Optimized Phosphorus Application Under Water Stress Enhances Photosynthesis, Physiological Traits, and Yield in Soybean During Flowering Stage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
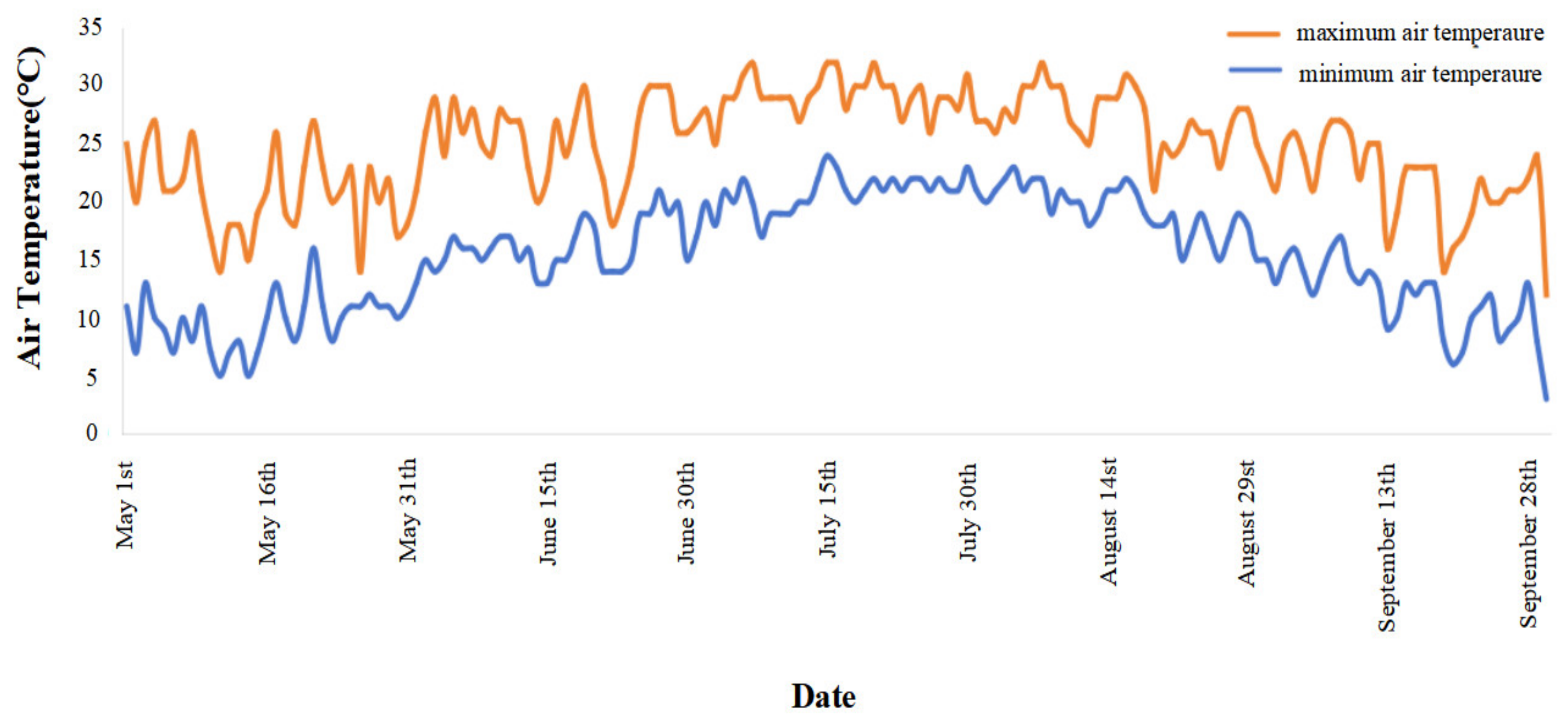
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.3.1. Field Capacity Measurement Using the Ring Knife Method
Soil Sample Collection
Wet Soil Mass Measurement
Dry Soil Mass Measurement
Field Capacity Calculation
2.3.2. Measurement of Leaf Photosynthetic Parameters
2.3.3. Measurement of Leaf Physiological Parameters
Leaf Antioxidant System Parameters
Leaf Osmotic Adjustment System Parameters
2.3.4. Measurement of Yield and Yield Components
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results
3.1. The Effect of Phosphorus Application on Photosynthetic Parameters Under Water Stress
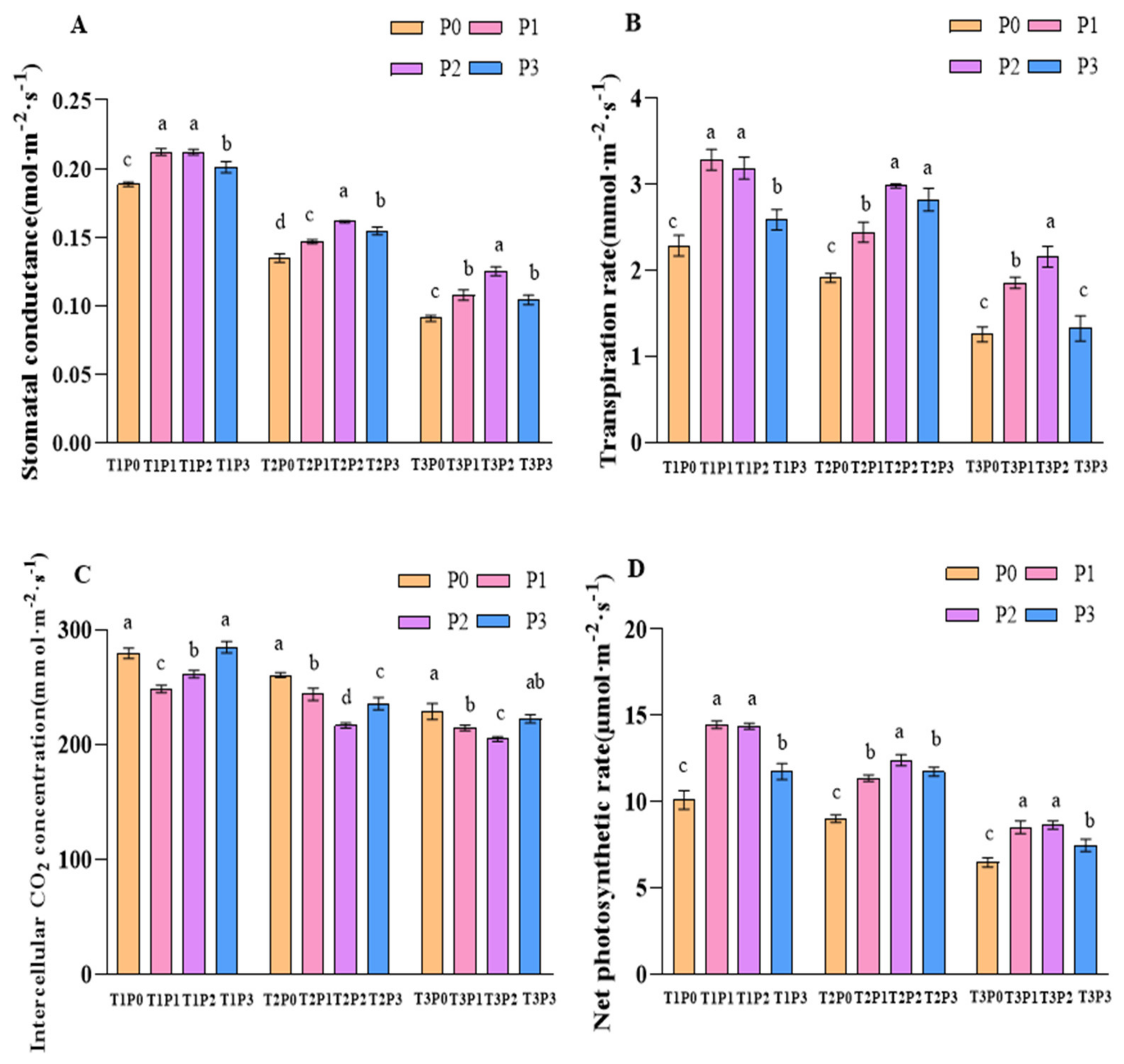
3.1.1. Stomatal Conductance (Gs)
3.1.2. Transpiration Rate (Tr)
3.1.3. Intercellular Carbon Dioxide Concentration (Ci)
3.1.4. Net Photosynthetic Rate (Pn)
3.2. The Effect of Phosphorus Application on the Antioxidant System Under Water Stress
3.2.1. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity
3.2.2. Membrane Lipid Peroxidation Content
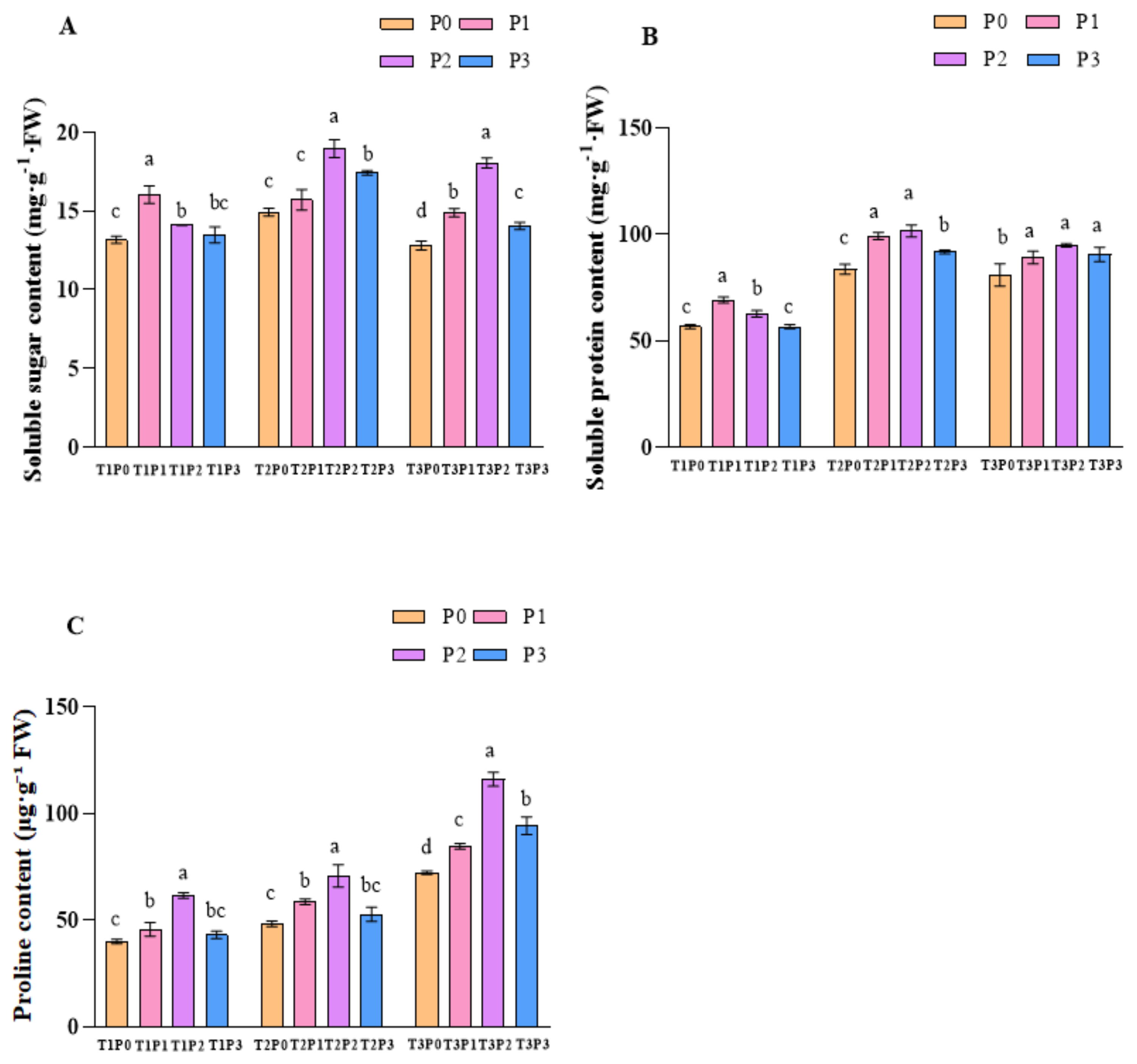
3.3. The Effect of Phosphorus Application on the Osmotic Adjustment System Under Water Stress
3.4. The Effect of Phosphorus Application on Soybean Yield Formation Under Water Stress
3.5. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. Photosynthetic Parameters
4.2. Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Membrane Lipid Peroxidation Content
4.3. Osmotic Adjustment System
4.4. Yield Formation
4.5. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GS | Stomatal conductance |
| TR | Transpiration rate |
| CI | Intercellular CO2 concentration |
| PN | Net photosynthetic rate |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase activity |
| POD | Peroxidase activity |
| H2O2 | Hydrogen peroxide content |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde content |
| SS | Soluble sugar content |
| SP | Soluble protein content |
| PRO | Proline content |
References
- Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Feng, F.; Tian, Z. Toward a “green revolution” for soybean. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 688–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, J.; Twardowska, I.; Wang, S.; Wei, S.; Chen, Y.; Ljupco, M. Prospective sustainable production of safe food for growing population based on the soybean (Glycine max L. Merr.) crops under Cd soil contamination stress. