Abstract
Soil organic carbon (SOC) constitutes the largest terrestrial carbon pool and plays a crucial role in climate regulation, soil fertility, and ecosystem functioning. Understanding its spatiotemporal dynamics is particularly important in semi-arid regions, where fragile environments and extensive ecological restoration may alter carbon cycling. The Loess Plateau, the world’s largest loess accumulation area with a history of severe erosion and large-scale vegetation restoration, provides a natural laboratory for examining how environmental gradients influence SOC storage over time. This study used a random forest model with multi-source environmental data to quantify soil organic carbon density (SOCD) dynamics in the 0–100 cm soil layer of the Loess Plateau from 2005 to 2020. SOCD showed strong spatial heterogeneity, decreasing from the humid southeast to the arid northwest. Over the 15-year period, total SOC storage increased from 4.84 to 5.23 Pg C (a 7.9% rise), while the annual sequestration rate declined from 0.046 to 0.020 kg·m−2·yr−1, indicating that the regional carbon sink may be approaching saturation after two decades of restoration. Among soil types, Cambisols were the largest carbon pool, accounting for over 44% of total SOC storage. Vegetation productivity emerged as the dominant driver of SOC variability, with clay content as a secondary factor. These results indicate that although ecological restoration has substantially enhanced SOC storage, its marginal benefits are diminishing. Understanding the spatial and temporal patterns of SOC and their environmental drivers provides essential insights for evaluating long-term carbon sequestration potential and informing future land management strategies. Broader generalization requires multi-regional comparisons, long-term monitoring, and deeper soil investigations to capture ecosystem-scale carbon dynamics fully.
1. Introduction
Soil organic carbon (SOC) constitutes the largest carbon pool within terrestrial ecosystems, with its storage and dynamic changes profoundly impacting global carbon cycling, ecosystem functions, and climate change regulation [1]. Global SOC storage is estimated at approximately 1500 Pg C, nearly double the atmospheric carbon pool and triple the biotic carbon pool [2]. As a fundamental basis for soil fertility and agricultural productivity, SOC also plays a crucial role in mitigating greenhouse gas emissions and achieving China’s “dual carbon” goals [3]. Therefore, the accurate quantification of Soil Organic Carbon Storage (SOCS)—defined as the total mass of organic carbon in a given soil volume which serves as a key soil function for climate regulation—is a scientific prerequisite for formulating evidence-based land management policies and tracking progress towards carbon neutrality goals [4,5].
The spatiotemporal distribution of soil organic carbon (SOC) is inherently complex, governed by interactions among climate, vegetation, topography, and soil properties [6,7,8,9,10]. This complexity is acutely amplified on the Loess Plateau, a region characterized by its fragmented topography and sensitive semi-arid climate [11]. While the ‘Grain for Green Program’ has led to significant and visible vegetation recovery since 1999, this success presents a new, critical scientific uncertainty [12]. Under the dual influence of the heterogeneous environmental factors and the overwhelming impact of anthropogenic vegetation restoration, it remains unclear which drivers are now dominant in controlling SOC’s spatiotemporal dynamics. Answering this is essential for accurately assessing the long-term effectiveness of this unprecedented ecological restoration, understanding carbon cycling in global arid regions, and designing more targeted and effective land management strategies for the future [13].
Previous studies on soil organic carbon (SOC) in the Loess Plateau have primarily focused on small watershed scales, relying on field surveys, geostatistical approaches, or models such as InVEST [14,15,16]. However, these methods are limited by sampling density and model assumptions, restricting their ability to capture the high-resolution spatiotemporal dynamics of SOC. Machine learning has been increasingly applied due to its powerful nonlinear fitting capabilities and advantages in handling high-dimensional time-series data [17]. Within this framework, the Random Forest (RF) model offers distinct benefits: it is robust to multicollinearity, performs well with moderate sample sizes, and provides variable-importance measures for identifying key environmental drivers, making it highly suitable for the methodology of this study [18,19]. Most existing SOC studies in the Loess Plateau remain constrained to surface soils or static spatial patterns [19,20]. Yet, evidence shows that SOCS in the 0–100 cm profile are approximately two to three times greater than those in the 0–20 cm surface layer [13]. Focusing only on surface soils thus risks substantially underestimating subsurface carbon pools. Incorporating the temporal dimension further enables the identification of dominant drivers of SOC variability in this ecologically fragile region and supports more accurate assessments of its long-term carbon sequestration potential, offering insights that move beyond the surface-oriented perspective of previous studies.
This study focuses on the Loess Plateau as the research area, employing random forest models coupled with multi-source spatiotemporal data to systematically analyze the spatiotemporal evolution patterns and influencing factors of soil organic carbon density (SOCD) at 0–100 cm depth during 2005–2020. By constructing high-precision spatiotemporal distributions of SOCD, this research aims to reveal spatial distribution patterns and temporal variation characteristics, quantify the relative importance and nonlinear effects of key factors including climate, vegetation, topography, and soil properties, thereby providing scientific evidence for ecosystem management and policy formulation under regional carbon neutrality goals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area Overview
The Loess Plateau is located in the middle reaches of the Yellow River in north-central China (33°41′–41°16′ N, 100°52′–114°33′ E), spanning over 1000 km from east to west and 750 km from north to south. It encompasses extensive regions west of the Taihang Mountains, east of the Riyue Mountain in Qinghai Province, north of the Qinling Mountains, and south of the Great Wall, covering a total area of approximately 640,000 km2, which accounts for 6.7% of China’s total land area (Figure 1). The region has an average elevation of approximately 1500 m, with mean annual temperatures ranging from 2.4 to 14.2 °C and mean annual precipitation of 300–650 mm, with precipitation predominantly concentrated during July–September. Apart from certain rocky mountainous areas, the region is extensively covered by loess deposits with an average thickness of 92 m, and more than 97% of the area has a soil depth greater than 100 cm, making it the largest loess accumulation region in the world [21,22].
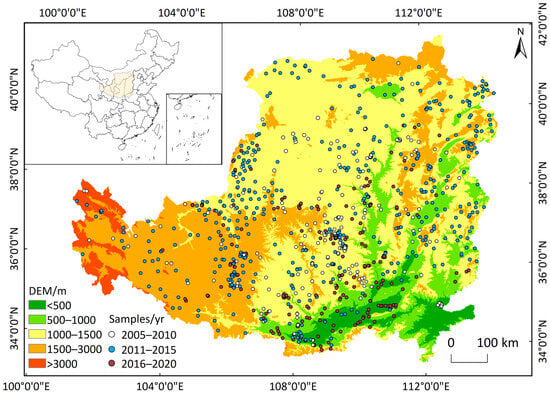
Figure 1.
