Composition Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Coupling with Nutrient Stoichiometry in Tea Garden Soils
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
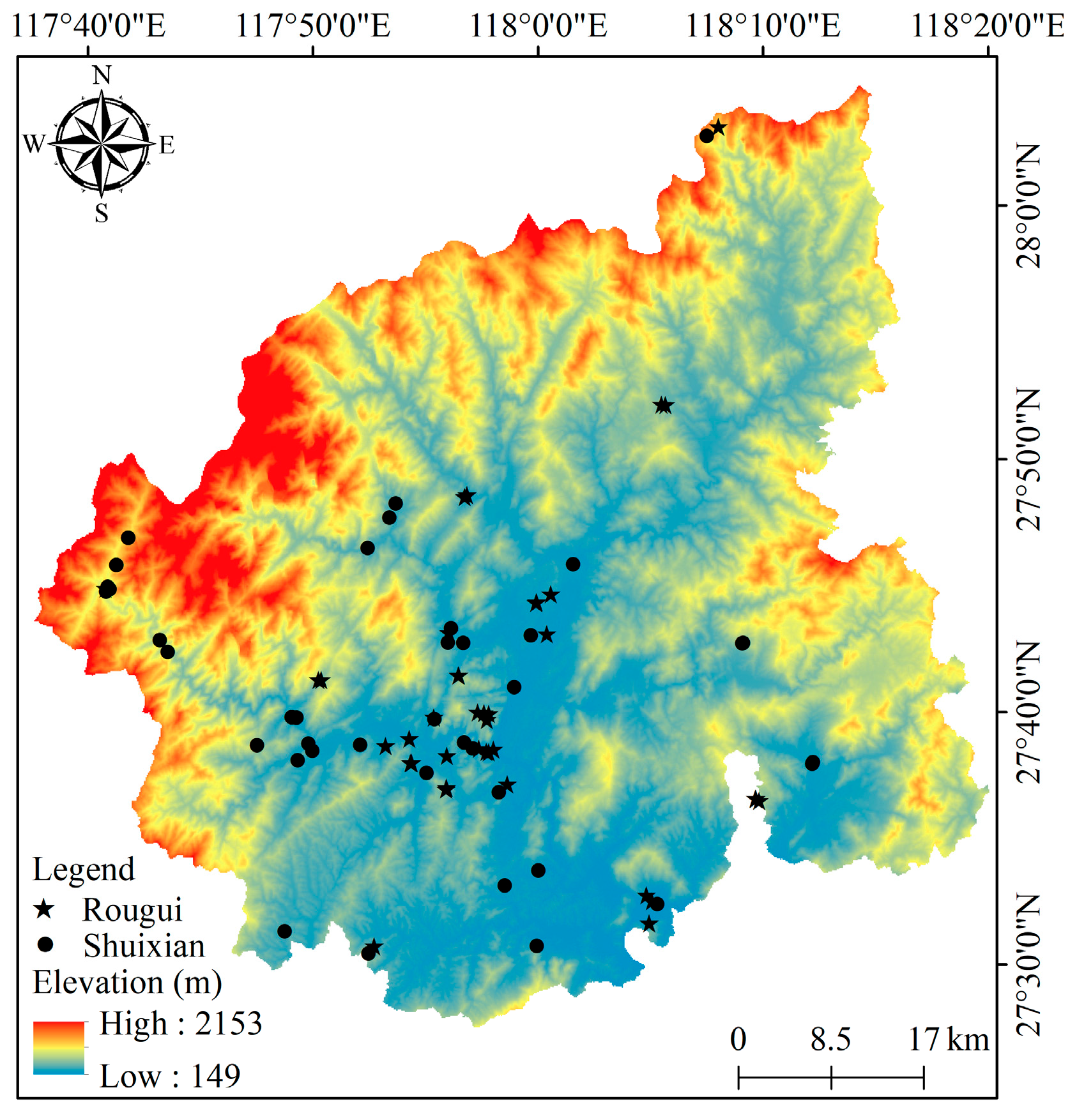
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling and Laboratory Analyses
2.3. Data Processing and Analysis
2.3.1. Spectral Indices
2.3.2. PARAFAC Modeling
2.3.3. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM)
2.3.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Soil Nutrient Contents and Stoichiometric Ratios in Wuyi Rock Tea Gardens
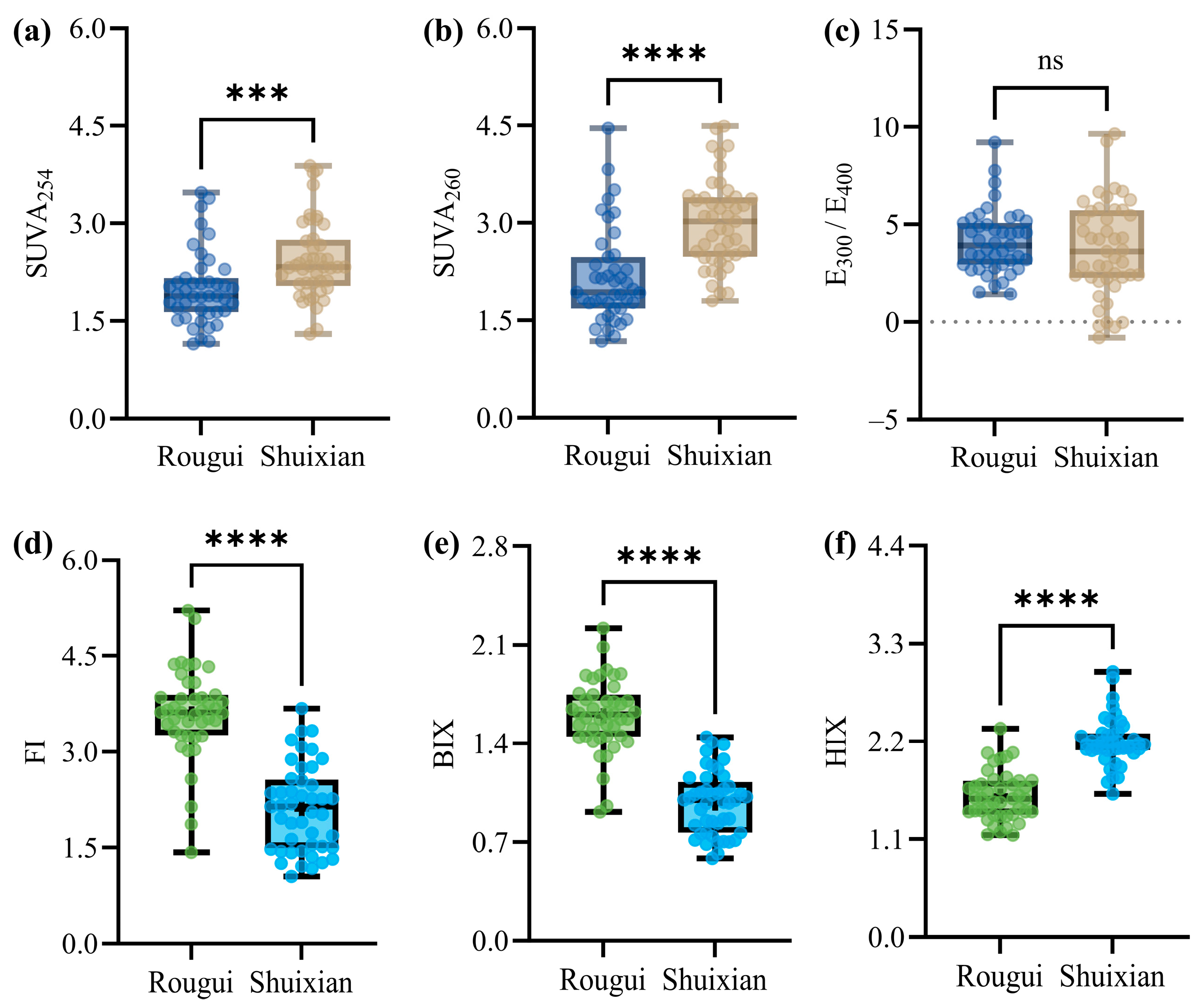
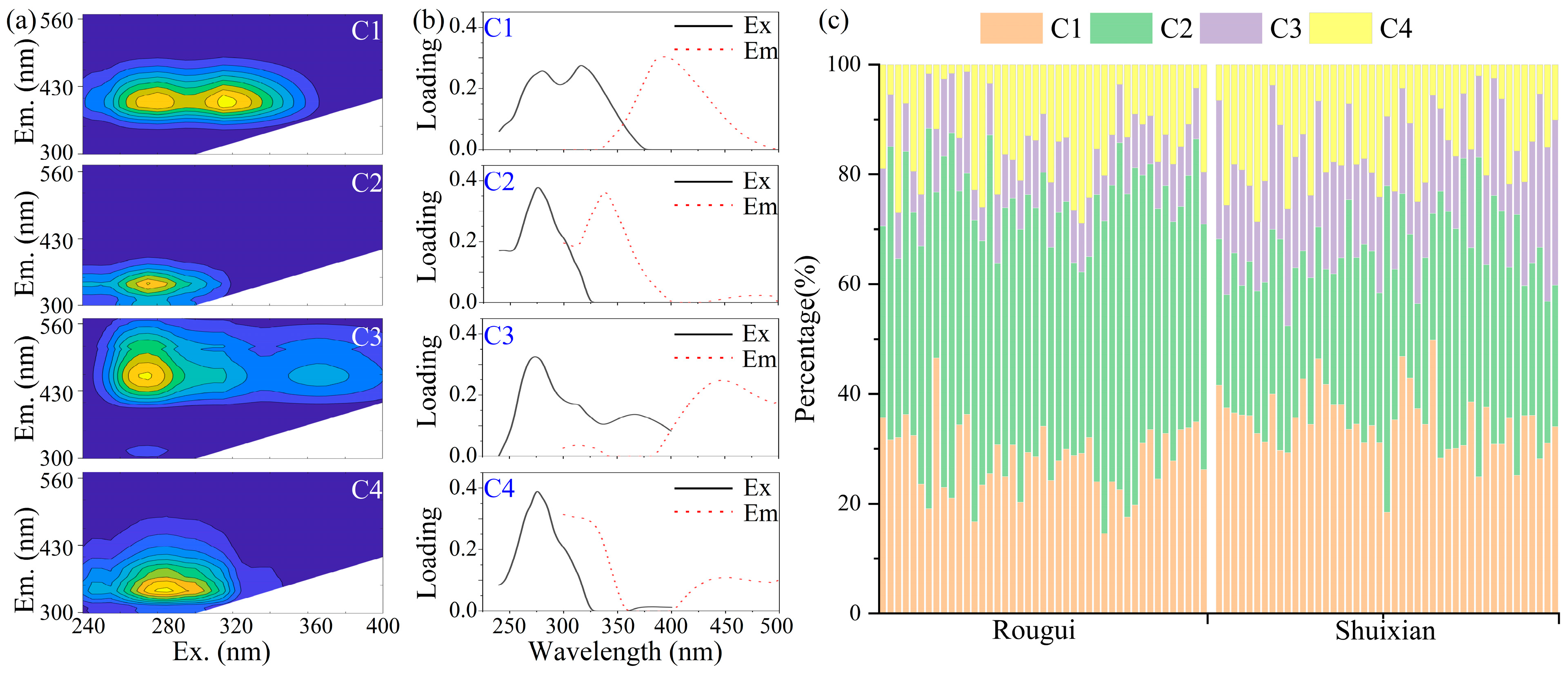
3.2. Spectral Parameters and Composition of Soil DOM in Wuyi Rock Tea Gardens
3.3. Relationships Between Soil Nutrient Indices and DOM Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Stoichiometric Characteristics of Soil Nutrients in Wuyi Rock Tea Gardens
4.2. Composition and Origin of DOM in Wuyi Rock Tea Soils
4.3. Response of DOM Composition to Nutrient Stoichiometry in Wuyi Rock Tea Soils
4.4. Limitations and Suggestions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DOM | Dissolved organic matter |
| C | Carbon |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| SOM | Soil organic matter |
| N | Nitrogen |
| AN | Alkali-hydrolysable nitrogen |
| P | Phosphorus |
| AP | Available phosphorus |
| AK | Available potassium |
| EEMs | Excitation–emission matrices |
| Ex | Excitation |
| Em | Emission |
| FI | Fluorescence index |
| HIX | Humification index |
| BIX | Biological index |
| PARAFAC | Parallel factor |
References
- Azeem, M.; Wang, J.; Kubwimana, J.J.; Kazmi, S.S.H.; Khan, Z.H.; He, K.; Han, R. Biochar-derived dissolved organic matter (BDOM) shifts fungal community composition: BDOM-soil DOM interaction. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 207, 105916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Z.; Hao, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, T.; Turner, B.L.; Kandeler, E.; Lambers, H.; Liu, Z. Climate and pedogenesis exert divergent controls on dissolved organic matter during long-term ecosystem development. Catena 2025, 254, 109004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filep, T.; Zacháry, D.; Jakab, G.; Szalai, Z. Chemical composition of labile carbon fractions in Hungarian forest soils: Insight into biogeochemical coupling between DOM and POM. Geoderma 2022, 419, 115867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Shi, P.; Min, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Li, Z. Spatiotemporal dynamics of river dissolved organic matter in small watershed with vegetation restoration on the Loess Plateau. Catena 2025, 259, 109357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Bai, M.; Yan, X.; Song, Y.; Yang, F.; Qian, F.; Yu, H. Applying