YOLOv8n-CSE: A Model for Detecting Litchi in Nighttime Environments
Abstract
1. Introduction
- A lightweight litchi cluster recognition network, YOLOv8n-CSE, was proposed for picking environment with weak light intensity, which could accurately identify litchi clusters in night environment.
- The image enhancement module CPA-Enhancer, which introduces chain thinking, can achieve very good results for the task of recognizing litchi clusters in low-light scenes at night.
- Lightweight SlimNeck and the introduction of the multi-scale linear attention mechanism module EfficientViT further improved the model’s performance in low-light environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
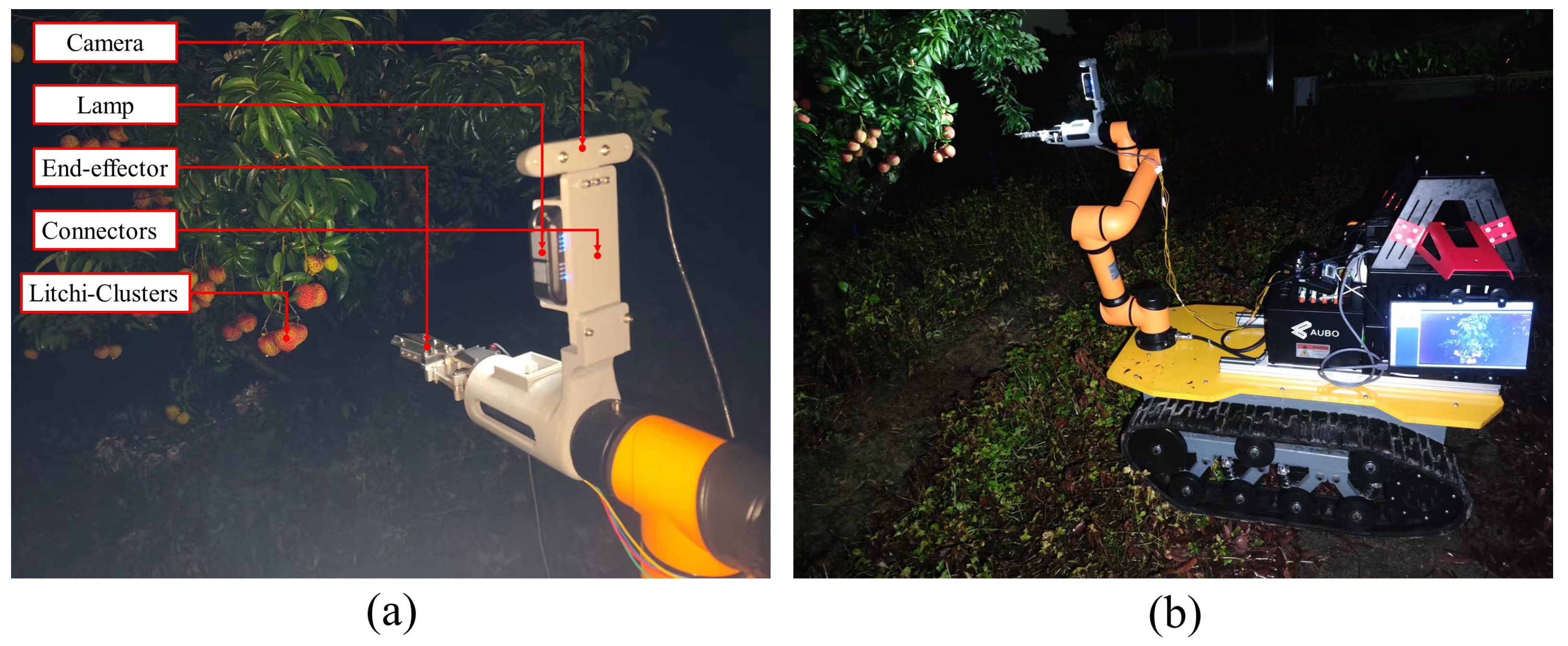
2.1.1. Data Acquisition
2.1.2. Data Augmentation
2.1.3. Dataset Details
2.2. Methodology
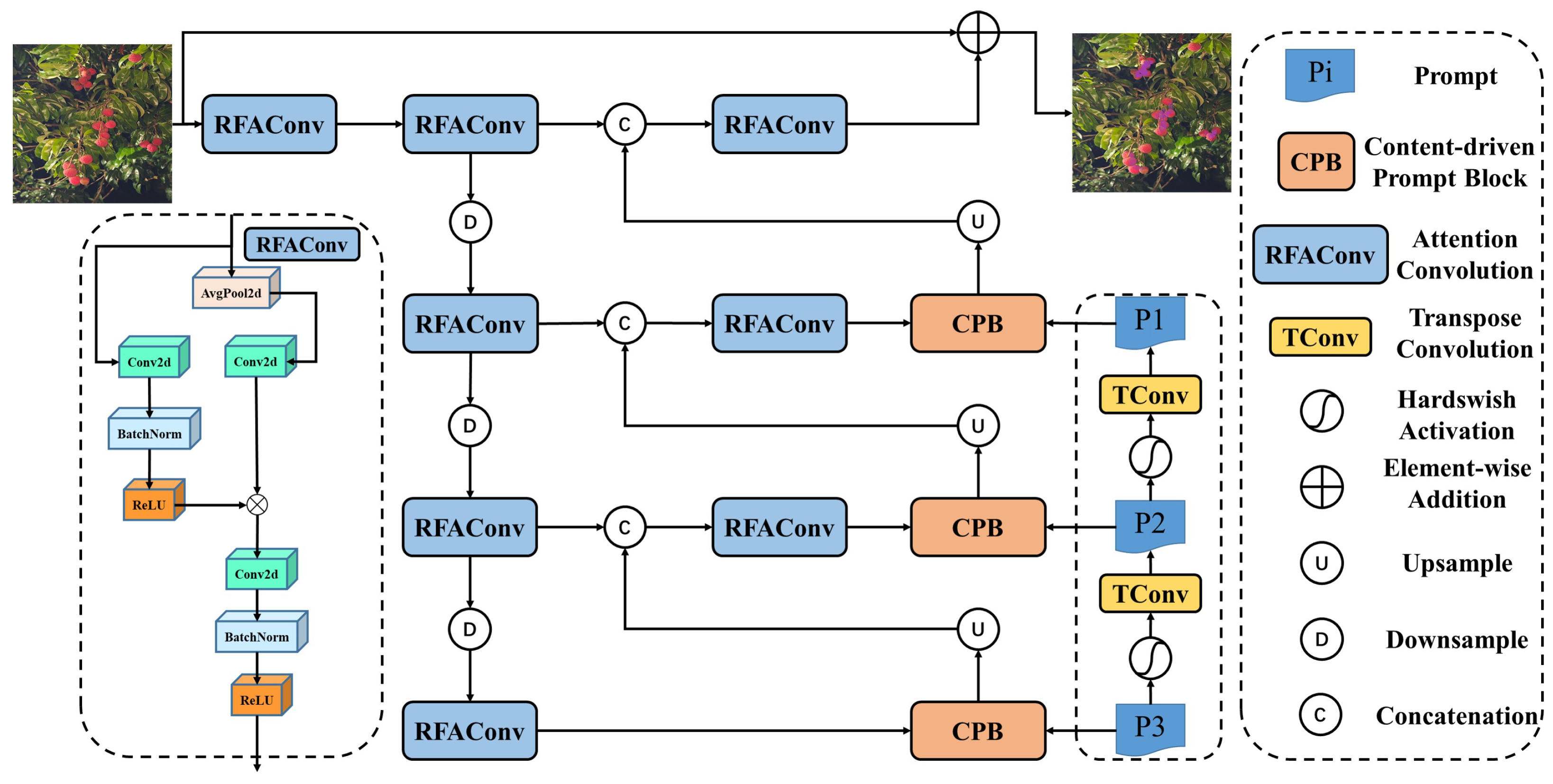
2.2.1. YOLOv8n-CSE Algorithm Model
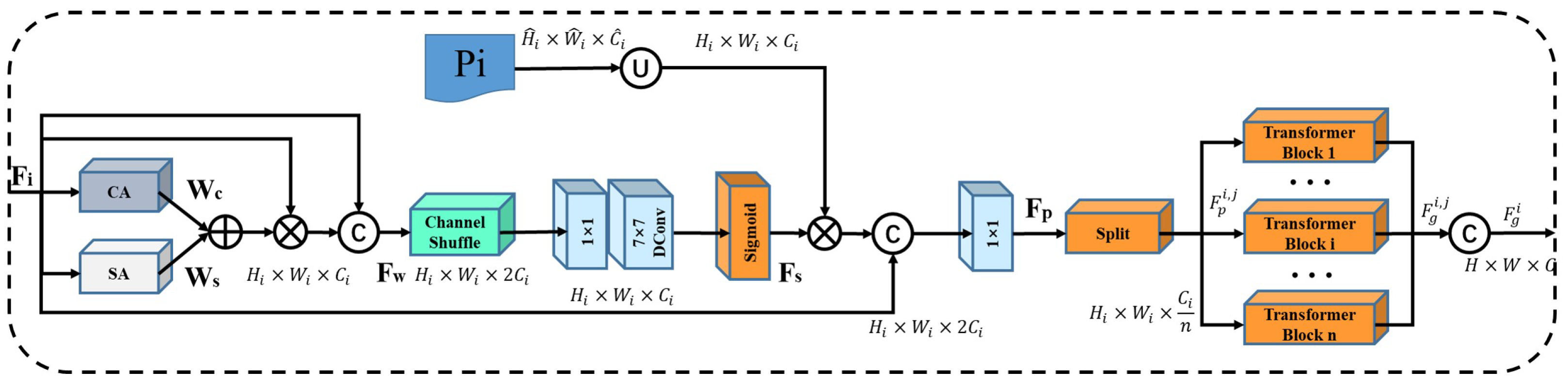
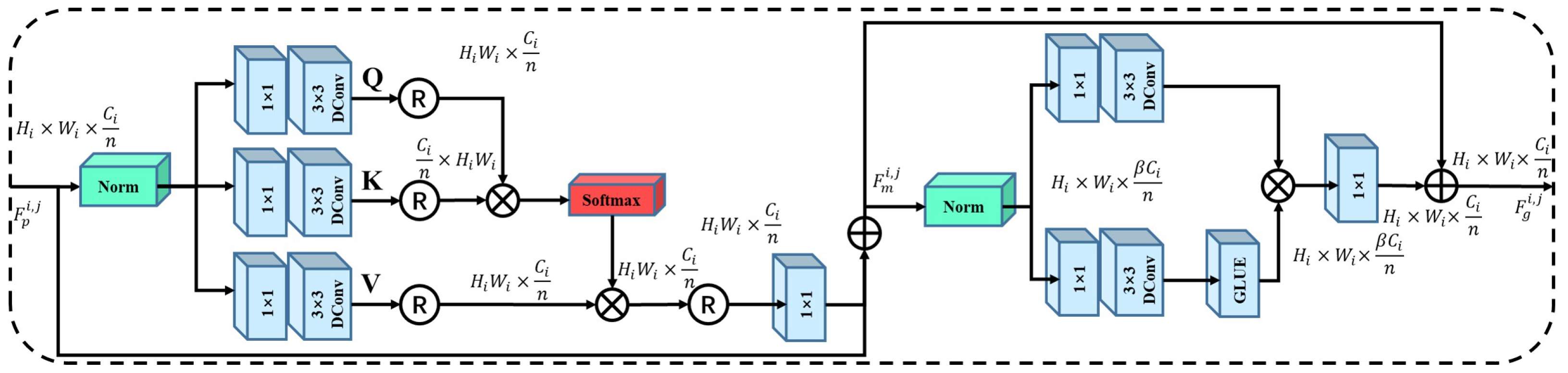
2.2.2. Chain Thinking Prompts Mechanism
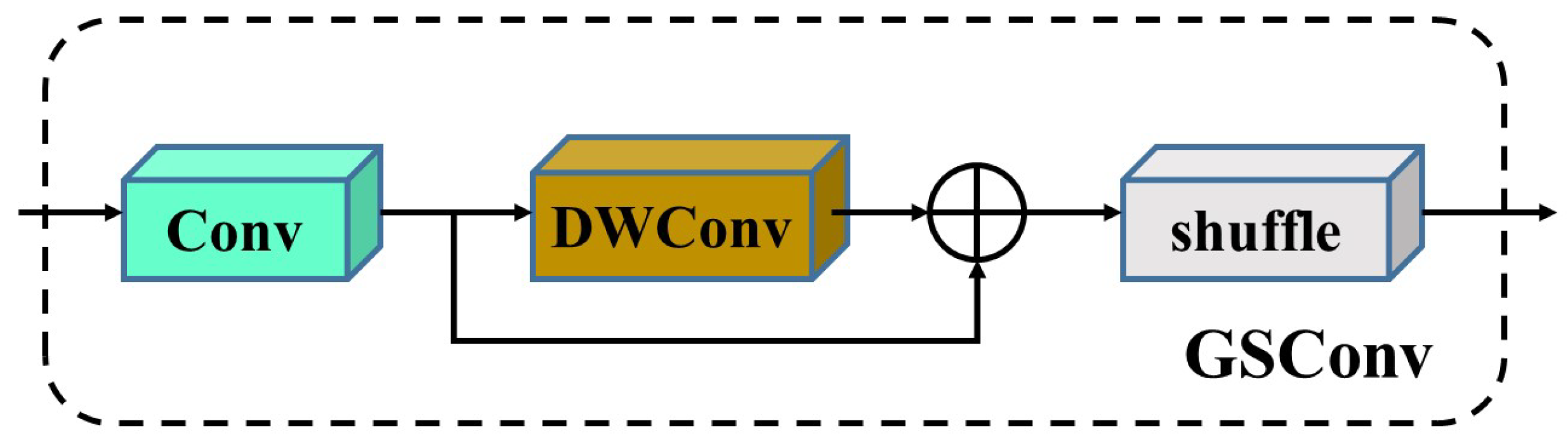
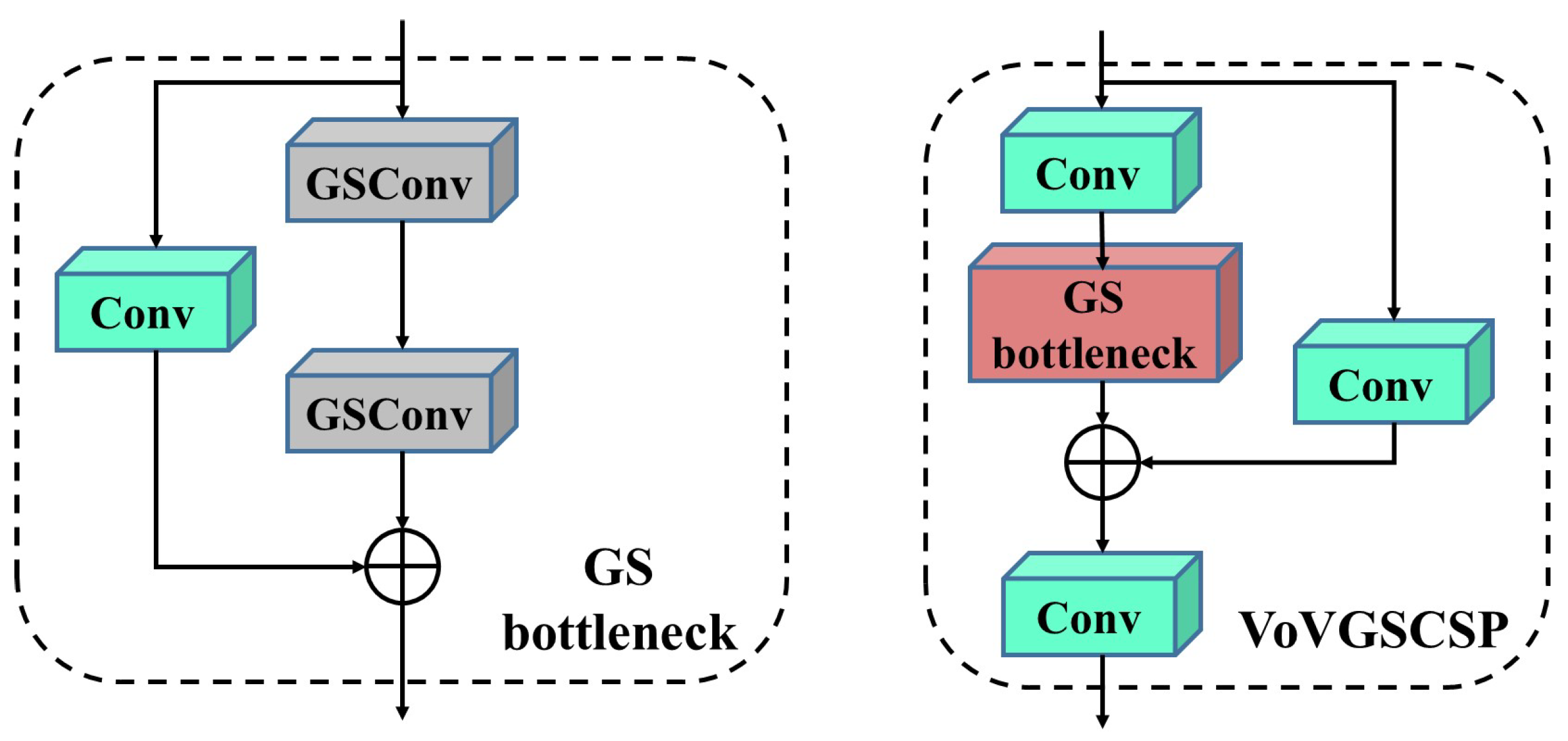
2.2.3. Lightweight Neck Slim
2.2.4. EfficientViT-Multiscale Linear Attention
2.3. Evaluation Metrics
2.4. Training Parameters and Experimental Environment
3. Results
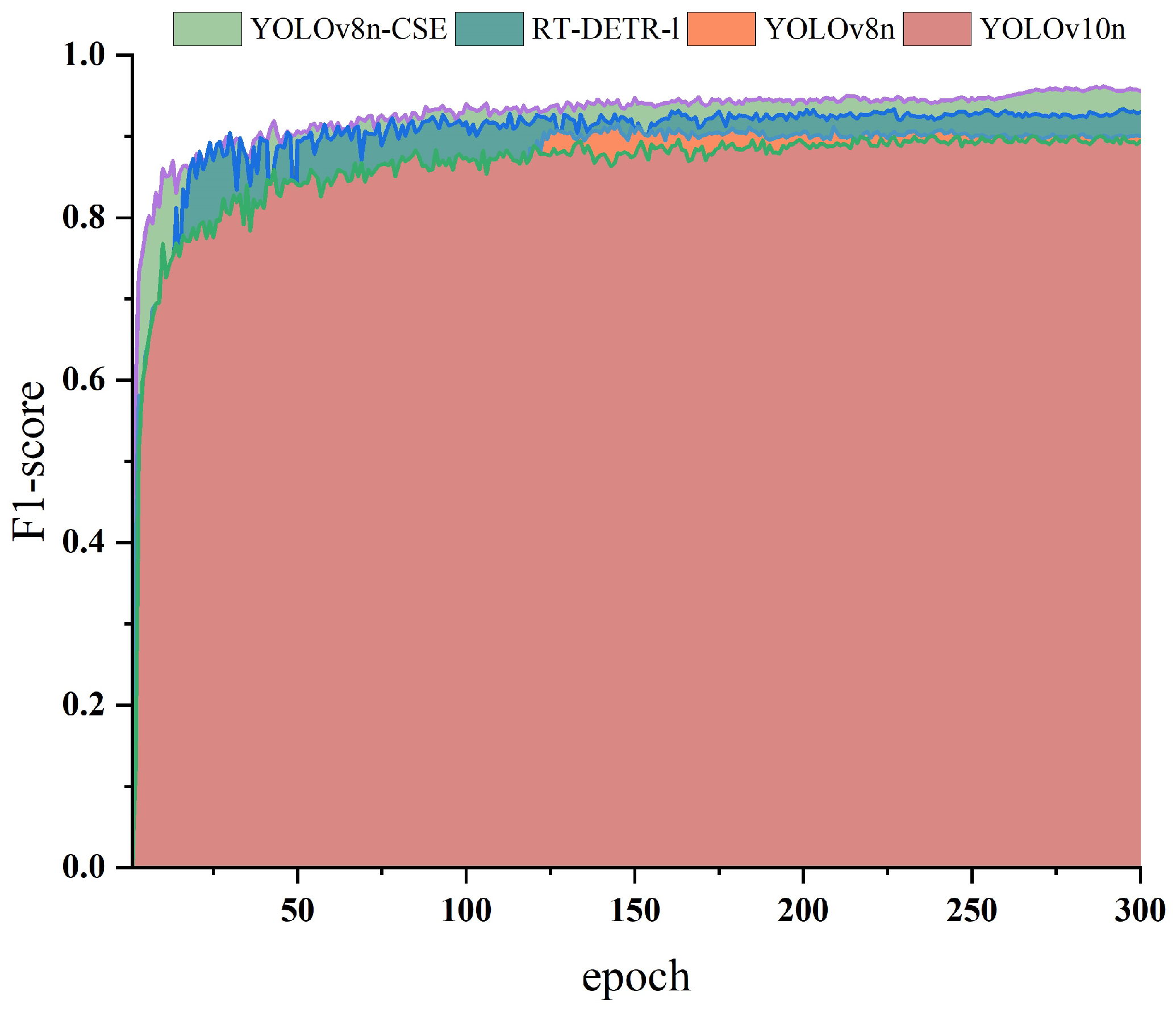
3.1. Experiments Were Conducted to Evaluate the Performance of YOLOv8n-CSE
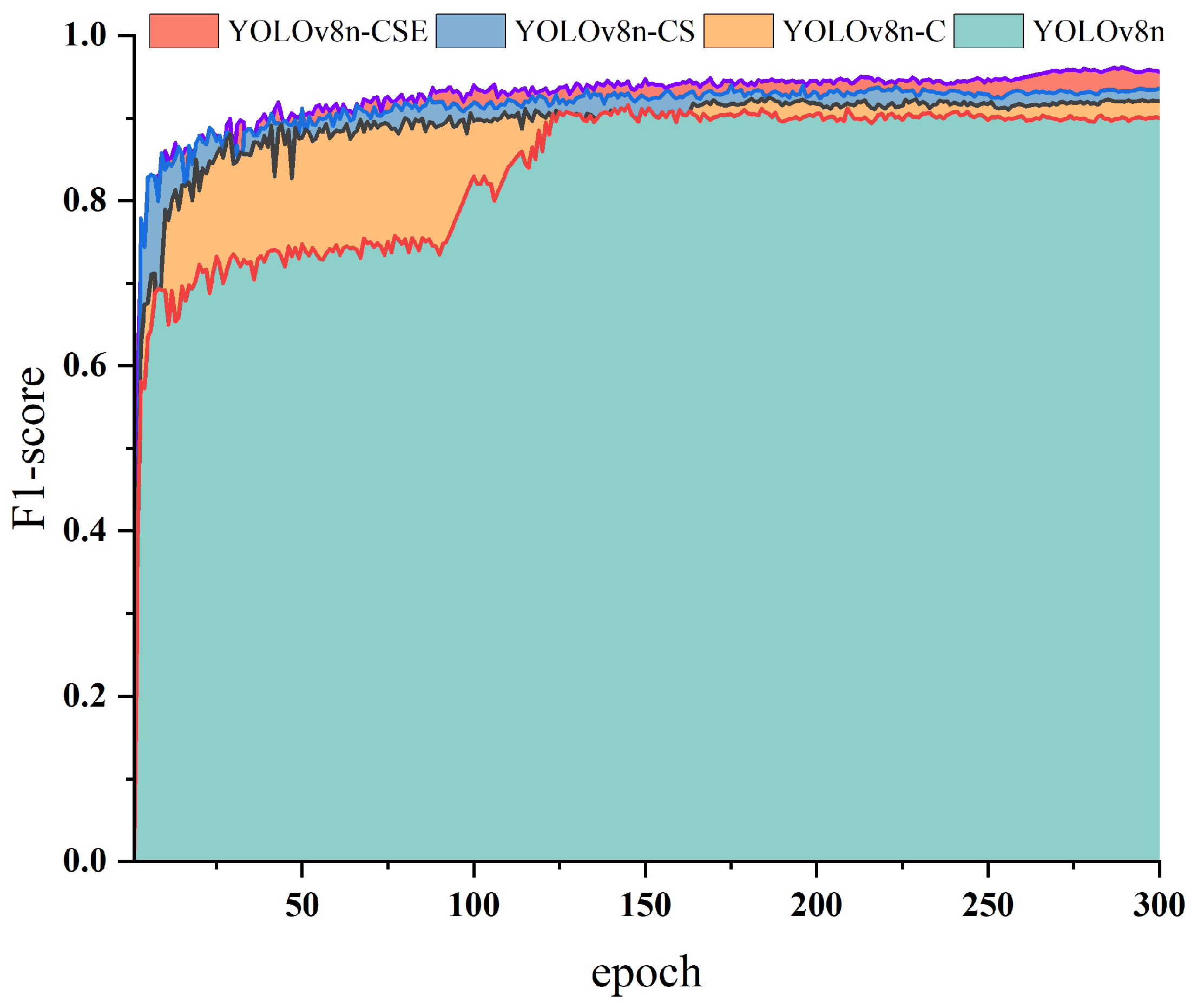
3.2. Ablation Experiments with YOLOv8n-CSE
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, J.; Zhang, S.; Zou, T.; Dong, L.; Peng, Z.; Wang, H. A Dense Litchi Target Recognition Algorithm for Large Scenes. Math. Probl. Eng. 2022, 2022, 4648105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, C.; Han, Q.; Wu, F.; Zou, X. A performance analysis of a litchi picking robot system for actively removing obstructions, using an artificial intelligence algorithm. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zou, X.; Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Zhu, M.; Lin, G. Recognition of ripe litchi in different illumination conditions based on Retinex image enhancement. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 170–178. [Google Scholar]
