Moderate P Fertilizer Promotes Cucumber Yields and Modulates Bacterial Community in the Wheat Cover Crop System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experiment Site and Study Design
2.2. Plants and Soil Sampling
2.3. Measurement of Cucumber Morphological Features and Yield
2.4. Measurement of Soil Enzyme Activity
2.5. Soil DNA Extraction and High Throughput Sequencing
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Cucumber Morphological Features and Yield
3.2. Soil Enzyme Activities
3.3. Effects on Soil Bacterial Community Composition
3.3.1. Alpha and Beta Diversity Analysis
3.3.2. Soil Micro-Bacterial Community Composition and Correlation Analysis
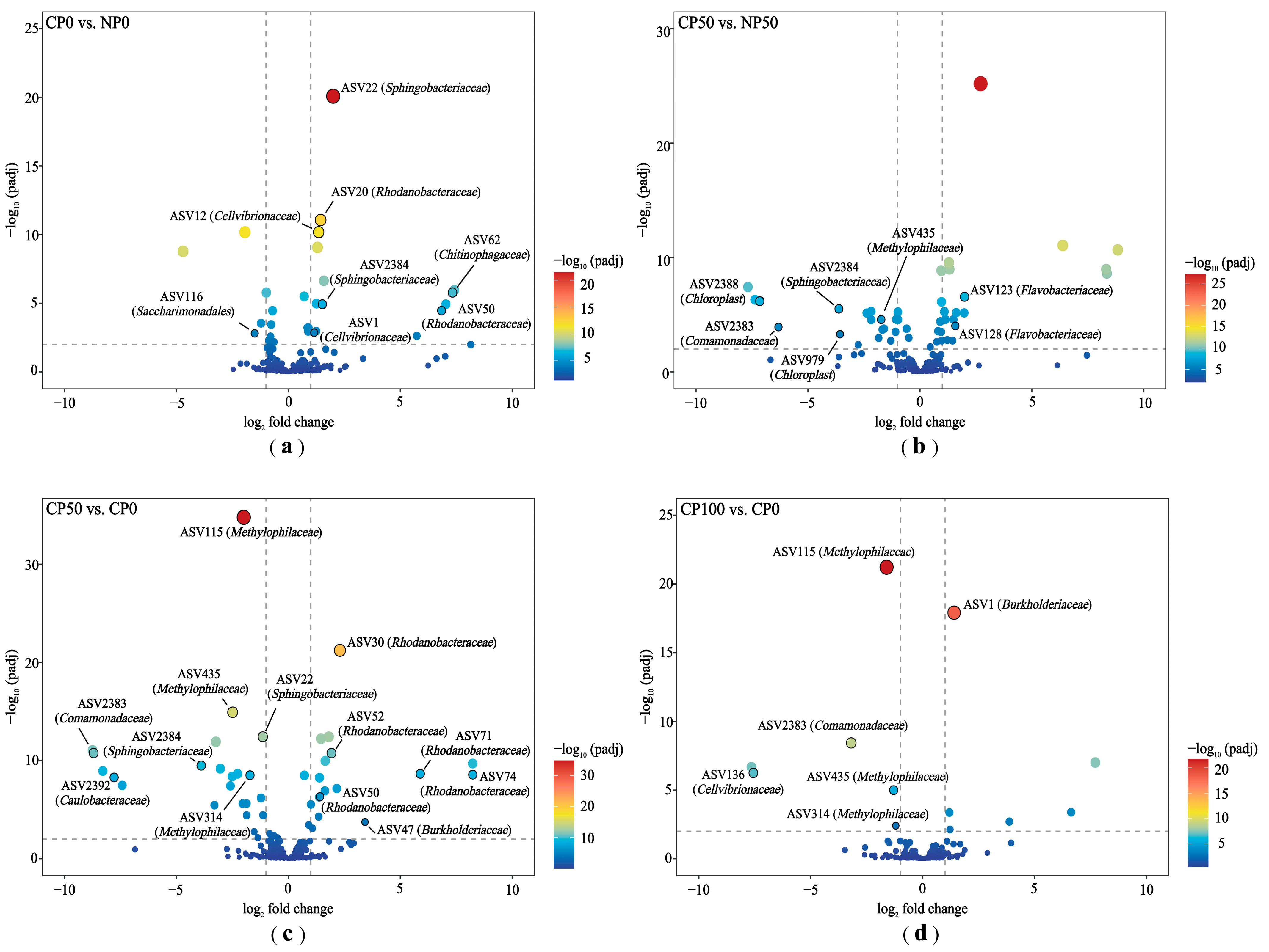
3.3.3. Differential Species of Soil Bacterial Community
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, X.; Li, S.; He, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tian, Y. Spectrum imaging for phenotypic detection of greenhoue vegetables: A review. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 225, 109346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Wu, F. Soil phenolics in a continuously mono-cropped cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) system and their effects on cucumber seedling growth and soil microbial communities. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 63, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Kou, C.L.; Christie, P.; Dou, Z.; Zhang, F. Changes in the soil environment from excessive application of fertilizers and manures to two contrasting intensive cropping systems on the North China Plain. Environ. Pollut. 2007, 145, 497–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahalvi, H.N.; Rafiya, L.; Rashid, S.; Nisar, B.; Kamili, A.N. Chemical fertilizers and their impact on soil health. In Microbiota and Biofertilizers; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; Volume 2, pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, C.; Nevins, C.; Camberato, J.; Kladivko, E.; Sadeghpour, A.; Armstrong, S. Carbon and nitrogen release from cover crop residues and implications for cropping systems management. