Rice–Potato Rotation Pattern Affects 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis and Productivity in Aromatic Rice Grains
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Site
2.3. Experimental Treatments and Design
2.4. Project Determination
2.4.1. Rice Plant Sampling and Rice Yield Determination
2.4.2. Collection and Determination of Soil Samples
2.4.3. Determination of Processing Quality and Nutritional Quality
2.4.4. Determination of 2-AP Content in Grains
2.4.5. Determination of Proline Content in Grains
2.4.6. Determination of Δ1-Pyrrolidine-5-Carboxylic Acid (P5C) in Grains
2.4.7. Determination of Δ1-Pyrroline Content in Grains
2.4.8. Determination of Proline Dehydrogenase (ProDH) Activity in Grains
2.4.9. Determination of Ornithine Aminotransferase (OAT) Activity in Grains
2.4.10. Determination of Diamine Oxidase (DAO) Activity in Grains
2.4.11. Determination of GABA Content and BADH Activity in Grains
2.5. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
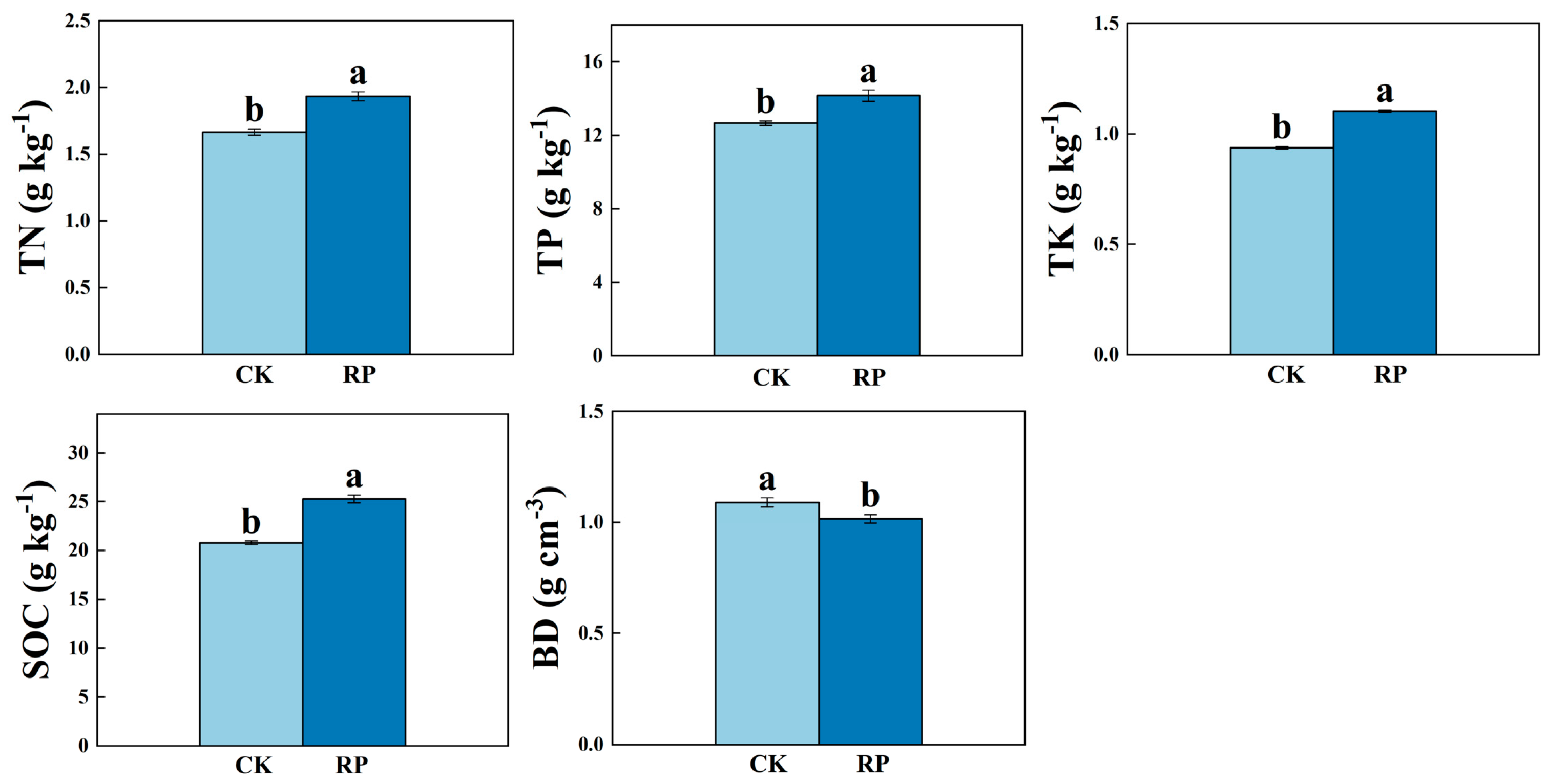
3.1. Paddy Soil Properties
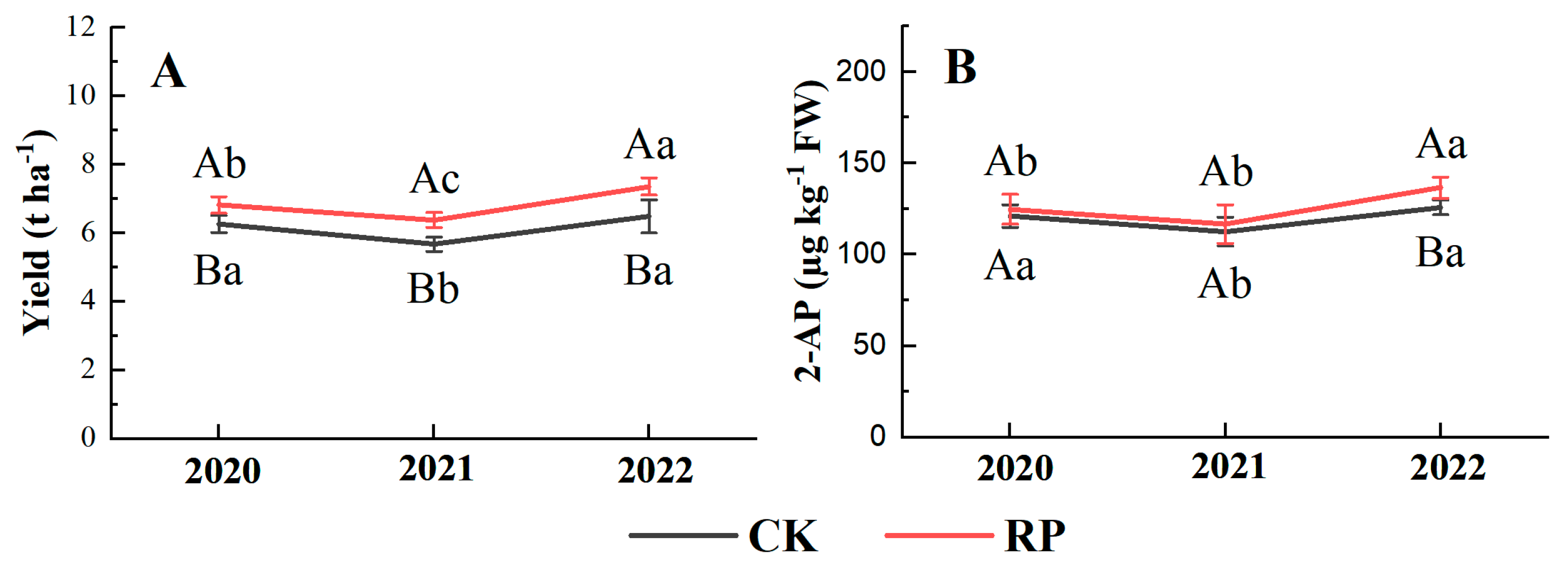
3.2. Yield and 2-AP Content in Grains
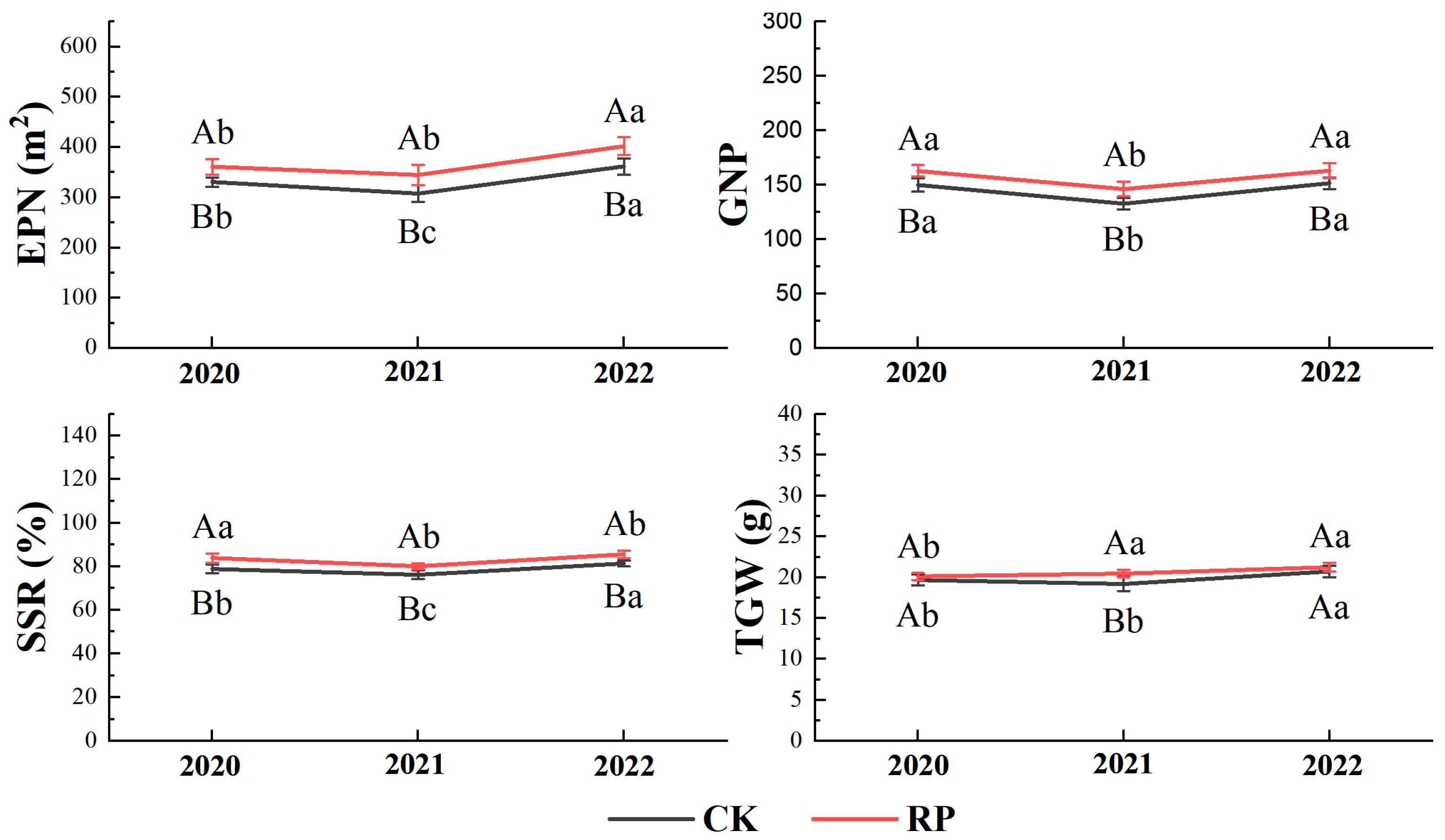
3.3. Yield Component
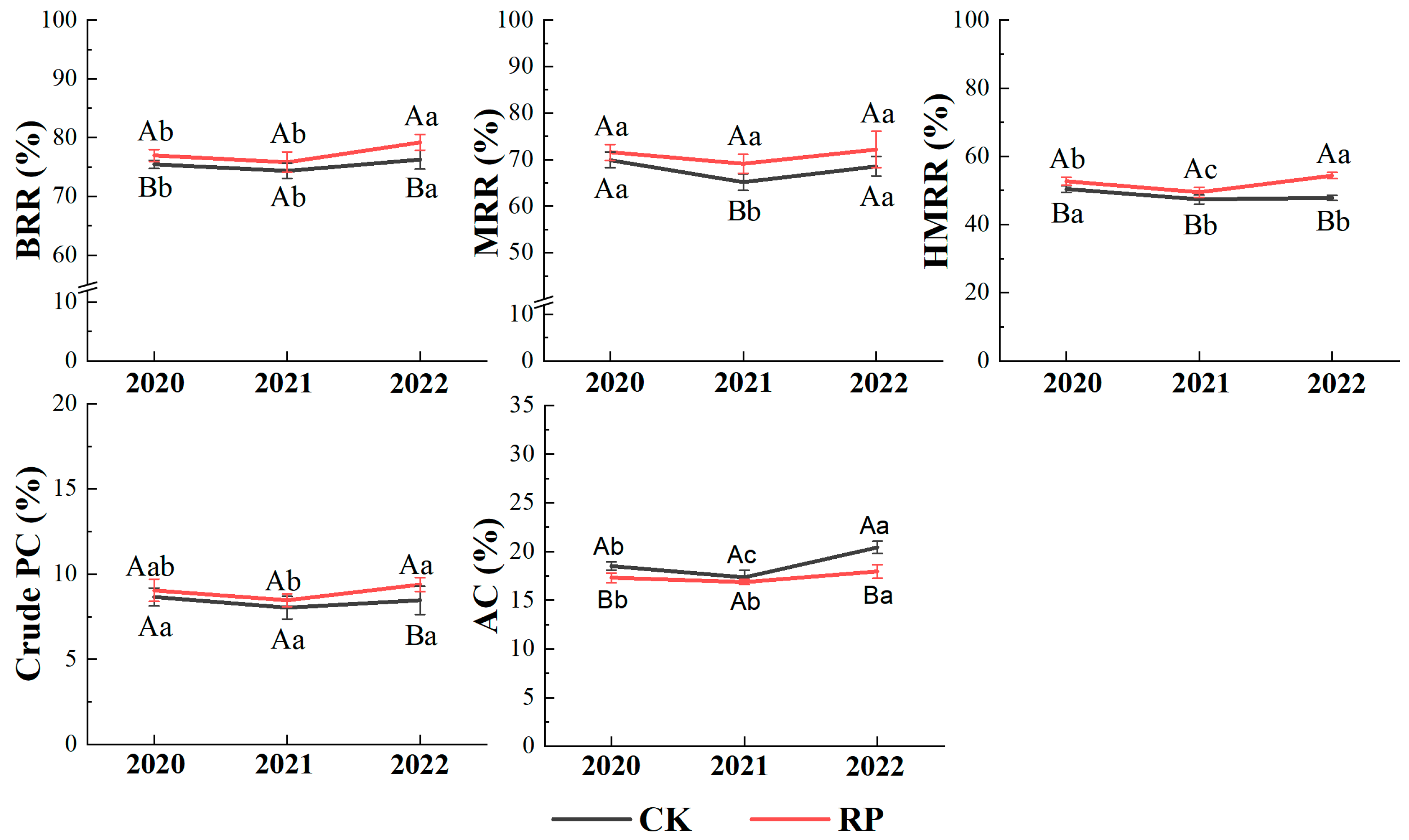
3.4. Rice Grain Quality
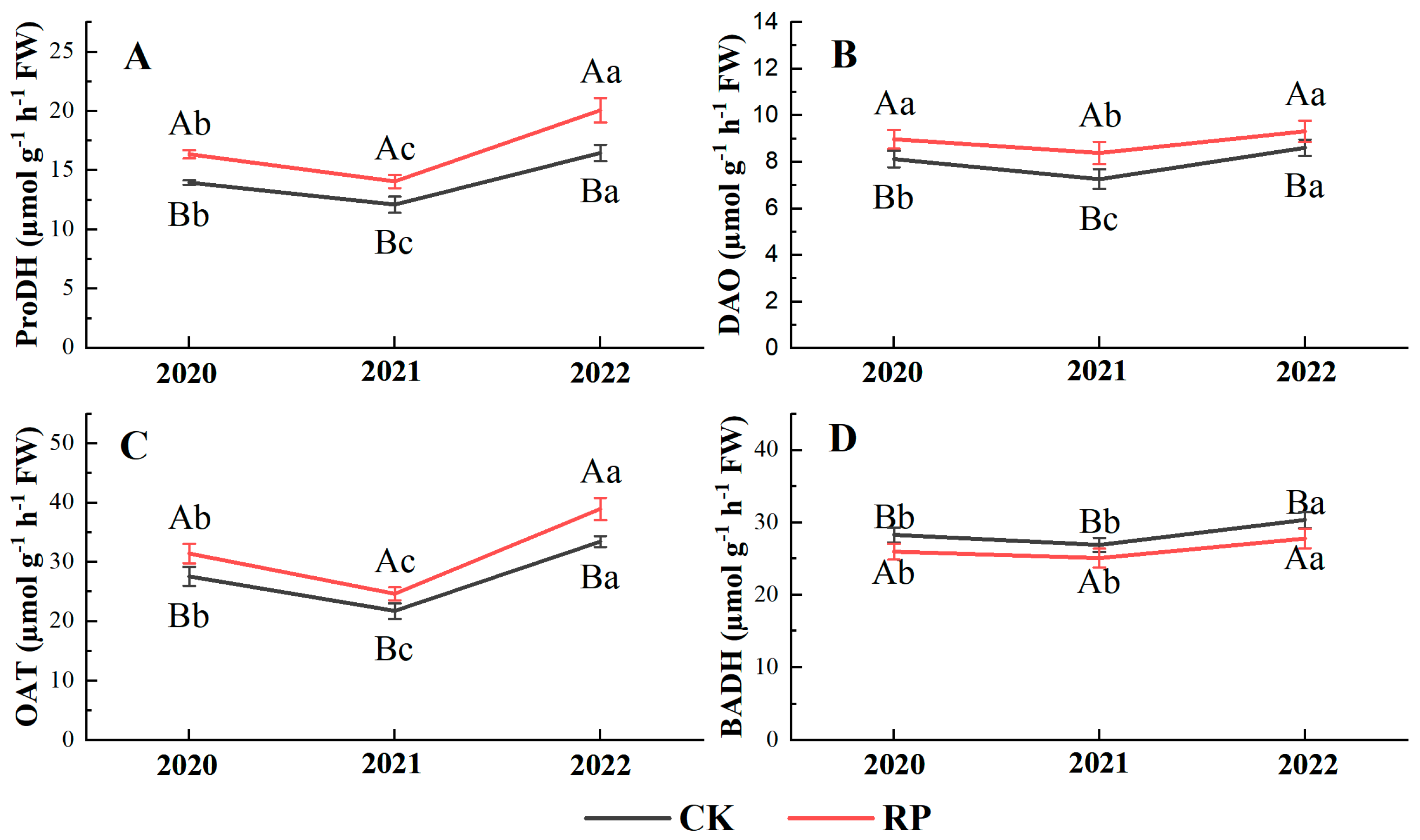
3.5. Precursors Involved in 2-AP Biosynthesis
3.6. Enzymes Involved in 2-AP Biosynthesis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giraud, G. The world market of fragrant rice, main issues and perspectives. Int. Food Agribus. Man. 2013, 16, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, W.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, L.; Ashraf, U.; Tang, X.; Pan, S.; Tian, H.; Mo, Z. Application of γ-aminobutyric acid under low light conditions: Effects on yield, aroma, element status, and physiological attributes of fragrant rice. Ecotox. Environ. Safe. 2021, 213, 111941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.G.; Duarte, G.; Mariutti, L.; Bragagnolo, N. Aroma profile of rice varieties by a novel SPME method able to maximize 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and minimize hexanal extraction. Food Res. Int. 2019, 123, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paule, C.M.; Powers, J.J. Sensory and chemical examination of aromatic and nonaromatic rices. J. Food Sci. 1989, 54, 343–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Wang, Z.; He, Y.; Xue, S.; Zhang, S.; Pei, M.; Liu, H.; Yu, Y.; Guo, D. Proline synthesis and catabolism-related genes synergistically regulate proline accumulation in response to abiotic stresses in grapevines. Sci. Hortic. 