A Study on the Preparation of Multifunctional Bacillus spp. Composite Inoculants and Their Ability to Promote Watermelon Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Medium
2.2. Strains
2.3. Screening of Functional Strains
2.4. Strain Identification
2.5. Test of Antagonism Between Functional Strains
2.6. Measurement of Growth Curves
2.7. Preparation of Liquid Inoculants
2.7.1. Preparation of Seed Liquid
2.7.2. Single-Factor Optimization of Liquid Inoculant
2.7.3. Plackett–Burman Design
2.7.4. Steepest Climb Test
2.7.5. Box–Behnken Response Surface Analysis
2.8. Screening of Substrate and Preparation of Solid Inoculant
2.9. Experiment on Growth-Promoting Effects of Inoculants in Watermelon
2.9.1. Pot Experiment Design
2.9.2. Determination Index and Method
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Functional Strain Screening
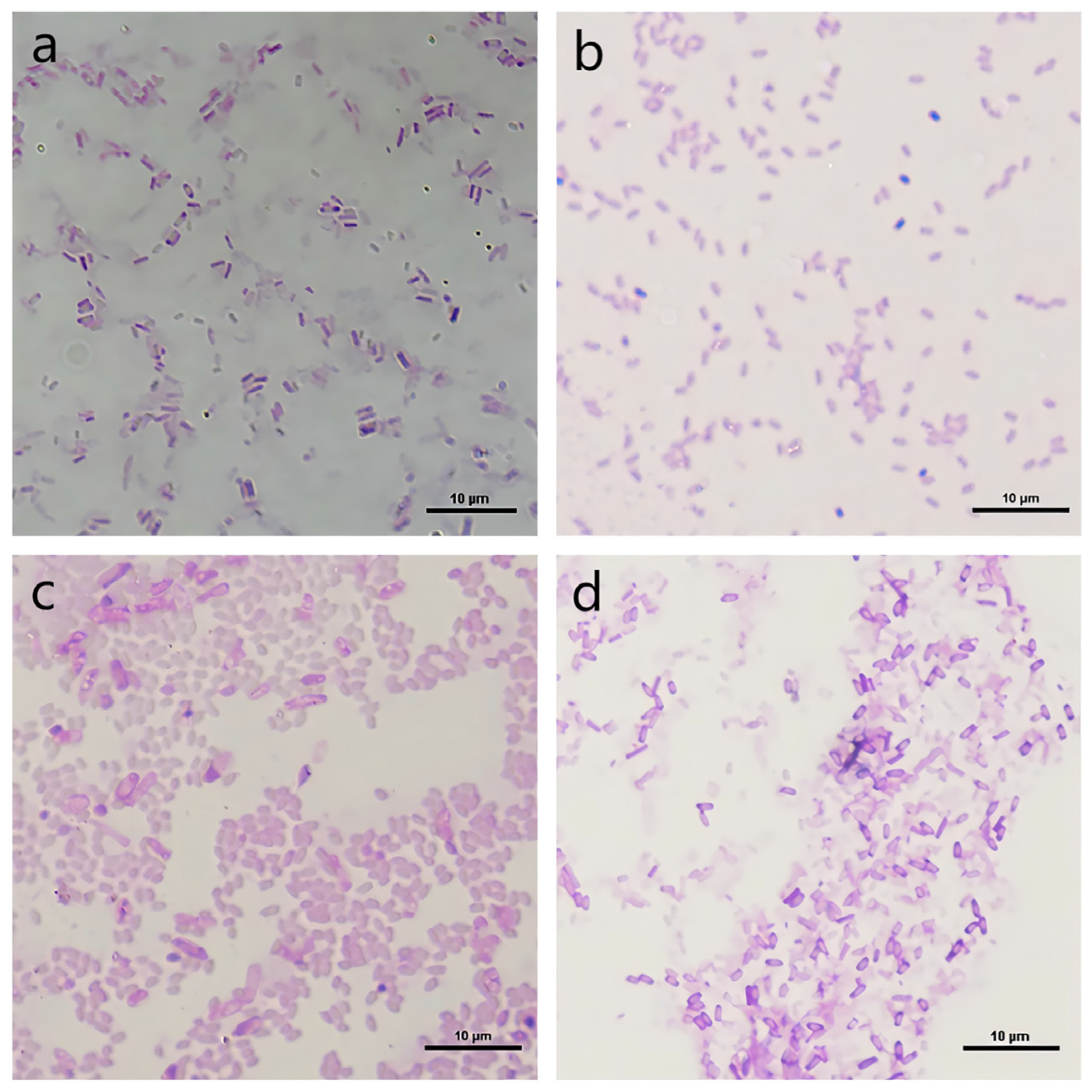
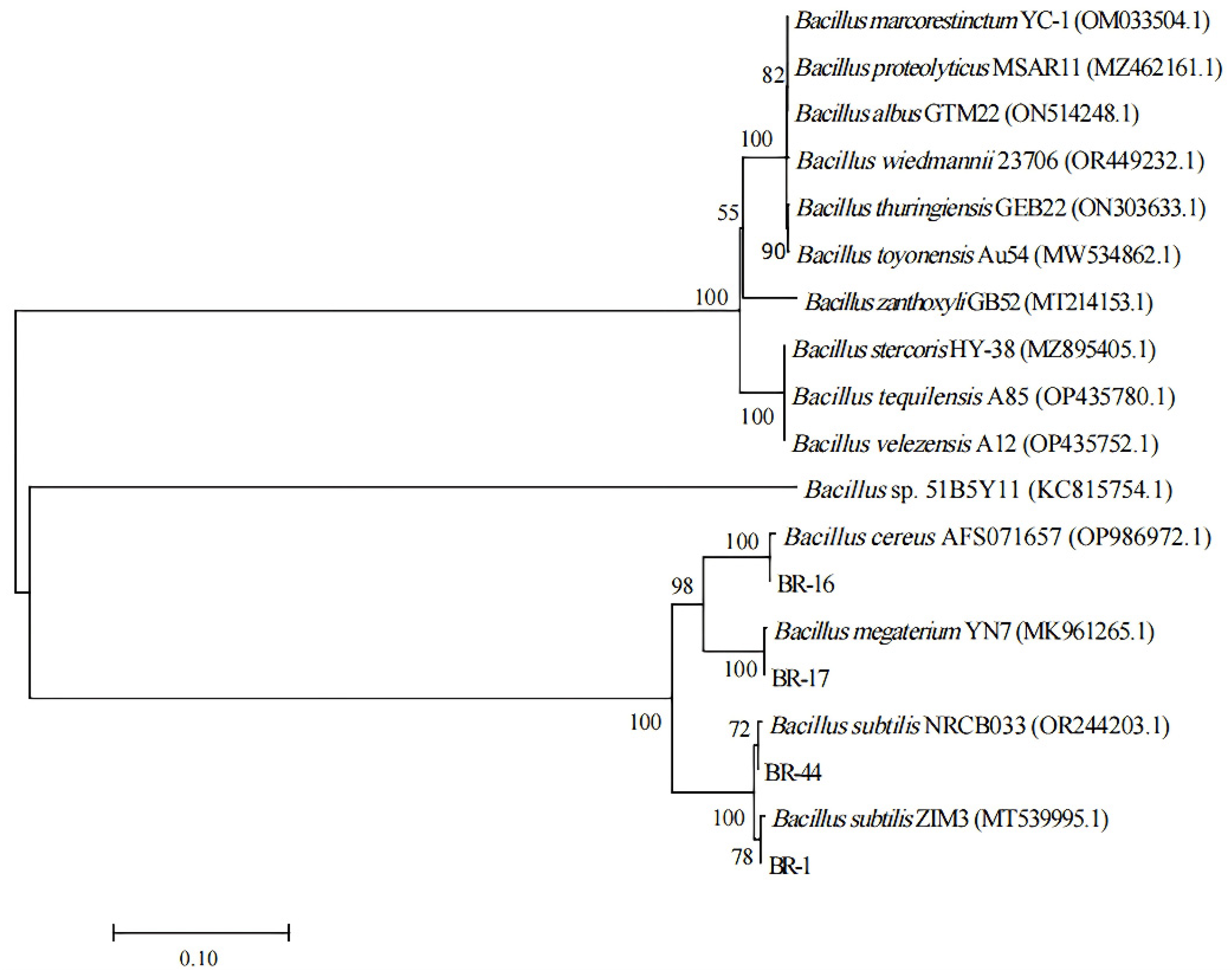
3.2. Classification and Identification of Functional Strains
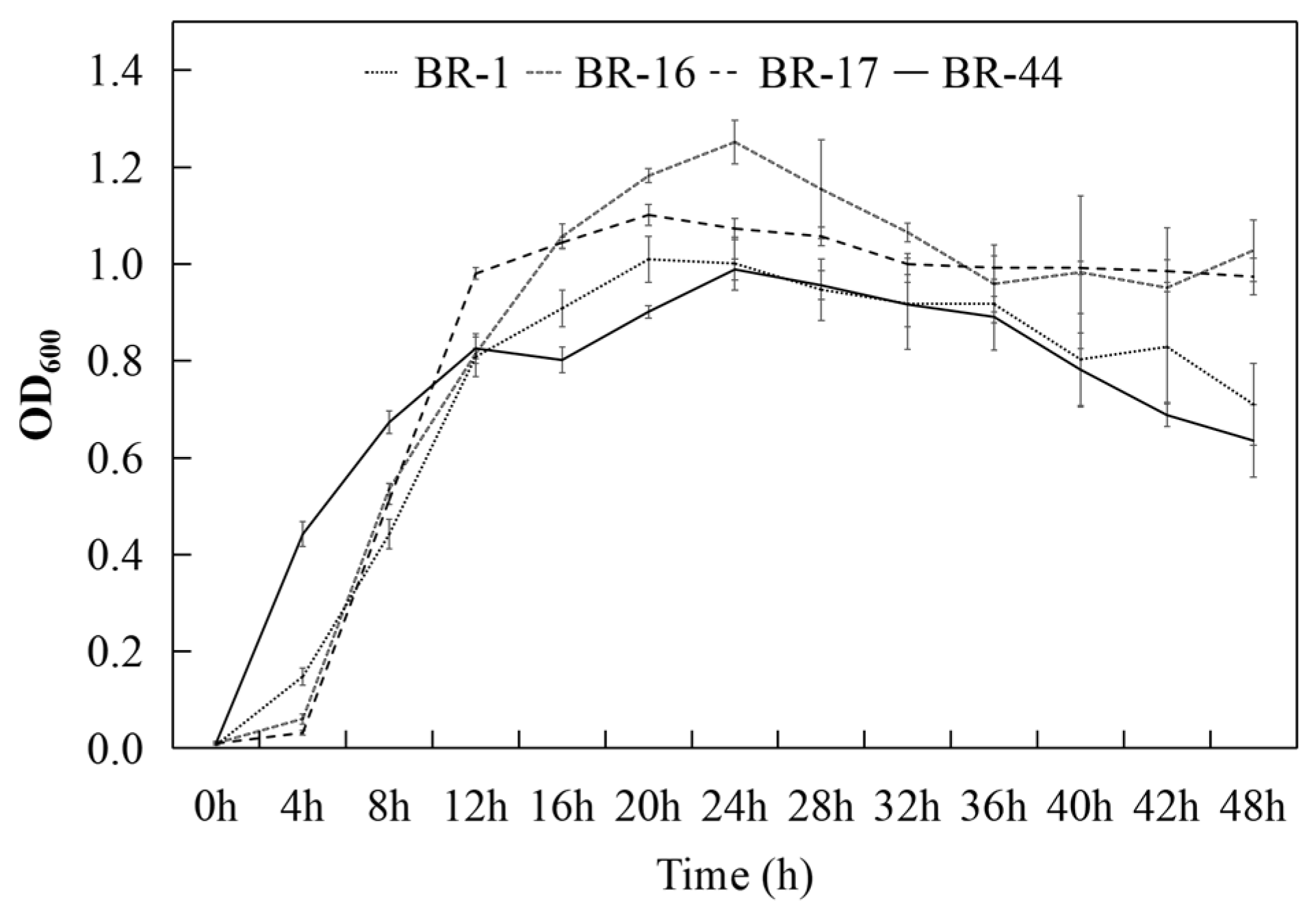
3.3. Antagonistic Reactions Between Strains and Their Growth Time Courses
3.4. Single-Factor Optimization of Liquid Fermentation Process
3.5. Plackett–Burman Analysis
3.6. Steepest Climb Test
3.7. Box–Behnken Response Surface Methodology
3.8. Effects of Different Substrates on Living Bacterial Counts of BR Inoculants
3.9. Effects of Inoculants on Growth Indicators of Watermelon Plants
3.10. Effects of Inoculants on Watermelon Yield and Fruit Quality
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dal Cortivo, C.; Barion, G.; Visioli, G.; Mattarozzi, M.; Mosca, G.; Vamerali, T. Increased root growth and nitrogen accumulation in common wheat following PGPR inoculation: Assessment of plant-microbe interactions by ESEM. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2017, 247, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, R.M.; Heredia Abarca, G.; Carmen Perea Rojas, Y.; Cruz Elizondo, Y.; García Guzman, K.Y. Selection and characterization of phosphate-solubilizing fungi and their effects on coffee plantations. Plants 2023, 12, 3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, A.M.; Awad, M.Y.; Hegab, S.A.; Gawad, A.M.A.E.; Eissa, M.A. Effect of potassium solubilizing bacteria (Bacillus cereus) on growth and yield of potato. J. Plant Nutr. 2021, 44, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Kim, A.L.; Hong, Y.K.; Shin, J.H.; Joo, S.H. A highly efficient auxin-producing bacterial strain and its effect on plant growth. