Abstract
Soil labile organic carbon (C) fractions play a key role in agricultural soil fertility. However, the effects of long-term organic substitution regimes on soil organic carbon (SOC), its labile fractions, stability, and vegetable yields as well as the relationships among these factors in the open-field are less well-studied. Hence, the objective of this study was to analyze the effects of long-term organic substitution regimes on SOC sequestration, labile C fractions [particulate organic C (POC), microbial biomass carbon (MBC), dissolved organic C (DOC), and readily oxidizable C (ROC)], SOC stability, the C pool management index (CMI), and vegetable yields in a long-term (13 years) open-field experiment. Five treatments were examined: 100% chemical nitrogen fertilizer (CN), substituting 25% of the chemical N with manure (MN) or straw (SN), and substituting 50% of the chemical N with manure (2MN) or manure plus straw (MSN). Compared to the CN, organic substitution treatments increased the average yields of vegetable, the SOC, the labile C fractions’ contents, and the C pool management index (CMI) to varying degrees, but only MSN reached significant levels for these factors. However, the MSN treatment had a significantly lower C stability index (SI) than the CN. 13C-NMR analyses also confirmed that organic substitution treatments increased the proportion of O-alkyl C and the OA/A, but reduced SOC stability. Pearson correlation analysis and the partial least squares path model indicated that labile C fractions were the mainly direct contributors to yield and SOC stability. Overall, substituting 50% of the chemical N with manure plus straw is a relatively ideal fertilization practice to improve vegetable yields and enhance C activity in an open field.
1. Introduction
Soil organic carbon (SOC), the largest C pool in the terrestrial ecosystem, has an important impact on soil nutrient cycling, microbial activities, and crop productivity in farmland, and is the core indicator of soil fertility [1]. Fertilization is a key factor affecting SOC [2]. Application of a single chemical fertilizer can indirectly increase SOC content by increasing crop residues and belowground production [3]. Organic substitution (e.g., commercial organic fertilizer, manure, and straw) of chemical fertilizer directly enhances SOC content, improves soil physical, chemical, and biological properties, and thereby enhances soil quality and crop yield [4,5,6]. However, different organic substitution regimes have different effects on increasing SOC content and crop yield [7,8,9,10]; hence, the proportion and type of substitution should be considered comprehensively.
Soil labile organic C is a component of organic C that is easily used by microorganisms and impacts crop yield, soil nutrient supply, and soil structure [11]. However, short-term changes in SOC are not sensitive to different farmland management measures [12]. Although labile organic C only accounts for a small proportion of SOC, its high activity, sensitivity, and turnover rate enable it to be a sensitive indicator reflecting SOC changes and also make it an important indicator for soil fertility and potential productivity, since its changes can mirror such field management practices as fertilization and tillage [13,14]. The application of organic fertilizers significantly influences the dynamics of SOC fractions, a concept well-established through extensive research. A meta-analysis based on 57 published studies disclosed that the addition of organic materials invariably improved the SOC composition and boosted the contents of various labile organic C fractions (e.g., POC, particulate organic C; MBC, microbial biomass C; DOC, dissolved organic C; and ROC, readily oxidizable C), thus having an impact on the stability and turnover of SOC [15]. In the short term, straw amendment has been noted to enhance the levels of labile soil carbon fractions, including DOC, ROC, and MBC [16]. However, prolonged investigations spanning over three decades reveal that the incorporation of organic materials, such as straw and manure, can elevate SOC levels without significantly affecting DOC levels [17]. These inconsistent results might be related to the differences in the environmental conditions, soil type, years of cultivation, and cropping system among study sites [12,18,19,20]. Moreover, based on changes in ROC and SOC, the C pool management index (CMI) was developed to assess the state and rate of change in agricultural soil C of the agro-ecosystem, which is also a useful parameter to evaluate the capacity of management practices to improve soil quality [16].
SOC stability is mainly related to soil organic carbon composition and agricultural management practices [15]. Organic substitution is not only a direct and effective measure to supplement C sources [21], but also influences SOC stability and drives soil C cycling [5]. However, many research results are inconsistent, with positive [22], negative [12], and neutral [23] effects on SOC stability being reported. These discrepancies may arise owing to varying cropping systems, types of crop straw, and specific site conditions, likely attributed to the complex processes of microbial humification and the decomposition of exogenous organic matter in the soil [5,24,25]. In addition, among various methods, the Walkley–Black and 13C-NMR methods are effective means to quantify the stability and composition of SOC, and can divide it into unstable/active and stable/inert fractions [25].
Open-field vegetables are one of the most important vegetable production systems in China, covering 80% of the planting area and accounting for 65% of production. However, owing to farmers’ pursuit of high vegetable yields and maximized economic benefits, the issue of improper fertilization is serious [26]. Long-term application of chemical fertilizers promotes soil organic matter mineralization [27], leading to soil quality degradation and nutrient imbalance, thereby reducing the sustainable productivity of farmland [28]. Organic fertilizers and straw contain abundant organic C sources and essential mineral nutrients required by plants [8]. As such, long-term and appropriate application of organic fertilizers/straw can effectively promote an increase in SOC content and enhance soil quality [29,30]. Meanwhile, reducing the use of chemical fertilizers is considered an important measure to safeguard food security in China and soil health [31]. Therefore, investigating the impact of long-term organic substitution of chemical fertilizers on SOC in open-field vegetable cultivation is particularly significant.
