Abstract
Callose plays an important role in plant development and in response to a wide range of biotic and abiotic stresses. However, the systematic identification of callose synthase (CalS), the major enzyme for callose biosynthesis, has been delayed in crops, especially in Solanaceae. In the current research, 18 CalS genes (NtCalS1–NtCalS18) were identified in Nicotiana tabacum and classified into four subfamilies. A comprehensive analysis of their physicochemical properties, gene structure, and evolutionary history highlighted their evolutionary conservation. We also identified a number of NtCalSs that responded to the infection with Phytophthora nicotianae and Ralstonia solanacearum, as well as to drought and cold treatments, by analyzing RNA-seq data. NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, a highly homologous gene pair, were selected to create mutants using the CRISPR-Cas9 technology for their drastic response to Phytophthora nicotianae infection as well as the strong expression levels in roots. The mutants with the simultaneous knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, compared with the control plants, displayed more resistance to tobacco black shank caused by Phytophthora nicotianae. Furthermore, the real-time quantitative PCR (qRT-PCR) assay showed that the knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 activated the signaling pathways mediated by plant hormones salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ET) before and after the infection of Phytophthora nicotianae and thus may have contributed to tobacco immunity against black shank. These findings contribute valuable information for further understanding the roles of CalS genes in tobacco stress responses and provide alternative genes for resistance improvement.
1. Introduction
Callose, known as β-1,3-glucan, is linked by β-1,3-glycosidic bonds and also contains a number of β-1,6-glucan branches and widely exists in higher plants [1]. Callose metabolism is tightly involved in plant development and a wide range of stress responses due to its chemical properties and effective barrier effect. In general, callose can be deposited on pollen, sieve plate, stomata, and pathogen attack sites [2,3]. Under pathogen attack, the deposition of callose can prevent the penetration of pathogens as physical barriers or inhibit their development [4]. The deposition of callose can be regulated by hormone signals, pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), resistance-associated chemicals, and secondary metabolites [5].
Callose synthase, the key enzyme in callose biosynthesis, therefore, has a major impact on plant development. Twelve CalS genes have been systematically identified and well characterized in Arabidopsis thaliana [6]. AtCalS7 is involved in the formation of the sieve plate pore, which directly affects the transport function of the phloem [7]. Mutation of AtCalS10 in Arabidopsis thaliana reduces callose deposition in the plasmodesmata and the cell plate, affecting cellular nutrient transport and signaling and the division of the cytoplasm [8]. AtCalS10 also affects the formation of stomata in plant leaves [8]. Callose synthase is essential for pollen development, and abnormal callose deposition and degradation leads to sterility in flowering plants. Several AtCalSs are involved in pollen development but have different functions. AtCalS5 plays an important role in pollen tube wall formation during pollen tube elongation [9]. AtCalS9 is required for both asymmetric and symmetric mitosis during gametogenesis [10]. AtCals10 affects the initial positioning of the cell plate in asymmetric mitosis [11]. AtCals11 and AtCals12 play a vital role in microspore tetrad formation [12].
In higher plants, callose deposition mediated by callose synthase is extremely important for biotic stress resistance [2,3,4]. Silencing of ClCals1 in Citrus limon increases plant susceptibility to Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri [13]. Down-regulation of HvGsl6, a homologue of AtCals12, in barley leads to a reduction of callose accumulation at infection sites and an increase in susceptibility to the pathogen Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei [14]. AtCalS12 (also known as PMR4) has been well studied in the interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and pathogens. During powdery mildew attacks, AtCalS12 regulates the callose biosynthesis at infection sites and thus affects plant immunity [15]. Surprisingly, it was found that Arabidopsis thaliana AtCalS12 mutants not only failed to synthesize callose at the infection site but were also more resistant to powdery mildew [16]. This surprising finding is consistent with subsequent research on downy mildew in Arabidopsis thaliana, in which AtCalS12 mutants were found to be more resistant to downy mildew [17]. To explain these contradictory findings, it has been proposed that pathogen-induced callose may negatively regulate the salicylic acid signaling pathway in plants [16]. It was also found that silencing the AtCalS12 homologue in tomato resulted in increased resistance to powdery mildew [18].
The CalS gene family was first well studied in Arabidopsis thaliana [6]. Subsequently, the systematic identification of CalS genes was carried out in several vascular plants, including Vitis vinifera [19], Brassica napus [20], Citrus sinensis [21], Zea mays [22], Gossypium hirsutum [23], Cucumis sativus [24], Glycine max [25], and Sorghum bicolor [26], and some CalS genes induced by abiotic and biotic stresses, but not related to root diseases, were identified. Although the CalS gene family has significant potential to enhance plant stress resistance, its systematic identification has been delayed in Solanaceae, which includes many important crops such as potato, tomato, eggplant, pepper, and tobacco. Tobacco is an important commercial crop worldwide and serves as a model plant for molecular and cellular biology research. Unlike tomato, eggplant, and pepper, tobacco is an allotetraploid and therefore provides an excellent platform to study the role of CalS genes in response to stress in polyploid plants, especially considering that tobacco is subject to a wide range of root diseases. Several high-quality tobacco genomes have been assembled in recent years [27,28,29], contributing to the further identification and analysis of tobacco CalS genes. In this study, we identified CalS genes in Nicotiana tabacum and analyzed their evolutionary processes, physicochemical properties, gene structures, conserved motifs, and expression profiles. Their expression patterns in response to the root diseases black shank and bacterial wilt were systematically investigated. Furthermore, tissue-specific expression, stress-induced expression, and functional analysis by CRISPR-Cas9-mediated gene editing highlighted the role of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in tobacco black shank resistance. Our research will contribute to a better understanding of this complex gene family and provide a solid basis for the breeding application of tobacco CalS genes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Pathogen Inoculation
The tobacco cultivar Honghuadajinyuan (HD) was used to generate the mutant materials with simultaneous knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, and the seeds of HD were obtained from the National Tobacco Germplasm Resource Genebank in the Tobacco Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, with the accession number 00000540. Gene editing of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in HD was performed using the CRISPR-Cas9 technology [30] by designing the single guide RNA (sgRNA) to the highly conserved sequences between NtCalS1 and NtCalS12. Finally, HD and two homozygous T2 lines, KO-1 and KO-2, with simultaneous knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, were employed to carry out functional verification. Tobacco seeds were sown in seedling trays and placed in an artificial climate chamber (25 °C, 16 h light/8 h dark, and 70% relative humidity). One-month-old seedlings were then transplanted into 50-hole trays. When the seedlings had grown to the five-leaf stage (about two months old), they were transplanted into 9 cm pots to evaluate their resistance to tobacco black shank using a field-isolated strain of Phytophthora nicotianae race 0 [31]. Phytophthora nicotianae were grown on oatmeal agar medium at 28 °C for 14 d and then inoculated into sterilized grains for a further 14 d. Subsequently, 1 g of grains was inoculated into the base of tobacco stems, and the disease severity was evaluated every day for the next week. At the same time, root samples were collected independently at 0, 24, and 48 h after inoculation and stored at −80 °C.