EEM spectra with absolute principal component coefficients to explore characteristic fingerprints and fractions of DOM from diverse land-use soils in a large-scale irrigation area. Catena 2024, 238, 107903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Shi, Z.; Ye, Q.; Liang, Y.; Liu, C. Chemodiversity of soil dissolved organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 54, 6174–6184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Fan, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yan, Y.; Shi, J.; Huo, C.; Wang, X. Erosion-driven vertical decoupling: Molecular signatures of dissolved organic matter and microbial coevolution in subsoil hotspots. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 15792–15802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Li, X.; Han, C.; Gao, L.; Wu, H.; Li, M. A new view into three-dimensional excitation-emission matrix fluorescence spectroscopy for dissolved organic matter. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 855, 158963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, W.; Li, L.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Mo, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Dissolved organic matter characteristics in soils of tropical legume and non-legume tree plantations. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 148, 107880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Liang, C.; Shen, G.; Lv, J.; Wu, H. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in various agricultural soils throughout China. Chemosphere 2017, 176, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Li, M.; Gao, X.; Duan, Y.; Cai, Y.; Li, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, Y. Changes in the characteristics of soil dissolved organic matter over time since inter-planting with white clover (Trifolium repens L.) in apple orchards on the Loess Plateau in China. Plant Soil 2024, 499, 293–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Tang, F.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Huang, L.; Hu, J.; Huang, C.; Huang, T. Stoichiometric insights into sediment carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus deposition in small forest reservoirs in southeast China under forest conversion and climate change. Catena 2025, 250, 108741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Hu, Z.; Li, X.; Wang, D.; Xu, C.; Hu, F.; Chen, X.; Liu, M. Land-use driven changes in elemental stoichiometry decouple the positive soil biodiversity-stability relationship. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2025, 209, 109907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Li, B.; Cao, E.