Spatial distribution of soil sample points in the Loess Plateau study area, overlaid on a Digital Elevation Model (DEM) showing topographic elevation. The legend specifies elevation classes in meters (m). The sample points are color-coded by their collection period (year, abbreviated as ‘yr’ in the legend): 2005–2010 (white), 2011–2015 (blue), and 2016–2020 (maroon). The inset map indicates the location of the study area within China.
2.2. Data Collection
2.2.1. Soil Organic Carbon Density
Soil organic carbon density data were obtained from four sources: the 2010s China terrestrial ecosystem carbon density dataset [23]; the Chinese Soil Series Database [24] (data for the Loess Plateau region); the 2005–2020 soil organic carbon density dataset for typical ecosystems in China’s Northwest arid region [25]; and published literature data retrieved from Web of Science (https://www.webofscience.com, accessed on 11 October 2024) and China National Knowledge Infrastructure (http://www.cnki.net, accessed on 15 October 2024). Literature searches were conducted using “soil organic carbon” and “Loess Plateau” as keywords. Literature data selection followed these criteria: (1) soil organic carbon data must be actual field monitoring data, excluding model-fitted and literature-derived statistical data; (2) field sampling monitoring period must be within 2005–2020. For samples lacking SOCD records but containing basic parameters such as soil bulk density, soil organic carbon content, and soil depth, calculations were performed using the following formula [23,26]:
where represents soil organic carbon density (kg·m−2), (g·kg−1) is the soil organic carbon concentration of layer i, is the bulk density of layer i (g·cm−3), is the thickness of layer i (cm), is the percentage content of >2 mm gravel in layer i (%), and is the total number of soil layers included in the calculation.
For sampling points from the literature where the actual soil depth was less than 100 cm, the SOCD was calculated based on this actual depth rather than extrapolated to 100 cm; for depths > 100 cm, only the 0–100 cm layer was considered. For points with only organic matter records, organic carbon was estimated using a conversion factor of 0.58 [23]. For missing bulk density values, the most accurate pedotransfer functions were applied [27].
Quality control procedures were rigorously applied to ensure data consistency and reliability across sources. All SOC values were converted to uniform units (kg·m−2) and depths standardized to 0–100 cm. Outliers outside the plausible ranges of SOC content and bulk density were excluded. For sampling points with identical geographic coordinates and sampling year across different sources, SOCD values were averaged to avoid duplication while preserving data integrity. Spatial screening ensured that all data points fell strictly within the Loess Plateau boundary. Temporal consistency was maintained by restricting data to 2005–2020. After these quality control steps, a total of 1309 sampling points were retained for analysis (Figure 1).
2.2.2. Environmental Variables
A total of 14 environmental variables were selected (Table 1), and all environmental variable raster maps were standardized to the WGS 1984 coordinate system with 1 km resolution. To provide an intuitive overview of the study area’s environmental background, Figure 2 illustrates the spatial distribution of key variables. These include the mean annual Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI), Net Primary Productivity (NPP), Mean Annual Precipitation (MAP), and Mean Annual Temperature (MAT) averaged over the 2005–2020 period. We employed the Genetic Soil Classification of China (GSCC) as a predictor variable. This soil classification system is defined for the entire soil profile rather than individual depth slices, serving as a homogeneous invariant throughout the 0–100 cm depth range. This variable has been utilized and validated in national-scale soil organic carbon assessments [28].

Table 1.
Information on environmental variables.
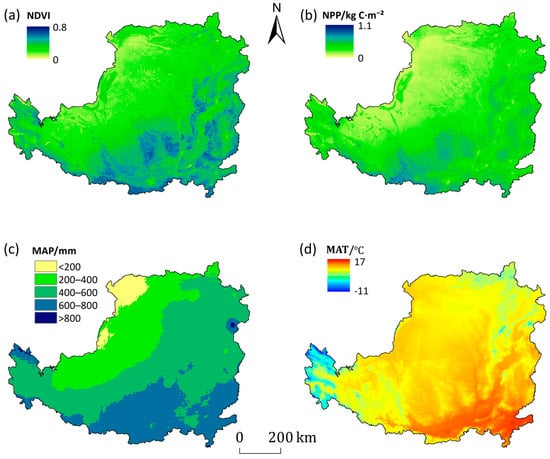
Figure 2.
Spatial distribution of key environmental variables in the Loess Plateau. (a) Mean annual Normalized Difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) from 2005 to 2020; (b) Mean annual Net Primary Productivity (NPP) from 2005 to 2020; (c) Mean annual precipitation (MAP) from 2005 to 2020; (d) Mean annual temperature (MAT) from 2005 to 2020.
All other datasets, such as those derived from SRTM or provided by OpenLandMap, are composite products representing contemporary conditions without a specific single-year timestamp.
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Random Forest Model
Random Forest (RF) offers core advantages in effectively reducing model variance, thereby achieving more robust and accurate predictive performance, and demonstrates strong robustness against overfitting due to its inherent ensemble mechanism [29]. The training model included 14 environmental variables (Table 1) and temporal trends, with 0–100 cm SOCD as the dependent variable. To obtain unbiased estimates of model performance and avoid information leakage caused by spatial autocorrelation, this study employed rigorous 5-fold Spatial Block Cross-Validation. After hyperparameter optimization through cross-validation, the final model’s key hyperparameters were set as follows: ntree = 1500, mtry = 18, min.node.size = 3. The model performed well on the test set of spatial cross-validation, with R2 = 0.701, RMSE = 1.99 kg·m−2, and MAE = 1.11 kg·m−2.
2.3.2. Soil Organic Carbon Storage Calculation
Soil organic carbon storage (SOCS) refers to the total amount of SOC contained in soil layers within a specific regional area, calculated as the product of SOCD and area. To analyze SOCS in the Loess Plateau region across different years and its magnitude of change, statistical analysis of SOCD raster maps was conducted using R language. The SOCS calculation method was based on a fixed depth of 0–100 cm. While we acknowledge the spatial variability of soil horizons within different classification units, this approach aligns with international carbon accounting practices and its validity for national-scale assessments in China has been well-established [30]. The SOCS calculation method was [31]:
where represents soil organic carbon storage (kg), is the soil organic carbon density of pixel i (kg·m−2), is the area of pixel i (m2), and is the total number of pixels.
2.3.3. Data Analysis
Sen’s slope estimation and Mann–Kendall test were employed to analyze temporal trends of SOCD and identify regions with significant changes [32]. Sen’s slope estimation is a non-parametric method for estimating the magnitude of time series trends, suitable for handling non-normally distributed data. The Mann–Kendall test was used to detect statistical significance of trends and is widely applied in environmental data analysis. The MannKendall function from the R 4.5.0 software package (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) to output p-values as the basis for judgment, determining whether p-values were less than the given significance level α (significant α < 0.05, extremely significant α < 0.01) to provide test classifications.
