Soil Nutrient Variability Analysis of Typical Planting Patterns in Agricultural Reclamation Areas of the Southern Dianchi Lake Basin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site Description
2.2. Experimental Design and Sampling Methods
2.3. Test Items and Analytical Methods
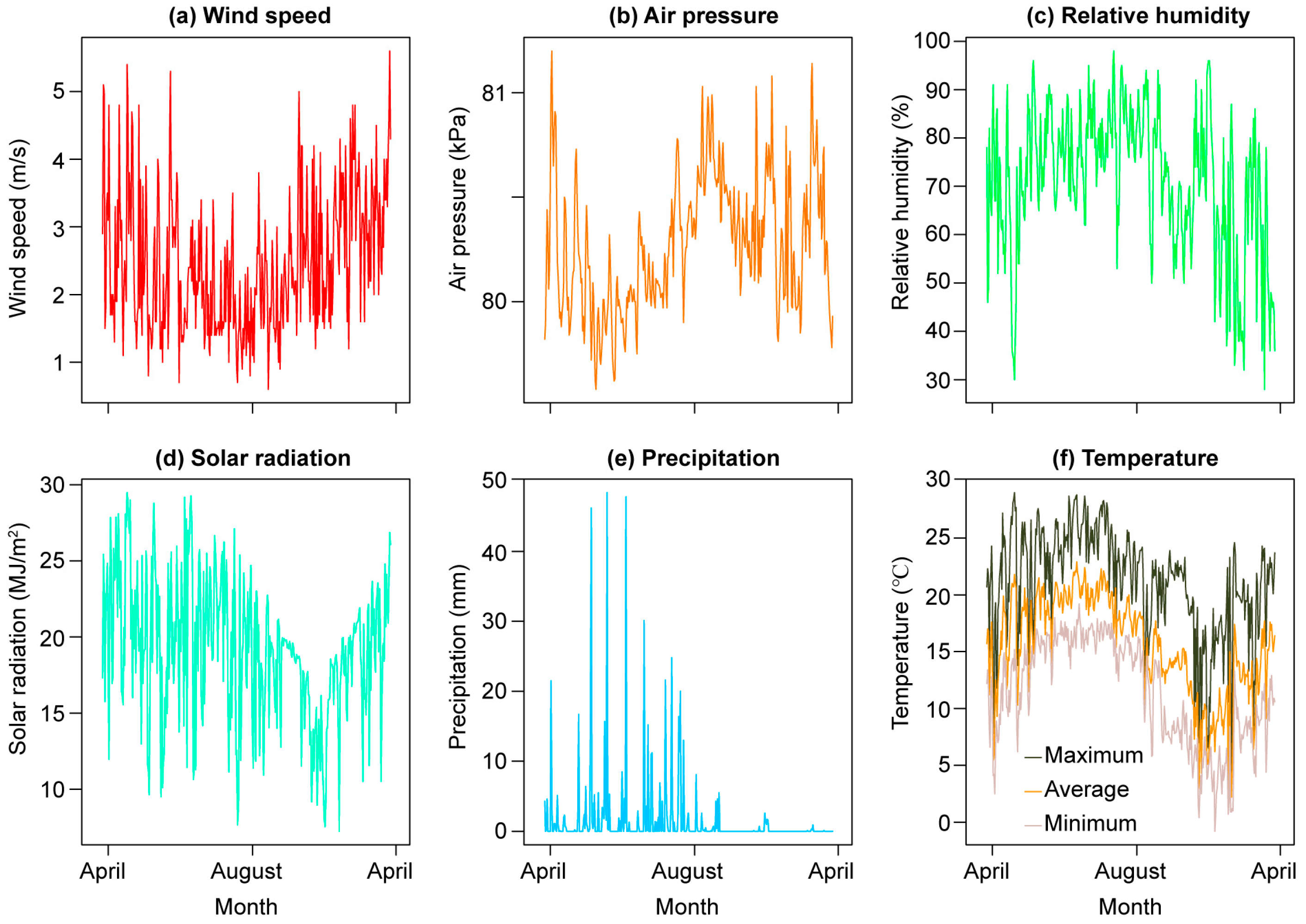
2.4. Environmental Factor Monitoring
2.5. Data Processing and Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Soil Physical Properties Under Different Cultivation Methods
3.2. Soil Nutrient Content
3.3. Soil Physicochemical Properties
3.4. Correlation Analysis of Soil Nutrients and Physicochemical Properties
4. Discussion
4.1. Soil Physical Structure Characteristics
4.2. Vertical Distribution Patterns of Soil Nutrients
4.3. Changes in Soil Chemical Environment
4.4. Reconstruction of Nutrient Cycling Relationships
4.5. Environmental Impact Assessment
4.6. Research Limitations and Application Value
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhao, J.K.; Lv, X.F.; Cai, Y.X. Research Review on the Development of High-Standard Facility Agriculture. Mod. Agric. Res. 2023, 29, 1–7. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. Research on the Development of Intelligent Control Technology for Greenhouse Facilities in Facility Agriculture. Agric. Prod. Process. 2024, 90–92. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Feng, Y.; Sun, Y. Source, Occurrence and Risks of Twenty Antibiotics in Vegetables and Soils from Facility Agriculture through Fixed-Point Monitoring and Numerical Simulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cai, X.Y. Problems Existing in Soil Ecology of Facility Agriculture in China and Their Solutions. Agric. Disaster Res. 2023, 13, 302–304. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sun, C.H.; Guo, L.L.; Chen, J.; Chen, L.Y. Soil Quality Degradation and Bioremediation in Facility Agriculture. Soil Water Conserv. Appl. Technol. 2024, 40–42. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hao, G.Z.; Song, F.Z.; Xu, L.; Zhu, G.Y. Estimation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Load in the Upper Reaches of Qingshui River Based on Output Coefficient Model. Sci. Technol. Eng. 2020, 20, 13919–13927. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tan, H.Y.; Ren, J.Q.; Zhang, Z.R.; Liang, Z.M. Fertilizer Reduction and Non-Point Source Pollution Control in Dianchi Basin. Yunnan Agric. 2022, 63–66. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Jiang, H.; Huang, X.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, J.; Wang, B.; Wu, W. Evaluating Nationwide Non-Point Source Pollution of Crop Farming and Related Environmental Risk in China. Processes 2023, 11, 2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, T.; Mao, Y.; Wang, F.; Yu, J.; Zhu, C. Current Situation of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution and Its Control. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2023, 234, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, W.N.; Wang, H.Y.; Meng, H.; Ning, Y.H.; Zhao, H.; Cui, X. Non-Point Source Pollution of Sunxi River and Its Relationship with Soil Organic Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Riparian Zone. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2024, 31, 117–125. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.X.; Nie, Y.X.; Zhang, Q.H.; Tong, S.C.; Zhao, J.; Liang, D.F.; Chen, W. Research Progress on Migration Process and Model of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Watershed. J. Environ. Eng. Technol. 2023, 13, 1364–1372. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xie, X.L.; Qian, F.; Zhao, J.; Song, Y.H. Scientific Problems and Technology Development Needs for Prevention and Control of Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution in Watersheds. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2023, 43, 152–157. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raklami, A.; Tahiri, A.; Bechtaoui, N.; Abdelhay, E.G.; Pajuelo, E.; Baslam, M.; Meddich, A.; Oufdou, K. Restoring the Plant Productivity of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil Using Phosphate Sludge, Marble Waste, and Beneficial Microorganisms. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 99, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Li, G.; Liu, Y. Regime Shift in Lake Dianchi (China) during the Last 50 Years. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2018, 36, 1075–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Jian, Y.; Zhou, F. Decline in Nitrogen Concentrations of Eutrophic Lake Dianchi Associated with Policy Interventions during 2002–2018. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Janssen, A.B.G.; de Klein, J.J.M.; Kroeze, C.; Strokal, M.; Ma, L.; Zheng, Y. Modeling Nutrients in Lake Dianchi (China) and Its Watershed. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.; Yang, C.H. Prospects of Flower Industry in Jinning District. Yunnan Agric. 2017, 69–71. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.F. SWOT Analysis of Flower Industry Development in Jinning District. Trop. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2022, 45, 47–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Han, Z.C. Analysis of Environmental Geological Problems of Kunyang Phosphate Mine in Yunnan. Green Sci. Technol. 2021, 23, 196–198. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, A. Ecological Reconstruction of Abandoned Mining Area of Kunyang Phosphate Mine. For. Surv. Plan. 2009, 34, 139–141. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sai, L.X.; Li, H.T.; Ma, Y.H.; Li, P.; Li, Y.Q.; Li, Q.J. Analysis of the Role of Farmers’ Professional Cooperatives in Driving the Development of Small Farmers—Taking Flower Professional Cooperatives in Jinning District as an Example. Agric. Dev. Equip. 2023, 94–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.K.; Xia, F.X. Research on Industrial Layout and Reconstruction of Villages in Watersheds under Environmental Hard Constraints of Dianchi Lake—Based on Actual Investigation of Rural Revitalization Return Industry Planning in Kunyang Street, Jinning District. Yunnan Agric. 2022, 16–19. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Six, J.; Elliott, E.T.; Paustian, K. Soil Macroaggregate Turnover and Microaggregate Formation: A Mechanism for C Sequestration under No-Tillage Agriculture. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2000, 32, 2099–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Dai, W.; Fang, K.; Gao, H.; Sha, Z.; Cao, L. Nutrient Characterization in Soil Aggregate Fractions with Different Fertilizer Treatments in Greenhouse Vegetable Cultivation. Agriculture 2022, 12, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Shao, M.; Gale, W.J.; Zhang, X.; Li, L. Dynamics of Aggregate-Associated Organic Carbon Following Conversion of Forest to Cropland. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2013, 57, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whalen, J.K.; Chang, C. Macroaggregate Characteristics in Cultivated Soils after 25 Annual Manure Applications. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2002, 66, 1637–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kayssi, A.W.; Al-Karaghouli, A.A.; Hasson, A.M.; Beker, S.A. Influence of Soil Moisture Content on Soil Temperature and Heat Storage under Greenhouse Conditions. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 1990, 45, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Zhao, X.; Huang, Z. Correlative Analyses between Quantities of Microbial Populations and Soil Physicochemical Property under Different Accumulation of Soil Plastic Film. In Progress in Environmental Science and Engineering; Xu, Q.J., Ju, Y.H., Ge, H.H., Eds.; Trans Tech Publications Ltd.: Durnten-Zurich, Switzerland, 2013; Volume 610–613, Pts 1–4; pp. 3091–3095. [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulska, I.; Romaneckas, K.; Jaskulski, D.; Gałęzewski, L.; Breza-Boruta, B.; Dębska, B.; Lemanowicz, J. Soil Properties after Eight Years of the Use of Strip-Till One-Pass Technology. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wen, Y.; Yang, X. Understanding the Responses of Soil Bacterial Communities to Long-Term Fertilization Regimes Using DNA and RNA Sequencing. Agronomy 2021, 11, 2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Hao, M.; Shao, M.; Gale, W.J. Changes in Soil Properties and the Availability of Soil Micronutrients after 18 Years of Cropping and Fertilization. Soil Tillage Res. 2006, 91, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Shao, L.; Liu, P.; Zhao, B.; Gu, L.; Dong, S.; Bing, S.H.