QTL Identification and Candidate Gene Prediction for Spike-Related Traits in Barley
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials
2.2. Field Trials and Phenotypic Evaluation
2.3. QTL Mapping and the RIL Population Genotyping
2.4. Identification of Parents’ Differential Gene DNA Sequences
3. Results
3.1. Spike Traits Evaluation of the RIL Population and Their Parents
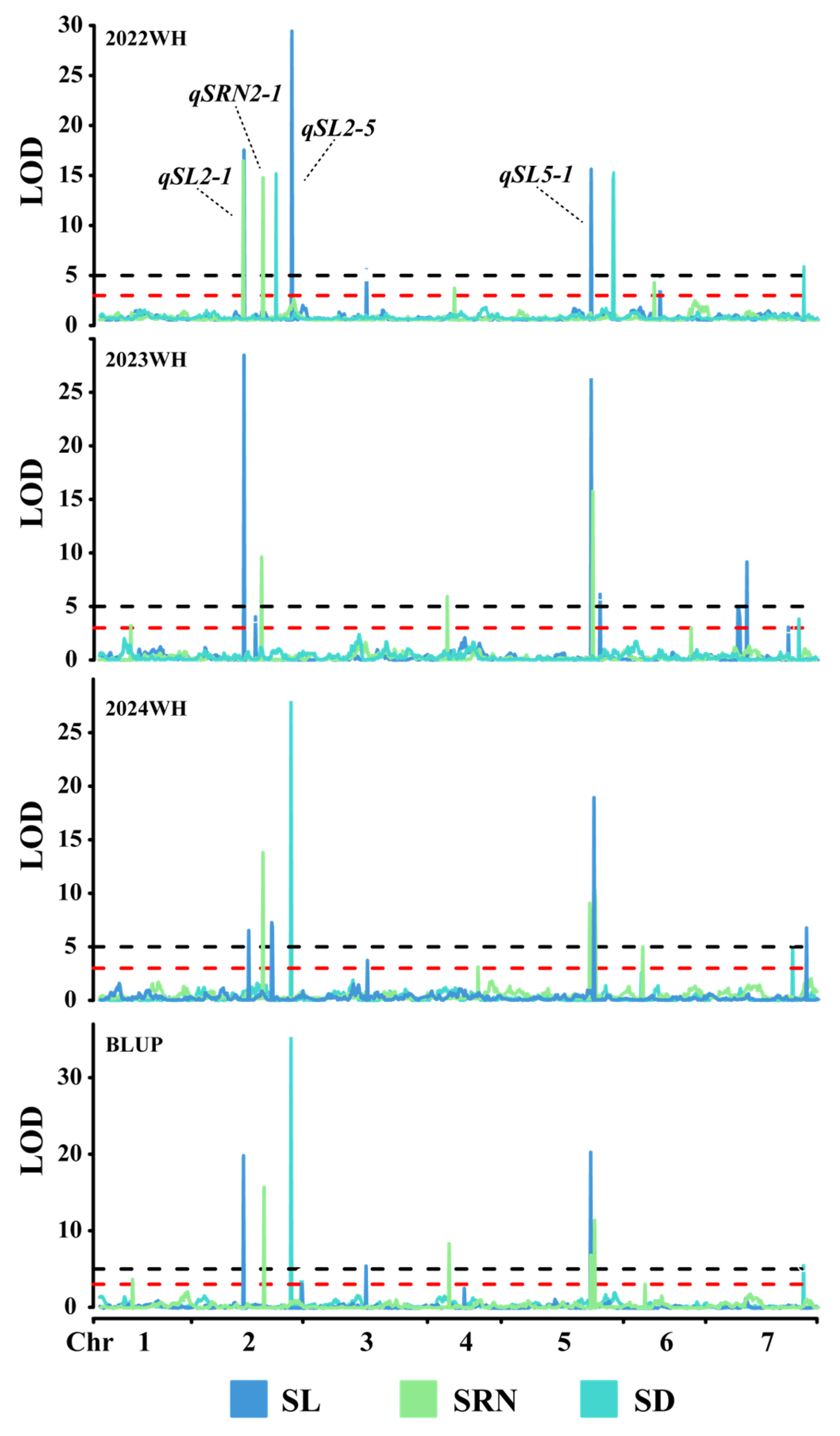
3.2. QTL Analysis
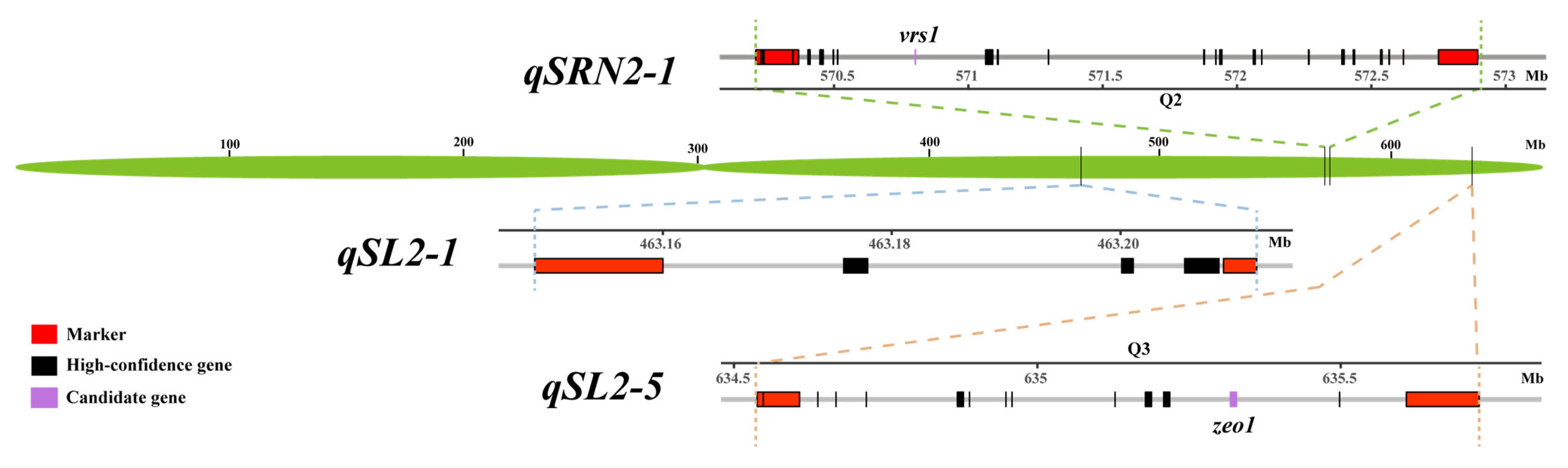
3.3. Candidate Gene Prediction and Analysis for Stable QTL Intervals
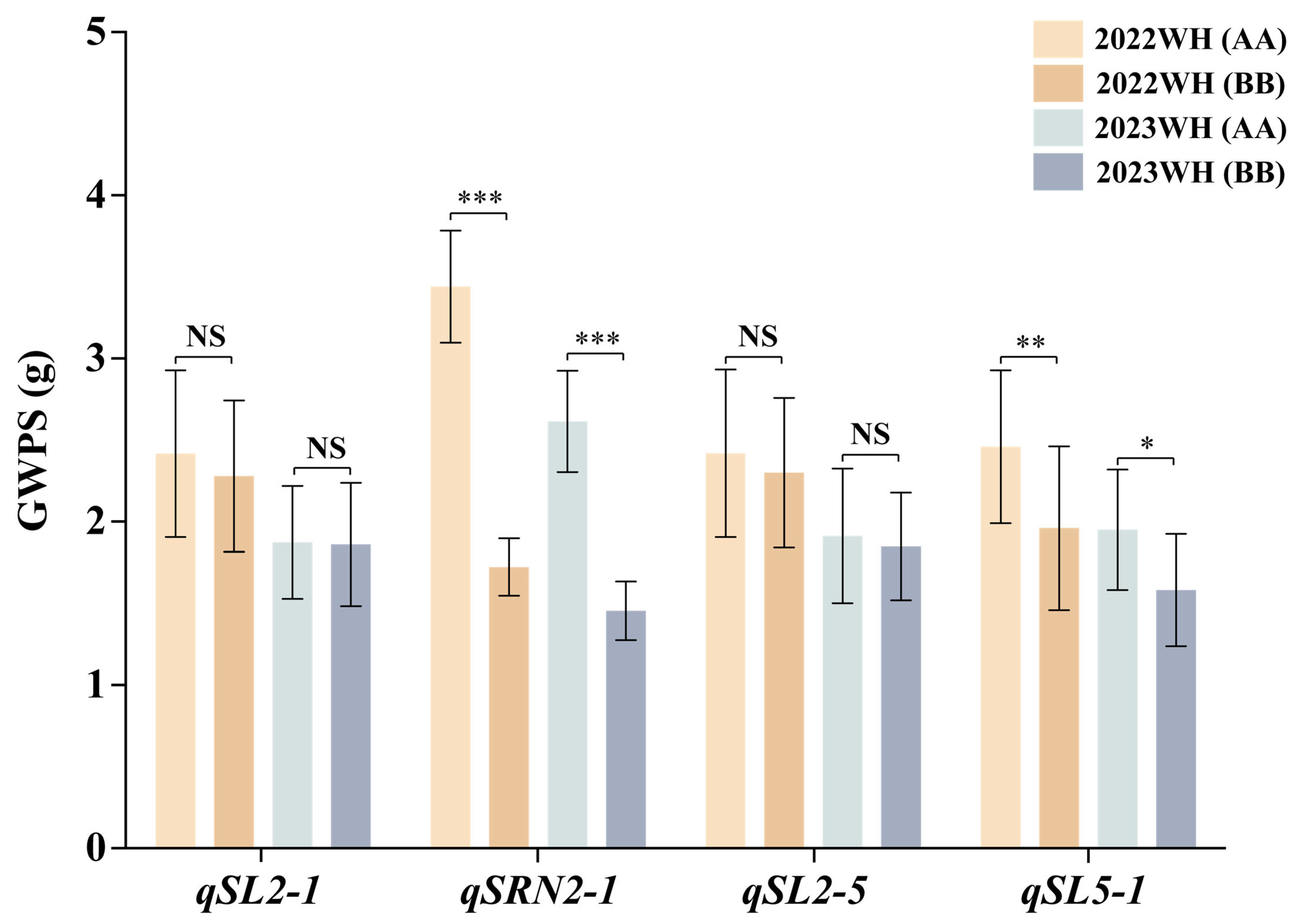
3.4. QTL Effects on Theoretical GWPS
4. Discussion
4.1. SD QTL Is Concurrent with SL Rather than SRN
4.2. vrs1 Is a Candidate Gene for the qSRN2-1
4.3. Analysis of Candidate Genes for Other Stable and Major QTLs
4.4. Different Genes and Loci Regulate SL in Different Ways
4.5. Study Limitations and Breeding Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| QTL | Quantitative trait locus |
| RIL | Recombinant inbred line |
| YJ | Yongjiabaidamai |
| H30 | Hua 30 |
| SL | Spike length |
| SRN | Spike rachis node number |
| SD | Spike density |
| SRL | Spike rachis node length |
| Vrs1 | Six-rowed spike 1 |
| Cly1 | Cleistogamy1 |
| Zeo1 | Zeocriton1 |
| Dps | Dense spike |
| TGW | Thousand-grains weight |
| GWPS | Grain weight per spike |
References
- Niu, C.; Cen, Q.; Chen, Y.; Yan, J.; Ding, N.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.; Fang, Y.; Xue, D. QTL analysis of Chlorophyll Content at different growth stages of Barley. Plant Growth Regul. 2022, 98, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raj, R.; Shams, R.; Pandey, V.K.; Dash, K.K.; Singh, P.; Bashir, O. Barley phytochemicals and health promoting benefits: A comprehensive review. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 14, 100677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, W.A. An Introduction to Barley: The Crop and the Model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1900, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakellariou, M.; Mylona, P.V. New Uses for Traditional Crops: The Case of Barley Biofortification. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faris, J.D.; Zhang, Z.; Garvin, D.F.; Xu, S.S. Molecular and comparative mapping of genes governing spike compactness from wild emmer wheat. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2014, 289, 641–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppolu, R.; Schnurbusch, T. Developmental pathways for shaping spike inflorescence architecture in barley and wheat. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, 278–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuma, S.; Schnurbusch, T. Of floral fortune: Tinkering with the grain yield potential of cereal crops. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 1873–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, X.; Li, G. Molecular Insights into Inflorescence Meristem Specification for Yield Potential in Cereal Crops. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Xu, D.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Dou, T.; Qin, D.; Guo, A.; Zhao, M.; Pei, H.; Zhao, M.; et al. Natural variations of HvSRN1 modulate the spike rachis node number in barley. Plant Commun. 2024, 5, 100670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casas, A.M.; Contreras-Moreira, B.; Cantalapiedra, C.P.; Sakuma, S.; Gracia, M.P.; Moralejo, M.; Molina-Cano, J.L.; Komatsuda, T.; Igartua, E. Resequencing theVrs1 gene in Spanish barley landraces revealed reversion of six-rowed to two-rowed spike. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsuda, T.; Li, W.; Takaiwa, F.; Oka, S. High resolution map around the vrs1 locus controlling two- and six-rowed spike in barley, Hordeum vulgare. Genome 1999, 42, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsuda, T.; Pourkheirandish, M.; He, C.; Azhaguvel, P.; Kanamori, H.; Perovic, D.; Stein, N.; Graner, A.; Wicker, T.; Tagiri, A.; et al. Six-rowed barley originated from a mutation in a homeodomain-leucine zipper I-class homeobox gene. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 1424–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, H.M.; Eggert, K.; Koppolu, R.; Alqudah, A.M.; Poursarebani, N.; Fazeli, A.; Sakuma, S.; Tagiri, A.; Rutten, T.; Govind, G.; et al. VRS2 regulates hormone-mediated inflorescence patterning in barley. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bull, H.; Casao, M.C.; Zwirek, M.; Flavell, A.J.; Thomas, W.T.B.; Guo, W.; Zhang, R.; Rapazote-Flores, P.; Kyriakidis, S.; Russell, J.; et al. Barley SIX-ROWED SPIKE3 encodes a putative Jumonji C-type H3K9me2/me3 demethylase that represses lateral spikelet fertility. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppolu, R.; Anwar, N.; Sakuma, S.; Tagiri, A.; Lundqvist, U.; Pourkheirandish, M.; Rutten, T.; Seiler, C.; Himmelbach, A.; Ariyadasa, R.; et al. Six-rowed spike4 (Vrs4) controls spikelet determinacy and row-type in barley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13198–13203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsay, L.; Comadran, J.; Druka, A.; Marshall, D.F.; Thomas, W.T.B.; Macaulay, M.; MacKenzie, K.; Simpson, C.; Fuller, J.; Bonar, N.; et al. INTERMEDIUM-C, a modifier of lateral spikelet fertility in barley, is an ortholog of the maize domestication gene TEOSINTE BRANCHED 1. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.T.; Law, I.F.W. Aspects of the Comparative Physilogy of Grain Yield in Cereals. Adv. Agron. 1976, 28, 301–359. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Kamal, R.; Shanmugaraj, N.; Rutten, T.; Thirulogachandar, V.; Zhao, S.; Hoffie, I.; Hensel, G.; Rajaraman, J.; Moya, Y.A.T.; et al. A molecular framework for grain number determination in barley. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, eadd0324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slafer, G.A.; Molina-Cano, J.L.; Savin, R.; Araus, J.L.; Romagosa, I. Barley Science: Recent Advances from Molecular Biology to Agronomy of Yield and Quality; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Yang, J.; McNeil, D.L.; Zhou, M. Identification and molecular mapping of a dwarfing gene in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and its correlation with other agronomic traits. Euphytica 2010, 175, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, J.M.; Corey, A.; Hayes, P.M.; Jobet, C.; Kleinhofs, A.; Kopisch-Obusch, A.; Kramer, S.F.; Kudrna, D.; Li, M.; Riera-Lizarazu, O.; et al. Molecular mapping of the Oregon Wolfe Barleys: A phenotypically polymorphic doubled-haploid population. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Sonokawa, R.; Miura, H.; Sawada, S. Dwarfing effect associated with the threshability gene Q on wheat chromosome 5A. Plant Breed. 2003, 122, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turuspekov, Y.; Mano, Y.; Honda, I.; Kawada, N.; Watanabe, Y.; Komatsuda, T. Identification and mapping of cleistogamy genes in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, K.; Xiao, J.