To characterize the relationship between the spatial variability of soil classes and the prediction results, and to facilitate comparison with other studies, the predicted SOCS for the 0–100 cm depth (treated as a single, uniform layer) were aggregated according to the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (WRB) soil groups. The Soil type distribution map of the study area divided according to WRB is shown in Supplementary Figure S1. This approach allows for a harmonized comparison of SOC distribution across different soil types and aligns with established practices in global assessments, such as the FAO’s Global Soil Organic Carbon Map (GSOCmap) methodology, which typically reports SOCS stratified by WRB soil units [33].
In addition, Shapley Additive Explanations (SHAP) and Partial Dependence (PD) analyses were employed to interpret model outputs and understand SOCD sensitivity to different influencing factors, providing deep insights into model robustness and reliability [34]. SHAP values quantify each feature’s contribution by estimating the average marginal impact across all possible feature combinations, ensuring consistent and fair assessment of each feature’s influence across different combinations. PD analysis reveals relationships between target responses and sets of input features by averaging the effects of all other features, enabling understanding of individual predictor variables’ primary impacts on model predictions.
2.3.4. Data Processing
Tabular data were recorded and organized in Excel 2016 (Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA). Slope, aspect, and Topographic Wetness Index (TWI) were calculated from 250 m resolution DEM images using ArcGIS 10.5 (Esri Inc., Redlands, CA, USA). RF model development, predictive distribution map generation and analysis, and sensitivity analysis were performed in R 4.5.0 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria), while mapping was completed using ArcGIS 10.5 and Python 3.6 (Python Software Foundation, Wilmington, DE, USA).
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of SOCD
Soil organic carbon density (SOCD) across the Loess Plateau demonstrated significant spatial heterogeneity. The overall pattern was characterized by a decrease from the southeast to the northwest, with the southern region increasing from east to west and the central region decreasing from east to west (Figure 3). High-value areas are primarily concentrated in the southwestern mountainous regions, the areas surrounding the Qinling and Liupan Mountains in the south, and the foothills of the Taihang and Lüliang Mountains in the east. Conversely, low-value areas are mainly distributed in the loess ridge-hill gully regions of the central Loess Plateau.
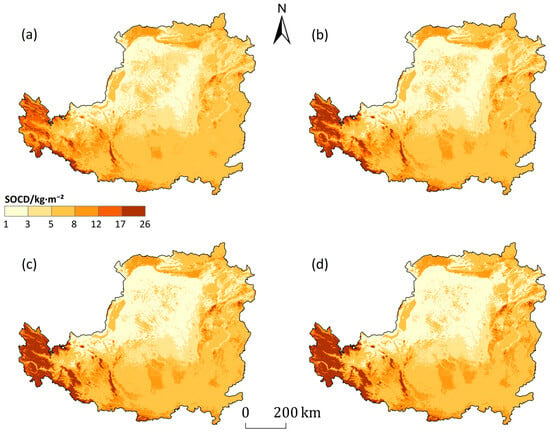
Figure 3.
Spatial distribution of soil organic carbon density (SOCD) in the 0–100 cm soil layer on the Loess Plateau. The panels show the SOCD for the years (a) 2005, (b) 2010, (c) 2015, and (d) 2020.
The total soil organic carbon storage (SOCS) in the Loess Plateau exhibited a continuous increasing trend from 2005 to 2020, rising steadily from 4.84 Pg to 5.23 Pg, which represents a total increase of 7.9%. The average annual increment in SOCD during this period was approximately 0.0315 kg·m−2·yr−1. Concurrently, the coefficient of variation (CV) for SOCD increased from 55.2% to 72.1%, indicating that the spatial heterogeneity of its distribution has intensified over time.
Carbon storage varies markedly among the different soil types of the Loess Plateau (Table 2). Among all soil groups, Cambisols represent the largest carbon pool, accounting for over 44% of the total storage throughout the study period and increasing from 2.16 Pg in 2005 to 2.32 Pg in 2020. The most significant relative increase was observed in the Kastanozems/Chernozems/Phaeozems complex, where SOCS grew by over 24% in 15 years. However, not all soil types showed an increase; for instance, the Arenosols/Dunes complex experienced a continuous decline in carbon storage, from 0.289 Pg to 0.237 Pg, reflecting potential soil degradation in localized areas.

Table 2.
Soil Organic Carbon Storage (SOCS) of Major World Reference Base Soil Groups in the 0–100 cm soil layer on the Loess Plateau (2005–2020).
WRB Abbreviation Reference: The abbreviations correspond to the Reference Soil Groups of the World Reference Base for Soil Resources (IUSS Working Group WRB, 2022). CM: Cambisols; FL/LP/RG/Rocks: Fluvisols/Leptosols/Regosols/Rocks Complex; KS/CH/PH: Kastanozems/Chernozems/Phaeozems Complex; AR/Dunes: Arenosols/Dunes Complex; DU/CL/GY/SC: Durisols/Calcisols/Gypsisols/Solonchaks Complex; LV/AL: Luvisols/Alisols Complex; AT: Anthrosols; CR: Cryosols; Other Minor Types: This category is the sum of all soil groups and land cover types with SOCS values consistently below the 0.05 Pg C threshold. It comprises Gleysols/Planosols/Stagnosols Complex (GL/PL/ST), Umbrisols (UM), and Andosols (AN).
3.2. Temporal Change Characteristics of SOCD
From 2005 to 2020, the Loess Plateau experienced a net increase in SOCD, though this trend was not uniform across the region (Figure 4). A trend analysis confirms this spatial divergence (Figure 4f). Approximately 32.2% of the total area, located mainly in the southeast, showed a statistically significant increase (p < 0.05). In contrast, 24.4% of the area, concentrated in the northern and central-western arid zones, exhibited a significant decrease. These opposing trends form a distinct spatial pattern along a southwest-northeast axis, with the most substantial gains occurring in the southern mountainous areas.
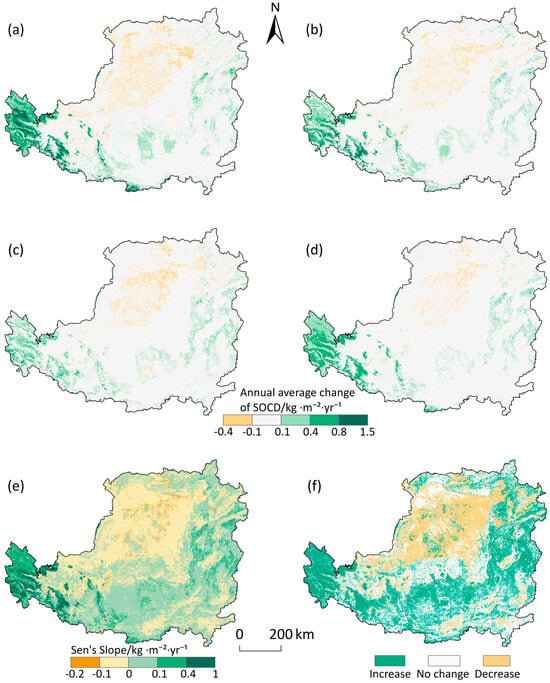
Figure 4.