2.2. Identification and Analysis of the CalS Gene Family in Tobacco
Since plant CalS proteins conservatively contain the Glucan_synthase (PF02364) and FKS1_dom1 (PF14288) domains, they were used to identify all candidate CalS genes in the Nicotiana tabacum ZY300 reference genome using the HMM search plugin of TBtools [32]. The conserved protein domains in the candidate members were confirmed using the Batch Web CD-Search tool in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) with an e-value < 0.01 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/bwrpsb/bwrpsb.cgi, accessed on 7 February 2025). Similarly, the CalS gene family was identified in Theobroma cacao, Helianthus annuus, Petunia axillaris, Capsicum annuum, Solanum tuberosum, Solanum lycopersicum, and Solanum melongena. EXPASY (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/, accessed on 7 February 2025) was used to calculate molecular weight (MW) and theoretical isoelectric point (pI). The number of transmembrane helices was predicted using TMHMM-2.0 (https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM-2.0/, accessed on 7 February 2025). MEGA 7.0 was used to construct phylogenetic trees using the neighbor-joining (NJ) method with 1000 bootstrap replications, and we then displayed them using the online iTOL tool (https://itol.embl.de/, accessed on 7 February 2025). MEME was employed to search conserved motifs, with a limit of 25 motifs and other default parameters. The exon-intron information and gene location information were fetched from the annotation files of the Nicotiana tabacum ZY300 reference genome and subsequently visualized using TBtools v2.210. MCScanX was used to identify CalS gene pairs from segmental duplication by analyzing the collinearity of NtCalSs and from tandem duplication.
2.3. RNA-Seq Data
RNA-seq data of different issues (root, shoot, and shoot apex), cold stress, drought stress, and Phytophthora nicotianae infection were downloaded from the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under the SRA accession numbers GSE95717, GSE173352, GSE214048, and GSE168854, respectively. RNA-seq data of Ralstonia solanacearum infection were downloaded from the Genome Sequence Archive in the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation (https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa/, accessed on 7 February 2025) under the BioProject number PRJCA019950.
2.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
Root samples collected independently at 0, 24, and 48 h after Phytophthora nicotianae inoculation were used to isolate total RNA using the VeZol-Pure Total RNA Isolation Kit (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). Subsequently, first-strand complementary DNA (cDNA) was synthesized with HiScript IV 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (+gDNA wiper) (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). The qRT-PCR assay was carried out on the Roche LightCycler 96 instrument (Basel, Switzerland) with ChamQ SYBR Color qPCR Master Mix (Vazyme Biotech Co., Ltd., Nanjing, China). Each PCR reaction contained 10 μL master mix, 7 μL ddH2O, 1 μL cDNA, and 1 μL of forward and reverse primers (5 μM). The qRT-PCR assay was performed with at least three technical replicates and as follows: 95 °C for 30 s and 95 °C for 10 s accompanied by 60 °C for 30 s with 40 cycles. Relative expression levels were calculated using the 2−ΔΔCt method [33] with the histone H3.3 encoding gene (NCBI Reference Sequence: XM_016638287.1) as an internal control, and the results were analyzed and displayed using GraphPad Prism 8.3.0 (San Diego, CA, USA). The one-way analysis of variance was used to determine significantly differential expression.
2.5. Functional Analysis of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12
To analyze the roles of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in tobacco black shank resistance, we created the mutant materials with simultaneous knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 based on the tobacco main cultivar HD. Two homozygous T2 lines were selected using the selection criteria of drastic changes in the NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 encoding proteins, consistent phenotype, and no off-target observations. Subsequently, the mutant materials and the control (HD) were inoculated with Phytophthora nicotianae to determine their resistance using the procedure described above. The disease symptoms were observed and then indicated as a disease index [34]. To further determine disease severity, DNA was extracted from root samples at 48 h post inoculation using the CTAB method, and Phytophthora nicotianae biomass was reflected by calculating the content of the 40S ribosomal protein S3A (WS21) encoding gene of Phytophthora nicotianae [34]. To analyze the potential mechanisms underlying black shank resistance, the expression patterns of marker genes related to plant hormones and reactive oxygen species (ROS) were analyzed in the mutant materials and HD using the qRT-PCR method. These genes include the SA-responsive genes NtCHN50, NtPAD4, and NtEDS1, the JA-responsive gene NtPR1b and NtPDF1.2, the ET production-associated genes NtACC Oxidase, NtEFE26, and NtACS6, and ROS production-associated gene NtSOD1 [35,36,37].
3. Results
3.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of NtCalSs
In general, CalS proteins contain the Glucan_synthase domain (PF02364) and the FKS1_dom1 domain (PF14288) [21,22]. Therefore, we identified 18 members containing the two conserved domains based on the Nicotiana tabacum reference genome, which were subsequently named NtCalS1–NtCalS18 according to their positions on the chromosomes. To elucidate the phylogenetic relationships of tobacco CalS genes, a phylogenetic tree including the CalS genes from Nicotiana tabacum, Vitis vinifera [19], Cucumis sativus [24], Arabidopsis thaliana [6], and Zea mays [22] was constructed (Figure 1). Based on the clustering results and available classification information, 18 NtCalSs were classified into four subfamilies, including eight Group-I members, two Group-II members, four Group-III members, and four Group-IV members. Group-I also included five members from cucumber, six members from Arabidopsis thaliana, four members from grape, and four members from maize. The number of CalS genes from the four species is 1, 2, 1, and 1 in Group-II, 1, 2, 2, and 2 in Group-III, and 2, 2, 1, and 2 in Group-IV. The CalS gene family appears to be evolutionarily conservative because Nicotiana tabacum, an allotetraploid, has almost twice as many CalS genes as the dicots cucumber, Arabidopsis thaliana, and grape, and the monocot maize in each group.
