Phosphorus Release Dynamics from Ashes during a Soil Incubation Study: Effect of Feedstock Characteristics and Combustion Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ash Production
| Ash | Units | DW550 | SD850 | MD550 | PM550 | PMW550 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Raw material | Dairy wastewater sludge | Side stream domestic wastewater sludge | Mainstream domestic wastewater digested sludge | Pig manure | Pig manure subjected to a 24 h water pre-treatment | |
| Type of combustion | Muffle | Muffle | Muffle | Combustion in commercial biomass boiler | Combustion in commercial biomass boiler | |
| Temperature | °C | 550 | 850 | 550 | 550–600 | 550–600 |
| P2O5 | % (dw) | 34.47 (±1.51) | 39.84 (±2.27) | 28.16 (±1.95) | 16.25 (±0.15) | 16.25 (±0.15) |
2.2. Soil Characteristics
2.3. Soil Incubation
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Ashes Characterisation
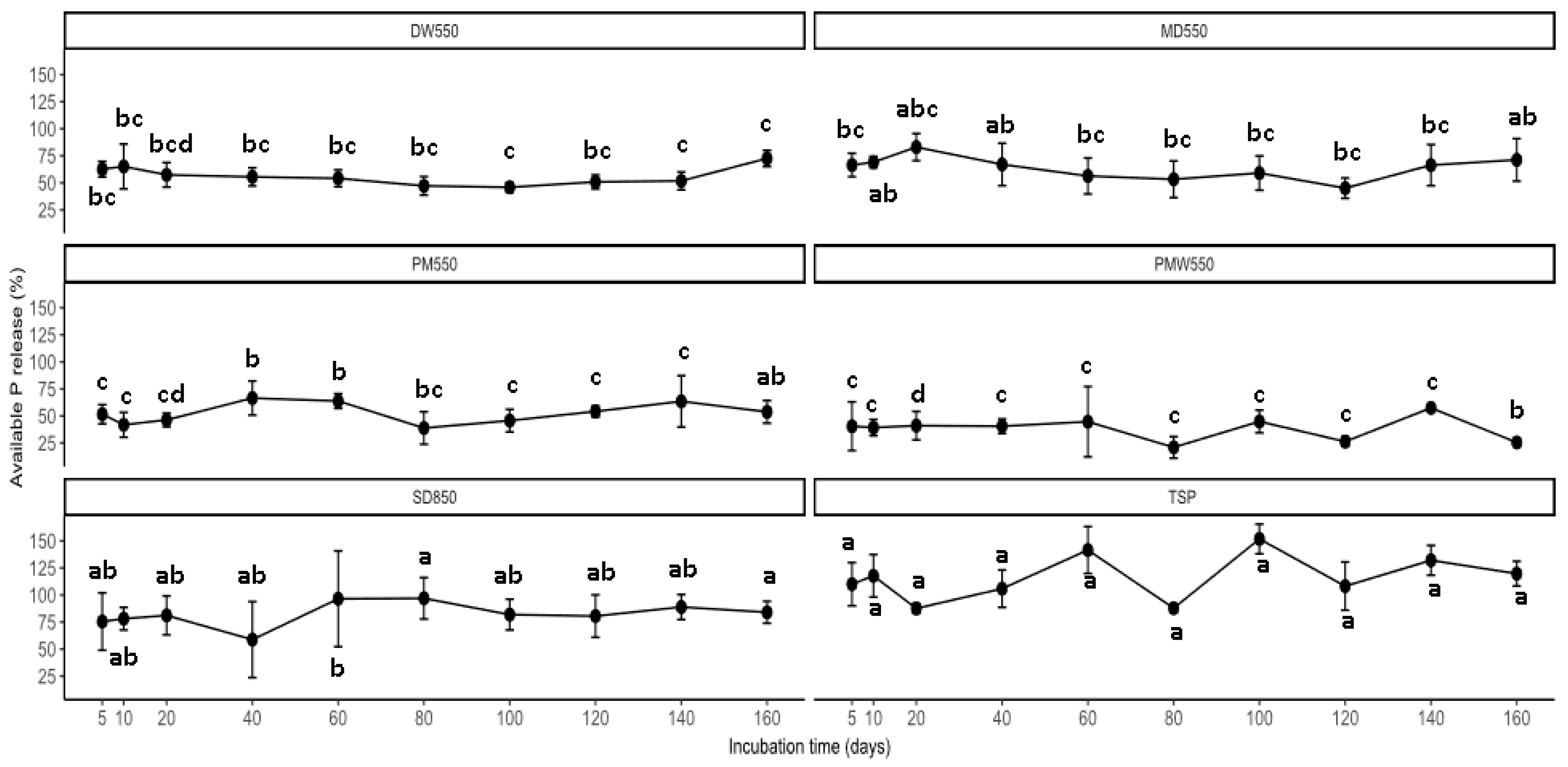
3.2. P Release Patterns
3.3. Pearson Correlation
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Ash Characterisation on P Release
4.2. Effect of Combustion Temperature on Ash P Release
4.3. Effect of the Raw Material on the P Release
4.4. Ashes Potential as Soil P Fertiliser
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
| BBFs | Bio-based fertilisers |
| BD | Bulk density |
| CAL | Calcium acetate lactate |
| CMA | Combustion manure ash |
| CMC | Component Material Category |
| CMAW | Combustion manure ash pretreated with water |
| CRD | Complete randomised design |
| DPAOs | Denitrifying polyphosphate accumulating organisms |
| dw | Dry weight |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| EBPR | Enhanced biological phosphorus removal |
| EU | European Union |
| FPR | Fertilising Products Regulation |
| OM | Organic matter |
| P | Phosphorus |
| REFLOW | Phosphorus recovery for fertilisers from dairy processing waste |
| PFC | Product Function category |
| PHA | Polyhydroxyalkanoates |
| Poly-P | Polyphosphate |
| PAOs | Polyphosphate accumulating organisms |
| PVC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| FERTIMANURE | Production of high-added value fertilisers from animal MANURE |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| TP | Total phosphorous |
| TSP | Triple superphosphate |
| VFAs | Volatile fatty acids |
| WWTP | Wastewater treatment plants |
| WHC | Water holding capacity |
References
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The story of phosphorus: Global food security and food for thought. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 2. COM/2017/0490; Communication on the 2017 List of Critical Raw Materials for the EU. European Commission: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–8.
