Differential Effects of Four Materials on Soil Properties and Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth in Contaminated Farmlands in Alpine Lead–Zinc Mining Areas, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
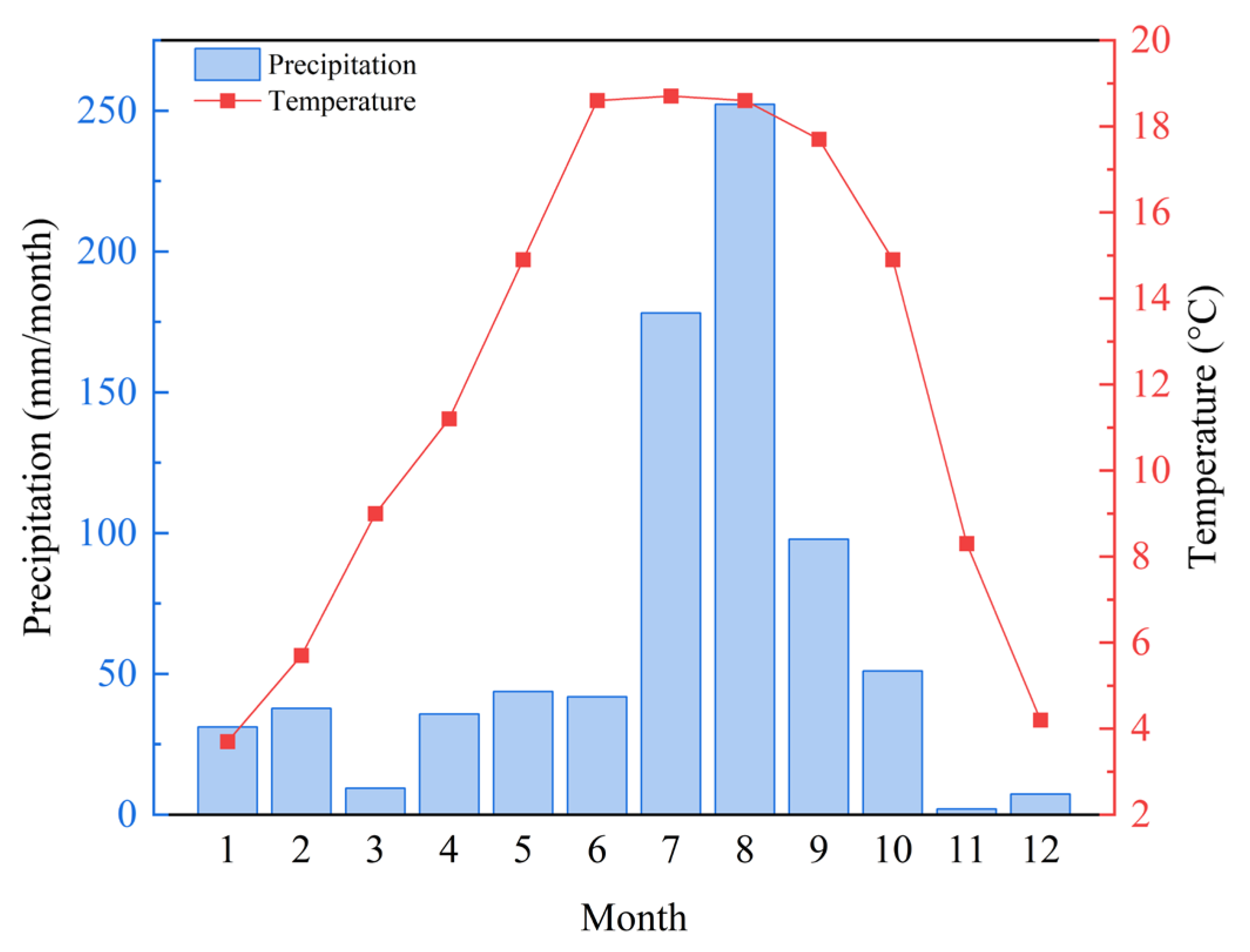
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Plot Experimental Design and Sample Collection
2.3. Determination of Soil Physicochemical and Biological Properties
2.4. Determination of Soil Heavy Metal Forms and Bioavailability
2.5. Determination of Phaseolus coccineus L. Biomass, Nutrient Content, Yield, Quality, and Heavy Metal Content