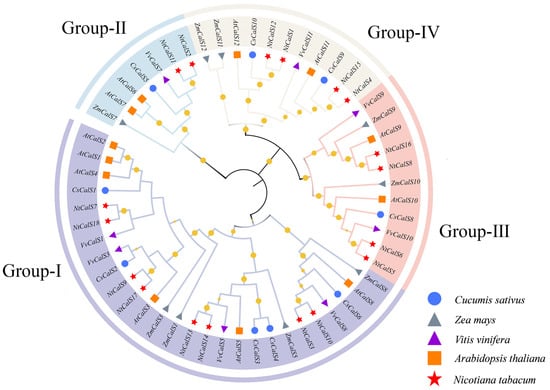
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic analysis of CalS proteins from Nicotiana tabacum, Vitis vinifera, Cucumis sativus, Arabidopsis thaliana and Zea mays. CalSs from Nicotiana tabacum, Vitis vinifera, Cucumis sativus, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Zea mays are marked with red star, purple triangle, blue circle, orange square, grey triangle, respectively. Bootstrap values > 50% are shown by yellow solid circles on the branches, and their sizes reflect the reliability.
We further analyzed the physicochemical properties of tobacco CalS proteins (Table S1). The results showed that their average protein length in Group-I, Group-II, Group-III, and Group-IV was 1944.4, 1908, 1883.5, and 1769 aa, respectively, accompanied by average molecular weights of 224.1, 221.9, 216.1, and 206.2 kDa. In addition, the theoretical isoelectric points (pI) of tobacco CalS proteins were all greater than 7, and they were therefore considered to be alkaline proteins. Apparently, there were no significant differences in these properties among the four subfamilies.
3.2. Gene Structure and Conserved Motif Analysis of NtCalSs
To further explore the phylogenetic relationships and potential function differentiation of NtCalSs, their conserved motifs, conserved domains, and gene structures were systematically analyzed. NtCalS proteins had a consistent distribution of conserved motifs, and there was no obvious divergence between different subfamilies (Figure 2a). Conserved domain analysis revealed that all members possessed the Glucan_synthase domain (PF02364) and the FKS1_dom1 domain (PF14288) (Figure 2b). In addition, Group-I and Group-II members also possessed the Vta1 domain (PF04652). The Vta1 domain was not highlighted in the conserved motif analysis, which may be due to the high similarity of NtCalS proteins and a motif identification limit of 25 failing to identify the conserved motif corresponding to Vta1. Gene structure analysis showed that members of Group-III had the longest gene sequences and that members of Group-I and Group-II had similar gene structures (Figure 2c). Interestingly, the four members of Group-IV had only a small number of introns, which is consistent with the results in cucumber [24] and maize [22] and further illustrates the evolutionary conservation of the CalS family.
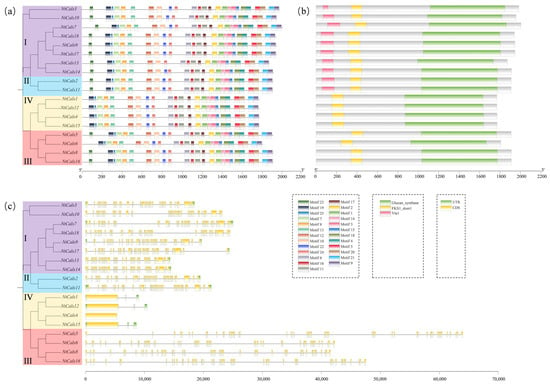
Figure 2.
Structure characteristics of NtCalSs in tobacco. (a) A schematic representation of 25 conserved motifs in tobacco CalS proteins is displayed, and different motifs are distinguished through colors. (b) Conserved domains of tobacco CalS proteins. (c) The exon is represented by a yellow box, the intron by a black line and the UTR by a green box.
3.3. Chromosomal Localization and Gene Duplication Events of NtCalSs
Based on the Nicotiana tabacum reference genome, 18 NtCalSs were located on 12 chromosomes. Among them, chromosomes 2 and 10 contained three CalS genes each, chromosomes 9 and 18 contained two CalS genes each, and the other eight chromosomes contained only one CalS gene each (Figure 3a). To investigate the expansion of the tobacco CalS family, MCScanX was employed to identify segmental and tandem duplications. Two tandem duplication gene pairs were identified, NtCalS8 and NtCalS9 on chromosome 9 and NtCalS16 and NtCalS17 on chromosome 18, while no segmental duplication gene pairs were identified (Figure 3a,b). Tobacco has undergone an ancient hexaploidization event shared by eudicots and a Solanaceae-specific polyploidization event [38], but we were unable to identify segmental duplications in the tobacco CalS family. One explanation could be that NtCalSs may play a crucial role in plant development and may have a dosage effect, so that they tend to restore the original gene number after a polyploidization event. This inference is consistent with the fact that the number of CalS is relatively stable in many species. In addition, NtCalSs belonging to the S and T subgenomes were found to have a strict correspondence (Figure 3b), further illustrating the evolutionary conservation of the tobacco CalS family.
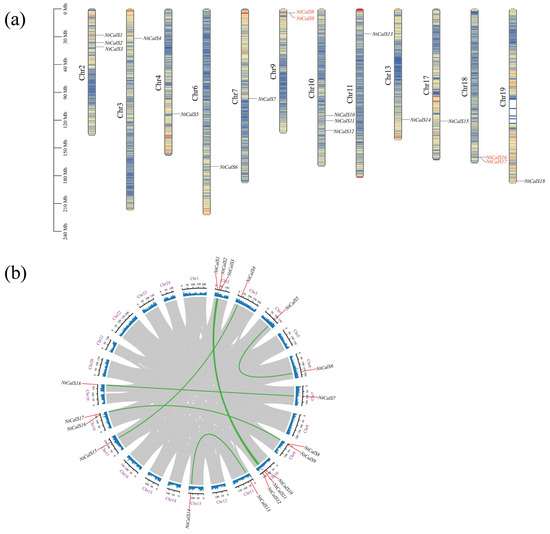
Figure 3.