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, C. Optimizing nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizer application for wheat yield on alkali soils: Mechanisms and effects. Agronomy 2025, 15, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumtong, S.; Chotamonsak, C.; Pongwongkam, P.; Cantiya, K. Chemical fertilization alters soil carbon in paddy soil through the interaction of labile organic carbon and phosphorus fractions. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnaz, K.R.; Corneo, P.E.; Keitel, C.; Dijkstra, F.A. Carbon and phosphorus addition effects on microbial carbon use efficiency, soil organic matter priming, gross nitrogen mineralization and nitrous oxide emission from soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 134, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Deng, C.; Gao, J.; Lu, J.; Zheng, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Deng, Y. Fertilizer types and nitrogen rates integrated strategy for achieving sustainable quinoa yield and dynamic soil nutrient-water distribution at high altitude. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 5599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumtong, S.; Foungyen, P.; Kanchai, K.; Chuephudee, T.; Chotamonsak, C.; Lapyai, D. Impact of reduced nitrogen inputs on soil organic carbon and nutrient dynamics in arable soil, northern Thailand: Short-term evaluation. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Dou, Y.; Wang, B.; Gunina, A.; Yang, Y.; An, S.; Chang, S.X. Soil stoichiometric imbalances constrain microbial-driven C and N dynamics in grassland. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 924, 171655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Liang, Y.; Ye, H.; Ye, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Shi, A. Spectral characteristics of dissolved organic matter in tea garden soil. Environ. Chem. 2025, 44, 3100–3109. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Liu, B.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Hou, J.; Cao, R.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, W. Status and influential factors of soil nutrients and acidification in Chinese tea plantations: A meta-analysis. Soil 2025, 11, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Zhang, J.; Yu, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Li, W.; Liu, Y.; Lu, T.; He, B.; et al. Root microbiota of tea plants regulate nitrogen homeostasis and theanine synthesis to influence tea quality. Curr. Biol. 2024, 34, 868–880.e866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, D.; Peng, S.