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, Z.; Nazir, A.; Asghar, H.N.; Zahir, Z.A. Interactive effect of siderophore-producing bacteria and l-tryptophan on physiology, tuber characteristics, yield, and iron concentration of potato. Potato Res. 2022, 65, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, K.; Ma, W.; Zheng, L.; Xu, H.; Cui, B.; Liu, R.; Yang, Y.; et al. Functional assembly of root-associated microbial consortia improves nutrient efficiency and yield in soybean. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2021, 63, 1021–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walia, A.; Mehta, P.; Chauhan, A.; Shirkot, C.K. Effect of Bacillus subtilis strain CKT1 as inoculum on growth of tomato seedlings under net house conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. India Sect. B Biol. Sci. 2014, 84, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthuraja, R.; Muthukumar, T. Isolation and characterization of potassium solubilizing Aspergillus species isolated from saxum habitats and their effect on maize growth in different soil types. Geomicrobiol. J. 2021, 38, 672–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posada-Uribe, L.F.; Romero-Tabarez, M.; Villegas-Escobar, V. Effect of medium components and culture conditions in Bacillus subtilis EA-CB0575 spore production. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 38, 1879–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klausmann, P.; Hennemann, K.; Hoffmann, M.; Treinen, C.; Aschern, M.; Lilge, L.; Heravi, K.M.; Henkel, M.; Hausmann, R. Bacillus subtilis high cell density fermentation using a sporulation-deficient strain for the production of surfactin. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 4141–4151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chettri, D.; Verma, A.K. Statistical optimization of cellulase production from Bacillus sp. YE16 isolated from yak dung of the Sikkim Himalayas for its application in bioethanol production using pretreated sugarcane bagasse. Microbiol. Res. 2024, 281, 127623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhuo, Y.; Lu, J.; Lai, Q.; Zhang, Y. Bacillus cereus liquid fertilizer was produced from Agaricus bisporus industrial wastewater. J. Biotechnol. 