- Adam, C.; Peplinski, B.; Michaelis, M.; Kley, G.; Simon, F.G. Thermochemical treatment of sewage sludge ashes for phosphorus recovery. Waste Manag. 2017, 29, 1122–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atienza-Martínez, M.; Rubio, I.; Fonts, I.; Ceamanos, J.; Gea, G. Effect of torrefaction on the catalytic post-treatment of sewage sludge pyrolysis vapors using γ-Al2O3. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Chen, H.; Zeng, X.; Li, Z.; Yu, W.; Xiao, K.; Hu, J.; Hou, H.; Liu, B.; Tao, S.; et al. A comparison between sulfuric acid and oxalic acid leaching with subsequent purification and precipitation for phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge incineration ash. Water Res. 2019, 159, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, L.; Wang, Q.; Li, J.-S.; Poon, C.S.; Cheeseman, C.R.; Donatello, S.; Tsang, D.C.W. Feasibility of wet-extraction of phosphorus from incinerated sewage sludge ash (ISSA) for phosphate fertilizer production: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 51, 939–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratz, S.; Vogel, C.; Adam, C. Agronomic performance of P recycling fertilizers and methods to predict it: A review. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2019, 115, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, L.; Geerts, S.; Van Caneghem, J. Closing the phosphorus cycle: Multi-criteria techno-economic optimization of phosphorus extraction from wastewater treatment sludge ash. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 713, 135543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshita, K.; Sun, X.; Kawaguchi, K.; Shiota, K.; Takaoka, M.; Matsukawa, K.; Fujiwara, T. Aqueous leaching of cattle manure incineration ash to produce a phosphate enriched fertilizer. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2016, 18, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiemenz, K.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Biomass ashes and their phosphorus fertilizing effect on different crops. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2010, 87, 471–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luyckx, L.; Van Caneghem, J. Recovery of phosphorus from sewage sludge ash: Influence of incineration temperature on ash mineralogy and related phosphorus and heavy metal extraction. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza-Martínez, M.; Gea, G.; Arauzo, J.; Kersten, S.R.A.; Kootstra, A.M.J. Phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge char ash. Biomass Bioenergy 2014, 65, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smol, M.; Kulczycka, J.; Henclik, A.; Gorazda, K.; Wzorek, Z. The possible use of sewage sludge ash (SSA) in the construction industry as a way towards a circular economy. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 95, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, H.; Shao, L.; He, P. Fraction distributions of phosphorus in sewage sludge and sludge ash. Waste Biomass Valoriz. 2012, 3, 355–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velis, C.A.; Longhurst, P.J.; Drew, G.H.; Smith, R.; Pollard, S.J.T. Biodrying for mechanical–biological treatment of wastes: A review of process science and engineering. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 2747–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 11466:1995; Soil Quality—Extraction of Trace Elements Soluble in Aqua Regia. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- APHA (2017); Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater (23rd ed.). American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2017; p. 2671.
- Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003; Revision of the Fertilisers Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 1–7.
- Regulation (EU) 2019/1009 OF; Regulation of the European Parliament and of the Council Laying Down Rules on the Making Available on the Market of EU Fertilising Products and Amending Regulations (EC) No 1069/2009 and (EC) No 1107/2009 and repealing Regulation (EC) No 2003/2003. European Union: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; p. 114.
- Petriglieri, F.; Petersen, J.F.; Peces, M.; Nierychlo, M.; Hansen, K.; Baastrand, C.E.; Nielsen, U.G.; Reitzel, K.; Nielsen, P.H. Quantification of Biologically and Chemically Bound Phosphorus in Activated Sludge from Full-Scale Plants with Biological P-Removal. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 5132–5140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ISO 10390:2021; Soil, Treated Biowaste and Sludge—Determination of pH. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021.
- ISO 11265:1994; Soil Quality—Determination of the Specific Electrical Conductivity. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1994.
- ISO 10694:1995; Soil Quality—Determination of Organic and Total Carbon after Dry Combustion (Elementary Analysis). ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1995.
- Ranst, E.; Verloo, M.; Demeyer, A.; Pauwels, J. Manual for the Soil Chemistry and Fertility Laboratory-Analytical Methods for Soils and Plants, Equipment, and Management of Consumables, 1st ed.; Ghent University: Ghent, Belgium, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder, J.; Kammann, L.; Helfrich, M.; Tebbe, C.C.; Poeplau, C. Impact of common sample pre-treatments on key soil microbial properties. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2021, 160, 108321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Parliament (EC). Purpose of Adding Thermal Oxidation Materials and Derivates as a Component Material Category in EU Fertilising Products (Text with EEA Relevance); European Parliament (EC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schüller, H. Die CAL-Methode, eine neue Methode zur Bestimmung des pflanzenverfügbaren Phosphates in Böden. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 1969, 123, 48–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdan, A.; Robles-Aguilar, A.A.; Liang, Q.; Pap, S.; Michels, E.; Meers, E. Substrate-Driven Phosphorus Bioavailability Dynamics of Novel Inorganic and Organic Fertilizing Products Recovered from Municipal Wastewater—Tests with Ryegrass. Agronomy 2022, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duboc, O.; Hernandez-Mora, A.; Wenzel, W.W.; Santner, J. Improving the prediction of fertilizer phosphorus availability to plants with simple, but non-standardized extraction techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 806, 150486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christel, W.; Bruun, S.; Magid, J.; Stoumann Jensen, L. Phosphorus availability from the solid fraction of pig slurry is altered by composting or thermal treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 169, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, H.; Shang, B.; Xin, H.; Zhu, Z. Characterization of animal manure and cornstalk ashes as affected by incineration temperature. Appl. Energy 2010, 88, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuligowski, K.; Poulsen, T.G.; Stoholm, P.; Pind, N.; Laursen, J. Nutrients and heavy metals distribution in thermally treated pig manure. Waste Manag. Res. 2008, 26, 347–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brod, E.; Falk Øgaard, A.; Sophie Müller-Stöver, D.; Holton Rubaek, G. Considering inorganic P binding in bio-based products improves prediction of their P fertiliser value. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 836, 155590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasina, M.; Jarosz, K. Chemical and Microbiological Techniques for Recovery and/or Removal of Elements from Incinerated Sewage Sludge Ash—A Review of Basic Methods. Energies 2023, 16, 2840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouliot, R.; Hugron, S.; Rochefort, L.; Godbout, S.; Palacios, J.H.; Groeneveld, E.; Jarry, I. Manure derived biochar can successfully replace phosphate rock amendment in peatland restoration. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 157, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, J.; Long, X.; Zhang, L.; Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Zhou, C.; Liu, X. The Discrepancy between Coal Ash from Muffle, Circulating Fluidized Bed (CFB), and Pulverized Coal (PC) Furnaces, with a Focus on the Recovery of Iron and Rare Earth Elements. Materials 2022, 15, 8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Cao, L.; Xing, G.; Bai, Z.; Shen, H.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z. Influence and its mechanism of temperature variation in a muffle furnace during calcination on the adsorption performance of rod-like MgO to Congo red. Front. Mater. Sci. 2018, 12, 304–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thind, H.S.; Singh, Y.; Sharma, S.; Singh, V.; Sran, H.S.; Singh, B. Phosphorus fertilizing potential of bagasse ash and rice husk ash in wheat–rice system on alkaline loamy sand soil. J. Agric. Sci. 2017, 155, 465–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, W.-T.; Liu, S.-C.; Chen, H.-R.; Chang, Y.-M.; Tsai, Y.-L. Textural and chemical properties of swine-manure-derived biochar pertinent to its potential use as a soil amendment. Chemosphere 2012, 89, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchimiya, M.; Hiradate, S. Pyrolysis Temperature-Dependent Changes in Dissolved Phosphorus Speciation of Plant and Manure Biochars. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 1802–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygens, D.; Saveyn, H. Technical Proposals for By-Products and High Purity Materials as Component Materials for EU Fertilising Products, EUR 31035 EN; Publications Office of the European Union: Luxembourg, 2022; ISBN 978-92-76-50116-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzet, S.; Peplinski, B.; Cornel, P. On wet chemical phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash by acidic or alkaline leaching and an optimized combination of both. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3769–3780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawrencia, D.; Wong, S.K.; Low, D.Y.S.; Goh, B.H.; Goh, J.K.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Soottitantawat, A.; Lee, L.H.; Tang, S.Y. Controlled Release Fertilizers: A Review on Coating Materials and Mechanism of Release. Plants 2021, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jala, S.; Goyal, D. Fly ash as a soil ameliorant for improving crop production—A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1136–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hale, S.E.; Nurida, N.L.; Mulder, J.; Sørmo, E.; Silvani, L.; Abiven, S.; Joseph, S.; Taherymoosavi, S.; Cornelissen, G. The effect of biochar, lime and ash on maize yield in a long-term field trial in a Ultisol in the humid tropics. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 719, 137455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-L.; Deng, Q.; Jian, S.; Li, J.; Kudjo Dzantor, E.; Hui, D. Effects of fly ash application on plant biomass and element accumulations: A meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 250, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smol, M.; Kulczycka, J.; Lelek, Ł.; Gorazda, K.; Wzorek, Z. Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of the integrated technology for the phosphorus recovery from sewage sludge ash (SSA) and fertilizers production. Arch. Environ. Prot. 2023, 46, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Parameter | Units | Mean ± SD |