2.6. Data Processing and Analysis
2.6.1. Statistical Analysis
2.6.2. Calculation of Subordinate Function Values
2.6.3. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) Analysis
3. Results
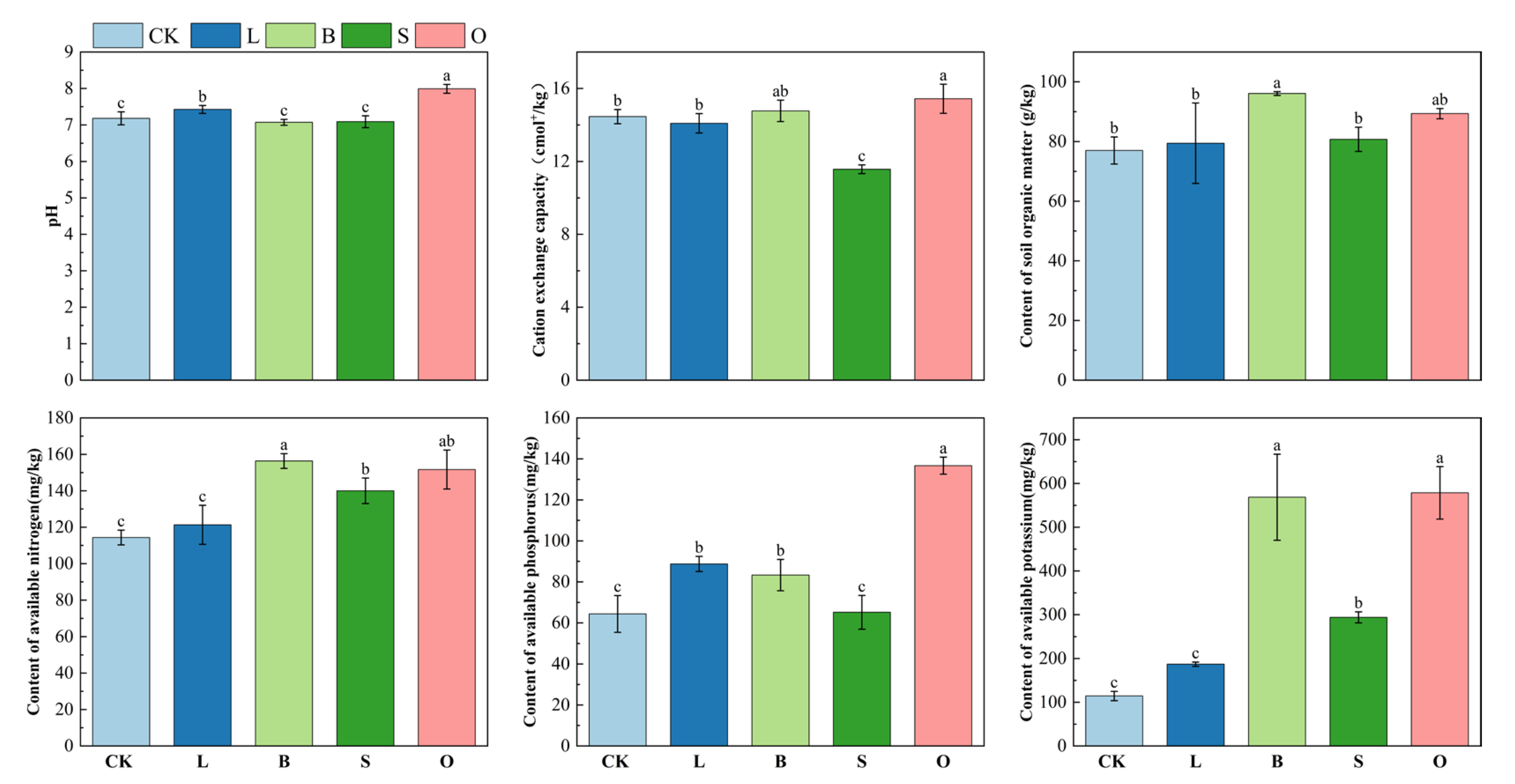
3.1. Effects of the Four Materials on the Physicochemical Properties of Contaminated Farmland Soil in the Lanping Lead–Zinc Mining Area
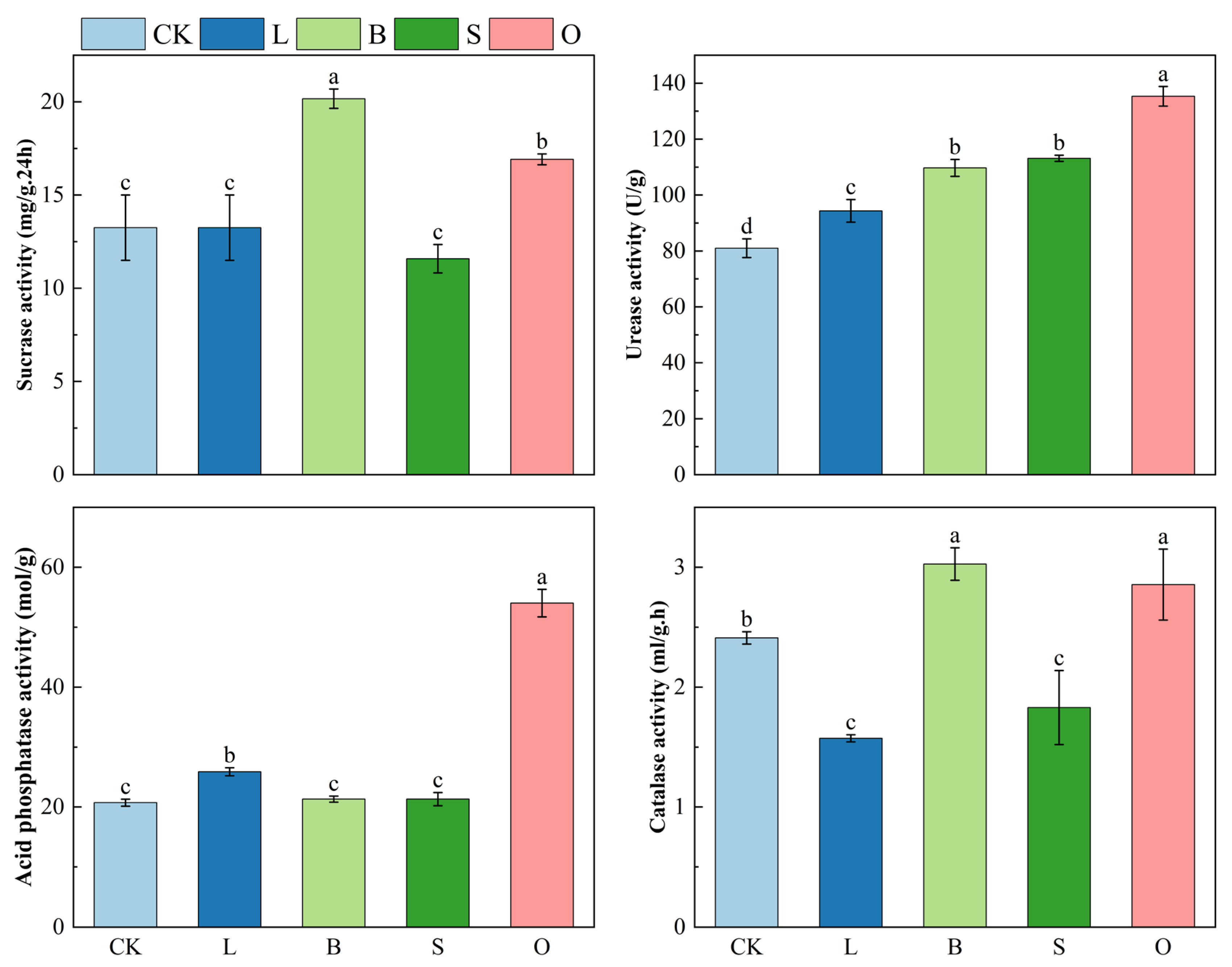
3.2. Effects of the Four Materials on Soil Enzyme Activity in Contaminated Farmland
3.3. Effects of the Four Materials on the Chemical Forms of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Farmland Soil
