Crab Shell Biochar and Compost Synergistically Mitigate Heavy Metal Toxicity in Soil–Plant System
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Soil Collection, Preparation, and Analysis
2.2. Compost Source and Characterization
2.3. Biochar Production and Characterization
2.4. Pot Experiment
2.5. Agronomic Analysis
2.5.1. Parameter for Growth
2.5.2. Parameter for Chlorophyll Contents
2.5.3. Stress and Antioxidant Parameter Analysis
2.5.4. Parameters for HMs Uptake
2.6. Post-Harvest Soil Analysis
2.7. Bioaccumulation Factor
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Result and Discussion
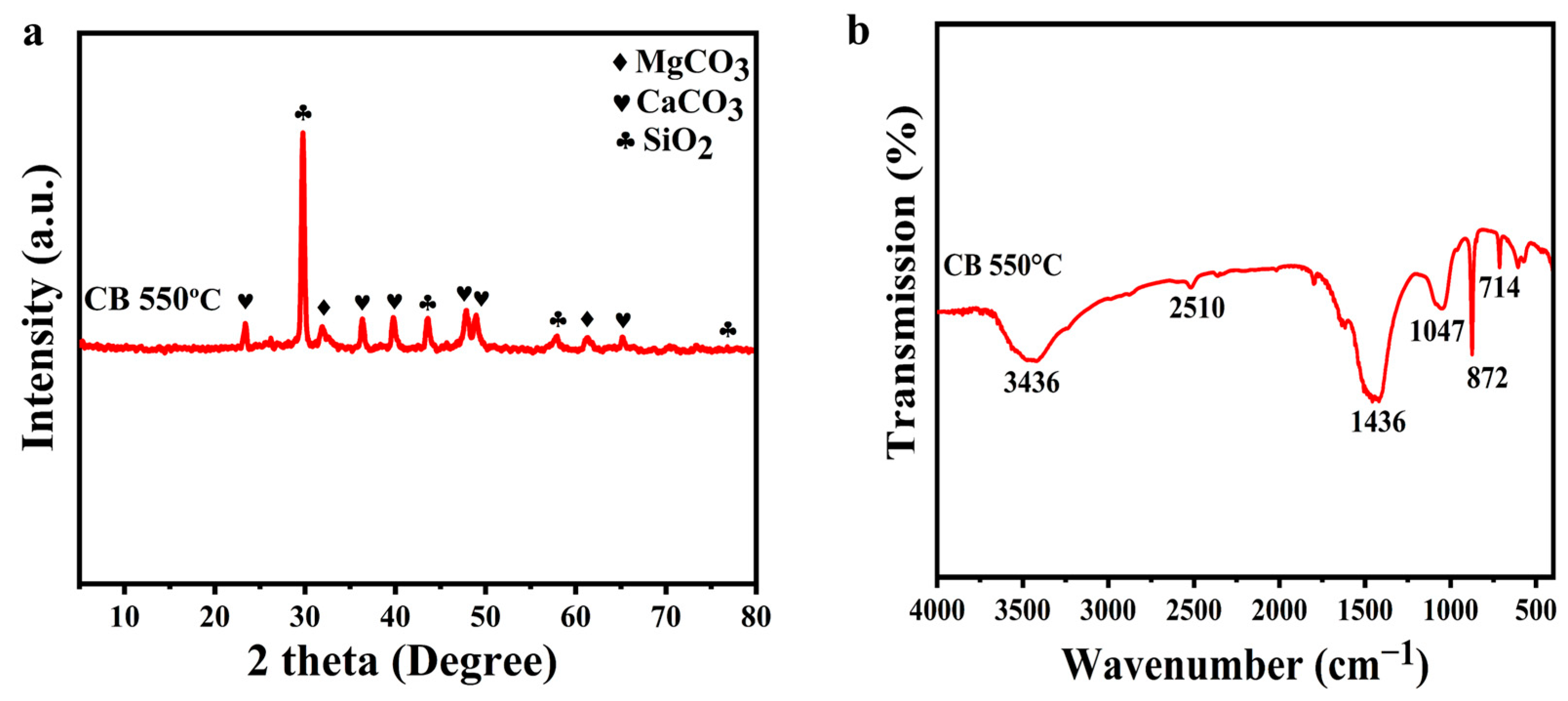
3.1. Biochar (CB) and Compost (CO) Key Characteristics
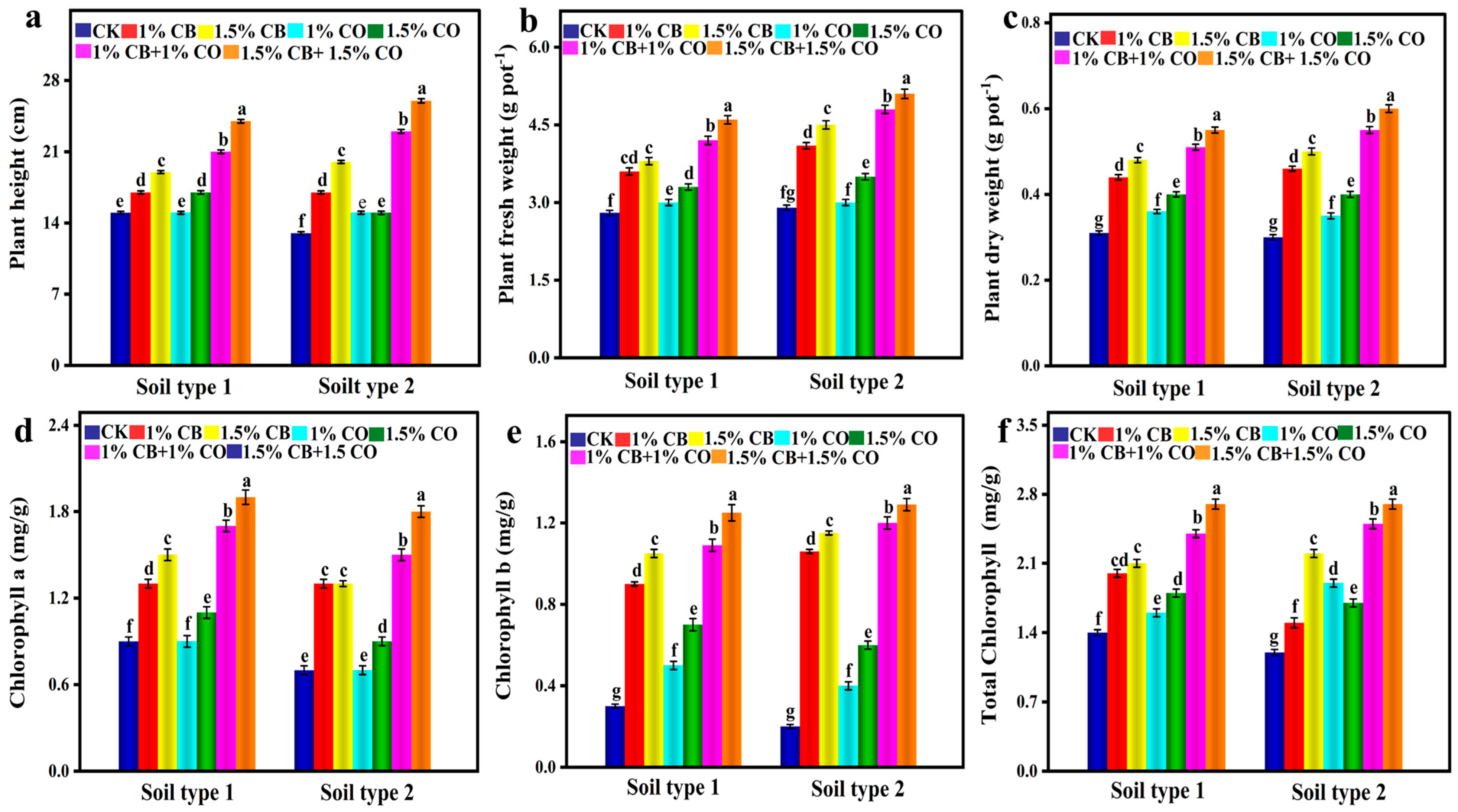
3.2. Effect of CB and CO on Development and Chlorophyll Contents of Plants
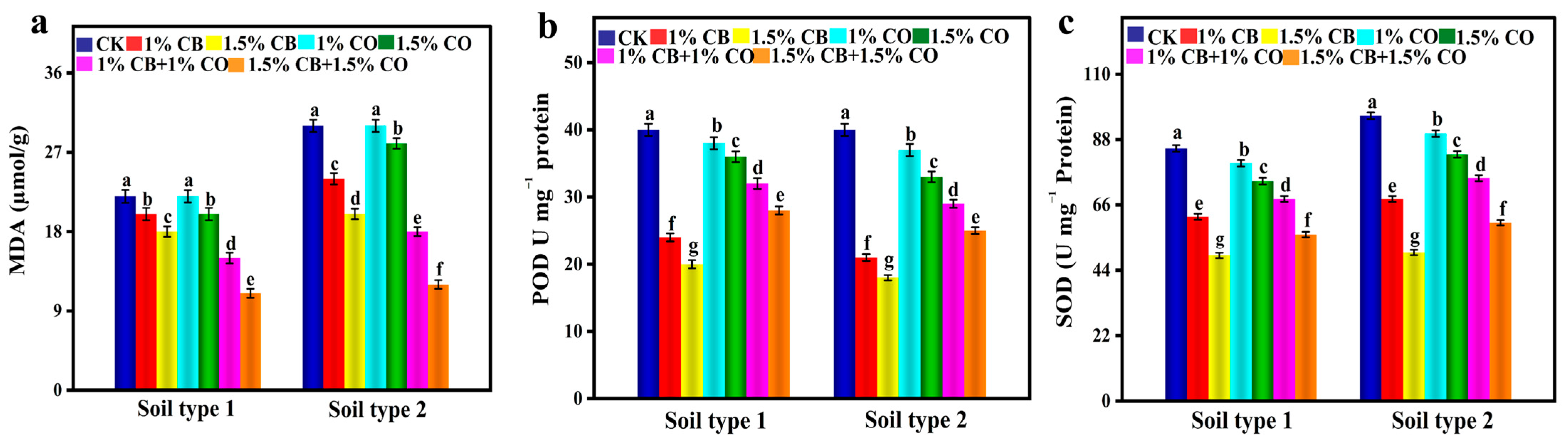
3.3. CB and CO Effect on Oxidant Activity and Antioxidant Enzymes of Spinach
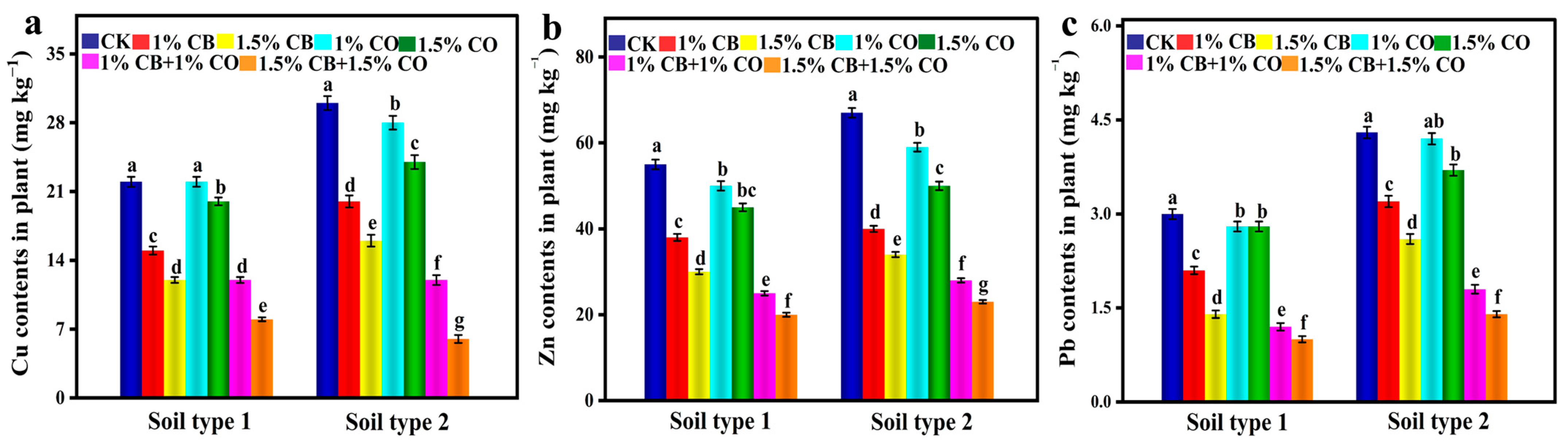
3.4. Plant Heavy Metal (HMs) Content
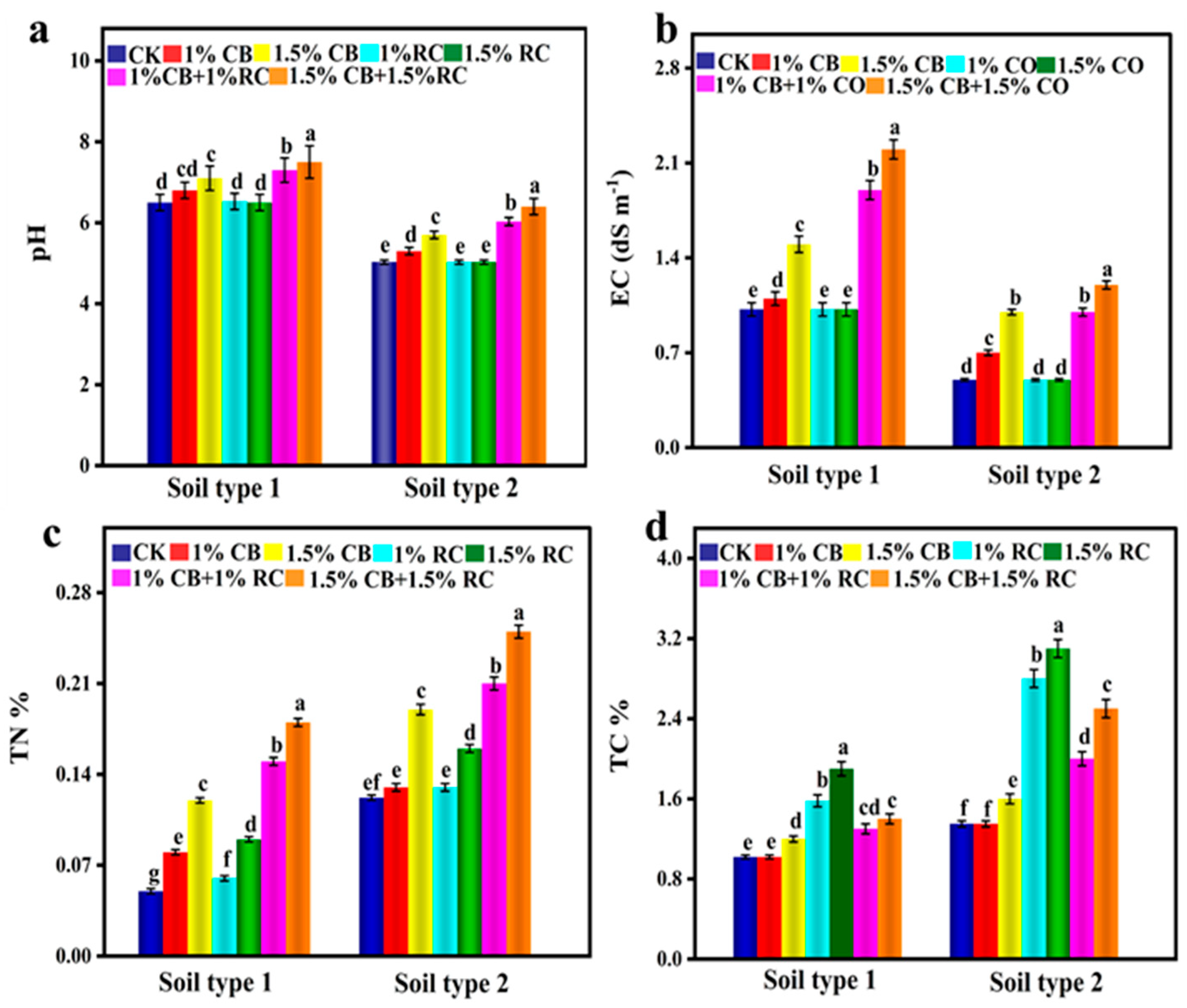
3.5. CB and CO Impact on Post-Harvest Soil Properties
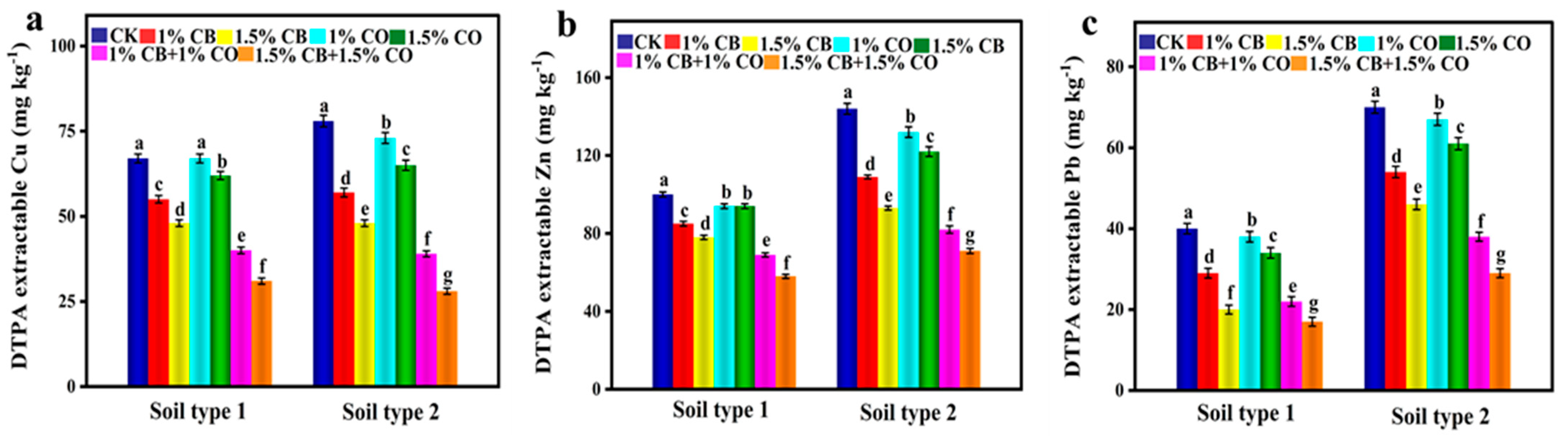
3.6. CB and CO Immobilized HMs (Cu, Zn, and Pb)
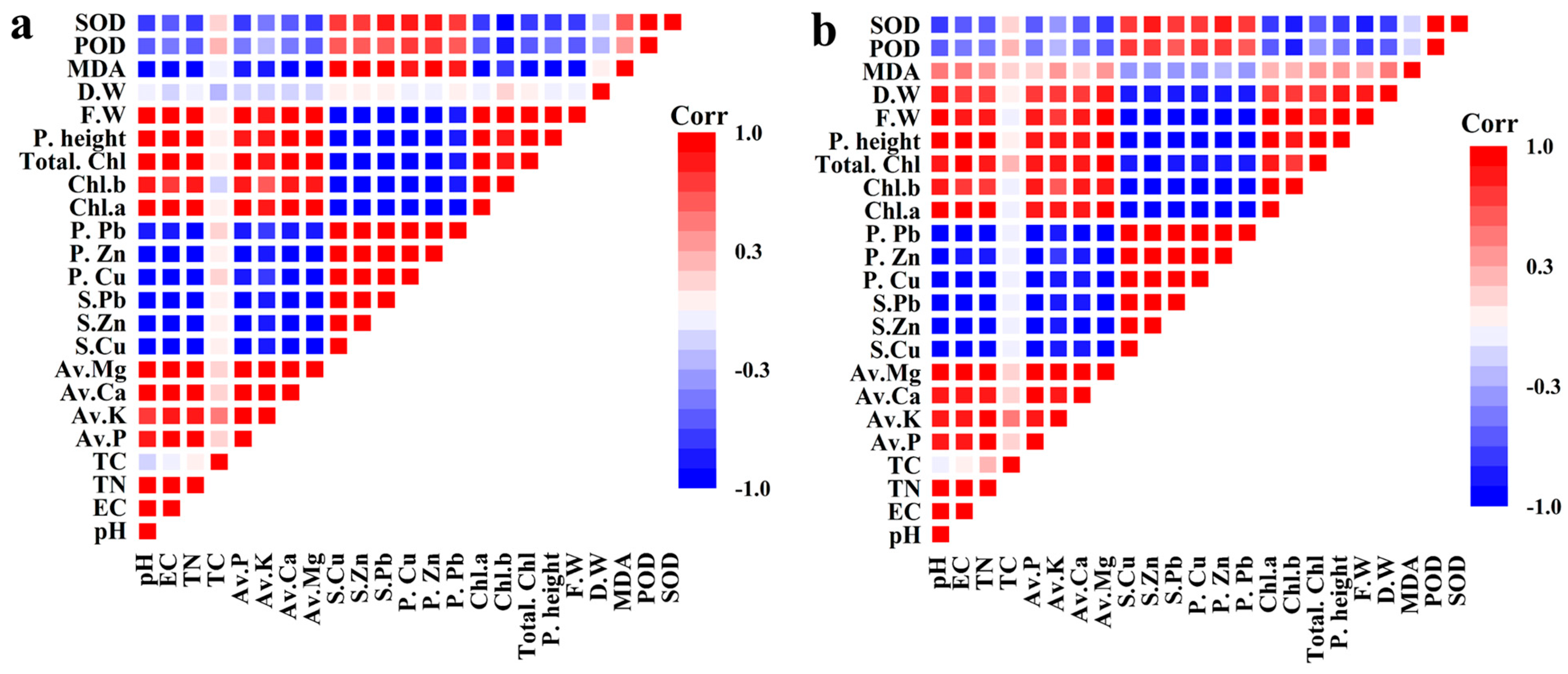
3.7. Analysis of Correlation for the Parameters Under Study
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qin, Y.; Tian, X.; Zhang, J.; Tu, Y.; Chen, C. Combined toxicity and ecological impacts of soil microplastics and heavy metals in rhizosphere microenvironments: A comprehensive review. J. Soils Sediments 2025, 25, 2551–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesa, F.; Kibacha, E.E.; Kamduli, Y.P.; Mng’ong’o, M.E. Lead and cadmium levels in selected leafy vegetables and their implications for public health, Mbeya, Tanzania. Food Humanit. 2025, 4, 100607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohiuddin, K.M.; Saha, P.; Hossain, M.T.; Nahar, K.; Ahmed, I.; Hoque, A.; Sultana, R.; Rahman, M.A. Assessment of Health Risk Due to Consumption of Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) Cultivated with Heavy Metal Polluted Water of Bhabadah Water-Logged Area of Bangladesh. Earth Syst. Environ. 2022, 6, 557–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aparicio, J.D.; Raimondo, E.E.; Saez, J.M.; Costa-Gutierrez, S.B.; Álvarez, A.; Benimeli, C.S.; Polti, M.A. The current approach to soil remediation: A review of physicochemical and biological technologies, and the potential of their strategic combination. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Q.; Luo, L.; Ma, Y.B.; Wei, D.P.; Hua, L. In situ immobilization remediation of heavy metals-contaminated soils: A review. Ying Yong Sheng Tai Xue Bao J. Appl. Ecol. 2009, 20, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar]
