Vertical Distribution of Soluble Organic Nitrogen Composition in Paddy Soils: Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Application Rates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site and Experimental Design
2.2. Soil Sampling
2.3. Soil Analysis
2.3.1. Analysis of Soil Basic Properties
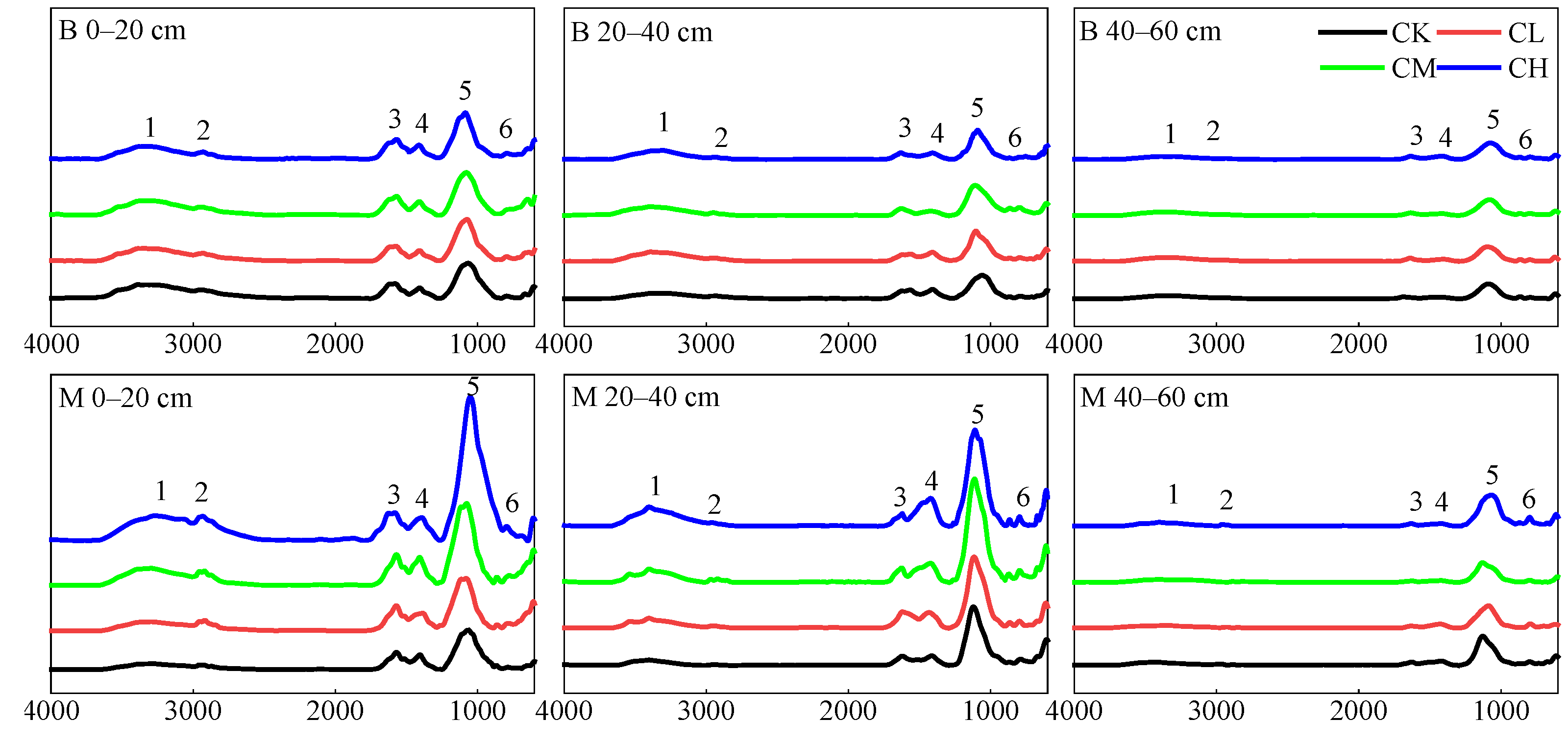
2.3.2. Analysis of Soil SON Composition
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Soil Physiochemical Properties Along Depth Gradients
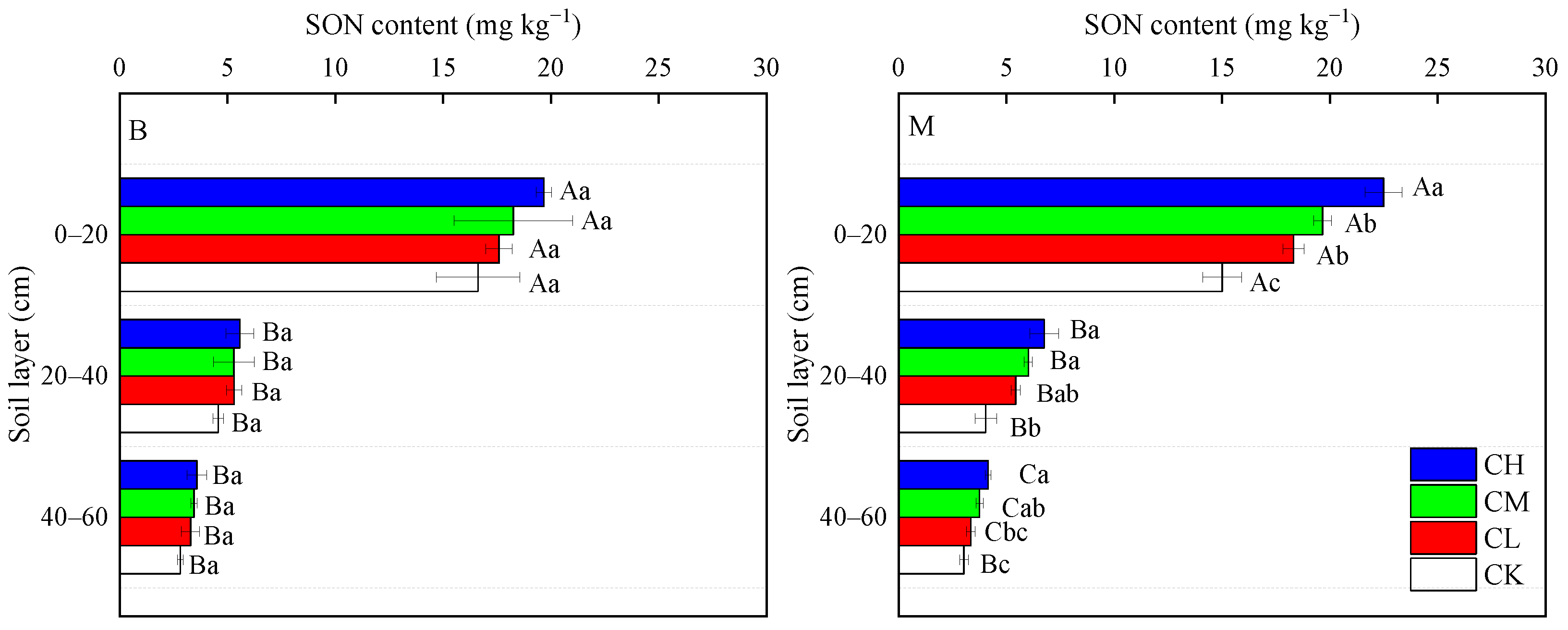
3.2. Soil SON Content Along Depth Gradients
3.3. Soil SON Composition Along Depth Gradients
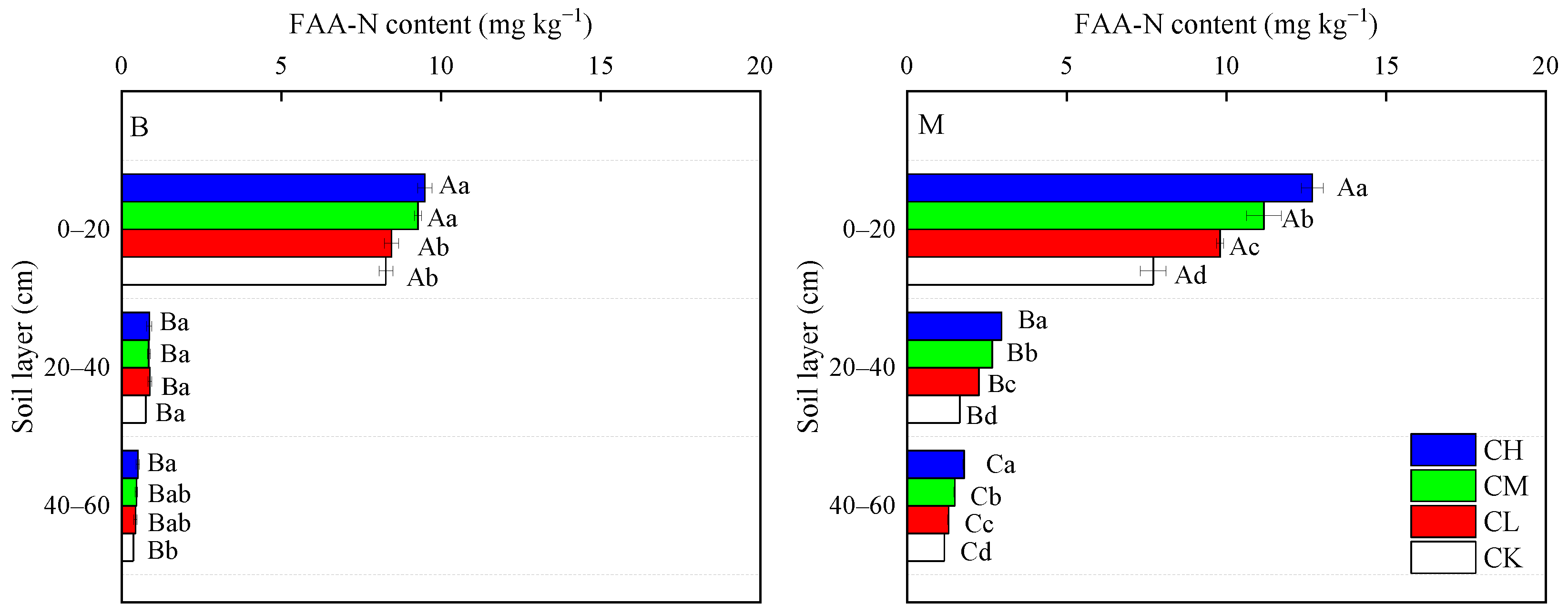
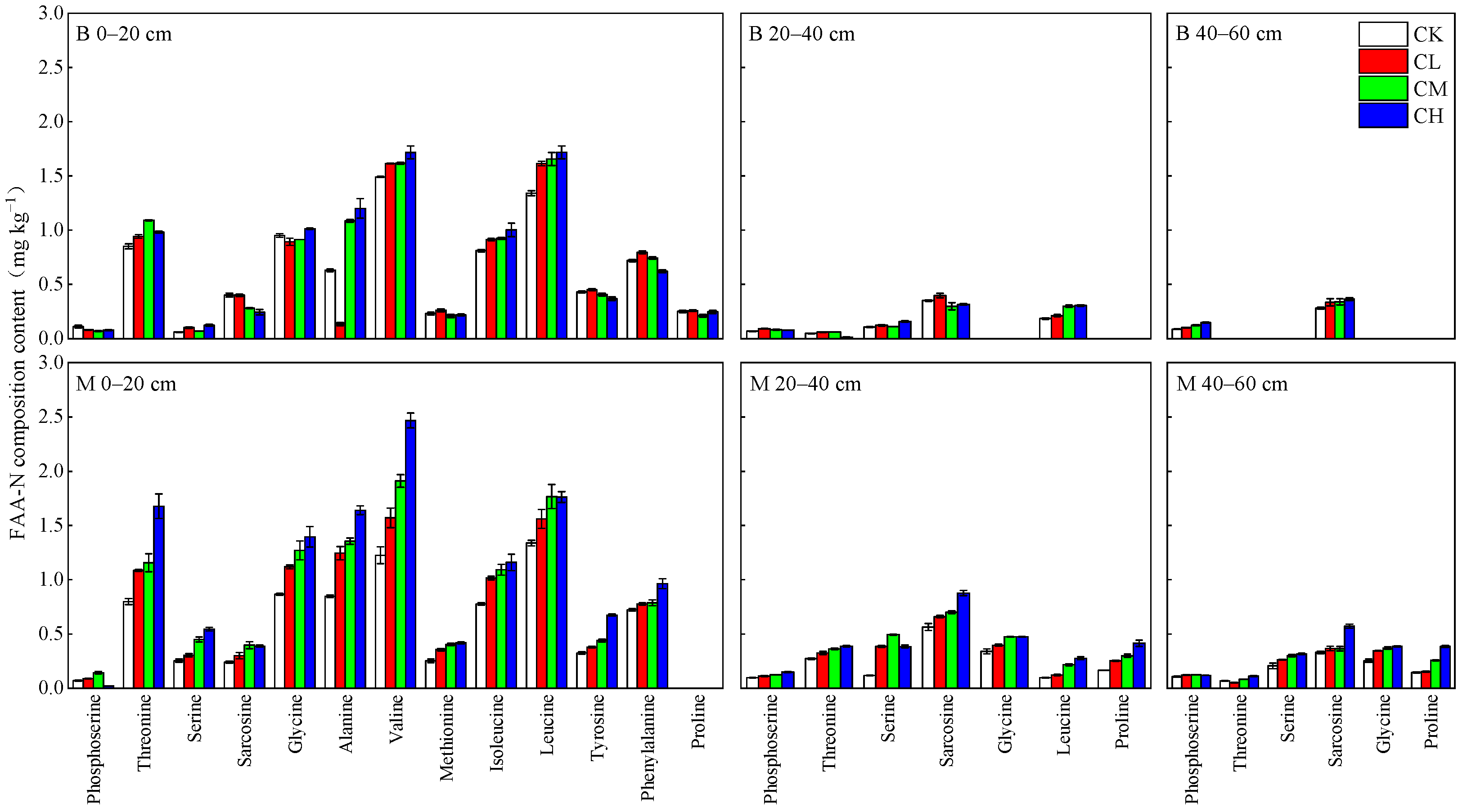
3.3.1. FAA-N Content and Composition
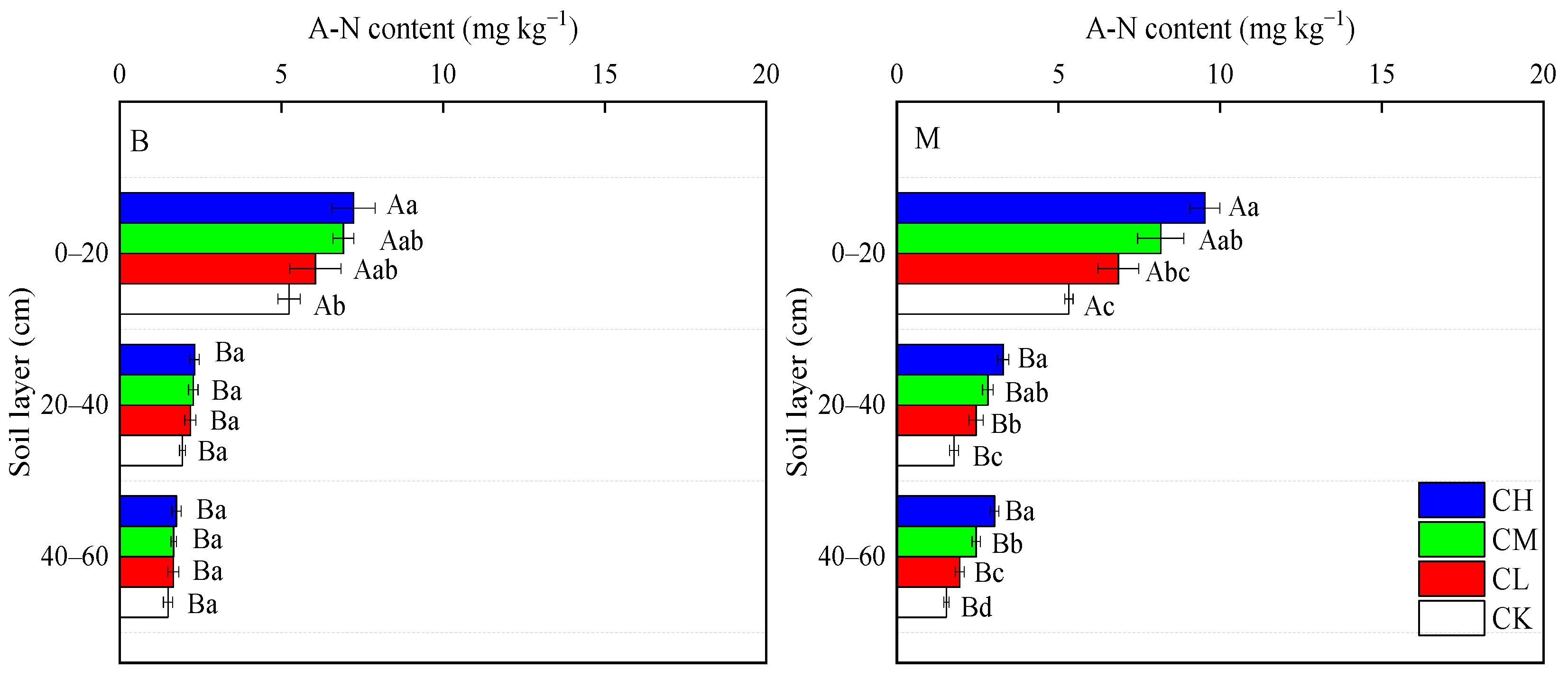
3.3.2. A-N Content
3.3.3. SP-N Content
3.3.4. Other SON Components
3.4. Soil SON Composition Ratios Along Depth Gradients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Toselli, M.; Baldi, E.; Marcolini, G.; Malaguti, D.; Quartieri, M.; Sorrenti, G.; Marangoni, B. Response of potted grapevines to increasing soil copper concentration. Aust. J. Grape Wine Res. 2019, 25, 306–314. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Effects of long-term fertilization on soil nitrogen dynamics and crop nitrogen uptake in a wheat-maize rotation system. Soil. Tillage Res. 2018, 180, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, D.V.; Macdonald, A.J.; Stockdale, E.A.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Fortune, S.; Gaunt, J.L.; Poulton, P.R.; Wakefield, J.A.; Webster, C.P.; Wilmer, W.S. Soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2000, 30, 374–387. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, S.; Zhao, L.; Lei, X.; Sarfraz, R.; Xing, S. Dissolved organic nitrogen distribution in differently fertilized paddy soil profiles: Implications for its potential loss. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 262, 58–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Y. Soluble organic nitrogen in agricultural soils: A review. Pedosphere 2024, 34, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, Z.; Huang, B.; Lu, C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Fang, Y. Dynamics of soil organic nitrogen and its relationship with soil organic carbon in a long-term fertilization experiment. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, F.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, G. Spectroscopic evidence of the improvement of reactive iron mineral content in red soil by long-term application of swine manure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0146364. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Effects of nitrogen fertilization on soil nitrogen dynamics and crop nitrogen uptake in a wheat-maize rotation system. Soil. Tillage Res. 2019, 190, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yücel, C.; Yücel, D.; Yücel, E. Effects of compost and cow manure amendments on soil nitrogen dynamics and crop nitrogen uptake. Soil. Tillage Res. 2020, 200, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, X.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, F. Effects of elevated nitrogen levels on soil nitrogen dynamics and crop nitrogen uptake. Soil. Tillage Res. 2017, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Azeez, J.O.; Van Averbeke, W. Nitrogen dynamics in soils amended with different types of fertilizers. Soil. Tillage Res. 2010, 110, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Shi, H.; Fei, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, G.; Wang, H. Progress and trends in research on soil nitrogen leaching: A bibliometric analysis from 2003 to 2023. Sustainability 2025, 17, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, L.; Sun, Y.; Wang, W.K. Ammonium nitrogen adsorption-desorption characteristics and its hysteresis of typical soils from Guanzhong Basin, China. Asian J. Chem. 2013, 25, 3850–3854. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Guo, W.