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 212, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Han, J.; Song, J.; Dong, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, J.; Tao, F. ChinaSoyArea10m: A dataset of soybean-planting areas with a spatial resolution of 10 m across China from 2017 to 2021. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2024, 16, 3213–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Linderholm, H.W.; Song, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y.; Tian, J.; Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Ren, G. Impacts of drought on maize and soybean production in northeast China during the past five decades. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zheng, S.; Bian, T.; Wu, T.; Li, X.; Fu, H.; Sun, Z.; Li, T. Photosynthetic characteristics combined with metabolomics analysis revealed potential mechanisms of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) yield reduction induced by different phosphorus stresses. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 302, 111156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskari, M.; Menexes, G.; Kalfas, I.; Gatzolis, I.; Dordas, C. Water stress effects on the morphological, physiological characteristics of maize (Zea mays L.), and on environmental cost. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, X.; Song, S.; Dong, S. Physiological response of soybean plants to water deficit. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 12, 809692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalal, V.K.; Tripathy, B.C. Water-stress induced downsizing of light-harvesting antenna complex protects developing rice seedlings from photo-oxidative damage. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, J.A.; de Carvalho, L.G.; Andrade, F.R. Gas exchange and water stress index in soybean cultivated under water deficit and soil compaction. Rev. Ceres 2022, 69, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.K.; Yang, Z.Q.; Li, Y.X.; Liu, Q.; Han, W. Effects of different levels of water stress on leaf photosynthetic characteristics and antioxidant enzyme activities of greenhouse tomato. Photosynthetica 2016, 54, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, J.R.; Müller, M.; Klein, V.A.; Rossato-Grando, L.G.; Barcelos, R.P.; Dalmago, G.A.; Chavarria, G. Soybean plant metabolism under water deficit and xenobiotic and antioxidant agent application. Biology 2020, 9, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurrieri, L.; Merico, M.; Trost, P.; Forlani, G.; Sparla, F. Impact of drought on soluble sugars and free proline content in selected Arabidopsis mutants. Biology 2020, 9, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.-Y.; He, J.; Turner, N.C.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Li, F.