- Ghandali, M.V.; Safarzadeh, S.; Ghasemi-Fasaei, R.; Zeinali, S. Heavy metals immobilization and bioavailability in multi-metal contaminated soil under ryegrass cultivation as affected by ZnO and MnO2 nanoparticle-modified biochar. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 10684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khater, E.-S.; Bahnasawy, A.; Hamouda, R.; Sabahy, A.; Abbas, W.; Morsy, O.M. Biochar production under different pyrolysis temperatures with different types of agricultural wastes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curcio, I.; Gigli, R.; Mormile, F.; Mormile, C. A comprehensive review on biochar, with a particular focus on nano properties and applications. Nano Trends 2025, 10, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omokaro, G.O.; Kornev, K.P.; Nafula, Z.S.; Chikukula, A.A.; Osayogie, O.G.; Efeni, O.S. Biochar for sustainable soil management: Enhancing soil fertility, plant growth and climate resilience. Farming Syst. 2025, 3, 100167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyam, S.; Ahmed, S.; Joshi, S.J.; Sarma, H. Biochar as a Soil amendment: Implications for soil health, carbon sequestration, and climate resilience. Discov. Soil 2025, 2, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Xu, Z.; Hou, D.; Gao, B.; Cao, X.; Ok, Y.S.; Rinklebe, J.; Bolan, N.S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Waste-derived biochar for water pollution control and sustainable development. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2022, 3, 444–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Pei, P.; Sun, Y.; Xu, Y.; Jia, H. Performance and mechanism of As(III/V) removal from aqueous solution by novel positively charged animal-derived biochar. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 290, 120836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Kumar, V.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Datta, S.; Bhatia, D.; Dhiman, J.; Samuel, J.; Prasad, R.; Singh, J. A sustainable paradigm of sewage sludge biochar: Valorization, opportunities, challenges and future prospects. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 269, 122259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khedulkar, A.P.; Thamilselvan, A.; Doong, R.