- Suo, R.; Gao, F.; Zhou, Z.; Fu, L.; Song, Z.; Dhupia, J.; Li, R.; Cui, Y. Improved multi-classes kiwifruit detection in orchard to avoid collisions during robotic picking. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 182, 106052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Su, Z.; Yang, S. Investigation and Analysis of the Litchi Production in China in 2023. Trop. Agric. China 2023, 3, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawn, N.; Ghosh, S.; Saha, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Ghosh, T.; Guha, S.; Sarkar, S.; Mukherjee, P.; Sanyal, T. A Review on Digital Twins Technology: A New Frontier in Agriculture. In Artificial Intelligence and Applications; Bon View Publishing Pte Ltd.: Singapore, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Han, Y.; Li, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, H. Vision based fruit recognition and positioning technology for harvesting robots. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2023, 213, 108258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Gu, Z.; He, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, J.; Mo, Y.; Li, P.; Huang, Z.; Wu, F. A lightweight improved YOLOv5s model and its deployment for detecting pitaya fruits in daytime and nighttime light-supplement environments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 220, 108914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, X.; Hu, K.; Zhou, H.; Kang, H.; Chen, C. FF3D: A Rapid and Accurate 3D Fruit Detector for Robotic Harvesting. Sensors 2024, 24, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, P.; Li, Z.; Lammers, K.; Lu, R.; Liu, X. Deep learning-based apple detection using a suppression mask R-CNN. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 147, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, N.; Xie, H.; Yang, X.; Zhan, K.; Liu, J. Recognition of cutting region for pomelo picking robot based on machine vision. In Proceedings of the 2019 ASABE Annual International Meeting. American Society of Agricultural and Biological Engineers, Boston, MA, USA, 7–10 July 2019; p. 1. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Fu, L.; Zhang, X.; Majeed, Y.; Li, R.; Karkee, M.; Zhang, Q. Multi-class fruit-on-plant detection for apple in SNAP system using Faster R-CNN. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 176, 105634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xiong, J.; Fang, X.; Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Lin, X.; Chen, S. A litchi fruit recognition method in a natural environment using RGB-D images. Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 204, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Mao, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, B. Clustered tomato detection and picking point location using machine learning-aided image analysis for automatic robotic harvesting. Precis. Agric. 2023, 24, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bac, C.W.; Hemming, J.; Van Henten, E.J. Stem localization of sweet-pepper plants using the support wire as a visual cue. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2014, 105, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Liu, D.; Meng, Y.; Liao, Q. Exploring the solutions via Retinex enhancements for fruit recognition impacts of outdoor sunlight: A case study of navel oranges. Evol. Intell. 2022, 15, 1875–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebahi, Y.; Gharra, M.; Rizzi, L.; Zournatzis, I. Combining Computer Vision, Artificial Intelligence and 3D Printing in Wheelchair Design Customization: The Kyklos 4.0 Approach. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Jing, T.; Chen, B.; Peng, J.; Zhang, X.; He, P.; Yin, H.; Sun, D.; Wang, W.; Xiao, A.; et al. Method for Segmentation of Litchi Branches Based on the Improved DeepLabv3+. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, L.; Liang, Z.; Peng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, L. Detection and Location of Litchi Fruit based on Object Detector and Depth Image. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering and Computer Applications (AEECA), Dalian, China, 18–19 August 2023; pp. 894–901. [Google Scholar]
- Bello, R.; Oladipo, M. Mask YOLOv7-based drone vision system for automated cattle detection and counting. Artif. Intell. Appl. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Chen, Z.; Luo, L.; Tang, Y.; Cheng, J.; Wei, H.; Wang, J. Dynamic visual servo control methods for continuous operation of a fruit harvesting robot working throughout an orchard. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 219, 108774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Ergu, D.; Liu, F.; Cai, Y.; Ma, B. A Review of Yolo algorithm developments. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2022, 199, 1066–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terven, J.; Córdova-Esparza, D.M.; Romero-González, J.A. A comprehensive review of yolo architectures in computer vision: From yolov1 to yolov8 and yolo-nas. Mach. Learn. Knowl. Extr. 2023, 5, 1680–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gai, R.; Chen, N.; Yuan, H. A detection algorithm for cherry fruits based on the improved YOLO-v4 model. Neural Comput. Appl. 2023, 35, 13895–13906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhaoxin, G.; Han, L.; Zhijiang, Z.; Libo, P. Design a robot system for tomato picking based on YOLO v5. IFAC-PapersOnLine 2022, 55, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Cao, H.; Jin, Y.; Zhong, Y.; Zhao, A.; Zou, X.; Wang, H. YOLOv8n-DDA-SAM: Accurate Cutting-Point Estimation for Robotic Cherry-Tomato