Chromosomal localization and gene duplication events of NtCalSs. (a) Chromosomal localization and tandem duplication events of NtCalSs. The 12 columns represent the 12 chromosomes in tobacco, and the inner fillings represent gene density, with blue to red representing gene density from low to high. The tandem duplication gene pairs are shown in red. (b) Segmental duplication events of NtCalSs. Grey lines indicate the collinear blocks in tobacco. No segmental duplication gene pairs were identified within subgenomes S and T. Green line links homologous genes between S and T subgenomes.
3.4. Evolutionary History of CalS Gene Family
To further investigate the evolutionary history of the tobacco CalS family, a phylogenetic tree was constructed using the protein sequences of a total of 117 CalS members from the monocots Zea mays [22] and Oryza sativa [39] and the dicots Theobroma cacao, Arabidopsis thaliana [6], Helianthus annuus, Petunia axillaris, Nicotiana tabacum, Capsicum annuum, Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, and Solanum melongena. The results showed that Group-I and Group-IV are present in all eleven species, whereas Group-II and Group-III are missing in some species (Figure 4a,b; Table S2). The CalS family, mainly Group-I, has been greatly expanded in sunflower (Helianthus annuus), which belongs to the Campanulids of the Asterids, possibly leading to functional differentiation or neofunctionalization. In contrast, the CalS family has remained relatively restricted in the Solanaceae species belonging to the Lamiids of the Asterids. Specifically, Petunia axillaris lacks Group-III and potato (Solanum tuberosum) lacks Group-II and Group-III, perhaps because unlike other Solanaceae species, Petunia axillaris has only 14 chromosomes (2n = 14), whereas potato produces stolons (underground stems) that swell into tubers under suitable environmental conditions [40,41]. In the case of the tobacco CalS family, it possesses all four subfamilies and maintains a relatively stable number, suggesting that NtCalSs play an important role in tobacco development or stress responses.
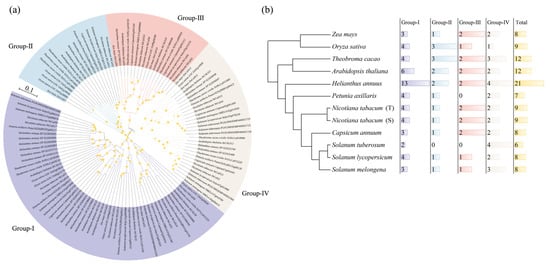
Figure 4.
Evolutionary history of CalS gene family. (a) Phylogenetic relationships of CalS genes from Zea mays, Oryza sativa, Theobroma cacao, Arabidopsis thaliana, Helianthus annuus, Petunia axillaris, Nicotiana tabacum, Capsicum annuum, Solanum lycopersicum, Solanum tuberosum, and Solanum melongena. Two members each of Zea mays and Oryza sativa were discarded due to their low integrity. (b) The number of CalS genes of the different subfamilies in the eleven species.
3.5. Expression Patterns of NtCalSs in Different Tissues
The expression patterns of NtCalSs in different tissues (root, shoot, and shoot apex) were analyzed using NCBI SRA data (GSE95717) (Figure 5). The results showed that the corresponding members between the S and T subgenomes had similar expression patterns. Members belonging to Group-II, Group-III, and Group-IV had high expression levels in all three tissues, especially in roots. In contrast, members belonging to Group-I had a more variable expression pattern. Specifically, NtCalS3 and NtCalS10 were mainly expressed in roots, NtCalS13 and NtCalS14 had almost no expression in the three tissues, and NtCalS7, NtCalS9, NtCalS17, and NtCalS18 showed similar expression patterns with members of Group-II, Group-III, and Group-IV. In addition to the Glucan_synthase domain (PF02364) and the FKS1_dom1 domain (PF14288), members of Group-I also possess the Vta1 domain (PF04652) (Figure 2b), and their more complex expression patterns, compared with members of Group-II, Group-III, and Group-IV, might suggest more complex functions.
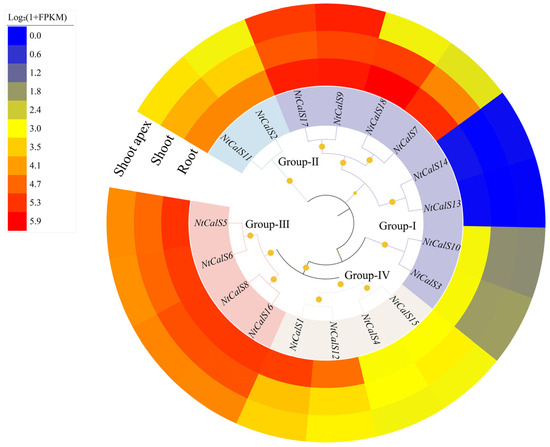
Figure 5.
Expression patterns of NtCalSs in different tissues. Heatmaps exhibit gene expression levels that are calculated as log2(1+FPKM), with blue to red representing low to high expression, and the original FPKM values are provided in Table S3.
3.6. Expression Patterns of NtCalSs Under Abiotic and Biotic Stresses
We further analyzed the expression patterns of NtCalS in response to cold (NCBI SRA accession: GSE173352), drought (NCBI SRA accession: GSE214048), Phytophthora nicotianae infection (NCBI SRA accession: GSE168854), and Ralstonia solanacearum infection (NGDC GSA accession: PRJCA019950) (Figure 6). As shown, members belonging to Group-II and Group-IV were barely responsive to cold and drought treatments. Group-III members responded slightly to cold and drought treatments. NtCalS9 and NtCalS17 in Group-I responded strongly to drought treatment. In case of biotic stresses, NtCalS7, NtCalS9, NtCalS17, and NtCalS18 in Group-I tended to decrease their expression after Phytophthora nicotianae and Ralstonia solanacearum infection, whereas Group-III members were induced moderately. Significantly, NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in Group-IV were highly induced by Phytophthora nicotianae and Ralstonia solanacearum infection and may therefore play an important role in immunity to tobacco root diseases.