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Hui, D. Nutrient resorption and stoichiometric characteristics of Wuyi Rock Tea cultivars. Forests 2023, 14, 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamau, D.M.; Spiertz, J.H.J.; Oenema, O. Carbon and nutrient stocks of tea plantations differing in age, genotype and plant population density. Plant Soil 2008, 307, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, B.; Nang, Z.; Xu, Z. Genotype and slope position control on the availability of soil soluble organic nitrogen in tea plantations. Biogeochemistry 2011, 103, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Yang, W.; Chen, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, W.; Ye, D.; Wu, L. Soil phosphorus pools, bioavailability and environmental risk in response to the phosphorus supply in the red soil of southern China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, D.; Zheng, S.; Tang, X.; Wu, J.; Guo, S. Effects of forest conversion on the stocks and stoichiometry of soil carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus at a county scale in subtropical China. Forests 2024, 15, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Wang, R.; Cai, J.; Meng, Y.; Wang, Z.; Feng, X.; Liu, H.; Turco, R.F.; Jiang, Y. Enhanced carbon acquisition and use efficiency alleviate microbial carbon relative to nitrogen limitation under soil acidification. Ecol. Process. 2021, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, G.; Zhang, C.; Melillo, J.M.; Hall, C.A.S. Pattern and variation of C:N:P ratios in China’s soils: A synthesis of observational data. Biogeochemistry 2010, 98, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, L.; Zheng, Z.; Li, T.; He, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Huang, H.; Yu, H.; Ye, D. Quantity and quality characteristics of DOM loss in sloping cropland under natural rainfall in southwestern China. Catena 2024, 240, 108000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Song, F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, S.; Feng, W.; Zuo, L.; Pu, J.; Xing, B.; Giesy, J.P.; Bai, Y. Investigation of eluted characteristics of fulvic acids using differential spectroscopy combined with gaussian deconvolution and spectral indices. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 11000–11011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fellman, J.B.; Hood, E.; Spencer, R.G.M. Fluorescence spectroscopy opens new windows into dissolved organic matter dynamics in freshwater ecosystems: A review. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 2452–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, J.; Ma, K.