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Yuan, C.; Cao, A.; You, F.M.; Yang, D.; An, S.; Wang, H.; et al. Rht23 (5Dq′) likely encodes a Q homeologue with pleiotropic effects on plant height and spike compactness. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2018, 131, 1825–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Baumann, U.; Fincher, G.B.; Collins, N.C. Flt-2L, a locus in barley controlling flowering time, spike density, and plant height. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2009, 9, 243–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houston, K.; McKim, S.M.; Comadran, J.; Bonar, N.; Druka, I.; Uzrek, N.; Cirillo, E.; Guzy-Wrobelska, J.; Collins, N.C.; Halpin, C.; et al. Variation in the interaction between alleles of HvAPETALA2 and microRNA172 determines the density of grains on the barley inflorescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16675–16680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taketa, S.; Yuo, T.; Sakurai, Y.; Miyake, S.; Ichii, M. Molecular mapping of the short awn 2 and dense spike 1genes on barley chromosome 7H. Breed. Sci. 2011, 61, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Druka, A.; Franckowiak, J.; Lundqvist, U.; Bonar, N.; Alexander, J.; Houston, K.; Radovic, S.; Shahinnia, F.; Vendramin, V.; Morgante, M.; et al. Genetic dissection of barley morphology and development. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 617–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahinnia, F.; Druka, A.; Franckowiak, J.; Morgante, M.; Waugh, R.; Stein, N. High resolution mapping of Dense spike-ar (dsp.ar) to the genetic centromere of barley chromosome 7H. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikołajczak, K.; Ogrodowicz, P.; Gudyś, K.; Krystkowiak, K.; Sawikowska, A.; Frohmberg, W.; Górny, A.; Kędziora, A.; Jankowiak, J.; Józefczyk, D.; et al. Quantitative Trait Loci for Yield and Yield-Related Traits in Spring Barley Populations Derived from Crosses between European and Syrian Cultivars. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lhundrup, N.; Guo, G.; Dol, K.; Chen, P.; Gao, L.; Chemi, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Nyema, T.; et al. Characterization of Genetic Diversity and Genome-Wide Association Mapping of Three Agronomic Traits in Qingke Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Q.; Dockter, C.; Sirijovski, N.; Zakhrabekova, S.; Lundqvist, U.; Gregersen, P.L.; Hansson, M. Analysis