Genome-Wide Analysis of NLP Genes in Peanut Reveals Significant Roles of AhNINa and AhNINb in Root Nodule Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
2.2. Root Nodule Induction
2.3. Hairy Root Transformation
2.4. Identification of the AhNIN and AhNLP Genes in Peanut
2.5. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Phylogenetic Analysis of the NIN and NLP Genes
2.6. Gene Structure, Chromosome Location, and Conserved Motif Detection
2.7. RNA Extraction and Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
2.8. Vector Construction, Subcellular Localization, and Promoter-GUS Analysis
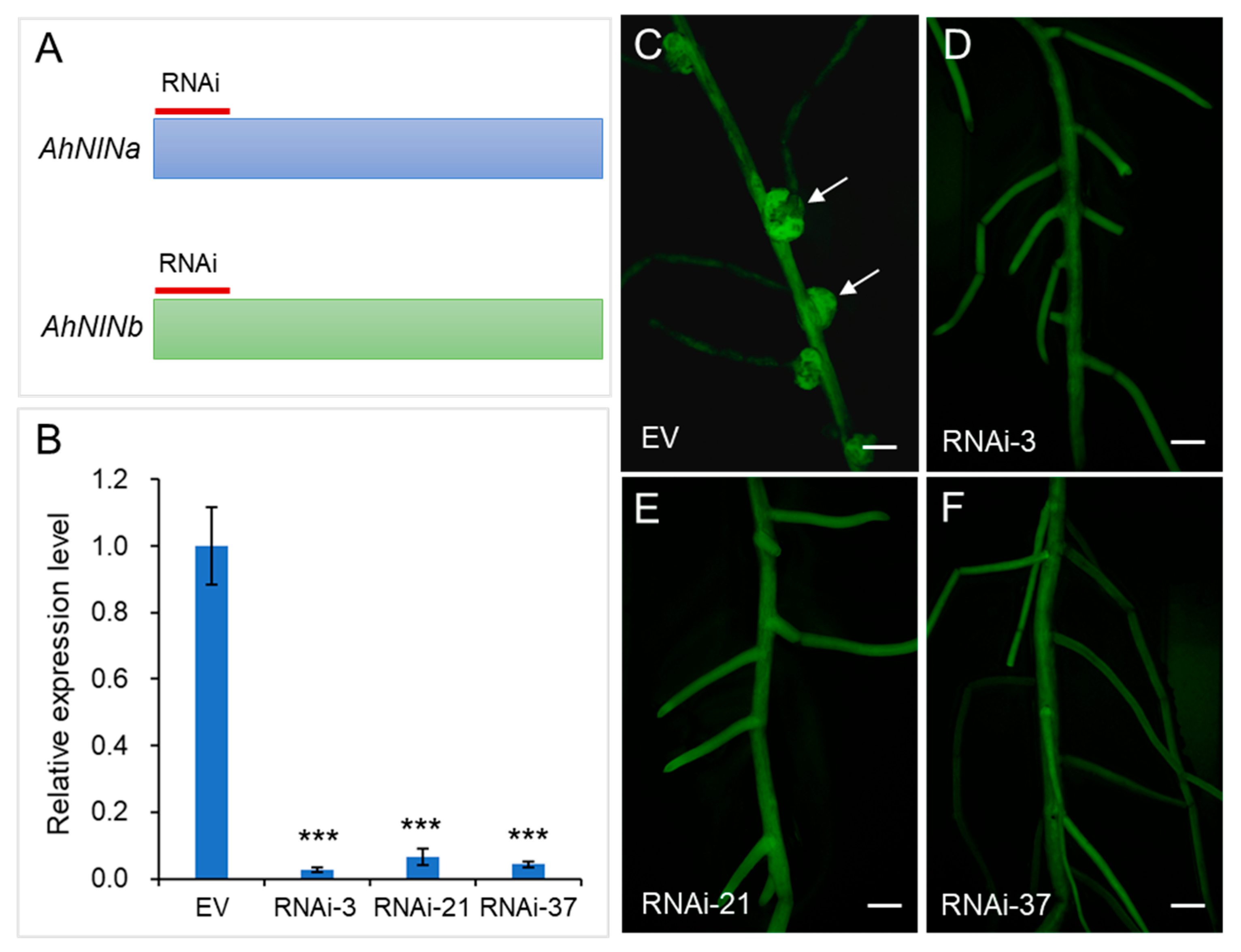
2.9. RNAi Analysis
2.10. Transcriptional Activation Activity Analysis and Yeast Cell Transformation
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Genome-Wide Identification of NLP Genes in Peanut
3.2. Phylogenetic Analysis and Chromosomal Locations of the AhNIN and AhNLP Genes
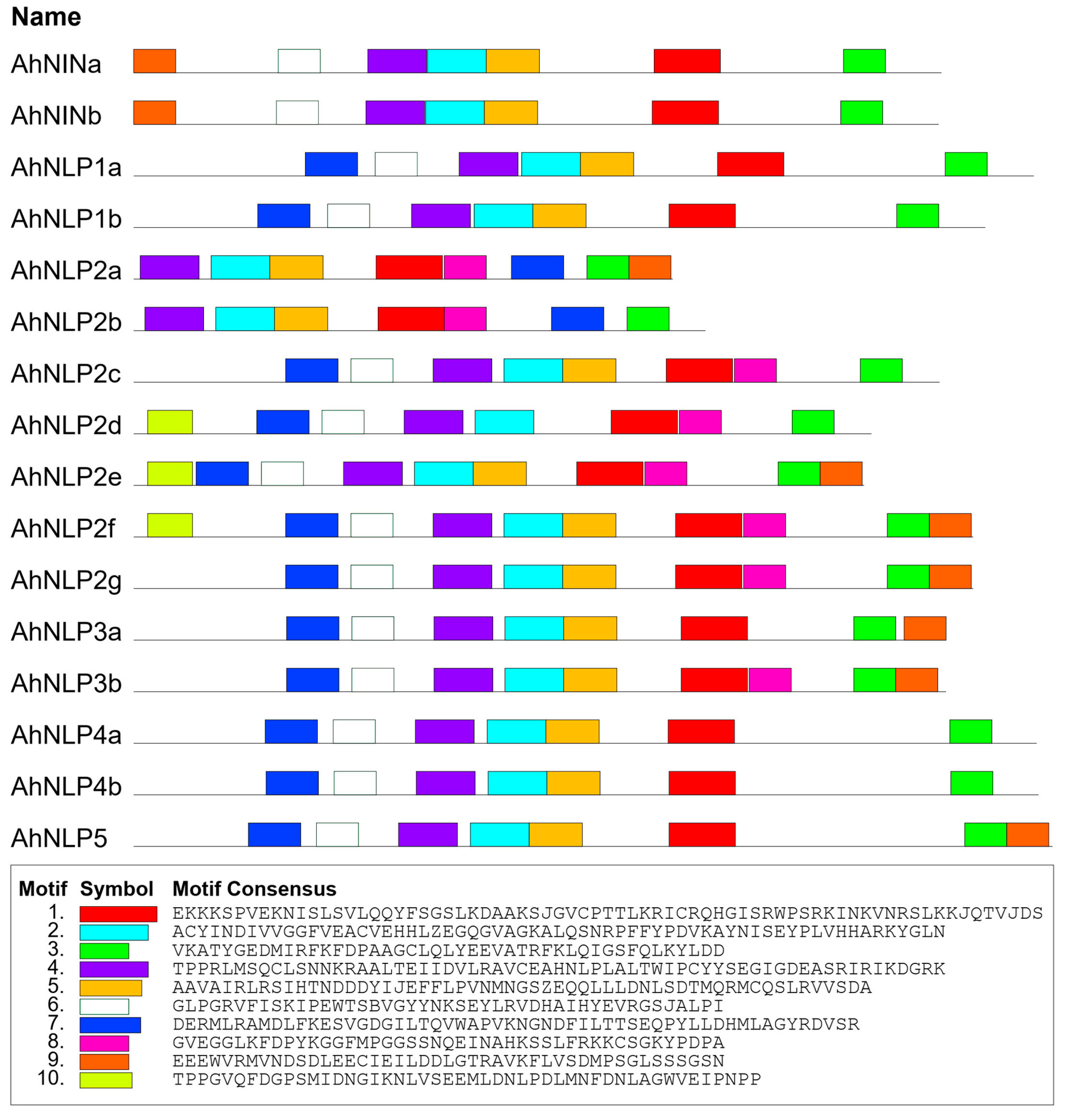
3.3. Conserved Motifs and Domains in AhNIN and AhNLP Proteins
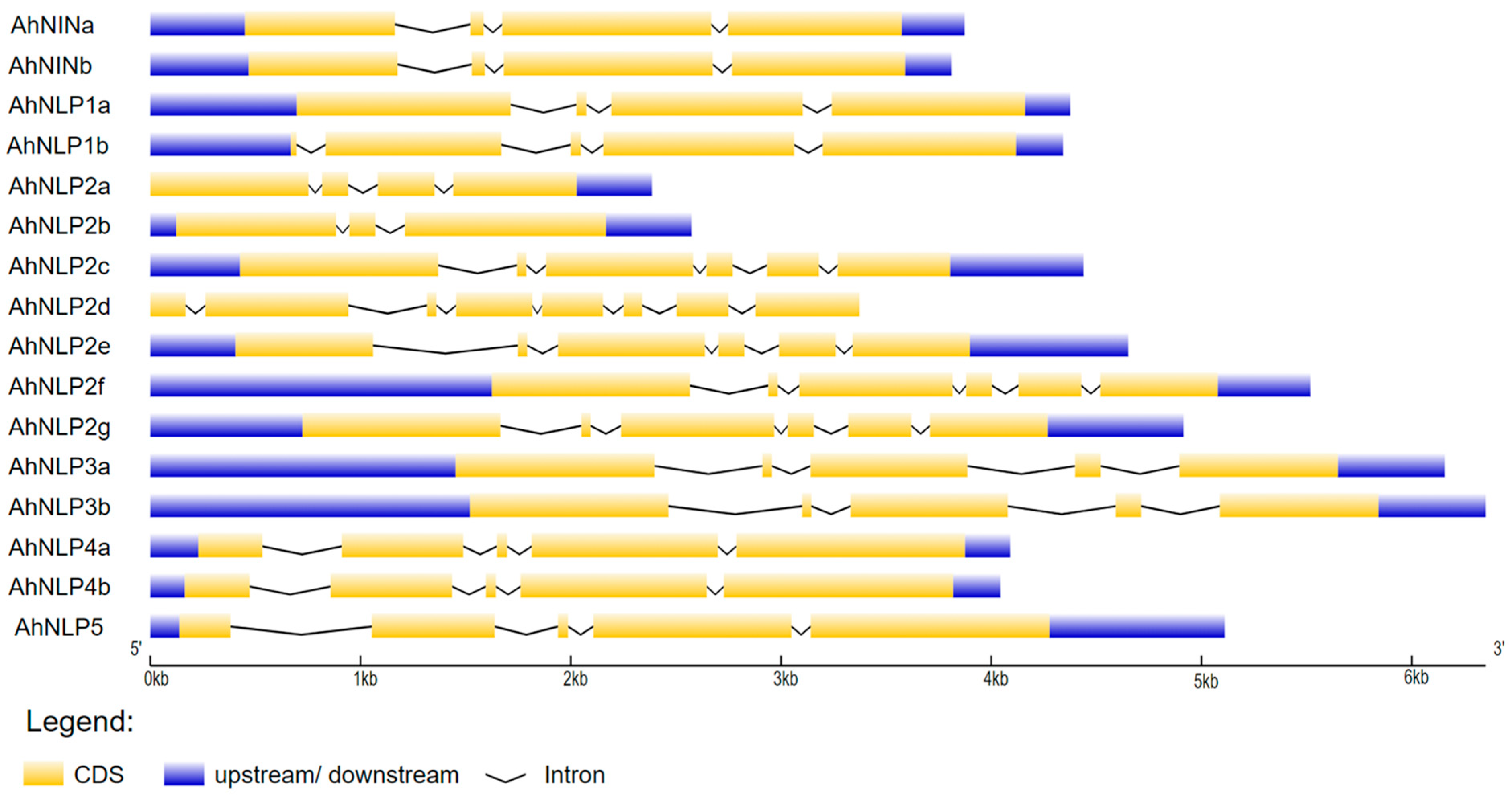
3.4. Gene Structure of the AhNIN and AhNLP Genes
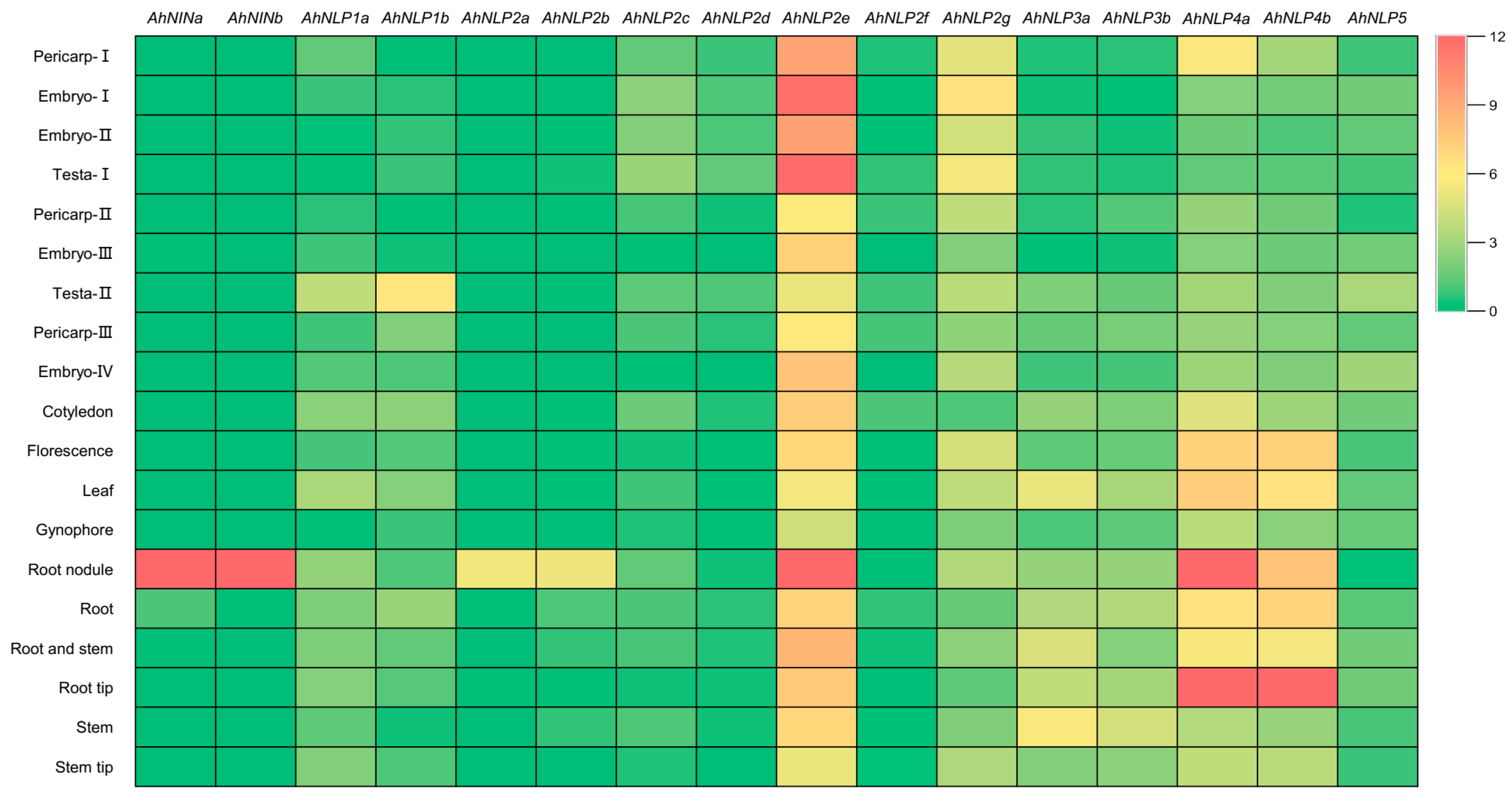
3.5. Expression Profiles of the AhNIN and AhNLP Genes
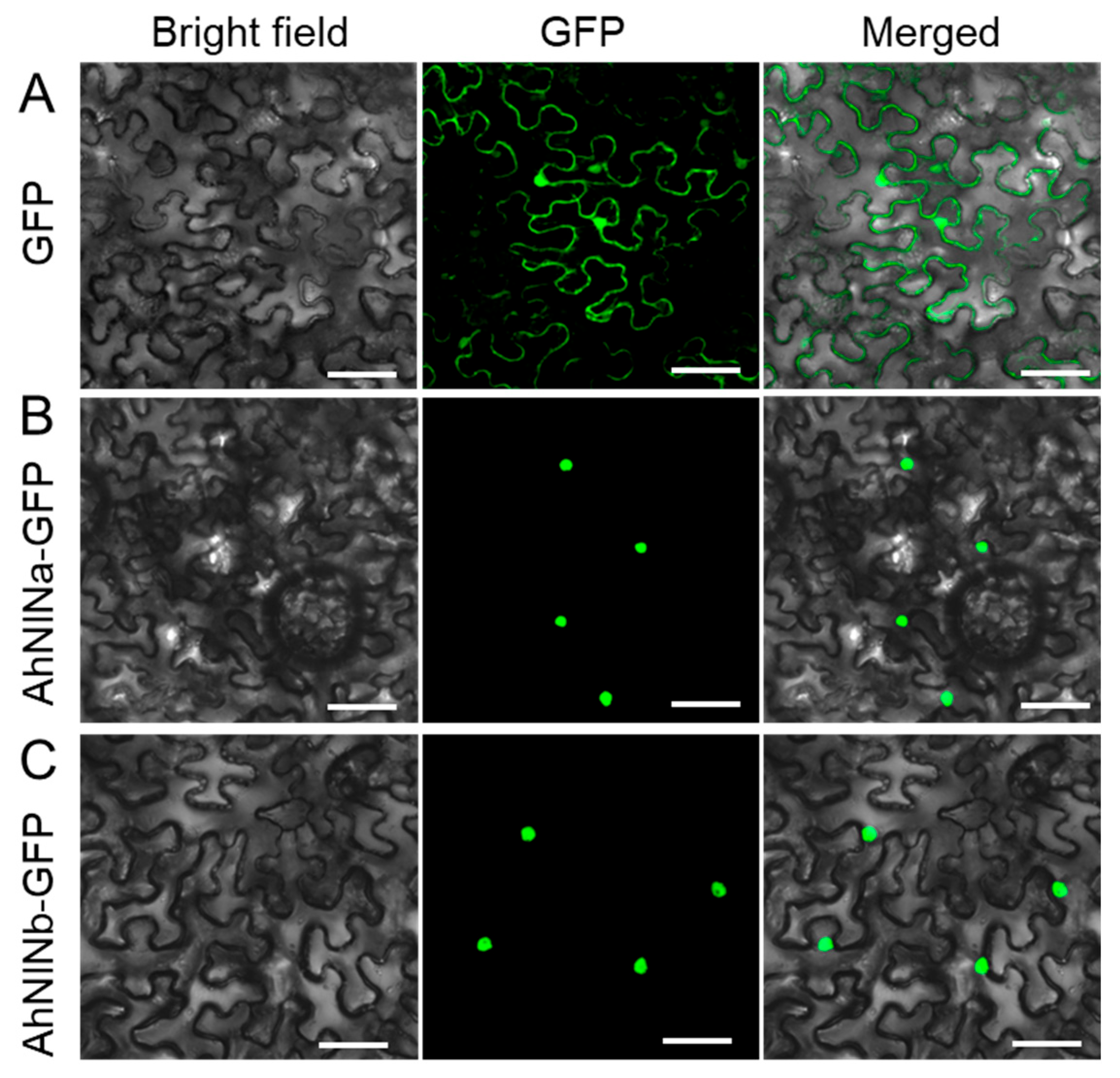
3.6. Nodule-Specific Expression Patterns of AhNINa and AhNINb
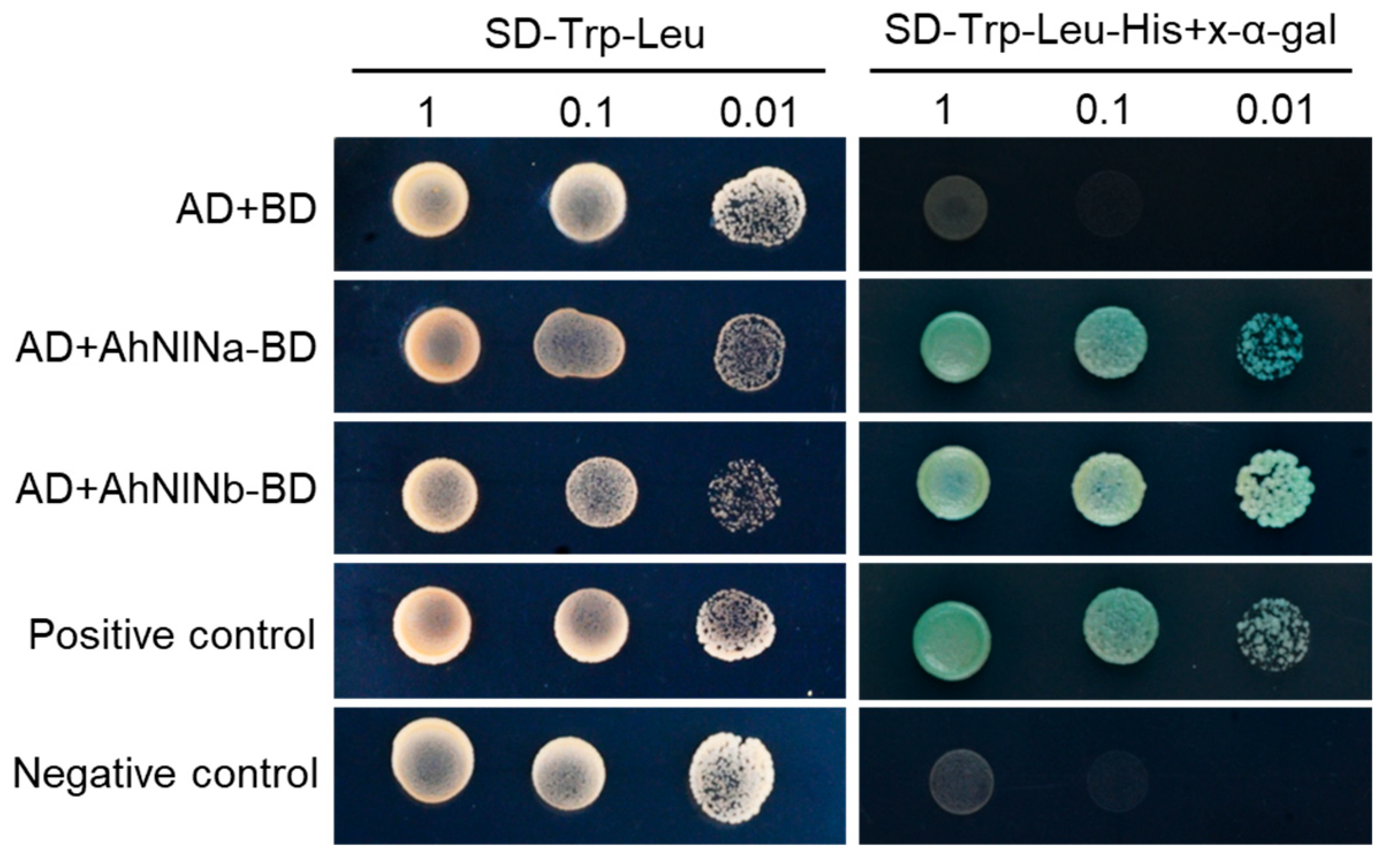
3.7. Both AhNINa and AhNINb Act as Transcriptional Activators
3.8. AhNINa and AhNINb Are Required for Nodule Formation in Peanut
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NIN | NODULE INCEPTION |
| NRE | Nitrate-responsive cis-element |
| ANR1 | ARABIDOPSIS NITRATE REGULATED 1 |
| NRT2 | NITRATE TRANSPORTER 2 |
| LBD37 | LATERAL ORGAN BOUNDARY DOMAIN 37 |
| AtTCP20 | TEOSINTE BRANCHED1/CYCLOIDEA/PROLIFERATING CELL FACTOR1-20 |
| CYP707A2 | CYTOCHROME P450 MONOOXYGENASE 707A2 |
| NFR5 | NOD FACTOR RECEPTOR 5 |
| CCaMK | Ca2+/CALMODULIN DEPENDENT KINASE |
| HK1 | HISTIDINE KINASE 1 |
| NSP2 | NODULATION SIGNALING PATHWAY 2 |
| NIR | NITRITE REDUCTASE |
| RNAi | RNA interference |
References
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, N.M. Nitrate: Nutrient and signal for plant growth. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 859–868. [Google Scholar][Green Version]
