Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preliminary Experiment
2.2. Pot Experiment
2.3. Plant and Soil Analyses
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
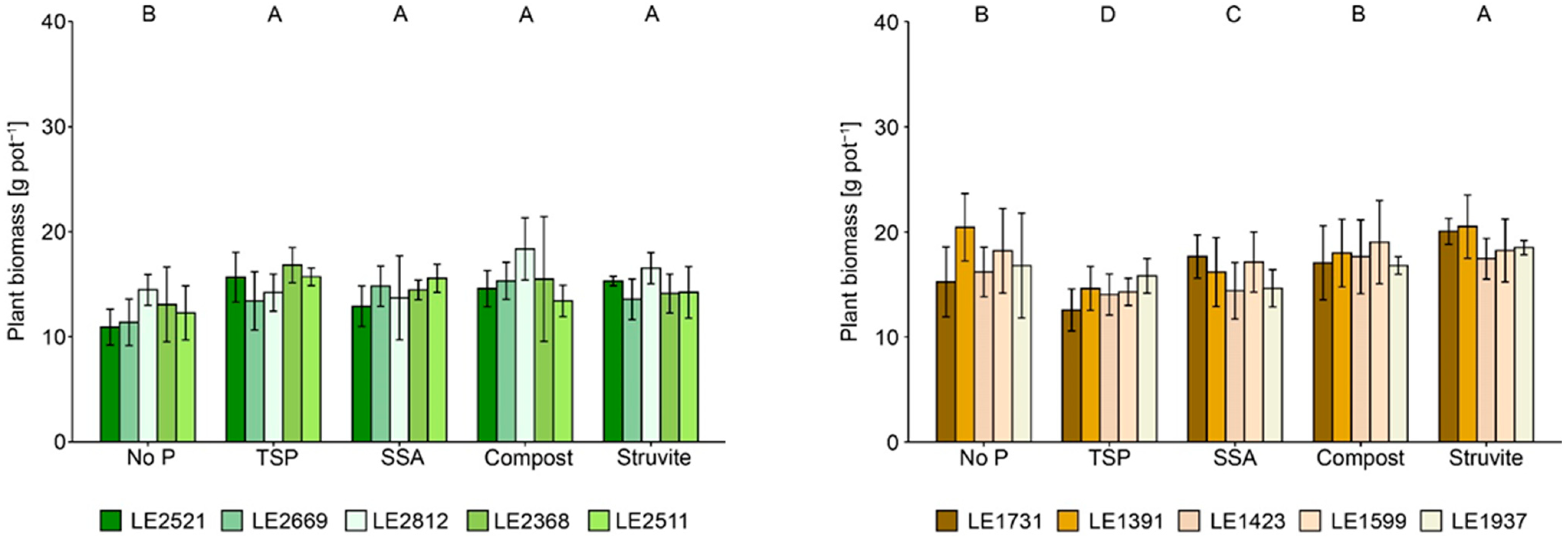
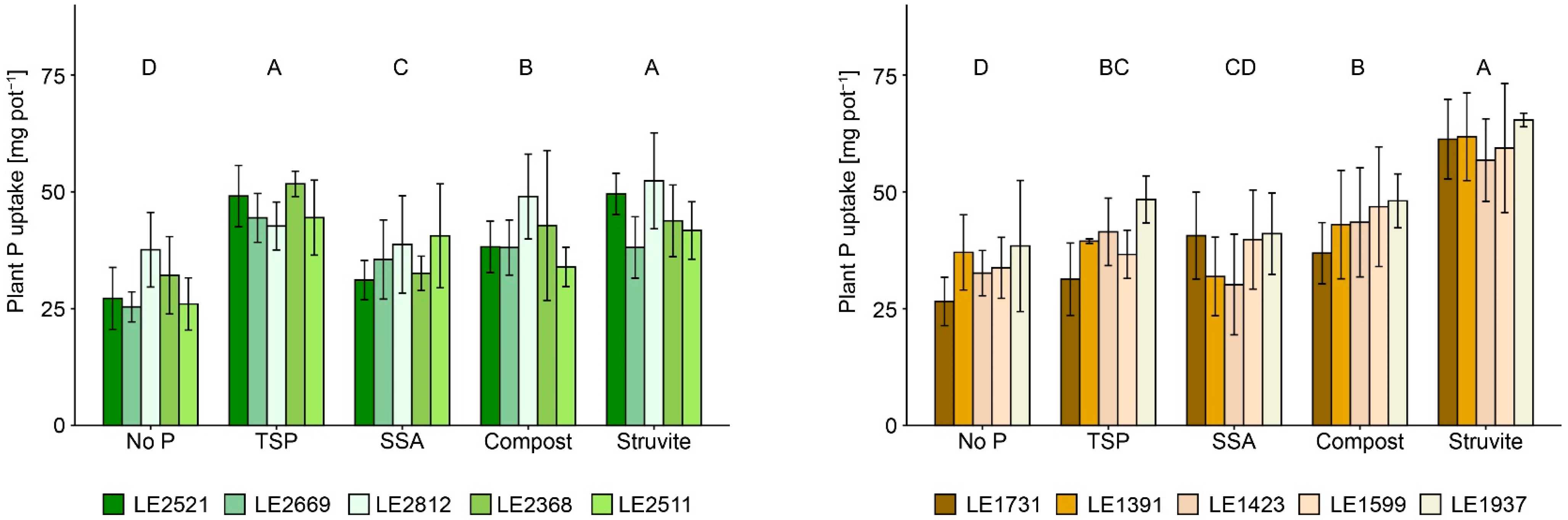
3.1. Plant Yield and Nutrient Uptake
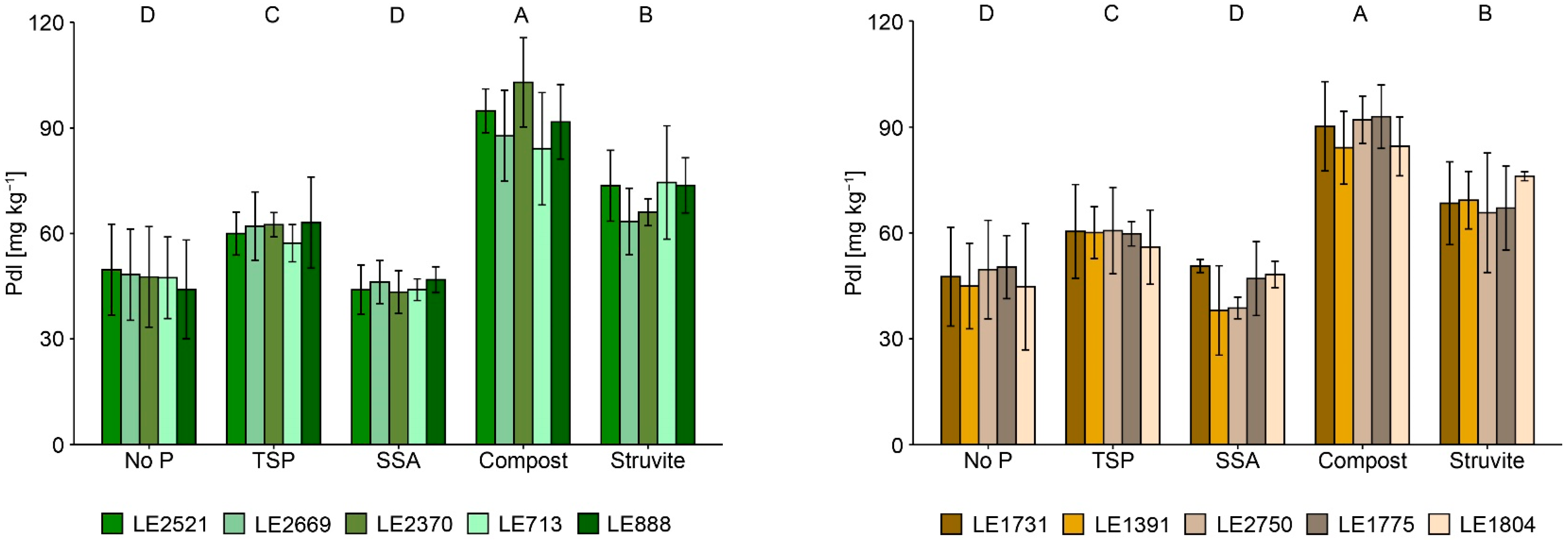
3.2. Plant Available P and P Fractions in Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. Inter- and Intraspecific Biomass Production and Nutrient Uptake
4.2. Effects of P-Recycling Fertilisers on the Performance of the Plants and on Soil Characteristics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Annicchiarico, P.; Barrett, B.; Brummer, E.C.; Julier, B.; Marshall, A.H. Achievements and Challenges in Improving Temperate Perennial Forage Legumes. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 327–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüscher, A.; Mueller-Harvey, I.; Soussana, J.F.; Rees, R.M.; Peyraud, J.L. Potential of legume-based grassland–livestock systems in Europe: A review. Grass Forage Sci. 2014, 69, 206–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombs, C.; Lauzon, J.D.; Deen, B.; Van Eerd, L.L. Legume cover crop management on nitrogen dynamics and yield in grain corn systems. Field Crops Res. 2017, 201, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, J.; Charlton, J.F.L.; Laidlaw, A.S. Temperate Forage Legumes; CAB International: Wallingford, UK; New York, NY, USA, 1998; ISBN 978-0-85199-214-3. [Google Scholar]
- Gaudin, A.; Janovicek, K.; Martin, R.C.; Deen, W. Approaches to optimizing nitrogen fertilization in a winter wheat–red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) relay cropping system. Field Crops Res. 2014, 155, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ketterings, Q.M.; Swink, S.N.; Duiker, S.W.; Czymmek, K.J.; Beegle, D.B.; Cox, W.J. Integrating Cover Crops for Nitrogen Management in Corn Systems on Northeastern U.S. Dairies. Agron. J. 2015, 107, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J. Nitrogen Fixation of Legumes; Clarendon: Oxford, UK, 1983; ISBN 978-0-19-854555-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Cardoso, J.A.; Zhu, S.; Liu, G.; Rao, I.M.; Lin, Y. Improving phosphorus acquisition efficiency through modification of root growth responses to phosphate starvation in legumes. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1094157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, D.H.; Kidder, G. Biological Nitrogen Fixation; University of Florida IFAS Extension Publication SL16: Gainesville, FL, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Drevon, J.-J.; Abadie, J.; Alkama, N.; Andriamananjara, A.; Amenc, L.; Bargaz, A.; Carlssonn, G.; Jaillard, B.; Lazali, M.; Ghoulam, C.; et al. Phosphorus Use Efficiency for N2 Fixation in the Rhizobial Symbiosis with Legumes. In Biological Nitrogen Fixation; de Bruijn, F.J., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 455–464. ISBN 978-1-119-05309-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, L.; Tang, X.; Vance, C.P.; White, P.J.; Zhang, F.; Shen, J. Interactions between light intensity and phosphorus nutrition affect the phosphate-mining capacity of white lupin (Lupinus albus L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 