-M. Phosphorus supply increases internode length and leaf characteristics, and increases dry matter accumulation and seed yield in soybean under water deficit. Agronomy 2021, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basal, O.; Szabó, A. Sole and combined effects of drought and phosphorus application on soybean. J. Central Eur. Agric. 2020, 21, 796–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Chen, L.; Yu, X.; Zhao, X.; Ma, Y.; Ren, Z. Phosphorus control as an effective strategy to adapt soybean to drought at the reproductive stage: Evidence from field experiments across northeast China. Soil Use Manag. 2015, 31, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathe, Z.; Stepanic, O.M.; Peredkov, S.; DeBeer, S. Phosphorus Kβ X-ray emission spectroscopy detects non-covalent interactions of phosphate biomolecules in situ. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 7888–7901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, S.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Yu, K.; Chao, M.; Han, S.; Zhang, D. Physiological and proteomics analyses reveal low-phosphorus stress affected the regulation of photosynthesis in soybean. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-T.; Lu, C.-T.; Tzen, J.T.C.; Yang, C.-Y. Physiological properties and molecular regulation in different edamame cultivars under drought stress. Agronomy 2021, 11, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Shi, R.; Deng, S.; Wang, H.; Hussain, S.; Wang, C.; Gong, C.; Bai, J. Application of low phosphorus on the basis of organic fertilizer can effectively improve yield and quality of tea plants. Beverage Plant Res. 2024, 4, e037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Lin, Y.; Yi, S.; Nie, T. Study on Soybean Water Demand and Irrigation Schedule in Western Heilongjiang Province Based on Cropwat Model. Appl. Ecol. Environ. Res. 2024, 22, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Sun, D.; Li, T.C.; Qi, Z.J.; Du, S.C.; Wang, B.; Huang, Y. Effects of water-saving irrigation and reduced phosphorus fertilizer application on the yield of paddy rice in black soil and the utilization and balance of soil phosphorus. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lier, Q.d.J.v. Field capacity, a valid upper limit of crop available water? Agric. Water Manag. 2017, 193, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maleki, A.; Naderi, A.; Naseri, R.; Fathi, A.; Bahamin, S.; Maleki, R. Physiological performance of soybean cultivars under drought stress. Bull. Environ. Pharmacol. Life Sci. 2013, 2, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp, C.; Fridovich, I. Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal. Biochem. 