- Mueller, N.D.; West, P.C.; Gerber, J.S.; MacDonald, G.K.; Polasky, S.; Foley, J.A. A tradeoff frontier for global nitrogen use and cereal production. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 054002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Lee, Z.; Jeong, E.; Kim, S.; Seo, J.S.; Um, T.; Shim, J.S. Signaling pathways underlying nitrogen transport and metabolism in plants. BMB Rep. 2023, 56, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Bisseling, T. Evolution of NIN and NIN-like genes in relation to nodule symbiosis. Genes 2020, 11, 777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Luo, J. Evolutionary analyses of NIN-like proteins in plants and their roles in nitrate signaling. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 3753–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauser, L.; Roussis, A.; Stiller, J.; Stougaard, J. A plant regulator controlling development of symbiotic root nodules. Nature 1999, 402, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Sun, J.; Li, X.; Guan, Y.; Xie, F. Asymmetric redundancy of soybean Nodule Inception (NIN) genes in root nodule symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 2022, 188, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsh, J.F.; Rakocevic, A.; Mitra, R.M.; Brocard, L.; Sun, J.; Eschstruth, A.; Long, S.R.; Schultze, M.; Ratet, P.; Oldroyd, G.E. Medicago truncatula NIN is essential for rhizobial-independent nodule organogenesis induced by autoactive calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Plant Physiol. 2007, 144, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borisov, A.Y.; Madsen, L.H.; Tsyganov, V.E.; Umehara, Y.; Voroshilova, V.A.; Batagov, A.O.; Sandal, N.; Mortensen, A.; Schauser, L.; Ellis, N.; et al. The sym35 gene required for root nodule development in pea is an ortholog of Nin from Lotus japonicus. Plant Physiol. 2003, 131, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.M.; Schinke, A.L.; Brooks, M.D.; Pasquino, A.; Leonelli, L.; Varala, K.; Safi, A.; Krouk, G.; Krapp, A.; Coruzzi, G.M. Transient genome-wide interactions of the master transcription factor NLP7 initiate a rapid nitrogen-response cascade. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. Arabidopsis NIN-like transcription factors have a central role in nitrate signalling. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chardin, C.; Girin, T.; Roudier, F.; Meyer, C.; Krapp, A. The plant RWP-RK transcription factors: Key regulators of nitrogen responses and of gametophyte development. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 5577–5587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Yuan, Y.; Dong, L.; Cui, G. Genome-wide investigation of NLP gene family members in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.): Evolution and expression profiles during development and stress. BMC Genom. 2023, 24, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Chang, W.; Fan, Y.; Sun, W.; Qu, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Tang, Z.; Li, J.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of NODULE-INCEPTION-Like Protein (NLP) family genes in Brassica napus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jagadhesan, B.; Sathee, L.; Meena, H.S.; Jha, S.K.; Chinnusamy, V.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S. Genome wide analysis of NLP transcription factors reveals their role in nitrogen stress tolerance of rice. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. An NLP-binding site in the 3′ flanking region of the nitrate reductase gene confers nitrate-inducible expression in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2013, 59, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaings, L.; Camargo, A.; Pocholle, D.; Gaudon, V.; Texier, Y.; Boutet-Mercey, S.; Taconnat, L.; Renou, J.P.; Daniel-Vedele, F.; Fernandez, E.; et al. The nodule inception-like protein 7 modulates nitrate sensing and metabolism in arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 57, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchive, C.; Roudier, F.; Castaings, L.; Bréhaut, V.; Blondet, E.; Colot, V.; Meyer, C.; Krapp, A. Nuclear retention of the transcription factor NLP7 orchestrates the early response to nitrate in plants. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.H.; Wu, J.; Tang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, S.M.; Wang, Y.P.; Zhu, Q.S.; Li, S.G.; Xiang, C.B. Overexpression of Arabidopsis NLP7 improves plant growth under both nitrogen-limiting and -sufficient conditions by enhancing nitrogen and carbon assimilation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, P.; Ripoll, J.J.; Wang, R.; Vuong, L.; Bailey-Steinitz, L.J.; Ye, D.; Crawford, N.M. Interacting TCP and NLP transcription factors control plant responses to nitrate availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 2419–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Easwaran, V.; Chau, V.; Okamoto, M.; Ierullo, M.; Kimura, M.; Endo, A.; Yano, R.; Pasha, A.; Gong, Y.; et al. NIN-like protein 8 is a master regulator of nitrate-promoted seed germination