Harvesting. Agriculture 2024, 14, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbey, S.; Pongener, A.; Kumar, V.; Nath, V. Effect of time of harvest and packaging on quality and shelf life of litchi fruit. In V International Symposium on Lychee, Longan and Other Sapindaceae Fruits 1211; ISHS: Brisbane, Australia, 2016; pp. 65–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zou, X.; Tang, Y.; Luo, L.; Feng, W. Localisation of litchi in an unstructured environment using binocular stereo vision. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 145, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Lu, J.; Zhou, M.; Yi, J.; Liao, M.; Gao, Z. A YOLOv3-based computer vision system for identification of tea buds and the picking point. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2022, 198, 107116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deka, B.; Chakraborty, D. UAV Sensing-Based Litchi Segmentation Using Modified Mask-RCNN for Precision Agriculture. IEEE Trans. AgriFood Electron. 2024; early access. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, J.; Lin, R.; Liu, Z.; He, Z.; Tang, L.; Yang, Z.; Zou, X. The recognition of litchi clusters and the calculation of picking point in a nocturnal natural environment. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 166, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, D.; Jia, W.; Ruan, C.; Tang, S.; Shen, T. A method of segmenting apples at night based on color and position information. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2016, 122, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Xiong, J.; Zheng, Z.; Zhong, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, S.; Yang, Z. A visual detection method for nighttime litchi fruits and fruiting stems. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2020, 169, 105192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, R. Image segmentation for whole tomato plant recognition at night. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2018, 154, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shorten, C.; Khoshgoftaar, T.M. A survey on image data augmentation for deep learning. J. Big Data 2019, 6, 1–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jocher, G.; Chaurasia, A.; Qiu, J. Yolo by Ultralytics, January 2023. Available online: https://github.com/ultralytics/ultralytics (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Peng, X. CPA-Enhancer: Chain-of-Thought Prompted Adaptive Enhancer for Object Detection under Unknown Degradations. arXiv 2024, arXiv:2403.11220 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Song, T.; Ye, Y.; Li, K.; Song, Y. RFAConv: Innovating spatial attention and standard convolutional operation. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2304.03198. [Google Scholar]
- Zamir, S.W.; Arora, A.; Khan, S.; Hayat, M.; Khan, F.S.; Yang, M.H. Restormer: Efficient Transformer for High-Resolution Image Restoration. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 5728–5739. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Wei, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhan, Z.; Ren, Q. Slim-neck by GSConv: A lightweight-design for real-time detector architectures. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2024, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chollet, F. Xception: Deep Learning With Depthwise Separable Convolutions. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.G.; Zhu, M.; Chen, B.; Kalenichenko, D.; Wang, W.; Weyand, T.; Andreetto, M.; Adam, H. MobileNets: Efficient Convolutional Neural Networks for Mobile Vision Applications. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1704.048612017. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Republic Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.; Lin, M.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet: An Extremely Efficient Convolutional Neural Network for Mobile Devices. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, N.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, H.T.; Sun, J. ShuffleNet V2: Practical Guidelines for Efficient CNN Architecture Design. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, H.; Li, J.; Hu, M.; Gan, C.; Han, S. EfficientViT: Lightweight Multi-Scale Attention for High-Resolution Dense Prediction. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Paris, France, 1–6 October 2023; pp. 17302–17313. [Google Scholar]
- Choromanski, K.; Likhosherstov, V.; Dohan, D.; Song, X.; Gane, A.; Sarlos, T.; Hawkins, P.; Davis, J.; Mohiuddin, A.; Kaiser, L.; et al. Rethinking Attention with Performers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2009.14794. [Google Scholar]
- Bolya, D.; Fu, C.Y.; Dai, X.; Zhang, P.; Hoffman, J. Hydra attention: Efficient attention with many heads. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Virtual Event, 6–8 February 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany; pp. 35–49. [Google Scholar]
- Katharopoulos, A.; Vyas, A.; Pappas, N.; Fleuret, F. Transformers are RNNs: Fast Autoregressive Transformers with Linear Attention. In Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning, Virtual, 13–18 July 2020; Volume 119, pp. 5156–5165. [Google Scholar]
- Mirhaji, H.; Soleymani, M.; Asakereh, A.; Mehdizadeh, S. Fruit detection and load estimation of an orange orchard using the YOLO models through simple approaches in different imaging and illumination conditionss. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2021, 191, 106533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

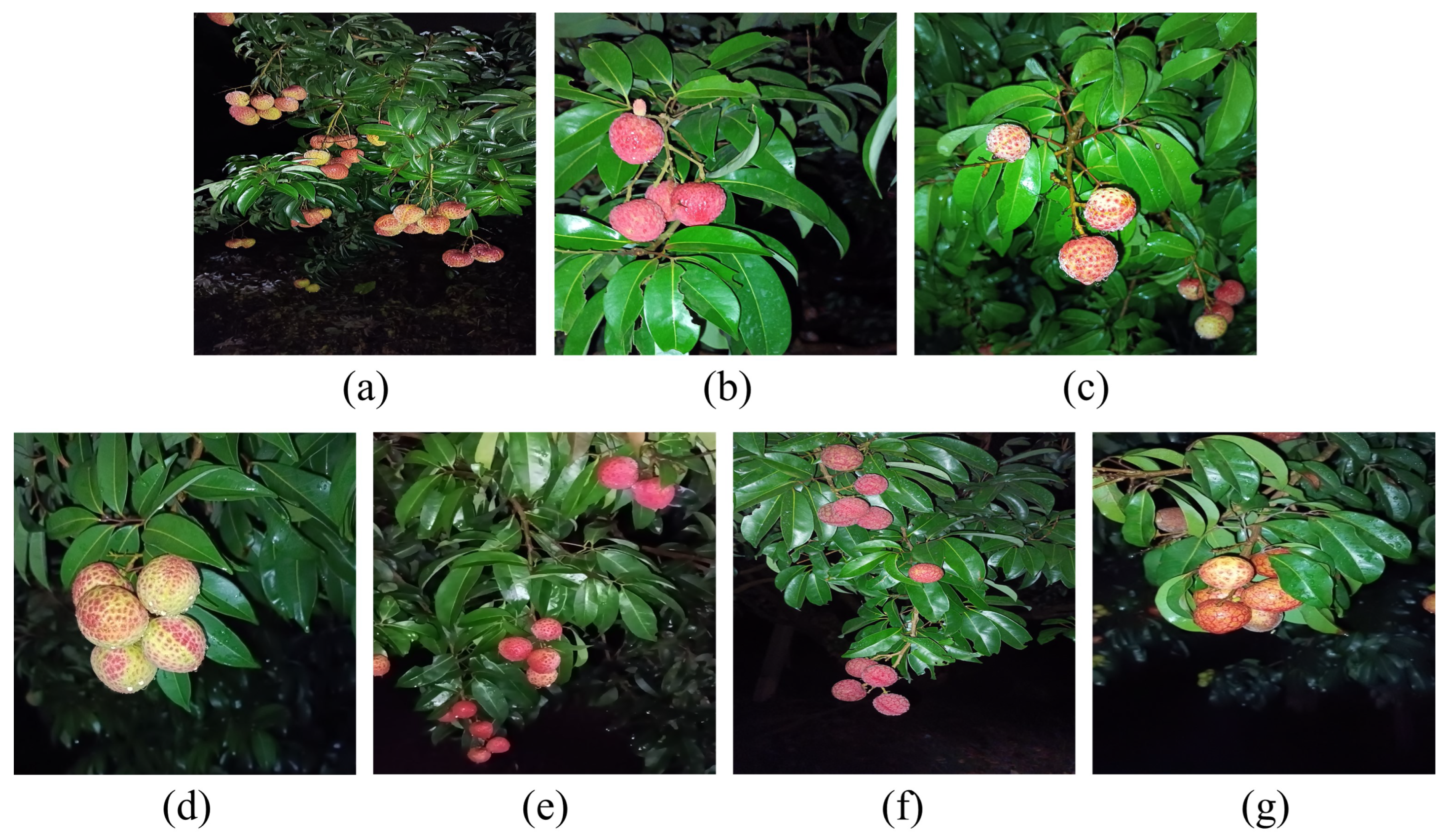





| Number of Images | |
|---|---|
| Train | 1383 |
| Validation | 395 |
| Test | 198 |
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Operating system | Windows 10 |
| Deep learning framework | Torch1.12.1+cu116 |
| Programming language | Python3.8 |