Trend analysis of soil organic carbon density (SOCD) in the 0–100 cm soil layer on the Loess Plateau from 2005 to 2020 (a–d). Annual average change rates of SOCD for the intervals 2005–2010, 2010–2015, 2015–2020, and 2005–2020. (e) The overall trend magnitude (Sen’s slope). The unit for all rates is kg·m−2·yr−1 (kilograms of soil organic carbon per square meter per year). (f) The results of the Mann–Kendall significance test, where ‘Increase’ denotes a statistically significant increasing trend (p < 0.05), ‘Decrease’ denotes a significant decreasing trend (p < 0.05), and ‘No change’ indicates a non-significant trend (p > 0.05).
While the overall trend was positive, resulting in a net SOCS increase of 0.387 Pg C (an approximate 8% rise from 2005 levels), the rate of carbon sequestration decelerated over time. The annual growth rate of SOCD slowed progressively from 0.046 kg·m−2·yr−1 in the 2005–2010 period to 0.020 kg·m−2·yr−1 by 2015–2020, indicating a maturing of the regional carbon sink.
3.3. Analysis of SOCD Influencing Factors
This study employed a Random Forest (RF) model combined with the SHAP method to analyze the hierarchical importance of factors influencing SOCD (Figure 5) and used Partial Dependence Plots (PDPs) to explore the marginal effects of key variables (Figure 6).
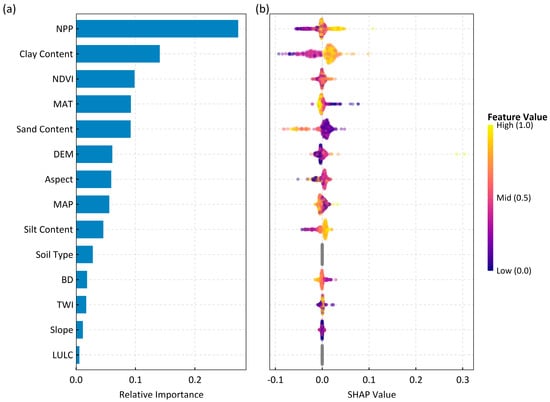
Figure 5.
SHAP (Shapley Additive Explanations) analysis of the Random Forest model for predicting Soil Organic Carbon Density (SOCD) in the 0–100 cm soil layer. (a) Global feature importance, with variables ranked by their mean absolute SHAP value, which represents their average impact on the model output. (b) SHAP summary plot, where each point represents the SHAP value for a single sample. The horizontal position shows the feature’s impact on the prediction, and the color indicates the feature’s original value (from low in purple to high in yellow). Predictor variable acronyms are defined as: NPP (Net Primary Productivity), NDVI (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index), MAT (Mean Annual Temperature), DEM (Digital Elevation Model), MAP (Mean Annual Precipitation), BD (Bulk Density), TWI (Topographic Wetness Index), and LULC (Land Use and Land Cover).
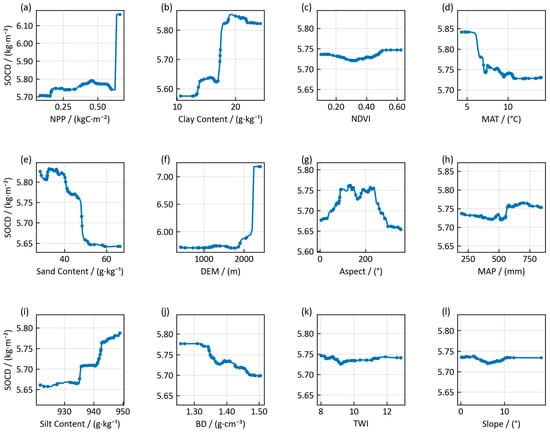
Figure 6.
Partial dependence plots (PDPs) showing the modeled relationship between key environmental variables and soil organic carbon density (SOCD) in the 0–100 cm soil layer. Each subplot isolates the effect of a single predictor variable (x-axis) on the model’s SOCD prediction (y-axis) by averaging the effects of all other variables. This reveals the direction and magnitude of each factor’s influence. To illustrate the data distribution that underpins these relationships, the actual values from the training dataset are shown as solid circles plotted directly onto the corresponding PDP curve. The density of these circles indicates the regions of the variable’s range where the model’s training was most heavily supported by data. Subplots: (a) Net primary productivity (NPP, kg C·m−2); (b) Clay content (g·kg−1); (c) Normalized difference vegetation index (NDVI); (d) Mean annual temperature (MAT, °C); (e) Sand content (g·kg−1); (f) Digital elevation model (DEM, m); (g) Aspect (°); (h) Mean annual precipitation (MAP, mm); (i) Silt content (g·kg−1); (j) Bulk density (BD, g·cm−3); (k) Topographic wetness index (TWI); (l) Slope (°).
The analysis revealed a clear hierarchy of influence (Figure 5a). Vegetation factors (Net Primary Productivity, NPP; Normalized Difference Vegetation Index, NDVI) were the dominant drivers of SOCD spatial variation. These were followed in importance by soil properties (clay, sand, and silt content), climatic factors (mean annual temperature and precipitation), and finally topographic features (elevation, aspect, etc.).
Vegetation productivity, the primary source of carbon input to the soil, exerted the most decisive influence. NPP was the single most important predictor, demonstrating a strong, positive relationship with SOCD (Figure 5b). The PDP analysis revealed a critical threshold effect: SOCD increased dramatically once NPP surpassed approximately 0.60 kg C·m−2, highlighting that a certain level of productivity is required to initiate significant carbon accumulation (Figure 6a). However, given that the number of data points within this range is limited, the underlying mechanisms remain uncertain and require more in-depth discussion. NDVI, another key vegetation indicator, showed a similar positive influence, though its effect was more gradual and tended to saturate at higher values (Figure 6c).
Soil texture emerged as a key control, with clay and sand content showing strong opposing effects. Clay content, the most important soil factor, was positively correlated with SOCD, exhibiting a sharp, step-wise increase in its marginal effect around 17–19 g·kg−1 (Figure 6b). This suggests its critical role in physically protecting organic matter from decomposition. Conversely, sand content exerted a strong negative influence, particularly when exceeding 45 g·kg−1, which likely reflects the poor aggregation and higher aeration in sandy soils that accelerate organic matter turnover (Figure 6e).