1971, 44, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egley, G.H.; Paul, R.N.; Vaughn, K.C.; Duke, S.O. Role of peroxidase in the development of water-impermeable seed coats in Sida spinosa L. Planta 1983, 157, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.P.; Choudhuri, M.A. Implications of water stress-induced changes in the levels of endogenous ascorbic acid and hydrogen peroxide in Vigna seedlings. Physiol. Plant. 1983, 58, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heath, R.L.; Packer, L. Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts: I. kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1968, 125, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yemm, E.W.; Willis, A.J. The estimation of carbohydrates in plant extracts by anthrone. Biochem. J. 1954, 57, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, N.; Yang, R.; Wang, L.; Sun, Q.; Li, D.; Cao, Y.; Weeda, S.; Zhao, B.; Ren, S.; et al. Melatonin promotes seed germination under high salinity by regulating antioxidant systems, ABA and GA 4 interaction in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, L.S.; Waldren, R.P.; Teare, I.D. Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 1973, 39, 205–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornic, G.; Fresneau, C. Photosynthetic carbon reduction and carbon oxidation cycles are the main electron sinks for photosystem II activity during a mild drought. Ann. Bot. 2002, 89, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Mei, X.; Yan, C.; Gong, D.; Zhang, Y. Effects of water stress on photosynthetic characteristics, dry matter translocation and WUE in two winter wheat genotypes. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 167, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Liu, L.; Shen, Q.; Yang, J.; Han, X.; Tian, F.; Wu, J. Effects of water stress on photosynthesis, yield, and water use efficiency in winter wheat. Water 2020, 12, 2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesniˇar, M.; Kastori, R.; Petrović, N.; Panković, D. Photosynthesis and chlorophyll fluorescence in sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) leaves as affected by phosphorus nutrition. J. Exp. Bot. 1994, 45, 919–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, C.R.; Adams, M.A. Phosphorus affects growth and partitioning of nitrogen to Rubisco in Pinus pinaster. Tree Physiol. 