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, B.; Yang, W.; Xing, S.; Ding, F. Increased soil soluble nitrogen stocks and decreased nitrogen leaching loss in rice paddy soil by replacing nitrogen fertilizer with Chinese milk vetch. Agronomy 2024, 14, 715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhou, C.; Shah, F.; Iqbal, A.; Ni, G. The role of Chinese Milk Vetch as cover crop in complex soil nitrogen dynamics in rice rotation system of South China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5798. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.H.; Park, K.D.; Jung, K.Y.; Ali, M.A.; Lee, D.; Gutierrez, J.; Kim, P.J. Effect of Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus L.) as a green manure on rice productivity and methane emission in paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2010, 138, 343–347. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Z.; Xie, J.; Liao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Nie, J.; Cao, W. Effect of reducing chemical fertilizer on rice yield, output value, content of soil carbon and nitrogen after utilizing the Milk Vetch. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 16, 266–271. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Lv, Y.; Nie, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, B.; Cao, W.; Li, M. Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Returning on Soil Properties, Microbial Community, and Rice Yield in Paddy Soil. Sustainability 2022, 14, 16065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, T.; Khan, A.A.; Aljerib, Y.M.A.; Tariq, M.; Li, D.; Geng, M.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q. Enhancement of fertilizer efficiency through Chinese milk vetch and rice straw incorporation. Plants 2025, 14, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Han, S.; Tang, S.; Cheng, W.; Bu, R.; Li, M.; Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Cao, W. Continuous multi-year application of Chinese milk vetch in paddy soil and its effect on soil aggregates distribution and their carbon and nitrogen content. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 868–880. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, W.; Zhou, L.; Yao, L.; Nie, J.; Jiang, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, H.; Zhu, B.; Wang, B. Water management alleviates greenhouse gas emissions by promoting carbon and nitrogen mineralization after Chinese milk vetch incorporation in a paddy soil. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 381, 109468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Xing, G.; Chen, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Cui, Z.; Yin, B.; Christie, P.; Zhu, Z.; et al. Excessive nitrogen accumulation in soils: Implications for nitrogen leaching and groundwater contamination. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 3041–3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.K. Methods of Soil Agricultural Chemical Analysis; China Agricultural Science and Technology Press: Beijing, China, 2000. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xing, S.; Chen, C.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, H.; Nang, Z.; Xu, Z. Soil soluble organic nitrogen and active microbial characteristics under adjacent coniferous and broadleaf plantation forests. J. Soils Sediments 2010, 10, 748–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yang, W.; Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, B.; Sarfraz, R.; Xing, S. Driving factors of soluble organic nitrogen dynamics in paddy soils: Structure equation modeling analysis. Pedosphere 2020, 30, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apichai, P.; Supanut, R.; Karun, T. A portable sol-gel urea colorimetric method for the determination of urea in feedstuffs. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126545. [Google Scholar]
- Sattayasai, N.; Sudmoon, R.; Nuchadomrong, S. Dendrobium findleyanum agglutinin: Production, localization, anti-fungal activity and gene characterization. Plant Cell Rep. 2009, 28, 1243–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losacco, D.; Campanale, C.; Tumolo, M.; Ancona, V.; Massarelli, C.; Uricchio, V.F. Evaluating