|---|---|---|
| pH | water, 1:5 (w/v) | 6.69 ± 0.06 |
| pH | KCl 1 M, 1:5 (w/v) | 6.01 ± 0.04 |
| EC | µS cm−1 | 112.43 ± 0.91 |
| WHC | % | 30.36 ± 0.87 |
| Bulk density | kg·m3 | 1348 ± 17.15 |
| Total P | mg P kg soil−1 | 62.15 ± 3.1 |
| Water soluble P | mg P kg soil−1 | 1.65 ± 0.05 |
| P available | mg P kg soil−1 | 5.49 ± 0.27 |
| Total Nitrogen | % | 0.054 ± 0.00 |
| Total Carbon | % | 0.970 ± 0.02 |
| Total Organic Carbon | % | 0.927 ± 0.17 |
| Exchangeable Potassium | mg K kg soil−1 | 301.23 ± 7.36 |
| Total Potassium | g K kg soil−1 | 5.11 ± 0.12 |
| Total Copper | mg Cu kg soil−1 | <3.33 ± 0.00 |
| Total Zinc | mg Zn kg soil−1 | 16.21 ± 0.38 |
| EU 2019/1009 Limit | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFC 1(A)(I) | |||||||
| Ash | Units | DW550 | SD850 | MD550 | PM550 | PMW550 | Solid Inorganic Fertiliser |
| Water-soluble P | % (TP) | 1.51 | 1.57 | 1.60 | 0.09 | n/a | |
| Ca | % (dw) | 4.1 | n/a | 4.4 | 15.0 | n/a | |
| Ca:TP Ratio | - | 0.27 | n/a | 0.36 | 2.08 | n/a | |
| Cd * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 0.57 (±0.09) | 0.57 (±0.01) | 0.56 (±0.16) | n/d | n/d | 3 |
| Cr (IV *) | mg kg−1 (dw) | n/d | n/d | 1.85 (±0.69) | 3.4 (±2.45) | 3.4 (±2.45) | 2 |
| Hg * | mg kg−1 (dw) | n/d | n/d | 0.73 (±0.22) | n/d | n/d | 1 |
| Ni * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 48.54 (±5.42) | 47.8 (±0.90) | 22.9 (±4.02) | 67 (±2.15) | 67 (±2.15) | 100 |
| Pb * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 16.81 (±3.27) | 16.10 (±0.42) | 50.61 (±8.47) | n/d | n/d | 120 |
| As * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 2.37 (±0.36) | 3.81 (±0.12) | n/d | n/d | 40 | |
| Cu * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 370.24 (±84.16) | 64.22 (±4.37) | 298.22 (±70.09) | 770 (±5.15) | 770 (±5.15) | 600 |
| Zn * | mg kg−1 (dw) | 2100 (±137) | 295.15 (±3) | 659 (±64) | 2000 (±1.2) | 2000 (±1.2) | 1500 |
| P2O5 Content | 0.8768 |
| Water-soluble P | 0.8687 |
| Ca | −0.8457 |
| Ca:P Ratio | −0.8459 |
| Cd | 0.6186 |
| Ni | −0.6416 |
| Cu | −0.8821 |
| Zn | −0.6326 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singla Just, B.; Binder, P.M.; Guerra-Gorostegi, N.; Díaz-Guerra, L.; Vilaplana, R.; Frison, N.; Meers, E.; Llenas, L.; Robles Aguilar, A. Phosphorus Release Dynamics from Ashes during a Soil Incubation Study: Effect of Feedstock Characteristics and Combustion Conditions. Agronomy 2024, 14, 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050935
Singla Just B, Binder PM, Guerra-Gorostegi N, Díaz-Guerra L, Vilaplana R, Frison N, Meers E, Llenas L, Robles Aguilar A. Phosphorus Release Dynamics from Ashes during a Soil Incubation Study: Effect of Feedstock Characteristics and Combustion Conditions. Agronomy. 2024; 14(5):935. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050935
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingla Just, Berta, Pablo Martín Binder, Nagore Guerra-Gorostegi, Laura Díaz-Guerra, Rosa Vilaplana, Nicola Frison, Erik Meers, Laia Llenas, and Ana Robles Aguilar. 2024. "Phosphorus Release Dynamics from Ashes during a Soil Incubation Study: Effect of Feedstock Characteristics and Combustion Conditions" Agronomy 14, no. 5: 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050935
APA StyleSingla Just, B., Binder, P. M., Guerra-Gorostegi, N., Díaz-Guerra, L., Vilaplana, R., Frison, N., Meers, E., Llenas, L., & Robles Aguilar, A. (2024). Phosphorus Release Dynamics from Ashes during a Soil Incubation Study: Effect of Feedstock Characteristics and Combustion Conditions. Agronomy, 14(5), 935. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050935