2002, 22, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.; Woo, K.C.; Wong, S.C. Effects of phosphorus nutrition on the response of photosynthesis to CO2 and O2, activation of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase and amounts of ribulose bisphosphate and 3-phosphoglycerate in spinach leaves. Photosynth. Res. 1988, 15, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Yang, C.; Mu, R. Effect of soil water-phosphorus coupling on the photosynthetic capacity of Robinia pseudoacacia L. seedlings in semi-arid areas of the Loess Plateau, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Hamed, S.; Lefi, E.; Chaieb, M. Effect of phosphorus concentration on the photochemical stability of PSII and CO2 assimilation in Pistacia vera L. and Pistacia atlantica Desf. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 142, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukmirović, A.; Škvorc, Ž.; Bogdan, S.; Krstonošić, D.; Bogdan, I.K.; Karažija, T.; Bačurin, M.; Brener, M.; Sever, K. Photosynthetic response to phosphorus fertilization in drought-stressed common beech and sessile oak from different provenances. Plants 2024, 13, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, W.; Ge, X.; Jia, Y. Effects of various levels of water stress on morpho-physiological traits and spectral reflectance of maize at seedling growth stage. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, Y.Q.; Song, L.L.; Jacobs, D.F.; Mei, L.; Liu, P.; Jin, S.H.; Wu, J.S. Physiological response to drought stress in Camptotheca acuminata seedlings from two provenances. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carstensen, A.; Herdean, A.; Schmidt, S.B.; Sharma, A.; Spetea, C.; Pribil, M.; Husted, S. The impacts of phosphorus deficiency on the photosynthetic electron transport chain. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, G.; Zhou, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus counteracted the adverse effects of salt on sorghum by improving ROS scavenging and osmotic regulation. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Sun, M.; He, W.; Wang, H.; Pan, H.; Yang, Q.; Lou, Y.; Zhuge, Y. Effect of phosphorus supplementation on growth, nutrient uptake, physiological responses, and cadmium absorption by tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea Schreb.) exposed to cadmium. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.; Hou, D.; O’connor, D.; Pan, S.; Zhu, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Mulder, J. Exogenous phosphorus treatment facilitates chelation-mediated cadmium detoxification in perennial ryegrass (Lolium perenne L.). J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 389, 121849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, W.-W.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Huang, Z.-R.; Ye, X.; Chen, L.-S.; Yang, L.