2022, 305, 111373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buttery, R.; Ling, L.; Juliano, B. 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline: An important aroma component of cooked rice. Chem. Indus. 1982, 23, 958–959. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Miao, Y.; Yuan, H.; Huang, F.; Sun, M.; He, L.; Liu, X.; Luo, J. Volatilome-based GWAS identifies OsWRKY19 and OsNAC021 as key regulators of rice aroma. Mol. Plant 2024, 17, 1866–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, L.G.; Hacke, A.; Bergara, S.F.; Villela, O.V.; Mariutti, L.; Bragagnolo, N. Identification of volatiles and odor-active compounds of aromatic rice by OSME analysis and SPME/GC-MS. Food Res. Int. 2021, 142, 110206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, Z.; Li, W.; Pan, S.; Fitzgerald, T.L.; Xiao, F.; Tang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, M.; Tian, H.; Tang, X. Shading during the grain filling period increases 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline content in fragrant rice. Rice 2015, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Shafiq, S.; Ashraf, U.; Qi, J.; Mo, Z.; Tang, X. Biosynthesis of 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice: Recent insights into agro-management, environmental factors, and functional genomics. J. Agr. Food Chem. 2023, 71, 4201–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonlaphdecha, J.; Maraval, I.; Roques, S.; Audebert, A.; Boulanger, R.; Bry, X.; Gunata, Z. Effect of Timing and Duration of Salt Treatment during Growth of a Fragrant Rice Variety on Yield and 2-Acetyl-1-pyrroline, Proline, and GABA Levels. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 3824–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, H.; Xie, W.; Pan, S.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Duan, M.; Wang, S.; Tang, X.; Mo, Z. Effects of Light Quality Treatments during the Grain Filling Period on Yield, Quality, and Fragrance in Fragrant Rice. Agronomy 2021, 11, 531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Huang, L.; Cheng, M.; Li, C.; Zhou, X.; Ullah, A.; Sarfraz, S.; Khatab, A.; Xie, G. Progresses in biosynthesis pathway, regulation mechanism and potential application of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2024, 215, 109047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Yang, Y.; Shi, W.; Ji, Q.; He, F.