2995–3003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Péret, B.; Clément, M.; Nussaume, L.; Desnos, T. Root developmental adaptation to phosphate starvation: Better safe than sorry. Trends Plant Sci. 2011, 16, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, X.; Liao, H. Genetic improvement for phosphorus efficiency in soybean: A radical approach. Ann. Bot. 2010, 106, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, D.L. Organic acids in the rhizosphere—A critical review. Plant Soil 1998, 205, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H. Phosphorus Acquisition and Utilization in Plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2022, 73, 17–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touhami, D.; McDowell, R.W.; Condron, L.M. Role of Organic Anions and Phosphatase Enzymes in Phosphorus Acquisition in the Rhizospheres of Legumes and Grasses Grown in a Low Phosphorus Pasture Soil. Plants 2020, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler-Löbermann, B.; Zicker, T.; Kavka, M.; Busch, S.; Brandt, C.; Stahn, P.; Miegel, K. Mixed cropping of maize or sorghum with legumes as affected by long-term phosphorus management. Field Crops Res. 2021, 265, 108120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichler, B.; Caus, M.; Schnug, E.; Köppen, D. Soil acid and alkaline phosphatase activities in regulation to crop species and fungal treatment. Landbauforsch. Völkenrode 2024, 54, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Darch, T.; Giles, C.D.; Blackwell, M.S.A.; George, T.S.; Brown, L.K.; Menezes-Blackburn, D.; Shand, C.A.; Stutter, M.I.; Lumsdon, D.G.; Mezeli, M.M.; et al. Inter- and intra-species intercropping of barley cultivars and legume species, as affected by soil phosphorus availability. Plant Soil 2018, 427, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Tang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Rengel, Z.; Whalley, W.R.; Shen, J. Major Crop Species Show Differential Balance between Root Morphological and Physiological Responses to Variable Phosphorus Supply. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Ryan, M.H.; Tibbett, M.; Cawthray, G.R.; Siddique, K.H.M.; Bolland, M.D.A.; Denton, M.D.; Lambers, H. Variation in morphological and physiological parameters in herbaceous perennial legumes in response to phosphorus supply. Plant Soil 2010, 331, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Culvenor, R.A.; Haling, R.E.; Stefanski, A.; Ryan, M.H.; Sandral, G.A.; Kidd, D.R.; Lambers, H.; Simpson, R.J. Variation in root traits associated with nutrient foraging among temperate pasture legumes and grasses. Grass Forage Sci. 2017, 72, 93–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gahoonia, T.S.; Ali, R.; Malhotra, R.S.; Jahoor, A.; Rahman, M.M. Variation in Root Morphological and Physiological Traits and Nutrient Uptake of Chickpea Genotypes. J. Plant Nutr. 2007, 30, 829–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.-F.; Wright, E.; Ge, Y.; Bell, J.; Xi, Y.; Bouton, J.H.; Wang, Z.