-T. Effects of phosphorus deficiency on the absorption of mineral nutrients, photosynthetic system performance and antioxidant metabolism in Citrus grandis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, D.; Miyagi, A.; Tazoe, Y.; Suganami, M.; Yamada, M.K.; Ueda, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Noguchi, K.; Hirotsu, N.; Makino, A. Phosphorus toxicity disrupts Rubisco activation and reactive oxygen species defence systems by phytic acid accumulation in leaves. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 2033–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoyerdi, F.F.; Shamshiri, M.H.; Estaji, A. Changes in some physiological and osmotic parameters of several pistachio genotypes under drought stress. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 198, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, A.M.; Rosen, M.K. ATP controls the crowd. Science 2017, 356, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngwenya, S.P.; Moloi, S.J.; Shargie, N.G.; Brown, A.P.; Chivasa, S.; Ngara, R. Regulation of proline accumulation and protein secretion in sorghum under combined osmotic and heat stress. Plants 2024, 13, 1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, R.; Sánchez, E.; Ruíz, J.M.; Lao, M.T.; Romero, L. Proline, betaine, and choline responses to different phosphorus levels in green bean. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2013, 44, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, N.; Dickman, M.B.; Becker, D.F. Proline modulates the intracellular redox environment and protects mammalian cells against oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 44, 671–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Jia, L.; Chen, H.; Wei, X. Zinc-induced oxidative damage, antioxidant enzyme response and proline metabolism in roots and leaves of wheat plants. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2013, 89, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, F.; Guo, C.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Z.; Kong, J.; He, Q.; Sharmin, R.A.; Zhao, T. Genome-wide association studies for dynamic plant height and number of nodes on the main stem in summer sowing soybeans. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Devi, N.S.; Chia, R.W.; Mirzaei, M.; Reijneveld, A.; Fontana, M.; Lo, K.-J. Changes on phosphorus fractions and paddy yield using different single super phosphate and rock phosphate rates under acid soil. J. Plant Nutr. 2024, 47, 1130–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Treatments | Field Capacity | Phosphate |
|---|---|---|
| T1P0 | 70 ± 5% | 0 mg/kg |
| T1P1 | 70 ± 5% | 40 mg/kg |
| T1P2 | 70 ± 5% | 50 mg/kg |
| T1P3 | 70 ± 5% | 60 mg/kg |
| T2P0 | 60 ± 5% | 0 mg/kg |
| T2P1 | 60 ± 5% | 40 mg/kg |
| T2P2 | 60 ± 5% | 50 mg/kg |
| T2P3 | 60 ± 5% | 60 mg/kg |
| T3P0 | 50 + 5% | 0 mg/kg |
| T3P1 | 50 + 5% | 40 mg/kg |
| T3P2 | 50 + 5% | 50 mg/kg |