of barley mutants ert-c.1 and ert-d.7 reveals two loci with additive effect on plant architecture. Planta 2021, 254, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, E.; Blake, V.C.; Cooper, L.; Wight, C.P.; Michel, S.; Cagirici, H.B.; Lazo, G.R.; Birkett, C.L.; Waring, D.J.; Jannink, J.-L.; et al. GrainGenes: A data-rich repository for small grains genetics and genomics. Database 2022, 2022, baac034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, L.A.; Li, T.; Zhang, H.; et al. Fine mapping and candidate gene mining of QSc/Sl.cib-7H for spike compactness and length and its pleiotropic effects on yield-related traits in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2024, 137, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powder, K.E. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Mapping. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2082, 211–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikram, M.; Rauf, A.; Rao, M.J.; Maqsood, M.F.K.; Bakhsh, M.Z.M.; Ullah, M.; Batool, M.; Mehran, M.; Tahira, M. CRISPR-Cas9 based molecular breeding in crop plants: A review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2024, 51, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wen, Y.; Guo, X. CRISPR/Cas9 for genome editing: Progress, implications and challenges. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R40–R46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Deng, G.; Su, Y.; Yang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, X.; Pu, X.; Yang, W.; et al. Genetic dissection of quantitative trait loci for grain size and weight by high-resolution genetic mapping in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2022, 135, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCouch, S.; Cho, Y.-G.; Yano, M.; Paul, E.; Blinstrub, M.; Morishima, H.; Kinoshita, T. Report on QTL nomenclature. Rice Genet. Coop. 1997, 14, 11–13. [Google Scholar]
- Navrátilová, P.; Toegelová, H.; Tulpová, Z.; Kuo, Y.T.; Stein, N.; Doležel, J.; Houben, A.; Šimková, H.; Mascher, M. Prospects of telomere-to-telomere assembly in barley: Analysis of sequence gaps in the MorexV3 reference genome. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2022, 20, 1373–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, S.K.; Wang, N.; Turuspekov, Y.; Pourkheirandish, M.; Sinsuwongwat, S.; Chen, G.; Sameri, M.; Tagiri, A.; Honda, I.