Effects of Auricularia auricula Residue on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Community Composition, Diversity, and Rice Yield
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Sampling and Design
2.3. Soil Fertility Analysis
2.4. Soil Enzyme Activity Analysis
2.5. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification, and Sequencing of Soil Samples
2.6. Data Processing and Statistical Analyses
3. Results
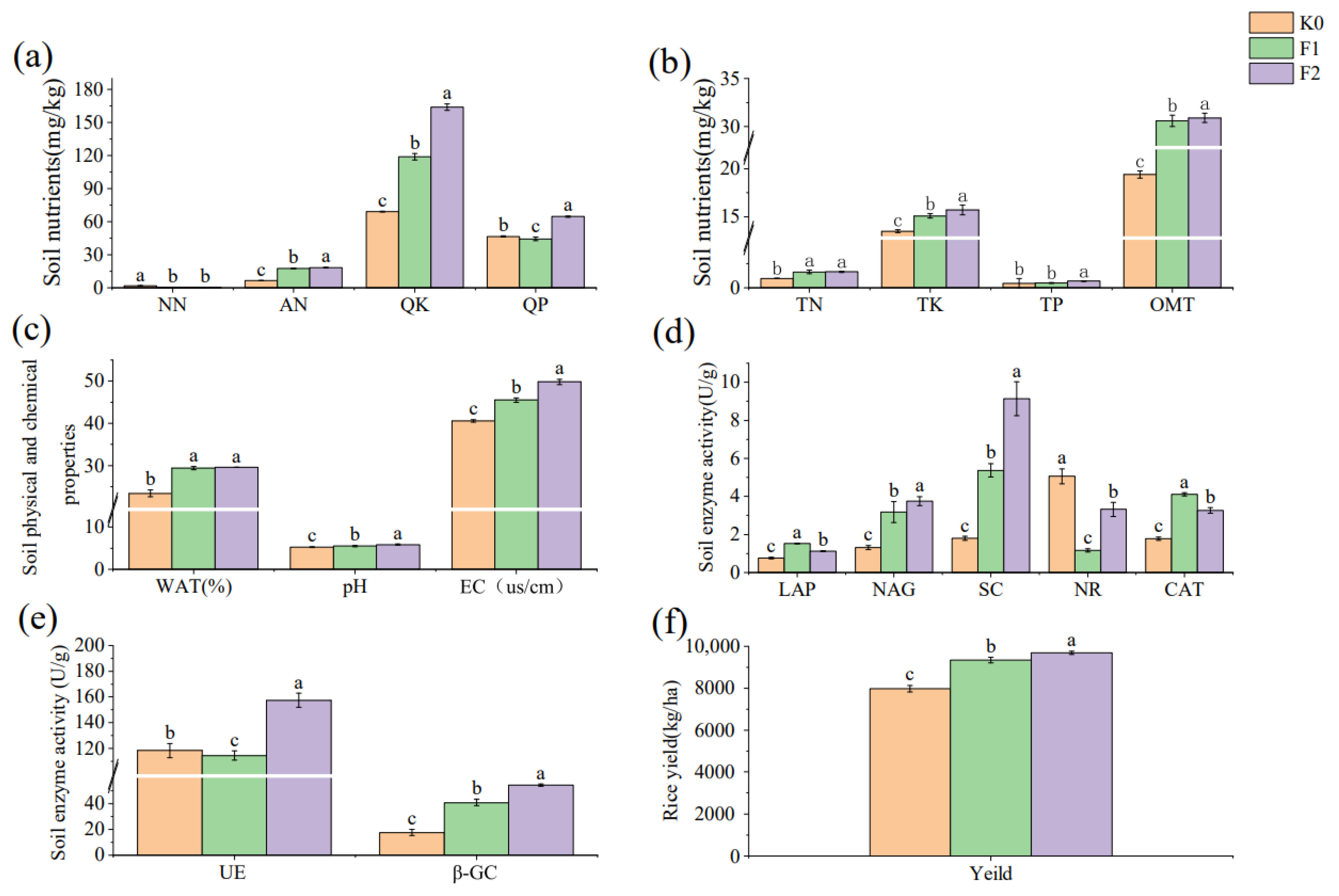
3.1. Effects of Mushroom Residue Application on Soil Nutrients, Physicochemical Properties, Extracellular Enzyme Activities, and Rice Yield
3.2. Effects of Mushroom Residue Application on Soil Microbial Diversity
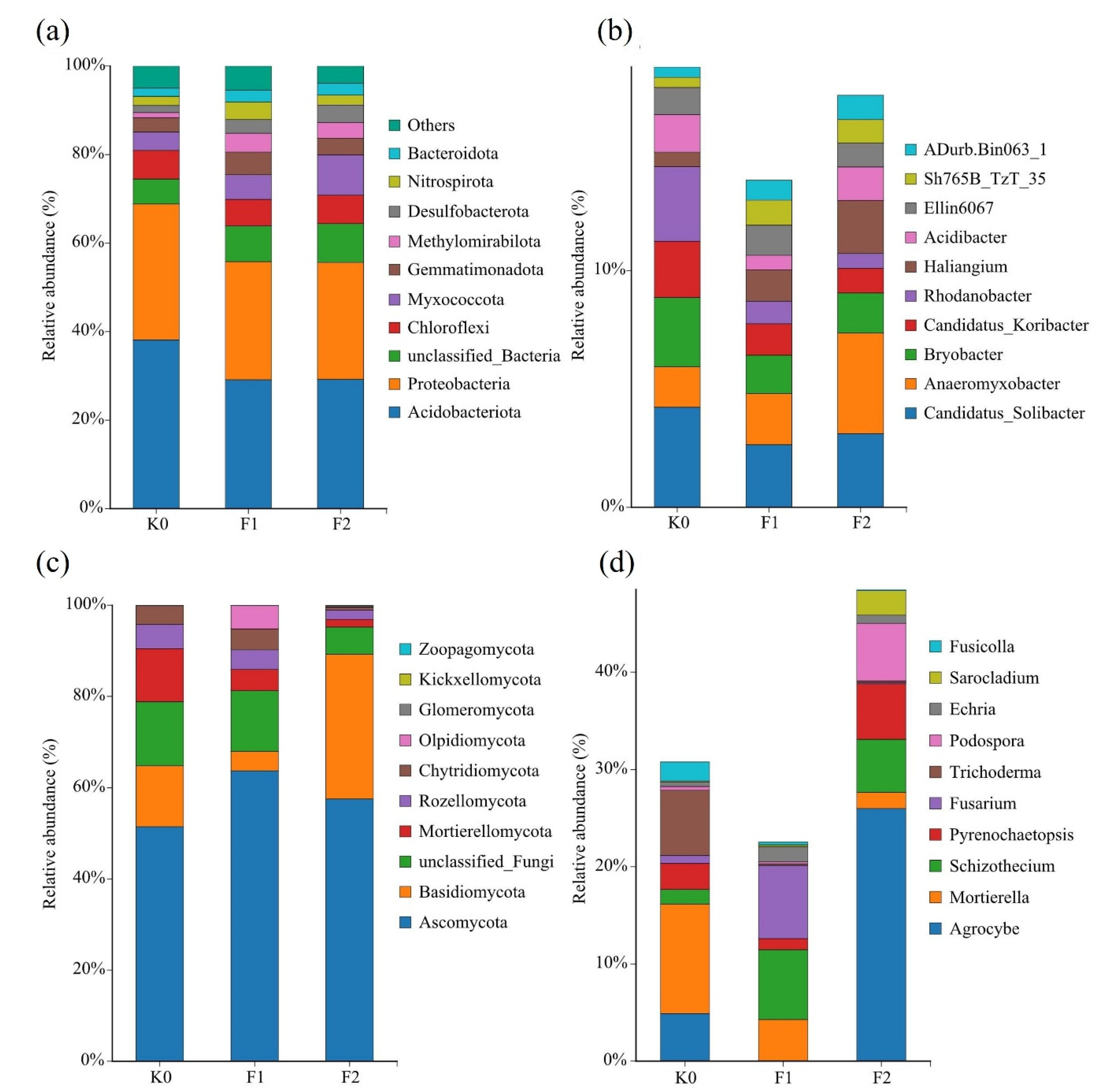
3.3. Distribution of Soil Microbial Species
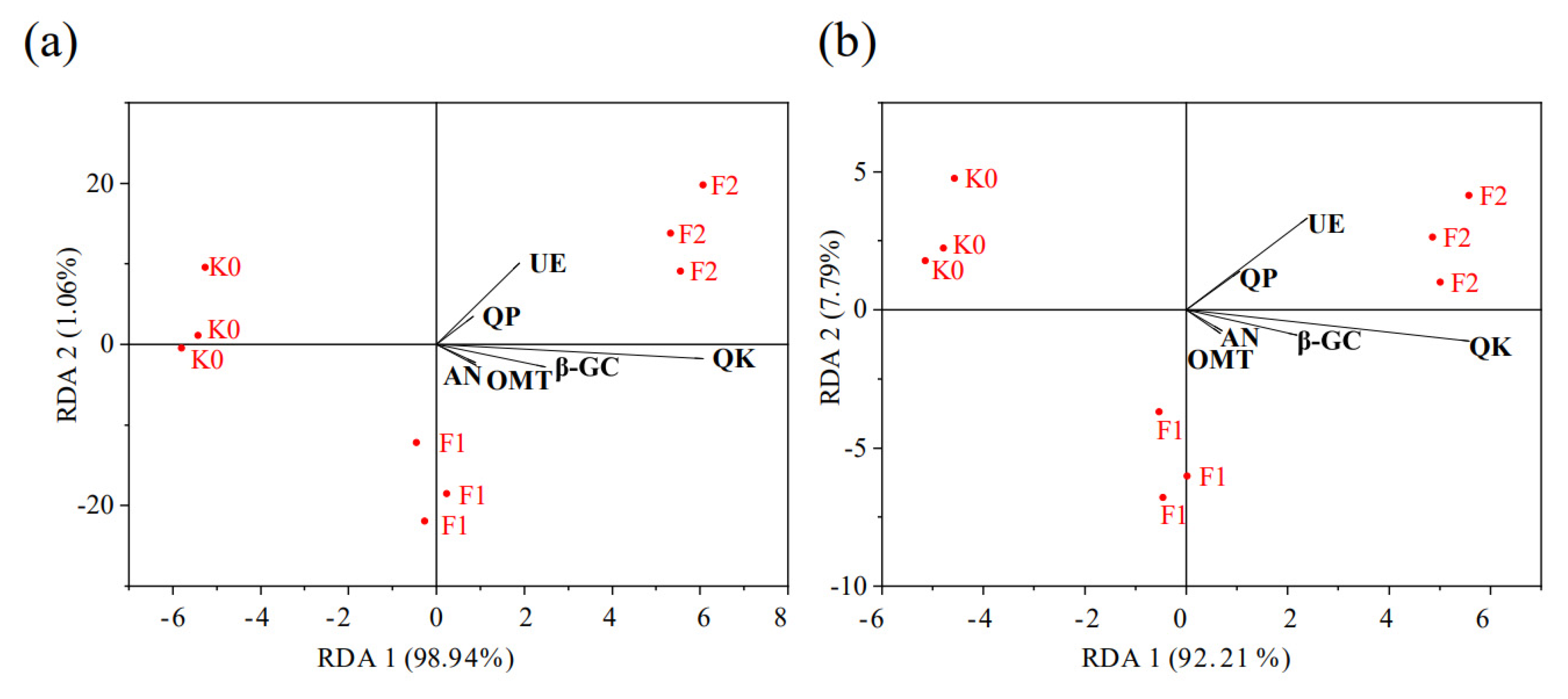
3.4. Redundancy Analysis (RDA) of Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activities, and Microbial Diversity
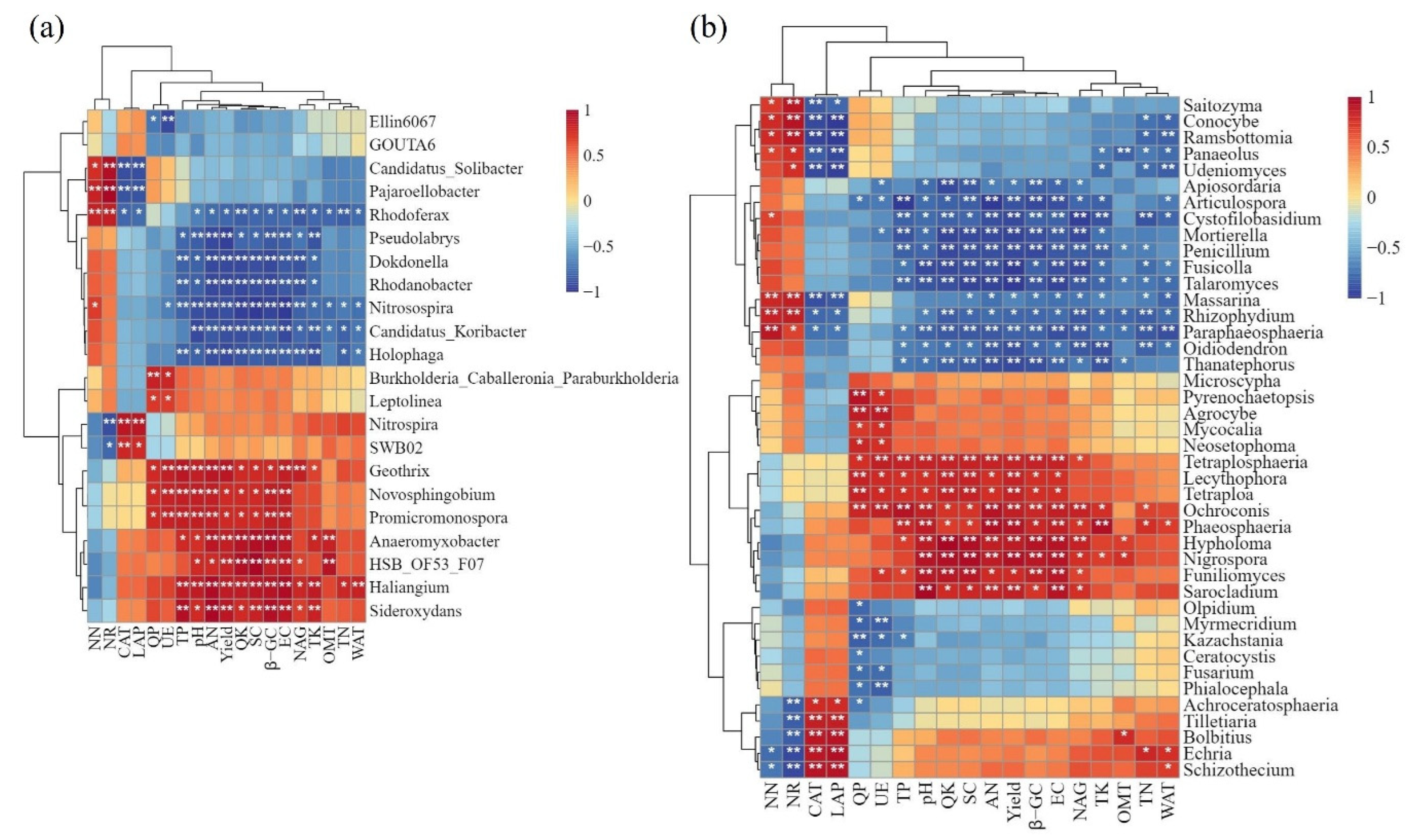
3.5. Correlation Analysis of Soil Microbial Diversity with Soil Nutrients, Enzyme Activities, and Rice Yield
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TK | Total phosphorus |
| NN | Nitrate nitrogen |
| AN | Ammonium nitrogen |
| QK | Available potassium |
| QP | Available phosphorus |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| OMT | Organic matter |
| WAT | Water content |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| LAP | Leucine aminopeptidase |
| SC | Sucrase |
| NR | Nitrate reductase |
| CAT | Catalase |
| UE | Urease |
| β-GC | β-Glucosidase |
| NAG | Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase |
| RDA | Redundancy analysis |
References
- Qiao, Y.L.; Tie, J.Z.; Wang, X.H.; Wei, B.H.; Zhang, W.B.; Liu, Z.C.; Zhang, G.B.; Lyu, J.; Liao, W.B.; Hu, L.L.; et al. Comprehensive evaluation on effect of planting and breeding waste composts on the yield, nutrient utilization, and soil environment of baby cabbage. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 341, 117941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.J.; Li, Y.; Tian, S.B.; Wei, J.Y.; Liao, D.X.; Feng, M.Y.; Zhang, H.; Zou, M.; Hang, X.N. Fungi Residue Returning: Effects on Soil Physicochemical Characters, Microorganisms and Enzyme Activity in Vegetable Field. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 36, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Sun, X. Changes in physical, chemical, and microbiological properties during the two-stage co-composting of green waste with spent mushroom compost and biochar. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 171, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.D.; Zhou, W.; Luo, L.; Li, Y.R.; Chen, Z.; Gu, Y.F.; Chen, Q.; Deng, O.P.; Xu, X.X.; Lan, T.; et al. Short-term responses of soil nutrients, heavy metals and microbial community to partial substitution of chemical fertilizer with spent mushroom substrates (SMS). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 157064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wang, C.J.; Huang, M.; Sun, N.; Zhang, W.J.; Xu, M.G. Meta-analysis of biochar application effects on soil fertility and yieldsof fruit and vegetables in greenhouse. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2018, 24, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.L.; Xu, K.Q.; Xiao, R.; Li, J.J.; Chen, X.M.; Wang, X.Y. Effects of Fertilizer with Gypsum Application on Growing Development and Nutrient Uptake of Potting Corn in Coastal Saline Soil. J. Anhui Sci. Technol. Univ. 2011, 25, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Pan, X.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Du, H.L.; Liu, F.M.; Hao, S. Response of Soil Nutrients and Microbial Communities to Increased Application of Mushroom Dreg in Albic Soil. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2025, 41, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Liu, W.; Huang, H.; Peng, Z.; Deng, L. Responses of Crop Yield, Soil Fertility, and Heavy Metals to Spent Mushroom Residues Application. Plants 2024, 13, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Zhang, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.Y.; Zhou, W.; Deng, L.J. Effects of Combined Application of Chemical Fertilizers with Different Mushroom Residues on Soil Fertility and Enzymes Activities. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 36, 364–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, L.P.; Fang, S.Z.; Tian, Y.; Guo, J. Variation of soil enzyme activity and microbial biomass in poplar plantations of different genotypes and stem spacings. J. For. Res. 2018, 29, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.L.; Wang, H.P.