the influence of nitrogen fertilizers and biochar on brassica oleracea L var botrytis by the use of Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.L.; Wang, J.; Yuan, K.; Zong, W.Z.; Guo, D. Vegetation affects pool size and composition of amino acids in Tibetan alpine meadow soils. Geoderma 2018, 310, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Peng, S.; Zhang, X.; Yan, D. Effects of water saving irrigation and controlled release nitrogen fertilizer managements on nitrogen losses from paddy fields. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 1, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.; Wang, Q.; Huang, X.; Yun, J.; Hu, Q.; Yang, G. Adsorption of amino acids at clay surfaces and implication for biochemical reactions: Role and impact of surface charges. Colloids Surf. B 2019, 183, 110458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Healey, J.R.; Willett, V.B.; Farrar, J.F.; Hodge, A. Composition and bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen in agricultural soils: Implications for nitrogen cycling and plant uptake. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2022, 165, 108521. [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser, K.; Kalbitz, K. Interactions between soluble organic nitrogen and soil colloids: Implications for nitrogen retention and mobility in agricultural soils. Geoderma 2023, 430, 116345. [Google Scholar]
- Michalzik, B.; Matzner, E. Dynamics of dissolved organic nitrogen and carbon in a Central European Norway spruce ecosystem. Eur. J. Soil. Sci. 1999, 50, 579–590. [Google Scholar]
- Kalbitz, K.; Solinger, S.; Park, J.H.; Michalzik, B.; Matzner, E. Mobility and bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen in soil: The role of molecular weight and hydrophobicity. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2020, 141, 107683. [Google Scholar]
