Combination of Polymer-Coated Urea and Rapid-Release Urea Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice by Improving Root and Shoot Activities
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Sampling and Measurement
2.2.1. Shoot Dry Weight and Nitrogen Use Efficiency
2.2.2. Root Traits and Non-Structural Carbohydrates (NSC)
2.2.3. Root Zeatin (Z) and Zeatin Riboside (ZR) Content
2.2.4. Leaf Photosynthetic Rate
2.2.5. Ammonia Volatilization
2.2.6. Final Harvest
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Grain Yield, NUE, and Ammonia Volatilization
3.2. Shoot Dry Matter Weight and Crop Growth Rate
3.3. Leaf Area Duration and Photosynthetic Rate
3.4. Root Morpho-Physiological Traits
3.5. NSC Remobilization and Harvest Index
3.6. Correlation Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bin Rahman, A.R.; Zhang, J. Trends in rice research: 2030 and beyond. Food. Energy Secur. 2023, 12, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Turchini, G.M. The evolution of the blue-green revolution of rice-fish cultivation for sustainable food production. Sustain. Sci. 2021, 16, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Long, H.L. Analysis of arable land loss and its impact on rural sustainability in Southern Jiangsu Province of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Zhao, X.; Pittelkow, C.M.; Fan, M.; Zhang, X.; Yan, X. Optimal nitrogen rate strategy for sustainable rice production in China. Nature 2023, 615, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Y. Evaluating the potential health and economic effects of nitrogen fertilizer application in grain production systems of China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Liu, G.; Ma, J.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Yagi, K. Effect of controlled-release fertilizer on mitigation of N2O emission from paddy field in South China: A multi-year field observation. Plant Soil 2013, 371, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C. Effects of controlled-release fertilizer on rice grain yield, nitrogen use efficiency, and greenhouse gas emissions in a paddy field with straw incorporation. Field Crops Res. 2020, 253, 107814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishfaq, M.; Akbar, N.; Zulfiqar, U.; Ali, N.; Jabran, K.; Nawaz, M.; Farooq, M. Influence of nitrogen fertilization pattern on productivity, nitrogen use efficiencies, and profitability in different rice production systems. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nut. 2021, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, J.; Fu, P.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fahad, S.; Peng, S.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; et al. Crop management based on multi-split topdressing enhances grain yield and nitrogen use efficiency in irrigated rice in China. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Hu, Q.; Liu, G.; Wei, H.; Zhang, H. Effects of a one-time application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on yield and nitrogen accumulation and utilization of late japonica rice in China. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Lu, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Hussain, S.; Ren, T.; Cong, R.; Li, X. Nitrogen losses, use efficiency, and productivity of early rice under controlled-release urea. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2018, 251, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Liu, Z.; Lyu, X.; Zheng, W. Synchronized relationships between nitrogen release of controlled release nitrogen fertilizers and nitrogen requirements of cotton. Field Crops Res. 2015, 184, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Wang, M.; Zheng, G.; Yao, Y.; Tao, R.; Zhu, M.; Ding, J.; Li, C.; Guo, W.; Zhu, X. Twice-split application of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer met the nitrogen demand of winter wheat. Field Crops Res. 2021, 267, 108163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ren, W.; Zhu, K.; Fu, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Z.; Gu, J.; Yang, J. Substituting readily available nitrogen fertilizer with controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer improves crop yield and nitrogen uptake while mitigating environmental risks: A global meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2024, 306, 109221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, J.; Xing, X.; Li, G.; Ding, Y.; Dou, F.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Tang, S.; Ding, C.; Chen, L. Effects of different controlled-release nitrogen fertilisers on ammonia volatilisation, nitrogen use efficiency and yield of blanket-seedling machine-transplanted rice. Field Crops Res. 2017, 205, 147–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, J.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Zhang, H.; Gu, J.; Zhang, J.; Yang, J. Alternate wetting and drying irrigation combined with the proportion of polymer-coated urea and conventional urea rates increases grain yield, water and nitrogen use efficiencies in rice. Field Crops Res. 2021, 268, 108165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, C.; Buresh, R.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Root and shoot traits for rice varieties with higher grain yield and higher nitrogen use efficiency at lower nitrogen rates application. Field Crops Res. 2015, 175, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.C.