| T3P3 | 50 + 5% | 60 mg/kg |
| Treatments | Pitch Number | Number of Pods Per Plant | Per Plant | Yield Per Plant | Grain Weight/100 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Piece (s) | Piece (s) | Piece (s) | (g) | (g) | |
| T1P0 | 13.75 ± 1.59a | 23.42 ± 6.70a | 51.00 ± 14.22b | 10.18 ± 3.16a | 18.69 ± 0.19b |
| T1P1 | 13.58 ± 1.32a | 27.58 ± 4.54a | 63.25 ± 14.84a | 11.77 ± 1.13a | 23.53 ± 0.13a |
| T1P2 | 13.67 ± 1.70a | 27.25 ± 2.98a | 51.42 ± 12.82b | 11.60 ± 2.65a | 23.21 ± 2.73a |
| T1P3 | 13.25 ± 1.30a | 26.83 ± 3.24a | 52.42 ± 4.13b | 11.54 ± 2.55a | 20.86 ± 0.21ab |
| T2P0 | 13.50 ± 1.80a | 21.67 ± 3.79a | 43.25 ± 6.17a | 9.10 ± 1.64a | 20.63 ± 0.54b |
| T2P1 | 12.67 ± 1.11a | 22.08 ± 3.57a | 45.25 ± 6.38a | 9.40 ± 1.20a | 21.16 ± 0.08b |
| T2P2 | 12.83 ± 0.99a | 23.42 ± 3.99a | 48.25 ± 10.69a | 10.58 ± 2.69a | 22.10 ± 0.14a |
| T2P3 | 13.33 ± 1.18a | 23.25 ± 3.59a | 44.17 ± 8.60a | 9.64 ± 1.22a | 22.54 ± 0.38a |
| T3P0 | 12.50 ± 1.19a | 19.75 ± 5.25b | 38.92 ± 8.22b | 7.63 ± 1.50b | 17.78 ± 0.56b |
| T3P1 | 12.75 ± 0.92a | 26.25 ± 5.18a | 54.00 ± 11.06a | 10.12 ± 1.50a | 21.40 ± 0.26a |
| T3P2 | 12.83 ± 1.14a | 25.83 ± 7.81a | 47.58 ± 13.40ab | 10.07 ± 2.63a | 21.25 ± 1.30a |
| T3P3 | 12.50 ± 1.66a | 22.33 ± 6.25ab | 39.50 ± 10.11b | 8.42 ± 2.50ab | 20.96 ± 1.18a |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Q.; Nie, T.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M. Optimized Phosphorus Application Under Water Stress Enhances Photosynthesis, Physiological Traits, and Yield in Soybean During Flowering Stage. Agronomy 2025, 15, 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020444
Chen Q, Nie T, Li Y, Li H, Sun Y, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Wang M. Optimized Phosphorus Application Under Water Stress Enhances Photosynthesis, Physiological Traits, and Yield in Soybean During Flowering Stage. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):444. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020444
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Qu, Tangzhe Nie, Yang Li, Hao Li, Yubo Sun, Yuzhe Wu, Yuxian Zhang, and Mengxue Wang. 2025. "Optimized Phosphorus Application Under Water Stress Enhances Photosynthesis, Physiological Traits, and Yield in Soybean During Flowering Stage" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020444
APA StyleChen, Q., Nie, T., Li, Y., Li, H., Sun, Y., Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., & Wang, M. (2025). Optimized Phosphorus Application Under Water Stress Enhances Photosynthesis, Physiological Traits, and Yield in Soybean During Flowering Stage. Agronomy, 15(2), 444. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020444