-Y. Improving phosphorus acquisition of white clover (Trifolium repens L.) by transgenic expression of plant-derived phytase and acid phosphatase genes. Plant Sci. 2009, 176, 479–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLachlan, J.W.; Haling, R.E.; Simpson, R.J.; Li, X.; Flavel, R.J.; Guppy, C.N. Variation in root morphology and P acquisition efficiency among Trifolium subterraneum genotypes. Crop Pasture Sci. 2019, 70, 1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, T.J.; Damon, P.; Rengel, Z. Phosphorus-efficient faba bean (Vicia faba L.) genotypes enhance subsequent wheat crop growth in an acid and an alkaline soil. Crop Pasture Sci. 2010, 61, 1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Liao, H.; Beebe, S.E.; Blair, M.W.; Lynch, J.P. QTL mapping of root hair and acid exudation traits and their relationship to phosphorus uptake in common bean. Plant Soil 2004, 265, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourley, C.J.P.; Allan, D.L.; Russelle, M.P. Defining phosphorus efficiency in plants. Plant Soil 1993, 155–156, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeri, N.K.; Lambers, H.; Tibbett, M.; Ryan, M.H. Moderating mycorrhizas: Arbuscular mycorrhizas modify rhizosphere chemistry and maintain plant phosphorus status within narrow boundaries: Moderating mycorrhizas. Plant Cell Environ. 2014, 37, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.E.; Hadobas, P.A.; Hayes, J.E.; O’Hara, C.P.; Simpson, R.J. Utilization of phosphorus by pasture plants supplied with myo-inositol hexaphosphate is enhanced by the presence of soil micro-organisms. Plant Soil 2001, 229, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawkins, C.; Yu, L.-X. Recent progress in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) genomics and genomic selection. Crop J. 2018, 6, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Brummer, E.C. Applied Genetics and Genomics in Alfalfa Breeding. Agronomy 2012, 2, 40–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, D.O.; Hansen, H.H.; Hallin, O.; Nussio, L.G.; Nadeau, E. A two-year comparison on nutritive value and yield of eight lucerne cultivars and one red clover cultivar. Grass Forage Sci. 2020, 75, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vleugels, T.; Amdahl, H.; Roldán-Ruiz, I.; Cnops, G. Factors Underlying Seed Yield in Red Clover: Review of Current Knowledge and Perspectives. Agronomy 2019, 9, 829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Dehmer, K.J.; Willner, E.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Specific and Intraspecific P Efficiency of Small-Grain Legumes as Affected by Long-Term P Management. Agronomy 2023, 13, 900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Bai, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, F. Phosphorus Dynamics: From Soil to Plant. Plant Physiol. 2011, 156, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.; Vaish, B.; Monika; Singh, U.K.; Singh, P.; Singh, R.P. Recycling of Organic Wastes in Agriculture: An Environmental Perspective. Int. J. Environ. Res. 2019, 13, 409–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zicker, T.; von Tucher, S.; Kavka, M.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Soil test phosphorus as affected by phosphorus budgets in two long-term field experiments in Germany. Field Crops Res. 2018, 218, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, A.; Åmand, L.-E.; Steenari, B.-M. Leaching of ashes from co-combustion of sewage sludge and wood—Part I: Recovery of phosphorus. Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krüger, O.; Grabner, A.; Adam, C. Complete Survey of German Sewage Sludge Ash. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 11811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Möller, K.; Oberson, A.; Bünemann, E.K.; Cooper, J.; Friedel, J.K.; Glæsner, N.; Hörtenhuber, S.; Løes, A.-K.; Mäder, P.; Meyer, G.; et al. Improved Phosphorus Recycling in Organic Farming: Navigating Between Constraints. In Advances in Agronomy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 147, pp. 159–237. ISBN 978-0-12-815283-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanzer, S.; Oberson, A.; Huthwelker, T.; Eggenberger, U.; Frossard, E. The Molecular Environment of Phosphorus in Sewage Sludge Ash: Implications for Bioavailability. J. Environ. Qual. 2014, 43, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battisti, M.; Simpson, R.J.; Stefanski, A.; Richardson, A.E.; Haling, R.E. Phosphorus fertiliser value of sewage sludge ash applied to soils differing in phosphate buffering and phosphate sorption capacity. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2022, 124, 279–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, R.; Steingrobe, B.; Römer, W.; Claassen, N. Effectiveness of recycled P products as P fertilizers, as evaluated in pot experiments. Nutr. Cycl. Agroecosyst. 2011, 91, 173–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanzer, S.; Oberson, A.; Berger, L.; Berset, E.; Hermann, L.; Frossard, E. The plant availability of phosphorus from thermo-chemically treated sewage sludge ashes as studied by 33P labeling techniques. Plant Soil 2014, 377, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, T.; Nelles, M.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Phosphorus application with recycled products from municipal waste water to different crop species. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 83, 466–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.D.; Parsons, S.A. Struvite formation, control and recovery. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3925–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latifian, M.; Liu, J.; Mattiasson, B. Struvite-based fertilizer and its physical and chemical properties. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 2691–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Shim, S.; Won, S.; Ra, C. Struvite recovered from various types of wastewaters: Characteristics, soil leaching behaviour, and plant growth. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 2864–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertzberger, A.J.; Cusick, R.D.; Margenot, A.J. A review and meta-analysis of the agricultural potential of struvite as a phosphorus fertilizer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2020, 84, 653–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huygens, D.; Saveyn, H.G.M. Agronomic efficiency of selected phosphorus fertilisers derived from secondary raw materials for European agriculture: A meta-analysis. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Inventory on Plant Genetic Resources in Germany. Available online: https://pgrdeu.genres.de/ex-situ-bestaende/ (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- ISO 3166-1:2020; Codes for the Representation of Names of Countries and Their Subdivisions—Part 1: Country Code. 4th ed. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. Available online: https://www.iso.org/obp/ui/en/#iso:std:iso:3166:-1:ed-4:v1:en (accessed on 26 November 2022).