- Knicker, H. Formation and turnover of soil organic matter: The role of microbial metabolites and amino acids in the stabilization of organic nitrogen. Soil. Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1398–1406. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, C.R.; Taranto, M.T. Chemical properties and mobility of free amino acids in soil: Implications for nitrogen cycling and plant nutrition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 158, 108264. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lin, Y.; Rensing, C.; Zhang, L.M.; Zhou, B.Q.; Xing, S.H.; Yang, W.H. Dynamic and migration characteristics of soil free amino acids in paddy soil applied with milk vetch. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, J.I.; Hare, P.E. Amino acid adsorption by clay minerals in distilled water. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trevino, S.R.; Scholtz, J.M.; Pace, C.N. Amino acid contribution to protein solubility: Asp, Glu, and Ser contribute more favorably than the other hydrophilic amino acids in RNase Sa. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 366, 449–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, K.T.; Lobmann, K.; Rades, T.; Grohganz, H. Improving co-amorphous drug formulations by the addition of the highly water soluble amino acid, proline. Pharmaceutics 2014, 6, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Clode, P.L.; Hill, P.W. Glycine as a key component of soil organic nitrogen: Dynamics, transformations, and implications for soil fertility. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107876. [Google Scholar]
- Su, M.Z.; Zhang, J.T.; Huo, S.L.; Xi, B.D.; Hua, F.; Zan, F.Y.; Qian, G.R.; Liu, J.Y. Microbial bioavailability of dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) in the sediments of Lake Shankou, Northeastern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 42, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Soil Layers | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | pH | Capillary Porosity (%) | Aeration Porosity (%) | Total Porosity (%) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | Total Nitrogen (g kg−1) | Available Phosphorus (mg kg−1) | Available Potassium (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 cm | 1.32 ± 0.03 c | 5.53 ± 0.06 c | 47.67 ± 0.98 a | 1.64 ± 0.22 a | 49.30 ± 1.00 a | 17.57 ± 0.42 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 6.52 ± 0.11 a | 30.20 ± 1.99 a |