-A.; Pandit, B. Sustainable high-energy supercapacitors: Metal oxide-agricultural waste biochar composites paving the way for a greener future. J. Energy Storage 2024, 77, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalali, M.; Panam, Z.; Jalali, M.; Buss, W. The impact of feedstock type and pyrolysis parameters on the physical and chemical properties of biochars for sorption, agricultural and carbon sequestration applications: A meta-analysis. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2025, 192, 107271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chafik, Y.; Sena-Velez, M.; Henaut, H.; Missbah El Idrissi, M.; Carpin, S.; Bourgerie, S.; Morabito, D. Synergistic Effects of Compost and Biochar on Soil Health and Heavy Metal Stabilization in Contaminated Mine Soils. Agronomy 2025, 15, 1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimpong, K.A.; Abban-Baidoo, E.; Marschner, B. Can combined compost and biochar application improve the quality of a highly weathered coastal savanna soil? Heliyon 2021, 7, e07089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, T.T.K.; Tra, V.T.; Le, T.H.; Nguyen, N.-K.-Q.; Tran, C.-S.; Nguyen, P.-T.; Vo, T.-D.-H.; Thai, V.-N.; Bui, X.-T. Compost to improve sustainable soil cultivation and crop productivity. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, R.O.; Kissel, D.E. Comparison of soil pH methods on soils of North America. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messing, I.; Mingot Soriano, A.M.; Nimblad Svensson, D.; Barron, J. Variability and compatibility in determining soil particle size distribution by sieving, sedimentation and laser diffraction methods. Soil Tillage Res. 2024, 238, 105987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anju, M.; Banerjee, D.K. Associations of cadmium, zinc, and lead in soils from a lead and zinc mining area as studied by single and sequential extractions. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 176, 67–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castaldi, P.; Demurtas, D.; Silvetti, M.; Deiana, S.; Garau, G. Interaction of the water soluble fraction of MSW-composts with Pb (II) and Cu (II) ions. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 192, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Tang, X.; Guan, Z.; Reid, B.J.; Rajapaksha, A.U.; Ok, Y.S.; Sun, H. Biochar increased water holding capacity but accelerated organic carbon leaching from a sloping farmland soil in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orngu, O.; Nwaoha, I.; Unagwu, B.; Etim, V.E. Oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus) cultivation using sawdust and different organic manures. Asian Food Sci. J. 2021, 20, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, M.K.; Kang, M.W.; Aqeel, M.; Javed, W.; Noman, A.; Khalid, N.; Lee, S.S. Unveiling the detrimental