- IUSS Working Group. WRB World Reference Base for Soil Resources 2014 (Update 2015); FAO: Rome, Italy, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kape, H. Richtwerte für Die Untersuchung und Beratung zur Umsetzung der Düngeverordnung Vom 26. Mai 2017 in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern; Ministerium für Landwirtschaft und Umwelt Mecklenburg-Vorpommern: Schwerin, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Kern, J.; Heinzmann, B.; Markus, B.; Kaufmann, A.C.; Soethe, N.; Engels, C. Recycling and Assessment of Struvite Phosphorus from Sewage Sludge. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. 2008, 10, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Riehm, H. Arbeitsvorschrift zur Bestimmung der Phosphorsäure und des Kaliums nach Lactatverfahren. Z. Pflanzenernährung Düngung Bodenkd. 1948, 40, 152–156. [Google Scholar]
- Hedley, M.J.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Chauhan, B.S. Changes in Inorganic and Organic Soil Phosphorus Fractions Induced by Cultivation Practices and by Laboratory Incubations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1982, 46, 970–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Stewart, J.W.B.; Cole, C.V. Pathways of Phosphorus Transformations in Soils of Differing Pedogenesis. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1984, 48, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiessen, H.; Moir, J.O. Characterization of available P by sequential extraction. In Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1993; ISBN 978-0-8493-3586-0. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- RStudio Team. RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R; RStudio, PBC.: Boston, MA, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- de Mendiburu, F.; Yaseen, M. Agricolae: Statistical Procedures for Agricultural Research; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Weisberg, S. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 3rd ed.; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hakala, K.; Jauhiainen, L. Yield and nitrogen concentration of above- and below-ground biomasses of red clover cultivars in pure stands and in mixtures with three grass species in northern Europe. Grass Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, E.J.; Zbiba, M.B. Effects of Herbicides on Nitrogen Fixation of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) and Red Clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Weed Sci. 1979, 27, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, W.A.; Penney, D.C.; Nyborg, M. Effects of soil acidity on rhizobia numbers, nodulation and nitrogen fixation by alfalfa and red clover. Can. J. Soil Sci. 1977, 57, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalburtji, K.L.; Mosjidis, J.A.; Mamolos, A.P. Effects of day-night temperature combinations under constant day length on emergence and early growth of Sericea lespedeza genotypes. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2007, 87, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robison, G.D.; Robinson, G.D.; Massengale, M.A. Effect of Night Temperature on Growth and Development of Alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). J. Ariz. Acad. Sci. 1969, 5, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leto, J.; Knežević, M.; Bošnjak, K.; Maćešić, D.; Štafa, Z.; Kozumplik, V. Yield and forage quality of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) cultivars in the lowland and the mountain regions. Plant Soil Environ. 2011, 50, 391–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucak, M.; Popović, S.; Čupić, T.; Španić, V.; Meglič, V. Variation in yield, forage quality and morphological traits of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.) breeding populations and cultivars. Zemdirb.-Agric. 