Climatic factors also exert a significant influence on SOC. Mean annual temperature was a significant negative driver, with SOCD declining sharply as temperatures rose above a threshold of approximately 6.5 °C, likely due to increased microbial respiration rates in warmer conditions (Figure 6d). The influence of mean annual precipitation was nonlinear; its positive effect on SOCD only became significant after rainfall exceeded approximately 550 mm (Figure 6h).
Topographic factors indirectly influenced SOCD by modifying local hydrothermal conditions and soil redistribution. Elevation showed a notable positive correlation, especially above 1900 m, where cooler temperatures likely slow decomposition rates (Figure 6f). Aspect also played a role, with higher SOCD values found on slopes oriented from southeast to southwest (100° to 250°), which typically balance sufficient solar radiation for plant growth with protection from excessive heat and moisture loss (Figure 6g). Other factors like slope and topographic wetness index (TWI) had lesser, more localized impacts (Figure 6k,l).
4. Discussion
4.1. Spatiotemporal Distribution Characteristics of SOCD
The results of this study indicate that soil organic carbon density (SOCD) across the Loess Plateau exhibits significant spatial heterogeneity, with an overall decreasing pattern from southeast to northwest (Figure 3). This spatial trend appears to align with the geographic gradients of temperature and precipitation, which have been reported to gradually decline from southeast to northwest across the region [35]. Such consistency suggests that climatic gradients may play an important role in shaping SOCD distribution. High-value areas were mainly found in the Qinling Mountains, Ziwu Ridge, and the eastern Lüliang and southern Taihang Mountains, where relatively dense vegetation cover could support greater organic matter inputs. In contrast, the central and western loess hill-gully regions, characterized by arid climate and sparse vegetation, likely experience limited organic matter input and severe soil erosion, contributing to the observed low SOCD. This spatial pattern is broadly consistent with Wu et al. [36], who estimated SOCS at 0–100 cm depth to be 3.91 Pg C, comparable to our estimate of 4–5 Pg C.
Temporally, SOCS across the Loess Plateau increased between 2005 and 2020, with a total rise of 7.9% and an average annual increment of 0.0315 kg·m−2·yr−1 (Figure 4). Approximately 32.2% of the area showed significant increases, mainly in the southeastern regions where ecological restoration programs were most intensive. This increase is likely linked to the large-scale ‘Grain for Green Program’, which in many areas improved vegetation cover and may have enhanced ecosystem net primary productivity, thereby potentially increasing organic matter inputs from litter and roots [37]. However, the growth rate of SOCD gradually slowed in the later years, indicating a transition from rapid accumulation to relative stabilization. Such a trend could imply threshold effects or partial saturation of carbon sequestration capacity, though further evidence is required to confirm this inference [38].
Differences among soil types also contributed to variations in SOC storage. Cambisols (CM) formed the largest carbon pool due to their extensive distribution and favorable conditions [39]. Arenosols/Dunes (AR/Dunes), located in severely degraded sandy areas, had very low SOC per unit area, likely due to minimal organic input and high susceptibility to wind and water erosion [40]. By contrast, despite their smaller extent, Kastanozems/Chernozems/Phaeozems (KS/CH/PH) and alluvial/colluvial soils (FL/LP/RG/Rocks) maintained relatively high SOCD per unit area, thus making a disproportionate contribution to total SOC storage. These findings suggest that both land degradation processes and intrinsic soil properties may jointly influence the carbon storage potential across the region.
4.2. Driving Factors of SOCD
Based on Random Forest and SHAP analyses, vegetation emerged as the dominant driver of SOCD spatiotemporal patterns, followed by soil physicochemical properties, climatic factors, and topography (Figure 5). Higher vegetation productivity generally implies greater organic matter input, which may help explain the positive association observed between NPP and SOCD [41]. Compared with NDVI—a reflectance-based index that does not directly measure annual net carbon uptake—NPP showed stronger predictive power in our model, likely because it integrates multiple controls such as climate, topography, and land use [42,43]. This finding is consistent with that reported by Li et al. [44]. The partial dependence plot (Figure 6a) indicates a pronounced increase in predicted SOCD once NPP reaches relatively high values in our dataset (NPP, kg C·m−2). This empirical pattern aligns with results reported by Zhou et al. [45], but should be interpreted as a statistical association rather than definitive causal evidence.
Soil properties also exerted a substantial influence, with soil texture (sand, silt, clay) showing significant associations with SOCD (Figure 5). Our PDPs indicated that clay content had the strongest positive effect at relatively higher concentrations (clay content, g·kg−1) (Figure 6b), similar to Dong et al. [46]. The well-documented role of clay in adsorbing and physically protecting organic matter [47] provides a plausible explanation for this pattern. By contrast, sand content was negatively associated with SOCD at relatively high values (sand content, g·kg−1) (Figure 6e), which may reflect faster organic matter turnover in coarse-textured soils [48]. In addition, soil type and bulk density are likely to influence SOCD indirectly by modifying aeration, water retention, and microbial habitat conditions.
Climatic factors appeared to operate primarily through the combined effects of temperature and precipitation on carbon inputs and decomposition. Mean annual temperature showed a negative association with SOCD (Figure 5); predicted SOCD declined in warmer areas (mean annual temperature, °C) (Figure 6d), consistent with expectations of accelerated decomposition under warmer conditions [49]. Mean annual precipitation exhibited a positive association in wetter regions (mean annual precipitation, mm) (Figure 6h), suggesting that water availability may be a limiting factor for vegetation growth and carbon accumulation in this semi-arid to arid region [50]. Together, the spatial variation in these hydrothermal conditions helps to explain, at least in part, the large-scale distribution of SOCD observed in this study (Figure 3).
Topographic factors modulated SOCD mainly at finer spatial scales. Elevation was associated with higher SOCD at the upper ranges sampled in this study (elevation, m) (Figure 6f), suggesting that high-altitude environments may function as relatively cool carbon pools [51]. Aspect influenced local microclimate; in our dataset, SOCD tended to be higher on slopes oriented roughly between 100° and 250° (Figure 6g). This pattern differs from Zhu et al. [9], and may reflect site-specific responses or data-resolution effects. Slope and the Topographic Wetness Index produced smaller but complex localized effects, likely through their influence on runoff, erosion, and soil moisture redistribution (Figure 6k,l) [52].
4.3. Generalizability and Limitations
The synergistic mechanisms identified in this study are consistent with findings from other semi-arid ecosystems. In the alpine semi-arid region of the Qilian Mountains, vegetation productivity has likewise been confirmed as a primary driver of SOC spatial variability [53]. In the Mediterranean region, empirical evidence indicates that farmland abandonment or vegetation restoration generally enhances soil carbon stocks, highlighting the universal role of vegetation recovery in increasing SOCD under semi-arid conditions [54]. At the global scale, cross-regional analyses of grasslands demonstrate a positive association between plant diversity, productivity, and soil carbon, consistent with the observed NPP–SOCD relationship in this study [55]. Taken together, these findings confirm the robustness of the identified mechanisms, while also suggesting that the magnitude of their effects may vary depending on regional soil properties, climatic regimes, and land use histories.