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Cleistogamous flowering in barley arises from the suppression of microRNA-guided HvAP2 mRNA cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 490–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sourdille, P.; Tixier, M.H.; Charmet, G.; Gay, G.; Cadalen, T.; Bernard, S.; Bernard, M. Location of genes involved in ear compactness in wheat (Triticum aestivum) by means of molecular markers. Mol. Breed. 2000, 6, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Wang, Y.; Yan, S.; Sun, D.; Sun, G. Population genetics and phylogenetic analysis of the vrs1 nucleotide sequence in wild and cultivated barley. Genome 2014, 57, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkelish, A.; Alqudah, A.M.; Alhudhaibi, A.M.; Alqahtani, H.; Börner, A.; Thabet, S.G. Inherited endurance: Deciphering genetic associations of transgenerational and intergenerational heat stress memory in barley. Plant Mol. Biol. 2025, 115, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thirulogachandar, V.; Alqudah, A.M.; Koppolu, R.; Rutten, T.; Graner, A.; Hensel, G.; Kumlehn, J.; Bräutigam, A.; Sreenivasulu, N.; Schnurbusch, T.; et al. Leaf primordium size specifies leaf width and vein number among row-type classes in barley. Plant J. 2017, 91, 601–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author (s) and contributor (s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor (s). MDPI and/or the editor (s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |


| Traits | Year | Parent | The YJ × H30 RIL Lines | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YJ | H30 | Min. | Max. | Mean | SD | Skewness | Kurtosis | CV (%) | H2 (%) | ||
| SL (cm) | 2022WH | 5.00 | 7.80 | 3.53 | 10.63 | 6.69 | 1.49 | 0.203 | −0.506 | 22.25 | 96.33 |
| 2023WH | 4.28 | 7.43 | 3.80 | 9.28 | 6.57 | 1.29 | −0.021 | −0.74 | 19.68 | ||
| 2024WH | 5.13 | 7.30 | 3.60 | 9.58 | 6.46 | 1.40 | 0.049 | −0.754 | 21.60 | ||
| BLUP | 4.05 | 9.24 | 6.57 | 1.30 | 0.03 | −0.821 | 19.73 | ||||
| SRN | 2022WH | 24.00 | 35.50 | 18.00 | 47.00 | 32.81 | 5.03 | −0.181 | −0.219 | 15.34 | 92.16 |
| 2023WH | 23.00 | 38.00 | 18.67 | 46.67 | 33.41 | 5.74 | −0.044 | −0.378 | 17.20 | ||
| 2024WH | 26.00 | 36.50 | 20.00 | 44.50 | 33.79 | 5.39 | −0.118 | −0.632 | 15.95 | ||