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, X.; Xu, M. Badh2, encoding betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase, inhibits the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline, a major component in rice fragrance. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1850–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, H.; Duan, M.; Kong, L.; He, L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Tang, X. The regulatory mechanism of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis in fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.) under different soil moisture contents. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 772728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Shafiq, S.; Tang, X. CRISPR-Cas9-mediated editing of BADH2 gene triggered fragrance revolution in rice. Physiol. Plantarum. 2023, 175, e13871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Waters, D.; Cordeiro, G.M.; Henry, R.J.; Reinke, R.F. A single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker linked to the fragrance gene in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Sci. 2003, 165, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinge, V.R.; Patil, H.B.; Nadaf, A.B. Aroma volatile analyses and 2AP characterization at various developmental stages in Basmati and Non-Basmati scented rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivars. Rice 2016, 9, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Park, Y. Discovery of a novel fragrant allele and development of functional markers for fragrance in rice. Mol. Breed. 2015, 35, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, P.; Luo, H.; He, J.; Mao, T.; Du, B.; Hu, L. Different tillage induces regulation in 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis in direct-seeded fragrant rice. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.; Luo, H.; Wang, Z.; Hu, L. Benefits of continuous plow tillage to fragrant rice performance. Agron. J. 2020, 112, 4171–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, B.; He, L.; Lai, R.; Luo, H.; Zhang, T.; Tang, X. Fragrant rice performances in response to continuous zero-tillage in machine-transplanted double-cropped rice system. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tang, X.; Pan, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, S.; Chen, C.; Dai, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of water-nitrogen interaction at tillering stage on aroma, grain yield and quality of aromatic rice. Acta Agric. Boreali-Sin. 2014, 1, 159–164. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Ashraf, U.; Tian, H.; Mo, Z.; Pan, S.; Anjum, S.; Duan, M.; Tang, X. Manganese-induced regulations in growth, yield formation, quality characters, rice aroma and enzyme involved in 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline biosynthesis in fragrant rice. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2016, 103, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hai, T.; Xiao, X.; Chao, L.; Wen, T.; Li, G.; Ke, W.; Kai, C.; Geng, S.; Xiao, P. Effects of Winter Cover Crop and Straw Returning on the Functional Diversity of Rhizosphere Microflora in Double-crop Rice Paddies. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2018, 19, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, J.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, J. Long term effects of crop rotation and fertilization on crop yield stability in southeast China. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Xiang, C. Collaborative network, technological progress and potato production in China. Potato Res. 2024, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Y. Mulching improves yield and water-use efficiency of potato cropping in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crop Res. 2018, 221, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Shi, Z.; Shi, J. Nutrient balance of agroecosystem in six provinces in Southern China. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2000, 33, 63–67. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Zheng, X.; Wang, D.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Zhang, X. Effect of long-term paddy-upland yearly rotations on rice (Oryza sativa) yield, soil properties, and bacteria community diversity. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 279641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, J.M. The inactivation of pea-seedling diamine oxidase by peroxidase and 1,5-diaminopentane. Biochem. J. 1967, 104, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, P.; Vishwakarma, S.K.; Upadhyay, V.B. Organic farming package for rice-potato cropping system. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2019, 8, 962–967. [Google Scholar]