2021, 327, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lebrazi, S.; Fadil, M.; Chraibi, M.; Fikri-Benbrahim, K. Screening and optimization of indole-3-acetic acid production by Rhizobium sp. strain using response surface methodology. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2020, 18, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Yan, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Bai, Z.; Yan, X.; Wang, N.; Liang, N.; Li, H. A microbial transformation using Bacillus subtilis B7-S to produce natural vanillin from ferulic acid. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slivinski, C.T.; Mallmann, E.; Araújo, J.M.; Mitchell, D.A.; Krieger, N. Production of surfactin by Bacillus pumilus UFPEDA 448 in solid-state fermentation using a medium based on okara with sugarcane bagasse as a bulking agent. Process Biochem. 2012, 47, 1848–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berikashvili, V.; Sokhadze, K.; Kachlishvili, E.; Elisashvili, V.; Chikindas, M.L. Bacillus amyloliquefaciens spore production under solid-state fermentation of lignocellulosic residues. Probiotics Antimicrob. Proteins 2018, 10, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campagnol, R.; Mello, S.D.C.; Barbosa, J.C. Vertical growth of mini watermelon according to the training height and plant density. Hortic. Bras. 2012, 30, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbou, M.; Chabbi, M.; Benicha, M. Assessment of pesticide use by determination of environmental indicators: Case study of watermelon from Loukkos (Northwest Morocco). Euro-Mediterr. J. Environ. Integr. 2023, 8, 463–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Piao, Y.; Zhang, F.; Hu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Nan, J. Promoting effects on watermelon and fermentation optimization of Plantibacter sp. WZW03. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 39, 970–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferchichi, N.; Toukabri, W.; Boularess, M.; Smaoui, A.; Mhamdi, R.; Trabelsi, D. Isolation, identification and plant growth promotion ability of endophytic bacteria associated with lupine root nodule grown in Tunisian soil. Arch. Microbiol. 