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Y.; Tan, H.; Yu, J.; Fang, F. Characteristics of dissolved organic matter (DOM) combined with as in Fe-rich red soils of tea plantations in the southern Anhui Province, east China. Agriculture 2024, 14, 2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, T.S.; Van Metre, P.C.; Carlisle, D.M. Linking the agricultural landscape of the midwest to stream health with structural equation modeling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 452–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Duan, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Yao, C.; Chen, Y.; Cao, W.; Niu, Y. Patterns and driving factors of soil ecological stoichiometry in typical ecologically fragile areas of China. Catena 2022, 219, 106628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Xia, Y.; Hu, Y.; Chen, X.; Rui, Y.; Gunina, A.; He, X.; Ge, T.; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; et al. Stoichiometry of carbon, nitrogen, and phosphorus in soil: Effects of agricultural land use and climate at a continental scale. Soil Tillage Res. 2021, 209, 104903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleveland, C.C.; Liptzin, D. C:N:P. stoichiometry in soil: Is. there a “Redfield ratio” for the microbial biomass? Biogeochemistry 2007, 85, 235–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Thornton, P.E.; Post, W.M. A global analysis of soil microbial biomass carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in terrestrial ecosystems. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2013, 22, 737–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, X.; He, P. The soil ecological stoichiometry characteristics of the highest latitude areas in the main tea-producing regions of China. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Ju, Y.; Chen, L.; Yang, X.; Long, Y.; Liu, X. Fertility assessment and risk management in tea plantations: Role of p-promoted metals’ availability. Agriculture 2025, 15, 953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Ni, K.; Shi, Y.; Yi, X.; Zhang, Q.; Fang, L.; Ma, L.; Ruan, J. Effects of long-term nitrogen application on soil acidification and solution chemistry of a tea plantation in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 252, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, X.; Ding, L.; Ye, J.; Jia, X.; Kong, X.; He, H. Effect of soil acidification on yield and quality of tea tree in tea plantations from Anxi County, Fujian Province. Chin. J. Appl. Environ. Biol. 2018, 24, 1398–1403. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Zhang, S.; Mu, E.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ding, A. Characterizing the spatiotemporal distribution of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in the Yongding River basin: Insights from flow regulation. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y. Generation and characterization of DOM in wastewater treatment processes. Chemosphere 2018, 201, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Xin, W.; Xu, T.; Yang, Z. Tea plant microorganisms in the improvement of tea quality. Trends Microbiol. 