2013, 100, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelling, K.A.; Matocha, J.E. Plant Analysis as an Aid in Fertilizing Forage Crops. In Soil Testing and Plant Analysis; Westerman, R.L., Ed.; SSSA Book Series; Soil Science Society of America: Madison, WI, USA, 2018; pp. 603–643. ISBN 978-0-89118-862-9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rech, I.; Withers, P.; Jones, D.; Pavinato, P. Solubility, Diffusion and Crop Uptake of Phosphorus in Three Different Struvites. Sustainability 2018, 11, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, I.; Gauro, A.; Müller, T.; Möller, K. Phosphorus bioavailability of sewage sludge-based recycled fertilizers. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2018, 181, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Liu, Y.; Kwag, J.-H.; Ra, C. Recovery of struvite from animal wastewater and its nutrient leaching loss in soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 2026–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achat, D.L.; Sperandio, M.; Daumer, M.-L.; Santellani, A.-C.; Prud’Homme, L.; Akhtar, M.; Morel, C. Plant-availability of phosphorus recycled from pig manures and dairy effluents as assessed by isotopic labeling techniques. Geoderma 2014, 232–234, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonvin, C.; Etter, B.; Udert, K.M.; Frossard, E.; Nanzer, S.; Tamburini, F.; Oberson, A. Plant uptake of phosphorus and nitrogen recycled from synthetic source-separated urine. AMBIO 2015, 44, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hinsinger, P.; Plassard, C.; Tang, C.; Jaillard, B. Origins of root-mediated pH changes in the rhizosphere and their responses to environmental constraints: A review. Plant Soil 2003, 248, 43–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuruzzaman, M.; Lambers, H.; Bolland, M.D.A.; Veneklaas, E.J. Distribution of Carboxylates and Acid Phosphatase and Depletion of Different Phosphorus Fractions in the Rhizosphere of a Cereal and Three Grain Legumes. Plant Soil 2006, 281, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geisseler, D.; Smith, R.; Cahn, M.; Muramoto, J. Nitrogen mineralization from organic fertilizers and composts: Literature survey and model fitting. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 1325–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, K.S.; Joergensen, R.G. Changes in microbial biomass and P fractions in biogenic household waste compost amended with inorganic P fertilizers. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chastain, J.P. Impact of Storage Time on the Composition of a Finished Compost Product: A Case Study. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2023, 39, 303–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, S.; Guo, X.; Wang, H. Comparison of the effects of different maturity composts on soil nutrient, plant growth and heavy metal mobility in the contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 250, 109525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Tran, H.-T.; Pu, M.; Zhang, T. Transformation characteristics of organic matter and phosphorus in composting processes of agricultural organic waste: Research trends. Mater. Sci. Energy Technol. 2023, 6, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matar, A.; Torrent, J.; Ryan, J. Soil and Fertilizer Phosphorus and Crop Responses in the Dryland Mediterranean Zone. In Soil Restoration; Lal, R., Stewart, B.A., Eds.; Advances in Soil Science; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1992; Volume 17, pp. 81–146. ISBN 978-1-4612-7684-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.; Rosen, C. Land application of sewage sludge incinerator ash for phosphorus recovery: A review. Chemosphere 2021, 274, 129609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Alfalfa | Red Clover | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accession | Origin | SAMPSTAT | Plant P Concentration [mg kg−1] | Accession | Origin | SAMPSTAT | Plant P Concentration [mg kg−1] |
| LE2812 | YEM | 300 | 4.29 | LE1731 | KGZ | 300 | 3.95 |
| LE2368 | FRA | 500 | 4.13 | LE1423 | FIN | 400 | 3.67 |
| LE2370 | DNK | 500 | 3.94 | LE1391 | GBR | 500 | 3.56 |
| LE2521 | DEU | 500 | 3.80 | LE2750 | HRV | 100 | 3.43 |
| LE713 | ROU | 500 | 3.03 | LE1599 | DEU | 300 | 3.17 |
| LE888 | DEU | 500 | 2.91 | LE1775 | RUS | 100 | 2.98 |