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 75, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittwer, R.A.; van der Heijden, M.G.A. Cover crops as a tool to reduce reliance on intensive tillage and nitrogen fertilization in conventional arable cropping systems. Field Crops Res. 2020, 249, 107736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romdhane, S.; Spor, A.; Busset, H.; Falchetto, L.; Martin, J.; Bizouard, F.; Bru, D.; Breuil, M.-C.; Philippot, L.; Cordeau, S. Cover crop management practices rather than composition of cover crop mixtures affect bacterial communities in No-Till agroecosystems. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Sekaran, U.; Wang, T.; Kumar, S. On-farm assessment of cover cropping effects on soil C and N pools, enzyme activities, and microbial community structure. J. Agric. Sci. 2021, 159, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wang, L.; Jacinthe, P.A.; Ren, W. Global synthesis of cover crop impacts on main crop yield. Field Crops Res. 2024, 310, 109343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’reilly, K.A.; Lauzon, J.D.; Vyn, R.J.; Van Eerd, L.L. Nitrogen cycling, profit margins and sweet corn yield under fall cover crop systems. Can. J. Soil Sci. 2012, 92, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, E.; Chiduza, C.; Muchaonyerwa, P. High biomass yielding winter cover crops can improve phosphorus availability in soil. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2014, 110, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahal, I.; Van Eerd, L.L. Cover crops increase tomato productivity and reduce nitrogen losses in a temperate humid climate. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 119, 195–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhou, X.; Duan, Y.; Fu, X.; Wu, F. Wheat cover crop promoted cucumber seedling growth through regulating soil nutrient resources or soil microbial communities? Plant Soil 2017, 418, 459–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Chen, S.; Ke, L.; Ma, G.; Zhao, X. Cover crops restore declining soil properties and suppress bacterial wilt by regulating rhizosphere bacterial communities and improving soil nutrient contents. Microbiol. Res. 2020, 238, 126505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortas, I.; Islam, K.R. Phosphorus Fertilization Impacts on Corn Yield and Soil Fertility. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2018, 49, 1684–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, M.; Wei, P.; Chai, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Siddique, K.H.M. Improving Wheat Yield and Phosphorus Use Efficiency through the Optimization of Phosphorus Fertilizer Types Based on Soil P Pool Characteristics in Calcareous and Non-Calcareous Soil. Agronomy 2023, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkhajeh, Y.K.; Huang, B.A.; Sorensen, H.; Holm, P.E.; Hansen, H.C.B. Phosphorus accumulation and leaching risk of greenhouse vegetable soils in Southeast China. Pedosphere 2021, 31, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynšt, J.; Urbánková, E.; Obdržálková, E.; Jančíková, S.; Smatanová, M. Effect of increasing rate of P fertilization on available P content in soil and plant uptake: Implications for P management. J. Plant Nutr. 2024, 47, 1834–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szigeti, N.; Hermann, T.; Juhos, K.; Tóth, G. Distribution pattern of major crops and their cultivation intensity indicated by soil phosphorus concentrations in Europe. J. Agron. 2023, 115, 1678–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Tang, J.W.; Li, C.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, S. Reducing potential of chemical fertilizers and scientific fertilization countermeasure in vegetable production in China. Plant Nutr. Fert. Sci. 2017, 23, 1480–1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, J.T.; Hansen, E.M.; Kandeler, E.; Hallama, M.; Christensen, B.T.; Rubæk, G.H. Effect of soil P status on barley growth, P uptake, and soil microbial properties after incorporation of cover crop shoot and root residues. J. Plant. Nutr. Soil Sci. 2021, 184, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais-Landry, G.; Frossard, E. Similar phosphorus transfer from cover