Differential Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity of Soils with Different Phosphorus Contents
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Soil, Earthworms and PSB
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.4. Methods for Measuring Phosphorus Adsorption and Desorption
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Inoculation with Earthworms and PSB on Soil P Adsorption
3.2. Effect of Inoculation with Earthworms and PSB on Soil P Adsorption Parameters
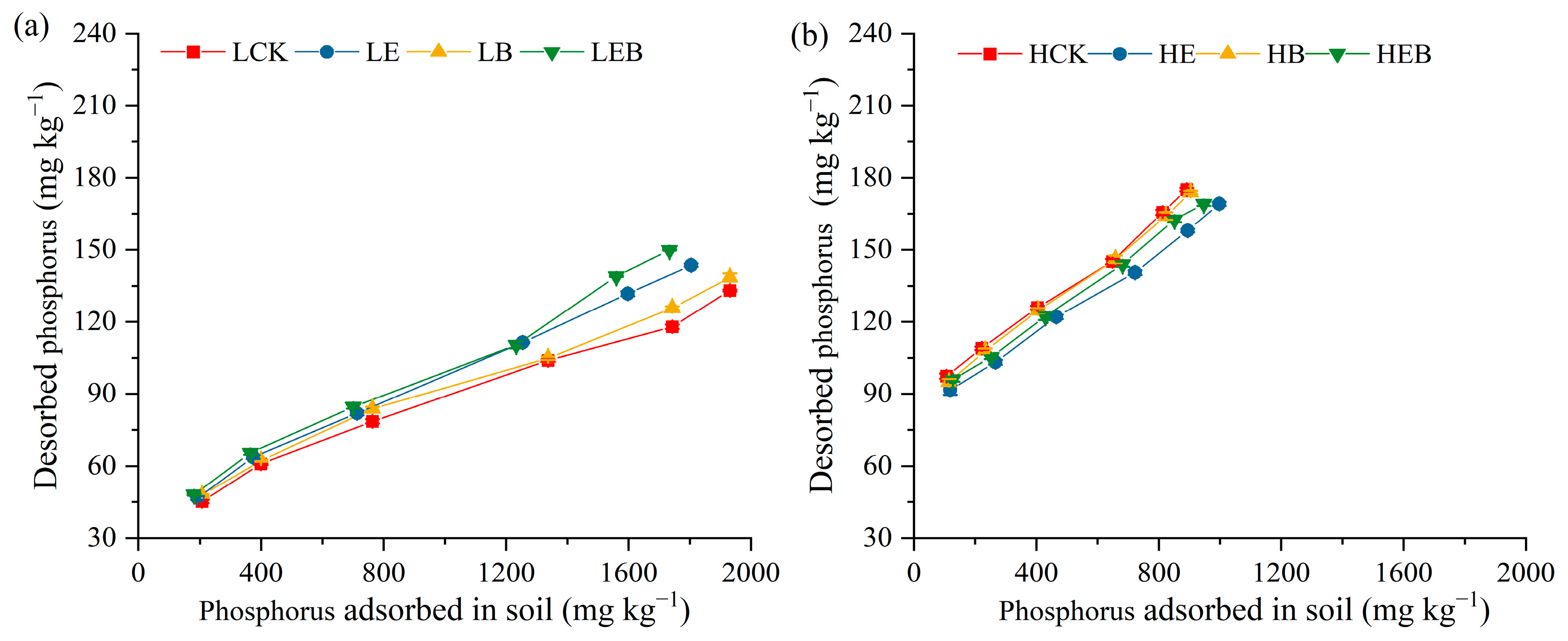
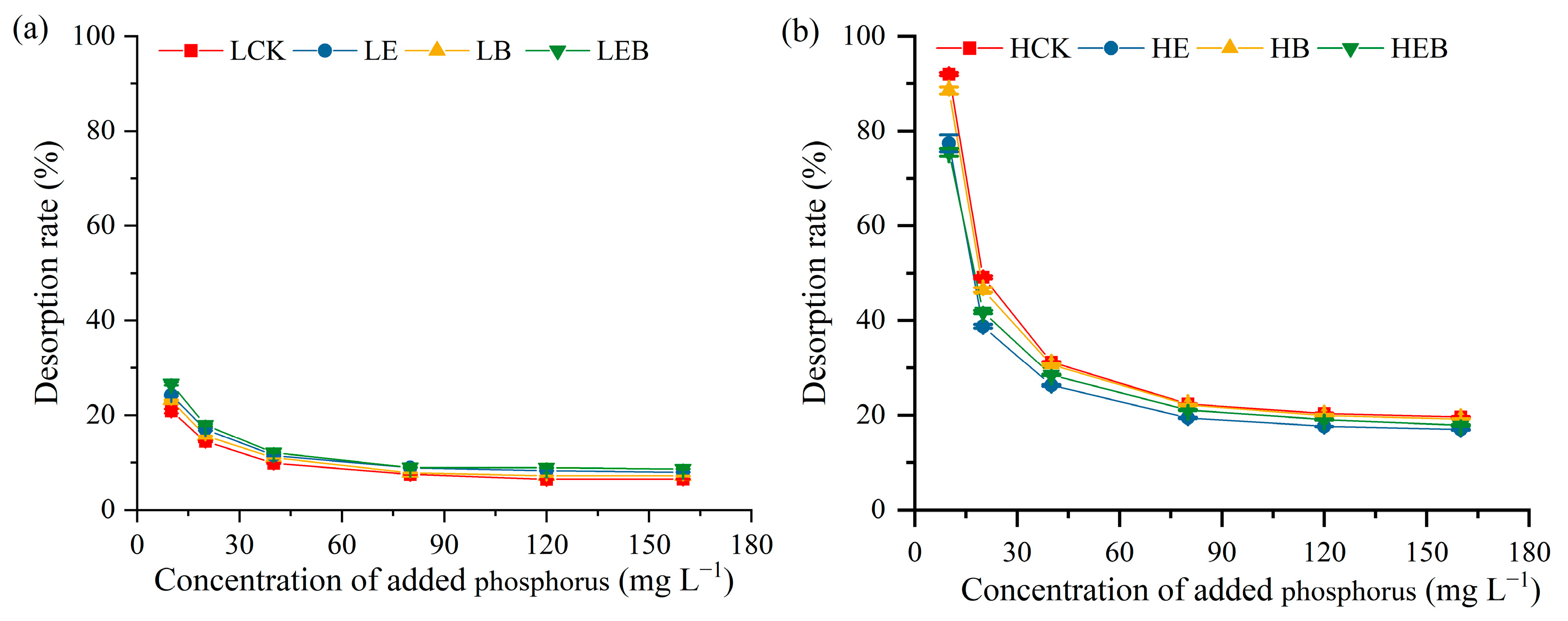
3.3. Effect of Inoculation with Earthworms and PSB on Soil P Desorption Characteristics
3.4. Effect of Inoculation with Earthworms and PSB on Soil Properties
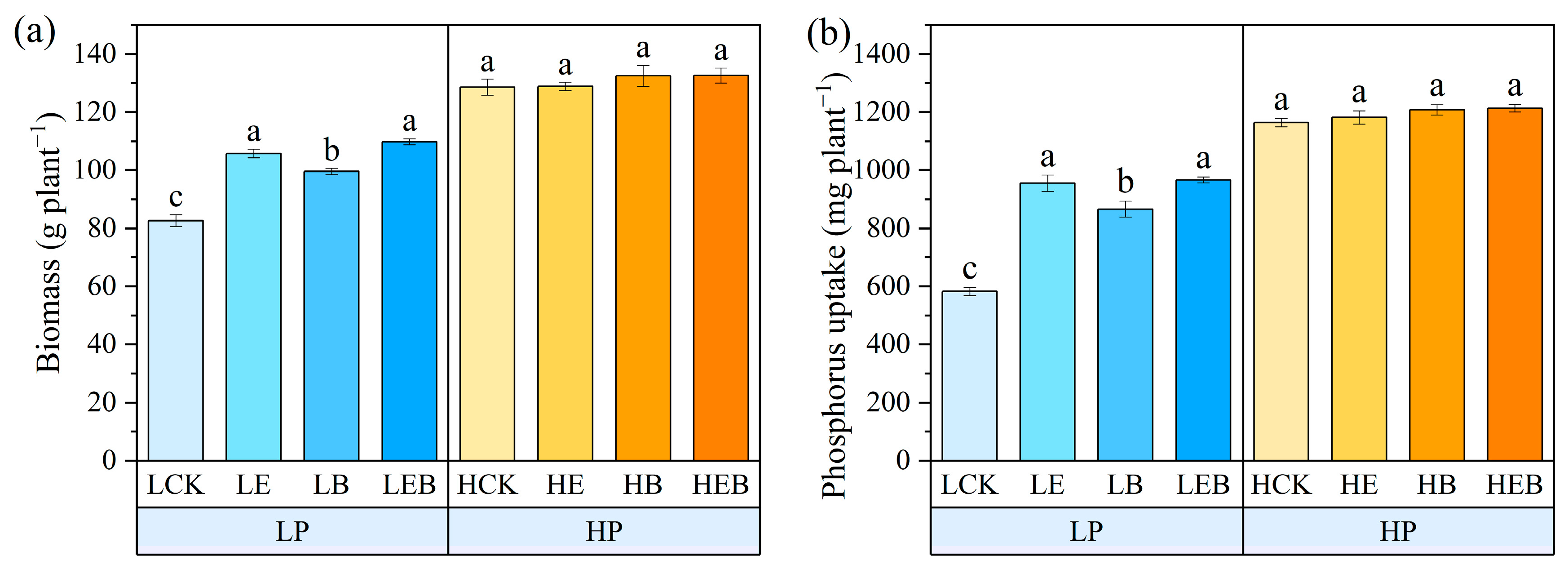
3.5. Effect of Inoculation with Earthworms and PSB on Tomato Biomass and Phosphorus Uptake
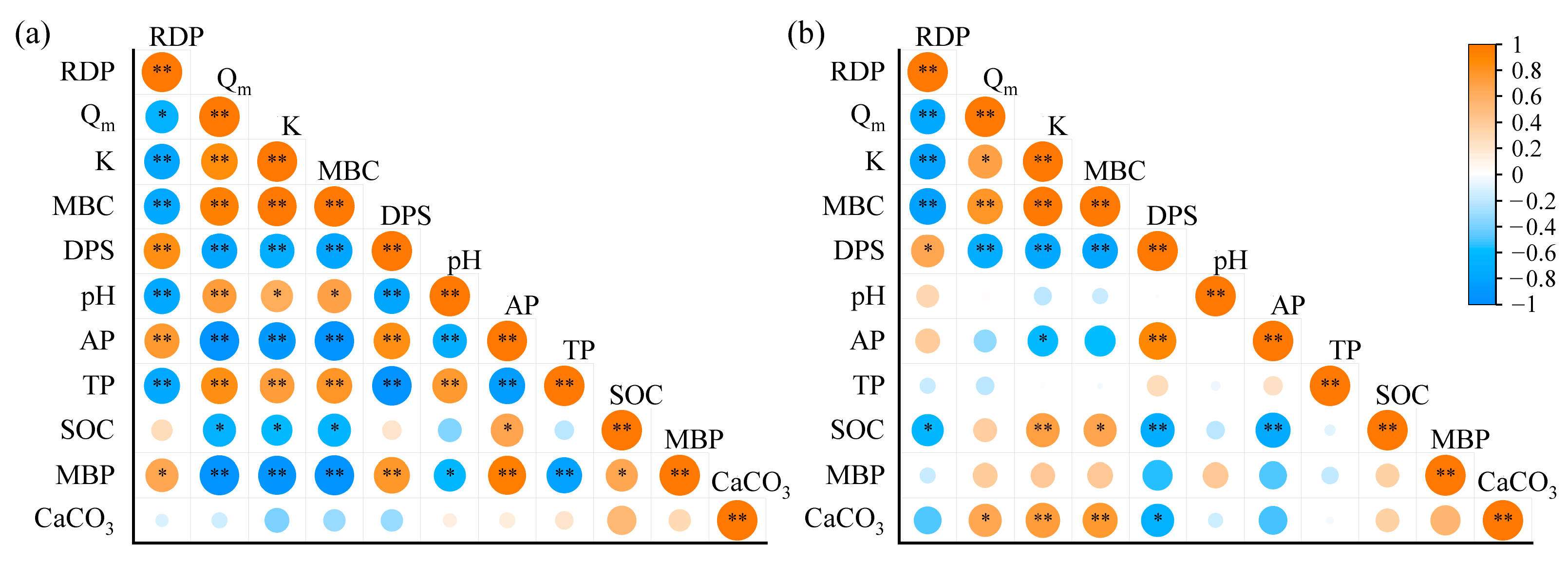
3.6. Adsorption–Desorption Properties of P in Response to Soil Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Characteristics of Soil P Adsorption Differ for Different P Levels
4.2. Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms or PSB on Soil P Adsorption and Desorption Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adesemoye, A.O.; Kloepper, J.W. Plant-microbes interactions in enhanced fertilizer-use efficiency. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 85, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Dang, T.; Hao, M. Phosphorus changes and sorption characteristics in a calcareous soil under long-term fertilization. Pedosphere 2008, 18, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejías, J.H.; Alfaro, M.; Harsh, J. Approaching environmental phosphorus limits on a volcanic soil of Southern Chile. Geoderma 2013, 207, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandermoere, S.; Ralaizafisoloarivony, N.A.; Van Ranst, E.; De Neve, S. Reducing phosphorus (p) losses from drained agricultural fields with iron coated sand (- glauconite) filters. Water Res. 2018, 141, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, P.; Das, S.; Shankhdhar, D.; Shankhdhar, S.C. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: Mechanism and their role in phosphate solubilization and uptake. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2021, 21, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wisawapipat, W.; Kheoruenromne, I.; Suddhiprakarn, A.; Gilkes, R.J. Phosphate sorption and desorption by Thai upland soils. Geoderma 2009, 153, 408–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, N.; Pindi, P.K.; Reddy, S.R. Phosphate-solubilizing microorganisms: A critical review. In Plant Biology and Biotechnology; Bahadur, B., Venkat Rajam, M., Sahijram, L., Krishnamurthy, K., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; pp. 307–333. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, Z.; Zhu, J.; Shao, W.; Zhang, K.; Li, M.; Whelan, M.J. Increasing plant availability of legacy phosphorus in calcareous soils using some phosphorus activators. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 256, 109952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaind, S. Phosphate dissolving fungi: Mechanism and application in alleviation of salt stress in wheat. Microbiol. Res. 2016, 193, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhakta, J.N.; Balaram, S.; Pallabi, B. Isolation and characterization of potential phosphate solubilizing bacteria from earthworm (metaphire posthuma) for applying as biofertilizer. Org. Agric. 2022, 12, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, J.K.; Banerjee, A.; Rai, M.; Naidu, R.; Meers, E. Potential application of selected metal resistant phosphate solubilizing bacteria isolated from the gut of earthworm (metaphire posthuma) in plant growth promotion. Geoderma 2018, 330, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ros, M.B.H.; Hiemstra, T.; van Groenigen, J.W.; Chareesri, A.; Koopmans, G.F. Exploring the pathways of earthworm-induced phosphorus availability. Geoderma 2017, 303, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandruszka, R.V. Phosphorus retention in calcareous soils and the effect of organic matter on its mobility. Geochem. Trans. 2006, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernández, L.; Agaras, B.; Zalba, P.; Wall, L.G.; Valverde, C. Pseudomonas spp. isolates with high phosphate-mobilizing potential and root colonization properties from agricultural bulk soils under no-till management. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2012, 48, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, C.L.; Glick, B.R. Bacterial biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid. Can. J. Microbiol. 1996, 42, 207–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.J. 16S/23S rRNA sequencing. In Nucleic Acid Techniques in Bacterial Systematics; Stackebrandt, E., Goodfellow, M., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1991; pp. 115–175. [Google Scholar]
