The Impact of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Growth and Comprehensive Evaluation of Irrigation Strategies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
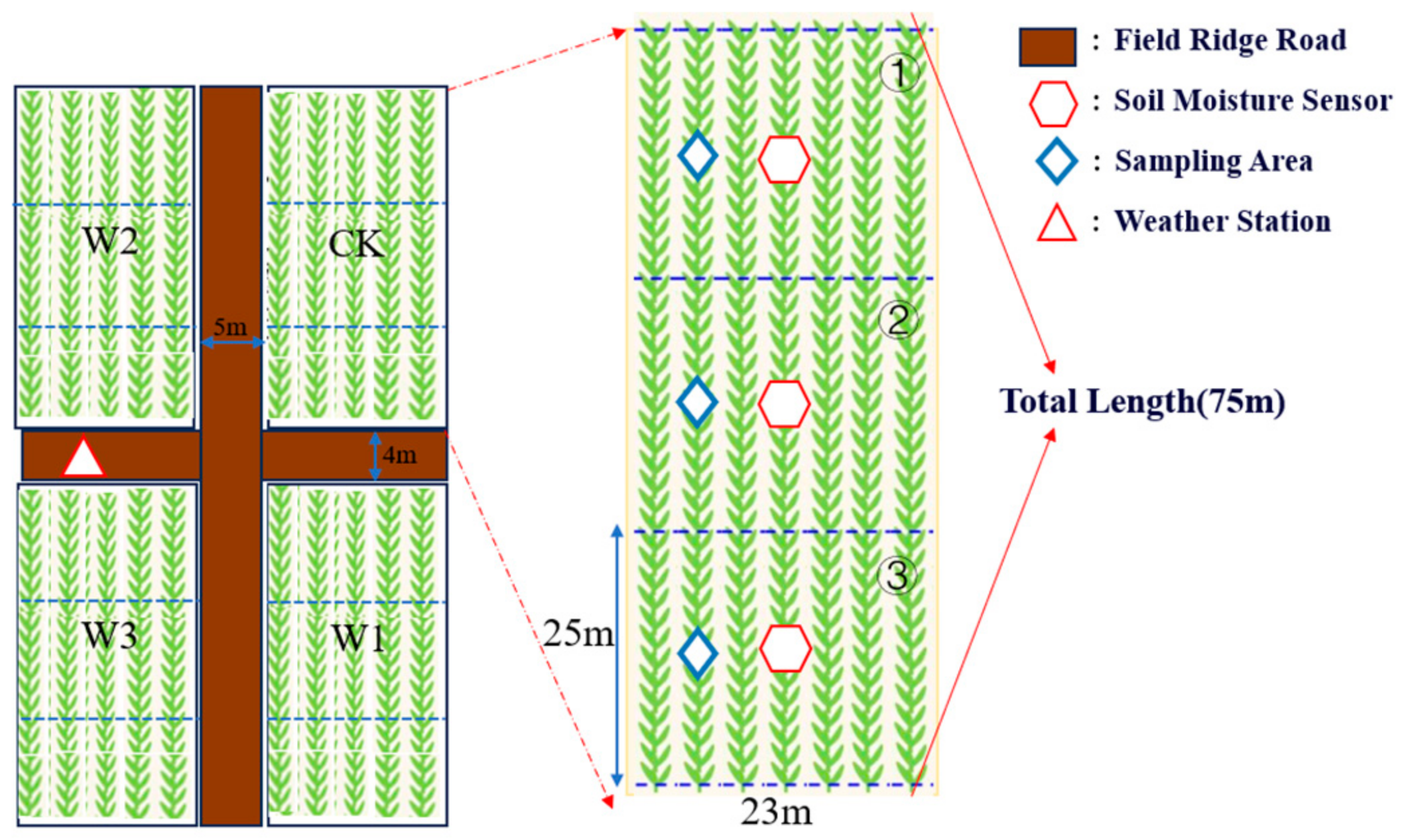
2.1. The Experimental Site
2.2. Experimental Materials and Treatments
2.3. Measurement Indicators and Methods
2.3.1. Plant Height Measurement
2.3.2. Biomass Measurement
2.3.3. Leaf Chlorophyll Content (SPAD Content)
2.3.4. Yield and Its Components
2.3.5. Rice Quality Measurement
2.3.6. Measurement of Stress Resistance Indicators
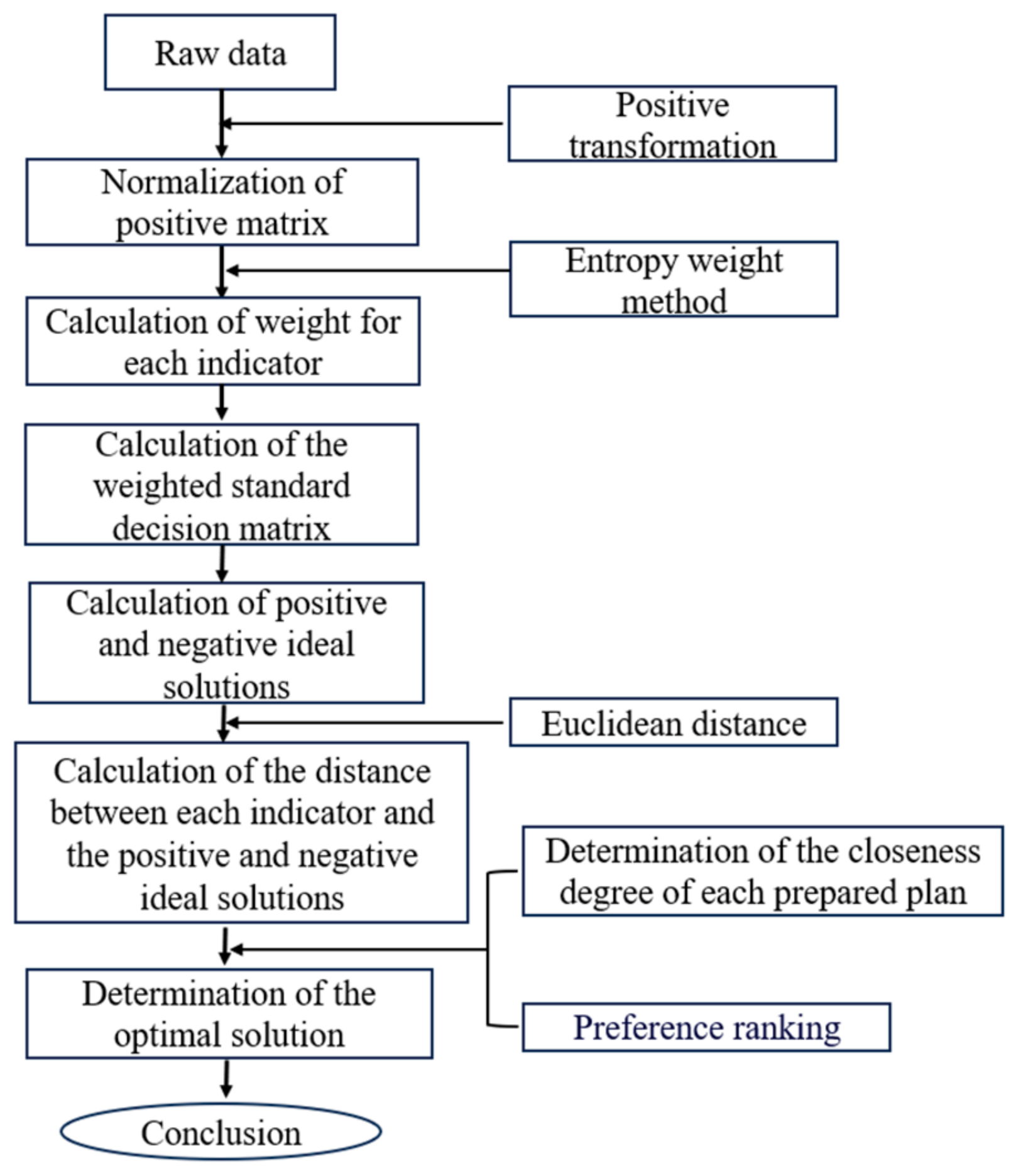
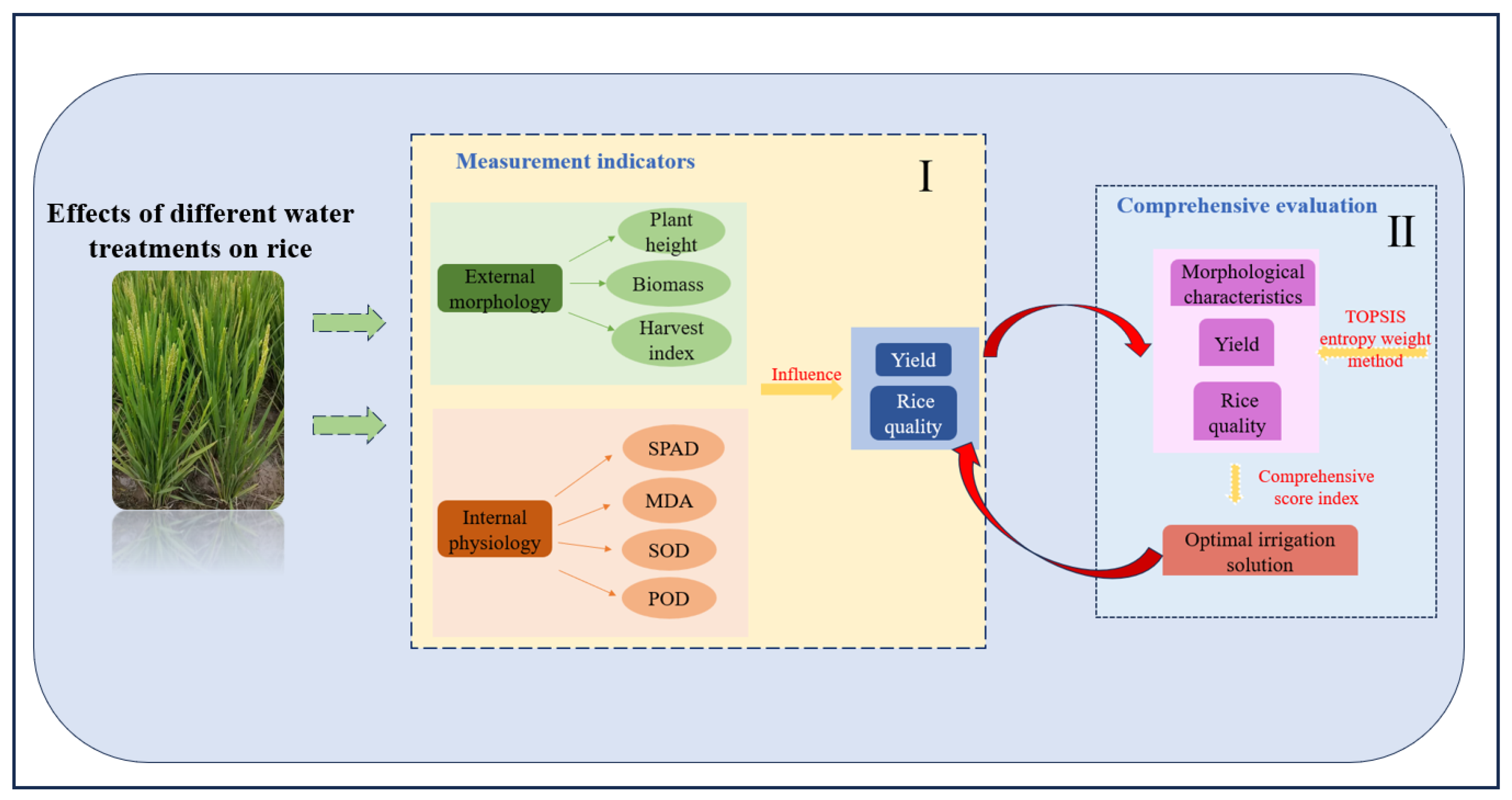
2.4. Comprehensive Evaluation Method for Irrigation Treatments
2.5. Data Statistics and Analysis
3. Results
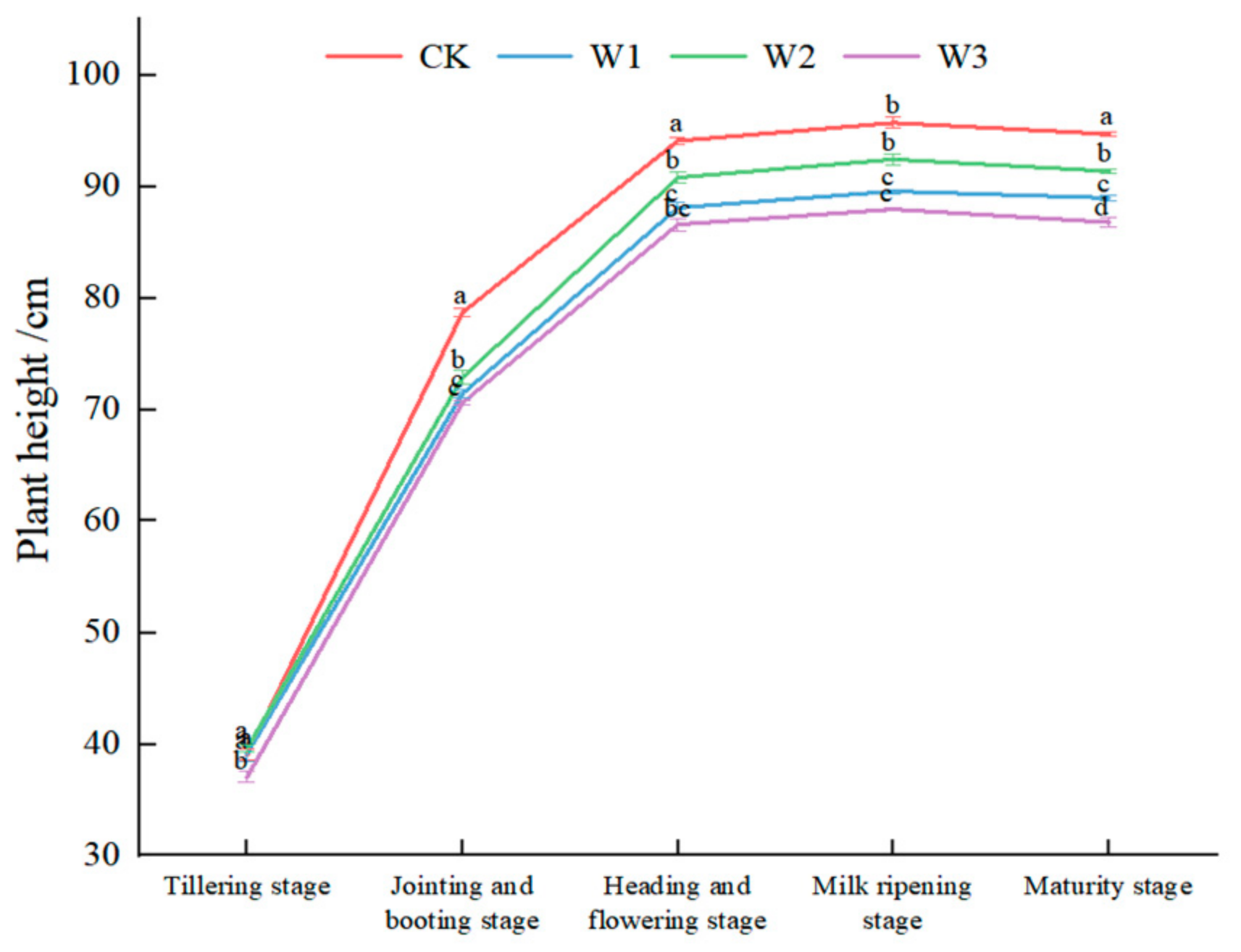
3.1. Effects of Different Water Treatments on Rice Plant Height
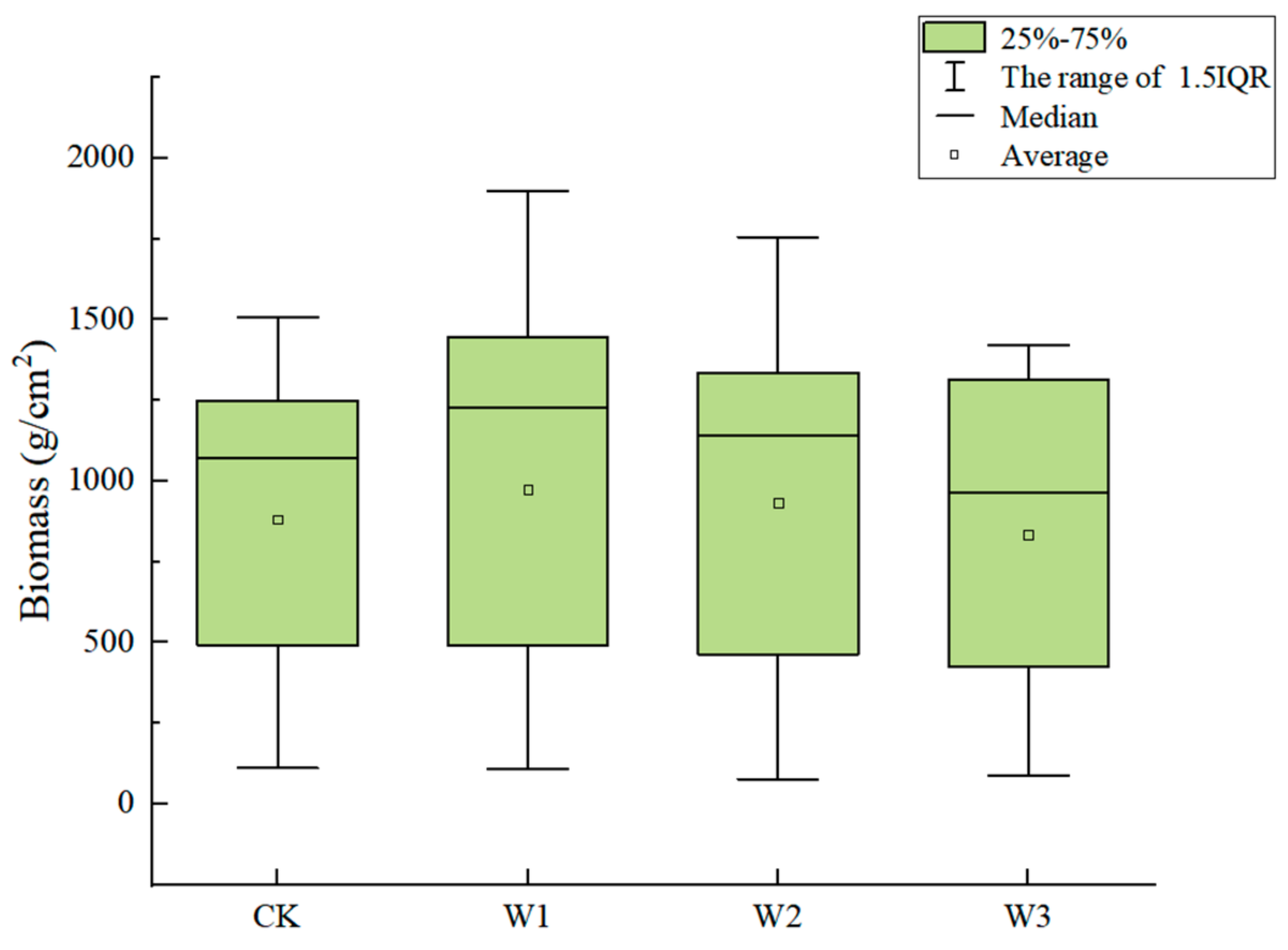
3.2. Effects of Different Water Treatments on Rice Biomass
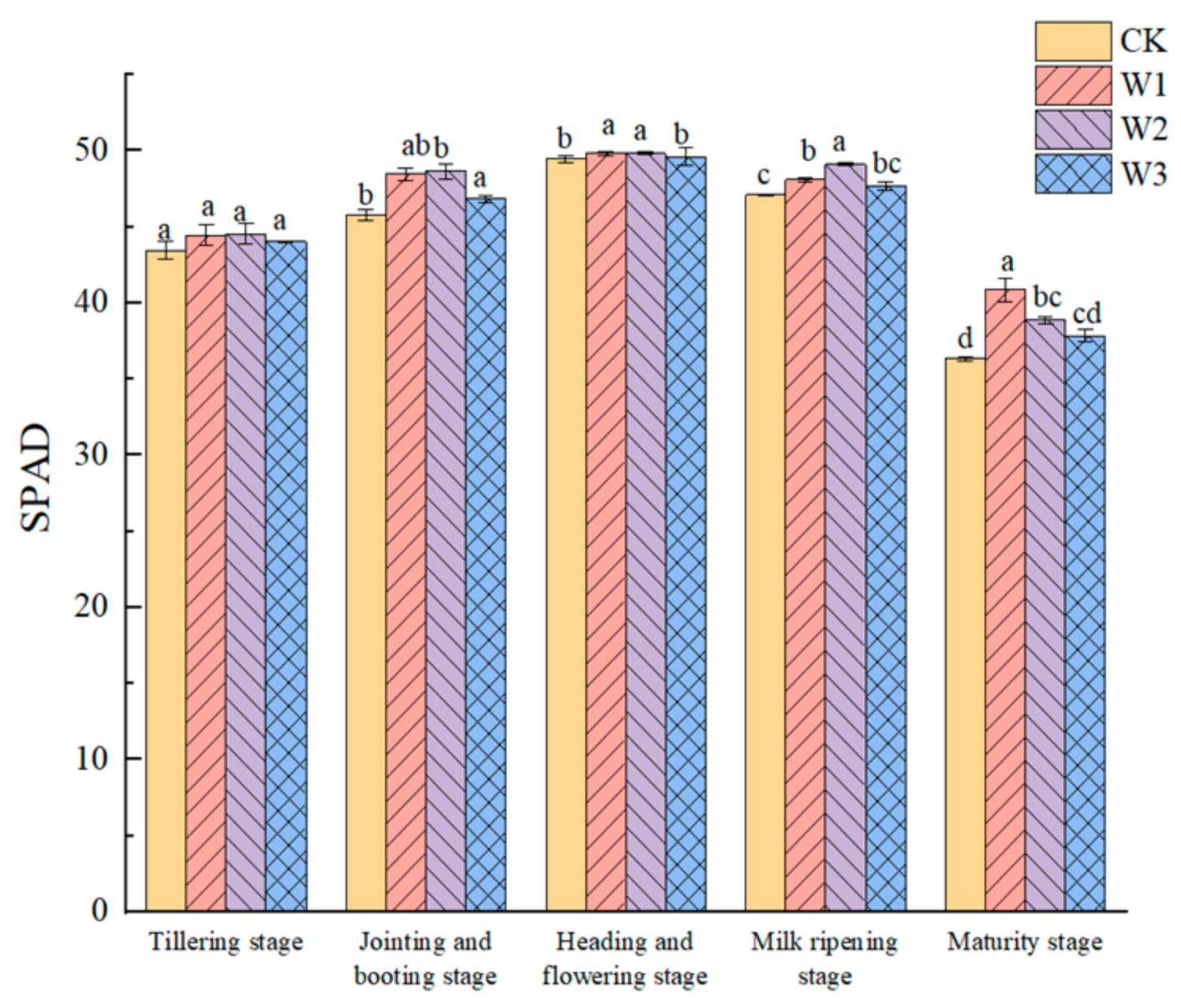
3.3. Effects of Different Water Treatments on SPAD of Rice Leaves