crop residues and water-soluble mineral fertilizer to soils and a subsequent crop. Plant Soil 2015, 393, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lozier, T.M.; Macrae, M.L.; Brunke, R.; Van Eerd, L.L. Release of phosphorus from crop residue and cover crops over the non-growing season in a cool temperate region. Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 189, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, X.; Wang, E.C. Impact of Winter Cover Crops on Total and Microbial Carbon and Nitrogen in Black Soil. Agronomy 2024, 14, 603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shi, C.; Han, X.; Wang, X.; Guo, Z.; Lu, X.; Zou, W.; Yan, J. Microbial Responses of Soil Fertility to Depth of Tillage and Incorporation of Straw in a Haplic Chernozem in Northeast. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2023, 33, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Nan, H.; Feng, K. Effects of reduced chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer application on soil microbial biomass, enzyme activity and cotton yield. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 311, 173–181. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Y.; Wang, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, X.; Huang, Y.; Christie, P. Response of Soil Enzymes and Microbial Communities to Root Extracts of the Alien Alternanthera philoxeroides. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2017, 64, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dong, Y.; Yi, Y.; Tian, J.; Xuan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Cao, J. Effects of phosphogypsum on enzyme activity and microbial community in acid soil. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 6189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; An, S. Identifying the Biogeographic Patterns of Rare and Abundant Bacterial Communities Using Different Primer Sets on the Loess Plateau. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Yang, G.; Hao, D.; Lu, Y.; Thein, K.; Simpson, B.; Chen, J.; Sun, R.; Alhalabi, O. 9p21 loss confers a cold tumor immune microenvironment and primary resistance to immune checkpoint therapy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 5606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, G.