- Okalebo, J.R.; Gathua, K.W.; Woomer, P.L. Laboratory Methods of Soil and Plant Analysis: A Working Manual, 2nd ed.; Sacred Africa, Nairobi Office: Nairobi, Kenya, 2002; pp. 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Abdala, D.B.; Ghosh, A.K.; Silva, I.R.D.; Novais, R.F.D.; Venegas, V.H.A. Phosphorus saturation of a tropical soil and related P leaching caused by poultry litter addition. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 162, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, R.; Sharma, V.K.; Das, D.; Biswas, D.R.; Mahapatra, P.; Shahi, D.K.; Barman, M.; Chobhe, K.A.; Chakraborty, D. Change in phosphorus availability, fractions, and adsorption-desorption by 46-years of long-term nutrient management in anAlfisol of eastern India. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 236, 105940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Huang, S.M.; Bao, D.J. Phosphorus adsorption and desorption characteristics of different textural fluvo-aquic soils under long-term fertilization. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaur, P. Rice straw management options impact soil phosphorus adsorption-desorption, kinetics and thermodynamics in rice-wheat system of north-western india. Soil Tillage Res. 2025, 248, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pautler, M.C.; Sims, J.T. Relationships between soil test phosphorus, soluble phosphorus and phosphorus saturation in Delaware soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 765–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamaizi, S.; Messiga, A.J.; Cade-Menun, B.; Cornelis, J.T.; Smukler, S.M. Environmental phosphorus risk classes for silage corn in the fraser valley, canada. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2025, 381, 109423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidari, S.; Reyhanitabar, A.; Oustan, S. Kinetics of phosphorus desorption from calcareous soils using DGT technique. Geoderma 2017, 305, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, M.T.; Robinson, J.S. Phosphorus sorption and availability in soils amended with animal manures and sewage sludge. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Guo, S.L.; Li, N.N.; Zhang, Y.J.; Jiang, J.S.; Wang, Z.Q.; Liu, Q.F.; Wu, D.F.; Sun, Q.Q.; Du, L.L.; et al. Phosphorus accumulation and sorption in calcareous soil under long-term fertilization. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0135160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrysostome, M.; Nair, V.D.; Harris, W.G.; Rhue, R.D. Laboratory validation of soil phosphorus storage capacity predictions for use in risk assessment. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 1564–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Jalali, M. Relation between various soil phosphorus extraction methods and sorption parameters in calcareous soils with different texture. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566–567, 1080–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Getie, A.; Kiflu, A.; Meteke, G. Phosphorus sorption characteristics of luvisols and nitisols in north ethiopian soils. Appl. Environ. Soil Sci. 2021, 2021, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Chao, H.; Zheng, X.; Deng, S.; Hu, F. Ecological role of earthworm intestinal bacteria in terrestrial environments: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 740, 140008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A. Short- and long-term effects of the endogeic earthworm Millsonia anomala(Omodeo)(Megascolecidae, Oligochaeta) of tropical savannas on soil organic matter. Biol. Fertil. Soils 1991, 11, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdala, D.B.; da Silva, I.R.; Vergütz, L.; Sparks, D.L. Long-term manure application effects on phosphorus speciation, kinetics and distribution in highly weathered agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2015, 119, 504–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regelink, I.C.; Weng, L.; Lair, G.J.; Comans, R.N.J. Adsorption of phosphate and organic matter on metal (hydr) oxides in arable and forest soil: A mechanistic modelling study. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobile, C.M.; Bravin, M.N.; Becquer, T.; Paillat, J.M. Phosphorus sorption and availability in an andosol after a decade of organic or mineral fertilizer applications: Importance of pH and organic carbon modifications in soil as compared to phosphorus accumulation. Chemosphere 2020, 239, 124709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.K.; Ma, J.J.; Liu, L.J. Effects of phosphate-solubilizing bacteria application on soil phosphorus availability in coal mining subsidence area in Shanxi. J. Plant Interact. 2017, 12, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashan, Y.; Kamnev, A.A.; de-Bashan, L.E. Tricalcium phosphate is inappropriate as a universal selection factor for isolating and testing phosphate-solubilizing bacteria that enhance plant growth: A proposal for an alternative procedure. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2013, 49, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, C.J.; Camberato, J.J. A critical review on soil chemical processes that control how soil ph affects phosphorus availability to plants. Agriculture 2019, 9, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, P.; Nayak, A.K.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Mohanty, S.; Kumar, A.; Raja, R.; Panda, B.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; et al. Effects of 42-year long-term fertilizer management on soil phosphorus availability, fractionation, adsorption-desorption isotherm and plant uptake in flooded tropical rice. Crop J. 2015, 5, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.P.; Wang, J.; Shao, M.A. Earthworm inoculation and straw return decrease the phosphorus adsorption capacity of soils in the Loess region, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 312, 114921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheekilote, N.; Samant, P.K.; Dwibedi, S.K.; Jena, B.; Mohapatra, K.K.; Nayak, H.S.; Garnaik, S. Exploring phosphorous dynamics within soil aggregate after 17 years long-term manuring in lateritic inceptisols in rice paddies. Geoderma Reg. 2025, 40, e00908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, J.S.; Rowell, D.L. The adsorption and precipitation of phosphate onto calcite. Soil Sci. 1981, 32, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mclaughlin, M.J.; Mcbeath, T.M.; Smernik, R.; Stacey, S.P.; Ajiboye, B.; Guppy, C. The chemical nature of P accumulation in agricultural soils-implications for fertiliser management and design: An australian perspective. Plant Soil 2011, 349, 69–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bossuyt, H.; Six, J.; Hendrix, P.F. Protection of soil carbon by micro-aggregates within earthworm casts. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2005, 37, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcinerney, M.; Little, D.J.; Bolger, T. Effect of earthworm cast formation on the stabilization of organic matter in fine soil fractions. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2001, 37, 251–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrader, S.; Rogasik, H.; Onasch, I.; Jégou, D. Assessment of soil structural differentiation around earthworm burrows by means of X-ray computed tomography and scanning electron microscopy. Geoderma 2007, 137, 378–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yuan, X.; Ge, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y. Rhizosphere effects promote soil aggregate stability and associated organic carbon sequestration in rocky areas of desertification. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2020, 304, 107126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Substrate | pH | Ec (µS cm−1) | Clay (%) | Silt (%) | Sand (%) | SOC (g kg−1) | TN (g kg−1) | TP (g kg−1) | CaCO3 (g kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | 7.73 | 242 | 13.37 | 25.62 | 61.01 | 11.44 | 1.17 | 0.57 | 15.24 | 30.61 |
| HP | 7.41 | 1312.64 | 20.43 | 33.85 | 45.72 | 33.76 | 3.74 | 2.13 | 17.61 | 206.51 |
| Treament | Langmuir Model | Freundlich Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C/Q = C/Qm + 1/K1Qm | R2 | Q = K2C1/n | R2 | ||
| LP | LCK | C/Q = 0.000351C + 0.01204 | 0.999 | Q = 126.009C0.660 | 0.984 |
| LE | C/Q = 0.000370C + 0.01687 | 0.999 | Q = 104.332C0.655 | 0.983 | |
| LB | C/Q = 0.000358C + 0.01388 | 0.999 | Q = 148.454C0593 | 0.967 | |
| LEB | C/Q = 0.000379C + 0.01815 | 0.998 | Q = 96.481C0.652 | 0.978 | |
| HP | HCK | C/Q = 0.000750C + 0.04737 | 0.999 | Q = 47.56C0.6092 | 0.981 |
| HE | C/Q = 0.000727C + 0.03538 | 0.990 | Q = 61.20C0.5903 | 0.960 | |
| HB | C/Q = 0.000752 + 0.04468 | 0.999 | Q = 53.70C0.5909 | 0.978 | |
| HEB | C/Q = 0.000743C + 0.04059 | 0.999 | Q = 40.51C0.6839 | 0.988 | |
| Treament | Readily Desorbable P (mg kg−1) | Qm (mg kg−1) | K | Maximum Buffer Capacity (mg kg−1) | Degree of P Saturation (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | LCK | 9.38 ± 0.17 b | 2835.71 ± 20.00 a | 0.0292 ± 0.0004 a | 82.85 ± 0.53 a | 1.09 ± 0.03 d |
| LE | 10.78 ± 0.43 a | 2587.63 ± 25.62 c | 0.0238 ± 0.0004 c | 61.55 ± 0.37 c | 1.28 ± 0.04 c | |
| LB | 10.83 ± 0.13 a | 2751.27 ± 23.17 b | 0.0271 ± 0.0005 b | 74.56 ± 0.7 b | 1.55 ± 0.05 b | |
| LEB | 11.33 ± 0.22 a | 2483.06 ± 24.89 d | 0.0240 ± 0.0002 c | 59.53 ± 0.17 d | 1.72 ± 0.03 a | |
| Earthworms | ** | ** | ** | ** | ** | |
| PSB | ** | ** | * | ** | ** | |
| Earthworms × PSB | ns | ns | * | ** | ns | |
| HP | HCK | 82.80 ± 0.72 a | 1333.77 ± 8.35 b | 0.0161 ± 0.0002 c | 21.45 ± 0.18 d | 15.09 ± 0.24 a |
| HE | 79.75 ± 0.49 b | 1394.77 ± 7.08 a | 0.0197 ± 0.0002 a | 27.50 ± 0.17 a | 13.95 ± 0.13 b | |
| HB | 82.80 ± 0.27 a | 1342.17 ± 6.45 b | 0.0165 ± 0.0002 c | 22.13 ± 0.15 c | 14.93 ± 0.21 a | |
| HEB | 81.67 ± 0.59 a | 1343.19 ± 6.85 b | 0.0186 ± 0.0001 b | 24.92 ± 0.06 b | 14.20 ± 0.27 b | |
| Earthworms | ** | ** | ** | ** | * | |
| PSB | ns | * | * | ** | ns | |
| Earthworms × PSB | ** | ** | ** | ** | ns |