3.4. Effects of the Four Materials on Bioavailable Heavy Metals Content in Contaminated Farmland Soil
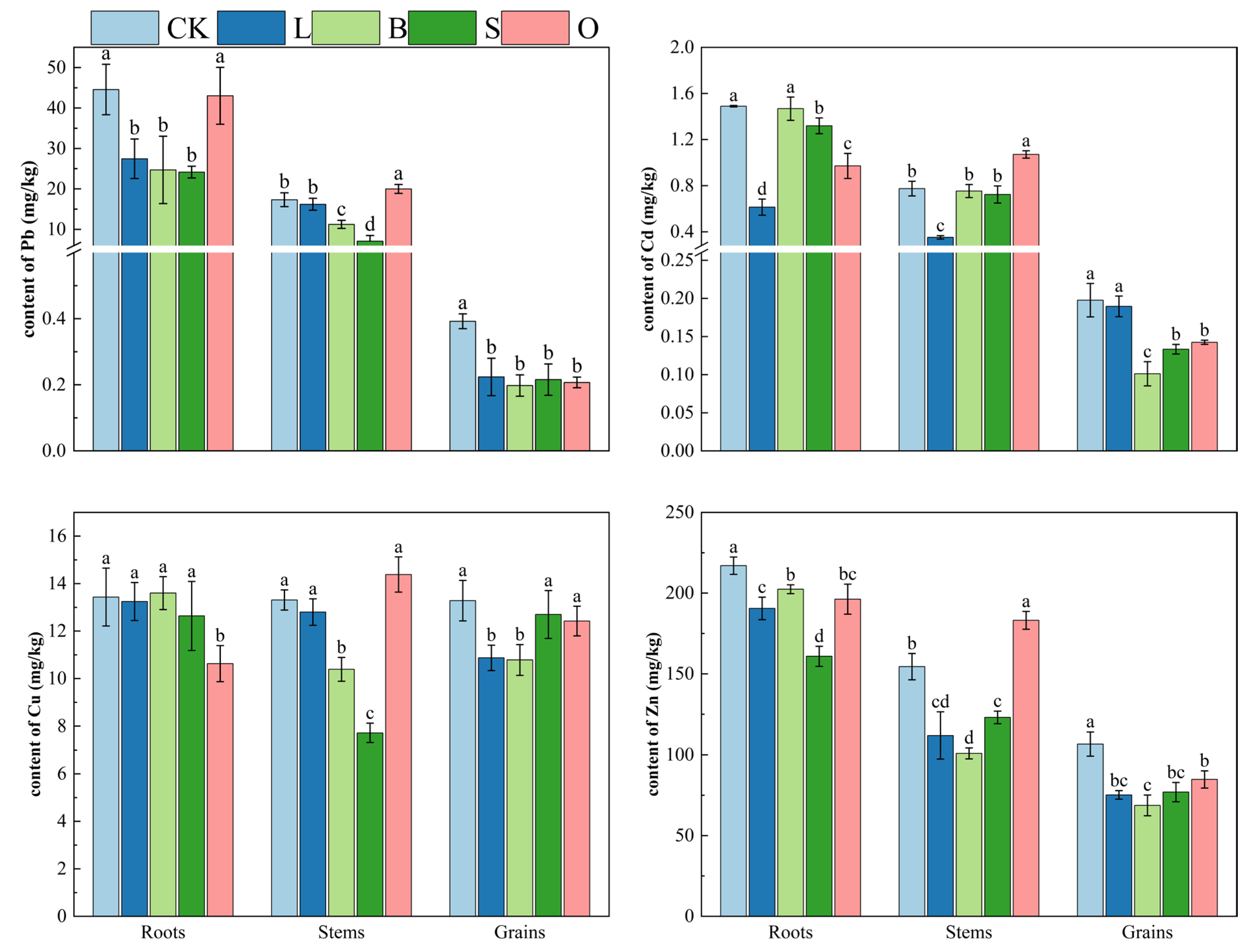
3.5. Effects of the Four Materials on Heavy Metal Accumulation in Phaseolus coccineus L.
3.6. Effects of the Four Materials on the Nutrient Content and Biomass of Phaseolus coccineus L.
3.7. Effects of the Four Materials on the Quality and Yield of Phaseolus coccineus L.
3.8. Correlations Between Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth and Soil Available Nutrients and the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals
3.9. Structural Equation Modeling
3.10. Applicability Assessment of the Four Materials for Heavy Metal Remediation
4. Discussion
4.1. Effects of the Four Materials on the Bioavailability of Heavy Metals in Contaminated Farmland Soil and the Accumulation of Heavy Metals in Crops
4.2. Improving Effects of the Four Materials on the Properties of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soil
4.3. Effects of the Four Materials on Crop Yield and Quality in Contaminated Soil
4.4. Practical Implications and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Zheng, C.; An, C.; Mi, Z. Spatial Distribution, Source Identification, and Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in the Soils from a Mining Region: A Case Study of Bayan Obo in Northwestern China. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2020, 27, 1276–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, P.; Wdowczyk, A.; Wiatkowska, B.; Szymańska-Pulikowska, A. Assessment of Heavy Metal Contamination of Agricultural Soils in Poland Using Contamination Indicators. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 156, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Chen, Q.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, B.; Chen, T.; Jin, J.; Yang, T.; et al. The Potential of Ferrihydrite-Synthetic Humic-like Acid Composite as a Soil Amendment for Metal-Contaminated Agricultural Soil: Immobilization Mechanisms by Combining Abiotic and Biotic Perspectives. Environ. Res. 2024, 250, 118470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Liu, H.; Li, J.; Chen, S.; uz Zaman, Q.; Sultan, K.; Rehman, M.; Saud, S.; El-Kahtany, K.; Fahad, S.; et al. Combined Passivators Regulate Physiological, Antioxidant Potential and Metals Accumulation in Potato Grown in Metals Contaminated Soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 168956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Li, D.; Xie, C.; Zheng, X.; Yin, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, K.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, B.; Hu, Y.; et al. Combined Apatite, Biochar, and Organic Fertilizer Application for Heavy Metal Co-Contaminated Soil Remediation Reduces Heavy Metal Transport and Alters Soil Microbial Community Structure. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 851, 158033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, A.E.-E.A.Z.; Selmy, S.A.H. Effect of pH on Removal of Cu, Cd, Zn, and Ni by Cement Kiln Dust in Aqueous Solution. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2017, 48, 1301–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, X.; He, D. Mechanistic Insight into pH-Dependent Adsorption and Coprecipitation of Chelated Heavy Metals by in-Situ Formed Iron (Oxy)Hydroxides. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 608, 864–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.H.; Zhao, L.Z.; Wang, A.Q.; Chen, T.H.; He, H.P. Current Fundamental and Applied Research into Clay Minerals in China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2016, 119, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barać, N.; Škrivanj, S.; Mutić, J.; Manojlović, D.; Bukumirić, Z.; Živojinović, D.; Petrović, R.; Ćorac, A. Heavy Metals Fractionation in Agricultural Soils of Pb/Zn Mining Region and Their Transfer to Selected Vegetables. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, W.; Zheng, K.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Chen, R. Stabilization of Heavy Metal-Contaminated Soils by Biochar: Challenges and Recommendations. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cheng, K.; Huo, X.; Meng, P.; Cai, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, J. Bioorganic Fertilizer Promotes Pakchoi Growth and Shapes the Soil Microbial Structure. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1040437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qi, R.; Yang, L. Ecological Restoration in High-Altitude Mining Areas: Evaluation Soil Reconstruction and Vegetation Recovery in the Jiangcang Coal Mining Area on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Front. Environ. Sci. 2025, 12, 1538243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Kong, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lu, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, A. Safe Utilization and Remediation Potential of the Mulberry-Silkworm System in Heavy Metal-Contaminated Lands: A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 927, 172352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Yao, X.; Yang, M.; Hu, S.; An, X.; Li, C. Co-Application of Sheep Manure and Commercial Organic Fertilizer Enhances Plant Productivity and Soil Quality in Alpine Mining Areas. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1488121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlett, M.; Hopkins, D.W.; Moffett, B.F.; Harris, J.A. The Effect of Earthworms and Liming on Soil Microbial Communities. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2009, 45, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Wu, P.; Jeyakumar, P.; Bolan, N.; Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, S.; Wang, B. Biochar as a Potential Strategy for Remediation of Contaminated Mining Soils: Mechanisms, Applications, and Future Perspectives. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 313, 114973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Liu, W.; Feng, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. The Role of Vegetation Restoration in Shaping the Structure and Stability of Soil Bacterial Community of Alpine Mining Regions. Plant Soil 2025, 513, 2903–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Bao, N.; Zhao, X.; Meng, D.; Han, Z. How Soil Physicochemical Properties and Microorganisms Change under Mining Activities in Alpine and High-Altitude Regions—A Case Study of a Copper Mine Area in Tibet Plateau. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, F.; Zeng, W.; Yuan, X.; Li, B.; Li, T.; Zu, Y.; Jiang, M.; Li, Y. Field Experiment on the Effects of Sepiolite and Biochar on the Remediation of Cd- and Pb-Polluted Farmlands around a Pb–Zn Mine in Yunnan Province, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 7743–7751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, L.; Li, B.; Li, Z.; He, Y.; Hu, W.; Zu, Y.; Zhan, F. Pollution and Health Risk Assessment of Heavy Metals in Farmlands and Vegetables Surrounding a Lead-Zinc Mine in Yunnan Province, China. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2022, 31, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corzo-Ríos, L.J.; Sánchez-Chino, X.M.; Cardador-Martínez, A.; Martínez-Herrera, J.; Jiménez-Martínez, C. Effect of Cooking on Nutritional and Non-Nutritional Compounds in Two Species of Phaseolus (P. vulgaris and P. coccineus) Cultivated in Mexico. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2020, 20, 100206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasakul, Y.; Aursalung, A.; Thangsiri, S.; Wongchang, P.; Sangkasa-ad, P.; Wongpia, A.; Polpanit, A.; Inthachat, W.; Tem-viriyanukul, P.; Suttisansanee, U. Nutritional Compositions, Phenolic Contents, and Antioxidant Potentials of Ten Original Lineage Beans in Thailand. Foods 2022, 11, 2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwember, A.R.; Carrasco, B.; Gepts, P. Unraveling Agronomic and Genetic Aspects of Runner Bean (Phaseolus coccineus L.). Field Crops Res. 2017, 206, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamkhi, I.; Cheto, S.; Geistlinger, J.; Zeroual, Y.; Kouisni, L.; Bargaz, A.; Ghoulam, C. Legume-Based Intercropping Systems Promote Beneficial Rhizobacterial Community and Crop Yield under Stressing Conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, F.; Nan, G.; Cao, M.; Gao, Y.; Guo, L.; Meng, X.; Yang, G. The Metal Distribution and the Change of Physiological and Biochemical Process in Soybean and Mung Bean Plants under Heavy Metal Stress. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2018, 20, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 15618-2018; Soil Environmental Quality Risk Control Standard for Soil Contamination of Agricultural Land. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2018.