in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Okitsu, T.; Yanagisawa, S. Nitrate-responsive NIN-like protein transcription factors perform unique and redundant roles in Arabidopsis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 5735–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, D.J. Infection and invasion of roots by symbiotic, nitrogen-fixing rhizobia during nodulation of temperate legumes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 280–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delamuta, J.R.; Ribeiro, R.A.; Menna, P.; Bangel, E.V.; Hungria, M. Multilocus sequence analysis (MLSA) of bradyrhizobium strains: Revealing high diversity of tropical diazotrophic symbiotic bacteria. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2012, 43, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.Y.; Gu, J.; Wang, E.T.; Ma, X.X.; Kang, S.T.; Huang, L.Z.; Cao, X.P.; Li, L.B.; Wu, Y.L. Wild peanut Arachis duranensis are nodulated by diverse and novel bradyrhizobium species in acid soils. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 37, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, V.; Ibañez, F.; Tonelli, M.L.; Valetti, L.; Anzuay, M.S.; Fabra, A. Phenotypic and phylogenetic characterization of native peanut bradyrhizobium isolates obtained from córdoba, argentina. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 34, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horta Araújo, N.; Nouwen, N.; Arrighi, J.F. Nodulating another way: What can we learn from lateral root base nodulation in legumes? J. Exp. Bot. 2024, 75, 3214–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Kumar, R.; Kumar, A.; Ibañez, F.; Wang, J.; Guo, B.; Sudini, H.K.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; DasGupta, M.; et al. Molecular basis of root nodule symbiosis between bradyrhizobium and ‘crack-entry’ legume groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plants 2020, 9, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, H.; Luo, Z.; Peng, Z.; Wang, J. The application of CRISPR/Cas9 in hairy roots to explore the functions of AhNFR1 and AhNFR5 genes during peanut nodulation. BMC Plant Biol. 2020, 20, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Chen, H.; Tan, L.; Shu, H.; Varshney, R.K.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Luo, Z.; Chitikineni, A.; Wang, L.; et al. Natural polymorphisms in a pair of NSP2 homoeologs can cause loss of nodulation in peanut. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 1104–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, A.; DasGupta, M. Silencing of putative Cytokinin Receptor Histidine Kinase1 inhibits both inception and differentiation of root nodules in Arachis hypogaea. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2018, 31, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kereszt, A.; Li, D.; Indrasumunar, A.; Nguyen, C.D.; Nontachaiyapoom, S.; Kinkema, M.; Gresshoff, P.M. Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of soybean to study root biology. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, D.S.; Bhatnagar-Mathur, P.; Cindhuri, K.S.; Sharma, K.K. Evaluation and validation of reference genes for normalization of quantitative real-time pcr based gene expression studies in peanut. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e78555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earley, K.W.; Haag, J.R.; Pontes, O.; Opper, K.; Juehne, T.; Song, K.; Pikaard, C.S. Gateway-compatible vectors for plant functional genomics and proteomics. Plant J. 2006, 45, 616–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Inzé, D.; Depicker, A. Gateway vectors for agrobacterium-mediated plant transformation. Trends Plant Sci. 2002, 7, 193–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, M.; Yanagisawa, S. The role of protein-protein interactions mediated by the PB1 domain of NLP transcription factors in nitrate-inducible gene expression. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakuraba, Y.; Zhuo, M.; Yanagisawa, S. RWP-RK domain-containing transcription factors in the Viridiplantae: Biology and phylogenetic relationships. J. Exp. Bot. 2022, 73, 4323–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.S.; Li, X.; Luo, Z.; Mysore, K.S.; Wen, J.; Xie, F. NIN interacts with NLPs to mediate nitrate inhibition of nodulation in Medicago truncatula. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Zhou, L.; Liang, S.; Bao, H.; Zhao, H. Genome-wide analysis of maize NLP transcription factor family revealed the roles in nitrogen response. Plant Growth Regul. 2018, 84, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Batra, R.; Gahlaut, V.; Gautam, T.; Kumar, S.; Sharma, M.; Tyagi, S.; Singh, K.P.; Balyan, H.S.; Pandey, R.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of gene family for RWP-RK transcription factors in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0208409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Monyo, E.; Ozias-Akins, P.; Liang, X.; Guimarães, P.; Nigam, S.N.; Upadhyaya, H.D.; Janila, P.; Zhang, X.; Guo, B.; et al. Advances in Arachis genomics for peanut improvement. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 639–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertioli, D.J.; Jenkins, J.; Clevenger, J.; Dudchenko, O.; Gao, D.; Seijo, G.; Leal-Bertioli, S.C.M.; Ren, L.; Farmer, A.D.; Pandey, M.K.; et al. The genome sequence of segmental allotetraploid peanut Arachis hypogaea. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sámano, M.L.; Nanjareddy, K.; Arthikala, M.K. NIN-like proteins (NLPs) as crucial nitrate sensors: An overview of their roles in nitrogen signaling, symbiosis, abiotic stress, and beyond. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2024, 30, 1209–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, D.; Nambara, E. Conserved and unique functions of NIN-like proteins in nitrate sensing and signaling. Plant Sci. 2023, 336, 111842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Su, S.X.; Wang, T.; Peng, G.H.; He, L.; Long, C.; Li, W. Identification and expression characteristics of NLP (NIN-like protein) gene family in pepper (Capsicum annuum L.). Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 6655–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, J.; Wen, X.; Deng, C.; Yang, X.; Dai, S. Genome-wide identification and characterization analysis of RWP-RK family genes reveal their role in flowering time of Chrysanthemum lavandulifolium. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S. Structure and regulatory function of plant transcription factors. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2001, 46, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheible, W.R.; Morcuende, R.; Czechowski, T.; Fritz, C.; Osuna, D.; Palacios-Rojas, N.; Schindelasch, D.; Thimm, O.; Udvardi, M.K.; Stitt, M. Genome-wide reprogramming of primary and secondary metabolism, protein synthesis, cellular growth processes, and the regulatory infrastructure of Arabidopsis in response to nitrogen. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2483–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sun, C.; Gu, R.; Mi, G.; Yuan, L. Phylogenetic, expression and functional characterizations of the maize NLP transcription factor family reveal a role in nitrate assimilation and signaling. Physiol. Plant. 2018. ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Guo, C.; Lou, S.; Jin, S.; Zeng, W.; Guo, Y.; Fang, J.; Xu, Z.; Zuo, Z.; Ma, L. Functional analyses unveil the involvement of moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis) group I and II NIN-LIKE PROTEINS in nitrate signaling regulation. Plant Sci. 2021, 306, 110862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lan, L.; Jin, Y.; Yu, N.; Wang, D.; Wang, E. Mechanisms underlying legume-rhizobium symbioses. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 244–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Liu, W.; Nandety, R.S.; Crook, A.; Mysore, K.S.; Pislariu, C.I.; Frugoli, J.; Dickstein, R.; Udvardi, M.K. Celebrating 20 years of genetic discoveries in legume nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 15–41. [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson, B.J.; Mens, C.; Hastwell, A.H.; Zhang, M.; Su, H.; Jones, C.H.; Chu, X.; Gresshoff, P.M. Legume nodulation: The host controls the party. Plant Cell Environ. 2019, 42, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Liu, J.; Zhu, H. Genetic and molecular mechanisms underlying symbiotic specificity in legume-rhizobium interactions. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Liu, H.; Xie, F. Cellular and molecular basis of symbiotic nodule development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2023, 76, 102478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griesmann, M.; Chang, Y.; Liu, X.; Song, Y.; Haberer, G.; Crook, M.B.; Billault-Penneteau, B.; Lauressergues, D.; Keller, J.; Imanishi, L.; et al. Phylogenomics reveals multiple losses of nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis. Science 2018, 361, eaat1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Velzen, R.; Holmer, R.; Bu, F.; Rutten, L.; van Zeijl, A.; Liu, W.; Santuari, L.; Cao, Q.; Sharma, T.; Shen, D.; et al. Comparative genomics of the nonlegume parasponia reveals insights into evolution of nitrogen-fixing rhizobium symbioses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E4700–E4709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjee, O.; Raul, B.; Ghosh, A.; Bhardwaj, A.; Bandyopadhyay, K.; Sinharoy, S. Nodule INception-independent epidermal events lead to bacterial entry during nodule development in peanut (Arachis hypogaea). New Phytol. 2022, 236, 2265–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Accession Number | Length (aa) | MW (kDa) | pI | Predicated Localization |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AhNINa | AH13G60030.1 | 865 | 95.61 | 6.33 | Nucleus |