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y. Effects of crop stubble on physicochemical properties of continuous cropping soil and cucumber yield and quality. Nat. Resour. 2012, 3, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, T.; Yan, J.; Zhu, D.; Liao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Cong, R.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Straw returning mediates soil microbial biomass carbon and phosphorus turnover to enhance soil phosphorus availability in a rice-oilseed rape rotation with different soil phosphorus levels. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 335, 107991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Lu, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, J. Reduction of chemical phosphate fertilizer application in a rice–rapeseed cropping system through continuous straw return. Field Crops Res. 2024, 312, 109399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyler, H.L. Winter cover crops and no till management enhance enzyme activities in soybean field soils. Pedobiologia 2020, 81, 150666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, Z.; Gong, Q.; Li, Z. Effects of cover crop in an apple orchard on microbial community composition, networks, and potential genes involved with degradation of crop residues in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2018, 54, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brennan, E.B.; Acosta-Martinez, V. Cover Crops and Compost Influence Soil Enzymes during Six Years of Tillage-Intensive, Organic Vegetable Production. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2019, 83, 624–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.; Wen, Z.; Li, X.; Song, X.; Wu, H.; Yang, P. Effects of straw return on bacterial communities in a wheat-maize rotation system in the North China Plain. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0198087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutan, J.; Rosenzweig, N.; Steinke, K. Impact of Cover Crops and Nitrogen Management on Soil Bacterial Alpha Diversity. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2023, 54, 2113–2125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.; Yuan, M.; Duan, Q.; Sun, R.; Shen, Y.; Yu, Q.; Li, S. Influence of phosphorus fertilization patterns on the bacterial community in upland farmland. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 155, 112761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, R.; Sun, T.; Liang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Sun, B. Organic amendments shift the phosphorus-correlated microbial co-occurrence pattern in the peanut rhizosphere network during long-term fertilization regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, A.; Sheaffer, C.; Wyse, D.; Staley, C.; Gould, T.; Sadowsky, M. Structure of bacterial communities in soil following cover crop and organic fertilizer incorporation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9331–9341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Xie, L.; Xu, L. Soil Bacterial Community Structure and Function under the Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer with Maize Straw. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Z.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Barberán, A.; Zhao, H.; Yu, M.; Yu, L.; Brookes, P.C.; Schadt, C.W.; Chang, S.; et al. Long-term nitrogen fertilization decreases bacterial diversity and favors the growth of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria in agro-ecosystems across the globe. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 3452–3461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asaf, S.; Numan, M.; Khan, A.L.; Al-Harrasi, A. Sphingomonas: From diversity and genomics to functional role in environmental remediation and plant growth. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2020, 40, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueiredo, G.; Gomes, M.; Covas, C.; Mendo, S.; Caetano, T. The Unexplored Wealth of Microbial Secondary Metabolites: The Sphingobacteriaceae Case Study. Microb. Ecol. 2022, 83, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estrada-de los Santos, P.; Rojas-Rojas, F.U.; Tapia-García, E.Y.; Vásquez-Murrieta, M.S.; Hirsch, A.M. To split or not to split: An opinion on dividing the genus Burkholderia. Ann. Microbiol. 