Research on the effects of different long-term organic substitutions for chemical fertilizers on SOC composition and stability has mainly focused on grain crops [32,33] and greenhouse vegetables [5,34], with scarce numbers of studies reported on open-field vegetables. Therefore, in the present study, a 13-year field trial was conducted under different organic substitution regimes in open-field vegetable systems. Our objectives were to (1) investigate the variations in vegetable yield and the sustainable yield index under different long-term fertilization regimes; (2) explore which organic substitution regimes have the greatest influence on SOC content, labile organic C fractions, SOC stability, and the CMI; and (3) illustrate the relationships between SOC, labile SOC fractions, SOC stability, vegetable yield, and the CMI.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
The local experiment was carried out from August 2009 to July 2022 with spring cabbage (Brassica oleracea L.) and autumn Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis) rotation in the open field of the Dahe Experimental Station, Hebei Academy of Agricultural and Forestry Sciences (N 38°1′48″, E 114°28′48″). The region has a warm–temperate continental monsoon climate, with an altitude of 78 m, an average annual precipitation of 496.6 mm, and an average annual temperature of 12.9 °C. The soil in the study has a clay loam texture and can be classified as calcareous cinnamon soil (FAO classification). Before the experiment, the physicochemical properties of the 0–20 cm soil layer were as follows: pH, 8.2; SOC, 11.3 g kg–1; NO3–-N, 40.0 mg kg–1; available phosphorus, 18.9 mg kg–1; and available potassium, 143.8 mg kg–1.
2.2. Experimental Design
The experimental trial was conducted in a randomized block design with three replications, each plot covering an area of 49 m2 (7 × 7 m). Five treatments were set up based on different types of N fertilizers applied: (1) 100% chemical N fertilizer (CN), (2) 75% chemical N plus 25% pig manure N (MN), (3) 50% chemical N plus 50% pig manure N (2MN), (4) 50% chemical N plus 25% pig manure N plus 25% corn straw N (MSN), and (5) 75% chemical N plus 25% corn straw N (SN). Before the trial commenced, the soil within each plot was maintained in its original state, and the surrounding soil layer was excavated to match the plot’s shape. PVC boards of 4 mm in thickness were buried at a depth of 100 cm and protruded 5 cm above the ground between the plots to the prevent lateral migration of nutrients and water. For spring cabbage, 14 rows were planted in each plot with 20 plants per row, spaced at 0.35 × 0.5 m. Autumn Chinese cabbage was planted with 12 rows per plot, with each row containing 12 plants, spaced at 0.58 × 0.58 m.
Equal amounts of NPK nutrients were applied in all treatments: 300, 150, and 300 kg ha–1 of N, P2O5, and K2O fertilizer for the spring cabbage season, respectively; and 300, 150, and 450 kg ha–1 of N, P2O5, and K2O fertilizer for the autumn Chinese cabbage season, respectively. The chemical fertilizers used were urea (N, 46%), calcium superphosphate (P2O5, 18%), and potassium sulfate (containing 51% K2O). In the spring cabbage season, commercial fermented pig manure (dry basis C–N–P2O5–K2O of 21.80–3.45–2.08–0.97%, with a water content of 28.72%) was used as the organic fertilizer, and corn straw (dry basis C–N–P2O5–K2O of 42.69–1.28–0.39–2.06%, with a water content of 8.72%) was used as the straw. For the autumn Chinese cabbage season, commercial pig manure (dry basis C–N–P2O5–K2O of 21.80–3.18–2.27–0.82%) and corn straw (dry basis C–N–P2O5–K2O of 42.69–1.12–0.35–1.53%) were used; the types of chemical fertilizers were the same as those used in the spring cabbage season. Detailed fertilizer data are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
Nitrogen (N) and carbon (C) inputs applied in different fertilization treatments during the spring cabbage season and autumn Chinese cabbage season.
Before planting spring cabbage, each crop residue treatment was evenly spread in the 20–30 cm soil layer. Subsequently, commercial manure, 40% inorganic nitrogen fertilizer, 100% inorganic phosphate fertilizer, and 50% inorganic potash were evenly sprinkled on the ground. Additionally, 20% inorganic nitrogen fertilizer and 20% inorganic potash fertilizer were applied at the rosette stage, while 40% inorganic nitrogen fertilizer and 30% inorganic potash fertilizer were applied at the nodulation stage. Autumn Chinese cabbage was fertilized before sowing in the same manner as spring cabbage. The fertilizer was spread and watered, and the amount of water applied to each plot was controlled by a water meter to ensure equality. The irrigation amount was 2245 m3 hm−2 during the spring cabbage season, and 2143 m3 hm−2 during the autumn Chinese cabbage season. Weeding, disease control, pest control, and other field management measures were conducted according to local practices.
2.3. Soil Sampling and Chemical Analysis
Soil samples were collected during the cabbage harvesting period (June 2022) using a five-point random sampling method, where five sampling points were randomly selected from each plot, and samples from the 0–20 cm soil layer were mixed and divided. Before soil sampling, surface debris was removed from the area. After sampling, fresh soil samples were sieved through a 2 mm mesh sieve, mixed, and a portion of the soil was air-dried for determining SOC fractions and SOC pools, and for performing 13C-NMR. Air-dried soil samples were subsequently sieved through a 100-mesh sieve, and SOC was measured using the external heating potassium dichromate oxidation method and assessed using a Multi N/C 3100/HT1300 analyzer (Analytik Jena AG, Hanau, Germany) [12].
POC was determined using 10 g of soil dispersed in 30 mL of 5 g L−1 sodium hexametaphosphate [(NaPO3)6] solution. The mixture was shaken, passed through a 53 μm sieve, and then dried at 60 °C to obtain particles with a size > 53 μm, which were analyzed separately [22].
MBC was determined using the fumigation-extraction method by the Multi N/C 3100/HT1300 analyzer (Analytik Jena AG, Germany) and was calculated as the difference between organic C in the fumigated and unfumigated soil samples with a correction factor of 0.45 [35].
DOC was measured by adding 50 mL of distilled water to 10 g of fresh soil (5:1, v/w) in a 100 mL polypropylene bottle. The samples were shaken on a shaker for 30 min at 180 rpm and then centrifuged for 10 min at 12,000 rpm. The upper suspension was filtered through a 0.45 μm filter into a bottle, and the filtrate was assessed using the Multi N/C 3100/HT1300 analyzer as described previously [36].
ROC was analyzed based on the work of Chan et al. [37], who used the modified Walkley–Black method, and its filtrate was assessed using the Multi N/C 3100/HT1300 analyzer as described previously. According to the ease with which SOC is oxidized, it was classified as very labile C (CVL), labile C (CL), less labile C (CLL), or recalcitrant C (CNL), with the sum of CVL and CL regarded as the active C pool (CA) and the sum of CLL and CNL regarded as the passive C pool (CP) [25].