2019, 201, 1333–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, D.; Pithwa, S.; Dhandhukia, P.; Thakker, J.N. Delineating Kocuria turfanensis 2M4 as a credible PGPR: A novel IAA-producing bacteria isolated from saline desert. J. Plant Interact. 2014, 9, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Hanif, A.; Farzand, A.; Sheikh, T.M.M.; Khan, A.R.; Suleman, M.; Ayaz, M.; Gao, X. Genetic screening and expression analysis of psychrophilic Bacillus spp. reveal their potential to alleviate cold stress and modulate phytohormones in wheat. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, X.; Wang, J.; Cui, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, X. A feasible biochar derived from biogas residue and its application in the efficient adsorption of tetracycline from an aqueous solution. Environ. Res. 2022, 207, 112175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthurson, V. Closing the global energy and nutrient cycles through application of biogas residue to agricultural land–potential benefits and drawbacks. Energies 2009, 2, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, N.; Islam, M.; Alamgir, M.; Kibria, M.G. Growth response of Indian spinach to biogas plant residues. IOSR J. Pharm. Biol. Sci. 2014, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abubaker, J.; Risberg, K.; Pell, M. Biogas residues as fertilisers–Effects on wheat growth and soil microbial activities. Appl. Energy 2012, 99, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Luo, Y.; Teng, Y. Type and preparation of medium. In Microbiological Research Methodology for Soil and Environment; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2008; pp. 52–63. [Google Scholar]
- Suliasih; Widawati, S. Isolation of Indole Acetic Acid (IAA) producing Bacillus siamensis from peat and optimization of the culture conditions for maximum IAA production. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2020, 572, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, N.K.; Verma, M. Modified microplate method for rapid and efficient estimation of siderophore produced by bacteria. 3 Biotech 2017, 7, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 20287-2006; Microbial Inoculants in Agriculture. Standards Press of China: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Zhao, Y.; Mao, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, W.; Di, H.J.; Ma, L.; Liu, W.; Li, B. The application of Bacillus Megaterium alters soil microbial community