| 20–40 cm | 1.57 ± 0.02 b | 5.95 ± 0.04 b | 41.28 ± 0.70 b | 1.33 ± 0.11 ab | 42.61 ± 0.76 b | 10.37 ± 0.63 b | 0.52 ± 0.04 b | 5.24 ± 0.15 b | 22.70 ± 2.42 ab |
| 40–60 cm | 1.66 ± 0.01 a | 6.31 ± 0.03 a | 39.21 ± 0.50 b | 1.14 ± 0.13 b | 40.35 ± 0.49 b | 8.17 ± 0.24 c | 0.35 ± 0.02 c | 4.38 ± 0.49 b | 20.68 ± 0.00 b |
| Period | Layers | Treatments | SON/SN | FAA-N/SON | A-N/SON | SP-N/SON |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background soil | 0–20 cm | CK | 56.26 ± 3.37 Aa | 49.69 ± 4.44 Aa | 31.96 ± 2.08 Ba | 12.34 ± 0.92 Aa |
| CL | 57.73 ± 1.64 Aa | 48.15 ± 0.98 Aa | 34.26 ± 3.32 Ba | 12.22 ± 0.36 Aa | ||
| CM | 57.42 ± 6.08 Aa | 49.58 ± 0.92 Aa | 36.95 ± 1.33 Ba | 12.01 ± 1.34 Aa | ||
| CH | 58.76 ± 1.74 Aa | 48.29 ± 0.64 Aa | 36.83 ± 4.03 Ba | 12.06 ± 1.27 Aa | ||
| 20–40 cm | CK | 58.21 ± 1.31 Aa | 16.75 ± 1.24 Ba | 42.83 ± 2.97 ABa | 10.94 ± 0.35 Aa | |
| CL | 57.21 ± 1.01 Aa | 16.69 ± 0.70 Ba | 41.89 ± 2.91 ABa | 10.46 ± 0.51 Aa | ||
| CM | 57.04 ± 5.07 Aa | 15.53 ± 1.28 Ba | 42.26 ± 3.08 ABa | 10.36 ± 1.31 Aa | ||
| CH | 57.53 ± 4.04 Aa | 16.00 ± 1.76 Ba | 43.09 ± 2.37 ABa | 11.11 ± 2.23 Aa | ||
| 40–60 cm | CK | 54.26 ± 2.67 Aa | 13.23 ± 0.97 Ca | 52.96 ± 6.45 Aa | 10.92 ± 0.49 Aa | |
| CL | 56.70 ± 1.14 Aa | 13.42 ± 1.41 Ca | 50.53 ± 4.02 Aa | 10.26 ± 0.81 Aa | ||
| CM | 55.69 ± 2.38 Aa | 13.56 ± 1.33 Ca | 48.70 ± 3.42 Aa | 10.68 ± 1.55 Aa | ||
| CH | 56.45 ± 2.55 Aa | 14.44 ± 0.54 Ca | 49.27 ± 0.59 Aa | 10.04 ± 1.16 Aa | ||
| Maturity stage | 0–20 cm | CK | 57.66 ± 0.94 Ab | 51.67 ± 2.40 Ab | 35.71 ± 2.30 Bb | 10.78 ± 1.27 Ab |
| CL | 59.79 ± 0.33 Aab | 53.59 ± 0.99 Aab | 40.18 ± 0.57 Bab | 14.01 ± 0.90 Aab | ||
| CM | 59.05 ± 0.48 Aab | 56.90 ± 1.20 Aab | 41.43 ± 2.89 Ba | 16.59 ± 1.69 Aa | ||
| CH | 61.22 ± 1.71 Aa | 58.41 ± 1.29 Aa | 42.34 ± 0.94 Ba | 18.06 ± 2.17 Aa | ||