effects of polylactic acid microplastics on rice seedlings and soil health. Chemosphere 2024, 355, 141771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthilkumar, M.; Amaresan, N.; Sankaranarayanan, A. Estimation of Malondialdehyde (MDA) by Thiobarbituric Acid (TBA) Assay. In Plant-Microbe Interactions: Laboratory Techniques; Senthilkumar, M., Amaresan, N., Sankaranarayanan, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2021; pp. 103–105. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, R.R.; Tasleem, M.; Singh, K.; Ahuja, S.; Sakhare, A.; Kumar, S.; Goswami, S.; Singh, S.; Singh, G.P.; Chinnusamy, V.; et al. NO protect the wheat embryo from oxidative damage by triggering the biochemical defence network and amylolytic activity. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2019, 24, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, S. Comparative antioxidant profiling and mineral estimation of Portulaca oleracea L. and Portulaca quadrifida L. Pharma Innov. J. 2023, 12, 6195–6205. [Google Scholar]
- Alia, N.; Sardar, K.; Said, M.; Salma, K.; Sadia, A.; Sadaf, S.; Toqeer, A.; Miklas, S. Toxicity and Bioaccumulation of Heavy Metals in Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) Grown in a Controlled Environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 7400–7416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, T.-X.; Lu, Z.-P.; Yue, M.; Li, B.-G.; Fu, A.-G.; Zhang, X.-D.; Li, Z.-H. Accumulation of livestock manure–derived heavy metals in the Hexi Corridor oasis agricultural alkaline soil and bioavailability to Chinese cabbage (Brassica pekinensis L.) after 4-year continuous application. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 341, 122969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibi, A.; Khan, H.; Hussain, S.; Arshad, M.; Wahab, F.; Usama, M.; Khan, K.; Akbal, F. Sustainable wastewater purification with crab shell-derived biochar: Advanced machine learning modeling & experimental analysis. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 390, 129900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Himanshu, M.; Verma, B.; Singh, R.; Lal, B.; Syed, A.; Elgorban, A.M.; Wong, L.S.; Srivastava, N. Evaluation of sustainability of fabrication process and characterization studies of activated carbon nanocatalyst from waste chestnut peels. J. Mol. Struct. 