| Treatment | pH | TP (mg kg−1) | AP (mg kg−1) | MBP (mg kg−1) | SOC (g kg−1) | CaCO3 (mg kg−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LP | LCK | 7.75 ± 0.05 a | 518.11 ± 1.14 a | 30.95 ± 0.61 d | 23.03 ± 0.16 d | 12.14 ± 0.22 b | 15.34 ± 0.25 b |
| LE | 7.62 ± 0.05 ab | 507.10 ± 1.27 b | 40.03 ± 0.94 b | 25.43 ± 0.22 b | 12.85 ± 0.11 a | 16.50 ± 0.22 a | |
| LB | 7.60 ± 0.04 ab | 505.19 ± 1.46 c | 35.33 ± 0.82 c | 23.66 ± 0.17 c | 12.01 ± 0.21 b | 13.85 ± 0.23 c | |
| LEB | 7.46 ± 0.05 b | 493.40 ± 1.35 d | 42.82 ± 0.92 a | 26.23 ± 0.15 a | 12.60 ± 0.16 ab | 14.87 ± 0.51 bc | |
| Earthworms | * | ** | ** | * | * | * | |
| PSB | * | ** | ** | * | ns | * | |
| Earthworms × PSB | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| HP | HCK | 7.22 ± 0.04 a | 2028.54 ± 2.04 a | 201.15 ± 2.51 a | 37.93 ± 0.17 b | 34.63 ± 0.61 b | 17.44 ± 0.20 b |
| HE | 7.21 ± 0.05 a | 2028.63 ± 2.51 a | 194.62 ± 2.73 ab | 38.46 ± 0.20 ab | 36.95 ± 0.40 a | 18.42 ± 0.26 a | |
| HB | 7.24 ± 0.04 a | 2029.88 ± 3.21 a | 200.38 ± 1.85 a | 38.36 ± 0.23 ab | 35.63 ± 0.76 ab | 17.10 ± 0.28 b | |
| HEB | 7.20 ± 0.04 a | 2028.50 ± 2.27 a | 190.62 ± 2.70 b | 38.71 ± 0.22 a | 37.45 ± 0.52 a | 18.25 ± 0.16 a | |
| Earthworms | ns | ns | * | ns | * | * | |
| PSB | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | |
| Earthworms × PSB | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns | ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dong, F.; Yu, L.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, T.; Yang, Q.; Yang, C.; Yang, L. Differential Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity of Soils with Different Phosphorus Contents. Agronomy 2025, 15, 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030659
Dong F, Yu L, Jiao Y, Wang T, Yang Q, Yang C, Yang L. Differential Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity of Soils with Different Phosphorus Contents. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):659. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030659
Chicago/Turabian StyleDong, Feiyu, Leixin Yu, Yimeng Jiao, Tianqi Wang, Qinghai Yang, Chuang Yang, and Lijuan Yang. 2025. "Differential Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity of Soils with Different Phosphorus Contents" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030659
APA StyleDong, F., Yu, L., Jiao, Y., Wang, T., Yang, Q., Yang, C., & Yang, L. (2025). Differential Effects of Inoculation with Earthworms and Phosphate-Solubilizing Bacteria on Phosphorus Adsorption Capacity of Soils with Different Phosphorus Contents. Agronomy, 15(3), 659. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030659