3.4. Effects of Different Water Treatments on MDA of Rice Leaves
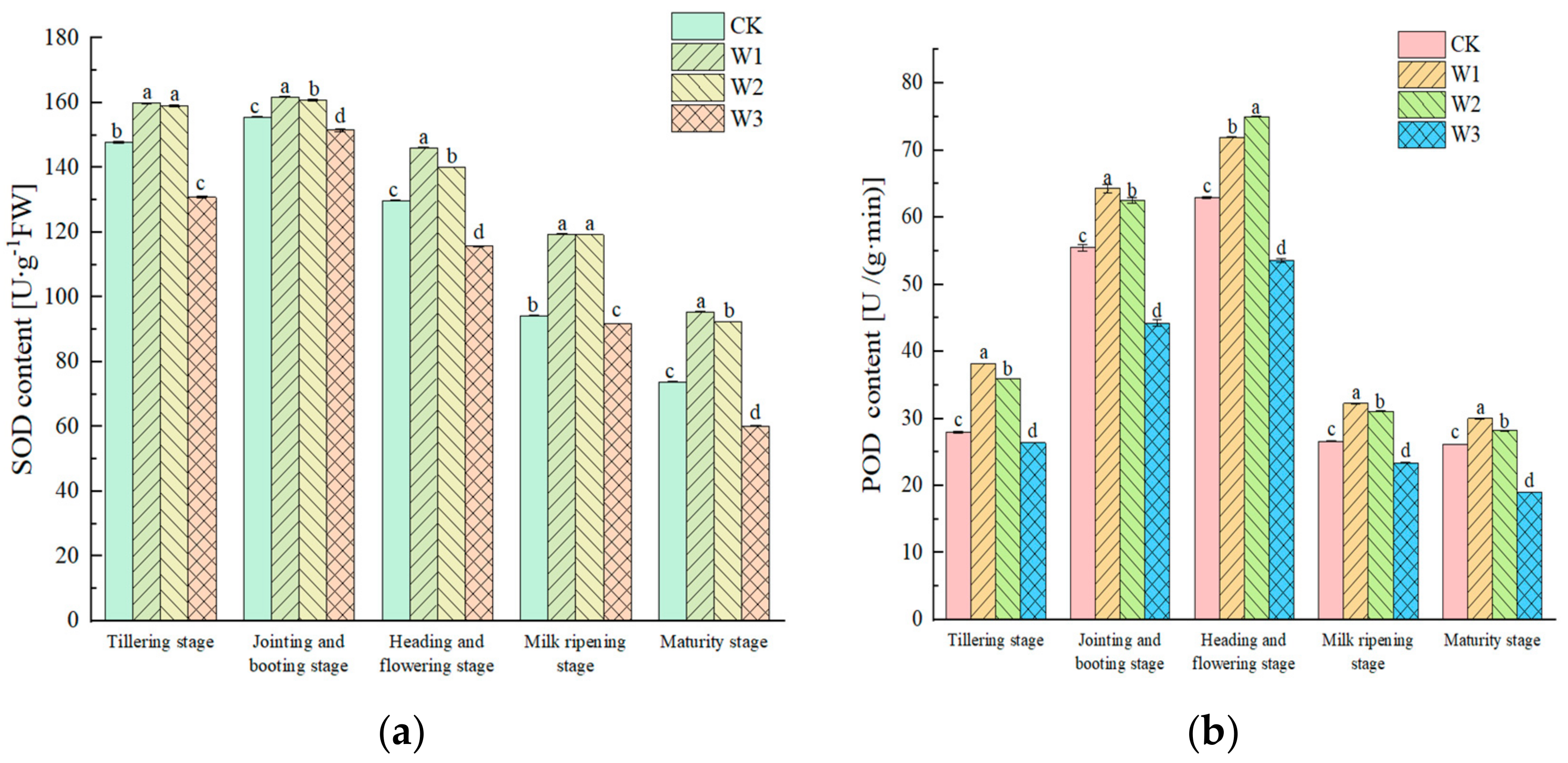
3.5. Effects of Different Water Treatments on Antioxidant Enzyme Activities in Rice Leaves
3.6. Effects of Different Water Treatments on Rice Yield and Its Components
3.7. Effects of Different Water Treatments on Rice Quality
3.8. Comprehensive Evaluation and Optimization of Irrigation Treatment Schemes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Q.H.; Wu, X.; Chen, B.C.; Xin, C.Y.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Z.W.; Ma, J.Q. Effects of different irrigation methods on grain quality of japonica rice in Huanghuai District of China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2014, 25, 2583–2590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladha, J.K.; Radanielson, A.M.; Rutkoski, J.E.; Buresh, R.J.; Dobermann, A.; Angeles, O.; Pabuayon, I.L.B.; Santos-Medellín, C.; Fritsche-Neto, R.; Chivenge, P.; et al. Steady agronomic and genetic interventions are essential for sustaining productivity in intensive rice cropping. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2110807118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Bian, S.F.; Liu, Z.M.; Wang, L.C.; Wang, Y.J.; Xu, W.H.; Zhou, Y. Drip irrigation incorporating water conservation measures: Effects on soil water–nitrogen utilization, root traits and grain production of spring maize in semi-arid areas. J. Integr. Agric. 2021, 20, 3127–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscolo, A.; Junker, A.; Klukas, C.; Weigelt-Fischer, K.; Riewe, D.; Altmann, T. Phenotypic and metabolic responses to drought and salinity of four contrasting lentil accessions. J. Exp. Bot. 2015, 66, 5467–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, K.; Chen, X.; Ridoutt, B.G.; Huang, J.; Scherer, L. Closing yield and harvest area gaps to mitigate water scarcity related to China’s rice production. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245, 106602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griglione, A.; Liberto, E.; Cordero, C.; Bressanello, D.; Cagliero, C. High-quality Italian rice cultivars: Chemical indices of ageing and aroma quality. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Duan, H.; Wang, S.J.; Su, J.-p.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.-q.; Tang, L.; Liu, X.-j.; Chen, W.-f. Moderate drought alleviates the damage to grain quality at high temperatures by improving the starch synthesis of inferior grains in japonica rice. J. Integr. Agric. 2022, 21, 3094–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y.; Yao, X.; Cao, W.; Zhu, Y. Effects of different soil water treatments on photosynthetic characteristics and grain yield in rice. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2012, 32, 7053–7060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, G.C.; Deng, S.; Liu, N.; Yu, S.-E.; Wang, M.-H.; She, D.-L. Effects of controlled irrigation and drainage on growth, grain yield and water use in paddy rice. Eur. J. Agron. 2014, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, S. Effects of Water Stress on Rice Growth and Grain Quality During Flowering. China Rice 2017, 23, 43–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, M.H.; Xie, Y.L.; Liu, X.B.; Wu, X.Z.; Zhao, B.H.; Yang, J.C. Effect of soil water potential on grain quality at different spike positions during grain filling in rice. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2011, 19, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, E.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, T. Effects of humic acid on japonica rice production under different irrigation practices and a TOPSIS-based assessment on the Songnen Plain, China. Irrig. Sci. 2021, 40, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T. High Quality Paddy Rice. National Standards of the People’s Republic of China 2017. National Public Service Platform for Standards Information Home Page. Available online: https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/gbQuery (accessed on 24 May 2024).