2025, 33, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Graiti, T.; Jakab, G.; Ujházy, N.; Vancsik, A.; Fodor, N.; Árendás, T.; Madarász, B.; Barcza, Z.; Márialigeti, K.; Szalai, Z. The composition of dissolved organic matter in arable lands: Does soil management practice matter? Agronomy 2022, 12, 2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajtha, K.; Bowden, R.D.; Crow, S.; Fekete, I.; Kotroczó, Z.; Plante, A.; Simpson, M.J.; Nadelhoffer, K.J. The detrital input and removal treatment (DIRT) network: Insights into soil carbon stabilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 640–641, 1112–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.; Yanagisawa, O.; Maeda, S.; Takatsu, S.; Ikka, T. Tea plant (Camellia sinensis L.) roots secrete oxalic acid and caffeine into medium containing aluminum. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2011, 57, 796–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Lin, J.; Cheng, S.; Wang, K.; Kumar, A.; Yu, Z.; Zhu, B. Linking soil dissolved organic matter characteristics and the temperature sensitivity of soil organic carbon decomposition in the riparian zone of the Three Gorges Reservoir. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Yang, Z.; Chu, R.; Toliċ, N.; Liang, L.; Graham, D.; Wullschleger, S.; Gu, B. Molecular insights into Arctic soil organic matter degradation under warming. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4555–4564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosi, E.R. Soluble Organic Matter, It Biodegradation, Dynamics and Abiotic Production. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Canterbury, Christchurch, New Zealand, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitkenhead, J.A.; McDowell, W.H. Soil C:N ratio as a predictor of annual riverine DOC flux at local and global scales. Global Biogeochem. Cycles. 2000, 14, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardans, J.; Rivas-Ubach, A.; Peñuelas, J. The C:N:P stoichiometry of organisms and ecosystems in a changing world: A review and perspectives. Perspect. Plant Ecol. Evol. Syst. 2012, 14, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Bicohe. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Schimel, J.S.; Liang, C. Quantifying asynchrony between microbial necromass and soil organic carbon for sustainable soil carbon management. Soil Biol. Bicohe. 2025, 211, 109950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, E.C.; Emilson, E.J.S.; Dittmar, T.; Braga, L.P.P.; Emilson, C.E.; Goldhammer, T.; Martineau, C.; Singer, G.; Tanentzap, A.J. Universal microbial reworking of dissolved organic matter along environmental gradients. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Fan, Z.; Wang, X. Erosion-induced low carbon availability exacerbates carbon loss: Insights from microbial carbon allocation and the chemo-diversity of carbon. Catena 2025, 252, 108894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhang, H.; Shi, A.; Nie, R.; Liang, Y.; Hong, Y.; Cheng, X.; Huang, L.; Zhang, J. “Acceptable limits” criteria of potentially toxic elements in ecological tea garden soil and priority control sources identification. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 303, 118986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDowell, W.H. DOM in the long arc of environmental science: Looking back and thinking ahead. Biogeochemistry 2022, 164, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Guo, J.; Zhou, Q. Progress in the interaction of dissolved organic matter and microbes (1991–2020): A bibliometric review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 16817–16829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, W.; Jiao, X.; He, Q.; Wang, F.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, Y. Insights into the complexity of dissolved organic matter in different soils using ultrahigh-resolution ESI-FT-ICR mass spectrometry. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2024, 202, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
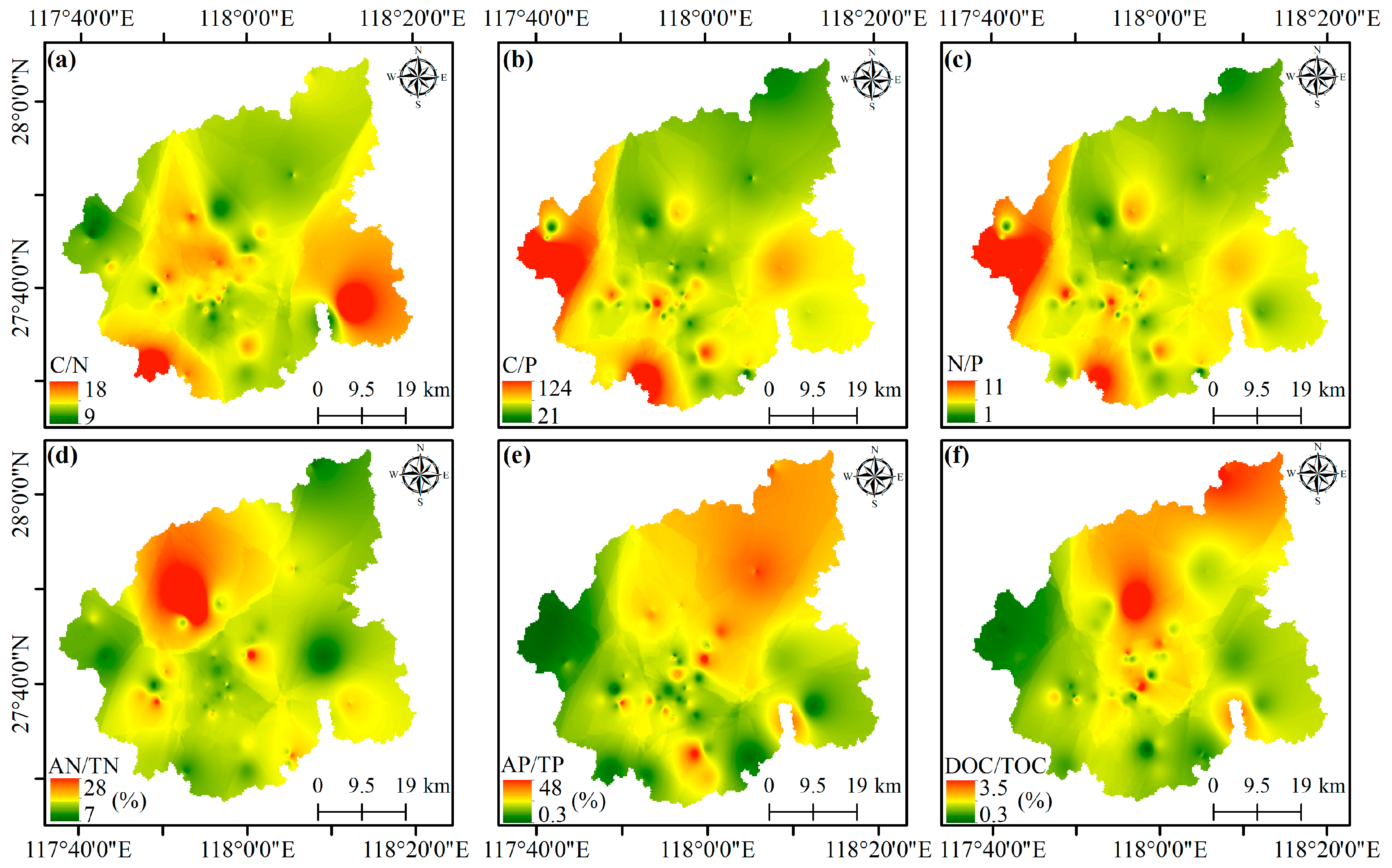


 ” indicates the corresponding C/N/P ratios of soil from tea gardens of different tea plant varieties, Rougui (n = 43); Shuixian (n = 45); “✩” indicates the average C/N/P ratios of soil across different land-use types or regional areas. The global and national-scale average soil C/N/P ratios were derived from [37] and [29], respectively. Average C/N/P values for global cropland and tropical/subtropical forest soils were taken from [38].
” indicates the corresponding C/N/P ratios of soil from tea gardens of different tea plant varieties, Rougui (n = 43); Shuixian (n = 45); “✩” indicates the average C/N/P ratios of soil across different land-use types or regional areas. The global and national-scale average soil C/N/P ratios were derived from [37] and [29], respectively. Average C/N/P values for global cropland and tropical/subtropical forest soils were taken from [38].
 ” indicates the corresponding C/N/P ratios of soil from tea gardens of different tea plant varieties, Rougui (n = 43); Shuixian (n = 45); “✩” indicates the average C/N/P ratios of soil across different land-use types or regional areas. The global and national-scale average soil C/N/P ratios were derived from [37] and [29], respectively. Average C/N/P values for global cropland and tropical/subtropical forest soils were taken from [38].