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Effect of Different Nitrogen and Irrigation Treatments on Yield and Nitrate Leaching of Summer Maize (Zea mays L.) under Lysimeter Conditions. Agric. Water Manag. 2014, 137, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Cui, Z.; Fan, M.; Vitousek, P.; Zhao, M.; Ma, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Yan, X.; Yang, J.; et al. Producing More Grain with Lower Environmental Costs. Nature 2014, 514, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.H.; Liu, X.J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.L.; Han, W.X.; Zhang, W.F.; Christie, P.; Goulding, K.W.T.; Vitousek, P.M.; Zhang, F.S. Significant Acidification in Major Chinese Croplands. Science 2010, 327, 1008–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xu, M.; Li, X.; Bian, Y.; Wang, F.; Yang, X.; Gu, C.; Jiang, X. Long-Term Plastic Greenhouse Cultivation Changes Soil Microbial Community Structures: A Case Study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 8941–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, T.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Shao, X.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Xu, H. Effects of Irrigation Regimes on Soil NO3−-N, Electrical Conductivity and Crop Yield in Plastic Greenhouse. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2019, 12, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, M.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Cao, C.; Li, X.; Kan, Z. Precision Fertilization and Irrigation: Progress and Applications. AgriEngineering 2022, 4, 626–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marschner, P.; Hatam, Z.; Cavagnaro, T.R. Soil Respiration, Microbial Biomass and Nutrient Availability after the Second Amendment Are Influenced by Legacy Effects of Prior Residue Addition. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2015, 88, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Christie, P.