- Zhang, S.Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Q. Plant Physiology Experimental Techniques Tutorial; Science Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Wu, Z.; Fu, L.; Dan, Z.; Long, W.; Yuan, Z.; Liang, T.; Zhu, R.; Hu, Z.; Wu, X. Responses of the Lodging Resistance of Indica Rice Cultivars to Temperature and Solar Radiation under Field Conditions. Agronomy 2022, 12, 2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.Y.; Liu, F.Y.; Yang, J.H.; Cui, X.W. Effects of water and salt stress on yield components and quality of rice in arid area. Water Sav. Irrig. 2024, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lv, T.B.; Ma, X.P.; Wang, D.W.; Bai, M.; Wang, Z.L.; Niu, J.R. Effects of water regulation and cultivation on rice growth and irrigation water use efficiency under drip irrigation. Southwest China J. Agric. Sci. 2020, 33, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Pu, S.; Lv, Y.; Ma, X.; Shen, X.; Mo, Y. Effects of different irrigation quotas on water consumption characteristics and water production efficiency of rice under film drip irrigation. Xinjiang Agric. Sci. 2021, 58, 1577–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, X.; Liu, K.; Gao, J.; Liu, L.J. Research advances of water-saving irrigation methods and their influences on rice yield. Hybrid. Rice 2022, 37, 7–13. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Ma, B.; Tian, J. Water production function and optimal irrigation schedule for rice (Oryza sativa L.) cultivation with drip irrigation under plastic film-mulched. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Li, S.; Xing, Z.; Cheng, S.; Guo, B.; Hu, Y.; Wei, H.; Gao, H.; Liao, P.; Wei, H.; et al. Differences in rice yield and biomass accumulation dynamics for different direct seeding methods after wheat straw return. Food Energy Secur. 2022, 11, e425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, T.; Bregaglio, S.; Confalonieri, R. A model to simulate the dynamics of carbohydrate remobilization during rice grain filling. Ecol. Model. 2016, 320, 366–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwivedi, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Natividad, M.A.; Quintana, M.R.; Chinnusamy, V.; Henry, A. Disentangling the Roles of Plant Water Status and Stem Carbohydrate Remobilization on Rice Harvest Index Under Drought. Rice 2023, 16, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Singh, P.; Choudhary, O.P.; Neemisha. Nitrogen and rice straw incorporation impact nitrogen use efficiency, soil nitrogen pools and enzyme activity in rice-wheat system in north-western India. Field Crops Res. 2021, 266, 108131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, H.; Fukuta, Y.; Obara, M.; Tomita, A.; Ishimaru, T.; Sasaki, K.; Fujita, D.; Kobayashi, N. Two Novel QTLs for the Harvest Index that Contribute to High-Yield Production in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 2021, 14, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Hu, G.; Zhang, Y.; Xiang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H. Advances of rice growth response to drought and its compensatory effects. China Rice 2020, 26, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Yuan, B. Effect of water and fertilizer coupling on growth, yield and nitrogen use efficiency of rice. J. Water Resour. Water Eng. 2020, 31, 199–207+215. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.; Ma, J.; Li, S.X.; Li, M.; Zhu, P.; Chen, Y. Effects of water stress on partial physiological characteristics and yield compensation in rice at booting stage. J. South. Agric. 2013, 44, 1448–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, H.; Sun, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, H.; Tian, F.; Ma, C.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; et al. Effects on Leaf Physiological Characteristics, Yield and Quality of Dry Seeding Rice: Water-saving Irrigation and Conventional Irrigation. Chin. Agric. Sci. Bull. 2020, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Z. Effects of different water management on yield and rice quality of dry-seeded rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2023, 37, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; She, Y.; Hu, C.; Wang, Q.; Wu, L.; You, C.; Ke, J.; He, H. Physiological Adaptation Mechanisms to Drought and Rewatering in Water-Saving and Drought-Resistant Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, B.; Zheng, F.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Z. The multiple roles of ascorbate in the abiotic stress response of plants: Antioxidant, cofactor, and regulator. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 598173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekanth, D.; Pawar, D.V.; Kumar, R.; Ratnakumar, P.; Sondhia, S.; Singh, P.K.; Mishra, J.S.; Chander, S.; Mukkamula, N.; Kiran Kumar, B. Biochemical and physiological responses of rice as influenced by Alternanthera paronychioides and Echinochloa colona under drought stress. Plant Growth Regul. 2023, 103, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poudel, M.; Mendes, R.; Costa, L.A.S.; Bueno, C.G.; Meng, Y.; Folimonova, S.Y.; Garrett, K.A.; Martins, S.J. The Role of Plant-Associated Bacteria, Fungi, and Viruses in Drought Stress Mitigation. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 743512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukić, N.; Kukavica, B.; Davidović-Plavšić, B.; Hasanagić, D. Plant stress memory is linked to high levels of anti-oxidative enzymes over several weeks. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2020, 178, 104166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Shao, G.; Lu, J.; Zhang, K.; Gao, Y.; Ding, J. Effects of controlled drainage on crop yield, drainage water quantity and quality: A meta-analysis. Agric. Water Manag. 2020, 239, 106253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Wang, H.; Zhu, R.; Zhai, L.; Hu, T. Post-effects of waterlogging on the rice growth at the jointing-booting stage. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2021, 37, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dossou-Yovo, E.R.; Kouadio, S.A.K.; Saito, K. Effects of mid-season drainage on iron toxicity, rice yield, and water productivity in irrigated systems in the derived savannah agroecological zone of West Africa. Field Crops Res. 2023, 296, 108901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sultana, S.; Faruque, M.; Islam, M.R. Rice grain quality parameters and determination tools: A review on the current developments and future prospects. Int. J. Food Prop. 2022, 25, 1063–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, J.; Tong, T.; Huang, S.; Mo, Z.; Tian, H.; Pan, S.; Duan, M.; Tang, X. Effects of different irrigation methods on yield, quality and water use efficiency of fragrant rice. Acta Agriculurae Boreali-Sin. 2020, 35, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Brunet-Loredo, A.; López-Belchí, M.D.; Cordero-Lara, K.; Noriega, F.; Cabeza, R.A. Assessing Grain Quality Changes in White and Black Rice under Water Deficit. Plants 2023, 12, 4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Ye, T.; Lu, J.; Zhang, G.; Li, X. Effects of interaction between irrigation mode and nitrogen application rate on the yield formation of main stem and tillers of rice. Chin. J. Rice Sci. 2021, 35, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanning, S.B.; Siebenmorgen, T.J.; Ambardekar, A.A.; Counce, P.A.; Bryant, R.J. Effects of nighttime air temperature during kernel development. Cereal Chem. 2012, 89, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Convertino, M.; Zhao, X.; Fitzgerald, M. Climate Change: Implications for the yield of edible rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shi, S.; Cheng, B.; Zhao, D.; Pan, K.; Cao, C.; Jiang, Y. Association between rice protein components and eating quality traits of different rice varieties under different nitrogen levels. J. Cereal Sci. 2023, 113, 103760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gu, D.; Li, K.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Yang, J. Response of grain quality to alternate wetting and moderate soil drying irrigation in rice. Crop Sci. 2019, 59, 1261–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wang, S.; Wang, F.; Zhu, Y. Genetic control and high temperature effects on starch giosynthesis and grain quality in rice. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 757997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.; Xue, L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Yang, L.; Xue, L. Yield and N utilization of transplanted and direct-seeded rice with controlled or slow-release fertilizer. Agron. J. 2019, 111, 1208–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NY/T. High Soil Testing. Agric. Ind. Stand. People’s Repub. China 2010. National Public Service Platform for Standards Information Home Page. Available online: https://std.samr.gov.cn/gb/gbQuery (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Chen, Y.S.; Hou, M.T.; Ma, D.; Han, X.H.; Zhang, R.Y.; Zhang, X.Z. Determination of Total Phosphorus in Soil by Alkali Fusion-Mo-Sb Anti Spectrophotometric Method. China Stand. 2018, S1, 193–196. [Google Scholar]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agrochemical Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Bi, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.; Zhang, F.; Hou, X.; Cheng, M.; Hu, W.; Wu, L.; et al. Multi-objective optimization of water and fertilizer management for potato production in sandy areas of northern China based on TOPSIS. Field Crops Res. 2019, 240, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, D.; Yan, C.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, L.; Li, N.; Wang, Z. Study on agronomic, economic and qualitative characters of different peanuts varieties with TOPSIS method evaluation. J. Shanxi Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 1986–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Soil Layer (cm) | pH | Total N (g kg−1) | Total P (g kg−1) | Total K (g kg−1) | Organic Matter (g kg−1) | EC (dS m−1) | Bulk Density (g cm−3) | Soil Water Content at Field Capacity (%) | Soil Porosity (%) | Soil Water Content at Saturation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–20 | 8.403 | 1.084 | 772.210 | 16.631 | 9.842 | 0.242 | 1.625 | 18.608 | 38.668 | 23.791 |
| 20–40 | 8.491 | 1.195 | 735.865 | 17.154 | 7.763 | 0.243 | 1.611 | 20.583 | 39.226 | 24.356 |
| 40–60 | 8.443 | 1.236 | 788.074 | 17.457 | 8.476 | 0.278 | 1.568 | 21.883 | 40.845 | 26.056 |
| Transplanting Day | Recovery Growth Stage | Tillering Stage | Jointing and Booting Stage | Heading and Flowering Stage | Milk Ripening Stage | Yellowing and Maturity Stage |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 June 2023 | 29 June 2023 to 4 July 2023 | 5 July 2023 to 4 August 2023 | 5 August 2023 to 30 August 2023 | 31 August 2023 to 25 September 2023 | 26 September 2023 to 9 October 2023 | 10 October 2023 to 28 October 2023 |