- Mo, Z.; Li, Y.; Nie, J.; He, L.; Pan, S.; Duan, M.; Tian, H.; Xiao, L.; Zhong, K.; Tang, X. Nitrogen application and different water regimes at booting stage improved yield and 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2AP) formation in fragrant rice. Rice 2019, 12, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, P.; Wang, J.; Li, C.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Cao, C. Soil quality indicators of integrated rice-crayfish farming in the Jianghan Plain, China using a minimum data set. Soil Till. Res. 2020, 204, 104732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Chen, A.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Lei, B.; Zhai, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, H. Cropping systems affect paddy soil organic carbon and total nitrogen stocks (in rice-garlic and rice-fava systems) in temperate region of southern China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Wang, E.; Li, C.; Cai, M.; Cheng, B.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Y. Use of protein content, amylose content, and RVA parameters to evaluate the taste quality of rice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 8, 758547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhang, T.; Zheng, A.; He, L.; Lai, R.; Liu, J.; Xing, P.; Tang, X. Exogenous proline induces regulation in 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline (2-AP) biosynthesis and quality characters in fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.). Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 13971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, G.; Honig, A.; Stein, H.; Suzuki, N.; Mittler, R.; Zilberstein, A. Unraveling Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate-proline cycle in plants by uncoupled expression of proline oxidation enzymes. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 26482–26492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ncube, B.; Finnie, J.F.; Van Staden, J. Dissecting the stress metabolic alterations in in vitro Cyrtanthus regenerants. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2013, 65, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, R.; Chen, H.; Gu, Z. Factors influencing diamine oxidase activity and γ-aminobutyric acid content of fava bean (Vicia faba L.) during germination. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 11616–11620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takabe, T.; Wada, K. Molecular cloning and functional characterization of two kinds of betaine-aldehyde dehydrogenase in betaine-accumulating mangrove Avicennia marina (Forsk.) Vierh. Plant Mol. Biol. 2001, 45, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. The influence of the type of crop residue on soil organic carbon fractions: An 11-year field study of rice-based cropping systems in southeast China. Agric. Ecosys. Environ. 2016, 223, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waheed, A.; Li, C.; Muhammad, M.; Ahmad, M.; Khan, K.A.; Ghramh, H.A.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, D. Sustainable potato growth under straw mulching practices. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Pan, X.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hang, X.; Yu, X.; Zhang, W. Effects of long-term fertilization on the weed growth and community composition in a double-rice ecosystem during the fallow period. Weed Biol. Manag. 2013, 13, 10–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Hussain, S.; Wu, L.; Qin, Z.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Khan, F.; Cao, W.; Geng, M. Greenhouse gas emissions, soil quality, and crop productivity from a mono-rice cultivation system as influenced by fallow season straw management. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2016, 23, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pramanik, P.; Haque, M.M.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, P.J. C and N accumulations in soil aggregates determine nitrous oxide emissions from cover crop treated rice paddy soils during fallow season. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 490, 622–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, S.; Zheng, X.; Yin, M.; Chu, G.; Xu, C.; Yan, J.; Chen, L.; Wang, D.; Zhang, X. Effect of various crop rotations on rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency in paddy–upland systems in southeastern China. Crop J. 2018, 6, 576–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Cui, Y.; Hao, X.; Wang, B.; Tian, X.; Li, X.; Qin, Y. Rice yield, quality, and soil fertility in response to straw incorporation and rotation pattern. J. Plant Nutr. Fert. 2021, 27, 1926–1937. [Google Scholar]