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Q.Y.; Lin, Q.; Luo, T. Effect of Mushroom Residue on Soil Property and Crop and Research Progress in its Recycling. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2015, 17, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.F.; Jiang, X.; Guan, D.W.; Wei, D.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, M.C.; Chen, S.F.; Li, L.; Cao, F.M.; Li, J. Long-term fertilization changes bacterial diversity and bacterial communities in the maize rhizosphere of Chinese Mollisols. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 125, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.H.; Chen, X.T.; He, H.; Dai, J.C.; Hu, J.; Dai, D.; Sun, P.; Wang, Z.; Wei, Z.; Wei, Y.H. Effects of Returning Stropharia rugosoannulata Cultivation Residue to Paddy Fields on Rice growth and Soil Environment. Acta Agric. Univ. Jiangxiensis 2023, 45, 349–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.H.; Ma, J.W.; Ye, Z.Q.; Di, C.Y.; Wang, X.D. Effects of continous application of edibe fungus residue on soil fertility preperties under rice-edible fungus rotation system. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.Y.; Fu, X.J.; Zhan, C.S.; Shi, Z.J.; Mao, X.Q.; Xu, N.C.; Wang, H.H. Performance and high-yielding cultural techniques of high-quality indica-japonica hybrid rice combination Yongyou 1540 planted as double-cropping late rice in Quzhou. Hybrid Rice 2022, 37, 125–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.J.; Stucki, J.W. The Determination of Nitrate and Nitrite in Soil Extracts by Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhine, E.D.; Mulvaney, R.L.; Pratt, E.J.; Sims, G.K. mproving the Berthelot reaction for determining ammonium in soil extracts and water. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1998, 62, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, B.; Xiao, S.Z.; Xiong, K.N.; Cheng, Q.W.; Luo, J.S. Comparative studies of the distribution characteristics of rocky desertification and land use/land cover classes in typical areas of Guizhou province, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 71, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vance, E.D.; Brookes, P.C.; Jenkinson, D.S. An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass C. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1987, 19, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cambardella, C.A.; Elliott, E.T. Particulate soil organic-matter changes across a grassland cultivation sequence. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1992, 56, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, L.; Liu, C.; Yu, L.; Song, C.; Peng, L.; Li, X.; Tao, L.; Li, G. Organic Matter Regulates Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterial and Archaeal Communities in the Surface Sediments of Ctenopharyngodon idellus Aquaculture Ponds. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.Q.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Zhang, Z.H.; Zhang, B.; Lu, Y.; Zeng, F.J. Effects of Different Irrigation Levels on the Yield and Quality of theCyperus esculentusL. at Tuber Stage. Acta Agrestia Sin. 2024, 32, 3636–3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Zhao, J.; Ma, J.; Zhu, Y.F.; Luo, Z.B. Effects of vegetation restoration on functional groups related to soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus cycles in open-pit mining area of the Loess Plateau. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2023, 60, 1507–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.Y.; Bao, Y.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhang, X.Y. Effects of Tartary Buckwheat Rotation on Enzyme Activities and Microorganisms in Rhizosphere Soil of Cultivated Potato in Yunnan Province. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2024, 26, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.H.; He, Z.X.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Xie, J.M.; Zhang, X.D. Effects of bio-organic fertilizer with microbial inoculants on the growth, physiological characteristics, yield and quality of garlic seedlings. J. Gansu Agric. Univ. 2022, 58, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.S.; Cheng, X.M.; Jiang, Z.; Qu, C.; Yan, H.; Wu, Q.N. Effects of Crop Rotation on the Growth, Quality and Soil Environment of Euryale ferox. J. Chin. Med. Mater. 