| Amount of Irrigation Water Applied (mm) According to the Crop Periods | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatments | Tillering Stage | Jointing and Booting Stage | Heading and Flowering Stage | Filling Stage | Maturity Stage | Total Irrigation | |
| CK | Upper Limit | 50.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 30.0 | Dry naturally | 1048.90 |
| Lower Limit | 20.0 | 20.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | |||
| W1 | Upper Limit | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | Dry naturally | 839.17 |
| Lower Limit | 12.6 | 12.6 | 12.6 | 10.4 | |||
| W2 | Upper Limit | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | Dry naturally | 734.29 |
| Lower Limit | 12.6 | 12.6 | 12.6 | 10.4 | |||
| W3 | Upper Limit | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | 14.8 | Dry naturally | 629.36 |
| Lower Limit | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 8.2 | |||
| Treatment | Economic Yield (g m−2) | Biological Yield (g m−2) | Harvest Index (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 941.505 a | 1486.853 a | 0.641 a |
| W2 | 792.570 ab | 1269.825 b | 0.624 ab |
| W3 | 796.455 ab | 1316.519 b | 0.603 ab |
| CK | 716.505 b | 1213.093 b | 0.591 b |
| Treatment | Grain Number per Panicle | Seed Setting Rate (%) | 1000-Grain Weight (g) | Effective Panicle Number (10−4 hm−2) | Theoretical Yield (kg hm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 180.79 ± 8.72 a | 71.79 ± 1.05 a | 22.98 ± 0.43 a | 313.43 ± 10.90 a | 9415.05 ± 993.75 a |
| W2 | 186.64 ± 3.66 a | 69.68 ± 0.52 a | 21.75 ± 0.11 b | 279.94 ± 6.89 bc | 7925.7 ± 237.15 ab |
| W3 | 178.84 ± 13.08 a | 67.48 ± 3.06 ab | 22.17 ± 0.23 ab | 298.99 ± 2.77 a | 7964.55 ± 713.85 ab |
| CK | 179.17 ± 1.55 a | 63.63 ± 1.31 bc | 23.32 ± 0.30 a | 269.90 ± 13.12 bc | 7165.05 ± 567.9 b |
| Treatment | Brown Rice Rate (%) | Milled Rice Rate (%) | Head Rice Rate (%) | Chalky Degree (%) | Starch (mg g−1) | Crude Protein (g kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 80.56 ± 0.17 a | 68.90 ± 0.10 a | 66.29 ± 0.41 a | 18.79 ± 1.33 a | 543.76 ± 11.30 a | 65.30 ± 1.23 b |
| W2 | 80.66 ± 0.84 a | 68.85 ± 0.89 a | 64.69 ± 1.37 a | 19.51 ± 0.68 a | 503.57 ± 25.92 ab | 67.50 ± 1.23 ab |
| W3 | 79.32 ± 2.02 a | 67.84 ± 2.04 a | 64.53 ± 1.94 a | 19.86 ± 2.83 a | 450.43 ± 13.95 b | 67.00 ± 0.64 ab |
| CK | 78.92 ± 1.15 a | 67.03 ± 0.79 a | 63.83 ± 0.52 a | 17.49 ± 0.18 a | 457.65 ± 27.67 b | 71.22 ± 0.33 a |
| Entropy Weight Method | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classification | Item | Type of Indicator | Entropy | Information Utility Value | Weight (%) | Positive Ideal Solution | Negative Ideal Solution |
| Morphological characteristics | Plant height (cm) | Positive indicators | 0.706 | 0.294 | 7.43 | 0.99998734 | 0.00001266 |
| SPAD | Positive indicators | 0.725 | 0.275 | 6.951 | 0.999978 | 0.000022 | |
| Yield | Grain number per panicle | Positive indicators | 0.454 | 0.546 | 13.82 | 0.99998718 | 0.00001282 |
| Seed setting rate (%) | Positive indicators | 0.764 | 0.236 | 5.971 | 0.99877751 | 0.00122249 | |
| 1000-grain weight (g) | Positive indicators | 0.711 | 0.289 | 7.309 | 0.99993645 | 0.00006355 | |
| Effective panicle number (10−4 hm−2) | Positive indicators | 0.747 | 0.253 | 6.392 | 0.99999812 | 0.00000188 | |
| Theoretical yield (kg hm−2) | Positive indicators | 0.693 | 0.307 | 7.772 | 0.99999996 | 4.00 × 10−8 | |
| Rice quality | Brown rice rate (%) | Positive indicators | 0.689 | 0.311 | 7.856 | 0.99994243 | 0.00005757 |
| Milled rice rate (%) | Positive indicators | 0.75 | 0.25 | 6.328 | 0.99994669 | 0.00005331 | |
| Head rice rate (%) | Positive indicators | 0.675 | 0.325 | 8.21 | 0.99995928 | 0.00004072 | |
| Chalky degree (%) | Positive indicators | 0.772 | 0.228 | 5.77 | 0.99995787 | 0.00004213 | |
| Starch (mg g−1) | Reverse indicators | 0.587 | 0.413 | 10.446 | 0.99999893 | 0.00000107 | |
| Crude protein (g kg−1) | Positive indicators | 0.773 | 0.227 | 5.744 | 0.99998313 | 0.00001687 | |
| Treatments | Positive Ideal Distance | Negative Ideal Distance | Comprehensive Score Index | Sales Revenue (RMB hm−2) | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W1 | 0.47036345 | 0.7640674 | 0.61896331 | 27,680.247 | 1 |
| W2 | 0.57064246 | 0.65861295 | 0.53578202 | 23,301.558 | 2 |
| W3 | 0.66330566 | 0.53327802 | 0.44566713 | 23,415.777 | 3 |
| CK | 0.86927266 | 0.46664142 | 0.34930497 | 21,065.247 | 4 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, C.; Lin, M.; He, L.; Tang, M.; Ma, J.; Sun, W. The Impact of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Growth and Comprehensive Evaluation of Irrigation Strategies. Agronomy 2024, 14, 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071363
Gao C, Lin M, He L, Tang M, Ma J, Sun W. The Impact of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Growth and Comprehensive Evaluation of Irrigation Strategies. Agronomy. 2024; 14(7):1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071363
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Chen, Meiwei Lin, Liang He, Minrui Tang, Jianing Ma, and Weihong Sun. 2024. "The Impact of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Growth and Comprehensive Evaluation of Irrigation Strategies" Agronomy 14, no. 7: 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071363
APA StyleGao, C., Lin, M., He, L., Tang, M., Ma, J., & Sun, W. (2024). The Impact of Water-Saving Irrigation on Rice Growth and Comprehensive Evaluation of Irrigation Strategies. Agronomy, 14(7), 1363. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14071363