composition, bioavailability of soil phosphorus and potassium, and cucumber growth in the plastic shed system of North China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 307, 107236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samaniego-Gámez, B.Y.; Garruña, R.; Tun-Suárez, J.M.; Kantun-Can, J.; Reyes-Ramírez, A.; Cervantes-Díaz, L. Bacillus spp. inoculation improves photosystem II efficiency and enhances photosynthesis in pepper plants. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2016, 76, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Fang, F.; Hu, J.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, A.; Gao, X.; Li, J. Synergistic effect of Bacillus subtilis and Paecilomyces lilacinus in alleviating soil degradation and improving watermelon yield. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1101975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denaya, S.; Yulianti, R.; Pambudi, A.; Effendi, Y. Novel microbial consortium formulation as plant growth promoting bacteria (PGPB) agent. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2021, 637, e012030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.H.; Vieira, R.H.; Macrae, A.; Sousa, O.V. Peptone preparation from fishing by-products. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2005, 85, 1235–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oren, A. Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katileviciute, A.; Plakys, G.; Budreviciute, A.; Onder, K.; Damiati, S.; Kodzius, R. A sight to wheat bran: High value-added products. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ram, H.; Malik, S.S.; Dhaliwal, S.S.; Kumar, B.; Singh, Y. Growth and productivity of wheat affected by phosphorus-solubilizing fungi and phosphorus levels. Plant Soil Environ. 2015, 61, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, J.; Shang, X.; Xue, L.; Ji, G.; Chang, S.; Niu, J.; Emaneghemi, B. Screening of siderophore-producing bacteria and their effects on promoting the growth of plants. Curr. Microbiol. 2022, 79, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Sang, T.; Tian, M.; Jahan, M.S.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Shu, S. Effects of Bacillus cereus on photosynthesis and antioxidant metabolism of cucumber seedlings under salt stress. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Variable | Number | Level | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low (−1) | High (+1) | ||