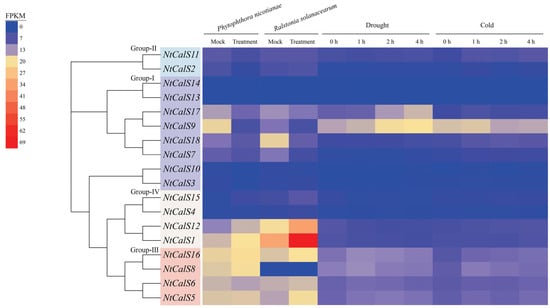
Figure 6.
Expression patterns of NtCalSs under abiotic and biotic stresses. Heatmaps show gene expression levels, with blue to red representing low to high expression, and the original FPKM values are shown in Table S4.
3.7. Functional Analysis of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12
NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, belonging to the T and S subgenomes respectively, are highly homologous genes with a protein identity of 99.21%. Considering the great potential of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in immunity to tobacco root diseases, we used the CRISPR-Cas9 technology to simultaneously knockout NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in a main tobacco cultivar, HD (Figure 7a). Two homozygous T2 lines were developed, one with two 1 bp insertions in NtCalS1 and a 359 bp deletion in NtCalS12 and another with a 10 bp deletion in NtCalS1 and a 361 bp deletion in NtCalS12. Considering that all mutations occurred in the CDS region, the encoded proteins should have undergone drastic changes, and we then analyzed the resistance of the mutants to tobacco black shank caused by Phytophthora nicotianae infection. The results showed that the knockout mutants exhibited greater resistance to tobacco black shank than the control, accompanied by less Phytophthora nicotianae content in the mutants (Figure 7b–d). Previous studies have shown that both overexpression and silencing of CalS have the potential to enhance disease resistance in plants [42,43]. In the present study, to investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying the enhanced black shank resistance caused by the knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12, the expression patterns of marker genes related to SA, JA, ET, and ROS pathways were analyzed in the knockout mutants (Figure 7e; Table S5). As shown, the marker genes were activated by the knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 before Phytophthora nicotianae infection and showed higher expression levels in the knockout mutants compared to the control after Phytophthora nicotianae infection. It is suggested that knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 may lead to changes in cell wall structure and composition, and the plant in turn initiates the cell wall integrity (CWI) maintenance mechanism [44,45].
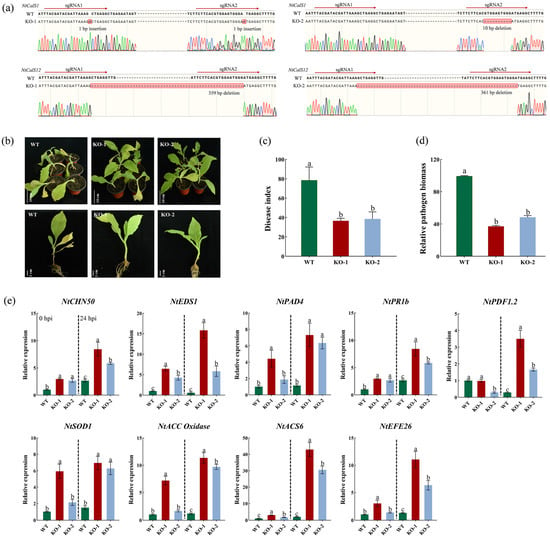
Figure 7.
Functional analysis of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12. (a) The identification of mutants with the simultaneous knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12. The red shadow indicates different types of editing. (b) Disease symptoms of the control and mutants inoculated with Phytophthora nicotianae at 5 days post inoculation (dpi). (c) Disease index of the control and mutants inoculated with Phytophthora nicotianae at 5 dpi. (d) Relative biomass of Phytophthora nicotianae in the roots of the control and mutants. (e) Expression patterns of marker genes related to SA (NtCHN50, NtEDS1 and NtPAD4), JA (NtPR1b and NtPDF1.2), ET (NtACC Oxidase, NtACS6 and NtEFE26) and ROS (NtSOD1) signaling pathways in the roots of the control and mutants. The panels on the left and right of the dashed line show the expression patterns at 0 h post inoculation (hpi) and 24 hpi, respectively. The significance of the difference is calculated using one-way analysis of variance, with different lowercase letters indicating significant differences at the 0.05 level.
4. Discussion
The CalS gene family is widely distributed in plants, and researchers have systematically identified CalS genes in some flowering plants, including Arabidopsis thaliana [6], Zea mays [22], barley [46], Oryza sativa [39], and cabbage [47], with CalS gene numbers of 12, 10, 6, 11, and 15, respectively. Typically, the CalS gene family has been classified into four subfamilies, including Group-III and Group-IV with the Glucan_synthase domain (PF02364) and the FKS1_dom1 domain (PF14288) and Group-I and Group-II that contain another Vta1 domain (PF04652) in addition to the above two domains. In terms of gene structure, Group-I, Group-II, and Group-III tend to be more complex, while Group-IV has fewer introns. In addition, CalS proteins usually have an isoelectric point greater than 7 and are alkaline proteins [23]. In the present study, we have identified 18 NtCalSs in Nicotiana tabacum, an allotetraploid, which is close to twice the number of CalS genes in the diploid plants Arabidopsis thaliana, Zea mays, and Oryza sativa. The tobacco CalS gene family is similar to that of other species in terms of phylogenetic classification, conserved domains, gene structure patterns, and physicochemical properties, indicating that the CalS gene family may play an important role in plant development and/or stress responses and thus has remained relatively stable in gene number and molecular properties.
In this study, we analyzed the expression patterns of NtCalSs in response to the abiotic stresses drought and cold and found that Group-III members responded slightly to drought and cold treatments, some members in Group-I had a strong response to drought treatments, while the members belonging to Group-II and Group-IV rarely responded to drought and cold treatments (Figure 6). Feng et al. found that cotton CalS genes of Group-III (i.e., Group-B in their study) were induced under cold, heat, salt, and drought treatments [23], suggesting that the CalS gene family has some conservation of function. Wang et al. systematically analyzed the expression patterns of CalS genes in cucumber in response to powdery mildew infection and found that CsCalS8, belonging to Group-III, was highly induced [24]. In this study, NtCalSs belonging to Group-II, Group-III, and Group-IV were expressed at high levels in roots, shoots, and shoot apex, with the highest expression in roots. Furthermore, we analyzed the expression patterns of NtCalSs in response to the infection of Phytophthora nicotianae and Ralstonia solanacearum, causing two main tobacco root diseases, black shank and bacterial wilt, respectively, and found that Group-III members were moderately induced and that NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in Group-IV were highly induced. It appears that these induced genes may play an important role in the interaction between tobacco and pathogens.