| AhNINb | AH17G00510.1 | 862 | 95.39 | 6.37 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP1a | AH08G02220.1 | 964 | 107.48 | 5.77 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP1b | AH17G22700.1 | 912 | 101.89 | 5.99 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP2a | AH03G04320.1 | 577 | 64.09 | 7.63 | Chloroplast |
| AhNLP2b | AH13G06340.1 | 612 | 67.84 | 7.65 | Chloroplast |
| AhNLP2c | AH03G04310.1 | 863 | 95.92 | 5.03 | Chloroplast/Nucleus |
| AhNLP2d | AH03G04850.1 | 790 | 87.87 | 4.86 | Chloroplast |
| AhNLP2e | AH10G03170.1 | 782 | 86.77 | 5.90 | Chloroplast |
| AhNLP2f | AH13G04800.1 | 899 | 99.32 | 5.23 | Chloroplast/Nucleus |
| AhNLP2g | AH13G06330.1 | 899 | 99.50 | 5.07 | Chloroplast/Nucleus |
| AhNLP3a | AH08G11530.1 | 870 | 96.79 | 6.78 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP3b | AH18G02990.1 | 870 | 96.85 | 6.68 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP4a | AH09G24840.1 | 967 | 107.52 | 5.70 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP4b | AH19G43090.1 | 969 | 107.84 | 5.75 | Nucleus |
| AhNLP5 | AH15G36260.1 | 984 | 109.25 | 5.48 | Nucleus |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Ren, Y.; Chen, G.; Wu, L.; Tian, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhan, F.; Wang, H.; et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of NLP Genes in Peanut Reveals Significant Roles of AhNINa and AhNINb in Root Nodule Development. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102377
Wang H, Ren Y, Chen G, Wu L, Tian Y, Xu Y, Lu Z, Wu Y, Zhan F, Wang H, et al. Genome-Wide Analysis of NLP Genes in Peanut Reveals Significant Roles of AhNINa and AhNINb in Root Nodule Development. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102377
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Hongfeng, Yan Ren, Guanghui Chen, Lijun Wu, Yanchen Tian, Yiteng Xu, Zhichao Lu, Yue Wu, Fudong Zhan, Hongwei Wang, and et al. 2025. "Genome-Wide Analysis of NLP Genes in Peanut Reveals Significant Roles of AhNINa and AhNINb in Root Nodule Development" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102377
APA StyleWang, H., Ren, Y., Chen, G., Wu, L., Tian, Y., Xu, Y., Lu, Z., Wu, Y., Zhan, F., Wang, H., & Yuan, M. (2025). Genome-Wide Analysis of NLP Genes in Peanut Reveals Significant Roles of AhNINa and AhNINb in Root Nodule Development. Agronomy, 15(10), 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102377