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, X. Maize Yield and Soil Fertility with Combined Use of Compost and Inorganic Fertilizers on a Calcareous Soil on the North China Plain. Soil Tillage Res. 2016, 155, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Ding, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, P.; Ding, X.; Wang, J. Dynamics of Maize Straw Residue 13C Incorporation into Aggregates of a Mollisol as Affected by Long-Term Fertilization. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Hu, X.; Song, S.; Sun, D. Greenhouse Management for Better Vegetable Quality, Higher Nutrient Use Efficiency, and Healthier Soil. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Gao, W.; Huang, S.; Tang, J.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Masiliūnas, D. Substitution of Manure for Chemical Fertilizer Affects Soil Microbial Community Diversity, Structure and Function in Greenhouse Vegetable Production Systems. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0214041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Burger, M.; Yang, L.; Gong, P.; Wu, Z. Changes in Soil Carbon and Enzyme Activity as a Result of Different Long-Term Fertilization Regimes in a Greenhouse Field. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qasim, W. Global greenhouse vegetable production systems are hotspots of soil N2O emissions and nitrogen leaching: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 116372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R. N and P Runoff Losses in China’s Vegetable Production Systems: Loss Characteristics, Impact, and Management Practices. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 663, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Tang, A.; Shen, J.; Cui, Z.; Vitousek, P.; Erisman, J.W.; Goulding, K.; Christie, P.; et al. Enhanced Nitrogen Deposition over China. Nature 2013, 494, 459–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Davidson, E.A.; Mauzerall, D.L.; Searchinger, T.D.; Dumas, P.; Shen, Y. Managing Nitrogen for Sustainable Development. Nature 2015, 528, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.S.; Gallegos-Cedillo, V.M.; Nájera, C.; Catalina, E.