13C NMR analysis [38] of the organic C chemical structure was carried out using the CPMAS solid-state 13C-NMR detection technique (13C-NMR, Bruker Avance III 400 NMR, Ettlingen, Germany), and the NMR spectra of the soil samples were classified into four regions based on chemical shifts: the alkyl C region (0–45 ppm), O-alkyl C region (45–110 ppm), aromatic C region (110–160 ppm), and the carbonyl C region (160–190 ppm).
2.4. Data Computation and Analysis
The sustainable yield index (SYI) is an important indicator of the sustainability of farm management practices, based on crop yields over a calendar year [39]:
where Ymean represents the mean yield (t ha–1), σ denotes the standard deviation, and Ymax denotes the maximum yield (t ha–1) of the vegetable during the trial.
The following indices were calculated based on the differences in C content between fertilizer treatments [40,41].
where CVL, CL, and CLL represent the fractions of highly, moderately, and minimally active organic C content, respectively, and SOC denotes the total organic C content. SOCReference is the organic C content (g kg–1) of the soil prior to the long-term orientation test.
Based on the relative proportions of alkyl C, O-alkyl C, carbonyl C, and aromatic C, the SOC hydrophobicity index (HI) and aromaticity index (AI) were calculated as follows [38]:
OA/A = (O-alkyl C)/(alkyl C)
HI = (alkyl C + aromatic C)/(O-alkyl C + carbonyl C)
AI = aromatic C/(aromatic C + alkyl C + O-alkyl C) × 100
The experimental data were compiled and analyzed using Excel 2019 (Microsoft Office). Duncan’s one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA, p < 0.05) was performed using IBM SPSS 19.0 software. The results were plotted using Origin 2021 software.
3. Results
3.1. Open-Field Vegetable Yields and Sustainability Index
Compared with single chemical fertilizer application, long-term organic substitution treatments increased the average yield of spring cabbage and autumn Chinese cabbage from 2009 to 2022 (Figure 1). When compared with the CN treatment, the 2MN, MSN, and SN treatments significantly enhanced the average yield of spring cabbage and autumn Chinese cabbage (p < 0.05). The MSN treatment showed the highest increases in the average yields of spring cabbage and autumn Chinese cabbage compared to CN, significantly increasing by 10.53% and 15.45%, respectively. Additionally, under different fertilization treatments, the SYI for cabbage was ranked highest to lowest as follows: MSN > SN > 2MN > CN > MN; and for Chinese cabbage, the ranking was MSN > CN > 2MN > MN > SN.
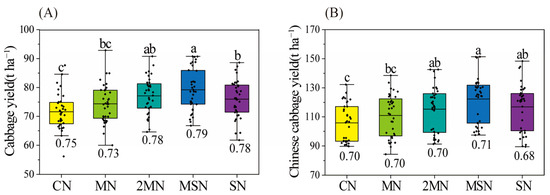
Figure 1.
Boxplots showing cabbage (A) and Chinese cabbage (B) yields for different fertilization treatments from 2009 to 2022. Upper and lower boundaries of the boxes represent the 75% and 25% quartiles, respectively. Horizontal lines represent the average value, and different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among different treatments. Numbers under the boxes represent the sustainable yield index (SYI) corresponding to different treatments. Values are the mean (n = 3) ± standard error.
3.2. SOC and Its Labile Fractions
All long-term manure/straw substitutions for chemical fertilizer treatments significantly increased the soil SOC, POC, MBC, DOC, and ROC contents (p < 0.05) compared with the CN treatment (Figure 2). Among them, the MSN treatment showed the greatest increases in SOC, POC, MBC, DOC, and ROC contents (80.39%, 119.53%, 135.93%, 71.56%, and 107.45%, respectively; Figure 2A–E). In addition, the POC, MBC, DOC, and ROC contents in the straw substitution treatment were higher than those in the manure-substitution-alone treatment (Figure 2B–E).
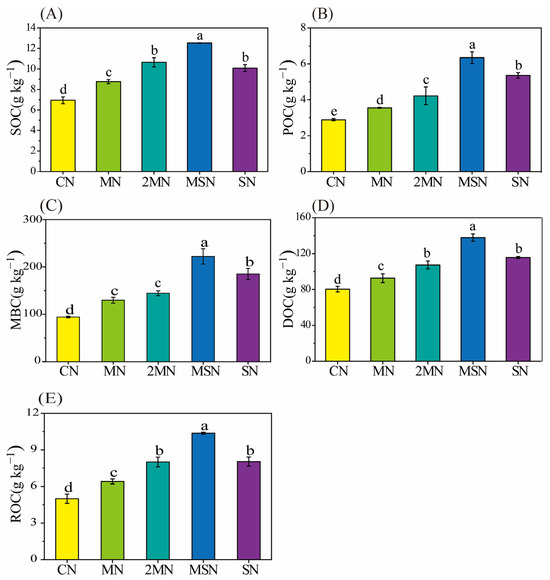
Figure 2.
Responses of soil organic carbon (SOC, (A)), particulate organic carbon (POC, (B)), microbial biomass carbon (MBC, (C)), dissolved organic carbon (DOC, (D)), and readily oxidizable carbon (ROC, (E)) to different fertilization treatments. Values are the mean (n = 3) ± standard error. Different lowercase letters indicate significant differences (p < 0.05) among different treatments.
3.3. SOC Stability Indicators and the CMI
Manure/straw substitution for chemical fertilizer altered the contents of various active and passive C pools in the soil (Table 2). The contents of CA (CVL and CL) and CP (CLL and CNL) ranked in descending order as MSN > SN > 2MN > MN > CN. Compared with the CN treatment, the MN, 2MN, MSN, and SN treatments significantly increased the soil CVL, CL, and CNL contents (p < 0.05), with increases ranging from 27.27 to 106.06%, 40.98–85.25%, and 5.49–35.94%, respectively. Moreover, the MSN and SN treatments also significantly increased the CLL content (p < 0.05) by 160.71% and 107.14%, respectively.