Considering that NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 are homologous genes belonging to the tobacco T and S subgenomes, respectively, and that they are highly expressed in tobacco roots and induced by Phytophthora nicotianae infection, we generated double knockout mutants of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 and further found that knocking out both of them significantly increased tobacco black shank resistance. NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 are highly homologous to AtCalS12 (PMR4) in Arabidopsis, StPMR4 in potato, and SlPMR4 in tomato. Arabidopsis mutants of AtCalS12 (PMR4) showed increased resistance to powdery mildew [16], silencing of StPMR4 increased resistance to late blight in potato [42], and silencing of SlPMR4 increased resistance to powdery mildew in tomato [18]. The plant has mechanisms to maintain cell wall integrity that can trigger plant defense responses by recognizing damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) or sensing the state of the cell wall-plasma membrane continuum [44,45]. Therefore, the knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 may have caused changes in cell wall composition and structure that triggered the plant defense response. To support this conclusion, we analyzed the expression patterns of well-known marker genes related to the SA, JA, ET, and ROS pathways, which are closely associated with plant immunity. In the present study, we used CHN50, EDS1, and PAD4 in the SA pathway [35], PR1b and PDF1.2 in the JA pathway [36,37]; ACC Oxidase, ACS6, and EFE26 in the ET pathway [35]; and SOD1 in the ROS pathway [37]. Knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 resulted in significant induction of these marker genes prior to Phytophthora nicotianae infection, and their expression levels were significantly higher in the mutants compared to the control after Phytophthora nicotianae infection (Figure 7), suggesting that the enhanced tobacco black shank resistance in the mutants may originate from the activation of plant immunity-related pathways. Similarly, the ET and JA pathways were activated in the Arabidopsis CESA3-deficient mutant, which exhibited enhanced resistance to the bacterium Pseudomonas syringae and the fungi Botrytis cinerea and Erysiphe cichoracearum [48,49]. Furthermore, inhibition of cellulose biosynthesis by chemical inhibitors also resulted in increased JA and ROS levels and deposition of lignin, which enhanced plant immunity [50,51]. Cellulose and callose, synthesized at the plasma membrane by the cellulose synthase complex and the callose synthase complex, respectively, are the two major glucan polymers in the plant cell wall. However, cellulose is the ubiquitous glucan in the plant cell wall, whereas callose is only found in specific cell walls, such as the cell plate, the outer wall of pollen, around the plasmodesma, and around sites of mechanical damage or pathogen infection [3]. Therefore, it is very surprising that the knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in this study led to a broad and strong activation of plant immunity-associated pathways. Although cell wall changes can trigger a series of defense responses mediated by plant hormones and activate the biosynthesis of antimicrobial compounds [44,45], the broad activation of SA, JA, ET, and ROS pathways in this study is still a confusing phenomenon, especially considering that SA and JA often interact antagonistically in response to pathogen infection [52]. A previous study in Arabidopsis showing that callose synthesis suppresses cell death induced by low-calcium conditions in leaves partially supports the results of the present study, in which the researchers proposed that potential cell wall damage under low-calcium conditions induced the expression of defense response genes (SA and JA) and that AtCalS9/GSL10-mediated callose synthesis might have contributed to alleviating cell wall damage [53]. SA, JA, ET, and ROS pathways play important roles in defense responses to bacteria, fungi, oomycetes and other pathogens. Knockout of NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 extensively activated these pathways in tobacco roots, suggesting great potential for broad-spectrum disease resistance. Therefore, investigating the role of knocking out NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 in defense against other tobacco root diseases, such as bacterial wilt caused by Ralstonia solanacearum and root rot caused by Fusarium oxysporum, will greatly facilitate their breeding application. However, it is noteworthy that the continuous and intense defense activation typically causes a growth retardation due to the growth-defense trade-off in plants [54,55]. A more feasible strategy for using NtCalS1 and NtCalS12 to improve resistance while avoiding a yield penalty may be to knock out one of the two genes, RNAi-mediated gene silencing, or to search for their function-deficient natural variation in germplasm resources.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we systematically analyzed the characteristics of the tobacco CalS gene family based on a high-quality tobacco genome and RNA-seq data. The results further highlighted the important potential of the CalS gene family in regulating tobacco development and response to biotic and abiotic stresses. Furthermore, knockout of a highly homologous gene pair, NtsCalS1 and NtsCalS12, increased tobacco black shank resistance, probably due to a broad and strong activation of plant immunity-associated pathways. Our findings contribute to a better understanding of the function of tobacco CalS genes and provide significant genes for resistance improvement.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15040884/s1, Table S1: List of CalS genes identified in Nicotiana tabacum in the current study; Table S2: List of CalS genes used in the current study; Table S3: The original FPKM values of NtCalSs in different tissues; Table S4. The original FPKM values of NtCalSs under abiotic and biotic stresses; Table S5: Primer sequences used in this study.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.L., L.C., Y.W. and D.L.; methodology, H.W., H.M., X.Q., Y.P., B.J. and L.W.; software, Y.Z. and H.S.; validation, H.W., H.M., Y.P., B.J., L.W., Y.W. and D.L.; formal analysis, H.W., H.M., X.Q., Y.Z., H.S. and Z.L.; investigation, Y.P., B.J. and L.W.; resources, Y.W., D.L. and A.Y.; data curation, H.W., H.M., X.Q., Y.Z. and H.S.; writing—original draft preparation, H.W., H.M. and Z.L.; writing—review and editing, X.Q., Z.L. and L.C.; visualization, H.W., Y.Z. and H.S.; supervision, A.Y. and L.C.; project administration, A.Y. and L.C.; funding acquisition, A.Y. and L.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program of CAAS (ASTIP-TRIC01), Youth Start-up Program of Tobacco Research Institute of CAAS (1610232023014) and Graduate Innovation Project of Yunnan University (KC-23235571).