- Zhen, B.; Zhou, X.; Lu, H.; Li, H. Effects of Waterlogging on Rice Growth at Jointing–Booting Stage. Water 2024, 16, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, J.H.; Lu, K.D.; Huo, Z.G.; Xie, N.; Huang, W.H. Effects of waterlogging stress on rice morphology and yield component at the jointing stage. Chin. J. Ecol. 2014, 33, 1818–1825. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Tang, X.R.; Tian, H.; Sheng, G.P.; Mei, Y.D.; Nie, J. Effects of different irrigation modes on aroma content of aromatic rice at booting stage. Guangdong Agric. Sci. 2013, 8, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, T.; Chen, Y.; Westby, A.P.; Ren, W. Soil physicochemical and biological properties of paddy-upland rotation: A review. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 856352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, R.; Shen, Y.; Kong, X.; Ge, B.; Sun, X.; Cao, M. Effects of Diverse Crop Rotation Sequences on Rice Growth, Yield, and Soil Properties: A Field Study in Gewu Station. Plants 2024, 13, 3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leesawatwong, M.; Jamjod, S.; Kuo, J.; Dell, B.; Rerkasem, B. Nitrogen fertilizer increases seed protein and milling quality of rice. Cereal Chem. 2005, 82, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Zhang, H.; Guo, B.; Xu, K.; Dai, Q.; Wei, C.; Zhou, G.; Huo, Z. Effects of nitrogen level on structure and physicochemical properties of rice starch. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 63, 525–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, P.; Luo, H.; He, Z.; He, L.; Zhao, H.; Tang, X.; Duan, M. Trans-Zeatin induced regulation of the biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice (Oryza sativa L.) seedlings. BMC Plant Biol. 2023, 23, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Teng, C.; Chang, J.; Chuang, H.; Ho, C.; Wu, M. Biosynthetic mechanism of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline and its relationship with Δ1-pyrroline-5-carboxylic acid and methylglyoxal in aromatic rice (Oryza sativa L.) callus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 7399–7404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potcho, P.M.; Imran, M.; Korohou, T.; Kamara, N.; Tang, X. Fertilizer Deep Placement Significantly Affected Yield, Rice Quality, 2-AP Biosynthesis and Physiological Characteristics of the Fragrant Rice Cultivars. Agronomy 2022, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Lin, J.; Xie, Q.; Shi, J.; Du, X.; Pan, S.; Tang, X.; Qi, J. Soil Microbial Functions Linked Fragrant Rice 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline with Soil Active Carbon Pool: Evidence from Soil Metagenomic Sequencing of Tillage Practices. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okpala, N.E.; Mo, Z.; Duan, M.; Tang, X. The genetics and biosynthesis of 2-acetyl-1-pyrroline in fragrant rice. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2019, 135, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