| LE2669 | ROU | 300 | 2.51 | LE1804 | SUN | 999 | 2.83 |
| LE2511 | FRA | 500 | 2.44 | LE1937 | DEU | 100 | 2.72 |
| P | N | Mg | K | Ca | Fe | Al | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TSP | 20.0 | ||||||
| SSA | 11.8 | 1.1 | 0.6 | 10.6 | 23.3 | 2.0 | |
| Compost | 0.4 | 2.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 | |||
| Struvite | 10.0 | 5.0 | 7.2 |
| Pcon [g kg−1] | Treatment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Accession | No P * | TSP * | SSA * | Compost * | Struvite * | Average | |||||
| Alfalfa | LE2812 | 2.59 ± 0.40 | Aa | 3.02 ± 0.37 | Aa | 2.87 ± 0.58 | Aa | 2.66 ± 0.12 | Aa | 3.16 ± 0.52 | Aab | 2.86 ± 0.44 |
| LE2521 | 2.47 ± 0.23 | Bab | 3.14 ± 0.20 | Aa | 2.42 ± 0.14 | Bab | 2.64 ± 0.43 | Ba | 3.24 ± 0.35 | Aa | 2.78 ± 0.44 | |
| LE2511 | 2.12 ± 0.11 | Bb | 2.82 ± 0.39 | Aa | 2.58 ± 0.56 | ABab | 2.53 ± 0.24 | ABa | 2.97 ± 0.40 | Aab | 2.60 ± 0.44 | |
| LE2368 | 2.46 ± 0.04 | Cab | 3.09 ± 0.25 | Aa | 2.25 ± 0.18 | Cb | 2.78 ± 0.17 | Ba | 3.09 ± 0.19 | Aab | 2.74 ± 0.38 | |
| LE2669 | 2.26 ± 0.23 | Cab | 3.37 ± 0.47 | Aa | 2.38 ± 0.32 | Cab | 2.48 ± 0.21 | BCa | 2.80 ± 0.19 | Bb | 2.66 ± 0.49 | |
| Average | 2.38 ± 0.27 | C | 3.09 ± 0.36 | A | 2.50 ± 0.42 | BC | 2.62 ± 0.25 | B | 3.05 ± 0.35 | A | 2.73 ± 0.44 | |
| Red clover | LE1731 | 1.75 ± 0.13 | Db | 2.73 ± 0.02 | ABab | 2.29 ± 0.37 | BCa | 2.17 ± 0.13 | CDb | 3.05 ± 0.36 | Aa | 2.38 ± 0.52 |
| LE1423 | 2.03 ± 0.30 | Cab | 2.94 ± 0.20 | Aab | 2.05 ± 0.33 | Cb | 2.44 ± 0.18 | Bb | 3.24 ± 0.24 | Aa | 2.54 ± 0.55 | |
| LE1391 | 1.80 ± 0.19 | Cb | 2.50 ± 0.05 | Bb | 1.96 ± 0.15 | Cb | 2.37 ± 0.22 | Bb | 3.02 ± 0.27 | Aa | 2.31 ± 0.51 | |
| LE1599 | 1.86 ± 0.14 | Cb | 2.56 ± 0.30 | Bb | 2.29 ± 0.24 | Ba | 2.44 ± 0.20 | Bb | 3.24 ± 0.47 | Aa | 2.44 ± 0.53 | |
| LE1937 | 2.26 ± 0.16 | Ca | 3.08 ± 0.40 | ABa | 2.10 ± 0.17 | Cab | 2.86 ± 0.26 | Ba | 3.53 ± 0.06 | Aa | 2.86 ± 0.57 | |
| Average | 1.91 ± 0.24 | E | 2.79 ± 0.30 | B | 2.13 ± 0.28 | D | 2.44 ± 0.28 | C | 3.20 ± 0.33 | A | 2.49 ± 0.55 | |
| Average | 2.16 ± 0.35 | E | 2.96 ± 0.37 | B | 2.33 ± 0.40 | D | 2.54 ± 0.28 | C | 3.12 ± 0.34 | A | 2.62 ± 0.51 | |
| Pcon [g kg−1] | Treatment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Accession | No P | TSP | SSA | Compost * | Struvite | Average | |||||
| Alfalfa | LE713 | 2.05 ± 0.18 | C | 2.70 ± 0.08 | A | 2.16 ± 0.22 | BC | 2.37 ± 0.16 | B | 2.82 ± 0.25 | A | 2.40 ± 0.35 |
| LE2370 | 1.95 ± 0.09 | D | 2.60 ± 0.12 | B | 2.22 ± 0.14 | C | 2.44 ± 0.08 | BC | 2.83 ± 0.25 | A | 2.41 ± 0.34 | |
| LE2521 | 2.12 ± 0.19 | C | 2.73 ± 0.18 | AB | 2.27 ± 0.11 | C | 2.51 ± 0.14 | B | 2.87 ± 0.12 | A | 2.50 ± 0.31 | |
| LE888 | 2.02 ± 0.21 | C | 2.88 ± 0.30 | A | 2.18 ± 0.15 | BC | 2.31 ± 0.16 | B | 2.76 ± 0.17 | A | 2.43 ± 0.39 | |
| LE2669 | 2.14 ± 0.05 | B | 2.77 ± 0.22 | A | 2.26 ± 0.07 | B | 2.42 ± 0.09 | AB | 2.73 ± 0.41 | A | 2.47 ± 0.32 | |
| Average | 2.06 ± 0.16 | D | 2.74 ± 0.20 | A | 2.22 ± 0.14 | C | 2.41 ± 0.14 | B | 2.80 ± 0.24 | A | 2.44 ± 0.34 | |
| Red clover | LE1731 | 2.19 ± 0.15 | B | 2.69 ± 0.32 | A | 2.26 ± 0.28 | B | 2.23 ± 0.21 | B | 2.55 ± 0.20 | A | 2.38 ± 0.29 |
| LE1391 | 2.12 ± 0.07 | B | 2.73 ± 0.24 | A | 2.20 ± 0.22 | B | 2.32 ± 0.13 | B | 2.79 ± 0.20 | A | 2.43 ± 0.33 | |
| LE2750 | 2.03 ± 0.09 | C | 2.56 ± 0.21 | AB | 2.32 ± 0.04 | BC | 2.11 ± 0.18 | C | 2.81 ± 0.30 | A | 2.38 ± 0.34 | |
| LE1775 | 2.11 ± 0.17 | C | 2.61 ± 0.08 | AB | 2.27 ± 0.23 | C | 2.31 ± 0.12 | BC | 2.74 ± 0.26 | A | 2.41 ± 0.29 | |
| LE1804 | 2.13 ± 0.05 | B | 2.77 ± 0.09 | A | 2.30 ± 0.06 | B | 2.26 ± 0.28 | B | 2.70 ± 0.16 | A | 2.43 ± 0.29 | |
| Average | 2.12 ± 0.11 | C | 2.67 ± 0.20 | A | 2.27 ± 0.18 | B | 2.25 ± 0.18 | B | 2.72 ± 0.23 | A | 2.41 ± 0.30 | |
| Average | 2.09 ± 0.14 | D | 2.70 ± 0.20 | A | 2.25 ± 0.16 | C | 2.33 ± 0.18 | B | 2.76 ± 0.23 | A | 2.42 ± 0.32 | |
| Ncon [g kg−1] | Treatment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Accession | No P * | TSP | SSA * | Compost * | Struvite | Average | |||||
| Alfalfa | LE2812 | 40.7 ± 4.6 | Aa | 36.1 ± 2.2 | ABa | 38.6 ± 3.8 | ABa | 37.8 ± 4.3 | ABa | 34.7 ± 1.2 | Bb | 37.6 ± 3.7 |