| BLUP | 21.12 | 43.77 | 33.28 | 4.63 | −0.054 | −0.498 | 13.91 | ||||
| SD (cm−1) | 2022WH | 4.81 | 4.55 | 3.47 | 7.94 | 5.05 | 0.94 | 0.671 | −0.099 | 18.68 | 85.89 |
| 2023WH | 5.38 | 5.15 | 3.11 | 7.28 | 5.17 | 0.87 | 0.379 | −0.244 | 16.80 | ||
| 2024WH | 5.04 | 5.01 | 3.47 | 8.30 | 5.38 | 1.02 | 0.611 | −0.086 | 18.98 | ||
| BLUP | 3.97 | 7.03 | 5.20 | 0.72 | 0.515 | −0.505 | 13.80 | ||||
| QTL | Traits | Environment | Chromosome | Position (cM) | Left Marker | Right Marker | LOD | PVE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qSL2-1 | SL/SRN | 22WH/23WH/BLUP | 2H | 75.5–76.5 | BM1294 | BM1295 | 16.82–28.48 | 14.23–20.38 |
| qSRN2-1 | SRN | 22WH/23WH/24WH/BLUP | 2H | 106.5–108.5 | BM1767 | BM1779 | 9.67–17.25 | 10.74–18.24 |
| qSL2-5 | SL/SD | 22WH/24WH/BLUP | 2H | 150.5–151.5 | BM1997 | BM1998 | 28.47–36.11 | 28.51–53.87 |
| qSL5-1 | SL/SRN | 22WH/23WH/24WH/BLUP | 5H | 126.5–133.5 | EM1736 | EM1797 | 7.53–26.88 | 9.93–20.79 |
| Stable and Major QTLs | Chromosomes | Morex V3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Left Physical Distance (bp) | Right Physical Distance (bp) | Interval Length (Mb) | ||
| qSL2-1 | 2H | 463,148,813 | 463,211,912 | 0.06 |
| qSRN2-1 | 2H | 570,208,797 | 572,896,231 | 2.69 |
| qSL2-5 | 2H | 634,533,780 | 635,723,402 | 1.19 |
| qSL5-1 | 5H | 526,921,437 | 537,239,981 | 10.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Cao, Q.; Wang, C.; Sun, G.; Ren, X. QTL Identification and Candidate Gene Prediction for Spike-Related Traits in Barley. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051185
Wang X, Chen J, Cao Q, Wang C, Sun G, Ren X. QTL Identification and Candidate Gene Prediction for Spike-Related Traits in Barley. Agronomy. 2025; 15(5):1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051185
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaofang, Junpeng Chen, Qingyu Cao, Chengyang Wang, Genlou Sun, and Xifeng Ren. 2025. "QTL Identification and Candidate Gene Prediction for Spike-Related Traits in Barley" Agronomy 15, no. 5: 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051185
APA StyleWang, X., Chen, J., Cao, Q., Wang, C., Sun, G., & Ren, X. (2025). QTL Identification and Candidate Gene Prediction for Spike-Related Traits in Barley. Agronomy, 15(5), 1185. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15051185