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are included in this published article and its additional files. RNA-seq data are available in the NCBI Sequence Read Archive under SRA accession numbers GSE95717, GSE173352, GSE214048, and GSE168854, and in the National Genomics Data Center, China National Center for Bioinformation under BioProject number PRJCA019950.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Chen, X.Y.; Kim, J.Y. Callose synthesis in higher plants. Plant Signal. Behav. 2009, 4, 489–492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Piršelová, B.; Matušíková, I. Callose: The plant cell wall polysaccharide with multiple biological functions. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2013, 35, 635–644. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Andargie, M.; Fang, R. The function and biosynthesis of callose in high plants. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Fan, B.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Z. Regulation and function of defense-related callose deposition in plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clay, N.K.; Adio, A.M.; Denoux, C.; Jander, G.; Ausubel, F.M. Glucosinolate metabolites required for an Arabidopsis innate immune response. Science 2009, 323, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Ellinger, D.; Voigt, C.A. Callose biosynthesis in Arabidopsis with a focus on pathogen response: What we have learned within the last decade. Ann. Bot. 2014, 114, 1349–1358. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, D.H.; Kölling, K.; Graf, A.; Pike, M.; Calder, G.; Findlay, K.; Zeeman, S.C.; Smith, A.M. Callose synthase GSL7 is necessary for normal phloem transport and inflorescence growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2011, 155, 328–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.Y.; Liu, L.; Lee, E.; Han, X.; Rim, Y.; Chu, H.; Kim, S.W.; Sack, F.; Kim, J.Y. The Arabidopsis callose synthase gene GSL8 is required for cytokinesis and cell patterning. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 105–113. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Hong, Z.; Sivaramakrishnan, M.; Mahfouz, M.; Verma, D.P. Callose synthase (CalS5) is required for exine formation during microgametogenesis and for pollen viability in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2005, 42, 315–328. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, B.; Wang, X.; Hong, Z. Precocious pollen germination in Arabidopsis plants with altered callose deposition during microsporogenesis. Planta 2010, 231, 809–823. [Google Scholar]
- Töller, A.; Brownfield, L.; Neu, C.; Twell, D.; Schulze-Lefert, P. Dual function of Arabidopsis glucan synthase-like genes GSL8 and GSL10 in male gametophyte development and plant growth. Plant J. 2008, 54, 911–923. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enns, L.C.; Kanaoka, M.M.; Torii, K.U.; Comai, L.; Okada, K.; Cleland, R.E. Two callose synthases, GSL1 and GSL5, play an essential and redundant role in plant and pollen development and in fertility. Plant Mol. Biol. 2005, 58, 333–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enrique, R.; Siciliano, F.; Favaro, M.A.; Gerhardt, N.; Roeschlin, R.; Rigano, L.; Sendin, L.; Castagnaro, A.; Vojnov, A.; Marano, M.R. Novel demonstration of RNAi in citrus reveals importance of citrus callose synthase in defence against Xanthomonas citri subsp. citri. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2011, 9, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, J.; Schober, M.S.; Shirley, N.J.; Singh, R.R.; Jacobs, A.K.; Douchkov, D.; Schweizer, P.; Fincher, G.B.; Burton, R.A.; Little, A. Down-regulation of the glucan synthase-like 6 gene (HvGsl6) in barley leads to decreased callose accumulation and increased cell wall penetration by Blumeria graminis f. sp. hordei. New Phytol. 2016, 212, 434–443. [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs, A.K.; Lipka, V.; Burton, R.A.; Panstruga, R.; Strizhov, N.; Schulze-Lefert, P.; Fincher, G.B. An Arabidopsis callose synthase, GSL5, is required for wound and papillary callose formation. Plant Cell 2003, 15, 2503–2513. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, M.T.; Stein, M.; Hou, B.H.; Vogel, J.P.; Edwards, H.; Somerville, S.C. Loss of a callose synthase results in salicylic acid-dependent disease resistance. Science 2003, 301, 969–972. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, X.; Hong, Z.; Chatterjee, J.; Kim, S.; Verma, D.P. Expression of callose synthase genes and its connection with Npr1 signaling pathway during pathogen infection. Planta 2008, 229, 87–98. [Google Scholar]
- Huibers, R.P.; Loonen, A.E.; Gao, D.; Van den Ackerveken, G.; Visser, R.G.; Bai, Y. Powdery mildew resistance in tomato by impairment of SlPMR4 and SlDMR1. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67467. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.; Jiao, L.; Fu, S.; Yin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, J. Callose synthase family genes involved in the grapevine defense response to downy mildew disease. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 56–64. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Zou, Z.; Fernando, W.G.D. Characterization of callose deposition and analysis of the callose synthase gene family of Brassica napus in response to Leptosphaeria maculans. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, L.M.; Galdeano, D.M.; D’Alessandre, N.D.R.; Breton, M.C.; Machado, M.A. Callose synthase family genes plays an important role in the Citrus defense response to Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2019, 155, 25–38. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Q.; Zhang, P.; Su, S.; Jiang, B.; Liu, X.; Li, C.; Yu, T.; Yi, H.; Tang, J.; Cao, M. Characterization and expression analyses of callose synthase enzyme (Cals) family genes in Maize (Zea mays L.). Biochem. Genet. 2022, 60, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, X.; Qu, Y.; Li, P.; Lu, Q.; Huang, J. Genome-wide analysis of the CalS gene family in cotton reveals their potential roles in fiber development and responses to stress. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12557. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Cao, S.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Yao, J.; Xia, X.; Zhang, R. Classification and expression analysis of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) callose synthase (CalS) family genes and localization of CsCalS4, a protein involved in pollen development. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2021, 35, 1992–2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zaynab, M.; Xu, Z.S.; Yad, H.A.; Hussain, A.; Sharif, Y.; Al-Yahyai, R.; Sadder, M.; Aloufi, A.S.; Li, S. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of CalS genes in Glycine max revealed their role in development and salt stress. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2024, 36, 103049. [Google Scholar]