| GPU | NVIDIA GeForce RTX 3090Ti |
| CPU | Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10700 @ 2.90 GHz |
| Parameter | Configuration |
|---|---|
| Epoch | 300 |
| Initial learning rate | 0.01 |
| Batch size | 16 |
| Momentum | 0.937 |
| Weight decay | 0.0005 |
| Model | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | F1-Score (%) | Processing Time per Photo (ms) | Param (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 93.28 | 87.07 | 94.83 | 90.07 | 25.00 | 3.01 |
| RT-DETR-l | 93.87 | 91.33 | 95.40 | 92.58 | 41.52 | 31.98 |
| YOLOv10n | 91.50 | 87.20 | 94.90 | 89.30 | 19.6 | 2.69 |
| YOLOv8n-CSE | 96.37% | 94.73 | 98.86 | 95.54 | 36.5 | 4.93 |
| Model Abbreviation | P (%) | R (%) | mAP@0.5 (%) | F1-Score (%) | Param (M) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| YOLOv8n | 93.28 | 87.07 | 94.83 | 90.07 | 3.01 |
| YOLOv8n-C | 93.68 | 89.00 | 96.05 | 92.28 | 6.26 |
| YOLOv8n-CS | 94.68 | 92.51 | 97.07 | 93.58 | 3.42 |
| YOLOv8n-CSE | 96.37 | 94.73 | 98.86 | 95.54 | 4.93 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, H.; Zhang, G.; Zhao, A.; Wang, Q.; Zou, X.; Wang, H. YOLOv8n-CSE: A Model for Detecting Litchi in Nighttime Environments. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091924
Cao H, Zhang G, Zhao A, Wang Q, Zou X, Wang H. YOLOv8n-CSE: A Model for Detecting Litchi in Nighttime Environments. Agronomy. 2024; 14(9):1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091924
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Hao, Gengming Zhang, Anbang Zhao, Quanchao Wang, Xiangjun Zou, and Hongjun Wang. 2024. "YOLOv8n-CSE: A Model for Detecting Litchi in Nighttime Environments" Agronomy 14, no. 9: 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091924
APA StyleCao, H., Zhang, G., Zhao, A., Wang, Q., Zou, X., & Wang, H. (2024). YOLOv8n-CSE: A Model for Detecting Litchi in Nighttime Environments. Agronomy, 14(9), 1924. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14091924







