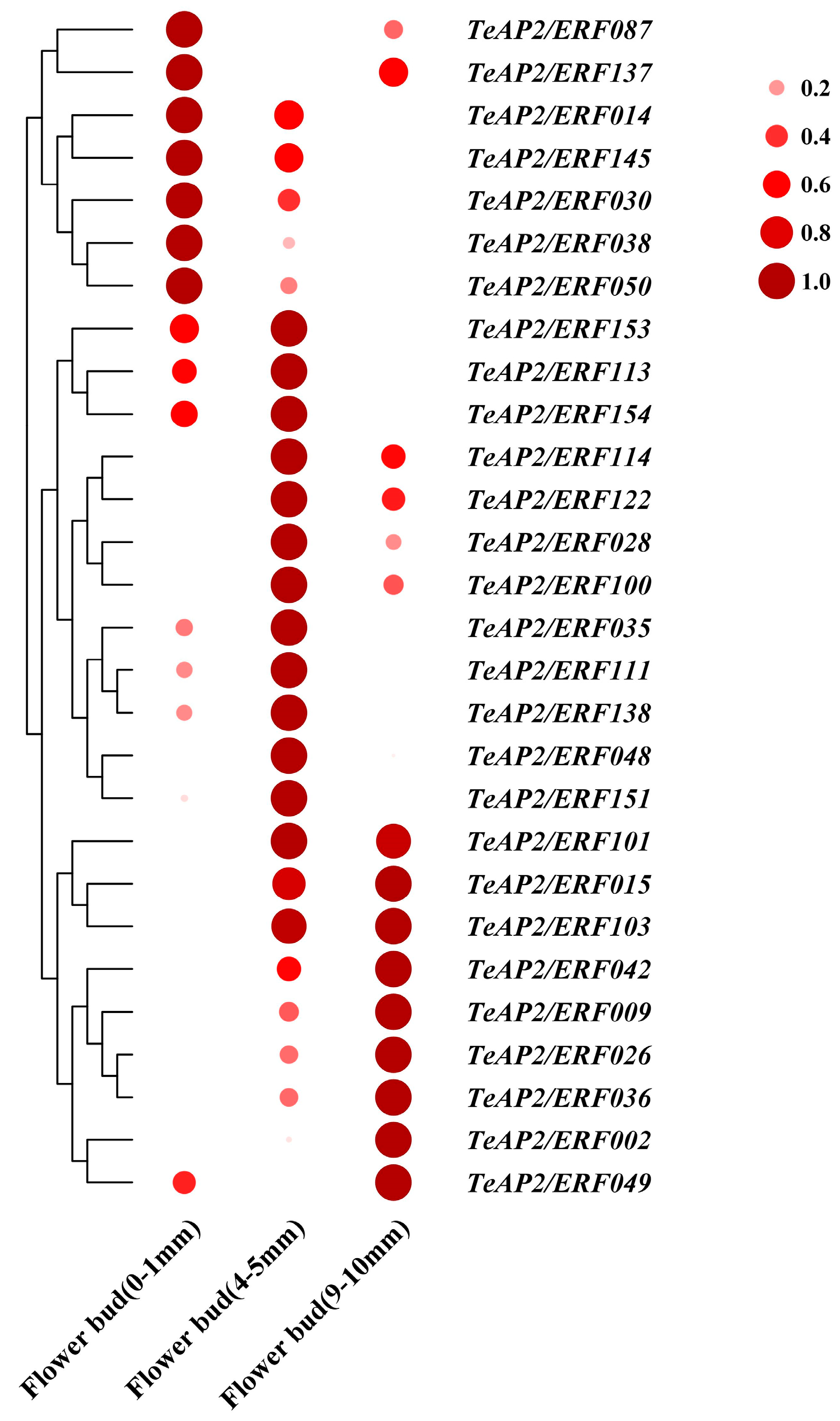


| Family | Subfamily | Group | Tagetes erecta | Lactuca sativa | Arabidopsis thaliana |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAV | 4 | 4 | 6 | ||
| Soloist | 2 | 2 | 1 | ||
| AP2 | AP2 | 18 | 20 | 10 | |
| ANT | 4 | 3 | 1 | ||
| AIL | 6 | 6 | 7 | ||
| ERF | DREB | A1 | 8 | 14 | 6 |
| A2 | 3 | 12 | 8 | ||
| A3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| A4 | 24 | 29 | 16 | ||
| A5 | 16 | 14 | 15 | ||
| A6 | 6 | 11 | 10 | ||
| ERF | B1 | 19 | 19 | 15 | |
| B2 | 6 | 6 | 5 | ||
| B3 | 37 | 45 | 17 | ||
| B4 | 3 | 9 | 7 | ||
| B5 | 2 | 10 | 8 | ||
| B6 | 18 | 23 | 12 | ||
| Total | 177 | 228 * | 145 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Chen, G.; Hu, S.; Liu, C.; Bao, M.; He, Y. Genomic Architecture of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta) and Insights into the Differential Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes During Floral Organ Specification. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051231
Li H, Chen G, Hu S, Liu C, Bao M, He Y. Genomic Architecture of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta) and Insights into the Differential Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes During Floral Organ Specification. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051231
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Hang, Guoqing Chen, Shirui Hu, Cuicui Liu, Manzhu Bao, and Yanhong He. 2025. "Genomic Architecture of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta) and Insights into the Differential Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes During Floral Organ Specification" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051231
APA StyleLi, H., Chen, G., Hu, S., Liu, C., Bao, M., & He, Y. (2025). Genomic Architecture of AP2/ERF Superfamily Genes in Marigold (Tagetes erecta) and Insights into the Differential Expression Patterns of AP2 Family Genes During Floral Organ Specification. Agronomy, 15(5), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051231