- Zou, K.; Liu, Y.; Wang, T.; Guan, M.; Li, X.; Li, J.; Yu, H.; Wu, D.; Du, J. Genomic identification of callose synthase (CalS) gene family in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) and comparative in silico expression analysis under aphid (Melanaphis sacchari) Infestation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierro, N.; Auberson, M.; Dulize, R.; Ivanov, N.V. Chromosome-level genome assemblies of Nicotiana tabacum, Nicotiana sylvestris, and Nicotiana tomentosiformis. Sci. Data 2024, 11, 135. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Tung, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, D.; Deng, Y.; Tian, Z.; Chen, H.; Wang, T.; Yin, W.; et al. High-quality assembled and annotated genomes of Nicotiana tabacum and Nicotiana benthamiana reveal chromosome evolution and changes in defense arsenals. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 423–437. [Google Scholar]
- Zan, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, M.; Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Han, Y.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Si, H.; Liu, Z.; et al. The genome and GeneBank genomics of allotetraploid Nicotiana tabacum provide insights into genome evolution and complex trait regulation. Nat. Genet. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Unver, T.; Zhang, B. CRISPR/Cas: A powerful tool for gene function study and crop improvement. J. Adv. Res. 2021, 29, 207–221. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, H.; Sun, M.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, D.; Jiang, C.; Ren, M.; Yuan, G.; Yu, W.; et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis reveals resistant and susceptible genes in tobacco cultivars in response to infection by Phytophthora nicotianae. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sun, M.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Xiao, B.; Yang, A.; Meng, H.; Cheng, L. Screening of tobacco genotypes for Phytophthora nicotianae resistance. J. Vis. Exp. 2022, 182, e63054. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, H.; Zhuang, R.R.; Chen, Y.T.; Deng, Y.; Cai, T.C.; Wang, S.Y.; Liu, Q.Z.; Tang, R.H.; Shan, S.H.; et al. Overexpression of the peanut CLAVATA1-like leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinase AhRLK1 confers increased resistance to bacterial wilt in tobacco. J. Exp. Bot. 2019, 70, 5407–5421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ding, W. Overexpression of NtPR-Q up-regulates multiple defense-related genes in Nicotiana tabacum and enhances plant resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tang, Y.; Tan, X.; Ding, W. NtRNF217, encoding a putative RBR E3 ligase protein of Nicotiana tabacum, plays an important role in the regulation of resistance to Ralstonia solanacearum infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abrouk, M.; Murat, F.; Pont, C.; Messing, J.; Jackson, S.; Faraut, T.; Tannier, E.; Plomion, C.; Cooke, R.; Feuillet, C.; et al. Palaeogenomics of plants: Synteny-based modelling of extinct ancestors. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 479–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, T.; Hayashi, T.; Nakayama, K.; Koike, S. Expression analysis of genes for callose synthases and Rho-type small GTP-binding proteins that are related to callose synthesis in rice anther. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Pan, S.; Cheng, S.; Zhang, B.; Mu, D.; Ni, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, S.; Li, R.; Wang, J.; et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the tuber crop potato. Nature 2011, 475, 189–195. [Google Scholar]
- Bombarely, A.; Moser, M.; Amrad, A.; Bao, M.; Bapaume, L.; Barry, C.S.; Bliek, M.; Boersma, M.R.; Borghi, L.; Bruggmann, R.; et al. Insight into the evolution of the Solanaceae from the parental genomes of Petunia hybrida. Nat. Plants 2016, 2, 16074. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Wolters, A.M.; Vossen, J.H.; Rouwet, M.E.; Loonen, A.E.; Jacobsen, E.; Visser, R.G.; Bai, Y. Silencing of six susceptibility genes results in potato late blight resistance. Transgenic Res. 2016, 25, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellinger, D.; Naumann, M.; Falter, C.; Zwikowics, C.; Jamrow, T.; Manisseri, C.; Somerville, S.C.; Voigt, C.A. Elevated early callose deposition results in complete penetration resistance to powdery mildew in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2013, 161, 1433–1444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bacete, L.; Melida, H.; Miedes, E.; Molina, A. Plant cell wall-mediated immunity: Cell wall changes trigger disease resistance responses. Plant J. 2018, 93, 614–636. [Google Scholar]
- Bacete, L.; Hamann, T. The role of mechanoperception in plant cell wall integrity maintenance. Plants 2020, 9, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schober, M.S.; Burton, R.A.; Shirley, N.J.; Jacobs, A.K.; Fincher, G.B. Analysis of the (1,3)-beta-D-glucan synthase gene family of barley. Phytochemistry 2009, 70, 713–720. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, Y.; Hou, L.; Guo, Y.; Ullah, I.; Yang, Y.; Yue, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the callose enzyme families of fertile and sterile flower buds of the chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). FEBS Open Bio 2019, 9, 1432–1449. [Google Scholar]
- Ellis, C.; Karafyllidis, I.; Wasternack, C.; Turner, J.G. The Arabidopsis mutant cev1 links cell wall signaling to jasmonate and ethylene responses. Plant Cell 2002, 14, 1557–1566. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-Blanco, C.; Feng, D.X.; Hu, J.; Sánchez-Vallet, A.; Deslandes, L.; Llorente, F.; Berrocal-Lobo, M.; Keller, H.; Barlet, X.; Sánchez-Rodríguez, C.; et al. Impairment of cellulose synthases required for Arabidopsis secondary cell wall formation enhances disease resistance. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, T.; Bennett, M.; Mansfield, J.; Somerville, C. Identification of cell-wall stress as a hexose-dependent and osmosensitive regulator of plant responses. Plant J. 2009, 57, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar]
- Mélida, H.; Largo-Gosens, A.; Novo-Uzal, E.; Santiago, R.; Pomar, F.; García, P.; García-Angulo, P.; Acebes, J.L.; Álvarez, J.; Encina, A. Ectopic lignification in primary cellulose-deficient cell walls of maize cell suspension cultures. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 357–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.; Tsuda, K. Salicylic acid and jasmonic acid crosstalk in plant immunity. Essays Biochem. 2022, 66, 647–656. [Google Scholar]
- Shikanai, Y.; Yoshida, R.; Hirano, T.; Enomoto, Y.; Li, B.; Asada, M.; Yamagami, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Shigenobu, S.; Tabata, R.; et al. Callose synthesis suppresses cell death induced by low-calcium conditions in leaves. Plant Physiol. 2020, 182, 2199–2212. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huot, B.; Yao, J.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Growth-defense tradeoffs in plants: A balancing act to optimize fitness. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Derbyshire, M.C.; Newman, T.E.; Thomas, W.J.W.; Batley, J.; Edwards, D. The complex relationship between disease resistance and yield in crops. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2024, 22, 2612–2623. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).