2024, 47, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eivazi, F.; Tabatabai, M.A. Factors affecting glucosidase and galactosidase activities in soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 1990, 22, 891–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.X.; Wang, H.X.; Wang, L.Y.; Song, Y.Z.; Li, X.; Yang, C.; Li, F.J. Effects of combined application of bacterial residue and chemical fertilizer on soil nutrients and enzyme activities in paddy field. Jiangsu Agric. Sci. 2024, 52, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, H.B.; Yue, Y.H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, T.T.; Zhao, Z.L.; Zhang, J.J.; Chen, H. Effects of the rice-mushroom rotation pattern on soil properties and microbial community succession in paddy fields. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1449922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Sun, R.B.; Sun, T.T.; Liang, Y.T.; Jiang, Y.J.; Sun, B. Organic amendments shift the phosphorus-correlated microbial co-occurrence pattern in the peanut rhizosphere network during long-term fertilization regimes. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2018, 124, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frąc, M.; Pertile, G.; Panek, J.; Gryta, A.; Oszust, K.; Lipiec, J.; Usowicz, B. Mycobiome composition and diversity under the long-term application of spent mushroom substrate and chicken manure. Agronomy 2021, 11, 410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nannipieri, P.; Trasar-Cepeda, C.; Dick, R.P. Soil enzyme activity: A brief history and biochemistry as a basis for appropriate interpretations and meta-analysis. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2017, 54, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borase, D.N.; Nath, C.P.; Hazra, K.K.; Senthilkumar, M.; Singh, S.S.; Praharaj, C.S.; Singh, U.; Kumar, N. Long-term impact of diversified crop rotations and nutrient management practices on soil microbial functions and soil enzymes activity. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Rong, F.L.; Zhu, H.Y.; Cao, F.B.; Chen, J.N.; Chen, F.L. Effects of adding vermicompost on soil fertility and enzyme activity of acidic paddy soil. J. Nucl. Agric. Sci. 2025, 39, 615–623. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Liang, H.; Huang, J.; Chen, Z.; Nie, Y.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y. Manipulation of the rhizosphere microbial community through application of a new bio-organic fertilizer improves watermelon quality and health. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; He, Z.C.; Yang, Y.H.; Jia, S.Q.; Yu, M.; Chen, X.J.; Shen, A.L. Linking soil microbial community dynamics to straw-carbon distribution in soil organic carbon. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Six, J.; Frey, S.D.; Thiet, R.K.; Batten, K.M. Bacterial and Fungal Contributions to Carbon Sequestration in Agroecosystems. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2006, 70, 555–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subhashini, D. Growth Promotion and Increased Potassium Uptake of Tobacco by Potassium-Mobilizing Bacterium Frateuria aurantia Grown at Different Potassium Levels in Vertisols. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2014, 46, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemp, N.D.; Vaughan, M.M.; McCormick, S.P.; Brown, J.A.; Bakker, M.G. Sarocladium zeae is a systemic endophyte of wheat and an effective biocontrol agent against Fusarium head blight. Biol. Control 2020, 149, 104329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clocchiatti, A.; Hannula, S.E.; Van den Berg, M.; Hundscheid, M.P.J.; De Boer, W. Evaluation of Phenolic Root Exudates as Stimulants of Saptrophic Fungi in the Rhizosphere. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 644046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenzinger, K.; Costa, O.Y.A.; Ho, A.; Koorneef, G.; Robroek, B.; Molenaar, D.; Korthals, G.; Bodelier, P.L.E. Steering microbiomes by organic amendments towards climate-smart agricultural soils. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2021, 57, 1053–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampelotto, P.H.; de Siqueira Ferreira, A.; Barboza, A.D.; Roesch, L.F. Changes in diversity, abundance, and structure of soil bacterial communities in Brazilian Savanna under different land use systems. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 66, 593–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Zhang, W.; Liu, T.X.; Chen, L.X.; Chen, P.C.; Li, F.B. Changes in the composition and diversity of microbial communities during anaerobic nitrate reduction and Fe(II) oxidation at circumneutral pH in paddy soil. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 94, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ka, J.O.; Cho, J.C. Members of the phylum Acidobacteria are dominant and metabolically active in rhizosphere soil. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2008, 285, 263–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sheng, H.F.; He, Y.; Wu, J.Y.; Jiang, Y.X.; Fung-Yee, T.N.; Zhou, H.W. Comparison of the levels of bacterial diversity in freshwater, intertidal wetland, and marine sediments by using millions of illumina tags. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 8264–8271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fullerton, H.; Moyer, C.L. Comparative single-cell genomics of Chloroflexi from the Okinawa trough deep-subsurface biosphere. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3000–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.P.; Wu, M.K.; Che, S.H.; Yuan, S.; Yang, X.; Li, S.Y.; Tian, P.; Wu, L.; Yang, M.Y.; Wu, Z.H. Effects of continuous straw returning on soil functional microorganisms and microbial communities. J. Microbiol. 2023, 61, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, O.; Gihring, T.M.; Dalton, D.D.; Chin, K.J.; Green, S.J.; Akob, D.M.; Wanger, G.; Kostka, J.E. Geobacter daltonii sp. nov., an Fe(III)- and uranium(VI)-reducing bacterium isolated from a shallow subsurface exposed to mixed heavy metal and hydrocarbon contamination. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2010, 60 Pt 3, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, W.; Liu, Y.; Yao, D.; Wang, N.; Ye, X.; Cui, Z.; Wang, H. Phylogenetic diversity of stochasticity-dominated predatory myxobacterial community drives multi-nutrient cycling in typical farmland soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 871, 161680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, G.; Wu, Z.; Wen, X.; Zhong, H.; Zhong, Z.; Yang, C.; Bian, F.; Gai, X. Responses of soil nutrients and microbial communities to intercropping medicinal plants in moso bamboo plantations in subtropical China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 2301–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, X.; Zheng, H.; Liao, Y.; Feng, L.; Jiang, L.; Liu, C.; Mao, Y.; Shen, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Ji, F. Effects of iron-based substrate on coupling of nitrification, aerobic denitrification and Fe(II) autotrophic denitrification in tidal flow constructed wetlands. Bioresour. Technol. 2022, 361, 127657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yang, Y.; Wen, J.L.; Mo, F.; Liu, Y. Continuous manure application strengthens the associations between soil microbial function and crop production: Evidence from a 7-year multisite field experiment on the Guanzhong Plain. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 338, 108082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbeva, P.; van Veen, J.A.; van Elsas, J.D. Microbial diversity in soil: Selection microbial populations by plant and soil type and implications for disease suppressiveness. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2004, 42, 243–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erica, D.; Maximilien, K.; Benoît, G.; Christine, A. Life cycle assessment of a circular, urban mushroom farm. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 288, 125668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Peng, Y.M.; Zhao, W.X.; Gao, X.; Wu, S.W.; Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, W.N.; Cui, X.Q.; Wu, J.Z.; et al. Effects of different tillage measures during summer fallow seasonontents and enzyme activities in dryland wheat field. Soil Fertil. Sci. China 2024, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yuan, W.; Zong, T.; Yu, B.; Xin, Y.; Lu, J.; Qiu, Q.; Ma, L.; Song, J. Effects of Auricularia auricula Residue on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Community Composition, Diversity, and Rice Yield. Agronomy 2025, 15, 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102313
Yuan W, Zong T, Yu B, Xin Y, Lu J, Qiu Q, Ma L, Song J. Effects of Auricularia auricula Residue on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Community Composition, Diversity, and Rice Yield. Agronomy. 2025; 15(10):2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102313
Chicago/Turabian StyleYuan, Weidong, Tingxuan Zong, Bin Yu, Ya Xin, Jia Lu, Qin Qiu, Lin Ma, and Jiling Song. 2025. "Effects of Auricularia auricula Residue on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Community Composition, Diversity, and Rice Yield" Agronomy 15, no. 10: 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102313
APA StyleYuan, W., Zong, T., Yu, B., Xin, Y., Lu, J., Qiu, Q., Ma, L., & Song, J. (2025). Effects of Auricularia auricula Residue on Soil Physicochemical Properties, Microbial Community Composition, Diversity, and Rice Yield. Agronomy, 15(10), 2313. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15102313