2015, 66, 1303–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, Z.; Tripathi, G.D.; Mishra, M.; Dashora, K. Actinomycetes-The microbial machinery for the organic-cycling, plant growth, and sustainable soil health. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 31, 101893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrión, V.J.; Pérez-Jaramillo, J.E.; Cordovez, V.; Tracanna, V.; de Hollander, M.; Ruiz-Buck, D.; Mendes, L.W.; van Ijcken, W.F.; Gomez-Exposito, R.; Elsayed, S.S. Pathogen-induced activation of disease-suppressive functions in the endophytic root microbiome. Science 2019, 366, 606–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, F.; Zhang, D.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, J. Effects of Long-Term Straw Returning and Nitrogen Fertilizer Reduction on Soil Microbial Diversity in Black Soil in Northeast China. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Song, Z.; Rong, C.; Hao, L.; Lai, Q.; Li, S.; Xu, Y. Kandeliimicrobium roseum gen. nov., sp. nov., a new member of the family Rhodobacteraceae isolated from mangrove rhizosphere soil. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2018, 68, 2158–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Li, X.; Song, J.; Jiang, W.; Liu, Y.; Fan, W. Bioremediation of cadmium-and zinc-contaminated soil using Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Chemosphere 2018, 197, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felestrino, É.; Assis, R.; Lemes, C.; Cordeiro, I.; Fonseca, N.; Villa, M.; Vieira, I.; Kamino, L.; Carmo, F.; Moreira, L. Alcaligenes faecalis associated with Mimosa calodendron rizhosphere assist plant survival in arsenic rich soils. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 1102–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Ahmad, M.; Mumtaz, M.; Ali, S.; Sarfraz, R.; Naveed, M.; Jamil, M.; Damalas, C. Integrated Application of Organic Amendments with Alcaligenes sp. AZ9 Improves Nutrient Uptake and Yield of Maize (Zea mays). J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