The findings of this study provide critical implications for land management policies aimed at achieving carbon neutrality in the Loess Plateau. The observed slowdown in SOCS accumulation suggests that the benefits of large-scale vegetation restoration projects, such as the “Grain-for-Green” program, are approaching saturation. This underscores the need to shift policy priorities from uniform vegetation expansion to sustainable and differentiated management. In the southeastern region, where favorable vegetation and climatic conditions prevail, sustainable ecosystem management and conservation agriculture practices should be adopted to consolidate and enhance existing carbon sequestration gains [56]. In contrast, in the central and western regions where SOC accumulation is slow or even declining, policies should prioritize local climatic and vegetation suitability, promote soil improvement, and implement targeted soil erosion control measures to strengthen ecological stability [57]. Such context-specific strategies are essential for optimizing soil carbon stocks in the Loess Plateau, safeguarding long-term ecological security, and contributing effectively to national carbon neutrality goals.
The present study is primarily based on the Loess Plateau region. Although the findings may bear certain similarities to other semi-arid regions, the identified dominant factors and predictive thresholds should not be directly extrapolated to these areas without careful consideration of their unique environmental and management contexts [58]. Future research could employ standardized indicators to conduct multi-regional comparative analyses, thereby more precisely delineating the boundary conditions under which these regulatory mechanisms apply. The data collection process for training the model in this study is generally consistent with the approaches reported in similar studies [18]. Nevertheless, it is important to note that the SOC data were not derived from direct field sampling. Despite applying data correction procedures and soil transfer functions, uncertainties remain due to sampling-stage errors in the source data, the subsequent analytical methods, and the heterogeneity of the environmental variables employed. These limitations may affect the accuracy of temporal analyses. To address this issue, future studies should prioritize the establishment of long-term, systematic regional monitoring networks to collect in situ data for model validation and calibration. Furthermore, although the 0–100 cm soil depth provides a representative basis for analysis, the substantial soil thickness of the Loess Plateau cannot be overlooked [13]. Considerable amounts of SOC remain in deeper soil layers [36], where dynamic changes differ markedly from those in the surface soil. This may result in an underestimation of the regional carbon stock. Future investigations should extend the sampling depth to deeper layers and conduct stratified analyses across soil horizons to build a more comprehensive and accurate understanding of ecosystem-scale carbon storage and its long-term dynamics.
5. Conclusions
This study quantified the spatiotemporal dynamics of soil organic carbon (SOC) in the 0–100 cm soil layer of the Loess Plateau from 2005 to 2020. SOC storage increased from 4.84 to 5.23 Pg C, though the annual sequestration rate declined markedly, indicating that the carbon sink effect may be reaching saturation after two decades of large-scale restoration. Spatial heterogeneity was evident, with significant increases concentrated in the humid southeast and decreases observed in arid northwestern areas. Cambisols were identified as the largest regional carbon pool, accounting for more than 44% of total SOC storage.
The observed slowdown in SOC accumulation suggests that future land management may need to move beyond uniform vegetation expansion and potentially adopt more sustainable, differentiated approaches. Our results indicate that southeastern regions could benefit from ecosystem-based management and conservation agriculture to maintain existing carbon gains, while central and western areas might emphasize soil improvement and erosion control to potentially enhance ecological stability. Although this study provides valuable insights into SOC dynamics, the findings appear to be specific to the Loess Plateau context. Broader applicability would likely require further multi-regional studies, improved monitoring networks, and deeper soil investigations to better capture long-term ecosystem-scale carbon dynamics.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/agronomy15102260/s1, Figure S1: Soil type distribution based on the World Reference Base (WRB) for Soil Resources Group. The abbreviations in the soil map legend correspond to the following Reference Soil Groups, listed in their order of appearance: Water; UM: Umbrisols; LV/AL: Luvisols/Alisols Complex; KS/CH/PH: Kastanozems/Chernozems/Phaeozems Complex; GL/PL/ST: Gleysols/Planosols/Stagnosols Complex; AN: Andosols; FL/LP/RG/Rocks: Fluvisols/Leptosols/Regosols/Rocks Complex; DU/CL/GY/SC: Durisols/Calcisols/Gypsisols/Solonchaks Complex; CR: Cryosols; CM: Cambisols; AT: Anthrosols; AR/Dunes: Arenosols/Dunes Complex.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu) and H.L.; methodology, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu) and K.Y.; software, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu) and D.C.; validation, M.D. and Y.Z. (Yichao Zhang); formal analysis, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu) and D.C.; investigation, M.D., X.W., Y.Z. (Yichao Zhang) and X.L.; resources, X.W. and X.L.; data curation, M.D., X.W., D.C., and Y.Z. (Yichao Zhang); writing—original draft preparation, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu); writing—review and editing, K.Y. and H.L.; visualization, Y.Z. (Yan Zhu); supervision, K.Y. and H.L.; project administration, H.L.; funding acquisition, H.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Natural Science Basic Research Program of Shaanxi (2025JCYBMS-285) and Yangling Science and Technology Program Project (2024NY-04).