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.H. Root morphology and physiology in relation to the yield formation of rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2012, 11, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.W.; Lu, D.K.; Wang, H.Z.; Li, Y. Morphological and physiological traits of rice roots and their relationships to yield and nitrogen utilization as influenced by irrigation regime and nitrogen rate. Agric. Water Manag. 2018, 203, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, W.; Liu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Jia, Y.; Yang, L.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Li, X.; et al. The response of grain yield and root morphological and physiological traits to nitrogen levels in paddy rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 713814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.W.; Jiang, M.M.; Lu, D.K.; Wang, H.Z.; Chen, M.C. Nitrogen forms affect the root characteristic, photosynthesis, grain yield, and nitrogen use efficiency of rice under different irrigation regimes. Crop Sci. 2020, 60, 2594–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, G.; Chen, P.; Zhu, H.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y. Shoot-root communication plays a key role in physiological alterations of rice (Oryza sativa) under iron deficiency. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.M.; Lo, S.F.; Ho, T.H.D. Source–sink communication: Regulated by hormone, nutrient, and stress cross-signaling. Trends Plant Sci. 2015, 20, 844–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahir, Z.A.; Asghar, H.N.; Arshad, M. Cytokinin and its precursors for improving growth and yield of rice. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 33, 405–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, J.L.; Ferguson, R.B.; Dobermann, A. Site-specific nitrogen and plant density management in irrigated maize. Agron. J. 2008, 100, 1193–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baral, B.R.; Pande, K.R.; Gaihre, Y.K.; Baral, K.R.; Sah, S.K.; Thapa, Y.B.; Singh, U. Real-time nitrogen management using decision support-tools increases nitrogen use efficiency of rice. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2021, 119, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Lv, T.; Yang, Z.; Wang, T.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hu, B.; Ren, W. Morphophysiological mechanism of rice yield increase in response to optimized nitrogen management. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Q.; Tang, G.; Zhong, L.; He, H.; Chen, X. Response to nitrogen deficiency and compensation on physiological characteristics, yield formation, and nitrogen utilization of rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beillouin, D.; Trépos, R.; Gauffreteau, A.; Jeuffroy, M.H. Delayed and reduced nitrogen fertilization strategies decrease nitrogen losses while still achieving high yields and high grain quality in malting barley. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 101, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasamy, S.; Ten Berge, H.F.M.; Purushothaman, S. Yield formation in rice in response to drainage and nitrogen application. Field Crops Res. 1997, 51, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Yan, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Deciphering the morpho–physiological traits for high yield potential in nitrogen efficient varieties (NEVs): A japonica rice case study. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 947–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Hu, Q.; Shi, Y.; Cui, K.; Nie, L.; Huang, J.; Peng, S. Low nitrogen application enhances starch-metabolizing enzyme activity and improves accumulation and translocation of non-structural carbohydrates in rice stems. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Welti, R.; Wang, X. Quantitative analysis of major plant hormones in crude plant extracts by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, W.; Xu, X.; He, P.; Ullah, S.; Zhang, J.; Cui, Z.; Zhou, W. Improving yield and nitrogen use efficiency through alternative fertilization options for rice in China: A meta-analysis. Field Crops Res. 2018, 227, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Yang, L.; Yan, T.; Xue, F.; Zhao, D. Nitrogen fertilizer reduction in rice production for two consecutive years in the Taihu Lake area. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 146, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamiji, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Palta, J.A.; Sakuratani, T.; Shiraiwa, T. N applications that increase plant N during panicle development are highly effective in increasing spikelet number in rice. Field Crops Res. 2011, 122, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, B.; Feng, X.; Tian, G.; Hu, X.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Optimizing nitrogen supply increases rice yield and nitrogen use efficiency by regulating yield formation factors. Field Crops Res. 2013, 150, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamura, T.; Hamada, H.; Iida, K.; Umeda, M. Correlation of the amount of nitrogen accumulated in the aboveground biomass at panicle initiation and nitrogen content of soil with the nitrogen uptake by lowland rice during the period from panicle initiation to heading. Plant Prod. Sci. 2003, 6, 302–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ye, C.; Ma, H.; Huang, X.; Xu, C.; Chen, S.; Chu, G.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D. Effects of increasing panicle-stage N on yield and N use efficiency of indica rice and its relationship with soil fertility. Crop J. 2022, 10, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Oikawa, S.; Hirose, T. Nitrogen-utilization efficiency in rice: An analysis at leaf, shoot, and whole-plant level. Plant Soil 2016, 404, 321–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Fan, L.; Chen, J.; Jiang, L.; Zou, Y. Continuous applications of biochar to rice: Effects on nitrogen uptake and utilization. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feller, U.; Fischer, A. Nitrogen metabolism in senescing leaves. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 1994, 13, 241–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaju, O.; Allard, V.; Martre, P.; Snape, J.W.; Heumez, E.; LeGouis, J.; Moreau, D.; Bogard, M.; Griffiths, S.; Hubbart, S.; et al. Identification of traits to improve the nitrogen-use efficiency of wheat genotypes. Field Crops Res. 2011, 123, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Yang, D.; Li, X.; Peng, S.; Wang, F. Coordination of high grain yield and high nitrogen use efficiency through large sink size and high post-heading source capacity in rice. Field Crops Res. 2019, 233, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegeder, M.; Masclaux-Daubresse, C. Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 2018, 217, 35–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.E.; Chen, H.Y.; Tseng, C.S.; Tsay, Y.F. Improving nitrogen use efficiency by manipulating nitrate remobilization in plants. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1126–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badshah, M.A.; Naimei, T.; Zou, Y.; Ibrahim, M.; Wang, K. Yield and tillering response of super hybrid rice Liangyoupeijiu to tillage and establishment methods. Crop J. 2014, 2, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, R.; Mohapatra, P.K. Regulation of spikelet development in rice by hormones. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Moral, M.G.; Del Moral, L.G. Tiller production and survival in relation to grain yield in winter and spring barley. Field Crops Res. 1995, 44, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasuquin, E.; Lafarge, T.; Tubana, B. Transplanting young seedlings in irrigated rice fields: Early and high tiller production enhanced grain yield. Field Crops Res. 2008, 105, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Xia, Y.; Liu, B.; Chang, C.; Xiao, L.; Shen, J.; Tang, L.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Individual and combined effects of jointing and booting low-temperature stress on wheat yield. Eur. J. Agron. 2020, 113, 125989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Xu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Gu, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; et al. Post-anthesis dry matter production and leaf nitrogen distribution are associated with root-derived cytokinins gradient in rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakakibara, H. Cytokinin biosynthesis and transport for systemic nitrogen signaling. Plant J. 2021, 105, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.E.; Meacham-Hensold, K.; Lemonnier, P.; Slattery, R.A.; Benjamin, C.; Bernacchi, C.J.; Lawson, T.; Cavanagh, A.P. The effect of increasing temperature on crop photosynthesis: From enzymes to ecosystems. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 2822–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kläring, H.P.; Krumbein, A. The effect of constraining the intensity of solar radiation on the photosynthesis, growth, yield and product quality of tomato. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2013, 199, 351–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, P.; Wang, J. Effects of light intensity and temperature on the photosynthesis characteristics and yield of lettuce. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, J. Simultaneously improving grain yield and water and nutrient use efficiencies by enhancing the harvest index in rice. Crop Environ. 2023, 3, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Natividad, M.A.; Quintana, M.R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Henry, A. Disentangling the roles of plant water status and stem carbohydrate remobilization on rice harvest index under drought. Rice 2023, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onoda, K.; Ohta, R.; Peter, M.A.; Edifor, R.; Hamajima, M.; Mae, A.; Murai, A.; Kondo, M.; Sekiya, N. Post-heading accumulation of nonstructural carbohydrates and nitrogen in rice (Oryza sativa L.) roots. Field Crops Res. 2024, 315, 109478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L. Progress in super-hybrid rice breeding. Crop J. 2017, 5, 100–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
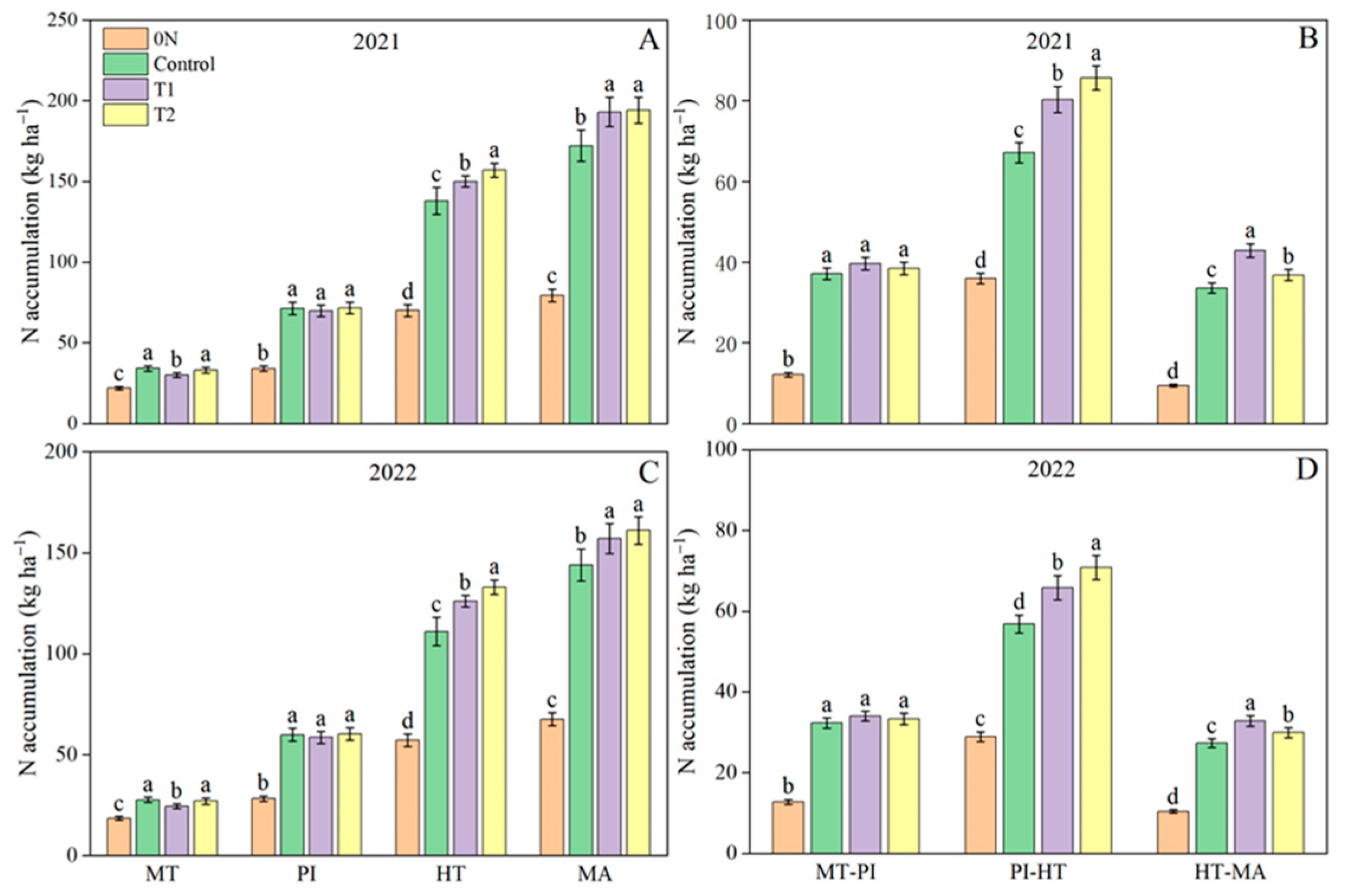

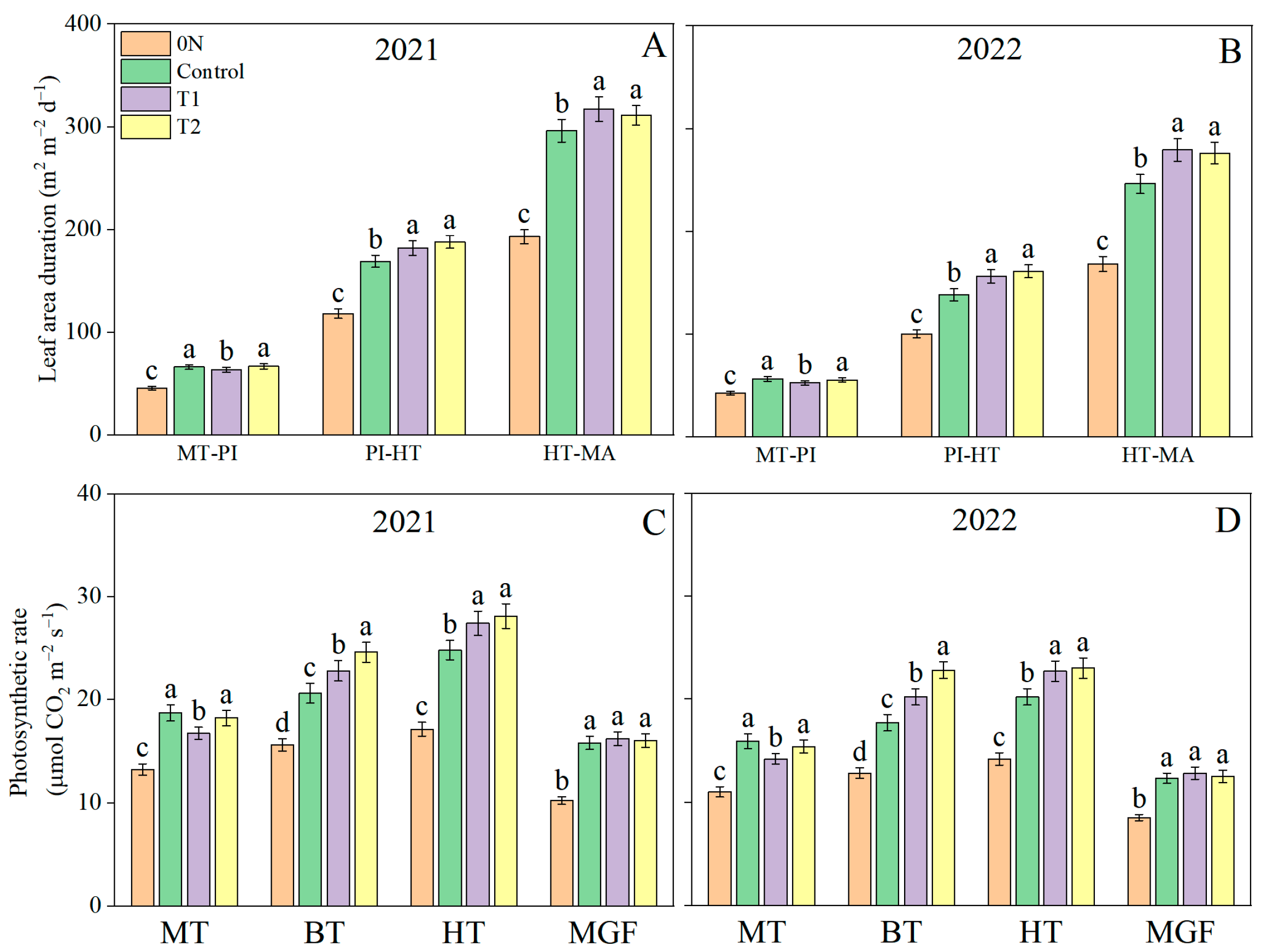

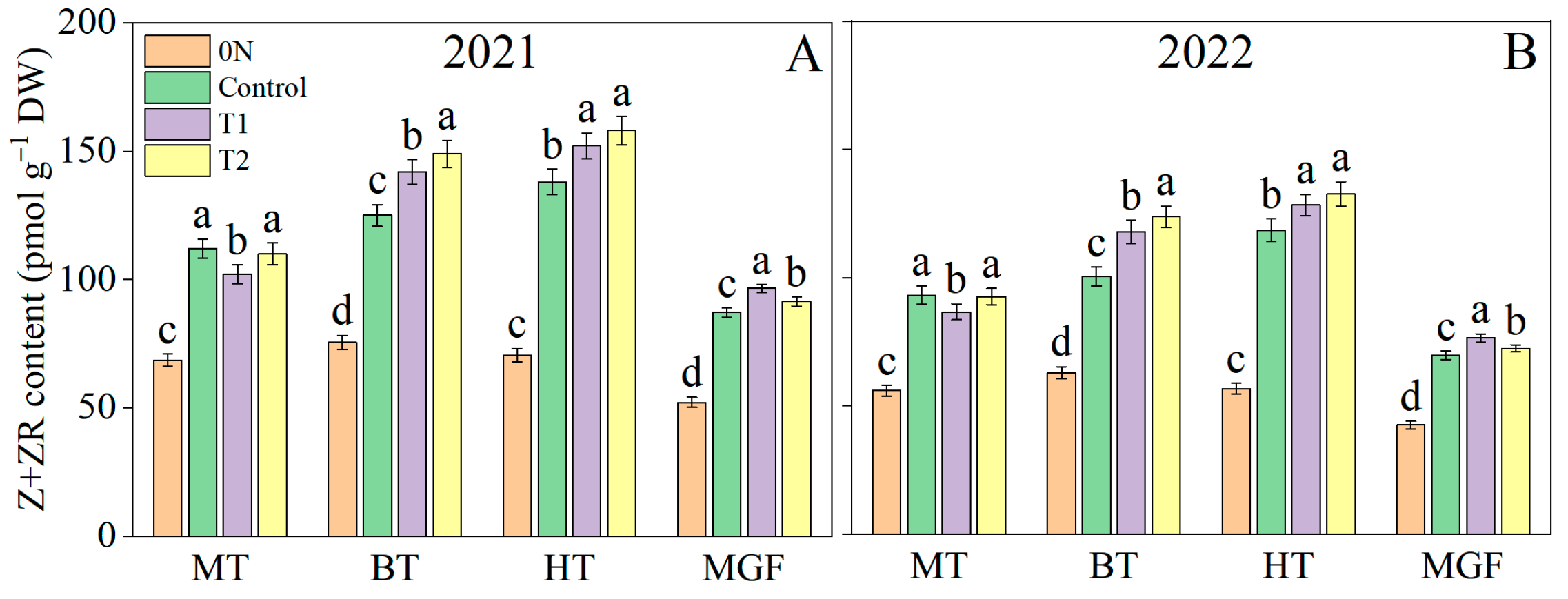

| Year/Treatment | Grain Yield (t ha−1) | Panicles (m2) | Spikelets per Panicle | Total Spikelets (103/m2) | Filled Grains (%) | Grain Weight (mg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||||
| 0N | 5.84 c | 179 c | 136 c | 24.3 c | 90.4 a | 26.5 a |
| Control | 9.02 b | 284 a | 146 b | 41.4 b | 85.8 b | 26.6 a |
| T1 | 9.17 b | 271 b | 157 a | 42.5 b | 85.5 b | 26.4 a |
| T2 | 9.76 a | 282 a | 160 a | 45.1 a | 85.4 b | 26.4 a |
| 2022 | ||||||
| 0N | 3.56 c | 192 c | 123 c | 23.7 c | 69.0 b | 24.9 a |
| Control | 7.21 b | 297 a | 135 b | 40.9 b | 78.9 a | 24.1 b |
| T1 | 7.43 b | 281 b | 147 a | 41.8 b | 77.3 a | 24.2 b |
| T2 | 7.96 a | 294 a | 149 a | 45.7 a | 77.8 a | 24.2 b |
| Analysis of Variance | ||||||
| Year (Y) | 883 ** | 65.8 ** | 124 ** | 13.6 ** | 765 ** | 2646 ** |
| Treatment (T) | 21.3 ** | 1145 ** | 125 ** | 775 ** | 7.87 ** | 25.0 ** |
| Y × T | 4.11 * | NS | NS | NS | 75.6 ** | 21.1 ** |