-G.; Ochoa, J.; Fernández, J.A. Advancing Protected Cultivation: A Pathway for Nutrient-Rich Vegetables. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2025, 44, 88–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.Q.; Liu, H.B.; Hu, W.L.; Zhai, L.M.; Lei, B.K. Effects of Different Agronomic Measures on Soil Organic Matter Components and Nitrogen Loss Risk. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2013, 26, 1578–1584. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S. Current Situation and Prospects of Agricultural Irrigation Water Coefficient Development. Smart Agric. Guide 2025, 5, 62–65+70. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment. National Implementation Plan for Agricultural Non-Point Source Pollution Monitoring and Assessment (2022–2025). 2022. Available online: https://www.mee.gov.cn/xxgk2018/xxgk/xxgk05/202209/t20220929_995346.html (accessed on 26 October 2025). (In Chinese)


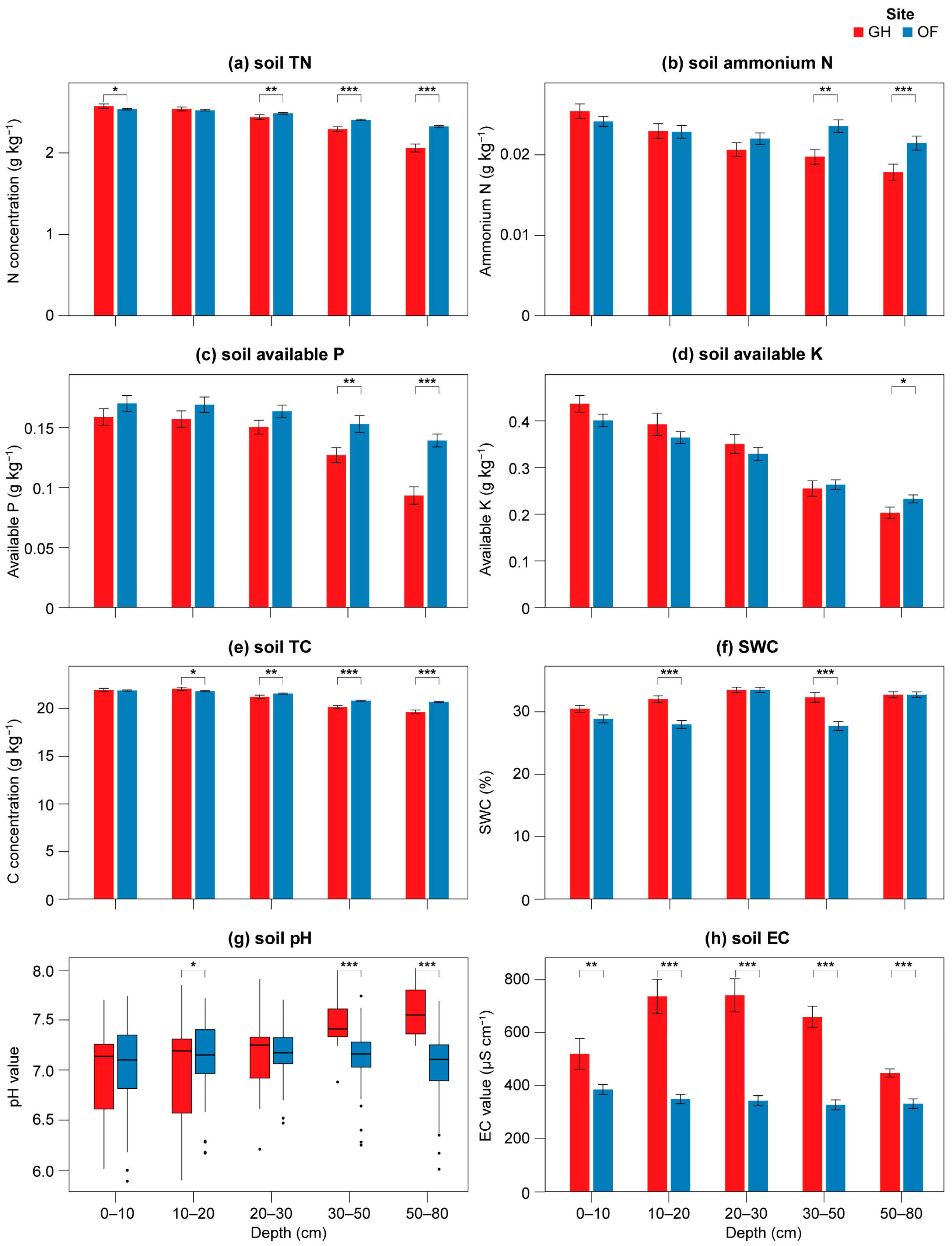
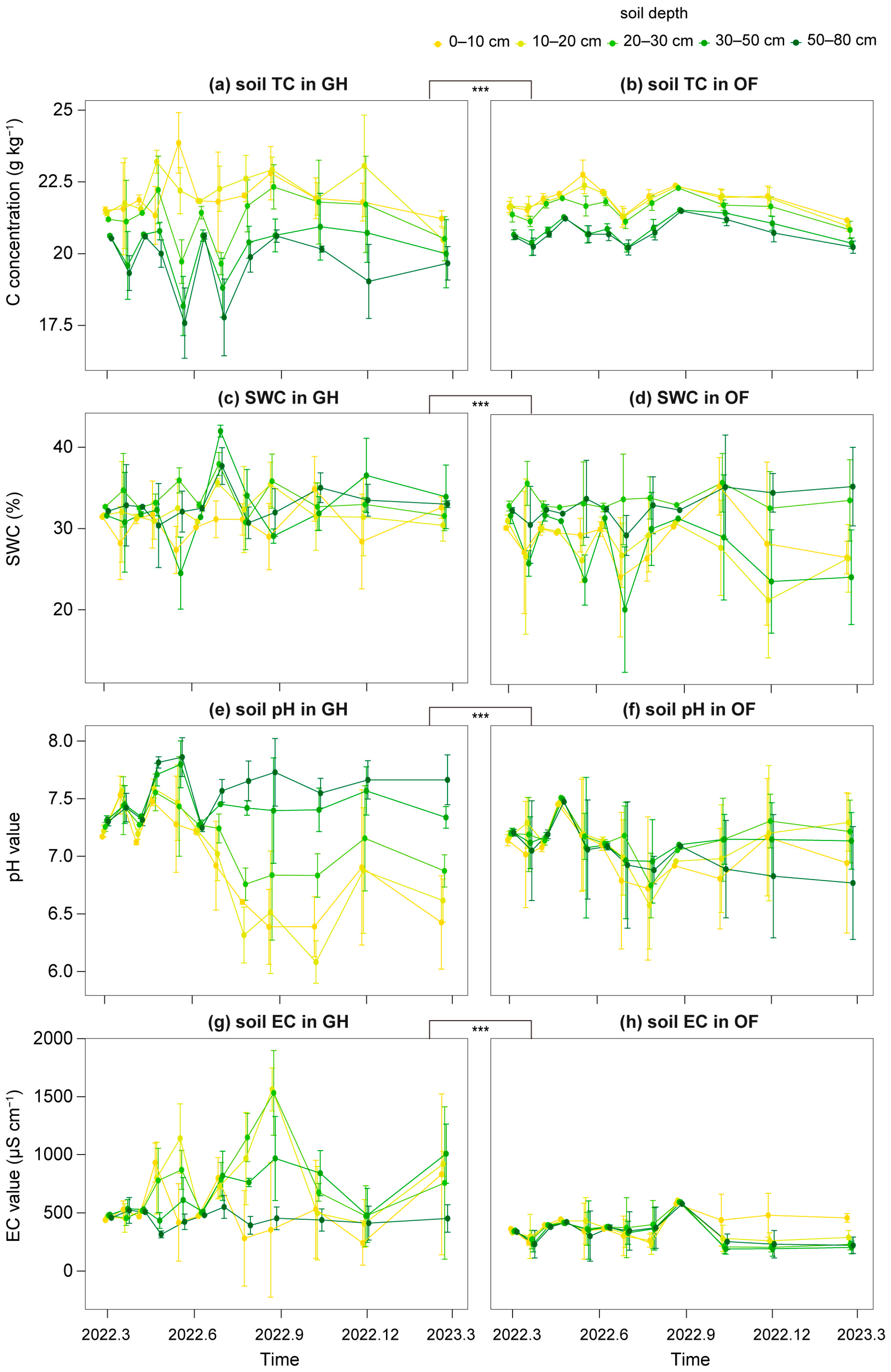
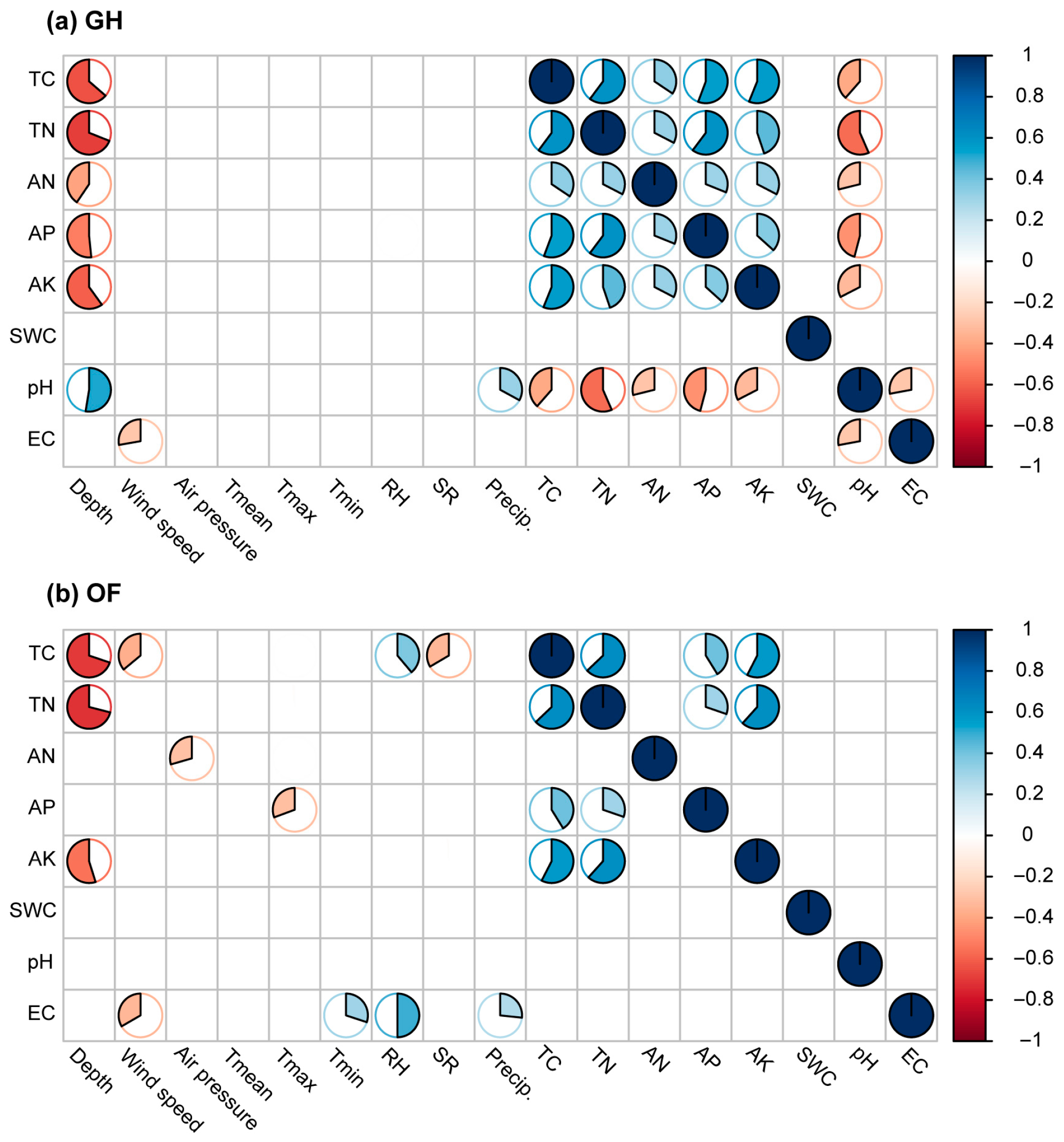
| Site | Depth (cm) | TN (g kg−1) | AN (g kg−1) | AP (g kg−1) | AK (g kg−1) | TC (g kg−1) | SWC (%) | pH | EC (μS cm−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF | 0~10 | 2.540 ± 0.010 | 0.024 ± 0.001 | 0.170 ± 0.007 | 0.401 ± 0.014 | 21.913 ± 0.064 | 28.858 ± 0.635 | 7.035 ± 0.055 | 385.592 ± 18.736 |
| 10~20 | 2.527 ± 0.010 | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 0.169 ± 0.006 | 0.364 ± 0.013 | 21.841 ± 0.059 | 27.967 ± 0.634 | 7.124 ± 0.046 | 349.511 ± 17.418 | |
| 20~30 | 2.489 ± 0.010 | 0.022 ± 0.001 | 0.164 ± 0.005 | 0.329 ± 0.014 | 21.588 ± 0.058 | 33.508 ± 0.413 | 7.174 ± 0.033 | 343.223 ± 18.859 | |
| 30~50 | 2.408 ± 0.010 | 0.024 ± 0.001 | 0.153 ± 0.007 | 0.263 ± 0.010 | 20.842 ± 0.060 | 27.706 ± 0.727 | 7.145 ± 0.039 | 327.496 ± 18.744 | |
| 50~80 | 2.329 ± 0.011 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.139 ± 0.005 | 0.233 ± 0.009 | 20.719 ± 0.057 | 32.715 ± 0.453 | 7.046 ± 0.047 | 332.185 ± 18.152 | |
| average | 2.459 ± 0.040 | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 0.159 ± 0.006 | 0.318 ± 0.031 | 21.381 ± 0.252 | 30.151 ± 1.230 | 7.105 ± 0.028 | 347.601 ± 10.267 | |