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article/Supplementary Material. Further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author(s).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Le Quéré, C.; Andrew, R.M.; Friedlingstein, P.; Sitch, S.; Hauck, J.; Pongratz, J.; Pickers, P.A.; Korsbakken, J.I.; Peters, G.P.; Canadell, J.G.; et al. Global Carbon Budget 2018. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2018, 10, 2141–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.B.; Wu, Y.P.; Hui, J.Y.; Sivakumar, B.; Meng, X.Y.; Liu, S.G. Projected Soil Organic Carbon Loss in Response to Climate Warming and Soil Water Content in a Loess Watershed. Carbon Balance Manag. 2021, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, W.H.; Chang, N.J.; Zhang, G.L.; Kang, J.H.; Yi, X.P.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.F.; Wang, L.G.; Li, H. Soil Organic Carbon Changes in China’s Croplands: A Newly Estimation Based on DNDC Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 905, 167107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.L.; Hu, N.; Qi, Y.X.; Zhao, W.Z.; Dong, Q.Q. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Soil Organic Carbon in Northwestern China Via Comparisons of Different Methods. Remote Sens. 2025, 17, 420. [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmeier, M.; Urbanski, L.; Hobley, E.; Lang, B.; von Lützow, M.; Marin-Spiotta, E.; van Wesemael, B.; Rabot, E.; Ließ, M.; Garcia-Franco, N.; et al. Soil Organic Carbon Storage as a Key Function of Soils—A Review of Drivers and Indicators at Various Scales. Geoderma 2019, 333, 149–162. [Google Scholar]
- Doetterl, S.; Stevens, A.; Six, J.; Merckx, R.; Van Oost, K.; Casanova Pinto, M.; Casanova-Katny, A.; Muñoz, C.; Boudin, M.; Zagal Venegas, E.; et al. Soil Carbon Storage Controlled by Interactions between Geochemistry and Climate. Nat. Geosci. 2015, 8, 780–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Gray, J.M.; Waters, C.M.; Anwar, M.R.; Orgill, S.E.; Cowie, A.L.; Feng, P.; Liu, D.L. Modelling and Mapping Soil Organic Carbon Stocks under Future Climate Change in South-Eastern Australia. Geoderma 2022, 405, 115442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.M.; Zhang, G.L.; Liu, F.; Lu, Y.Y.; Yang, F.; Yang, F.; Yang, M.; Zhao, Y.G.; Li, D.C. Comparison of Boosted Regression Tree and Random Forest Models for Mapping Topsoil Organic Carbon Concentration in an Alpine Ecosystem. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 60, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Feng, Q.; Qin, Y.Y.; Cao, J.J.; Zhang, M.X.; Liu, W.; Deo, R.C.; Zhang, C.Q.; Li, R.L.; Li, B.F. The Role of Topography in Shaping the Spatial Patterns of Soil Organic Carbon. CATENA 2019, 176, 296–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, N.N.; Wei, X.R.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.T.; Shao, M.A.; Jia, X.X.; Li, X.Z.; Zhang, Q.Y. Soil Texture Determines the Distribution of Aggregate-Associated Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorous under Two Contrasting Land Use Types in The Loess Plateau. CATENA 2019, 172, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, L.; Li, L.; Bai, Z. Analysis of Desertification and the Driving Factors over the Loess Plateau. Geocarto Int. 2023, 38, 2290175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Dong, Y.S.; Wang, Y.Q.; Wei, X.R.; Wang, Y.F.; Cui, B.L.; Zhou, W.J. Natural Vegetation Restoration is More Beneficial to Soil Surface Organic and Inorganic Carbon Sequestration than Tree Plantation on The Loess Plateau of China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 485–486, 615–623. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Zhang, P.P.; Song, Y.; Li, Z.M.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Sun, H.; Qiao, J.; Wang, Y.Q.; An, S.S. The Structure and Development of Loess Critical Zone and its Soil Carbon Cycle. Carbon Neutrality 2024, 3, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.H.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Xu, G.C.; Gao, H.D.; Cheng, Y.T.; Chang, E.H.; Yuan, S.L.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Z.H. Spatial Distribution of Soil Organic Carbon and its Influencing Factors under the Condition of Ecological Construction in a Hilly-Gully Watershed of the Loess Plateau, China. Geoderma 2017, 296, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, J.L.; Li, S.J. Spatial Variability of Soil Organic Carbon in a Watershed on the Loess Plateau. Pedosphere 2009, 19, 486–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.H.; Zhao, Z.H. Analysis of Carbon Storage and its Contributing Factors—A Case Study in the Loess Plateau (China). Energies 2018, 11, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengl, T.; Mendes de Jesus, J.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Ruiperez Gonzalez, M.; Kilibarda, M.; Blagotić, A.; Shangguan, W.; Wright, M.N.; Geng, X.Y.; Bauer-Marschallinger, B.; et al. Soilgrids250m: Global Gridded Soil Information Based on Machine Learning. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169748. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Biswas, A.; Su, H.; Cao, J.; Hong, S.; Wang, H.; Dong, X. Quantifying changes in soil organic carbon density from 1982 to 2020 in Chinese grasslands using a random forest model. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1076902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Du, Z.P.; Li, X.Y.; Bao, Z.Y.; Zhao, N.; Yue, T.X. Incorporation of High Accuracy Surface Modeling into Machine Learning to Improve Soil Organic Matter Mapping. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, L.X.; Zhang, P.P.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.Q.; Xu, C.; Zhang, L.K.; An, S.S.; Kuzyakov, Y. Large-Scale Ecosystem Carbon Stocks and Their Driving Factors across Loess Plateau. Carbon Neutrality 2023, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.Y.; Deng, L.; Wu, G.L.; Wang, K.B.; Shangguan, Z.P. Large-Scale Soil Organic Carbon Mapping Based on Multivariate Modelling: The Case of Grasslands on the Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.J.; Jia, X.X.; Shao, M.A. Loess Thickness Variations Across the Loess Plateau of China. Surv. Geophys. 2018, 39, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, N.P.; Yu, G.R. A dataset of carbon density in Chinese terrestrial ecosystems (2010s). China Sci. Data 2019, 4, 90–96. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.L. Chinese Soil Taxonomy: Central and Western China Volume; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Su, W.; Guo, X.B.; Chu, Y.; Fan, B.; Ji, H.F.; Lan, Z.D.; Li, G.Z.; Li, X.J.; Luo, Y.Q.; Re, P.K.Y.; et al. A dataset of soil organic carbon density of typical ecosystems in the arid areas of Northwest China from 2005 to 2020. China Sci. Data 2024, 9, 56–69. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.T.; Bai, X.; Yao, W.Q.; Li, P.F.; Hu, J.F.; Kang, L. Spatioemporal Dynamics and Driving Forces of Soil Organic Carbon Changes in an Arid Coal Mining Area of China Investigated Based on Remote Sensing Techniques. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; He, N.P.; Yu, G.R.; Wen, D.; Gao, Y.; He, H.L. Differences in Pedotransfer Functions of Bulk Density Lead to High Uncertainty in Soil Organic Carbon Estimation at Regional Scales: Evidence from Chinese Terrestrial Ecosystems. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2015, 120, 1567–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, D.S.; Shi, X.Z.; Wang, H.J.; Sun, W.X.; Warner, E.D.; Liu, Q.H. National Scale Analysis of Soil Organic Carbon Storage in China Based on Chinese Soil Taxonomy. Pedosphere 2007, 17, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breiman, L. Random Forests. Mach. Learn. 