| Year/Treatments | TNU (kg hm−2) | AEN (kg kg−1) | IEN (kg kg−1) | REN (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021 | ||||
| 0N | 79.4 c | - | 73.6 a | - |
| Control | 172 b | 13.3 b | 52.5 b | 38.6 b |
| T1 | 193 a | 13.8 b | 47.5 c | 47.3 a |
| T2 | 194 a | 16.2 a | 50.1 b | 47.8 a |
| 2022 | ||||
| 0N | 67.5 c | - | 52.7 a | - |
| Control | 144 b | 15.4 b | 50.1 a | 31.9 b |
| T1 | 157 a | 16.1 b | 46.1 b | 37.3 a |
| T2 | 161 a | 18.3 a | 50.7 a | 39.0 a |
| Analysis of Variance | ||||
| Year (Y) | 586 ** | 47.1 ** | 66.3 ** | 137 ** |
| Treatment (T) | 1894 ** | 33.8 ** | 92.4 ** | 49.9 ** |
| Y × T | 22.9 ** | NS | 45.8 ** | NS |
| Year/Treatment | NSC Accumulation in the Stem (g/m2) | NSC Remobilization (%) | Harvest Index | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heading | Maturity | |||
| 2021 | ||||
| 0N | 154 d | 71.5 d | 53.6 a | 0.490 a |
| Control | 210 c | 104 c | 50.5 b | 0.465 b |
| T1 | 228 b | 129 a | 43.4 c | 0.441 c |
| T2 | 240 a | 115 b | 52.1 b | 0.460 b |
| 2022 | ||||
| 0N | 146 d | 93.5 d | 36.0 c | 0.302 c |
| Control | 198 c | 105 c | 47.0 a | 0.416 a |
| T1 | 218 b | 132 a | 39.3 b | 0.399 b |
| T2 | 232 a | 124 b | 46.6 a | 0.413 a |
| Analysis of Variance | ||||
| Year (Y) | 291 ** | 123 ** | 62 ** | 601 ** |
| Treatment (T) | 662 ** | 251 ** | 44.7 ** | 37 ** |
| Y × T | NS | 18 ** | 35.8 ** | 114 ** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, R.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, K.; Gu, J.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Combination of Polymer-Coated Urea and Rapid-Release Urea Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice by Improving Root and Shoot Activities. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071585
Xu R, Fu J, Zhang Y, Sun Z, Xu Y, Zhang W, Zhu K, Gu J, Wang Z, Yang J. Combination of Polymer-Coated Urea and Rapid-Release Urea Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice by Improving Root and Shoot Activities. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071585
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Rongyue, Jiangyao Fu, Yajun Zhang, Zhiwei Sun, Yuemei Xu, Weiyang Zhang, Kuanyu Zhu, Junfei Gu, Zhiqin Wang, and Jianchang Yang. 2024. "Combination of Polymer-Coated Urea and Rapid-Release Urea Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice by Improving Root and Shoot Activities" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071585
APA StyleXu, R., Fu, J., Zhang, Y., Sun, Z., Xu, Y., Zhang, W., Zhu, K., Gu, J., Wang, Z., & Yang, J. (2024). Combination of Polymer-Coated Urea and Rapid-Release Urea Increases Grain Yield and Nitrogen Use Efficiency of Rice by Improving Root and Shoot Activities. Agronomy, 14(7), 1585. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071585