2025, 1321, 139810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remy, L.; Christophe, V.; Vuillet, C.; Covelli, A.; Couturaud, B.; Sudre, G.; Fleury, E.; Charlot, A. Thermosensitive Cellulosic Biohybrid Comb Copolymers by the Passerini-3CR: 2-Fold Functionalization and Subsequent Thermal Response. Biomacromolecules 2025, 26, 4637–4650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayan, M.B.; Jagadish, K.; Abhilash, M.R.; Namratha, K.; Srikantaswamy, S. Comparative study on the effects of surface area, conduction band and valence band positions on the photocatalytic activity of ZnO-MxOy heterostructures. J. Water Resour. Prot. 2019, 11, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; He, L.; Tu, G.; Yang, Z.; Yang, W.; Tang, J.; Cao, W.; Wang, H. Simultaneous immobilization of Pb, Cd and As in soil by hybrid iron-, sulfate-and phosphate-based bio-nanocomposite: Effectiveness, long-term stability and bioavailablity/bioaccessibility evaluation. Chemosphere 2021, 266, 128960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, M.; Neugschwandtner, R.W.; Konvalina, P.; Asadi, H.; Kopecký, M.; Amirahmadi, E. Comparative effects of biochar and compost applications on water holding capacity and crop yield of rice under evaporation stress: A two-years field study. Paddy Water Environ. 2023, 21, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Song, B.; Yan, H.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Q.; Ye, H.; Qin, L.; Lai, C. Biochar-compost as a new option for soil improvement: Application in various problem soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 870, 162024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Mishra, S.M.; Tiwari, A.; Tirkey, A.; Tiwari, A.; Dubey, R.; Alamri, S.; Pandey, S.K. A systematic study on synergistic effect of biochar-compost in improving soil function and reducing cadmium toxicity in Spinacia oleracea L. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Sarmah, A.K.; Bordoloi, S.; Bolan, S.; Padhye, L.P.; Van Zwieten, L.; Sooriyakumar, P.; Khan, B.A.; Ahmad, M.; Solaiman, Z.M.; et al. Soil acidification and the liming potential of biochar. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 317, 120632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pohland, A.C.; Bernát, G.; Geimer, S.; Schneider, D. Mg2+ limitation leads to a decrease in chlorophyll, resulting in an unbalanced photosynthetic apparatus in the cyanobacterium Synechocytis sp. PCC6803. Photosynth. Res. 2024, 162, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; You, L.-C.; Lyu, H.-H.; Liu, Y.-X.; He, L.-L.; Hu, Y.-D.; Luo, F.-C.; Yang, S.-M. Role of biochar–mineral composite amendment on the immobilization of heavy metals for Brassica chinensis from naturally contaminated soil. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, M.; Pan, J.; Mubeen, S.; Ma, W.; Luo, D.; Cao, S.; Saeed, W.; Liao, C.; Chen, P. Biochar Assisted Phyto-stabilization of Cd and Pb Contaminated Mining Soil Using Kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.). J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2023, 23, 4955–4970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.J.; Duan, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiao, J.; Cheng, P.; Yang, L.; Wei, W.; Shen, Q.; Ji, P.; Yang, Y.; et al. Antioxidant Defense System in Plants: Reactive Oxygen Species Production, Signaling, and Scavenging During Abiotic Stress-Induced Oxidative Damage. Horticulturae 2025, 11, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Qi, J.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; He, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, A. Immobilization of heavy metals in vegetable-growing soils using nano zero-valent iron modified attapulgite clay. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 686, 476–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medyńska-Juraszek, A.; Bednik, M.; Chohura, P. Assessing the influence of compost and biochar amendments on the mobility and uptake of heavy metals by green leafy vegetables. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 7861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skic, K.; Adamczuk, A.; Gryta, A.; Boguta, P.; Tóth, T.; Jozefaciuk, G. Surface areas and adsorption energies of biochars estimated from nitrogen and water vapour adsorption isotherms. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 30362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraf, M.; Janeeshma, E.; Arif, N.; Yadav, V.; Zahra, N.; Bouzroud, S.; Mirmazloum, I.; Yadi, R.; Hasanuzzaman, M. Biochar for the Mitigation of Metal/Metalloid Stress in Plants. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2024, 43, 3303–3319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leng, L.; Xiong, Q.; Yang, L.; Li, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, S.; Li, H.; Huang, H. An overview on engineering the surface area and porosity of biochar. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 763, 144204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrow, N.J.; Hartemink, A.E. The effects of pH on nutrient availability depend on both soils and plants. Plant Soil 2023, 487, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh Yadav, S.P.; Bhandari, S.; Bhatta, D.; Poudel, A.; Bhattarai, S.; Yadav, P.; Ghimire, N.; Paudel, P.; Paudel, P.; Shrestha, J.; et al. Biochar application: A sustainable approach to improve soil health. J. Agric. Food Res. 2023, 11, 100498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, X.; Huang, D.; Zhi, Y.; Li, Y.; Dong, D.