2001, 45, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Yu, G.R.; He, N.P.; Wang, Q.F.; Gao, Y.; Wen, D.; Li, S.G.; Niu, S.L.; Ge, J.P. Carbon Storage in China’s Terrestrial Ecosystems: A Synthesis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.M.; Zhang, X.C.; Pang, G.W.; Han, F.P. The Estimation of Soil Organic Carbon Distribution and Storage in a Small Catchment Area of the Loess Plateau. CATENA 2013, 101, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prăvălie, R.; Nita, I.A.; Patriche, C.; Niculiță, M.; Birsan, M.V.; Roșca, B.; Bandoc, G. Global Changes in Soil Organic Carbon and Implications for Land Degradation Neutrality and Climate Stability. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IUSS Working Group WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources. In International Soil Classification System for Naming Soils and Creating Legends for Soil Maps, 4th ed.; International Union of Soil Sciences (IUSS): Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fabregat-Palau, J.; Ershadi, A.; Finkel, M.; Rigol, A.; Vidal, M.; Grathwohl, P. Modeling PFAS Sorption in Soils Using Machine Learning. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025, 59, 7678–7687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Spatial Distribution of Ecosystem Carbon Storage and its Influencing Factors on the Loess Plateau. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 6786–6799. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.Z.; Deng, L.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Huang, Y.Y.; Song, X.D.; Nie, M.; Deng, J.M.; Zhao, P.; Liao, Y.; Dong, L.B.; et al. Soil Organic and Inorganic Carbon Pools in the Loess Plateau: New Estimation, Change and Trade-Offs. Global Planet. Chang. 2025, 253, 104951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.J.; Liu, Z.P.; Gao, J.L.; Lugato, E.; Ren, Y.Q.; Shao, M.A.; Wei, X.R. The Grain for Green Project Eliminated the Effect of Soil Erosion on Organic Carbon on China’s Loess Plateau between 1980 and 2008. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2021, 322, 107636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, R.; Bossio, D. Dynamics and Climate Change Mitigation Potential of Soil Organic Carbon Sequestration. Environ. Manag. 2014, 144, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.W.; Liang, Y.K.; Zamanian, K.; Zhao, X.N. Renaturation on the Loess Plateau: Significant Increase in Soil Organic Carbon under Different Soil Types Over Two Decades. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lian, J.; Luo, Y.; Niu, Y.; Gong, X. Spatial Pattern of Soil Organic Carbon and Total Nitrogen, and Analysis of Related Factors in an Agro-Pastoral Zone in Northern China. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0197451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.L.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Vegetation Type and Soil Moisture Drive Variations in Leaf Litter Decomposition Following Secondary Forest Succession. Forests 2021, 12, 1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, D.C.; Kauffman, J.B.; Murdiyarso, D.; Kurnianto, S.; Stidham, M.; Kanninen, M. Mangroves Among the Most Carbon-rich Forests in the Tropics. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.Y.; Li, M.Y.; Xu, H.; Guo, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y.C.; Wu, X.J.; Feng, L.C.; Chen, J.; Lu, X.; et al. Spatiotemporal Variation and Driving Factors of Vegetation Net Primary Productivity in a Typical Karst Area in China from 2000 to 2010. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 132, 108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Sun, S.B.; Han, J.C.; Yan, J.W.; Liu, W.B.; Wei, Y.; Lu, N.; Sun, Y.Y. Impacts of Chinese Grain for Green Program and Climate Change on Vegetation in the Loess Plateau during 1982–2015. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 177–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.H.; Ren, C.J.; Wang, C.K.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Luo, Y.Q.; Luo, Z.K.; Du, Z.G.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y.H.; Jiao, S.; et al. Global Turnover of Soil Mineral-Associated and Particulate Organic Carbon. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, L.B.; Fan, J.W.; Li, J.W.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Wu, J.Z.; Li, A.; Shangguan, Z.P.; Deng, L. Forests Have a Higher Soil C Sequestration Benefit Due to Lower C Mineralization Efficiency: Evidence from the Central Loess Plateau Case. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2022, 339, 108144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keiluweit, M.; Nico, P.S.; Kleber, M.; Fendorf, S. Are Oxygen Limitations under Recognized Regulators of Organic Carbon Turnover in Upland Soils? Biogeochemistry 2016, 127, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witzgall, K.; Vidal, A.; Schubert, D.I.; Höschen, C.; Schweizer, S.A.; Buegger, F.; Pouteau, V.; Chenu, C.; Mueller, C.W. Particulate Organic Matter as a Functional Soil Component for Persistent Soil Organic Carbon. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.W.; Wu, Y.P.; Liu, S.G.; Zhao, W.Z.; Xiao, J.F.; Winowiecki, L.A.; Vågen, T.G.; Xu, J.C.; Yin, X.W.; Wang, F.; et al. The Grain-for-Green Project Offsets Warming-Induced Soil Organic Carbon Loss and Increases Soil Carbon Stock in Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 837, 155469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.Q.; Nie, M.; Pendall, E.; Reich, P.B.; Pei, J.M.; Noh, N.J.; Zhu, T.; Li, B.; Fang, C.M. Biogeographic Variation in Temperature Sensitivity of Decomposition in Forest Soils. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 1873–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.Y.; Zhou, L.H.; He, X.J.; Wei, P.; Lin, D.M.; Qian, S.H.; Zhao, L.; Luo, M.; Yin, X.H.; Zeng, L.; et al. Effects of Elevation Gradient on Soil Carbon and Nitrogen in a Typical Karst Region of Chongqing, Southwest China. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2022, 127, e2021JG006742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.B. Environmental Variables Controlling Soil Organic Carbon in Top- and Sub-Soils in Karst Region of Southwestern China. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 90, 624–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.J.; Si, J.H.; Jia, B.; Zhou, D.M.; Zhu, X.L.; Ndayambaza, B.; Bai, X.; Wang, B.Y. Soil Organic Carbon Distribution and Multi-Scale Drivers in Semi-Arid Alpine Regions: Implications for Carbon Storage Function Stability. Environ. Manag. 2025, 393, 126989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Sala, G.; Galati, A.; Crescimanno, M.; Cerdà, A.; Badalamenti, E.; La Mantia, T. Agricultural Land Abandonment in Mediterranean Environment Provides Ecosystem Services via Soil Carbon Sequestration. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 576, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spohn, M.; Bagchi, S.; Biederman, L.A.; Borer, E.T.; Bråthen, K.A.; Bugalho, M.N.; Caldeira, M.C.; Catford, J.A.; Collins, S.L.; Eisenhauer, N.; et al. The Positive Effect of Plant Diversity on Soil Carbon Depends on Climate. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 6624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Wang, K.; Li, J.; Shangguan, Z.; Deng, L. Mixed Plantations Have More Soil Carbon Sequestration Benefits than Pure Plantations in China. For. Ecol. Manag. 2023, 529, 120654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.F.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Z.H.; López-Vicente, M.; Wu, G.L. Effectiveness of Re-vegetated Forest and Grassland on Soil Erosion Control in the Semi-arid Loess Plateau. CATENA 2020, 195, 104787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.A.; Wieder, W.R.; Bonan, G.B.; Fierer, N.; Raymond, P.A.; Crowther, T.W. Managing Uncertainty in Soil Carbon Feedbacks to Climate Change. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).