- Yang, Y.; Chen, W.; Meng, D.; Ma, C.; Li, H. Investigation of Arsenic Contamination in Soil and Plants along the River of Xinzhou Abandoned Gold Mine in Qingyuan, China. Chemosphere 2024, 359, 142350. [Google Scholar]
- Pagani, A.; Mallarino, A.P. Soil pH and Crop Grain Yield as Affected by the Source and Rate of Lime. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2012, 76, 1877–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil and Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Frankeberger, W.T.; Johanson, J.B. Method of Measuring Invertase Activity in Soils. Plant Soil 1983, 74, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.L.; Temple, K.L. Some Variables Affecting the Measurement of “Catalase Activity” in Soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1964, 28, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabatabai, M.A.; Bremner, J.M. Use of p-Nitrophenyl Phosphate for Assay of Soil Phosphatase Activity. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1969, 1, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevauviller, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Ure, A.M.; Rubio, R.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Fiedler, H.D.; Griepink, B. Evaluation of a Sequential Extraction Procedure for the Determination of Extractable Trace Metal Contents in Sediments. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1994, 349, 808–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Chen, X.; Vancov, T.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, W.; Hong, L.; Yao, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, W.; Hong, C. Combined Remediation Effect of Ryegrass-Earthworm on Heavy Metal Composite Contaminated Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2025, 494, 138477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Xiao, H.; Guo, Q.; Song, B.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Okoli, C.P. Heavy Metal Contents and Enrichment Characteristics of Dominant Plants in Wasteland of the Downstream of a Lead-Zinc Mining Area in Guangxi, Southwest China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 151, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Zhao, C.; Fu, Q.; Meng, F.; Liu, D.; Li, M. Freeze-Thaw Cycles Affect Hydrothermal and Heavy Metal Transport Mechanisms in Porous Media: Closed and Transient Flooded System Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2025, 966, 178750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Wu, Q. Vertical Distribution Characteristics of Soil Mercury and Its Formation Mechanism in Permafrost Regions: A Case Study of the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. J. Environ. Sci. 2022, 113, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Lian, W.; Tian, S.; Yu, Q.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Fan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zheng, J.; et al. Utilizing Ragweed and Oyster Shell Derived Biochar as an Effective Stabilizer for the Restoring Cd and Pb- Contaminated Soil. Geoderma Reg. 2024, 37, e00816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, N.; Hoodaji, M.; Kalbasi, M.; Chavoshi, E. Biochar Amendment for the Alleviation of Heavy Metals Stress in Corn (Zea mays L.) Plants Grown in a Basic Soil. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 4807–4816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Brookes, P.C.; Shan, S.; Xu, J.; Liu, X. Effects of Remediation Agents on Microbial Community Structure and Function in Soil Aggregates Contaminated with Heavy Metals. Geoderma 2022, 425, 116030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamid, Y.; Tang, L.; Sohail, M.I.; Cao, X.; Hussain, B.; Aziz, M.Z.; Usman, M.; He, Z.; Yang, X. An Explanation of Soil Amendments to Reduce Cadmium Phytoavailability and Transfer to Food Chain. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Bing, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, K.; Jiang, J.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Q.; Xue, R. Remediation of Cd(II), Zn(II) and Pb(II) in Contaminated Soil by KMnO4 Modified Biochar: Stabilization Efficiency and Effects of Freeze–Thaw Ageing. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 487, 150619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lwin, C.S.; Kim, Y.-N.; Lee, M.; Jung, H.; Kim, K.-R. In Situ Immobilization of Potentially Toxic Elements in Arable Soil by Adding Soil Amendments and the Best Ways to Maximize Their Use Efficiency. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2024, 24, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Yang, L.; Joseph, S.; Shi, W.; Bian, R.; Zheng, J.; Li, L.; Shan, S.; Pan, G. Utilization of Biochar Produced from Invasive Plant Species to Efficiently Adsorb Cd (II) and Pb (II). Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 317, 124011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, J.F.; Heng, Z.W.; Teoh, H.C.; Chong, W.C.; Pang, Y.L. Recent Development of Magnetic Biochar Crosslinked Chitosan on Heavy Metal Removal from Wastewater—Modification, Application and Mechanism. Chemosphere 2022, 291, 133035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, L.; Pan, G.; Li, L.; Bian, R.; Liu, X.; Yan, J.; Quan, G.; Ding, C.; Chen, T.; Liu, Y.; et al. Continuous Immobilization of Cadmium and Lead in Biochar Amended Contaminated Paddy Soil: A Five-Year Field Experiment. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 93, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, M.; Lu, L.; He, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Zhu, Y. Applications of Biochar and Modified Biochar in Heavy Metal Contaminated Soil: A Descriptive Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 14041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Liu, D.; Fu, Q.; Hou, R.; Li, Q.; Cui, S.; Li, M. Research on the Adsorption Mechanism of Cu and Zn by Biochar under Freeze-Thaw Conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, P.; Li, S.; Deng, W.; Li, S.; Ni, W.; Zhang, S. Freeze-Thaw and Dry-Wet Alternation Regulate the Impacts of Fe-C Based Passivator on Soil Heavy Metals Immobilization. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2025, 13, 117971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Niu, C.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.; Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Shan, X. Experimental Investigation of the Erodibility of Soda Saline-Alkali Soil under Freeze-Thaw Cycle from a Microscopic View. CATENA 2023, 232, 107430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, S.; Wu, L.; Qi, W.; Chen, J.; Ye, Z.; Ma, J.; Liu, D. Effects of Bio-Organic Fertilizer on Soil Fertility, Yield, and Quality of Tea. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 5109–5121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Cai, X.; Li, B.; Zhan, F.; Zu, Y.; He, Y. Organic Materials Promote Rhododendron Simsii Growth and Rhizosphere Soil Properties in a Lead–Zinc Mining Wasteland. Plants 2024, 13, 891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ampong, K.; Thilakaranthna, M.S.; Gorim, L.Y. Understanding the Role of Humic Acids on Crop Performance and Soil Health. Front. Agron. 2022, 4, 848621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Niu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, H.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y. Application of Carbon-Based Nutrient Fertilizer Improved Soil Fertility and Seed Yield of Paeonia ostii ‘Feng Dan’. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 212, 118348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Xia, J.; Yang, H.; Liu, J.; Shao, P. Biochar and Effective Microorganisms Promote Sesbania cannabina Growth and Soil Quality in the Coastal Saline-Alkali Soil of the Yellow River Delta, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 756, 143801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Xie, L.; Liu, K.; Wang, J.; Zhu, H.; Song, Q.; Shu, X. Co-Pyrolysis of Sewage Sludge and Cotton Stalks. Waste Manag. 2019, 89, 430–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Sun, B.; Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Drosos, M.; Li, L.; Pan, G. The Water-Soluble Pool in Biochar Dominates Maize Plant Growth Promotion Under Biochar Amendment. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Cao, W.; Chou, Y.; Peng, E. Experimental Study on the Change in Freezing Temperature During the Remediation of Pb-Contaminated Soils with Biochar. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yang, Z.; Ye, Q.; Peng, Z.; Zhu, S.; Chen, H.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Deng, L.; Shu, X.; et al. Positive Effects of Organic Amendments on Soil Microbes and Their Functionality in Agro-Ecosystems. Plants 2023, 12, 3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abad-Valle, P.; Álvarez-Ayuso, E.; Murciego, A.; Pellitero, E. Assessment of the Use of Sepiolite Amendment to Restore Heavy Metal Polluted Mine Soil. Geoderma 2016, 280, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Wen, J.; Wang, Q.; Xing, L.; Hu, X. Mobilization or Immobilization? The Effect of HDTMA-Modified Biochar on As Mobility and Bioavailability in Soil. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 207, 111565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amalina, F.; Abd Razak, A.S.; Zularisam, A.W.; Aziz, M.A.A.; Krishnan, S.; Nasrullah, M. Comprehensive Assessment of Biochar Integration in Agricultural Soil Conditioning: Advantages, Drawbacks, and Future Prospects. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2023, 132, 103508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, E.; Kim, K.-H.; Kwon, E.E. Biochar as a Tool for the Improvement of Soil and Environment. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1324533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Q.; Duan, X.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Yao, X. Biochar Application in Combination with No Tillage Enhanced Yield and Grain Quality of Ratoon Rice. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, W.; Nan, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dong, D.; Qin, Y.; Li, S.; Wu, W. Stress Resistance Enhancing with Biochar Application and Promotion on Crop Growth. Biochar 2024, 6, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Ullah, S.; He, L.; Zhao, Q.; Iqbal, A.; Wei, S.; Shah, T.; Ali, N.; Bo, Y.; Adnan, M.; et al. Combined Application of Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer Improves Rice Yield, Microbial Activity and N-Metabolism in a Pot Experiment. PeerJ 2020, 8, e10311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, R.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y. Accumulation Characteristics, Driving Factors, and Model Prediction of Cadmium in Soil-Highland Barley System on the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 453, 131407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Guo, A.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Fan, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Qin, S. Partial Substitution of Chemical Fertilizer with Organic Manure Enhances Yield Attributes and Tuber Quality in Potato. J. Soil. Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 3932–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quiliche, R.; Santiago, B.; Baião, F.A.; Leiras, A. A Predictive Assessment of Households’ Risk against Disasters Caused by Cold Waves Using Machine Learning. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 98, 104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhadkaria, A.; Srivastava, N.; Bhagyawant, S.S. A Prospective of Underutilized Legume Moth Bean (Vigna aconitifolia (Jacq.) Marechàl): Phytochemical Profiling, Bioactive Compounds and in Vitro Pharmacological Studies. Food Biosci. 2021, 42, 101088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Chen, X.; Hu, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Hong, Y. Effects of Distribution, Structure and Interactions of Starch, Protein and Cell Walls on Textural Formation of Cooked Rice: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 127403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


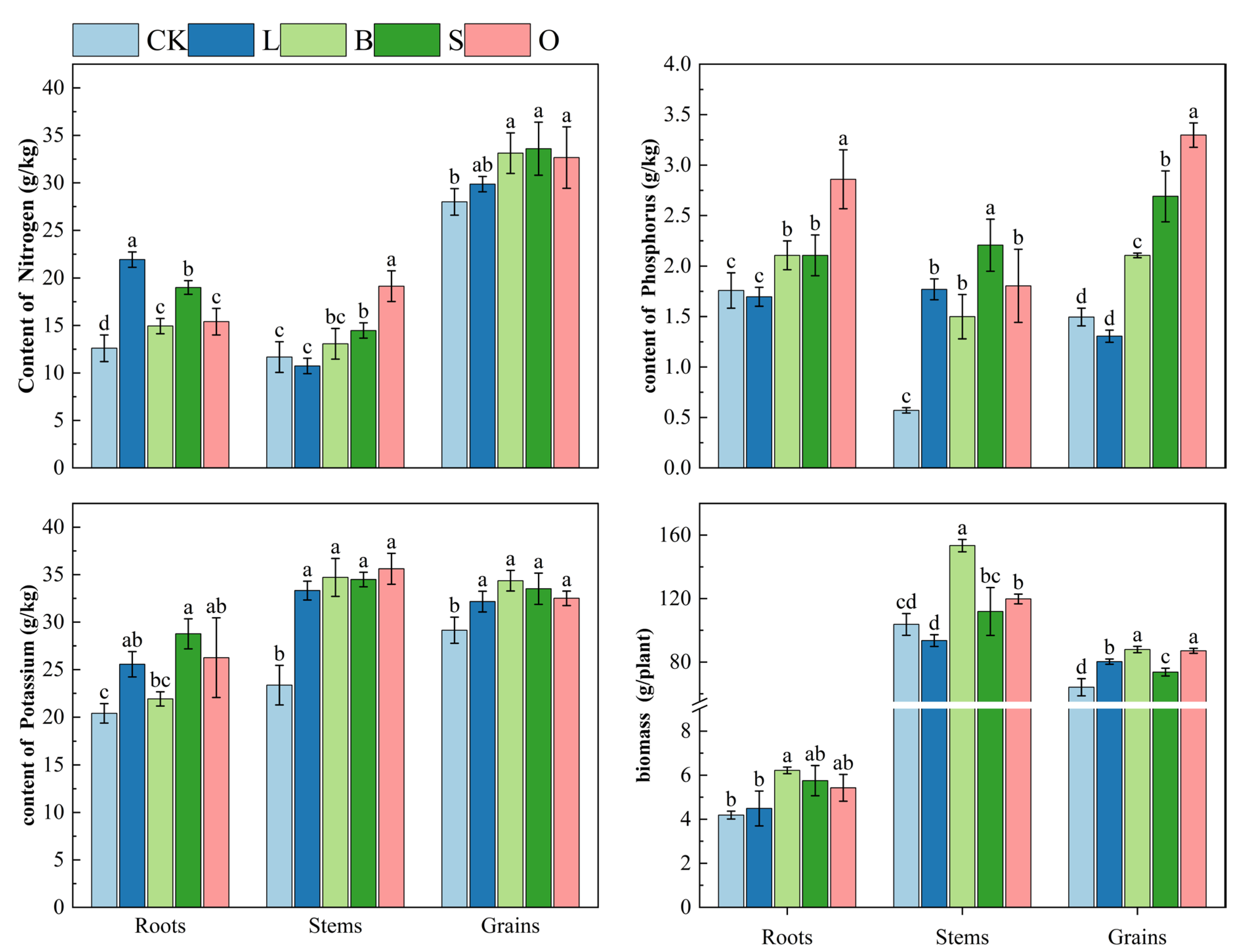
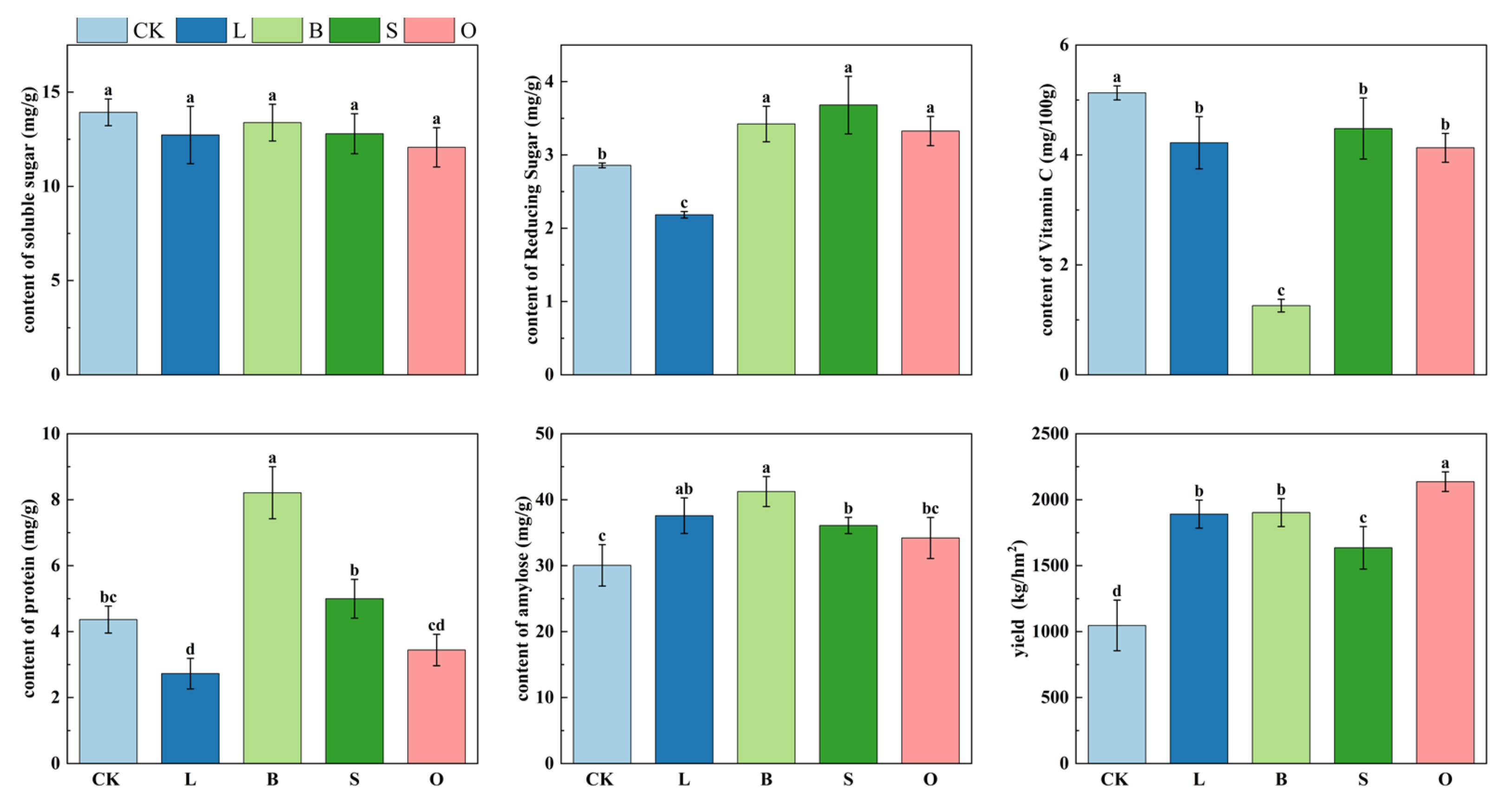

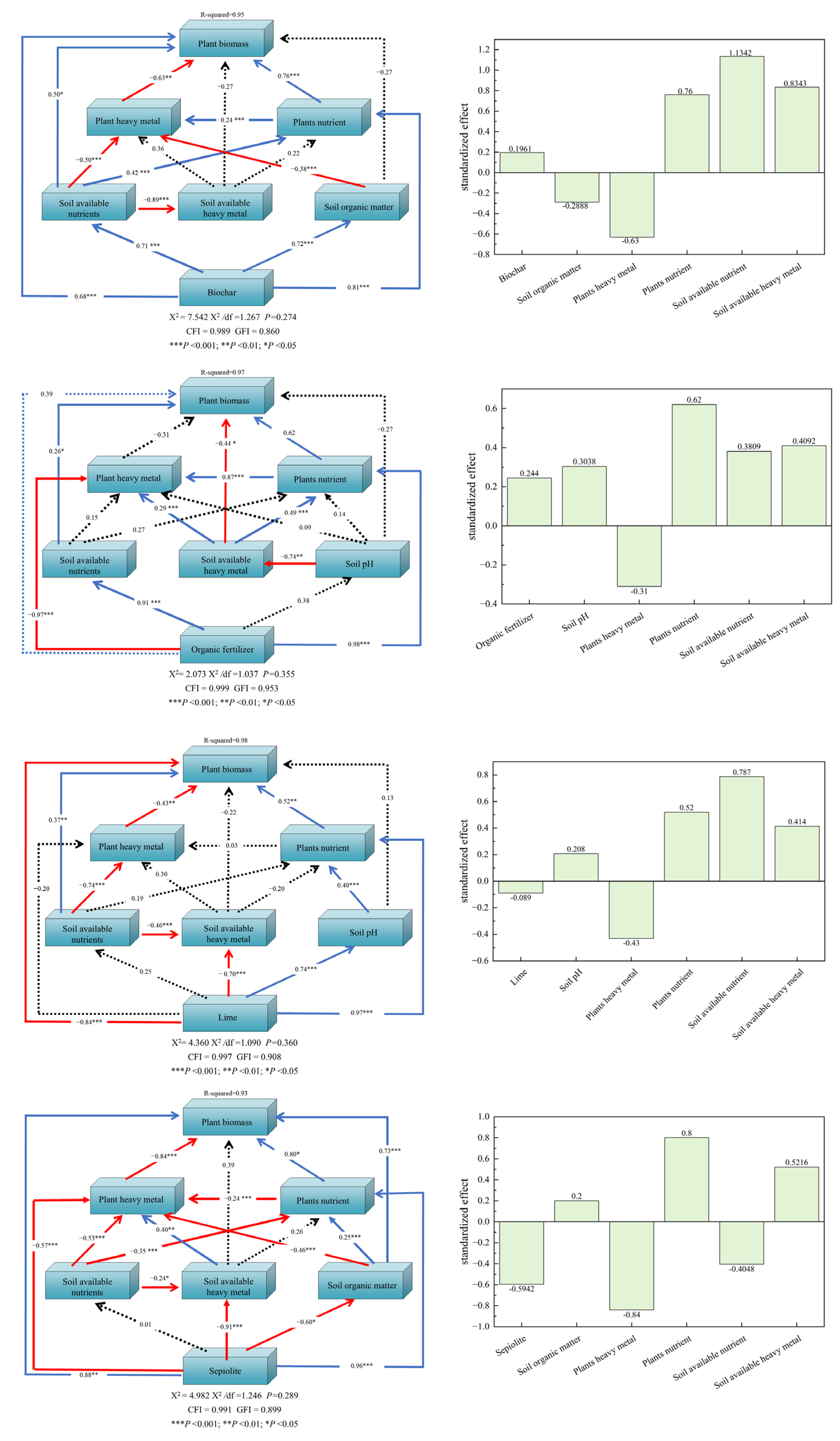
| Indicator | Extremely Rich | Rich | Relatively Rich | Moderate | Poor | Extremely Poor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Organic matter(g/kg) | >40 | 30~40 | 20~30 | 10~20 | 6~10 | <6 |
| Total N (g/kg) | >2 | 1.5~2 | 1~1.5 | 0.75~1 | 0.5~0.75 | <0.5 |
| Total P (g/kg) | >1 | 0.8~1 | 0.6~0.8 | 0.4~0.6 | 0.2~0.4 | <0.2 |
| Total K (g/kg) | >25 | 20~25 | 15~20 | 10~15 | 5~10 | <5 |
| Available N (mg/kg) | >150 | 120~150 | 90~120 | 60~90 | 30~60 | <30 |
| Available P (mg/kg) | >40 | 20~40 | 10~20 | 5~10 | 3~5 | <3 |
| Available K (mg/kg) | >200 | 150~200 | 100~150 | 50~100 | 30~50 | <30 |
| Materials | pH | Pb (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Cu (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L (Lime) | 12.20 | 1.39 | 0.21 | — | — |
| B (Biochar) | 8.84 | 5.41 | — | — | — |
| S (Sepiolite) | 9.35 | 2.72 | — | — | — |
| O (organic fertilizer) | 7.89 | 18.2 | 2.27 | 156 | 245 |
| Index | L | B | S | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plant biomass | 0.15 | 0.72 | 0.48 | 0.43 |
| Plant nutrient | 0.53 | 0.68 | 0.86 | 0.91 |
| Plants heavy metal | 0.72 | 0.91 | 0.94 | 0.33 |
| Soil available heavy metal | 0.86 | 0.74 | 0.91 | 0.09 |
| Soil available nutrient | 0.47 | 0.44 | 0.12 | 0.85 |
| Mean value | 0.55 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.52 |
| Ranking number | 3 | 1 | 2 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, X.; Yang, Q.; Meng, W.; He, X.; He, Y.; He, S.; Chen, Q.; Zhan, F.; He, J.; Bai, H. Differential Effects of Four Materials on Soil Properties and Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth in Contaminated Farmlands in Alpine Lead–Zinc Mining Areas, Southwest China. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112467
He X, Yang Q, Meng W, He X, He Y, He S, Chen Q, Zhan F, He J, Bai H. Differential Effects of Four Materials on Soil Properties and Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth in Contaminated Farmlands in Alpine Lead–Zinc Mining Areas, Southwest China. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112467
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Xiuhua, Qian Yang, Weixi Meng, Xiaojia He, Yongmei He, Siteng He, Qingsong Chen, Fangdong Zhan, Jianhua He, and Hui Bai. 2025. "Differential Effects of Four Materials on Soil Properties and Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth in Contaminated Farmlands in Alpine Lead–Zinc Mining Areas, Southwest China" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112467
APA StyleHe, X., Yang, Q., Meng, W., He, X., He, Y., He, S., Chen, Q., Zhan, F., He, J., & Bai, H. (2025). Differential Effects of Four Materials on Soil Properties and Phaseolus coccineus L. Growth in Contaminated Farmlands in Alpine Lead–Zinc Mining Areas, Southwest China. Agronomy, 15(11), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112467