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, H.; Tang, Y.; et al. Effects of biochar on soil properties as well as available and TCLP-extractable Cu contents: A global meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 32853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, W.; Mehmood, S.; Mahmood, M.; Ali, S.; Núñez-Delgado, A.; Li, W. Simultaneous immobilization of lead and arsenic and improved phosphorus availability in contaminated soil using biochar composite modified with hydroxyapatite and oxidation: Findings from a pot experiment. Environ. Res. 2023, 235, 116640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, E.A.; El-Sherbini, M.A.A.; Selim, E.-M.M. Effects of biochar on soil properties, heavy metal availability and uptake, and growth of summer squash grown in metal-contaminated soil. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 301, 111097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Han, H.; Gao, C.; Wang, Y.; Dong, B.; Xu, Z. Organic amendments for in situ immobilization of heavy metals in soil: A review. Chemosphere 2023, 335, 139088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Luo, G.; Yan, B.; Su, N.; Zeng, P.; Kang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xie, G. Dissolved organic matter evolution can reflect the maturity of compost: Insight into common composting technology and material composition. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.-X.; Liu, H.-T.; Wu, S.-B. Humic substances developed during organic waste composting: Formation mechanisms, structural properties, and agronomic functions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 662, 501–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.; Malik, Z.; Parveen, A.; Zong, Y.; Abbasi, G.H.; Rafiq, M.T.; Shaaban, M.; Mustafa, A.; Bashir, S.; Rafay, M.; et al. Biochar alleviates Cd phytotoxicity by minimizing bioavailability and oxidative stress in pak choi (Brassica chinensis L.) cultivated in Cd-polluted soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, G.; Fan, Q.; Sun, J.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Gao, B.; Yan, J. Characteristics of organo-mineral complexes in contaminated soils with long-term biochar application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 384, 121265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.A.; Naveed, M.; Ashraf, S.; Mustafa, A.; Ali, Q.; Rafique, M.; Alamri, S.; Siddiqui, M.H. Performance of Zea mays L. cultivars in tannery polluted soils: Management of chromium phytotoxicity through the application of biochar and compost. Physiol. Plant. 