| Peptone (g/L) | A | 15 | 20 |
| Sucrose (g/L) | B | 10 | 15 |
| KCl (g/L) | C | 2 | 4 |
| Initial pH | D | 7 | 8 |
| Bottled fluid volume (mL/250 mL) | E | 50 | 100 |
| Inoculum size (%) | F | 6 | 8 |
| Incubation temperature (°C) | G | 28 | 30 |
| Shaking speed (r/min) | H | 170 | 190 |
| Incubation time (h) | J | 20 | 24 |
| Variable | Level | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| −1 | 0 | 1 | |
| Bottled fluid volume (mL/250 mL) | 25 | 50 | 75 |
| Incubation temperature (°C) | 30 | 31 | 32 |
| Shaking speed (r/min) | 190 | 200 | 210 |
| Testing Order Number | Inoculum Size (mL/250 mL) | Temperature (°C) | Shaking Speed (r/min) | Bacterial Biomass (OD600) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 125 | 28 | 170 | 1.724 |
| 2 | 100 | 29 | 180 | 1.773 |
| 3 | 75 | 30 | 190 | 1.819 |
| 4 | 50 | 31 | 200 | 1.863 |
| 5 | 25 | 32 | 210 | 1.827 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, L.; Liu, K.; Lan, F.; Xiao, W.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Wen, Y.; Wang, X.; Shi, X. A Study on the Preparation of Multifunctional Bacillus spp. Composite Inoculants and Their Ability to Promote Watermelon Growth. Agronomy 2025, 15, 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020350
Li L, Liu K, Lan F, Xiao W, Wang B, Zhou J, Zhang J, Wen Y, Wang X, Shi X. A Study on the Preparation of Multifunctional Bacillus spp. Composite Inoculants and Their Ability to Promote Watermelon Growth. Agronomy. 2025; 15(2):350. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020350
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Lin, Ke Liu, Fafa Lan, Wentao Xiao, Baoping Wang, Jing Zhou, Jitao Zhang, Yunjie Wen, Xiuhong Wang, and Xiangyuan Shi. 2025. "A Study on the Preparation of Multifunctional Bacillus spp. Composite Inoculants and Their Ability to Promote Watermelon Growth" Agronomy 15, no. 2: 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020350
APA StyleLi, L., Liu, K., Lan, F., Xiao, W., Wang, B., Zhou, J., Zhang, J., Wen, Y., Wang, X., & Shi, X. (2025). A Study on the Preparation of Multifunctional Bacillus spp. Composite Inoculants and Their Ability to Promote Watermelon Growth. Agronomy, 15(2), 350. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15020350