Table 2.
Soil oxidizable organic C fractions and C pool indicators in the open vegetable fields under different fertilization treatments.
All organic substitution treatments significantly increased soil LI, CPI, and CMI values compared with the sole chemical fertilizer treatment (p < 0.05; Table 2), with increases of 2.92–13.45%, 26.42–80.19%, and 29.75–103.80%, respectively, but MSN treatment significantly reduced the SI by 22.73%. As the application of manure increased, the LI, CPI, and CMI increased accordingly, with significant differences among treatments (p < 0.05). Among the organic substitution treatments, MSN treatment had the highest LI (1.94), CPI (1.91), and CMI (369.71), significantly exceeding others (p < 0.05), with LI, CPI and CMI increases of 4.30–10.23%, 17.90–42.54%, and 24.97–57.07%, respectively. But the SI was also significantly decreased by 19.05–26.09%.
3.4. SOC Chemical Composition
The organic substitution treatments altered the relative proportions of the SOC functional groups (Figure 3; Table 3). O-alkyl C had the highest relative proportion, ranging from 31.07% to 35.50%, followed by alkyl C (25.87–26.72%), aromatic C (22.48–25.17), and carbonyl C (16.14–17.03%). The data are shown in Table 3. Compared with the sole chemical fertilizer treatment, the SN treatment showed the greatest increase in the relative proportion of O-alkyl C (14.26%), and the largest decreases in alkyl C (3.18%), aromatic C (10.69%), and carbonyl C (5.23%). The MSN treatment exhibited similar trends. This indicates that straw can provide a higher relative proportion of easily degradable C (e.g., O-alkyl C) to the soil, while reducing the relative proportion of recalcitrant C (e.g., aromatic C), thereby altering SOC stability.
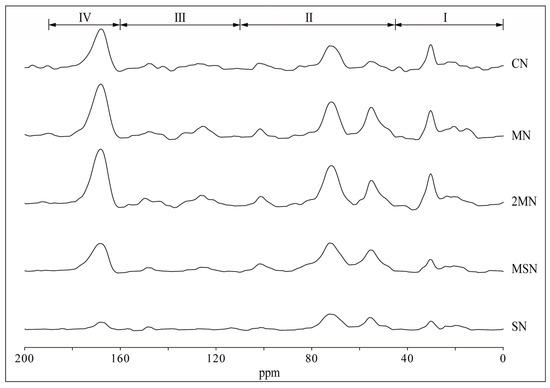
Figure 3.
13C-NMR spectra of soils under different fertilization treatments. I, alkyl C zone; II, O-alkyl C zone; III, aromatic C zone; IV, carbonyl C zone.

Table 3.
Effects of different fertilization treatments on SOC functional groups and the SOC quality index in the open fields used for the vegetables.
Compared with the CN treatment, the MN, 2MN, MSN, and SN treatments increased the soil O-alkyl C/alkyl C ratio by 0.59%, 1.29%, 16.15%, and 18.01%, respectively (Table 3). The hydrophobicity index (HI) and the aromaticity index (AI) values decreased in the order of CN > MN > 2MN > MSN > SN. With increasing organic fertilizer application, the OA/A ratio also increased, while the HI and the AI showed the opposite trend. Compared with replacing chemical fertilizer with organic fertilizer alone, the MSN and SN treatments increased the O-alkyl C/alkyl C ratio and decreased the HI and the AI values.
3.5. Correlation Analysis and PLS-PM Analysis
Correlations between SOC, different labile C fractions, the CMI, and yield care shown in Table 4. The CMI was significantly related to SOC, POC, DOC, MBC, and ROC; the correlations were stronger than those between SOC and POC, DOC, MBC, and ROC. Thus, the total active C component was closely related to but also different from SOC. The SOC, DOC, MBC, ROC, the CMI and the cabbage yield of 2022 were positively correlated. In addition, the SI was significantly and negatively correlated with all factors except for yield.

Table 4.
Pearson correlations between SOC, soil labile organic C fractions, CMI, and yield.
To better explore the complex interrelationships of organic substitution fertilization, labile C fractions, SOC, vegetable yields, and the SI, we carried out PLS-PM (Figure 4). Manure (standardized path coefficient, b = 0.48, p < 0.001) and straw (b = 1.02, p < 0.001) application significantly and positively influenced POC (with a loading value of 0.95), MBC (0.99), DOC (0.97), and ROC (0.93) contents. Furthermore, the increasing labile organic C fraction contents induced by organic amendment application had positive effects on increasing vegetable yields (b = 0.58, p < 0.05) and a negative effect on the SI value (b = −0.99, p < 0.05). SOC content, which was significantly and positively affected by manure (b = 0.82, p < 0.001) and straw (b = 1.00, p < 0.01) application, played the prominent role in directly shaping vegetable yields (b = 0.48, p < 0.05), but we did not observe the SI.
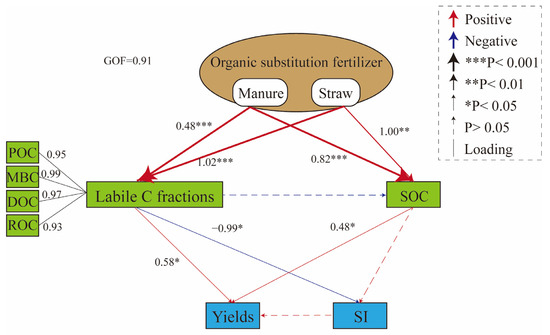
Figure 4.
Partial least squares path model showing the relationship among fertilization, labile organic C fractions, SOC stability indicators, SOC, vegetable yields, and the CMI. GOF, goodness-of-fit, was calculated to assess the model. The numbers near the red and blue arrows are the standardized path coefficients, which were calculated after 1000 bootstraps. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001. SOC, soil organic carbon; POC, particulate organic carbon; MBC, microbial biomass carbon; DOC, dissolved organic carbon; ROC, readily oxidizable carbon; SI, Soil Carbon Stability Index.