| GH | 0~10 | 2.578 ± 0.027 | 0.025 ± 0.001 | 0.159 ± 0.007 | 0.436 ± 0.018 | 21.964 ± 0.168 | 30.465 ± 0.550 | 6.966 ± 0.079 | 519.670 ± 57.715 |
| 10~20 | 2.543 ± 0.024 | 0.023 ± 0.001 | 0.157 ± 0.007 | 0.392 ± 0.024 | 22.095 ± 0.170 | 32.022 ± 0.529 | 6.989 ± 0.088 | 737.047 ± 64.536 | |
| 20~30 | 2.443 ± 0.028 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.150 ± 0.006 | 0.350 ± 0.020 | 21.234 ± 0.191 | 33.489 ± 0.450 | 7.174 ± 0.057 | 740.942 ± 62.782 | |
| 30~50 | 2.295 ± 0.029 | 0.020 ± 0.001 | 0.127 ± 0.006 | 0.255 ± 0.016 | 20.168 ± 0.179 | 32.318 ± 0.783 | 7.466 ± 0.035 | 658.998 ± 40.778 | |
| 50~80 | 2.063 ± 0.049 | 0.018 ± 0.001 | 0.093 ± 0.007 | 0.203 ± 0.013 | 19.657 ± 0.196 | 32.723 ± 0.473 | 7.574 ± 0.039 | 447.442 ± 15.286 | |
| average | 2.385 ± 0.094 | 0.021 ± 0.001 | 0.137 ± 0.012 | 0.327 ± 0.043 | 21.024 ± 0.484 | 32.203 ± 0.500 | 7.234 ± 0.124 | 620.820 ± 59.028 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Miao, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, L.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, Y. Soil Nutrient Variability Analysis of Typical Planting Patterns in Agricultural Reclamation Areas of the Southern Dianchi Lake Basin. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112566
Miao Z, Wu J, Zhao L, Cheng F, Zhang Y. Soil Nutrient Variability Analysis of Typical Planting Patterns in Agricultural Reclamation Areas of the Southern Dianchi Lake Basin. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112566
Chicago/Turabian StyleMiao, Zhuojun, Junen Wu, Lei Zhao, Feng Cheng, and Yuchen Zhang. 2025. "Soil Nutrient Variability Analysis of Typical Planting Patterns in Agricultural Reclamation Areas of the Southern Dianchi Lake Basin" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112566
APA StyleMiao, Z., Wu, J., Zhao, L., Cheng, F., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Soil Nutrient Variability Analysis of Typical Planting Patterns in Agricultural Reclamation Areas of the Southern Dianchi Lake Basin. Agronomy, 15(11), 2566. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112566