| LE2521 | 42.3 ± 1.0 | Aa | 36.2 ± 3.9 | Ba | 38.9 ± 4.3 | ABa | 39.4 ± 3.7 | ABa | 38.5 ± 2.4 | ABa | 39.0 ± 3.6 | |
| LE2511 | 40.1 ± 1.9 | ABa | 37.0 ± 3.1 | Ba | 39.0 ± 3.2 | ABa | 41.0 ± 2.6 | Aa | 37.2 ± 3.6 | ABab | 38.9 ± 3.1 | |
| LE2368 | 40.5 ± 3.0 | Aa | 34.8 ± 3.8 | Ba | 39.7 ± 3.9 | Aa | 41.6 ± 3.4 | Aa | 39.9 ± 1.8 | Aa | 39.3 ± 3.8 | |
| LE2669 | 41.9 ± 2.4 | Aa | 36.9 ± 4.4 | Ba | 39.7 ± 3.8 | ABa | 39.9 ± 1.1 | ABa | 38.4 ± 2.4 | ABa | 39.4 ± 3.2 | |
| Average | 41.1 ± 2.7 | A | 36.2 ± 3.3 | D | 39.2 ± 3.4 | BC | 39.9 ± 3.2 | AB | 37.7 ± 2.8 | CD | 38.8 ± 3.5 | |
| Red clover | LE1731 | 33.7 ± 0.8 | Ba | 37.5 ± 1.4 | Aab | 37.6 ± 2.2 | Aa | 35.7 ± 1.9 | ABa | 36.6 ± 2.0 | Abc | 36.2 ± 2.1 |
| LE1423 | 36.8 ± 3.0 | Aa | 38.4 ± 2.0 | Aa | 37.5 ± 4.2 | Aa | 39.3 ± 1.7 | Aa | 39.4 ± 1.1 | Aa | 38.3 ± 2.6 | |
| LE1391 | 34.0 ± 1.9 | ABa | 33.7 ± 2.9 | ABc | 32.0 ± 1.5 | Bb | 36.5 ± 2.0 | Aa | 35.0 ± 0.7 | ABc | 34.2 ± 2.2 | |
| LE1599 | 36.4 ± 2.6 | Aa | 35.2 ± 0.3 | Abc | 38.3 ± 1.7 | Aa | 35.8 ± 3.0 | Aa | 39.4 ± 2.3 | Aa | 37.0 ± 2.5 | |
| LE1937 | 36.4 ± 1.1 | Aa | 36.1 ± 0.9 | Aabc | 36.1 ± 4.9 | Aa | 37.7 ± 0.9 | Aa | 37.9 ± 1.8 | Aab | 36.8 ± 2.6 | |
| Average | 35.4 ± 2.3 | B | 36.4 ± 2.3 | AB | 36.2 ± 3.7 | AB | 37.1 ± 2.3 | A | 37.5 ± 2.3 | A | 36.5 ± 2.7 | |
| Average | 38.4 ± 3.8 | A | 36.3 ± 2.8 | B | 37.7 ± 3.8 | A | 38.6 ± 3.1 | A | 37.6 ± 2.5 | A | 37.7 ± 3.3 | |
| Ncon [g kg−1] | Treatment | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Species | Accession | No P * | TSP * | SSA * | Compost * | Struvite * | Average | |||||
| Alfalfa | LE713 | 36.2 ± 2.7 | Aa | 37.6 ± 1.4 | Aa | 35.7 ± 1.4 | Aab | 37.7 ± 2.2 | Aa | 37.7 ± 1.5 | Aa | 36.9 ± 1.9 |
| LE2370 | 35.4 ± 2.0 | Aa | 37.1 ± 1.5 | Aa | 36.3 ± 1.3 | Aab | 38.0 ± 2.4 | Aa | 37.4 ± 1.3 | Aa | 36.8 ± 1.8 | |
| LE2521 | 36.6 ± 3.5 | Aa | 36.0 ± 1.2 | Aa | 36.6 ± 1.5 | Aa | 37.1 ± 1.7 | Aa | 36.0 ± 1.0 | Aa | 36.5 ± 1.8 | |
| LE888 | 34.9 ± 1.2 | Ba | 36.1 ± 1.5 | ABa | 34.3 ± 0.3 | Bb | 37.6 ± 2.4 | Aa | 36.2 ± 1.0 | ABa | 35.8 ± 1.8 | |
| LE2669 | 37.1 ± 3.4 | Aa | 36.1 ± 1.0 | Aa | 34.8 ± 1.3 | Aab | 36.7 ± 1.5 | Aa | 36.0 ± 1.4 | Aa | 36.1 ± 1.9 | |
| Average | 36.0 ± 2.5 | BC | 36.5 ± 1.3 | ABC | 35.6 ± 1.4 | C | 37.4 ± 1.9 | A | 36.6 ± 1.3 | AB | 36.4 ± 1.8 | |
| Red clover | LE1731 | 31.8 ± 1.4 | Aa | 32.1 ± 1.8 | Aa | 32.4 ± 2.2 | Aa | 30.9 ± 1.2 | Aab | 31.3 ± 2.2 | Aab | 31.7 ± 1.7 |
| LE1391 | 32.1 ± 0.4 | Aa | 32.8 ± 1.6 | Aa | 32.1 ± 2.7 | Aa | 30.9 ± 1.7 | Aab | 32.5 ± 1.0 | Aab | 32.1 ± 1.6 | |
| LE2750 | 30.2 ± 0.7 | Bb | 33.0 ± 2.5 | Aa | 33.5 ± 2.1 | Aa | 32.3 ± 0.8 | ABa | 31.8 ± 1.4 | ABab | 32.2 ± 1.9 | |
| LE1775 | 31.2 ± 1.1 | Aab | 31.4 ± 1.8 | Aa | 31.2 ± 0.5 | Aa | 29.8 ± 0.5 | Ab | 30.3 ± 1.4 | Ab | 30.8 ± 1.2 | |
| LE1804 | 31.3 ± 0.5 | Bab | 33.5 ± 1.1 | Aa | 32.6 ± 0.4 | ABa | 33.0 ± 2.5 | ABa | 33.3 ± 1.2 | ABa | 32.7 ± 1.5 | |
| Average | 31.3 ± 1.1 | B | 32.6 ± 1.8 | A | 32.4 ± 1.8 | A | 31.4 ± 1.8 | B | 31.8 ± 1.7 | AB | 31.9 ± 1.7 | |
| Average | 33.7 ± 3.1 | B | 34.5 ± 2.5 | A | 34.0 ± 2.3 | AB | 34.5 ± 3.6 | A | 34.2 ± 2.9 | AB | 34.2 ± 2.9 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, Y.; Dehmer, K.J.; Willner, E.; Turan, V.; Eichler-Löbermann, B. Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser. Agronomy 2024, 14, 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050901
Hu Y, Dehmer KJ, Willner E, Turan V, Eichler-Löbermann B. Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser. Agronomy. 2024; 14(5):901. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050901
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Yue, Klaus J. Dehmer, Evelin Willner, Veysel Turan, and Bettina Eichler-Löbermann. 2024. "Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser" Agronomy 14, no. 5: 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050901
APA StyleHu, Y., Dehmer, K. J., Willner, E., Turan, V., & Eichler-Löbermann, B. (2024). Assessment of Inter- and Intraspecific P Efficiency in Forage Legumes as Affected by Recycling Fertiliser. Agronomy, 14(5), 901. https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy14050901