| 20–40 cm | CK | 55.47 ± 2.33 Aa | 41.80 ± 3.93 ABa | 44.61 ± 5.30 ABa | 12.34 ± 1.18 Aa | |
| CL | 56.64 ± 1.08 Ba | 41.64 ± 1.45 Ba | 45.04 ± 2.80 Ba | 13.85 ± 0.23 Aa | ||
| CM | 56.80 ± 2.21 Ba | 44.83 ± 2.98 Ba | 47.23 ± 4.23 Ba | 14.52 ± 2.06 ABa | ||
| CH | 57.13 ± 2.56 Ba | 44.51 ± 3.73 Ba | 49.22 ± 3.87 Ba | 15.00 ± 2.01 ABa | ||
| 40–60 cm | CK | 51.47 ± 3.44 Aa | 38.90 ± 2.49 Ba | 50.74 ± 0.71 Aa | 10.46 ± 1.16 Aa | |
| CL | 51.66 ± 1.72 Ba | 39.08 ± 1.70 Ba | 58.10 ± 0.55 Aa | 11.19 ± 1.49 Aa | ||
| CM | 53.58 ± 0.77 Ba | 38.81 ± 2.44 Ba | 63.31 ± 1.79 Aa | 10.81 ± 0.58 Ba | ||
| CH | 54.84 ± 1.25 Ba | 39.44 ± 3.02 Ba | 61.22 ± 1.53 Aa | 11.09 ± 1.96 Ba |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, J.; Xiang, L.; Ding, F.; Huang, H.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, C.; Xing, S.; Liu, S. Vertical Distribution of Soluble Organic Nitrogen Composition in Paddy Soils: Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Application Rates. Agronomy 2025, 15, 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040833
Yang J, Xiang L, Ding F, Huang H, Zhou B, Zhao C, Xing S, Liu S. Vertical Distribution of Soluble Organic Nitrogen Composition in Paddy Soils: Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Application Rates. Agronomy. 2025; 15(4):833. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040833
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Jing, Le Xiang, Fenghua Ding, Hongyu Huang, Biqing Zhou, Chengsen Zhao, Shihe Xing, and Shuxin Liu. 2025. "Vertical Distribution of Soluble Organic Nitrogen Composition in Paddy Soils: Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Application Rates" Agronomy 15, no. 4: 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040833
APA StyleYang, J., Xiang, L., Ding, F., Huang, H., Zhou, B., Zhao, C., Xing, S., & Liu, S. (2025). Vertical Distribution of Soluble Organic Nitrogen Composition in Paddy Soils: Effects of Chinese Milk Vetch Application Rates. Agronomy, 15(4), 833. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15040833