4. Discussion
4.1. Vegetable Yield Response to Different Fertilization Treatments over Time
The productivity of crops is significantly influenced by the soil quality, thus well-managed soil can support sustainable production and improve crop yields [16]. Previous studies have demonstrated that the long-term application of fertilizers and organic matter can increase crop yields [42,43,44]. Our results showed that substituting 50% of chemical N with a manure plus straw regime significantly increased spring cabbage (10.53%) and autumn Chinese cabbage yields (15.45%) compared with sole chemical fertilizer application (Figure 1). This is consistent with the results of Zhang et al. [45], who reported increased yields in greenhouse vegetables with long-term organic substitution. This may be because the nutrients fixed in organic fertilizer and straw are slowly released throughout the crop growing season, reducing nutrient loss compared with mineral fertilizer application. Their combined input provides ample nutrients for vegetables, improves soil quality, and promotes yield enhancement [43,44].
The SOC, DOC, MBC, and ROC were significantly and positively correlated with the cabbage yield of 2022 (Table 4 and Figure 4), which indicated that long-term organic substitution regimes could increase crop productivity by improving the SOC content. This suggests that the active C pools improve the crop yield possibly by maintaining a better soil quality. Zhu et al. [16] and Ma et al. [46] also reported positive effects on the crop yield and soil productivity after organic materials’ application, which were attributed mainly to the improved soil physical, chemical, and biological properties. Additionally, the SYI was employed to assess the impact of agricultural practices on crop yield sustainability [39]. A lower standard deviation and higher SYI value indicate greater yield stability under the fertilization regime [47]. Here, substituting 50% of chemical N with manure plus straw yielded the highest SYI value (Figure 1), suggesting that this treatment not only increases the yields of spring cabbage and autumn Chinese cabbage but also ensures the sustainability of field vegetable production.
4.2. Response of SOC Fraction Content to Different Fertilization Treatments over Time
Long-term substitution of chemical fertilizers with manure/straw is an important measure for enhancing SOC content. The carbonaceous materials within manure and straw directly influence the content of SOC and its composition through their transformation and distribution in the soil [48]. This study found that compared with sole chemical fertilizer application, all manure/straw substitution treatments significantly increased SOC, POC, DOC, MBC and ROC contents in the soil (Figure 2A–E), which is consistent with previous research [12,18,49]. This increase was attributed to the long-term input of exogenous organic C into the soil through organic fertilizer/straw, which directly or indirectly boosted SOC and its fractions [7]. In this study, the soil labile organic C fractions (POC, DOC, MBC, and ROC) were significantly and positively correlated with the SOC (Table 4). Such correlations suggested that the SOC was a crucial factor influencing the labile C fractions [12]. This is likely because organic materials provide large labile organic matter inputs, and are C sources for microbial activity that converts organic C into labile organic C [50]. Likewise, the depletion in the labile C pools could also provide an early indication of decreased SOC [4]. POC, MBC, DOC, and SOC were positively associated, with similar results reported by Xu et al. [51]. Additionally, under the same substitution rate, straw application resulted in a higher amount of SOC content in soil compared with that under organic fertilizer application (Figure 2A) owing to the higher C input from straw under equivalent N input conditions (Table 1), higher C/N, and slower microbial decomposition [52].
The results of this study showed that the soil labile C fractions of all straw application regimes (MSN and SN) were higher than those of the manure substitution regimes alone (MN and 2MN) (Figure 2B–E), which is consistent with the findings of Jin et al. [53]. This can be attributed to (1) labile organic C fractions primarily originating from easily decomposable plant residues, root exudates, soil microbial residues, and metabolites [54]; and (2) the higher soil C/N of straw compared with that of manure (Table 1), which, upon incorporation into the soil, rapidly releases large amounts of C and induces dissolved organic matter (DOM) release [52]. However, Zhang et al. [18] found opposing results in maize monocropping on black soil, indicating differences due to soil type, organic fertilizer type, C input level, and crop type.
4.3. SOC Stability in Response to Different Fertilization Treatments over Time
The soil lability index (LI), stability index (SI), OA/A, hydrophobicity index (HI), and aromaticity index (AI) were used to comprehensively evaluate SOC stability under the different long-term fertilization treatments. Higher LI values indicate a higher content of an active organic C pool, attributed to the rapid decomposition and mineralization of organic C; conversely, lower values suggest less decomposition and accumulation of organic matter [55]. In this study, the LI under manure/straw substitution treatments was significantly higher than that under CN (Table 2), but the SI was the opposite and PLS-PM analysis indicated that the labile organic C fractions drove the decrease in the SI value (Table 4 and Figure 4). This is similar to the findings of Luan et al. [4], who observed substantial active C (CVL and CL) in long-term organic fertilizer and maize straw applications in greenhouse vegetable systems. Moreover, it is also corroborated by Liu et al. [24], who found that long-term chemical fertilizer application promotes the depletion of CVL, thereby enhancing SOC stability. Additionally, this study found that manure plus straw substitution for chemical fertilizer increased the LI in SOC (Table 2), which was attributed to (1) manure supplying nutrients that promote crop growth and increase crop biomass; and (2) straw enhancing microbial activity, stimulating the secretion of unstable C compounds by roots, and collectively increasing unstable C [4,24].
In this study, all organic substitution treatments increased the relative proportion of O-alkyl C (readily degradable C) in the soil and reduced the relative proportion of aromatic C (difficult-to-degrade C) (Table 3), which is similar to the findings of Zhang et al. [56]. The main reasons for this are likely that (1) exogenous organic materials contain a higher proportion of readily degradable C, leading to an increase in the readily degradable C fraction upon their input into the soil [57] and an increase in the relative proportion of O-alkyl C; that the (2) input of exogenous organic materials promotes an increase in root exudates, which contain a relatively higher proportion of O-alkyl C, increasing the relative proportion of readily degradable C [58]; and that (3) the addition of organic materials promotes the formation of soil aggregates, enhancing the physical protection of organic matter, which reduces its susceptibility to microbial decomposition and thereby increases the proportion of O-alkyl C [59]. The OA/A can be used to assess the humification degree of organic C, with a higher value indicating lower organic C stability [60], while the HI and the AI show the opposite trend [61]. In this study, compared with long-term sole chemical fertilizer application and sole organic fertilizer substitution for chemical fertilizer, long-term straw substitution for chemical fertilizer resulted in a relatively higher OA/A, and a lower HI and AI (Table 3), similar to the results of Yuan et al. [62] and Luan et al. [4]. This may be attributable to the stronger stimulation of soil organic matter by the addition of straw, which enhances microbial growth and activity, accelerates the decomposition of soil organic matter, further degrades more recalcitrant C, simplifies the molecular structure of organic C, and increases the proportion of unstable organic C components [62].