2021, 173, 129–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, F.; Malik, Z.; Masood, N.; Rizwan, M.; Hamoud, Y.A.; Shaghaleh, H.; Noreen, S.; Yong, J.W.H. Synergistic effects of biochar and abscisic acid improved root morphology, antioxidant defense system and decreased availability and bioaccumulation of cadmium in Triticum aestivum (L.) under cadmium stress. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 38, 104121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeel, M.; Khalid, N.; Tufail, A.; Ahmad, R.Z.; Akhter, M.S.; Luqman, M.; Javed, M.T.; Irshad, M.K.; Alamri, S.; Hashem, M.; et al. Elucidating the distinct interactive impact of cadmium and nickel on growth, photosynthesis, metal-homeostasis, and yield responses of mung bean (Vigna radiata L.) varieties. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 27376–27390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Soils Type | Treatments | Bioaccumulation Factor (BF) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Pb | ||
| Soil type 1 | Control | 0.32 | 0.55 | 0.075 |
| 1% CB | 0.27 | 0.44 | 0.072 | |
| 1.5% CB | 0.25 | 0.40 | 0.070 | |
| 1% CO | 0.32 | 0.53 | 0.073 | |
| 1.5% CO | 0.32 | 0.47 | 0.072 | |
| 1% CB +1% CO | 0.30 | 0.36 | 0.054 | |
| 1.5% CB +1.5% CO | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.052 | |
| Soil type 2 | Control | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.061 |
| 1% CB | 0.35 | 0.36 | 0.059 | |
| 1.5% CB | 0.33 | 0.36 | 0.056 | |
| 1% CO | 0.38 | 0.44 | 0.061 | |
| 1.5% CO | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.060 | |
| 1% CB + 1% CO | 0.30 | 0.34 | 0.052 | |
| 1.5% CB + 1.5% CO | 0.21 | 0.32 | 0.048 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aslam, F.; Jamait, A.; Wang, S.; Hussain, M.M.; Wang, X. Crab Shell Biochar and Compost Synergistically Mitigate Heavy Metal Toxicity in Soil–Plant System. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102427
Aslam F, Jamait A, Wang S, Hussain MM, Wang X. Crab Shell Biochar and Compost Synergistically Mitigate Heavy Metal Toxicity in Soil–Plant System. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102427
Chicago/Turabian StyleAslam, Fozia, Arbab Jamait, Shengsen Wang, Muhammad Mahroz Hussain, and Xiaozhi Wang. 2025. "Crab Shell Biochar and Compost Synergistically Mitigate Heavy Metal Toxicity in Soil–Plant System" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102427
APA StyleAslam, F., Jamait, A., Wang, S., Hussain, M. M., & Wang, X. (2025). Crab Shell Biochar and Compost Synergistically Mitigate Heavy Metal Toxicity in Soil–Plant System. Agronomy, 15(10), 2427. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102427