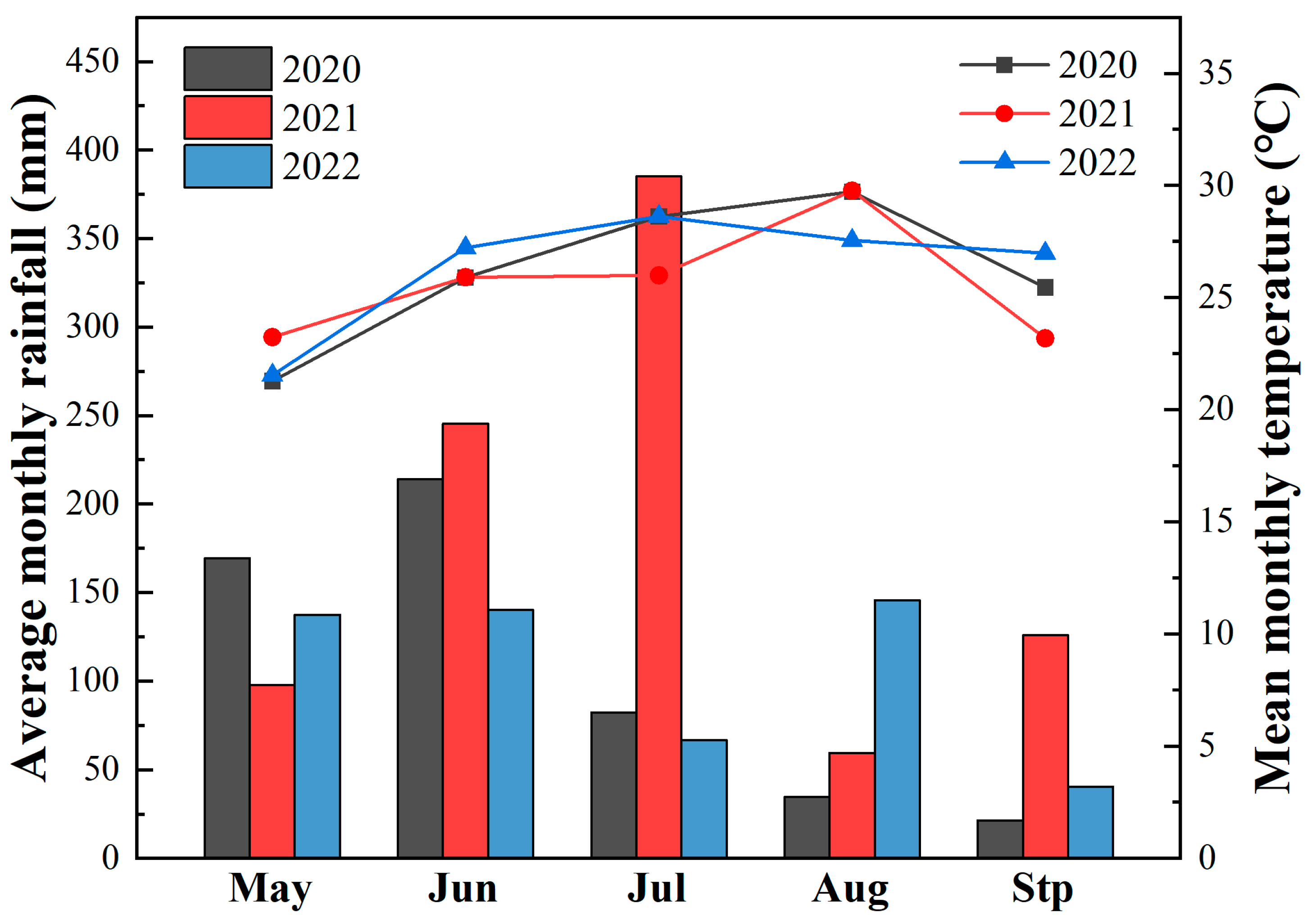

| Tillage Pattern | Year | Crop | Planting Date | Harvesting Date |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aromatic rice–winter fallow (CK) | 2020 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 15 May 2020 | 4 September 2020 |
| 2021 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 13 May 2021 | 5 September 2021 | |
| 2022 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 14 May 2022 | 4 September 2022 | |
| Aromatic rice–potato rotation (RP) | 2020 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 15 May 2020 | 4 September 2020 |
| Huashu-5 | 3 December 2020 | 19 February 2021 | ||
| 2021 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 13 May 2021 | 5 September 2021 | |
| Huashu-5 | 5 December 2021 | 21 February 2022 | ||
| 2022 | Meixiangzhan-2 | 14 May 2022 | 4 September 2022 | |
| Huashu-5 | 3 December 2022 | 18 February 2023 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, F.; Shen, C.; Feng, D.; Zhu, S.; Lu, J.; Zhu, J.; Qiu, X.; Chen, K.; Du, B.; Xu, J. Rice–Potato Rotation Pattern Affects 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis and Productivity in Aromatic Rice Grains. Agronomy 2025, 15, 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010097
Hu F, Shen C, Feng D, Zhu S, Lu J, Zhu J, Qiu X, Chen K, Du B, Xu J. Rice–Potato Rotation Pattern Affects 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis and Productivity in Aromatic Rice Grains. Agronomy. 2025; 15(1):97. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010097
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Fengqin, Congcong Shen, Dehao Feng, Shuangbing Zhu, Jian Lu, Jianqiang Zhu, Xianjin Qiu, Kai Chen, Bin Du, and Jianlong Xu. 2025. "Rice–Potato Rotation Pattern Affects 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis and Productivity in Aromatic Rice Grains" Agronomy 15, no. 1: 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010097
APA StyleHu, F., Shen, C., Feng, D., Zhu, S., Lu, J., Zhu, J., Qiu, X., Chen, K., Du, B., & Xu, J. (2025). Rice–Potato Rotation Pattern Affects 2-Acetyl-1-Pyrroline Biosynthesis and Productivity in Aromatic Rice Grains. Agronomy, 15(1), 97. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy15010097