4.4. Response of C Pool Management Indices to Different Fertilization Treatments over Time
The CMI comprehensively considers variations in both total SOC and active organic C in soil, which is also a useful parameter to evaluate the capacity of management practices to improve soil quality [63]. Compared with sole chemical fertilizer application, manure/straw replacing chemical fertilizer can increase the soil CMI [24,64]. Liu et al. [24] also confirmed that the CMI of 0–20 cm of soil under no fertilizer or chemical fertilizer application decreased, indicating that the long-term absence of fertilizer or the application of inorganic fertilizer does not lead to organic C accumulation. The findings of this study (Table 2) are consistent with those of the aforementioned studies, showing an increased soil CMI with long-term organic substitution of chemical fertilizer, indicating a positive transformation of soil due to manure/straw. Furthermore, this study found that the soil CMI was highest with the combined application of manure plus straw substituting for chemical fertilizer (Table 2), similar to the findings of Zhu et al. [16] and He et al. [54]. This can be attributed to the increased C input and organic matter content from annual organic manure and straw, thereby enhancing the organic C LI and subsequently increasing CMI values [12]. Wang et al. [65] also showed that straw return treatments led to a higher rate of organic matter decomposition and nutrient cycling, which would accelerate the conversion of nutrients from being organic to being inorganic via mineralization. Additionally, the CMI was significantly correlated with labile organic C fractions and SOC (Table 4), as was previously reported by Zhu et al. [16] and Yuan et al. [50]. Therefore, the CMI may be a sensitive indicator of changes in soil quality due to the organic substitution of chemical fertilizers.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we found that long-term organic substitution of chemical fertilizer treatment had obvious impacts on open-field vegetable systems in many aspects such as vegetable yield, soil organic carbon and its active components, stability, and the relationship of these indicators. Different treatments had different effects. Overall, substituting 50% of chemical N with manure plus straw strongly enhanced SOC, POC, DOC, MBC, LFOC contents, the CMI value, and the average vegetable yield, but led to decreased SOC stability. Labile organic C fractions were highly correlated with SOC, the CMI, yield, and the SI, and had a direct impact on yield and SOC stability. These research results had important reference value for rational fertilization, improving soil quality, and ensuring the sustainable production of open-field vegetables. Future study would focus on how long-term manure/straw substitution regimes affected the microbiological mechanisms of SOC fraction changes in open-field vegetable systems.
Author Contributions
All the authors contributed to the study conception and design. Writing—original draft and writing—review and editing were performed by Y.W. and L.W. Data curation and original draft writing were performed by R.L. and H.W. Investigation was performed by G.W. and X.W. (Xinyue Wen). Formal analysis and writing—review and editing were performed by C.L. Writing—review and editing, supervision, funding acquisition, and project administration were performed by S.H. and X.W. (Xiubin Wang). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Financial support was provided by the China Agriculture Research System (CARS-23-B04), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32272816), the Agricultural Science and Technology Innovation Program (No. CAAS-ZDRW202201), and the S&T Program of Hebei (22326901D).
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available on request.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Editor and reviewers, during the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Lal, R. Digging deeper: A holistic perspective of factors affecting soil organic carbon sequestration in agroecosystems. Glob. Change Biol. 2018, 24, 3285–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, C.E.; Halvorson, A.D.; Delgado, J.A. Long-term N fertilization and conservation tillage practices conserve surface but not profile SOC stocks under semi-arid irrigated corn. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 171, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.; Hai, N.; Huang, B.; Deng, W. Effects of long-term fertilization and residue management on soil organic carbon changes in paddy soils of China: A meta-analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2015, 204, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X. Partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with organic amendments affects soil organic carbon composition and stability in a greenhouse vegetable production system. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 191, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, P.; Gabhane, V.; Kadu, P.; Kharche, V.; Jadhao, S.; Turkhede, A.; Gajjala, R.C. Long-term nutrient management effects on organic carbon fractions and carbon sequestration in Typic Haplusterts soils of Central India. Soil Use Manag. 2023, 40, e12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Gao, T.; Wu, S.; Wu, L.; Lai, X.; Xu, H.; Hu, H.; Ma, Y. Effects of Straw Returning and New Fertilizer Substitution on Rice Growth, Yield, and Soil Properties in the Chaohu Lake Region of China. Plants 2024, 13, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, X.; Shan, J.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, Z.; Ji, J.; Hou, H.; Xia, W.; Liu, Y. Effects of long-term manure substitution regimes on soil organic carbon composition in a red paddy soil of southern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2022, 221, 105395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.; Yang, N.; Lu, C.; Qin, X.; Siddique, K.H.M. Soil organic carbon, total nitrogen, available nutrients, and yield under different straw returning methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 214, 105171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhan, P.; Thomas, B.W.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, X.; Zhang, Y. Organic carbon and nitrogen accumulation in orchard soil with organic fertilization and cover crop management: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 852, 158402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Kongsurakan, P.; Sereenonchai, S.; Hatano, R. Soil Organic Carbon in Sandy Paddy Fields of Northeast Thailand: A Review. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jílková, V.; Jandová, K.; Cajthaml, T.; Devetter, M.; Kukla, J.; Starý, J.; Vacířová, A. Organic matter decomposition and carbon content in soil fractions as affected by a gradient of labile carbon input to a temperate forest soil. Biol. Fert. Soils 2020, 56, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Lin, Z.; Song, Z.; Cooper, J.M.; Zhao, B. Soil labile organic carbon fractions and soil organic carbon stocks as affected by long-term organic and mineral fertilization regimes in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2018, 175, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koković, N.; Saljnikov, E.; Eulenstein, F.; Čakmak, D.; Buntić, A.; Sikirić, B.; Ugrenović, V. Changes in Soil Labile Organic Matter as Affected by 50 Years of Fertilization with Increasing Amounts of Nitrogen. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz-Romero, V.; Lopez-Bellido, R.J.; Fernandez-Garcia, P.; Redondo, R.; Murillo, S.; Lopez-Bellido, L. Effects of tillage, crop rotation and N application rate on labile and recalcitrant soil carbon in a Mediterranean Vertisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 169, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zou, M.; Yin, Q.; Qiu, Y.; Qin, W. Effect of organic material addition on active soil organic carbon and microbial diversity: A meta-analysis. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 241, 106128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Hu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, J.; Tao, B.; Meng, Y. Short-term responses of soil organic carbon and carbon pool management index to different annual straw return rates in a rice–wheat cropping system. Catena 2015, 135, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P. Structure and function of the soil microbial community in a long-term fertilizer experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2003, 35, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yan, J.; Han, X.; Zou, W.; Chen, X.; Lu, X.; Feng, Y. Labile organic carbon fractions drive soil microbial communities after long-term fertilization. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 32, e01867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrunalini, K.; Chandra, M.S.; Naresh, R.K.; Gupta, S.K. Precision Agriculture Practices Improves Soil Aggregation, Aggregate Associated Organic Carbon Fractions and Nutrient Dynamics in Cereal-based Systems of North-West India: An Overview. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 40–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, N.C.; Chandra, M.S.; Vivek; Naresh, R.K.; Yadav, S. Soil Carbon Pools, Carbon and Nitrogen Storage Pattern in Soil Aggregate Fractions under Long-term Application of Organic and Synthetic Fertilizers in Rice-Wheat System: A Review. Curr. J. Appl. Sci. Technol. 2020, 39, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparna, K.; Pasha, M.A.; Rao, D.L.N.; Krishnaraj, P.U. Organic amendments as ecosystem engineers: Microbial, biochemical and genomic evidence of soil health improvement in a tropical arid zone field site. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.; Zhu, J.; Yang, J.; Guo, Y.; Meng, X.; Ren, S.; Du, J.; Wen, S.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J.; et al. Straw return plus zinc fertilization increased the accumulations and changed the chemical compositions of mineral-associated soil organic carbon. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2023, 357, 108699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapfumo, P.; Mtambanengwe, F.; Vanlauwe, B. Organic matter quality and management effects on enrichment of soil organic matter fractions in contrasting soils in Zimbabwe. Plant Soil 2007, 296, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, J.; Ai, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, Q.; Xue, S.; Liu, G. 16-Year fertilization changes the dynamics of soil oxidizable organic carbon fractions and the stability of soil organic carbon in soybean-corn agroecosystem. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 265, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, A.K.; Dwivedi, B.S.; Dey, A.; Meena, M.C.; Chakraborty, D. Temperature Sensitivity of Soil Organic Carbon as Affected by Crop Residue and Nutrient Management Options Under Conservation Agriculture. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4183–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd–Elrahman, S.H.; Saudy, H.S.; El–Fattah, D.A.A.; Hashem, F.A.E. Effect of Irrigation Water and Organic Fertilizer on Reducing Nitrate Accumulation and Boosting Lettuce Productivity. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2022, 22, 2144–2155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Dwivedi, G.K.; Tewari, S.; Paul, J.; Anand, R.; Kumar, N.; Kumar, P.; Singh, H.; Kaushal, R. Carbon Mineralization and Inorganic Nitrogen Pools under Terminalia chebula Retz.-Based Agroforestry System in Himalayan Foothills, India. For. Sci. 2020, 66, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, D.K.; Pandey, P.C.; Nanda, G.; Gupta, S. Long-term effects of inorganic fertilizer and farmyard manure application on productivity, sustainability and profitability of rice-wheat system in Mollisols. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 65, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Krause, H.-M.; Fliessbach, A.; Mäder, P.; Steffens, M. Fertilizer quality and labile soil organic matter fractions are vital for organic carbon sequestration in temperate arable soils within a long-term trial in Switzerland. Geoderma 2022, 426, 116080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubar, K.A.; Huang, L.; Lu, J.; Li, X.; Xue, B.; Yin, Z. Long-term tillage and straw returning effects on organic C fractions and chemical composition of SOC in rice-rape cropping system. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 2018, 65, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Wesenbeeck, C.; Keyzer, M.A.; van Veen, W.C.M.; Qiu, H. Can China’s overuse of fertilizer be reduced without threatening food security and farm incomes? Agric. Syst. 2021, 190, 103093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Shi, L.; Fu, Q.; Chen, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, Q. Influence mechanisms of long-term fertilizations on the mineralization of organic matter in Ultisol. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 201, 104594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Peng, X.; Huang, Q.; Zhang, W. Soil aggregation and organic carbon fractions affected by long-term fertilization in a red soil of subtropical China. Geoderma 2010, 154, 364–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Zhu, L.; Lv, Y.; Zhu, K.; Liu, X.; Zhao, R. Response of organic carbon fractions and microbial community composition of soil aggregates to long-term fertilizations in an intensive greenhouse system. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blagodatskaya, E.; Yuyukina, T.; Blagodatsky, S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Turnover of soil organic matter and of microbial biomass under C3-C4 vegetation change: Consideration of 13C fractionation and preferential substrate utilization. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, D.L.; Willett, V.B. Experimental evaluation of methods to quantify dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and dissolved organic carbon (DOC) in soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2006, 38, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.Y.; Bowman, A.; Oates, A. Oxidizible organic carbon fractions and soil quality changes in an Oxic Paleustalf under different pasture leys. Soil Sci. 2001, 166, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, A.; Hu, X.; Shah, S.A.A.; Abrar, M.M.; Maitlo, A.A.; Kubar, K.A.; Saeed, Q.; Kamran, M.; Naveed, M.; Boren, W.; et al. Long-term fertilization alters chemical composition and stability of aggregate-associated organic carbon in a Chinese red soil: Evidence from aggregate fractionation, C mineralization, and 13C NMR analyses. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 2483–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Hu, C.; Chen, Y.; Qiao, Y.; Liu, D.; Fan, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, Z. Crop yield stability and sustainability in a rice-wheat cropping system based on 34-year field experiment. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 113, 125965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Yuan, S.; Gao, W.; Tang, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, H.; Huang, S. 10-Year fertilization alters soil C dynamics as indicated by amino sugar differentiation and oxidizable organic C pools in a greenhouse vegetable field of Tianjin, China. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2022, 169, 104226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Qu, Q.; Lu, B.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Xue, S. Variation in soil organic carbon stability and driving factors after vegetation restoration in different vegetation zones on the Loess Plateau, China. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 204, 104727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, K.; Wang, X.; Ai, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, J. Carbon sequestration and yields with long-term use of inorganic fertilizers and organic manure in a six-crop rotation system. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Evgenia, B.; Zhang, Y.; Wan, Y.; Hu, Q.-j.; Zhang, C.-M.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.-q.; Shi, X.-j. Substituting nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer with optimal amount of crop straw improves rice grain yield, nutrient use efficiency and soil carbon sequestration. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3345–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.; Zhang, W.; Xu, M.; Wang, B.; Wen, S.; Shah, S.A.A. Soil fertility and crop yield after manure addition to acidic soils in South China. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2018, 111, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-J.; Gao, W.; Luan, H.-A.; Tang, J.-W.; Li, R.-N.; Li, M.-Y.; Zhang, H.-Z.; Huang, S.-W. Effects of a decade of organic fertilizer substitution on vegetable yield and soil phosphorus pools, phosphatase activities, and the microbial community in a greenhouse vegetable production system. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 2119–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Woolf, D.; Fan, M.; Qiao, L.; Li, R.; Lehmann, J. Global crop production increase by soil organic carbon. Nat. Geosci. 2023, 16, 1159–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuti, M.D.; Pal, R.S.; Mahanta, D.; Pandey, B.M.; Bisht, J.K. Soil Chemical and Biological Activities under Vegetable Intensive Colocasia-based Cropping System in Indian Sub-Himalayas. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2020, 51, 948–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Wu, Q. Effects of Substituting Manure for Fertilizer on Aggregation and Aggregate Associated Carbon and Nitrogen in a Vertisol. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Gall, A.R.; Saeed, M.F.; Li, S.; Filley, T.; Wang, J. Plastic film mulching and nitrogen fertilization enhance the conversion of newly-added maize straw to water-soluble organic carbon. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 197, 104527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, G.; Huan, W.; Song, H.; Lu, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Zhou, J. Effects of straw incorporation and potassium fertilizer on crop yields, soil organic carbon, and active carbon in the rice–wheat system. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Lou, Y.; Sun, X.; Wang, W.; Baniyamuddin, M.; Zhao, K. Soil organic carbon active fractions as early indicators for total carbon change under straw incorporation. Biol. Fert. Soils 2011, 47, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, Y.; Cong, P.; Wang, J.; Guo, W.; Pang, H.; Zhang, L. Depth of straw incorporation significantly alters crop yield, soil organic carbon and total nitrogen in the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 205, 104772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Bol, R.; An, T.; Zheng, L.; Li, S.; Pei, J.; Wang, J. Long-term fertilization and plastic film mulching modify temporal incorporation of 13C/15N-labelled particulate organic matter. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2023, 74, e13386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Peng, M.; Lu, W.; Ru, S.; Hou, Z.; Li, J. Organic fertilizer substitution promotes soil organic carbon sequestration by regulating permanganate oxidizable carbon fractions transformation in oasis wheat fields. Catena 2023, 221, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demisie, W.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, M. Effect of biochar on carbon fractions and enzyme activity of red soil. Catena 2014, 121, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Gregorich, E.G.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Liang, A.; Fan, R.; Sun, B. No-tillage with continuous maize cropping enhances soil aggregation and organic carbon storage in Northeast China. Geoderma 2018, 330, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Zhang, J.; Chi, F.; Zhou, B.; Wei, D.; Kuang, E.; Jiang, Y.; Mi, G.; Chen, Y.p. Response of the chemical structure of soil organic carbon to modes of maize straw return. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumann, K.; Marschner, P.; Kuhn, T.K.; Smernik, R.J.; Baldock, J.A. Microbial community structure and residue chemistry during decomposition of shoots and roots of young and mature wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) in sand. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2011, 62, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; He, P. Both carbon sequestration and yield are related to particulate organic carbon stability affected by organic amendment origins in mollisol. J. Soils Sediments 2021, 21, 3044–3056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Masiliūnas, D. Organic amendment increases soil respiration in a greenhouse vegetable production system through decreasing soil organic carbon recalcitrance and increasing carbon-degrading microbial activity. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 2877–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; Di, H. Effects of long-term mowing on the fractions and chemical composition of soil organic matter in a semiarid grassland. Biogeosciences 2017, 14, 2685–2696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, H.; Chen, G.; Wang, S. Seven years of biochar amendment has a negligible effect on soil available P and a progressive effect on organic C in paddy soils. Biochar 2022, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, S.; Zhu, L.; Liu, J.; Bu, L.; Yue, S.; Shen, Y.; Li, S. Sensitivity of soil organic carbon stocks and fractions to soil surface mulching in semiarid farmland. Eur. J. Soil Biol. 2015, 67, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary, S.; Dheri, G.S.; Brar, B.S. Long-term effects of NPK fertilizers and organic manures on carbon stabilization and management index under rice-wheat cropping system. Soil Tillage Res. 2017, 166, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Lai, D.Y.F.; Wang, C.; Pan, T.; Zeng, C. Effects of rice straw incorporation on active soil organic carbon pools in a subtropical paddy field. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 152, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).