” indicates the corresponding C/N/P ratios of soil from tea gardens of different tea plant varieties, Rougui (n = 43); Shuixian (n = 45); “✩” indicates the average C/N/P ratios of soil across different land-use types or regional areas. The global and national-scale average soil C/N/P ratios were derived from [37] and [29], respectively. Average C/N/P values for global cropland and tropical/subtropical forest soils were taken from [38].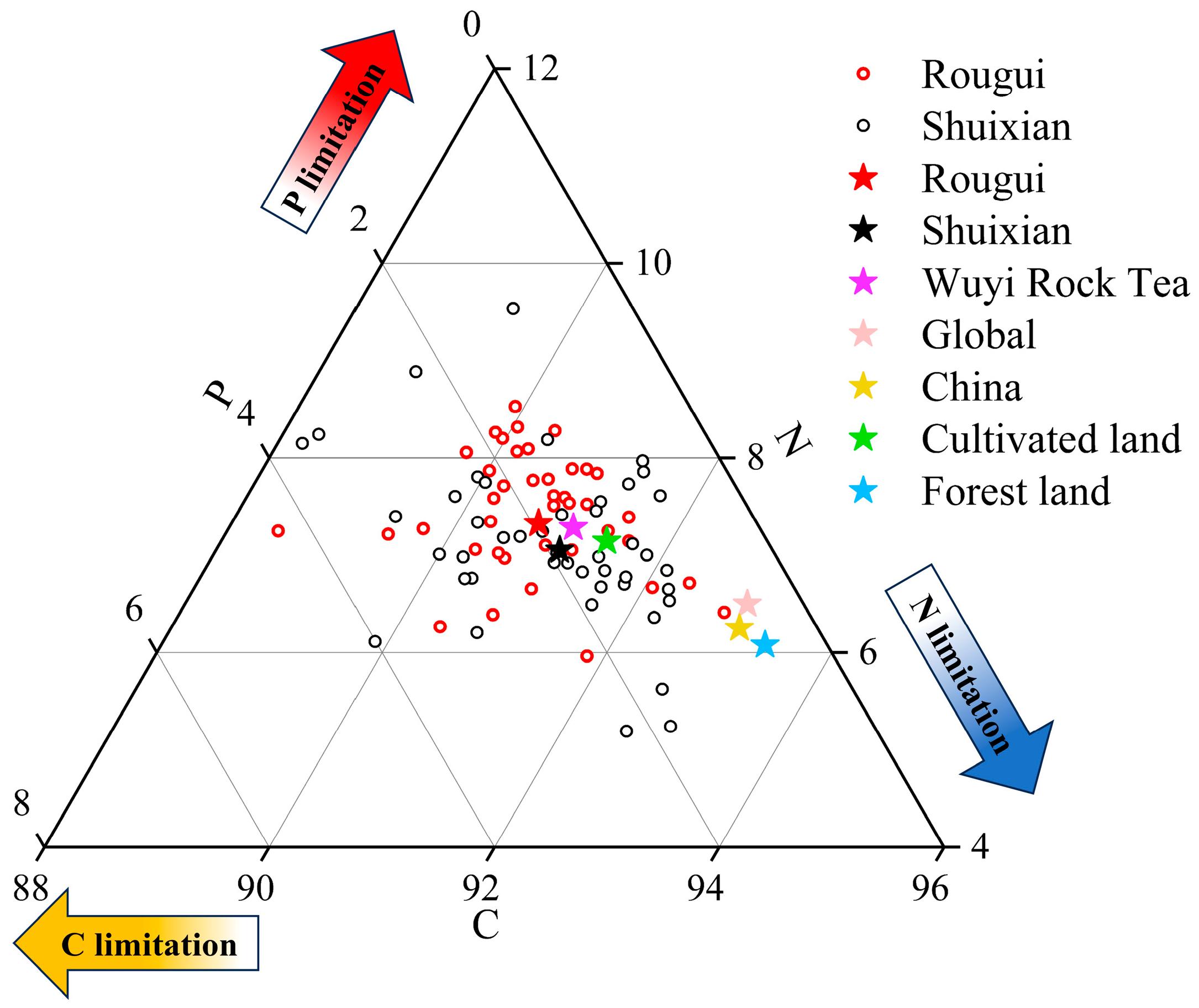
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ye, H.; Hou, M.; Shi, A.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Composition Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Coupling with Nutrient Stoichiometry in Tea Garden Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112449
Ye H, Hou M, Shi A, Liang Y, Zhang Y. Composition Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Coupling with Nutrient Stoichiometry in Tea Garden Soils. Agronomy. 2025; 15(11):2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112449
Chicago/Turabian StyleYe, Hongmeng, Mengqian Hou, Aowen Shi, Yuting Liang, and Yongbin Zhang. 2025. "Composition Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Coupling with Nutrient Stoichiometry in Tea Garden Soils" Agronomy 15, no. 11: 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112449
APA StyleYe, H., Hou, M., Shi, A., Liang, Y., & Zhang, Y. (2025). Composition Characteristics of Dissolved Organic Matter and Its Coupling with Nutrient Stoichiometry in Tea Garden Soils. Agronomy, 15(11), 2449. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15112449