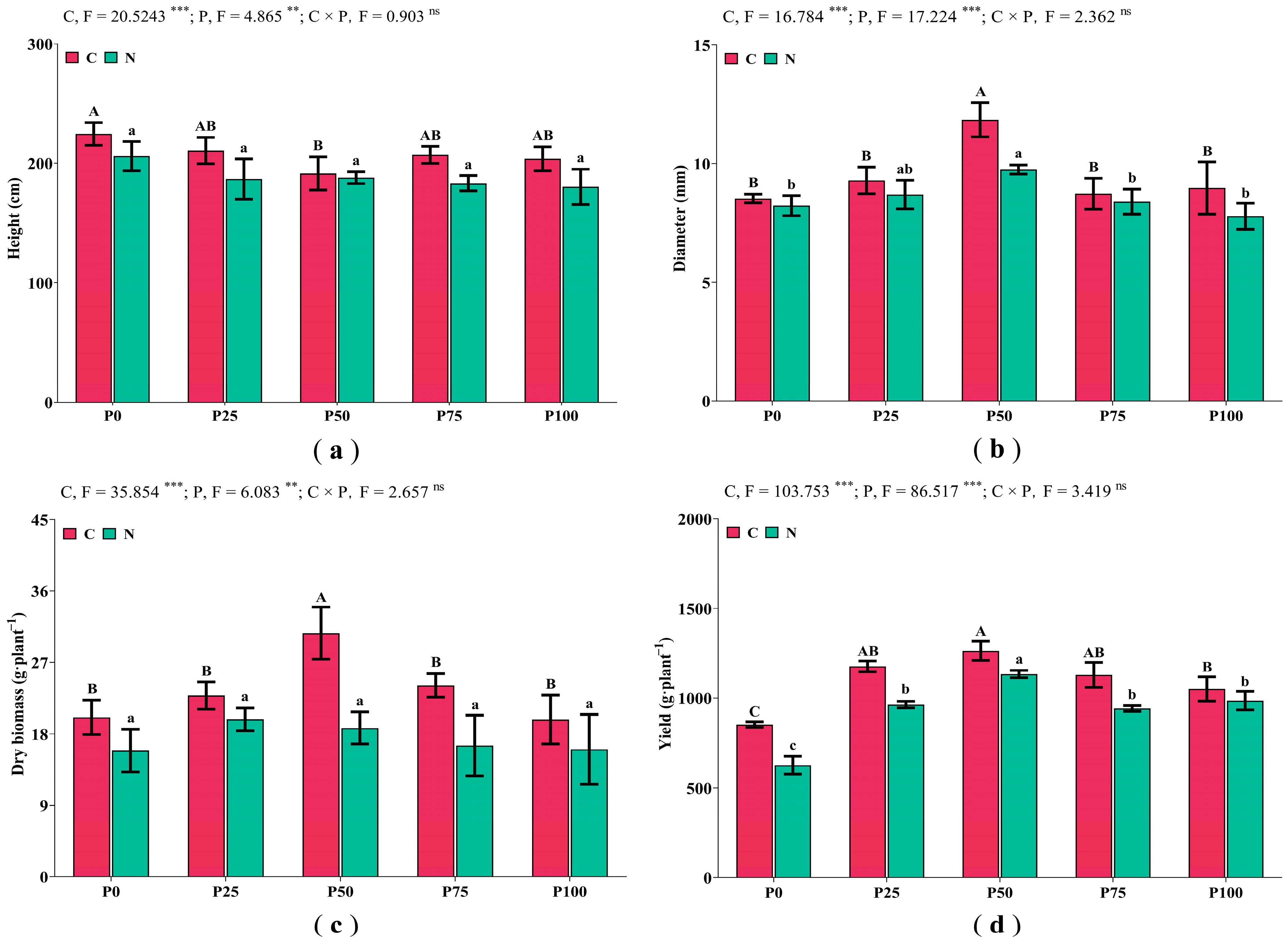
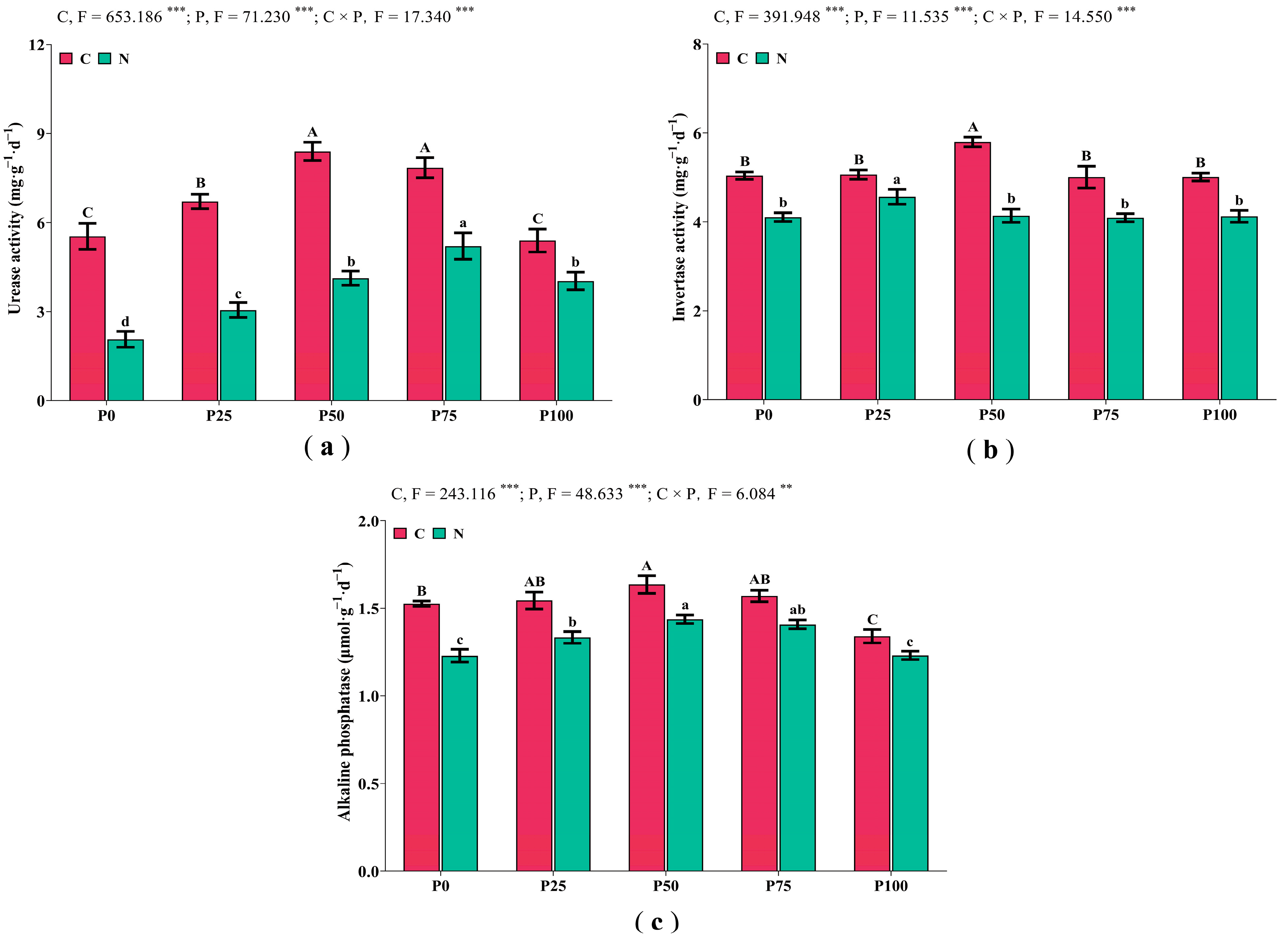
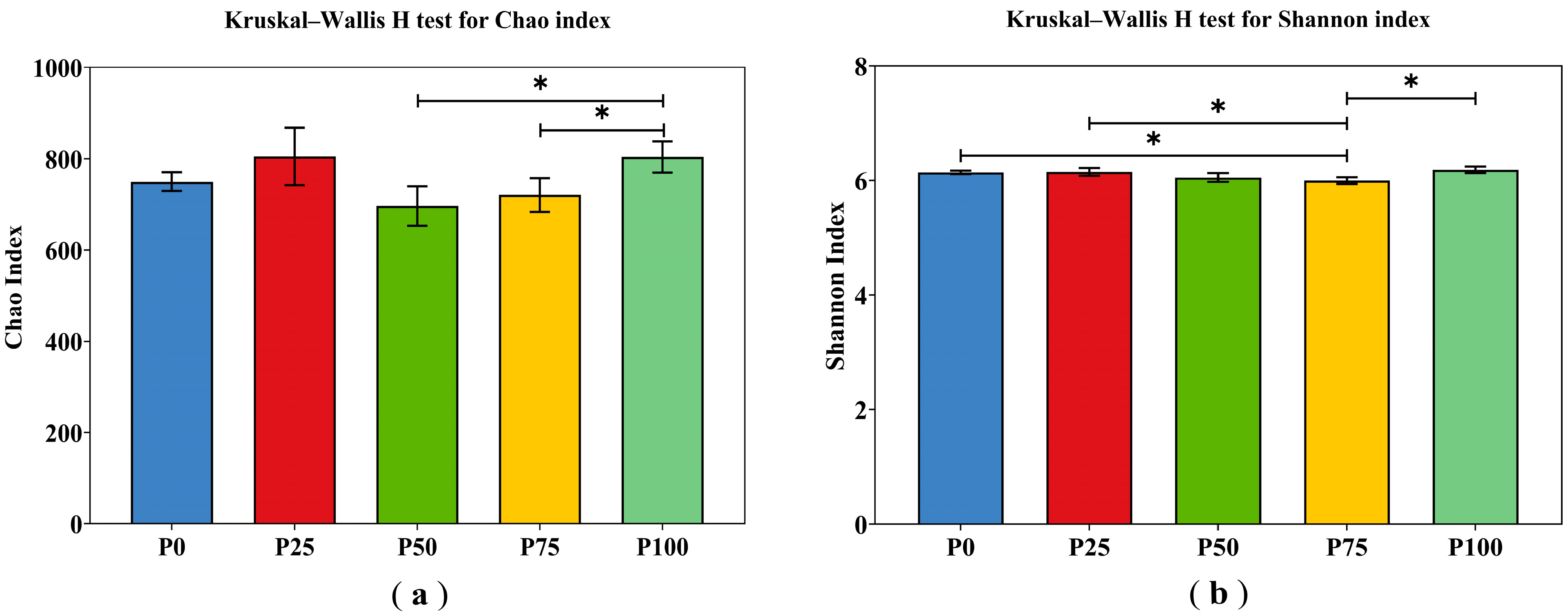

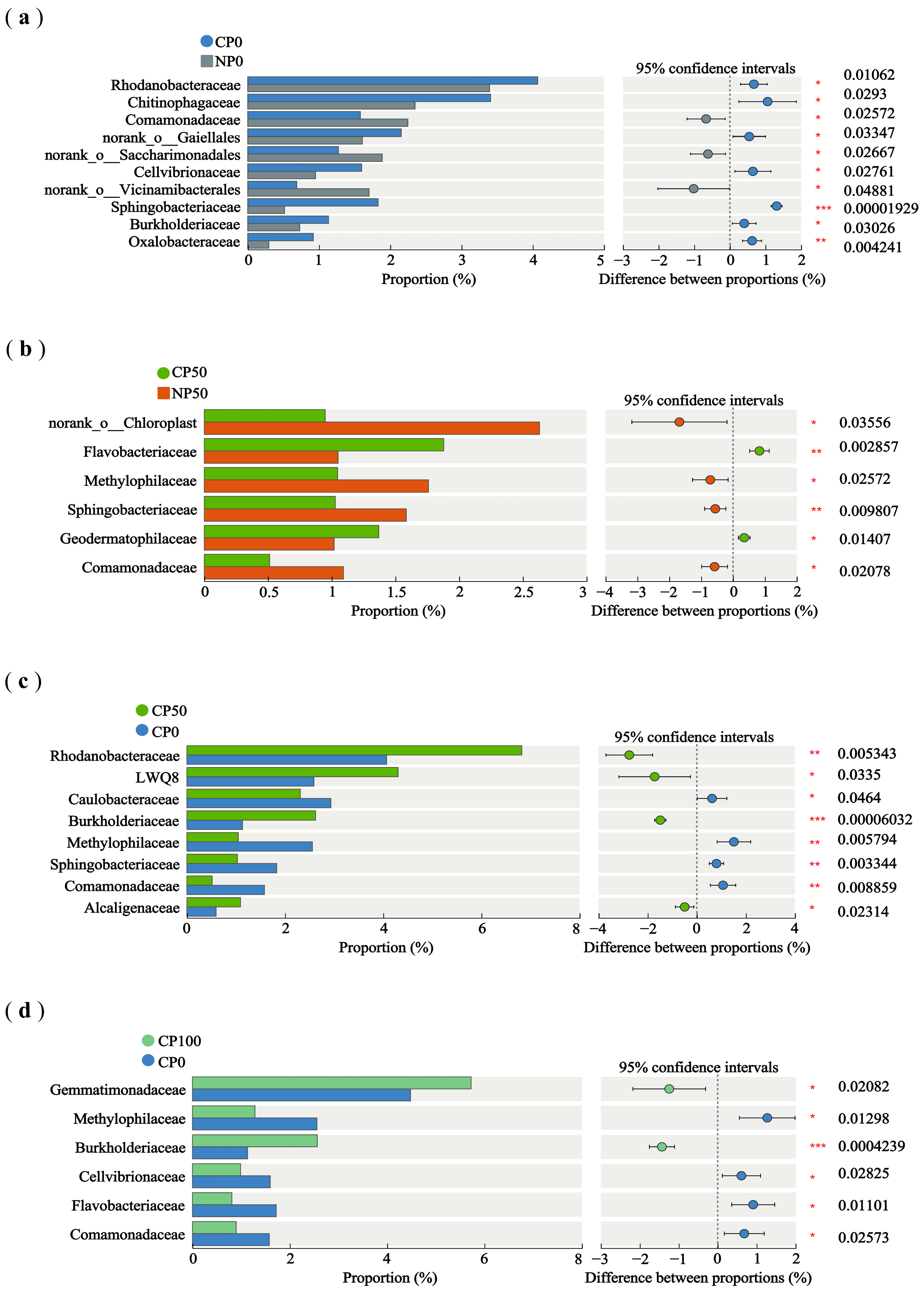
| Planting Pattern | Code of P Level | Amount of Superphosphate Input (g·pot−1) |
|---|---|---|
| C (N) | P0 | 0 |
| P25 | 4.4 | |
| P50 | 8.71 | |
| P75 | 13.07 | |
| P100 | 17.42 |
| Chao Index | Shannon Index | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F Values | p Values | F Values | p Values | |
| C (Wheat cover crop) | 1.964 | 0.176 | 1.017 | 0.325 |
| P (Phosphorus) | 3.571 | 0.024 | 6.133 | 0.002 |
| C × N (Wheat cover crop × Phosphorus) | 2.739 | 0.058 | 0.949 | 0.457 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, K.; Zhang, L.; Ullah, A.; Ibrahim, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, D.; Zhou, X.; Wu, F.; Liu, S. Moderate P Fertilizer Promotes Cucumber Yields and Modulates Bacterial Community in the Wheat Cover Crop System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030624
Cao K, Zhang L, Ullah A, Ibrahim M, Zhang Y, Gao D, Zhou X, Wu F, Liu S. Moderate P Fertilizer Promotes Cucumber Yields and Modulates Bacterial Community in the Wheat Cover Crop System. Agronomy. 2025; 15(3):624. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030624
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Kunpeng, Linlin Zhang, Asad Ullah, Musawar Ibrahim, Yu Zhang, Danmei Gao, Xingang Zhou, Fengzhi Wu, and Shouwei Liu. 2025. "Moderate P Fertilizer Promotes Cucumber Yields and Modulates Bacterial Community in the Wheat Cover Crop System" Agronomy 15, no. 3: 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030624
APA StyleCao, K., Zhang, L., Ullah, A., Ibrahim, M., Zhang, Y., Gao, D., Zhou, X., Wu, F., & Liu, S. (2025). Moderate P Fertilizer Promotes Cucumber Yields and Modulates Bacterial Community in the Wheat Cover Crop System. Agronomy, 15(3), 624. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15030624







